基金项目:地震预测研究所基本科研业务专项“川滇地区地壳运动模型的研究”(0207690201)和国家科技攻关计划“大地形变与大地震危险区预测研究”(2008BAC44B02-0103)共同资助.
(Institute of Earthquake Science,CEA,Beijing 100036,China)
备注
基金项目:地震预测研究所基本科研业务专项“川滇地区地壳运动模型的研究”(0207690201)和国家科技攻关计划“大地形变与大地震危险区预测研究”(2008BAC44B02-0103)共同资助.
采用复小波分析技术,分析了中国大陆GPS基准站水平向时间序列的多时间尺度和周期性变化特征。结果 表明,青藏高原GPS站的南北分量在2007年初至汶川大地震发生前,出现一个周期的准同步周年振荡异常,且向北方向的半周期波峰振幅明显高于各点在印尼苏门答腊巨震后大尺度北东向长趋势运动的加速度,这可能是导致龙门山闭锁段破裂的重要触发因子。这种振荡的周期集中在汶川大地震前355~375天,与地球绕太阳公转周期非常一致。
The article analyzed multi-time scale characteristics and seasonal changes of horizontal time series of GPS fiducial stations in Mainland China by complex wavelet analysis techniques.The results showed that,from early 2007 to the Wenchuan earthquake,a quasi-synchronous annual cycle abnormal oscillation occurred in north-south components in GPS stations of Tibet Plateau.The northward amplitudes were significantly higher than their accelerations of large-scale trends in north-east movement after the great Sumatra earthquake in Indonesia.The phenomenon was explained as follows.The great Sumatra earthquake in Indonesia might be an important trigger