基金项目:“十一五”国家科技支撑项目(2006BAC01B02-03-04,2006BAC01B02-02-01)和山西省地震局基金(SBK-0705)项目联合资助.
(1.山西省地震局,太原 030021; 2.太原大陆裂谷动力学国家野外科学观测研究站,太原 030025; 3.中国地震局地壳应力研究所,北京 100085; 4.中国地震应急搜救中心,北京 100049)
(1.Earthquake Administration of Shanxi Province,Taiyuan 030021,Shanxi,China)(2.National Continental rift Valley Dynamics Observatory of Taiyuan,Taiyuan 030025,Shanxi,China)(3.The Institute of Crustal Dynamics,Beijing 100085,China)(4.National Earthquake Response Support Service,Beijing 100049,China)
ground fluid,identification,quantitative determination,precursor anomaly,North China
备注
基金项目:“十一五”国家科技支撑项目(2006BAC01B02-03-04,2006BAC01B02-02-01)和山西省地震局基金(SBK-0705)项目联合资助.
收集华北地区地下流体观测资料并进行系统分析,采用定量方法判定异常,对该区强震前的前兆异常特征进行了研究。提出地下流体存在着趋势上升型的中期异常和转折型的中短期异常,且不同地震的前兆异常图像具有相似性; 依据大量异常资料,给出了华北地区中长期和中短期前兆异常的统计特征,以期能为华北地区年度会商的地震预测提供较为确切的依据。
Precursor anomaly characteristics before strong earthquakes in North China region are studied by the method of quantitatively determining anomalies based on systematic collection and analysis of observation data of underground fluid in this region.The results indicate that medium-term precursor anomalies with uptrend and medium-short-term with transition of underground fluid appeared before earthquakes,and precursor anomaly graphs were comparable before different earthquakes.Statistic characteristics of medium-long-term and medium-short-term precursor anomalies are presented based on a larger amount of anomaly data.These results can provide accurate evidence for annual earthquake prediction of this region.
引言
