基金项目:国家科技支撑计划“十一五”子专题(2006BAC01B02-03-02)资助.
(1.甘肃省地震局,兰州 730000; 2.宁夏回族自治区地震局,银川 750001; 3.青海省地震局,西宁 810001; 4.陕西省地震局,西安 710068)
(1. Earthquake Administration of Gansu Province, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu, China)(2. Earthquake Administration of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Yinchuan 750001, Ningxia, China)(3. Earthquake Administration of Qinghai Province, Xining 810001, Qinghai, China)(4. Earthquake Administration of Shaanxi Province, Xi'an 710068, Shaanxi, China)
gas radon; dynamic variation characteristics; monitoring efficiency; Gansu and its adjacent areas
备注
基金项目:国家科技支撑计划“十一五”子专题(2006BAC01B02-03-02)资助.
分析了甘肃及其附近地区数字化气氡观测资料的年、月、日动态特征,根据以往的水氡震例评估了其地震前兆监测效能,认为从气氡观测资料中有可能识别出以破年变为标志的中期前兆异常,但很难识别以阶变和脉冲为特征的短期异常。另外,气氡的动态稳定性不如水氡,目前以气氡观测完全取代水氡观测的条件还不成熟,应经过大量的长期观测实践再作抉择。
There have been 13 digital observation stations of gas radon in Gansu and its adjacent areas so far. We analyze the yearly, monthly and daily dynamic variation characteristics of gas radon, and evaluate their monitoring efficiency by comparing them with water-radon records. The result shows that it is possible to get the medium-term precursory anomaly characterized by breaking annual variation, but hard to get the short-term precursory anomaly characterized by step-change and pulse. For gas-radon is less stable than water radon, it's not mature completely replacing water radon observation by gas radon observation, and a great deal of observation practice is also needed.
引言
氡是一种放射性气体,是镭衰变的中间产物。氡在岩石的孔隙和裂隙中以自由氡、吸附氡和封闭氡的形式存在,在地下水中以溶解氡的形式存在。自由逸出水面的氡称为逸出氡。实验证明,氡反应灵敏,当受到外界的压力、振动等影响时,容易从其赋存的介质中逃逸出来,因此,当地下应力发生变化时,地下水中的氡浓度会出现不同程度的变化(阴朝明等,2001; 孟晓春,2005)。氡作为地下流体学科中的敏感组分,在我国已有40年的研究历史,目前,我国已建成庞大的氡元素观测网,氡在地震分析预报中起着十分重要的作用。