factor leading to the breakdown of Longmenshan locked segments.This cycle of Oscillation before the Wenchuan earthquake concentrated in between 355 days and 375 days(with the earth around the sun very consistent cycle),leading to the reasons for this change is unclear,pending further in-depth study.
引言
2008年5月12日汶川大地震发生后,很多学者对汶川大地震发生的动力学成因进行了研究和探讨,其中最具代表性的观点如下:印度板块向北推挤,形成了“世界屋脊”青藏高原,随着高原不断隆升,地壳加厚,其内部温度也逐渐升高,结果导致高原内部物质由弹性向流变性质转变。在推挤压力与重力的作用下,青藏高原的物质向东、向北流动,导致高原在这两个方向上的增生(曾融生,孙为国,1992; Royden et al,1997,2008; 吴小平等,2008)。在物质东流的过程中,受到坚硬的四川盆地的阻挡,导致应变在龙门山断裂带内高度积累(张培震,2008; 朱守彪,张培震,2009; 陈祖安等,2009)。GPS资料得到的中国大陆水平速度场(相对于华南地块)也能反映出青藏高原的物质流动方向及其在龙门山断裂速率明显减小的分布图像。GPS等形变资料同时也表明,汶川大地震的发生是龙门山断裂带受到西侧巴颜喀拉地块的推挤导致大尺度、长时期、缓慢的地壳应变积累的结果(李延兴等,2009; 朱文耀等,2003)。中国大陆的GPS连续站观测反映了青藏高原相对于华南地块的整体刚性运动近年来有较明显增强(李延兴等,2009),使之成为汶川大地震发生的直接动力背景。那么,在青藏高原物质向东、向北流动过程中,青藏高原内部随时间的运动过程如何?当龙门山断裂带的应变积累达到断裂强度时,是什么因素直接触发了大地震?这些至今仍是值得深入研究的科学问题。大时空尺度的GPS连续站资料,不仅能反映地壳运动的长趋势过程,同时其周期振荡还能反映微观的地球物理现象(朱文耀等,2003; 符养等,2006; 方颖等,2007)。本文利用中国地壳运动观测网络基准站GPS连续观测资料,研究其时间序列周期振荡特点,对上述科学问题进行初步探讨。
1 方法介绍
1.1 最小二乘配置方法介绍最小二乘配置的误差方程为
V=BZZ+GY-L,(1)
VZ=Z-LZ.(2)
