基金项目:2011年度陕西省科学技术发展计划项目“汾渭断裂带地壳运动的非均匀负位错模拟与应变积累研究”(2011JM5016)与国家自然科学基金项目“汶川大震对应变积累的影响研究”(40974005)共同资助.
(中国地震局第二监测中心,陕西 西安 710054)
(The Second Monitoring and Application Center,CEA,Xi'an 710054,Shaanxi,China)
GPS; section deformation; strain accumulation; influence of great earthquake; the Fen-Wei Fracture Belt
备注
基金项目:2011年度陕西省科学技术发展计划项目“汾渭断裂带地壳运动的非均匀负位错模拟与应变积累研究”(2011JM5016)与国家自然科学基金项目“汶川大震对应变积累的影响研究”(40974005)共同资助.
利用1999~2009年汾渭断裂带GPS速度场观测资料,研究了跨断裂剖面变形动态演化特性、应变积累的分段差异性以及汶川大地震等的可能影响。结果 表明:近10年来山西断陷带南段、渭河盆地中东部应变积累相对较快,山西断陷带北端的蔚广盆地南缘断裂、渭河断裂西段也存在一定程度应变积累。汶川大地震影响相对明显,2007~2009年应变积累明显增强的有渭河断裂西段、山西断陷带南段和蔚广盆地南缘断裂。
Using velocity-field data observed by GPS from 1999 to 2009 in the Fen-Wei Fracture Belt,we study the features of the dynamic evolution of the cross-fracture section deformation,the difference of strain accumulation between fracture segments,and the possible influence of the MS8.0 Wenchuan Earthquake on the Belt. The result shows that in recent 10 years,the southern segment of the Shanxi Fracture and the middle-eastern Weihe Basin displayed relatively faster strain-accumulation,the southern margin fault of the Weiguang Basin and the western segment of the Weihe fracture also existed strain accumulation to some extent. All these variation obviously resulted from the Wenchuan Earthquake. From 2007 to 2009,the strain accumulation increased in the western segment of the Weihe Fracture,the southern segment of the Shanxi Fracture and the southern fault in the margin of the Weiguang Basin.