地下水中气体的动态变化监测是地下流体地震前兆监测的主要手段之一。由于地下水中逸出气参与地下水的循环,而且气体对地下深处的应力—应变反映灵敏,会向压力减小的方向讯速运移,携带的信息量也较为丰富(武建华等,2002),因此受到地震科研人员的重视。自20世纪70年代以来,国内外地震学者为了实现数字化氡的观测,曾研制不同种类的脱气装置(陈华静等,2002)。“九五”期间,我国部分水氡观测仪器进行了数字化改造,近年来已完成了模拟观测向数字化观测的转变。笔者对甘肃及其邻区数字化气氡观测的现状进行了初步分析,希望能对该项观测技术在今后地震监测预报中发挥更好的作用提供一些参考。
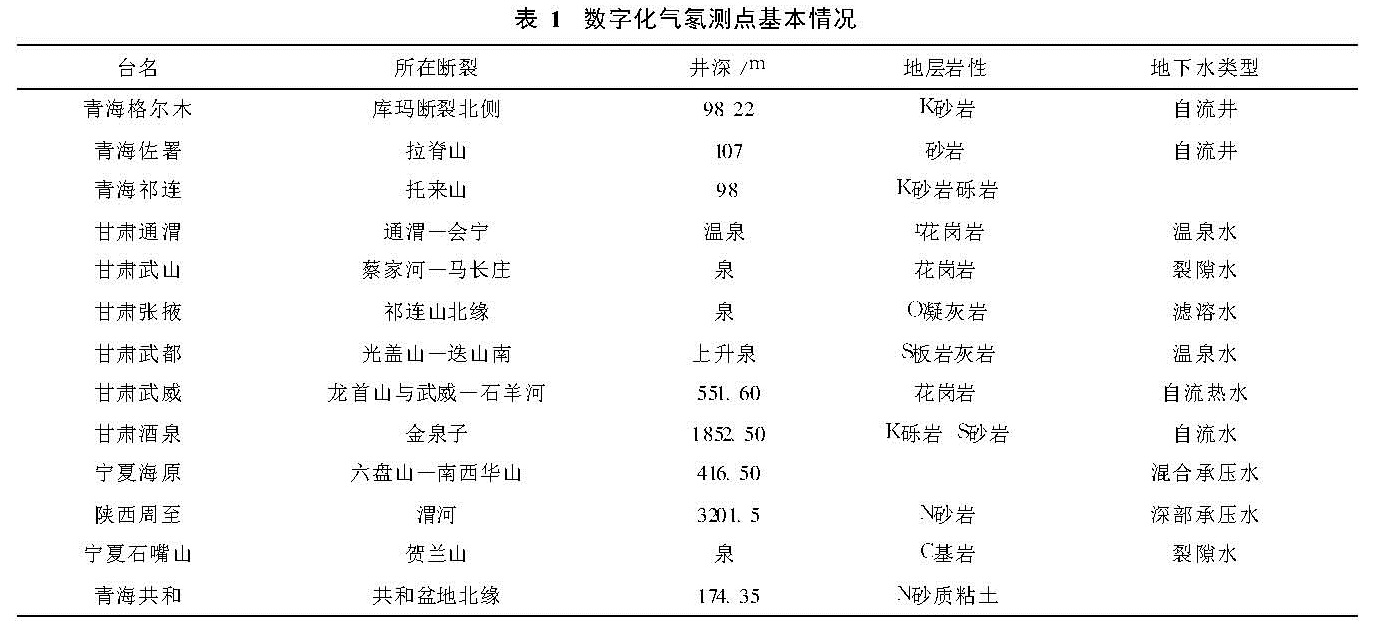
1 气氡测点(井)概况
在甘肃、青海、宁夏及陕西地区共有数字化气氡观测点13个,其基本情况列于表1。
其中宁夏石嘴山、海原,陕西周至,甘肃酒泉、武威、武都,青海共和等几个测点的资料较好,下面对这几个测点的情况略作介绍。
石嘴山地震台位于鄂尔多斯块体西北角与贺兰山断隆区交汇部位,地质构造复杂,主要以EW和SN向构造为主体,展布范围宽,规模大。采样泉点位于贺兰山东麓石炭系地层内,泉水出露系贺兰山东麓大断裂控制的下降泉,是石炭系基岩裂隙水。
海原地震台位于海原县城南侧,南、西华山
北麓。采样泉点在台站—西南方向南华山脚下的小山村内,该泉为下降泉。海原地震台靠近海原活动断裂,位于1920年8.5级地震的极震区,该台资料对开展活动断裂研究、地震前兆观测与地震机制研究有较大的参考价值。
周至地震台位于陕西省周至县县城西关,地处汾渭断陷盆地西安—周至凹陷西端,秦岭北缘大断裂与岐山—马召断裂的交汇地带。岩性为老第三系渐新统砂岩,该点为深部承压水取样井。
酒泉金1号井地处酒东盆地营尔凹陷金泉子断裂带上,井深1 852.50 m,周围干扰因素较少。
武威扎子沟观测井位于腾格里沙漠的边缘,在龙首山断裂与武威—石羊河隐状断裂的交汇处。该井是一口自流低温热水井,钻孔基底为加里东期花岗岩,含水层深度为530 m,含水层单一,流量稳定,不受大气降水影响,但附近有抽水干扰。
武都地震台地处南北地震带中段、秦岭构造带西端。观测点为上升泉,泉水出露于NEE向的断层破碎带上。断层破碎带的北盘为上志留系厚层状灰岩,南盘为板岩和千枚岩。该地区历史上曾发生过武都8.0级大地震。