方程(1)为真实的误差方程,方程(2)为描述信号的虚拟观测值。其中,BZ为信号的系数阵,Z为随机信号估值,G为经典平差问题的系数阵,Y为经典平差问题需要求解的待定参数,L为观测值,LZ为信号的虚拟观测值。根据间接平差理论和矩阵反演理论求解误差方程的解,具体的计算过程见於宗俦和鲁林成(1978)的研究。
1.2 复小波数学分析技术介绍小波变换是一种具有可变分辨率的时域和频域中的信号分析方法,通过它可对母小波进行平移和比例变换,利用一簇函数逼近信号或一个函数。因为Morlet小波是三角函数和高斯函数的集成,因此它在空间大地测量和地球物理数据分析中得到了很好的应用(刘贵忠,邸双亮,1992)。
对于时间序列分析而言,复小波变换比实小波变换有很多优势。复值基函数小波可获得振幅和位相两方面的信息,因此更适用于捕获一些振荡行为。此外,复数形式小波的实部和虚部的位相差为π/2,能够很好地消除用实数型小波变换系数作为判据而产生的虚假振荡,且能够很好地对资料序列进行时频局部化分析。研究表明,复Morlet小波在分析时间序列周期方面存在优势。
因此本文在进行连续小波变换时选用复Morlet小波:
ψ(x)=1/((πfb)1/2)·exp(2iπfcx)·exp(-x2/fb).(3)
其中ω0=2πfc≥5(满足容许条件),fb为带宽,fc为中心频率。
由帕斯瓦尔方程可知,正交小波基下的小波变换具有守恒的性质,即∑Mm=1∑Nn=1│Wf(m,n)│2=‖f‖2,│Wf(m,n)│2对应于能量密度,定义某个尺度m下的小波能量为Em=∑n│Wf(m,n)│2,尺度m下的小波方差为V2m=σ2m=1/Nεn=1/N∑n│Wf(m,n)│2,小波方差可以看作随机信号序列在单一尺度下的平均能量,各尺度的小波方差形成尺度域的能谱。小波方差反映了波动的能量随尺度的分布,可以用来确定一个时间序列中各种尺度扰动的相对强度,对应峰值处的尺度即为该序列的主要时间尺度,即主要周期。小波方差的局部波峰值即为时间序列的主要周期。
2 数据预处理
用于分析的数据采用中国地壳运动观测网络的GPS基准站资料,全国共有29个GPS基准站点,从1999年3月开始观测,至今(本文资料截止到2009年3月24日)已积累了10年的资料。GPS数据的处理流程如下:首先用GAMIT软件处理GPS原始观测数据,获取测站和卫星轨道的单日松弛解; 然后用GLOBK 软件将每日松弛解和SOPAC(Scripps Orbital and Permanent Array Center)产出的全球IGS跟踪站的单日松弛解合并,得到包含所有GPS测站的单日松弛解; 最后获得基准站在全球参考框架(ITRF2000)下的单天原始坐标系列。中国地壳运动观测网络的数据很大程度上依赖SOPAC的全球解,以实现全球的参考框架。本文对此数据的水平方向时间序列进行进一步的分析和解释。