引言
汾渭断裂带即山西断陷带与陕西渭河盆地断裂区的总称,其北起晋冀蒙交界地区,南抵陕西关中,由一系列近NE—NNE、近EW向正断层构成,但也有一些段落兼走滑特性,以右旋为主,尤其是山西断陷带构成,有史记载,公元前280年以来汾渭断裂带共发生8级地震2次、7.0~7.9级地震6次(马宗晋,1982; 苏怡之,王进英,1991; 张世民,2000)。2008年5月12日,距汾渭断裂带最近处约200 km的龙门山断裂带发生汶川8.0级大震后,中国地震局第二监测中心等单位在震区及其周边作了GPS观测,结果显示大震对渭河盆地尤其是其西部影响明显(张希等,2009a,2009b,2010a,2010b)。近两年多来汾渭断裂带中小地震明显增多:继2009年3月28日山西原平4.2级地震后,2009年11月5日至2010年6月5日短短7个月里连续发生2009年11月5日陕西高陵4.4级、2010年1月24日山西河津4.8级、2010年4月5日山西阳高4.5级与2010年6月5日山西阳曲4.6级地震。2011年3月7日山西忻州又发生一次4.2级地震,这些地震的发生可能是因为汾渭断裂带受到了汶川大地震的影响。2010年以来陕西渭河盆地中东部至山西断陷带中南段有多处定点连续形变与流体前兆测项出现显著异常①,使得地学工作者对汾渭断裂带的关注度明显提高。笔者利用1999年有较密集观测点以来,至2009年已积累10年的GPS水平运动速度场结果(观测周期2~3年,2011年仍在复测中),通过投影计算,研究跨断裂剖面变形的动态演化特性、应变积累的分段差异性,以及汶川地震等8级大震的可能影响。
1 跨汾渭断裂带剖面变形计算方法与说明
谈到剖面变形及其反映的应变积累特性,张培震等(2009)与张希等(2011)对汶川大震前跨龙门山断裂GPS(选取)剖面与长水准观测剖面的变形分析,都显示断裂两侧数十千米至一二百千米范围内明显的位移差异变化,越靠近断裂,位移变化量越小、呈现一种类似“S”或反“S”的形态特征。通过考查断裂两侧一定范围内位移
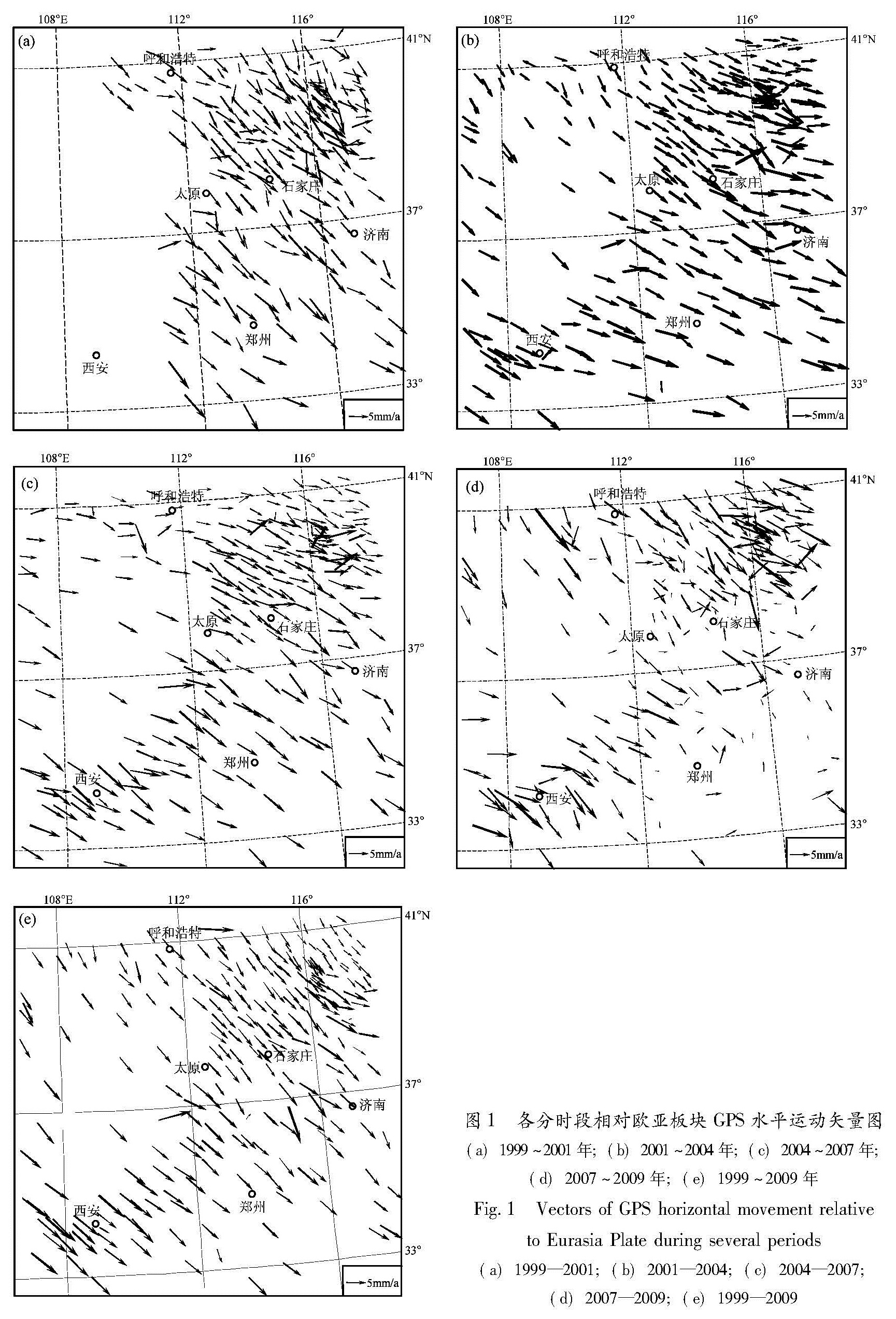
图1 各分时段相对欧亚板块GPS水平运动矢量图
(a)1999~2001年;(b)2001~2004年;(c)2004~2007年;
(d)2007~2009年;(e)1999~2009年
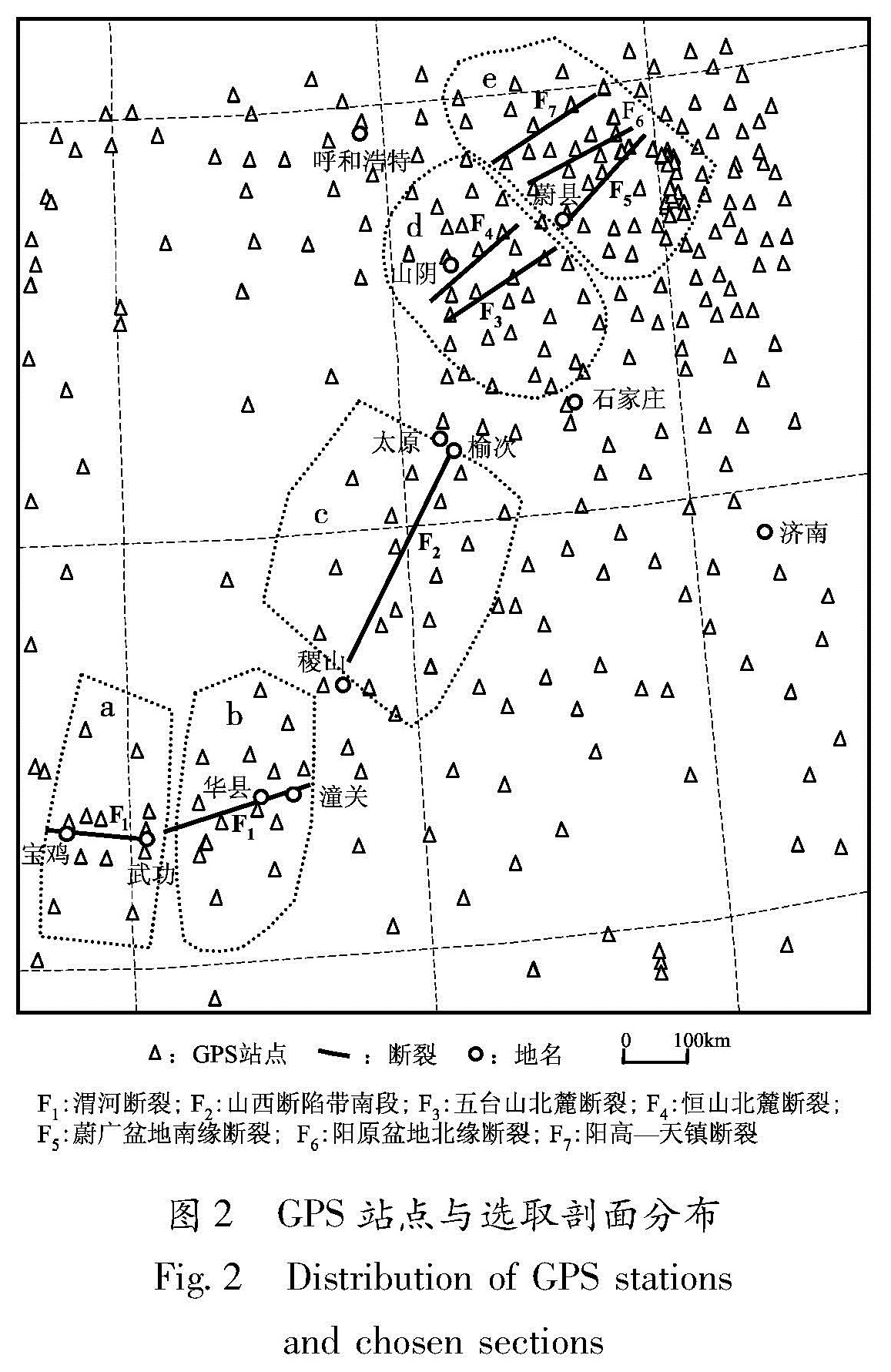
Fig.1 Vectors of GPS horizontal movement relative to Eurasia Plate during several periods(a)1999—2001;(b)2001—2004;(c)2004—2007; (d)2007—2009;(e)1999—2009相对变化与曲线形态,可以估计跨断裂处能量积聚的基本特性。要做到这一点,断裂两侧站点不能太少、数量也要均衡。