共和地震台位于青海省海南藏族自治州共和县恰卜恰镇。境内地质条件复杂,断裂带纵横交错,北部有青海南山隐伏断裂、拉脊山断裂,西南有阿尼玛卿断裂、西部有卾拉山断裂、东南有贵德—泽库断裂,南部有中铁断裂。观测井深174.35 m,属第三系承压水层中的自流水,水流稳定,不受外界干扰。该地区地震活动频繁,1990年发生过7.0级地震。
2 氡观测
气氡与水氡观测,虽然都为地下水中氡的观测,但观测对象、仪器与观测方法均有所不同。模拟水氡观测的对象主要为水中溶解氡,采用FD-125、FD-150K、FD-150型等测氡仪,测的是地下水中溶解气与游离气体中氡的含量,其浓度单位(Bq/L)的含义是每升水中的氡含量。数字化气氡观测的对象是逸出氡,它既包含有地下水自深部向浅部运移过程中由于温度、压力降低自然逸出的氡气,也有经过气水分离装置脱出的部分溶解气体的氡,测的是混合气体的氡含量,一般采用SD-3A自动测氡仪(仪器本底为每分钟20个脉冲)观测,整点采样,自动测试,每日产出24个时值(车用太等,2002; 邢玉安等,2000),其浓度单位虽然也为Bq/L,但含义为每升气体中氡的含量。两种仪器的工作原理都是根据氡的放射性设计的。但由于观测对象和采集观测样品的方法不同,数字化气氡与模拟水氡观测的物理含义是完全不同的(刘成龙等,2006)。
3 气氡的动态分析
笔者对收集到的甘肃及其邻区13个数字化气氡观测点的资料进行了分析,结果发现:甘肃武威、酒泉、武都(2005年以后),宁夏石嘴山、海原和陕西周至6个测点的资料突变和缺数较少,多数时段可以利用或可以分段使用; 青海共和、甘肃通渭和张掖3个测点的资料经过处理以后可以分段使用; 其余4个测点的资料无法使用。观测资料主要有脉冲和突变(台阶变化)两种大的变化,对观测资料进行分析后发现,造成这两种变化主要是由电压瞬间不稳、突然断电、脱气装置故障(或气量不足)、传输等问题引起的(特别是资料无法使用的几个点),而不是地震前兆异常。整体来看,气氡观测资料的稳定性较差。
还有一种比较特殊的干扰也会引起资料有规律的变化。比如甘肃张掖台,因距离居民点较远,无法连接正常电源,所以采用的是太阳能电池板供电。受冬、夏季日照时间不同的影响,电瓶电压呈现季节性变化,所以氡测值也随电压出现明显的季节性变化。这种干扰目前在其它台尚未发现。