选取站点时舍去了数据可靠性差、连续性差的站点(URUM、SHAO、YONG),同时也舍去了观测时间较短的站点(ZHNZ、QDAO)。选取了印度板块上连续性较好的IISC和HYDE站(图1)。时间序列中会出现数据中断的现象,本文采用最小二乘配置(江在森等,2003)进行插值处理。此外,对时间序列中的白噪声同样采用最小二乘配置进行平滑滤波。具体分析前,首先去掉水平时间序列中的线性项和由各种原因引起的点位阶跃项,如:由仪器或天线变更引起的位移,大地震引起的同震位移,或由某些未知的原因引起的点位变化等。
另外,中国地壳运动观测网络数据中心的数据在2006年11月14日之前,采用的是天线的相对相位中心模型; 之后,采用的是绝对相位中心模型,这一模型的改变对高程向结果的影响比较显著,且主要表现为阶跃项。对水平向时间序列的分析结果显示,2006年11月14日前后水平向时间序列的变化并不显著。
3 GPS水平向时间序列的振荡特征
本文采用复Morlet小波的实部系数,对中国大陆及周边GPS水平时间序列的东西分量和南北分量的振荡特征进行分析。
复Morlet小波系数实部的变化趋势与信号的起伏是基本一致的,等值线中心为高低值中心(正小波系数为高值,即波峰值; 负小波系数为低值,即波谷值),中心值的大小可以反映出波动的振荡强度。利用小波系数实部的趋势变化图像可以分析各个站点水平时间序列的多时间特性和振荡特征。
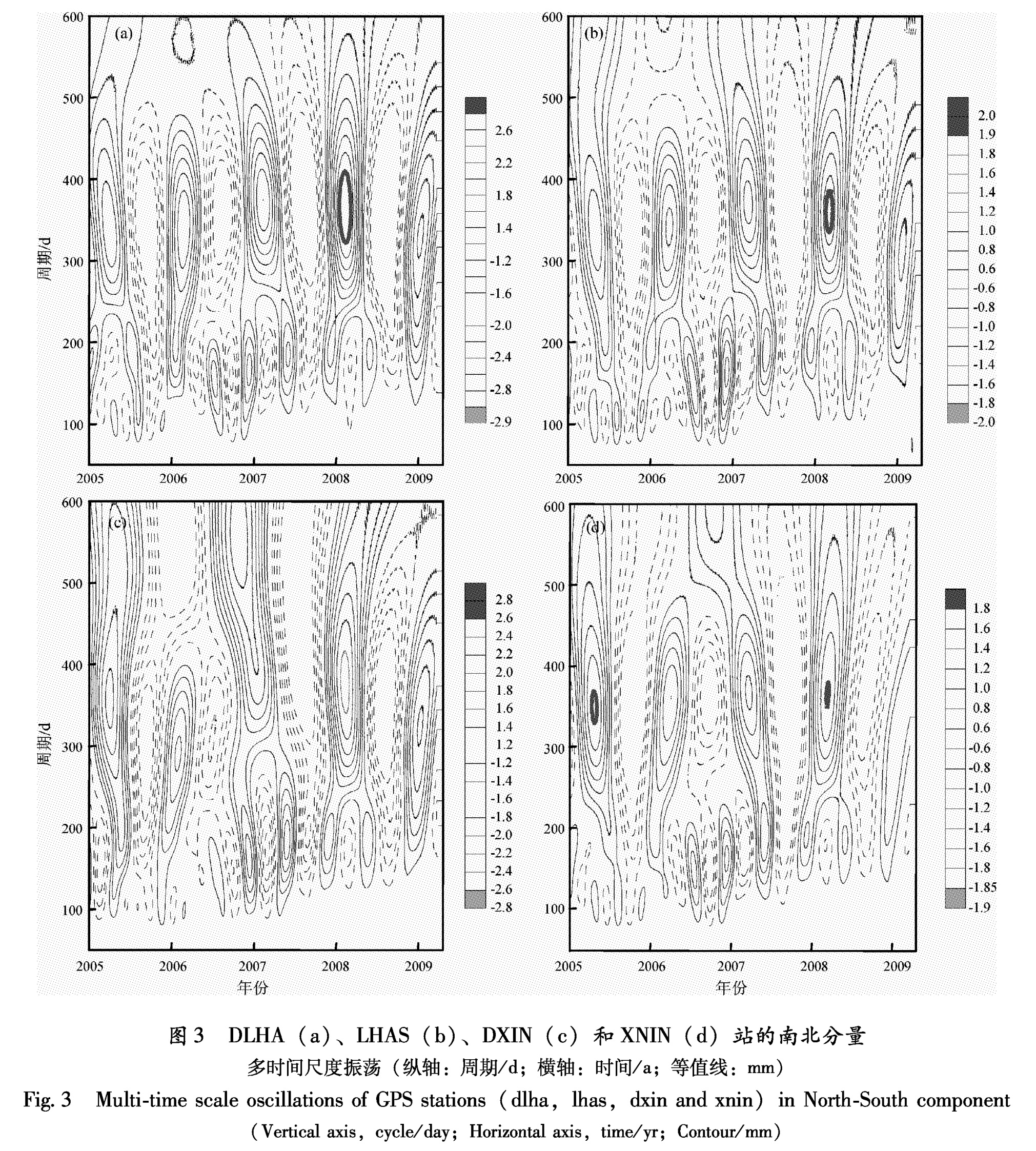
为避免小波边缘效应的影响,本文对1999年3月观测以来的GPS资料进行小波系数实部的分析,通过分析受大地震影响比较显著的站点(DLHA、LUZH等),发现震后趋势变化对周期振荡的影响会覆盖季节、周年甚至几年的多时间尺度,而对单一尺度的周年变化或季节性变化的影响很小,为此,本文在分析周期的振荡效应时,没有考虑震后变形的影响。GPS水平时间序列的复Morlet小波系数实部图像表明:GPS水平运动的周期以周年振荡为主,且时间尺度分布在比较宽的时间段内(300~420天)。季节性振荡比较弱,其强度远远小于周年振荡的强度,时间尺度主要分布在150~200天的时间段。
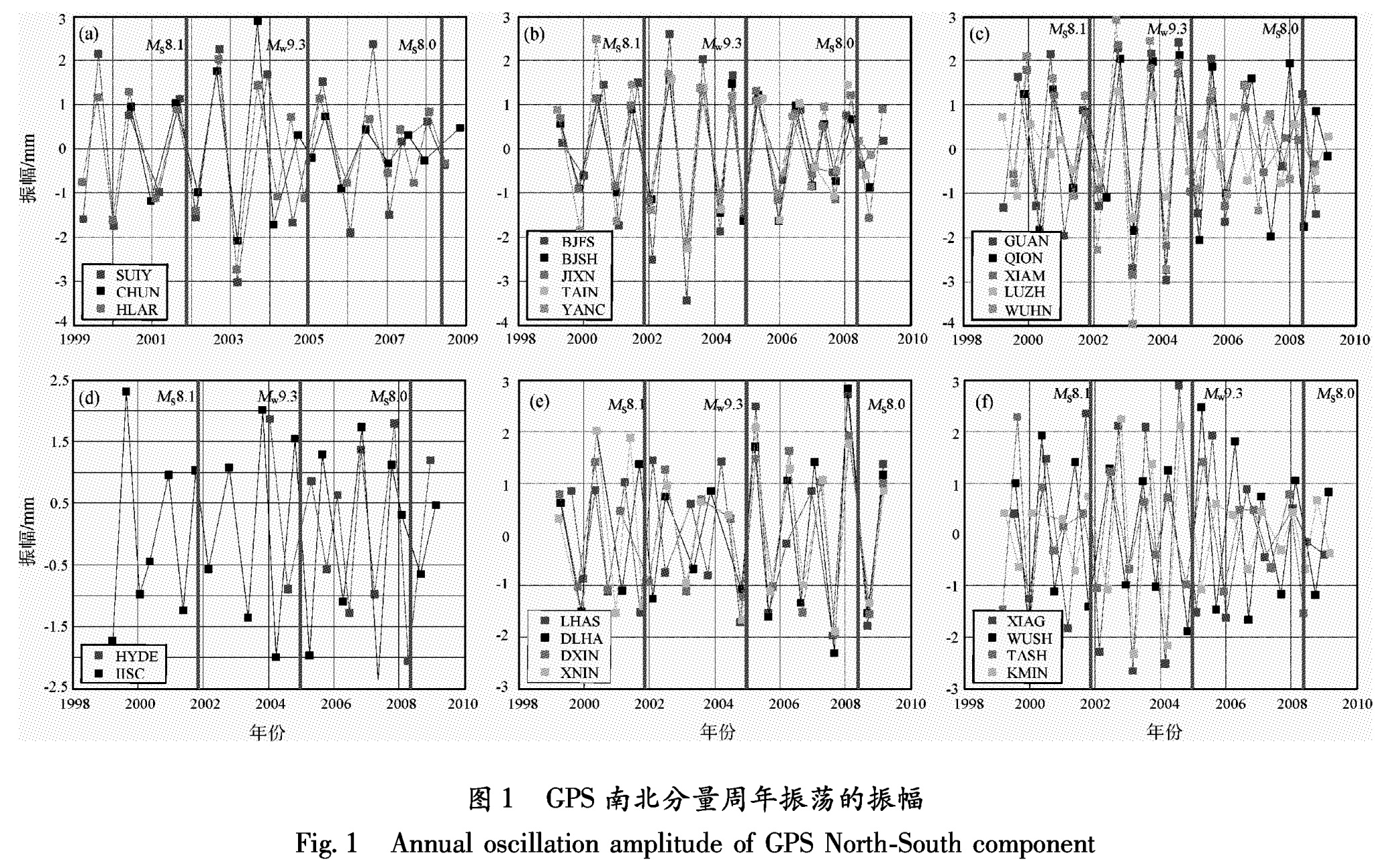
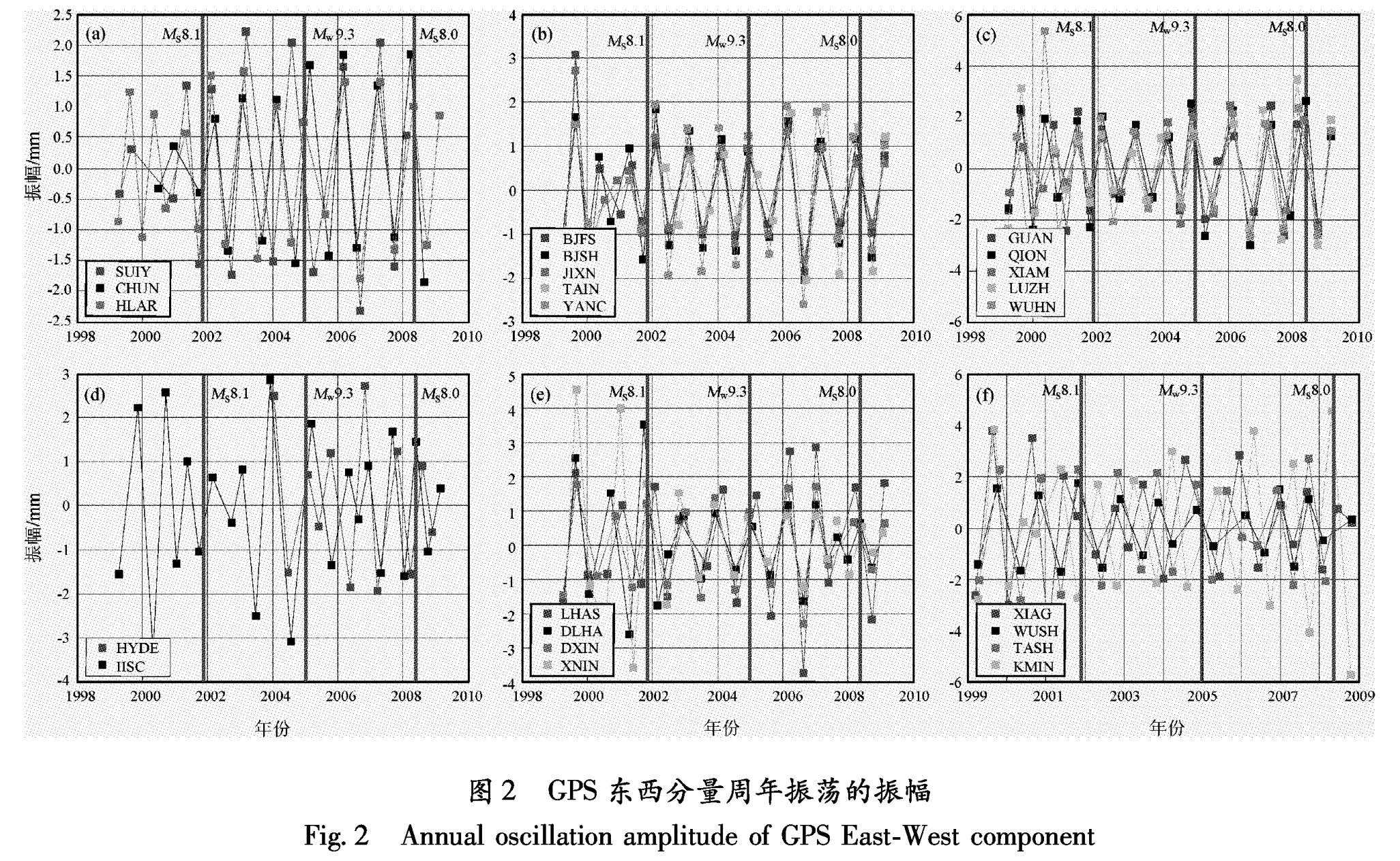