大量观测资料表明,强震前地下流体异常过程具有阶段性,表现出中长期、中短期、短期及短临等异常变化。长期以来,很多学者研究重点为短期和短临异常的变化(刘耀炜,施锦,2000; 邵永新等,2001; 黄辅琼等,2002; 张立等,2006),而对于地下流体中期变化的研究却很少。为此,本文采用定性和定量相结合的方法,主要分析了华北地区自1976年以来M≥6.0地震的地下流体中期和中短期异常特征,以期为中期和中短期预测指标的拟定提供依据。
1 研究资料与地震的选定
1.1 观测资料的收集与筛选华北地区的地下流体观测井(泉)与测项众多,但由于种种原因,只有其中一部分地下流体测项对地震有良好的异常反应。因此,“筛选”是研究工作的关键环节之一。
可用资料必须符合4个条件:(1)连续观测时间长,一般10年以上;(2)测试工作符合规范;(3)人为干扰小:无人为干扰引起的台阶状或其它变化;(4)正常动态明显,具有明显的年变化和多年周期变化(王吉易等,2002 a,b,2003)。
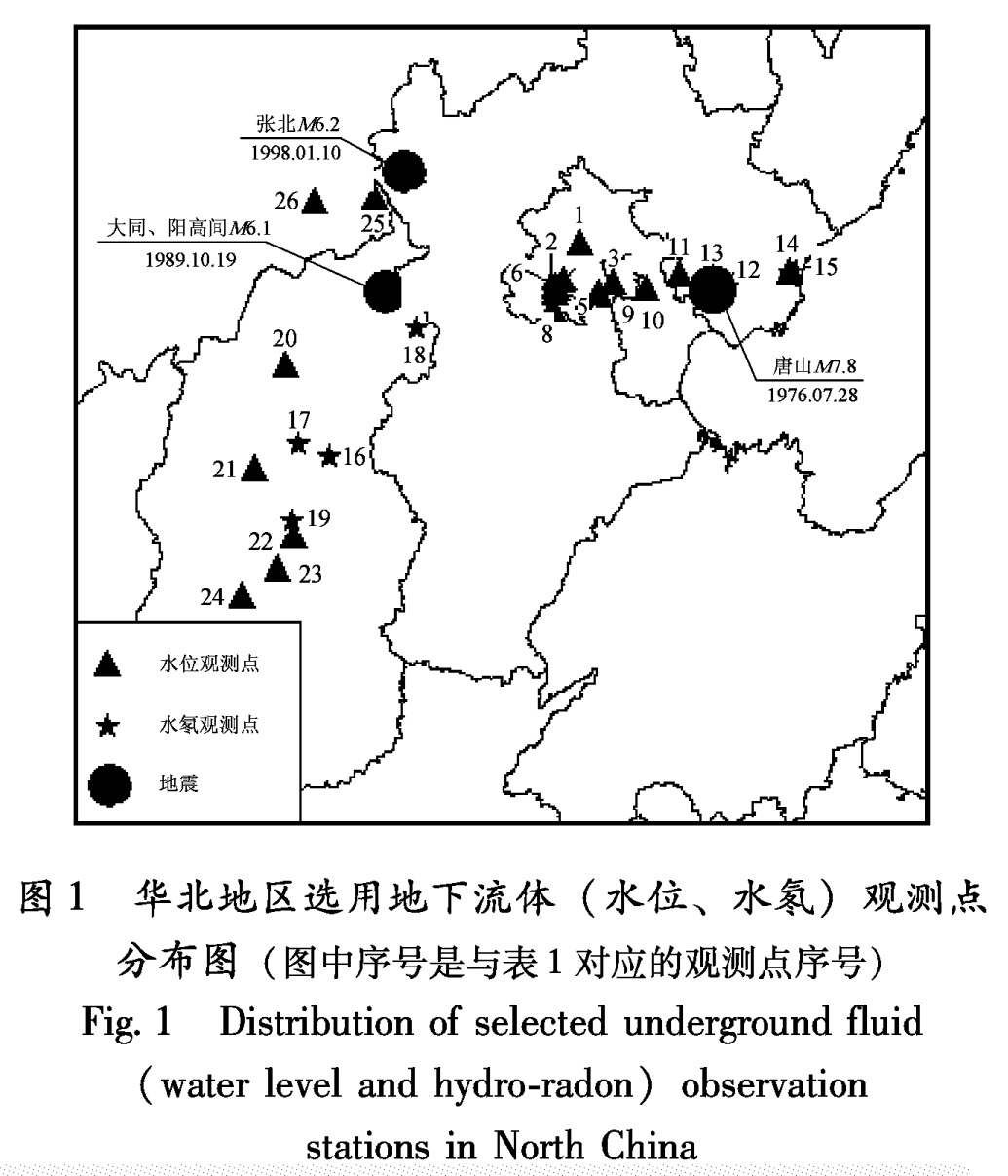
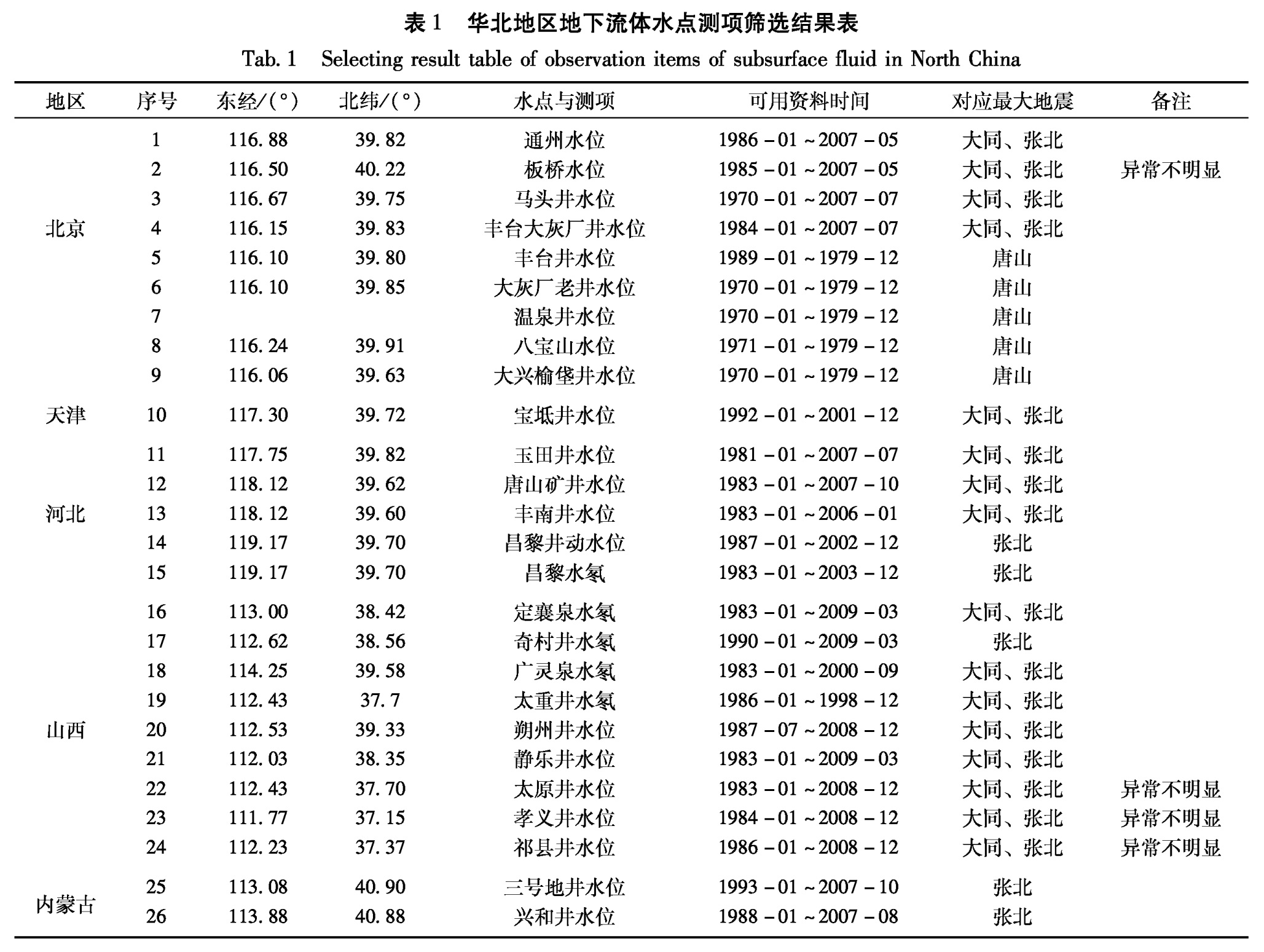
本次研究共收集到华北地区地下流体观测资料65个,其中包括48个水位观测资料和17个水氡观测资料。根据上述筛选原则,共选出21口水位观测井和5眼水氡观测井泉(图1、表1)。
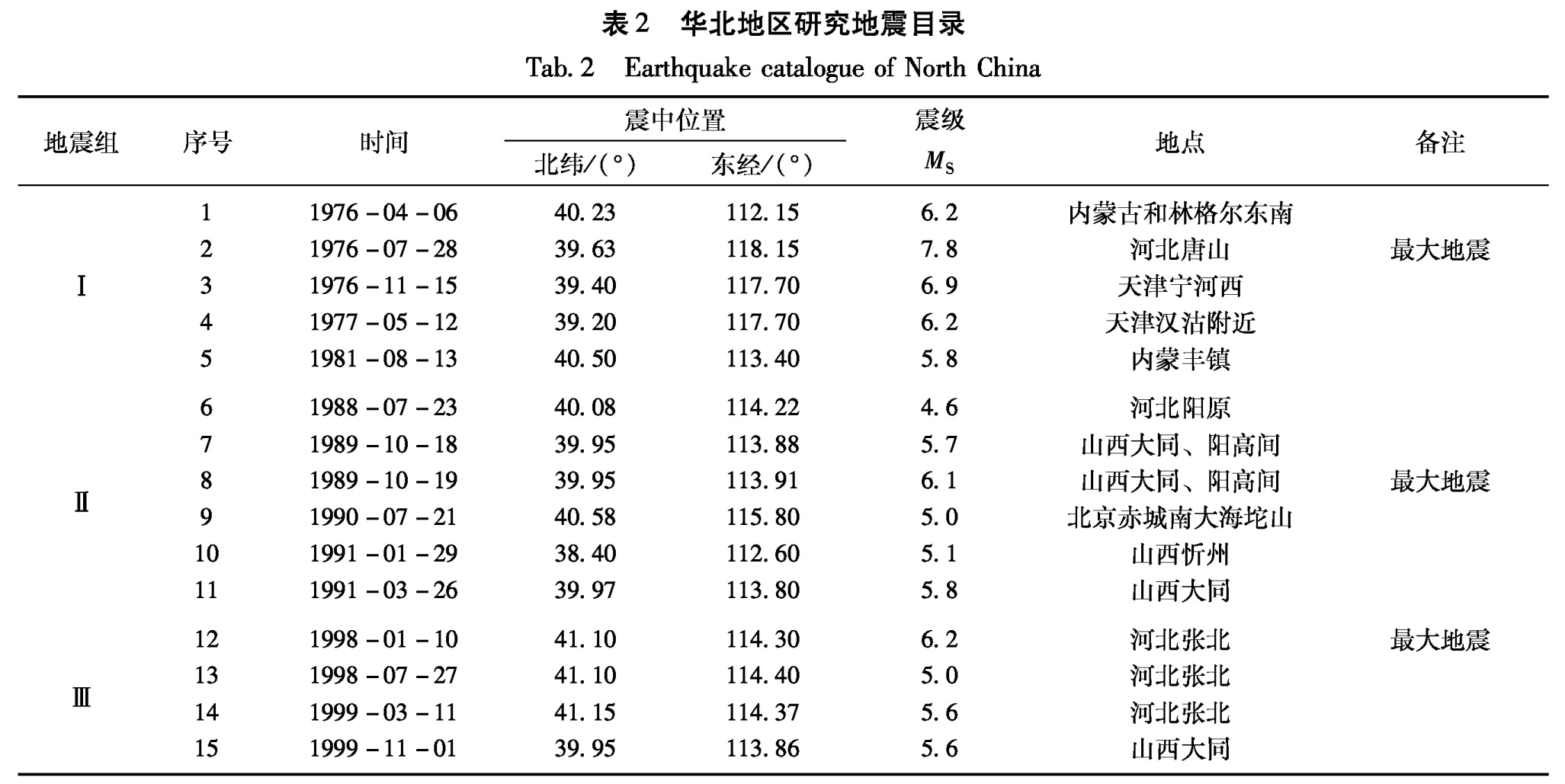
Tab.1 Selecting result table of observation items of subsurface fluid in North China1.2 研究地震的选定依据李钦祖等(1994,1995)的研究,强震的发生具有成组性。20世纪70年代以来,该区共
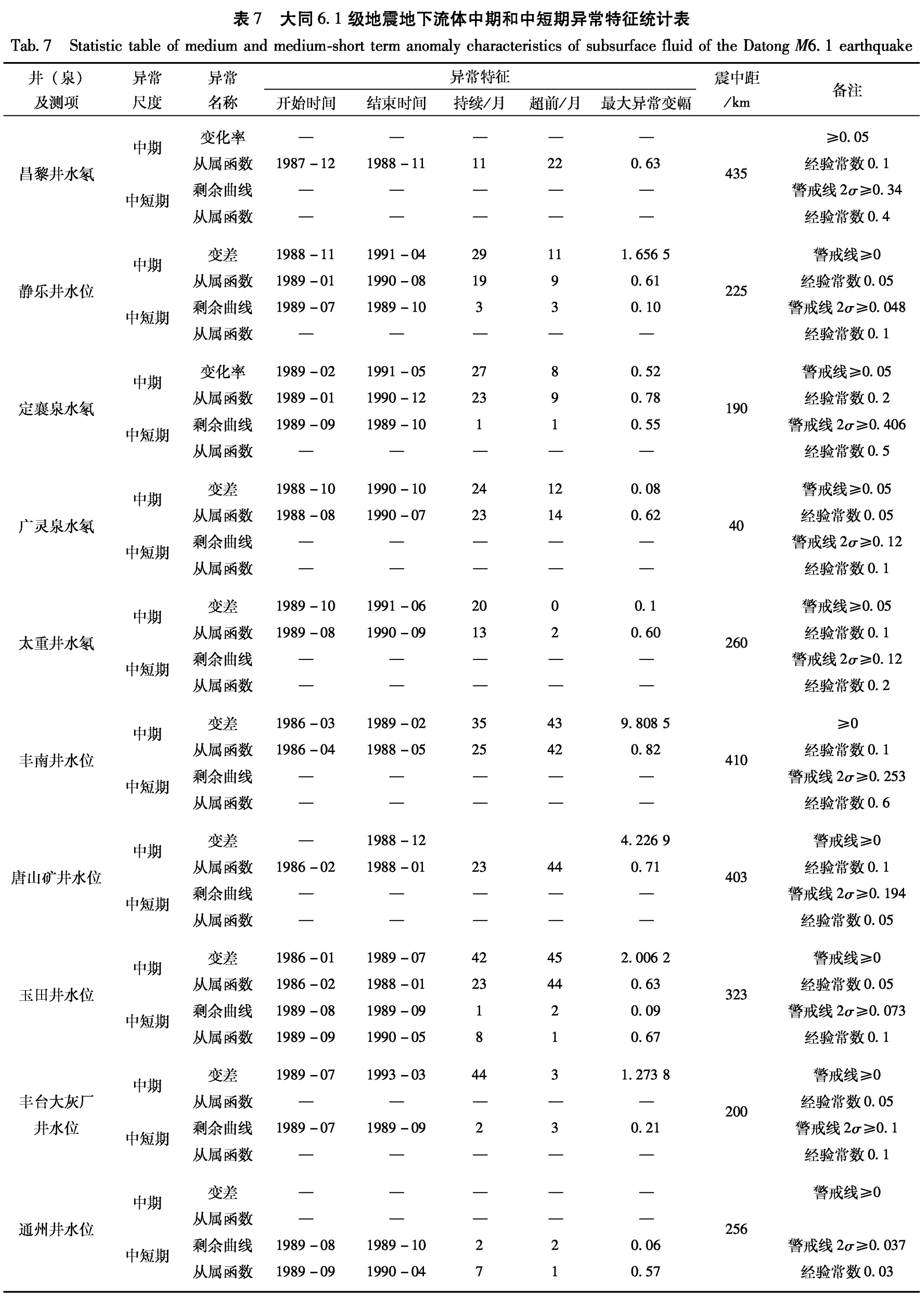
发生3组强地震,其中最大地震分别为唐山7.8级、大同6.1级和张北6.2级地震(表2)。
2 单点单项中期和中短期异常的定量判定方法
大量资料与研究表明,地下流体的中期、中短期异常,与地震的关系为“上升—下降—地震”,或“上升—发震—下降”(王吉易等,2008)。其中上升变化称为“中期”异常,其持续时间一般为1~5年; 由上升转折后出现的下降变化,称为“中短期”异常,也称“破年变”异常,一般出现在震前1年内,也有超过1年的。其判定方法如下 刘喜兰.2003.华北地区地下流体短期异常判定和预测.(杨明波等,2006; 范雪芳等,2002,2007):
(1)中期异常为上升异常变化。其判定方法列于表3。
(2)中短期异常为由上升转折后出现的下降变化(王吉易等,2008)。异常判定方法见表4。
说明:(1)ki为观测值变化斜率; ri为观测值M(t)与t间的相关系数; α为经验常数;
(2)将滑动平均、变差、变差率及从属函数的计算值,一律置放在右端点;
(3)滑动平均、变化率及从属函数的计算,采用ShepWin软件(刘耀炜编)。变差值计算,采用EIS2000软件。
说明:(1)ki为观测值变化斜率; ri为滑动平均值M(t)与时间t的相关系数; α为经验常数;
(2)将滑动平均、剩余值及从属函数等值置放于右端点;
(3)滑动平均、剩余值及从属函数的计算,采用ShepWin软件;
(4)中期从属函数异常转折下降后出现的中短期异常,为中短期前兆异常。
3 地下流体前兆异常实例
4 地下流体前兆异常时空特征
5 认识与讨论
(1)大量实际资料研究表明,华北地区6级以上地震前流体(水位、水氡)测点的中期异常表现为趋势性上升变化,而由趋势上升转变为下降变化,则为中短期异常,即为“破年变”异常。
(2)中期异常的判定可采用从属函数法和变差(或变化率)分析方法; 中短期异常的判定,则采用剩余曲线和从属函数两种方法。这些方法的特点在于:采用了比较合适的“时间结构参数”,也就是采用了较为合适的数据平滑窗长及拟合窗长。资料处理结果表明,这样的方法是有效的。