汾渭断裂带及其周围积累有中国地壳运动网络工程项目1999~2001年、2001~2004年、2004~2007年、2007~2009年4个分时段及1999~2009年总时段相对欧亚板块的水平运动速度场结果(图1)。如图2所示,笔者尽可能选取两侧站点多、且站点数比较均衡的主要断裂(分5个区a~e、8条断裂段,其中的山西断陷带南段包含罗云山、霍山山前、太谷和平遥断裂),向两侧各扩展约100 km,求取其内GPS站点相对断层线垂向距离及速度投影,计算所得GPS剖面各时段与总时段位移动态演化情况(图3)。鉴于汾渭断裂带断裂深度基本为一二十千米,其构造活动影响到地表的位移变化范围有限(两侧各几十千米),再考虑该断裂带两侧GPS站点布设、周围其它断裂分布的实际情况,故在断裂两侧各取约100 km范围分析研究是比较可行的。
(1)为将相对欧亚板块GPS水平运动速度投影至平行于断裂走向与垂直于走向的法线方向,所用断裂段应该是直线段。实际断裂构造不完全笔直,只能用直线段近似或分段近似,故图2中线段为实际断裂分布,它们由基于GIS的地震预报分析系统Mapsis软件中“中国断层.Tab”文件绘制,与图3有关的断裂段倾向见图3相应文字叙述,黑色粗线段为对选定断裂直线近似后的剖面断层段。至于包含数条小断裂而且也不够整齐的山西断陷带南段,是本文需要了解其两侧变形差异与应变积累特性的重要段落,但其两侧GPS站点太少,不适合逐条计算,只能简化为一条直线段分隔两侧站点,其倾向取多数断裂的倾向,最终目的是计算其两侧一定范围内块体间总体变化差异,对其它断裂段也是如此。
(2)GPS水平运动速度投影,分平行于走向和垂直于走向的法线方向两个分量(图3)。图中横坐标为相对断层垂向距离,定义下盘为负、上盘为正; 纵坐标为所有站点投影后速率减去下盘最远站点的速率所得相对位移变化平行于走向的分量,规定正值变化反映左旋走滑,负值则为右旋走滑; 垂直于走向即法线方向的分量,规定正值变化反映压性、负值则表示拉张。此外,还规
定断层走向与倾向是遵循“右手规则”的,即伸出右手,手心向上,五指方向为断层走向方向、拇指即指向断层上盘。鉴于计算时将断裂两侧站点(正东、正北向)速率按平行于走向和垂直于走向两个方向投影,不管上盘取在断裂左侧还是右侧,计算时走向角度值(与正北向顺时针夹角)、起点(下盘最远处)会相应变化,故即使选定断层段两侧还有平行断裂而且倾向不同,也不会影响选定断层段两侧一定范围内挤压或拉张、右旋或左旋的差异特性。具体计算步骤如下:①寻找剖面选取范围(图2中虚线框所围区域)内GPS站点,假设有n个,其高斯投影坐标为(xi,yi),相应正东、正北向速度值为(ui,vi),i=1,…,n; ②计算各站点与断层直线段的垂向距离,判断其在断裂的哪一侧,下盘站点垂向距离再乘以-1,以区分上、下盘; 进而寻找下盘距断层段垂向距离绝对值最大(即距断层最远)的点,作为位移变化起点即基准点; ③针对每个站点,求速度投影平行于走向和法线方向分量(pi,qi),其中pi=uisin(φi)+vicos(φi), qi=-uicos(φi)+visin(φi), i=1,…,n,这里的φi为按“右手规则”断层走向与正北向顺时针夹角; ④用每个站点速度投影分量分别减去基准点速度投影分量值,即得到相对位移变化分量值。
(3)如上所述,200 km范围可能跨过数条接近于平行的断裂,其不同倾向对张、压性分析无影响。而GPS水平运动速度投影到不同的断裂其两侧变化曲线却存在差异,所以本文选择两侧站