为了分析汶川大地震的震前响应,本文重点研究2005年以后的小波系数实部序列。为了直观地反映各GPS站点周年的振荡,从小波系数实部中提取出振荡区间在300~420天之间的波谷、波峰的振幅值(图1,图2),计算精度为±0.1 mm,没有提取绝对值小于0.1 mm的振幅。
2008年5月12日汶川大地震前,位于青藏高原中南部的LHAS,北缘的DLHA、XNIN站及北缘以外的DXIN站 青藏高原的边界以“大陆强震机理”(973项目)一级活动地块的划分为参考., 在2007年初至汶川大地震发生前南北分量出现一个周期的周年振荡异常,且波峰半周期的时间段集中在355~375天(图3)。站点表现为准同步的变化,异常从波谷到波峰。北向波峰振幅最大的站点依次为,DLHA(2.9 mm)、LHAS(2.8 mm)、DXIN(1.9 mm)、XNIN(1.8 mm),高于2004年底印尼巨震后各点的北东向长趋势运动(DLHA(2.0 mm/a)、LHAS(1.7 mm/a)、DXIN(1.4 mm/a)、XNIN(1.2 mm/a))。其它站点的南北分量没有这种现象。本文进一步分析了印度板块中部的IGS站IISC、HYDE站的南北分量的振荡特征,与DLHA、LHAS、DXIN、XNIN相对比,这两个站的周年振荡存在65°~ 80°的相位差,没有时间上的相关性。此外,位于青藏高原东南偶的XIAG、KMIN站的南北分量没有这种现象。
而中国大陆GPS基准站及印度板块的IGS站(IISC、HYDE)的东西分量在同一时间段的周年振荡都较弱。
4 影响因素的分析
周年振荡现象是非常普遍的地球物理现象,影响机制非常复杂(Dong,Bock,1989; Dong et al,1998,2002; 王敏等,2005),虽然在GPS数据处理中已经做了相应的改正 中国地壳运动观测网络《数据处理说明》.,但仍存在由模型误差引起的影响。汶川大地震前LHAS、DLHA、DXIN和XNIN 4个站点出现准同步的周年振荡异常,为了分析其可能的影响因素,本文从以下几个方面进行讨论:
为了分析不同参考框架(顾国华,2006)对周期振荡结论的影响,本文进一步对东部基准(包括华北地块和东北亚地块的GPS站点)、欧亚基准下的时间序列进行了分析,其振荡特点与全球框架基本一致。
标墩本身的不稳定因素、标墩基础岩石的热胀冷缩、多路径效应误差、风剪力等都是与测站周围的环境有关的周年变化(袁林果等,2008; John,2008)。青藏高原中南部到北缘跨度约700公里,因而这种大范围同步的方向一致的现象不是小空间尺度的因素引起的。