(3)依据大量异常的统计资料,给出了中期与中短期异常的时间定量特征。据此可拟定出发震时间的预测指标。
(4)趋势异常本身并不是某一个地震的“专有”前兆,而是多个地震的“共同前兆”。因为,从成因来看,趋势异常不是来自震源的“源兆”,而是“外因性”的“场兆”。这一特点决定了一组趋势异常变化并不只对应一个地震,而是对应一个地震的活跃时段,即趋势异常为多个强震、中强震的共同前兆。
(5)大量异常资料表明(表5、表7、表8),异常的最大变幅、持续时间与震级的大小没有直接关系。
(6)从观测资料看,地下流体的异常变化都直接或间接地与其它物理参量的动态变化有关。为此,今后要加强地下流体与其它学科观测量之间物理联系的研究。这可能是寻求不同学科前兆综合的途径之一。
致谢:本研究工作得到河北省地震局王吉易研究员及中国地震局地质研究所车用太研究员的悉心指导和帮助,谨致衷心谢意。
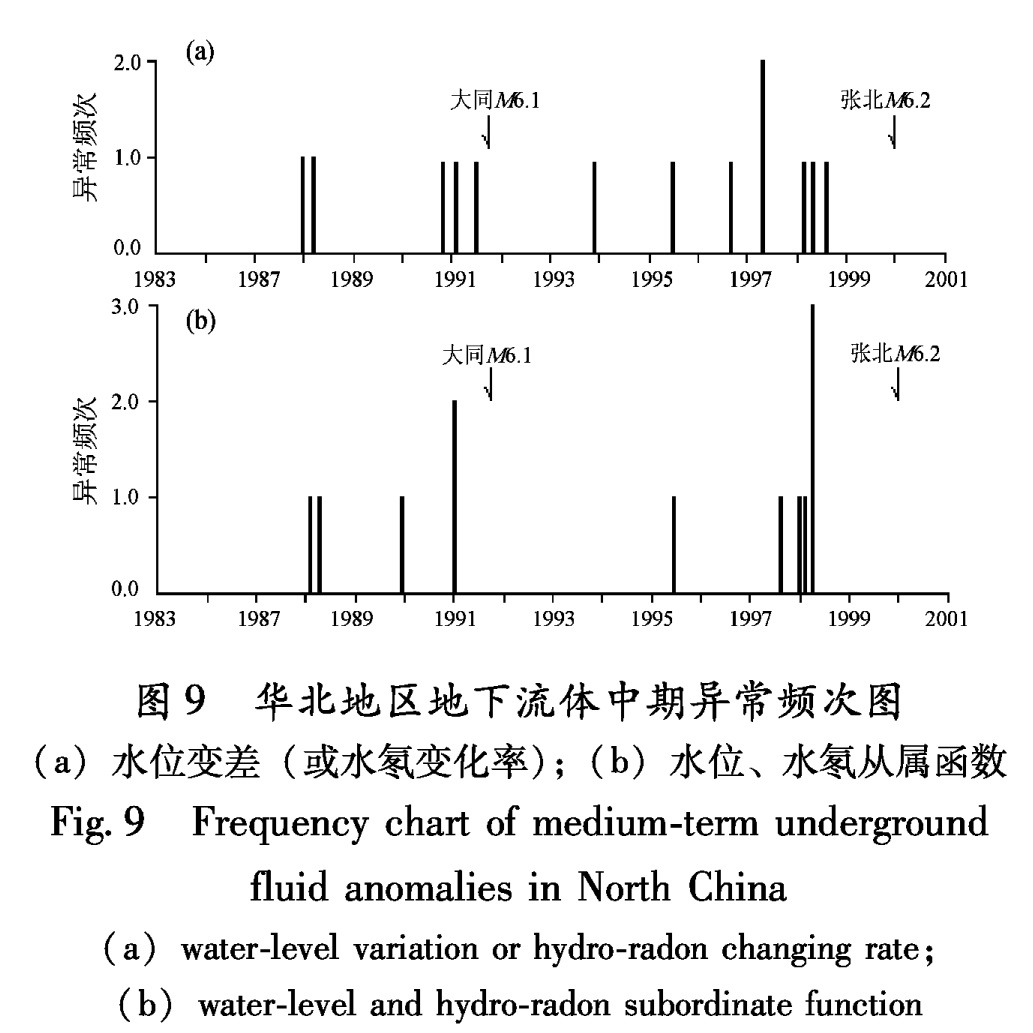
4.1 前兆异常的成从性利用统计资料(表5、表7、表8),得出水位变差与变化率、从属函数等中期异常频次图(图9)。并在异常的开始时间点上,画出一条短竖线来表示一个异常。可见:
(1)地下流体的变差(或变化率)和从属函数异常的频次,在时间上相对集中,即具有成从性。
(2)变差(或变化率)中期异常于强震前3~4年开始出现,而且多数异常集中在地震前2年。
(3)从属函数中期异常,于强震前3年开始出现,而多数异常集中在地震前2年。
4.2 异常的时间分布特征通过系统分析1976年唐山7.8级、1989年大同6.1级和1998年张北6.2级地震前出现的大量异常变化(表5、表7、表8)。根据21个观测井资料统计,得到如下结果。
4.2.1 中期异常(1)从属函数异常
异常持续时间:最小为 6 个月,最大为42个月,平均为19.2个月; 异常超前时间:最小为2个月,最大为 44 个月,平均为 21.8个月。图9 华北地区地下流体中期异常频次图(a)水位变差(或水氡变化率);(b)水位、水氡从属函数
Fig.9 Frequency chart of medium-term underground fluid anomalies in North China (a)water-level variation or hydro-radon changing rate; (b)water-level and hydro-radon subordinate function(2)变差或变化率异常
异常持续时间:最小为 3 个月,最大为64个月,平均为 31.4 个月; 异常超前时间:最小为0个月,最大为 45 个月,平均为 22.0个月。
4.2.2 中短期异常(1)从属函数异常
异常持续时间:最小为2个月,最大为17个月,平均为 7.2 个月; 异常超前时间:最小为1个月,最大为 12 个月,平均为 5.2 个月。
(2)剩余值异常
异常持续时间:最小为 1 个月,最大为3个月,平均为1.8个月; 异常超前时间:最小为1个月,最大为 11 个月,平均为 4.8个月。
4.3 异常的空间分布异常空间分布广泛,异常点的最大震中距达420 km。
- 范雪芳,王吉易.2001.预测发震时间的水氡滑动变化率值及其检验[J].地震,2l(1):85-93.
- 范雪芳,张淑亮,王吉易.2002.地下流体中期和中短期前兆异常的四种判定方法[J].地震,22(4):136-139.
- 范雪芳,张淑亮.2007.山西及其邻区地下流体强震中期和中短期预测时间方法的研究[J].西北地震学报,29(2):177-182.
- 黄辅琼,邓志辉,顾瑾平,等.2002.张北地震地下流体异常场的研究[J].地震,22(4):114-122.