图3 渭河断裂西段剖面(a)、渭河断裂中东段剖面(b)、山西断陷带南段剖面(c)、恒山北麓断裂剖面(d)和蔚广盆地南缘断裂剖面(e)的变化(图中纵细线、横细线分别表示断层位置、位移变化零值线。蓝色虚线表示1999~2001年剖面变化; 红色、绿色、紫色虚线分别表示2001~2004、2004~2007、2007~2009年剖面变化; 黑色粗实线表示1999~2009年即最长时间尺度的剖面变化)
Fig.3 Section variation at the western segment of Weihe fracture(a),at the middle-eastern segment of Weihe fracture(b),at the southern segment of Shanxi fracture(c),at the northern margin fault of Hengshan(d),and at the southern margin fault of Weiguang Basin(e)点较多、站点数相差不大的8条断层段(图2),通过剖面变化计算,希望能找到差异变化较大、能够呈现一种可能与应变积累有关、类似“S”或反“S”型的变形特征。
(4)研究区内1999~2001年、2001~2004年、2004~2007年、2007~2009年4个时段GPS站点速度(分别于1999、2001、2004、2007、2009年观测了5期,利用GAMIT/GLOBK软件处理获得相邻时段的速度场结果)均方根差均值分别为1.2、1.6、1.3、1.4 mm/a,而1999~2009年总时段站点速度均方根差均值仅0.4 mm/a,也没有出现断裂某一侧均方根差都大、而另一侧都小的情况,加上本文所用方法属于线性计算,计算前还剔除个别均方根差很大的站点,笔者认为所获得的跨断裂剖面变化曲线的拉张或挤压、左旋或右旋趋势特征是有意义的。
2 跨汾渭断裂带剖面变形与应变积累分析
2.1 跨渭河断裂剖面变形分析渭河断裂西段(宝鸡—武功段,南倾,图3a,断层段长度约130 km,断层两侧共12个GPS站点)在汶川大震前及近10年略微有点左旋、但上、下两盘差异微弱,2007~2009年上盘相对下盘差异量值大增,右旋变化显著; 而法线方向两盘差异总体变化也较稳定并以拉张为主,相对走滑分量明显,1999~2001年、2001~2004年总体拉张,2004~2007年略微反向(由上一时段的拉张转为挤压),2007~2009年该断裂段恢复拉张变化、速度剧增,上盘相对下盘最远处最大变化量达6.9 mm/a,是1999~2009年总时段两盘速度差异的4倍。总体上该断裂段剖面变形以拉张变化为主与地质活动背景一致,反映了一定的应变积累特性,近10年最长时间尺度两盘速度差异变化约1.6 mm/a; 受汶川大地震影响显著、应变积累加速,与万永革等(2009)的库仑应力变化计算结果一致。