大气、非海洋潮汐、积雪和土壤水等质量负荷引起的变化(Teryo,2006),尤其是青藏高原地区积雪引起的变化,主要表现为垂向的周年变化,对水平方向的影响很小,垂向的形变量约为水平方向的5倍(袁林果等,2008)。而青藏高原主体部分GPS站点的垂向分量在汶川大地震前没有出现准同步的周年振荡异常,因而排除了大空间尺度质量负荷造成的影响。
地球自转在南北方向造成离心运动的位移量(王连捷等,1997; 申小海等,2008)远远小于LHAS、DLHA、DXIN和XNIN各站的波峰值。
上述分析表明,不同参考框架、与测站有关的小空间尺度的周年变化、质量负荷和地球自转引起的大空间尺度的周年变化等,都不是造成汶川大地震前青藏高原主体部分(LHAS、DLHA、DXIN和XNIN)南北向准同步周年振荡异常的根本原因。这种南北向准同步周年振荡显著增大的现象,可能是2007年初至2008年汶川地震前青藏高原出现向北的运动进一步增强的扰动变化的真实反映。而这种周年尺度的扰动变化对龙门山断裂带所增加的一个附加力,主要是导致其剪切力
图3 DLHA(a)、LHAS(b)、DXIN(c)和XNIN(d)站的南北分量多时间尺度振荡(纵轴:周期/d; 横轴:时间/a; 等值线:mm)
Fig.3 Multi-time scale oscillations of GPS stations(dlha,lhas,dxin and xnin)in North-South component (Vertical axis,cycle/day; Horizontal axis,time/yr; Contour/mm)增强,可能对龙门山断裂带的大破裂有触发作用。
5 结论与讨论
青藏高原主体部分(LHAS,DLHA、XNIN,DXIN)的周年振荡从2007年初开始,出现准同步增强,并且在汶川大地震前出现北方向的高波峰现象,振幅明显高于2004年底印尼巨震后各点的北东向长趋势运动。
如果把印尼巨震后青藏高原相对华南地块的北东向运动增强,作为汶川大地震发生的直接动力背景,那么各站出现的准同步北方向的高波峰现象所反映的青藏高原出现向北的运动进一步增强的扰动变化,就是一个重要的附加力,由于该力大于长趋势运动产生的推挤力,导致龙门山断裂带出现一个剪切的附加力,这可能就是导致龙门山断裂带闭锁段破裂的重要触发因子。
此外,这种振荡的周期在汶川大地震前集中在355~375天,与地球绕太阳公转周期非常一致,导致这种变化的原因尚不清楚,有待进一步深入研究。
- 陈祖安,林邦慧,白武明,等.2009.2008年汶川8.0级地震孕震机理研究[J].地球物理学报,52(2):408-417.