- 李钦祖,于利民,王吉易,等.1994.成组活动是中国大陆强地震的一个基本特点[J].地震学报,16(1):11-17.
- 李钦祖,于利民.1995.中国大陆强地震的成组活动和概率预报[J].地震研究,18(1):90-107.
- 刘耀炜,施锦.2000.强震地下流体前兆信息特征[J].地震学报,22(1):102-107.
- 邵永新,李一兵,田山,等.2001.利用地下流体异常预测强震危险区的标志与方法[J].西北地震学报,23(2):125-130.
- 王吉易,贾炯,范雪芳,等.2008.中国地震预报探索,水诱发异常机理与华北强震中短期预测新探索[M].北京:地震出版社.268-275.
- 王吉易,宋贯一,曹志成,等.2002a.地下水诱发的浅层前兆异常及其机理与有关的地震预报问题(1)[J].华北地震科学,20(2):27-41.
- 王吉易,宋贯一,曹志成,等,2002b.地下水诱发的浅层前兆异常及其机理与有关地震预报问题(2)[J].华北地震科学,20(3):1-13.
- 王吉易,宋贯一,曹志成,等.2003.地下水诱发的浅层前兆异常及其机理与有关的地震预报问题(3)[J].华北地震科学,21(1):1-10.
- 杨明波,王吉易,刘喜兰,等.2006.北京及邻近地区中等以上地震地下流体异常识别与特征研究[J].地震,26(3):53-63.
- 张立,平建军,苏有锦.2006.云南地区综合地震前兆信息量及其短期映震能力分析[J].地震研究,29(4):325-331.
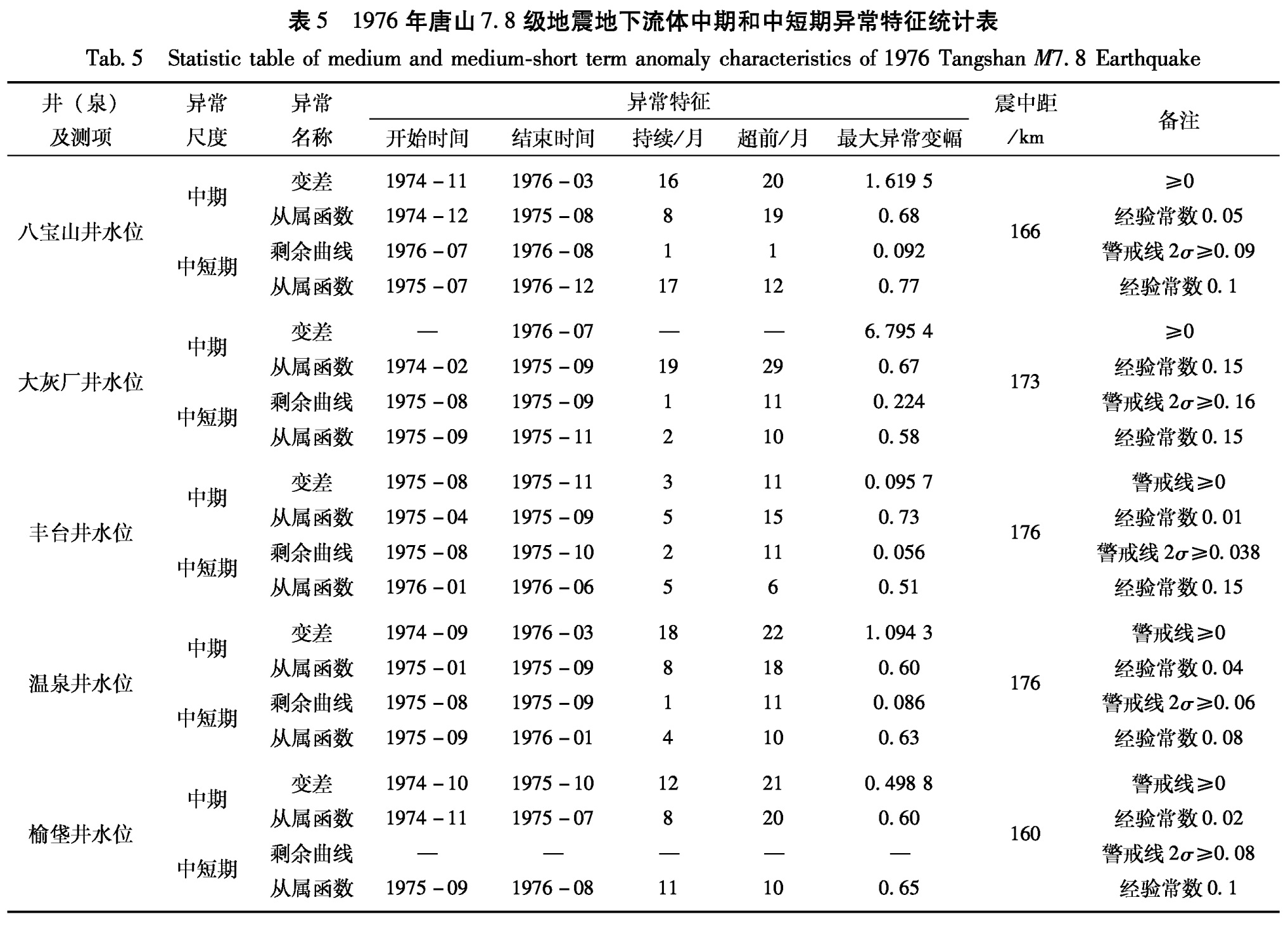
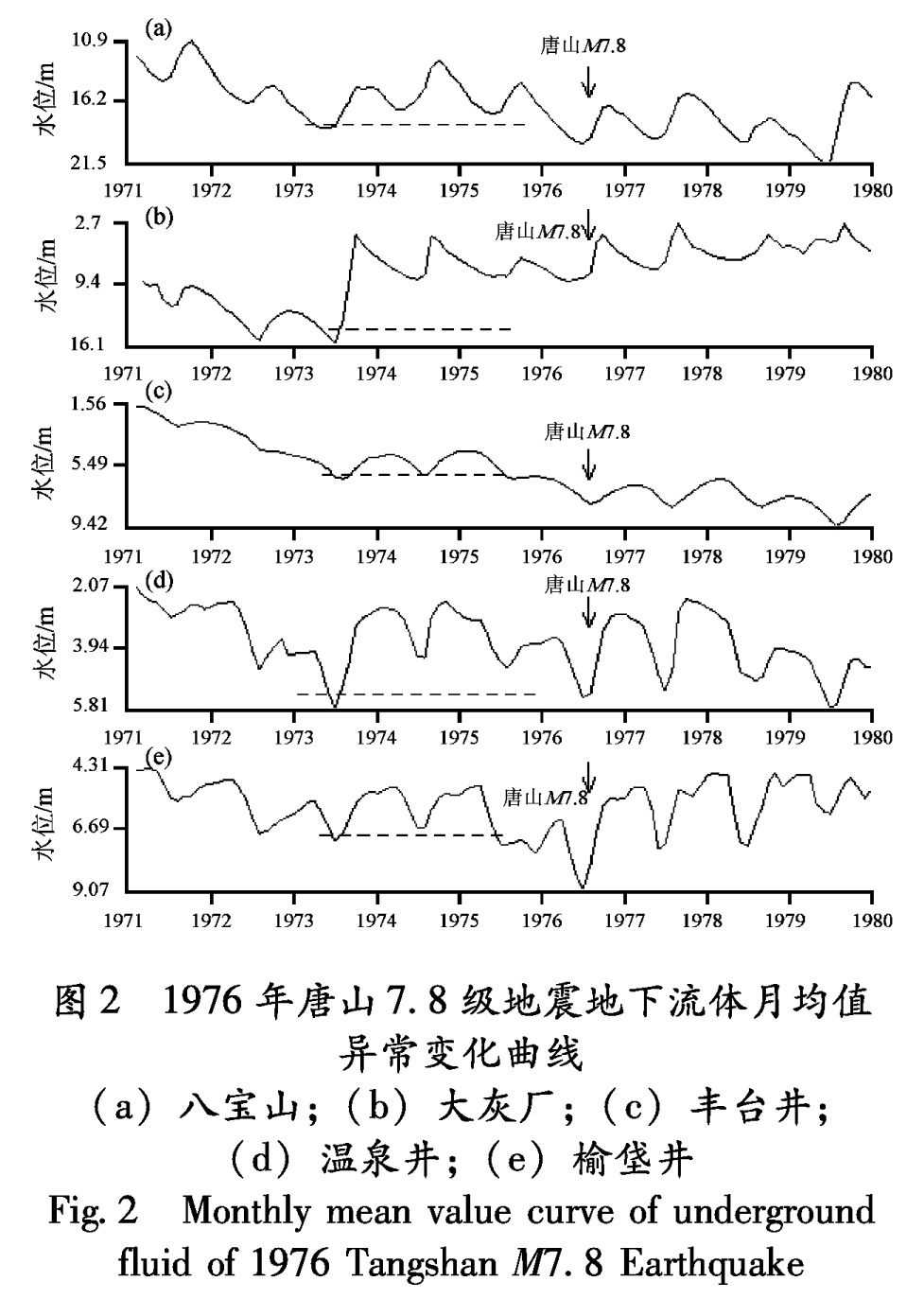
3.1 1976年唐山7.8级地震1976年唐山7.8级地震前,地下流体出现月均值、变差及从属函数中期异常变化。1973年8月以后,北京八宝山、北京大兴榆垡、温泉、大灰厂、丰台等井水位月均值从最低点同步转折上升,出现了趋势性异常变化; 1974年9月开始,出现变差中期异常; 1974年2月以后,出现从属函数中期异常(图2,表5)。
表5 1976年唐山7.8级地震地下流体中期和中短期异常特征统计表
Tab.5 Statistic table of medium and medium-short term anomaly characteristics of 1976 Tangshan M7.8 Earthquake图2 1976年唐山7.8级地震地下流体月均值异常变化曲线
(a)八宝山;(b)大灰厂;(c)丰台井;
(d)温泉井;(e)榆垡井