渭河断裂中东段(武功—华县—潼关段,南倾,图3b,断层段长度约209 km,断裂两侧共14个GPS站点)右旋特征清晰,1999~2009年总时段两盘速度差异为2~3 mm/a左右,2001~2004年两盘右旋差异弱于1999~2001年; 2004~2007年、2007~2009年,尤其后一时段右旋变化明显加速。断裂两侧法线方向1999~2001年的相对变化反映弱压性,2001~2004年时段较1999~2001年时段压性差异减弱、断裂附近略微反向(由上一时段的压性转为拉张),2004~2007年该断裂段压性明显,2007~2009年则出现相反的拉张特性,不排除是受汶川大震调整(负)影响的可能。1999~2009年总时段反映右旋兼弱压性变化,有一定程度应变能积累。总体来看,昆仑山口西巨震与汶川大地震对其均有影响,这种影响可能以调整为主,所得结果与张希等(2009b)库仑应力变化计算结果一致。
2.2 跨山西断陷带剖面变形分析山西断陷带南段(稷山—榆次段,以北西倾为主,图3c,断层段长度约316 km,断裂两侧共18个GPS站点),由南至北包含罗云山断裂、霍山山前断裂、太谷断裂、平遥断裂)右旋走滑明显,2001~2004年右旋走滑略弱于1999~2001年(不排除受昆仑山口西8.1级大震弱调整影响),2004~2007年右旋走滑略增,2007~2009年断裂附近两盘差异微弱; 而断裂两侧法线方向相对拉张特性也非常清晰,1999~2001年、2001~2004年、2004~2007年3个时段变化基本稳定,2007~2009年断裂两盘差异明显增强,比走滑分量改变明显,汶川地震的影响总体为正。近10年来最长时间尺度右旋、拉张差异均明显(至少2~3 mm/a),与构造背景一致,总体反映应变积累特性。
山西断陷带北段五台山北麓断裂走滑特征不显著(图略),1999~2001年、2001~2004年、2004~2007年、2007~2009年4个小时段呈现波动、右旋变化稳定,两盘差异偏小; 法线方向两盘差异也如此,只有2007~2009年拉张增强,总体上应变积累并不快。而与其平行的恒山北麓断裂(图3d,北西倾,断层段长度约135 km,断裂两侧共25个GPS站点)右旋变化要比五台山北麓断裂明显一些,但应变积累总体不高(汶川大地震对其有些扰动影响,波动性增强但正、负影响尚难确定); 法线方向变化分量也是如此,昆仑山口西大地震调整影响、汶川大地震影响(正影响略微明显)也比五台山北麓断裂明显,总体上1999~2009年右旋拉张略占优势,与构造背景一致,但长时间尺度剖面变化远没有山西断陷带南段乃至渭河断裂显著。
山西断陷带北端、晋冀蒙交界区附近的蔚广盆地南缘断裂(蔚县附近,北西倾,图3e,断层段长度约163 km,断裂带两侧共46个GPS站点)走滑方向波动明显,尤其是在2007~2009年; 法线方向变化分量以拉张为主要特性,量值较走滑量明显,与构造背景一致,尤其是2007~2009年,拉张差异大幅增强。总体来看,1999~2009年垂直于断裂走向两侧的拉张差异也接近2 mm/a,存在一定程度的应变积累。阳原盆地北缘断裂(图略)长时间尺度走滑方向两盘差异不大、只有2007~2009年右旋为主的波动加剧; 法线方向两盘差异也是如此弱于蔚广盆地南缘断裂。阳高—天镇断裂(图略)的剖白变形与应变积累情况与阳原盆地北缘断裂相似,汶川大震也可能对其造成扰动影响。