- 方颖,江在森,顾国华.2007.用网络滤波方法探讨华北地块边界带运动[J].地震研究,30(2):152-156.
- 符养,肖义国,韩英,等.2006.利用TOPEX卫星测高资料研究全球海面高周年和半周年波动传播规律[J].地球物理学报,49(6):1 635-1 643.
- 顾国华.2006.参考框架、坐标变换和地壳运动[J].测绘通报,8:24-28.
- 江在森,方颖,武艳强,等.2009.汶川8.0级地震前区域地壳运动与变形动态过程[J].地球物理学报,52(2):505-518.
- 江在森,马宗晋,张希,等.2003.GPS初步结果揭示的中国大陆水平应变场与构造变形[J].地球物理学报,46(3):352-358.
- 李延兴,张静华,周伟,等.2009.汶川8.0地震孕育发生的机制与动力学问题[J].地球物理学报,52(2):519-530.
- 刘贵忠,邸双亮.1992.小波分析及其应用[M].西安:西安电子科技大学出版社.
- 申小海,曾峰,薛克武.2008.地壳板块的运动及其驱动力[J].河南科学,26(3):343-347.
- 王连捷,张利容,王薇,等.1997.地球自转速率变化引起的全球应力场[J].地质力学学报,3(3):12-20.
- 王敏,沈正康,董大南.2005.非构造形变对GPS 连续站位置时间序列的影响和修正[J].地球物理学报,48(5):1045-1052.
- 吴小平,黄雍,胡家富,等.2008.汶川MS8.0巨震产生的完全库仑破裂应力变化及其余震震群[J].地震研究,31(4):317-323.
- 於宗俦,鲁林成.1978.测量平差基础[M].北京:测绘出版社.
- 袁林果,丁晓利,陈武,等.2008.香港GPS基准站坐标序列特征分析[J].地球物理学报,51(5):1 372-1 384.
- 曾融生,孙为国.1992.青藏高原岩石圈及其东部邻区的地震活动性和震源机制以及高原物质东流的讨论[J].地震学报,14(增刊):523-533.
- 张培震.2008.青藏高原东缘川西地区的现今构造变形、应变分配与深部动力过程[J].中国科学 D 辑:地球科学,38(9):1 041-1 056.
- 朱守彪,张培震.2009.2008年汶川MS8.0地震发生过程的动力学机制研究[J].地球物理学报,52(2):418-427.
- 朱文耀,符养,李彦.2003.GPS高程导出的全球高程振荡运动及季节变化[J].中国科学(D辑),33(5):470-481.
- Dong D,fnag P,Bock.Y,et al Dong,P Fang,Y Bock,et al.2002 Anatomy of apparent seasonal variation from GPS-derived site position[J].J Geophys Res,107,10.1029/2001JB000573.
- Dong D,Hening T A,King R W D,et al.1998.Estimating regional deformation from a combination of space and terrestrial geodetic data[J].J.Geod.,72:200-214.
- Dong D.Bock Y.1989.Global Positioning System network analysis with phase ambiguity resolution applied to crustal deformation studies in California[J].J Geophys Res,94:3 949-3 966.
- Royden L H,Burchfiel B C,King R W,et al.1997.Surface deformation and lower crustal flow in eastern Tibet[J].Science,276(2):788-790.
- Royden L H,Burchfiel B C,Robert D van der Hilst.2008.The geological evolution of the Tibetan plateau[J].Science,321:1 054-1 058.