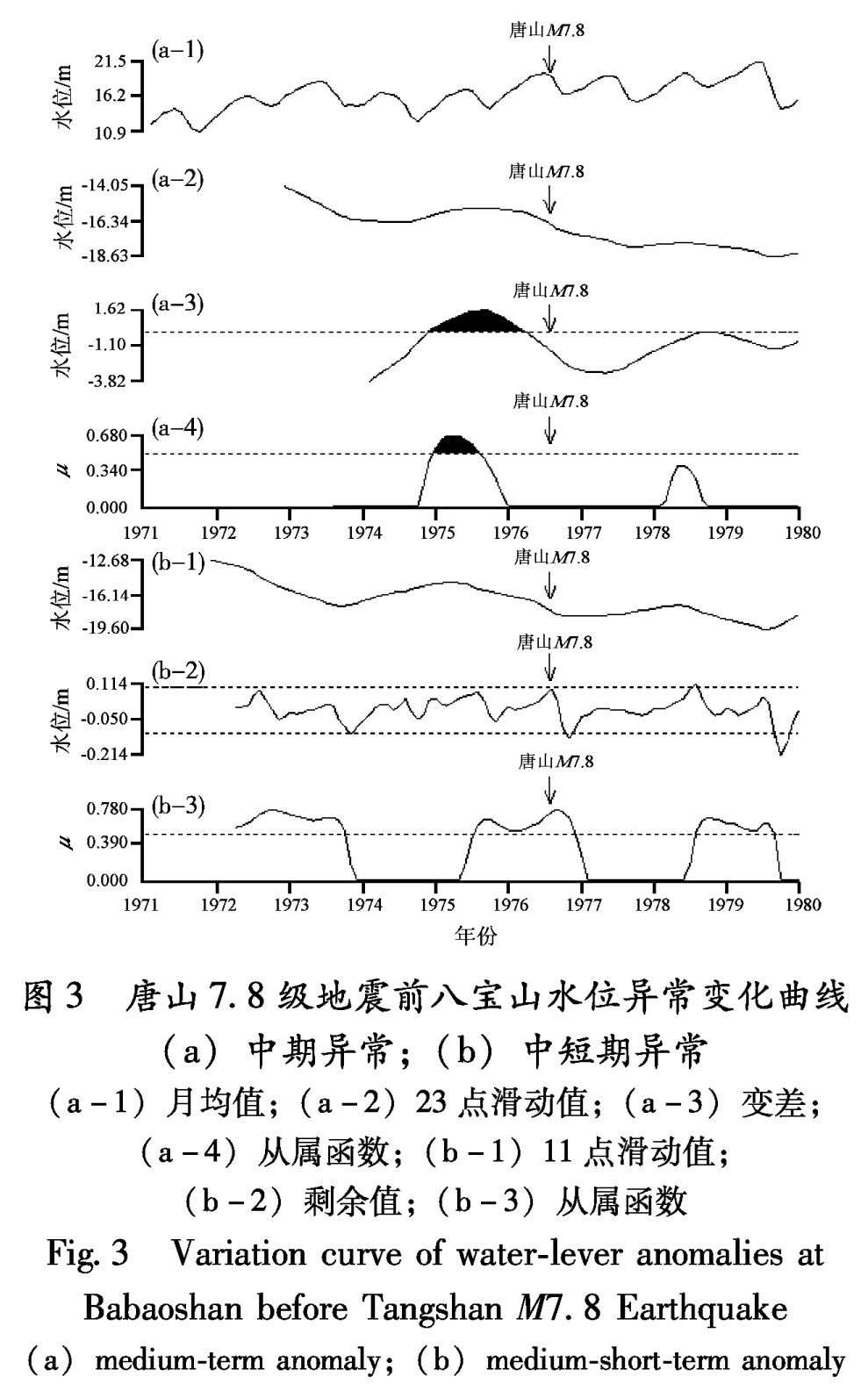
Fig.2 Monthly mean value curve of underground fluid of 1976 Tangshan M7.8 Earthquake3.1.1 北京八宝山井水位1973年6月(震前37个月)八宝山井水位月均值出现趋势性高值异常。变差方法分析时间为1974年11月至1976年3月,异常超前时间为20个月。从属函数异常的时间为1974年12月至1975年8月,异常超前时间为19个月(图3、表5)。中短期异常剩余值异常时间为1976年7月至8月,异常超前时间为1个月; 从属函数中短期异常时间为1975年7月至1976年12月,异常超前时间为12个月(图3、表5)。
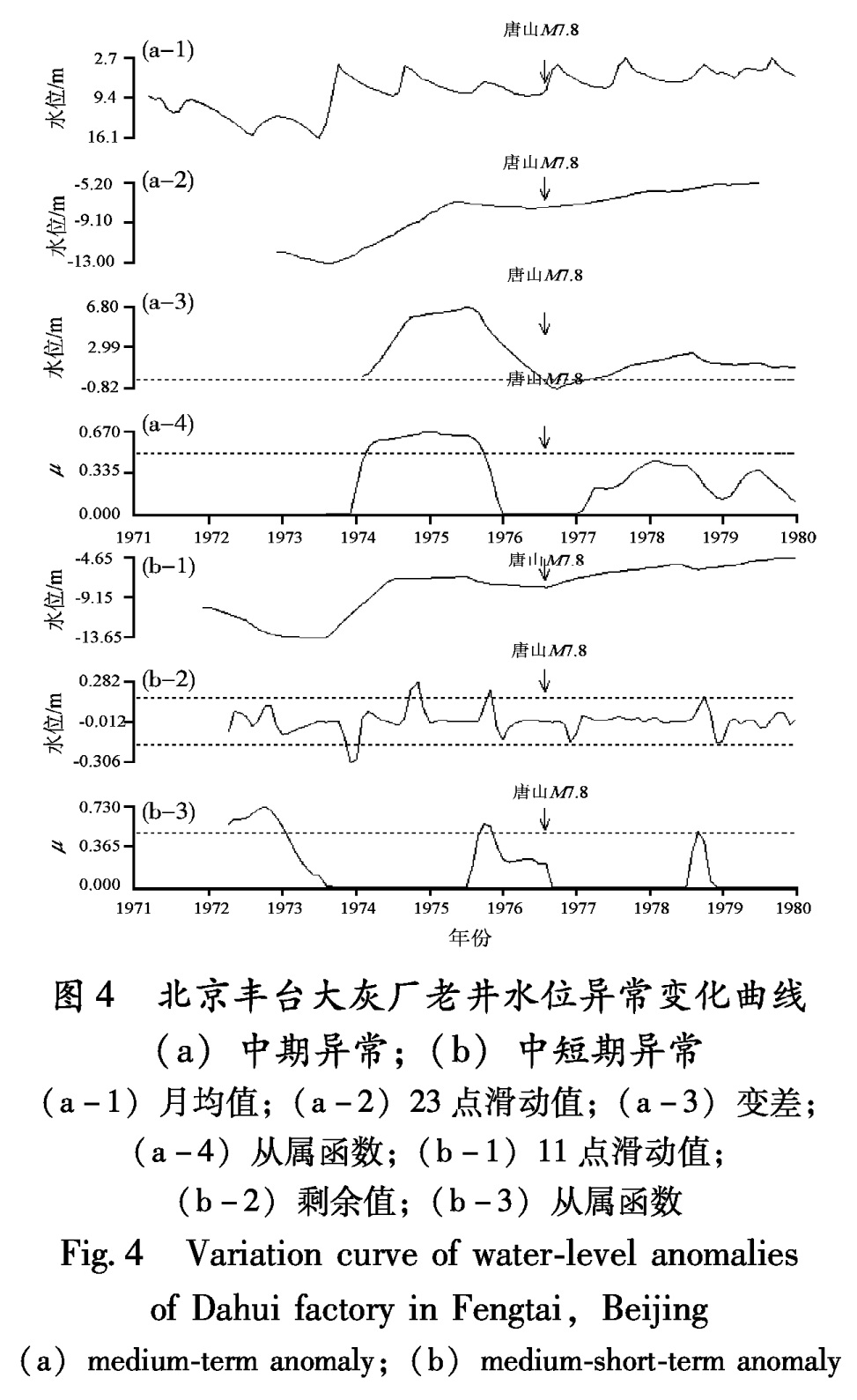
3.1.2 北京丰台大灰厂老井水位变差分析方法异常的时间为开始观测至1976年7月,异常超前时间为30个月; 从属函数异常时间为1974年2月至1975年9月,异常超前时间为29个月(图4,表5)。中短期异常剩余曲线分析异常时间为1975年8月至1975年9月,异常超前时间为11个月; 从属函数异常时间为1975年9月至1975年11月,异常超前时间为10个月(图4、表5)。
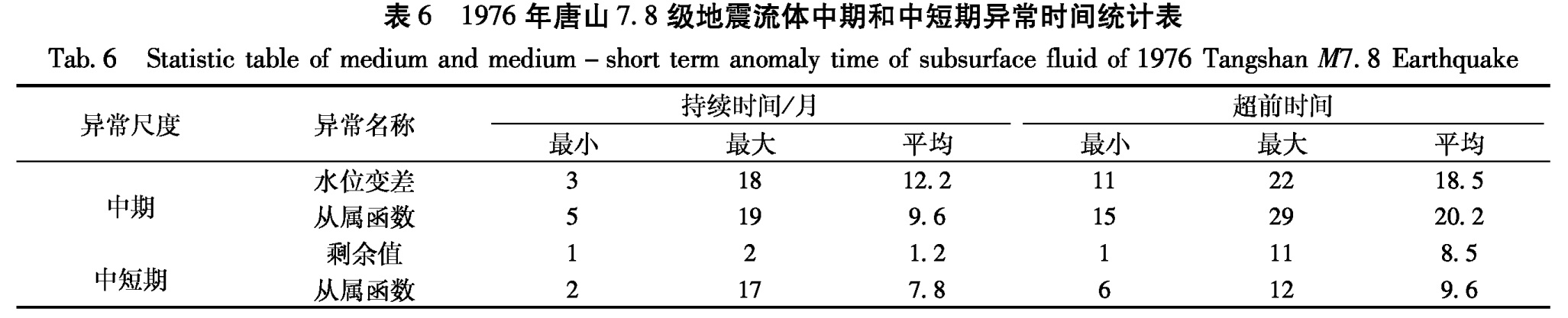
依据1976年唐山地震的异常资料(表5)统计,将其时间分布特征列于表6。
图3 唐山7.8级地震前八宝山水位异常变化曲线
(a)中期异常;(b)中短期异常
(a-1)月均值;(a-2)23点滑动值;(a-3)变差;
(a-4)从属函数;(b-1)11点滑动值;
(b-2)剩余值;(b-3)从属函数
Fig.3 Variation curve of water-lever anomalies at Babaoshan before Tangshan M7.8 Earthquake (a)medium-term anomaly;(b)medium-short-term anomaly图4 北京丰台大灰厂老井水位异常变化曲线
(a)中期异常;(b)中短期异常
(a-1)月均值;(a-2)23点滑动值;(a-3)变差;
(a-4)从属函数;(b-1)11点滑动值;
(b-2)剩余值;(b-3)从属函数