3.1 气氡的年动态分析对观测资料相对稳定的气氡测点以月均值为基础绘制气氡年动态曲线,其形态变化有一定的规律性, 多数为“夏低冬高”型与“平稳波动”型。具有“夏低冬高”型年动态的测点有宁夏海原、石嘴山台,陕西周至台,甘肃武威、酒泉台等测点; 属“平稳波动”型的有青海共和及甘肃武都、通渭等测点。有年变形态特征的测点,有利于识别中强地震前可能出现的以破年变为标志的中期前兆异常(刘成龙等,2006)。
3.2 气氡的月动态分析气氡的月动态曲线是以日均值为基础绘制而成的(选择资料比较稳定的周至、武都、石嘴山、海原测点)。2006年1月的月动态特征分析结果表明,月动态类型多样,月变幅不等,表现出较大的不稳定性。月动态具有起伏的特征,其规律性不明显,变化幅度也偏大。这样的特征,根据以往的水氡震例,是不利于识别地震前的阶变、脉冲等短期或短临前兆异常的(张炜等,1992; 车用太等,2005)。
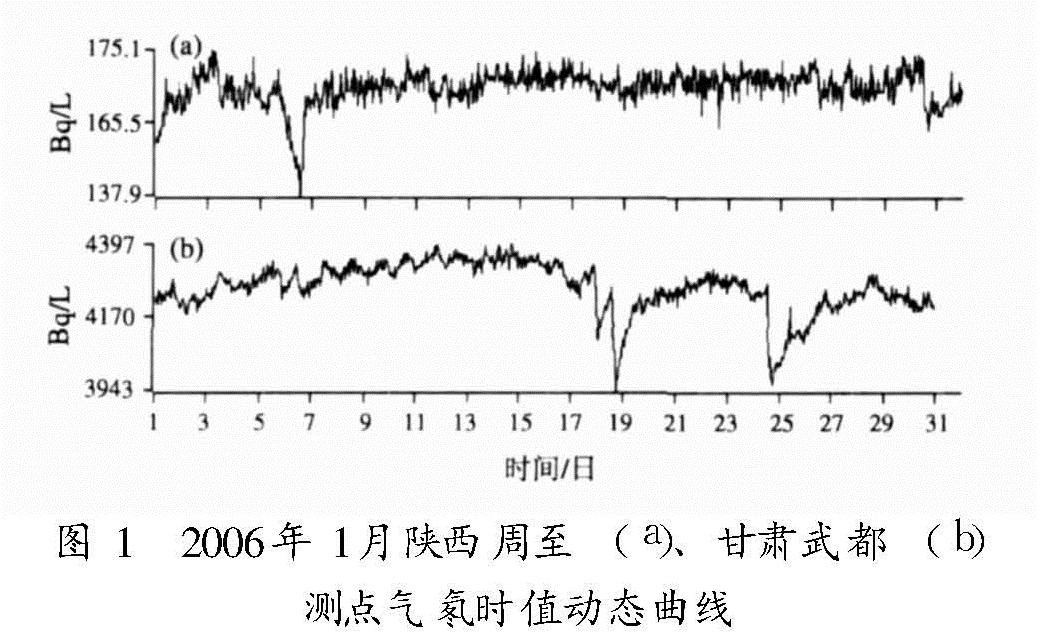
3.3 气氡的日动态分析气氡的日动态曲线是以时值为基础绘制而成的,其日动态特征是不稳定起伏,且变幅较大。多数测点的日变幅往往比月变幅大,说明观测系统本身存在不稳定性。如果取2006年1月份的日动态,气氡的日动态不稳定性表现得更为突出,尤其是陕西周至和甘肃武都测点,因日动态不稳定而表现出的突变更多、幅度也更大(图1)。气氡日动态的不稳定,会严重影响气氡观测在地震前兆监测中的效能。根据以往水氡震例中总结出来的前兆异常形态及幅度等特征(汪成民等,1988; 张炜等,1992),在这样不稳定的气氡日动态中,是很难识别出脉冲、阶变等短临前兆异常的(刘成龙等,2006)。
4 水氡与气氡资料的对比
在甘肃及其邻区已实现数字化观测的测点中,目前只有武都台和通渭台模拟水氡与数字化气氡在并行观测。笔者用这两个台的资料对水氡与气氡观测资料进行了对比分析。
4.1 观测仪器及观测原理武都台和通渭台模拟水氡观测采用FD-125型测氡仪,数字化气氡观测采用SD-3A型自动测氡仪。FD-125型测氡仪测的是地下水溶解氡(是每升水中的氡浓度),其测值为早上9点的采样值; SD-3A型测氡仪测的是地下水逸出氡(每升水逸出气体的氡浓度),其测值可能是9点之前流经采样口水的逸出氡,测值有一个时间滞后问题。两种仪器的工作原理都是根据氡的放射性而设计的。水氡和气氡两种观测技术,就其仪器工作原理和观测步骤而言,基本相同,不同的是观测对象和观测样品的采集方法。