需要补充说明的是,由于五台山北麓断裂、阳原盆地北缘断裂、阳高—天镇断裂在1999~2009年期间剖面变化偏弱(多数断裂2007~2009年即汶川大震期间扰动变化增强),限于篇幅,本文略去相应剖面图; 对恒山北麓断裂只给出2004~2007年、2007~2009年、1999~2009年剖面变化。事实上本文所获得的,仅是一种观测资料所反映的10年间的剖面位移变化,与长期地质资料显示的构造活动特性、量值可能一致,也可能存在差异,但本文计算结果至少表明汾渭断裂带拉张(即正断)为主、兼走滑(右旋占多数)的基本特性与地质背景一致。
3 结论与讨论
就1999~2009年10年的长时间尺度而言,汾渭断裂带应变积累速度总体偏慢,但其中的山西断陷带南段(稷山—榆次段)、渭河盆地中东部(武功—华县—潼关段)即晋—陕交界及其附近地区应变积累速度相对较快,两盘变化差异2~3 mm/a,甚至达到3 mm/a以上,剖面变化曲线大体上表现出可能与应变积累有关的类似反“S”型的特征,较张培震等(2009)、张希等(2011)估算的汶川大地震前跨龙门山断裂数十至200 km长度的剖面变化最高近2 mm/a的差异速度略快。山西断裂带北端的蔚广盆地南缘断裂、渭河断裂西段也存在一定程度的应变积累,断裂两侧差异变化达1.6~2 mm/a左右; 其它段落变化相对稳定。2001年昆仑山口西8.1级大地震对部分段落有弱(松弛)调整影响; 而2008年汶川8.0级大地震的影响更为明显和普遍,2007~2009年应变积累明显增强(可能包含促进影响)的有渭河断裂西段、山西断裂带南段、北端的蔚广盆地南缘断裂等,但也不排除包含该次大震部分孕震信息的可能性,有些段落2004~2007年就增强或张压特性转换。其它段落显示出不同程度的扰动影响。近两年多来陕西高陵,山西河津、阳曲、忻州发生的4级以上地震位于晋—陕交界及其附近,阳高地震则位于山西断裂带北端以西,这些地震均发生在应变积累相对明显、且受汶川大地震影响的区域或其附近。
- 马宗晋.1982.地震与断裂关系的讨论,中国活动断裂[M].北京:地震出版社.
- 苏怡之,王进英.1991.汾渭地震带的地震活动性[J].内陆地震,6(2):143-150.
- 万永革,沈正康,盛书中,等.2009.2008年汶川大地震对周围断层的影响[J].地震学报,31(2):128-139.
- 张培震,闻学泽,徐锡伟,等.2009.2008年汶川8.0级特大地震孕育和发生的多单元组合模式[J].科学通报,54(7):944-953.
- 张世民.2000.汾渭地堑系盆地发育进程的差异及其控震作用[J].地质力学学报,6(2):30-37.
- 张希,崔笃信,蒋锋云.2009a.基于GPS观测的汶川地震参数反演与库仑应力变化分析[J].地震研究,32(4):351-356.
- 张希,崔笃信,张四新,等.2009b.地形变观测揭示的汶川MS8.0级地震同震响应与影响[J].武汉大学学报:信息科学版,34(10):1204-1209.
- 张希,王庆良,唐红涛,等.2011.汶川地震孕震背景与同震变化的铲形断层位错模拟[J].地球学报,32(2):189-194.
- 张希,王双绪,张晓亮,等.2010a.昆仑山与汶川强烈地震对青藏块体东北缘地壳运动及应变积累的影响[J].地球学报,31(1):32-42.
- 张希,张晓亮,张四新,等.2010b.青藏块体东北缘近期GPS水平运动特征与汶川大震影响[J].地震研究,33(4):265-268.