Fig.4 Variation curve of water-level anomalies of Dahui factory in Fengtai,Beijing (a)medium-term anomaly;(b)medium-short-term anomaly3.2 大同—阳高6.1级和张北6.2级地震两次地震间隔8年多,使用相同的判别指标,对流体观测资料进行分析。其地震前兆异常的特征列于表7和表8。
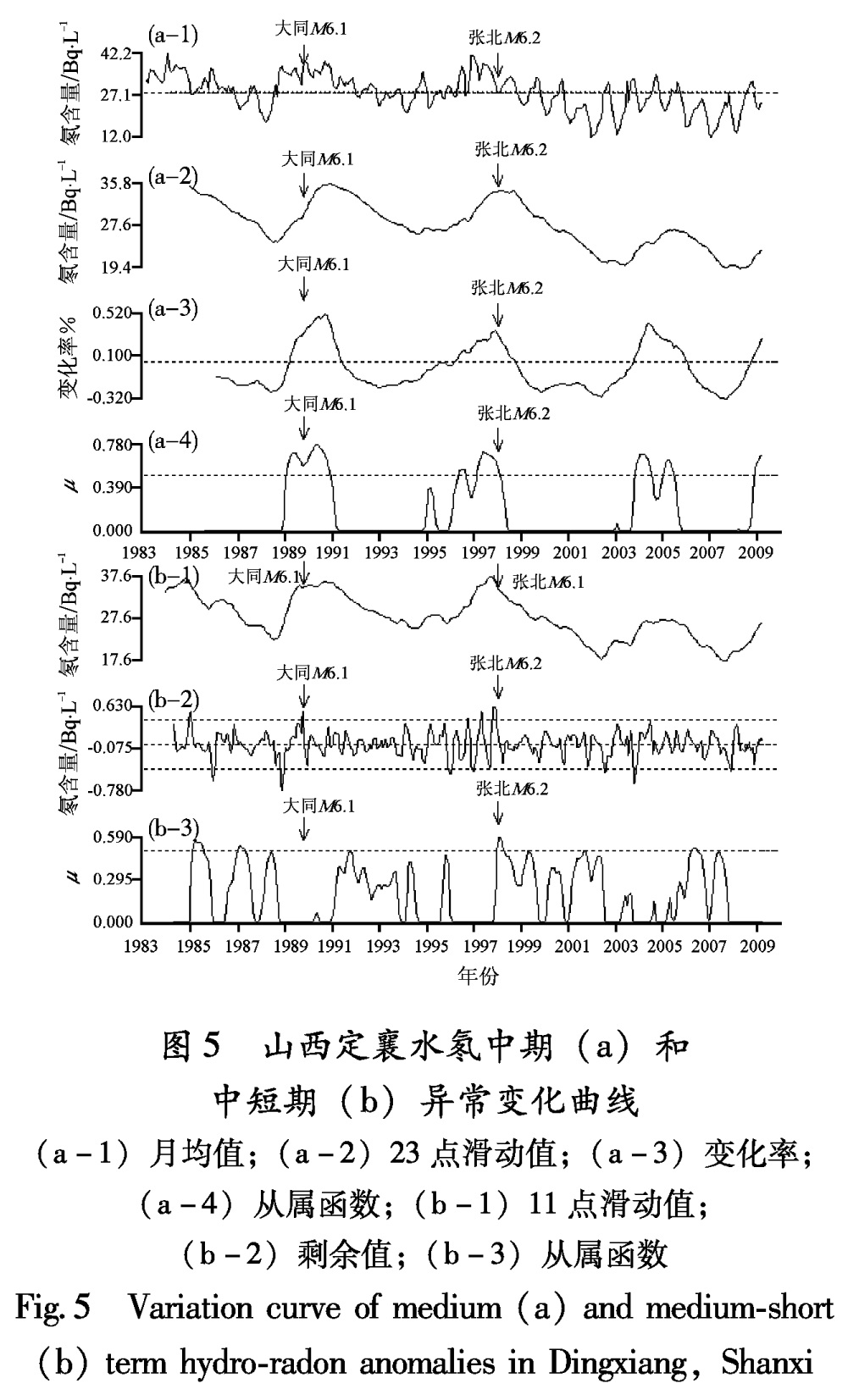
3.2.1 定襄泉水氡在1989年10月19日山西大同6.1级和1998年1月10日河北张北6.2级地震前,定襄泉水氡都有明显的中期和中短期异常变化,并据此作出过比较好的中期预测。
(1)1989年大同6.1级地震
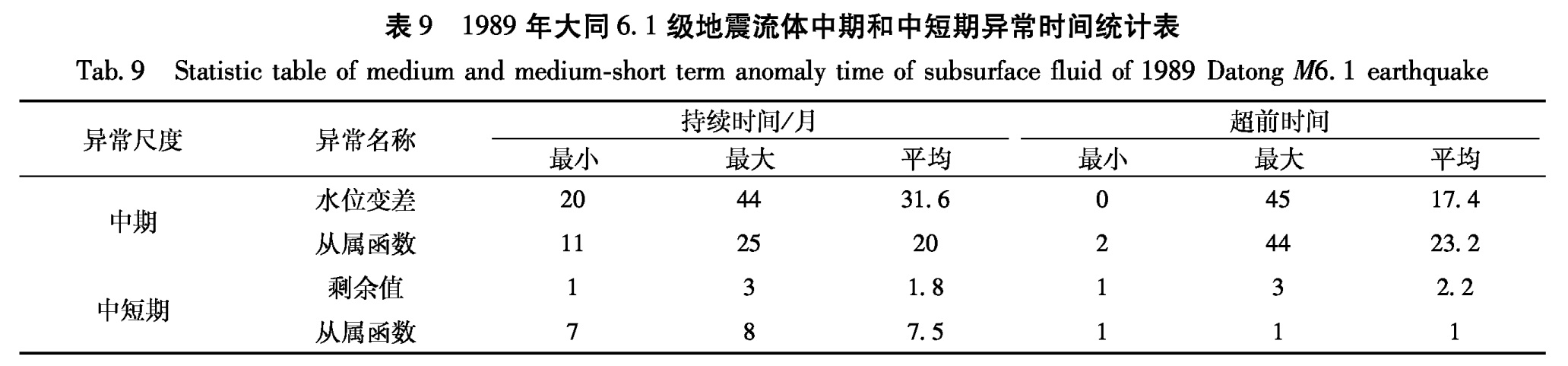
1988年6月定襄泉水氡月均值出现了大于均值的高值,持续时间42个月,异常超前时间17个月。1989年2月至1991年5月,出现变化率中期异常,异常超前时间为8个月。1989年1月至1990年12月,出现从属函数中期异常,超前时间9个月(图5、表7)。
中短期异常:剩余曲线异常时间为1989年9月至1989年10月,超前时间为1个月。
(2)1998年张北6.2级地震
1996年4月至1998年10月,定襄泉水氡月均值出现大于均值的异常,异常持续时间28个月,异常超前时间19个月。1996年3月至1998年10月出现变化率中期异常,超前时间22个月。1996年4月至1998年2月出现从属函数中期异常,超前时间21个月(图5、表8)。
表7 大同6.1级地震地下流体中期和中短期异常特征统计表
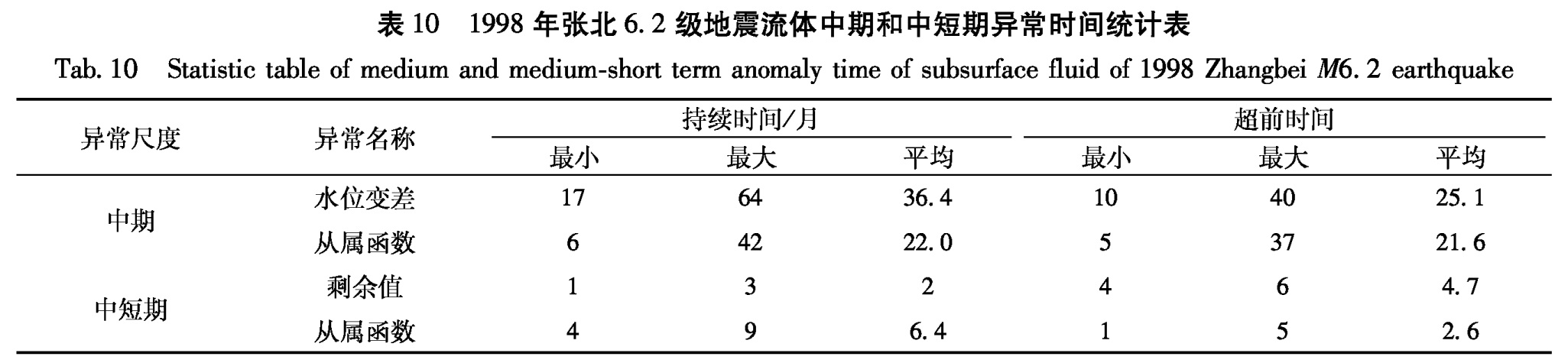
Tab.7 Statistic table of medium and medium-short term anomaly characteristics of subsurface fluid of the Datong M6.1 earthquake表8 张北6.2级地震地下流体中长期和中短期异常特征统计表
Tab.8 Statistic table of medium-long and medium-short term anomaly characteristics of subsurface fluid of the Zhangbei M6.2 earthquake图5 山西定襄水氡中期(a)和中短期(b)异常变化曲线
(a-1)月均值;(a-2)23点滑动值;(a-3)变化率;
(a-4)从属函数;(b-1)11点滑动值;
(b-2)剩余值;(b-3)从属函数
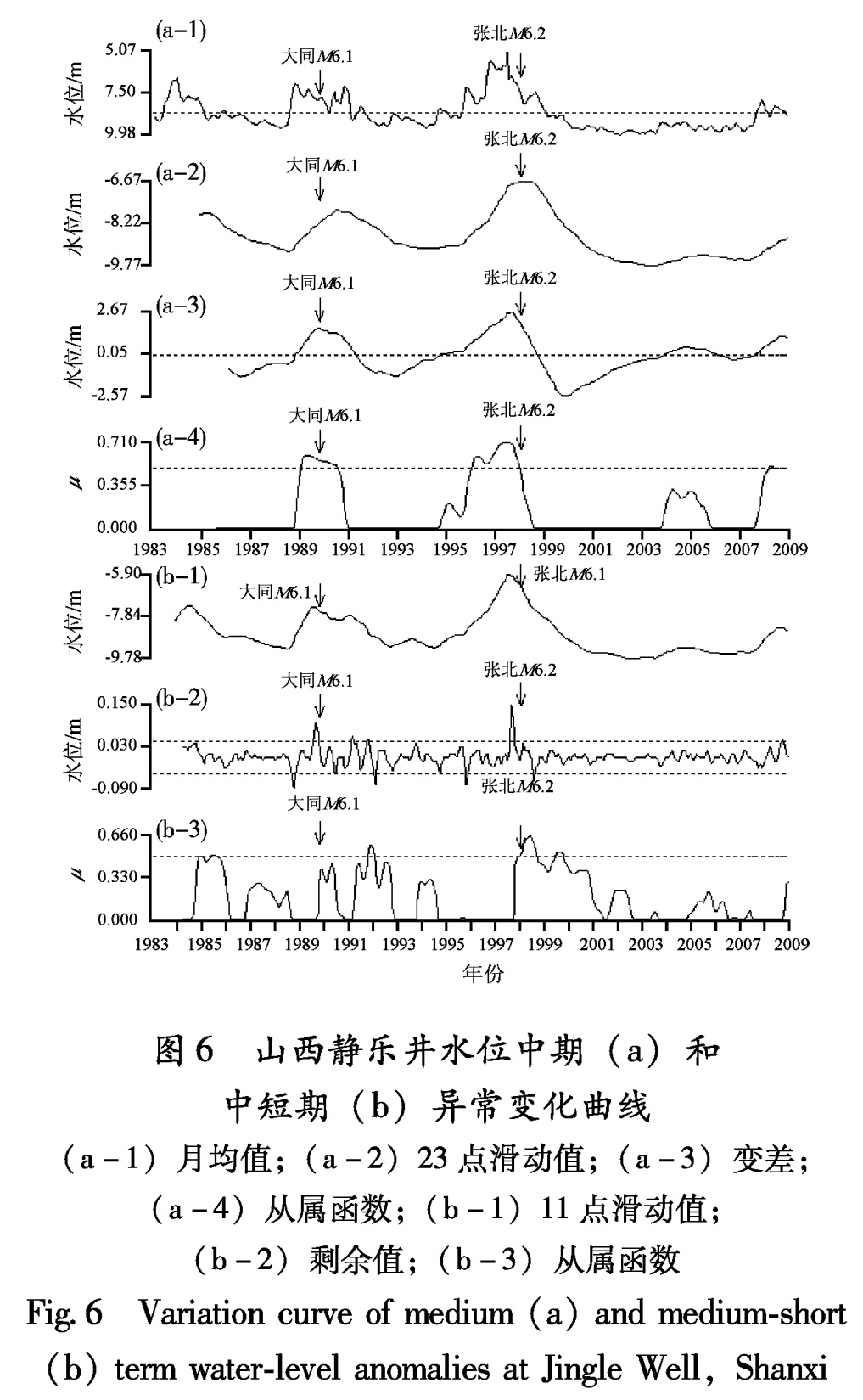