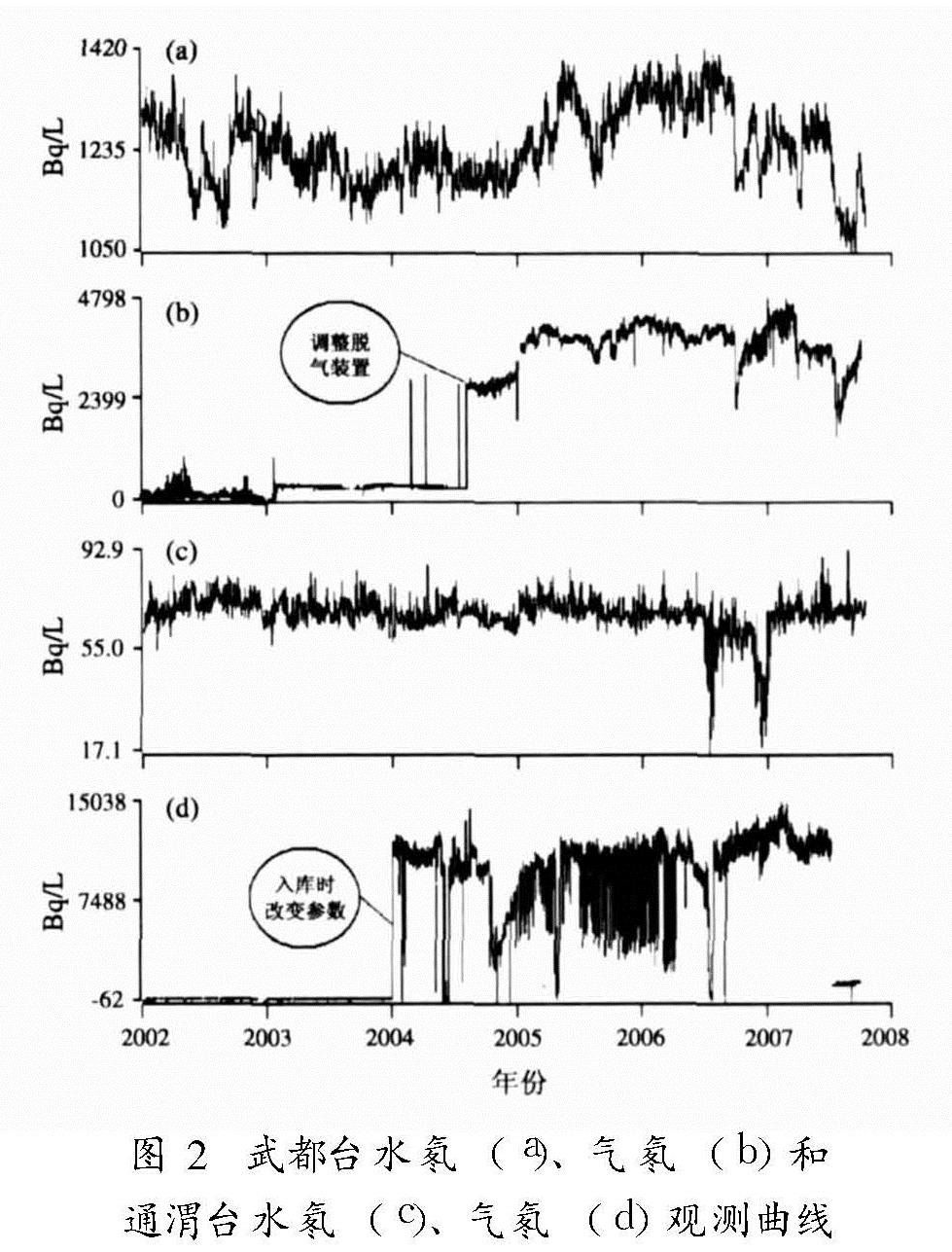
4.2 资料动态一致性对比分析数字化气氡观测资料与模拟水氡观测资料的一致性对比,主要是看数字化观测资料与模拟观测资料能否互相衔接、由模拟观测资料中总结得到的预报方法与经验能否适用于数字化观测资料(耿杰等,2002)从图2中可以看出,武都台和通渭台的水氡与气氡动态变化差异较大。首先是测值大小悬殊,武都台水氡在1 000~1 400 Bq/L之间变化,气氡从2 000 Bq/L波动上升到4 900 Bq/L; 通渭台水氡在60~100 Bq/L之间变化,气氡变化幅度更大,从300 Bq/L变化至13 000 Bq/L左右。我们分析,这两个点气氡波动幅度大可能还与仪器标定时的参数有关。另外,水氡的年变幅和年均值均比气氡的小,而且稳定。另外,水氡与气氡的年动态也不一致。
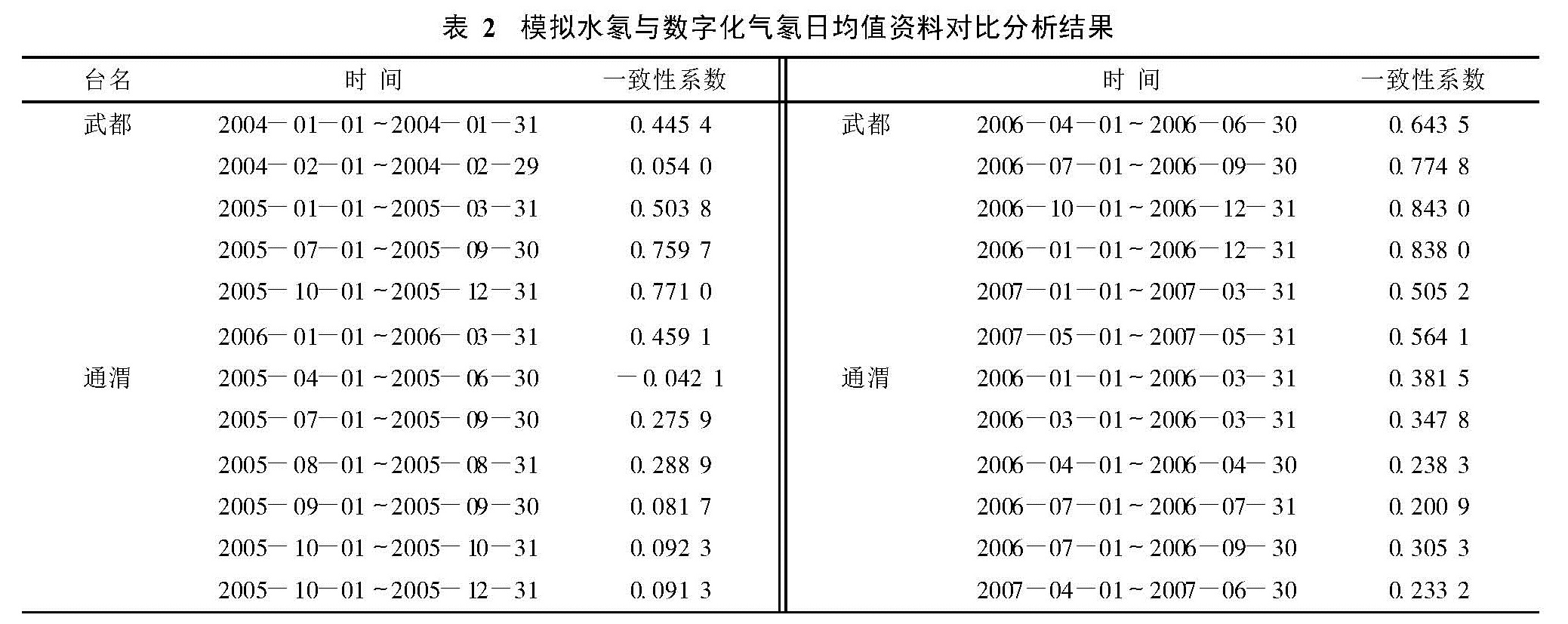
对武都殿沟泉、通渭温泉数字和模拟资料进行一致性对比分析的结果见表2。
从表中可以看出,武都台水氡与气氡2005年以后一致性较好,而该测点气氡2004年8月改装了脱气装置,这说明原先气氡测值的不稳定与脱气装置有着直接的关系; 通渭台水氡与气氡一致性较差,气氡波动很大,在2006年4月对脱气装置进行改装以后,气氡的稳定性明显改变,但与水氡的一致性仍然不是太好。
5 结论与讨论
(1)资料较稳定的几个测点的气氡年动态表现出一定的规律性,因此有可能识别出破年变异常的地震中期前兆异常; 但由于变幅较大,所以只可能识别出特别显著的异常,幅度较小的异常可能被淹没在正常的起伏中。
(2)多数测点的月、日动态规律性差,起伏大,在这样的动态背景下很难识别出以阶变、脉冲等为特征的短期与短临前兆异常。