Fig.5 Variation curve of medium(a)and medium-short (b)term hydro-radon anomalies in Dingxiang,Shanxi图6 山西静乐井水位中期(a)和中短期(b)异常变化曲线
(a-1)月均值;(a-2)23点滑动值;(a-3)变差;
(a-4)从属函数;(b-1)11点滑动值;
(b-2)剩余值;(b-3)从属函数
Fig.6 Variation curve of medium(a)and medium-short (b)term water-level anomalies at Jingle Well,Shanxi中短期异常:1997年10月至1997年12月出现剩余曲线中短期转折异常,持续时间为2个月,超前时间3个月; 从属函数中短期异常时间为1997年12月至1998年4月,异常超前时间1个月。
3.2.2 静乐井水位(1)1989年大同6.1级地震
1988年7月至1991年9月静乐井水位月均值出现高值异常,异常超前时间16个月。1988年11月至1991年4月,出现变差中期异常,异常超前时间为11个月。1989年1月至1990年8月,出现从属函数中期异常,超前时间9个月。
中短期异常:剩余曲线异常时间为1989年7月至1989年10月,超前时间为3个月(图6、表7)。
(2)1998年张北6.2级地震
1995年6月至1998年9月静乐井水位月均值出现大于均值的高值异常,异常超前时间31个月。1994年9月至1998年9月,出现变差中期异常,超前时间40个月。1996年1月至1998年1月出现从属函数中期异常,异常超前时间24个月(图6、表8)。
中短期异常:1997年8月至1997年11月出现剩余曲线中短期转折异常,该异常的持续时间为3个月,异常超前时间5个月; 从属函数异常时间为1997年12月至1998年9月,异常超前时间1个月。
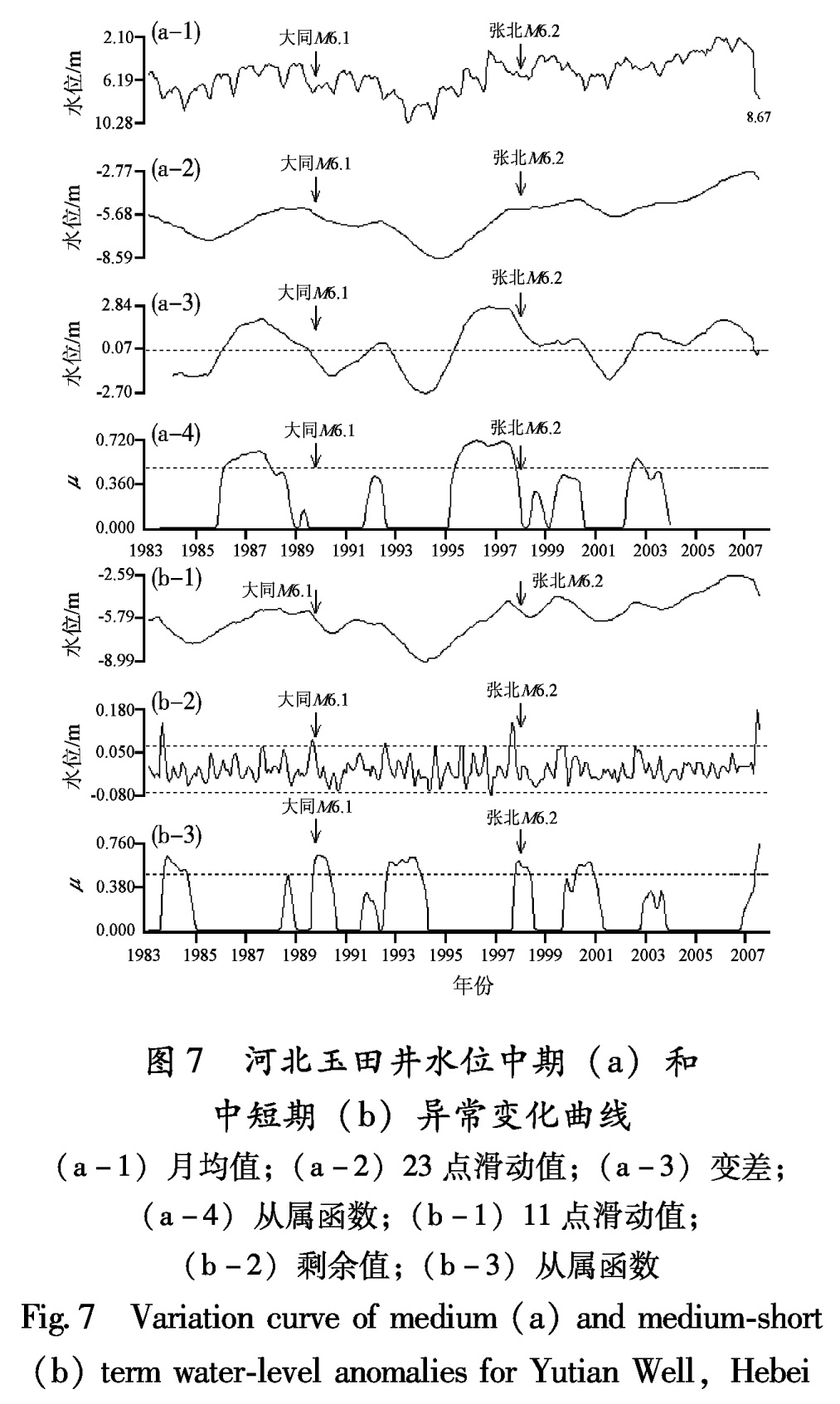
3.2.3 玉田井水位(1)1989年大同6.1级地震
1986年1月至1989年7月玉田井水位出现变差异常,异常超前时间为45个月; 1986年2月至1988年1月,出现从属函数异常,超前时间44个月(图7、表7)。中短期异常提取结果,1989年8月至1989年9月出现剩余曲线异常变化,异常超前时间2个月; 1989年9月至1990年5月出现从属函数异常变化,异常超前时间1个月。
(2)1998年张北6.2级地震