(3)与模拟水氡观测相比,数字化气氡观测采样率大大提高,数字传输、保存和资料处理快捷方便,比人工观测误差减少,从而使氡的信息量大大增加,为捕捉地震短临异常信息提供了有利条件。但气氡的动态稳定性不如水氡,所以,气氡观测直接取代水氡观测的条件还不成熟。要发挥数字化气氡观测在地震预报中的作用,作为新的观测手段推广应用,还需要进一步完善观测技术,解决观测仪器的稳定性问题,特别是脱气装置中存在的问题,比如脱气效率低,自然脱出的气体压力低导致气路容易堵塞,装置内气、水分离的截面较大、井水流量引起动水位变化幅度较大、空气被回收到观测仪器内等因素而导致观测结果产生较大误差。其次,要充分认识气氡观测资料的正常动态规律及其影响因素,这样才能获取真实可靠的地震前兆信息。
(4)数字化气氡与模拟水氡观测的物理含义不同,所以对数字化气氡观测资料的数据分析与异常提取,只能借鉴模拟观测资料的一些处理方法,而不能完全照搬,还需要做更多的工作并总结研究出新的预测指标和更适合数字化资料的处理方法。
- 车用太,孔令昌,陈华静,等. 2002. 地下流体数字化观测技术[M]. 北京:地震出版社.
- 车用太,鱼金子. 2005. 地下流体典型异常的调查与研究[M]. 北京:地震出版社.
- 陈华静,张朝明,朱方保,等. 2002. 气体数字化观测气水分离装置研究[J]. 地震,22(1):105-109.
- 耿杰,冯志军,吴春华. 2002. 聊古一井数字化氡与模拟水氡观测资料的对比评价[J]. 地震,22(4):81-88.
- 刘成龙,鱼金子,赵文忠,等. 2006. 京津冀地区氡的数字化观测及其地震前兆监测效能评估[J]. 地震,26(4)113-120.
- 孟晓春.2005. 地震信息分析技术[M]. 北京:地震出版社.
- 汪成民, 车用太,万迪堃,等. 1988. 地下水微动态研究[M]. 北京:地震出版社.
- 武建华,刑玉安,朱自强,等. 2002. 数字化测逸出氡替代模拟测水氡的理论与实践[J]. 地震,22(4):100-104.
- 邢玉安,张平,武建华,等. 2000. SD-3A自动测氡仪山东网逸出氡资料分析与研究[J]. 华北地震科学,18(2):12-17.
- 阴朝明,高荣胜,付子忠,等. 2001. 地震前兆台网观测技术[M]. 北京:地震出版社.
- 张炜,李宣瑚,鄂秀满,等. 1992. 水文地球化学地震前兆观测与预报[M].北京:地震出版社.