中期异常:1995年5月至2000年8月,出现变差异常,超前时间32个月; 1995年5月至1997年10月,出现从属函数异常,异常超前时间32个月(图7、表8)。中短期异常:1997年8月至1997年10月出现剩余曲线异常变化,异常超前时间5个月; 1997年10月至1998年5月出现从属函数异常变化,异常超前时间3个月。
3.2.4 唐山矿井水位(1)1989年大同6.1级地震
1986年10月至1988年12月唐山矿井水位出现月均值高值异常,超前时间26个月。1986年1月至1988年12月出现变差中期异常,超前时间为45个月(图8、表7); 1986年2月至1988年1月,出现从属函数中期异常,超前时间44个月。
图7 河北玉田井水位中期(a)和中短期(b)异常变化曲线
(a-1)月均值;(a-2)23点滑动值;(a-3)变差;
(a-4)从属函数;(b-1)11点滑动值;
(b-2)剩余值;(b-3)从属函数
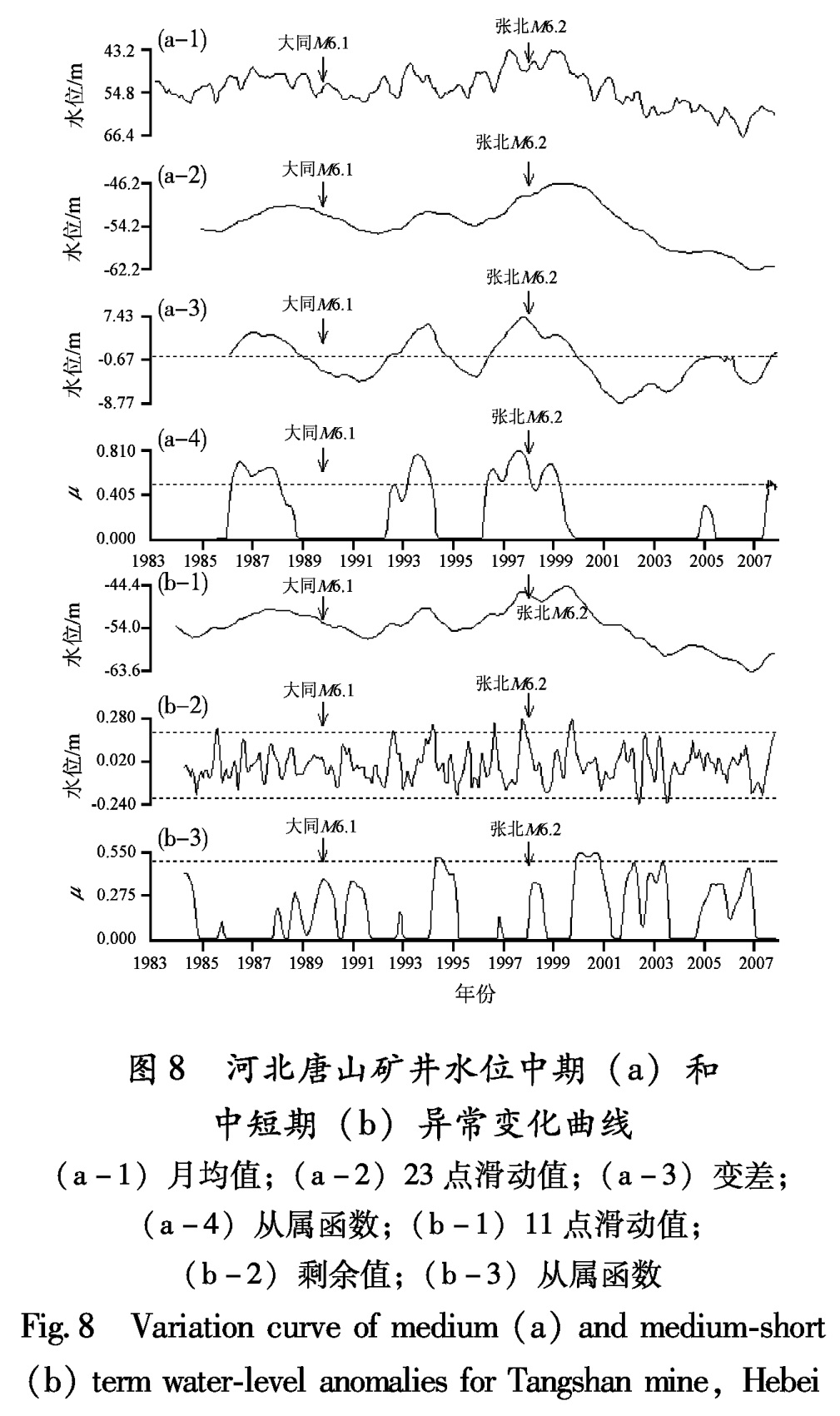
Fig.7 Variation curve of medium(a)and medium-short(b)term water-level anomalies for Yutian Well,Hebei图8 河北唐山矿井水位中期(a)和中短期(b)异常变化曲线
(a-1)月均值;(a-2)23点滑动值;(a-3)变差;
(a-4)从属函数;(b-1)11点滑动值;
(b-2)剩余值;(b-3)从属函数
Fig.8 Variation curve of medium(a)and medium-short(b)term water-level anomalies for Tangshan mine,Hebei(2)1998年张北6.2级地震
1995年11月至2000年4月唐山矿井水位月均值出现大于均值的高值异常,异常超前时间26个月。1996年5月至1999年12月出现变差中期异常,超前时间20个月; 1996年5月至1999年3月出现从属函数中期异常,超前时间20个月(图8、表8)。中短期异常:1997年9月至1997年11月出现剩余曲线异常变化,超前时间4个月。
依据异常资料(表6、表7)统计,大同和张北地震的时间分布特征分别列于表8和表9。
表9 1989年大同6.1级地震流体中期和中短期异常时间统计表
Tab.9 Statistic table of medium and medium-short term anomaly time of subsurface fluid of 1989 Datong M6.1 earthquake