基金项目:中国地震局地震研究所基金“三峡水库蓄水后等效应力场的变化与胡家坪MS4.1级地震的关系研究”(IS201056088)资助.
备注
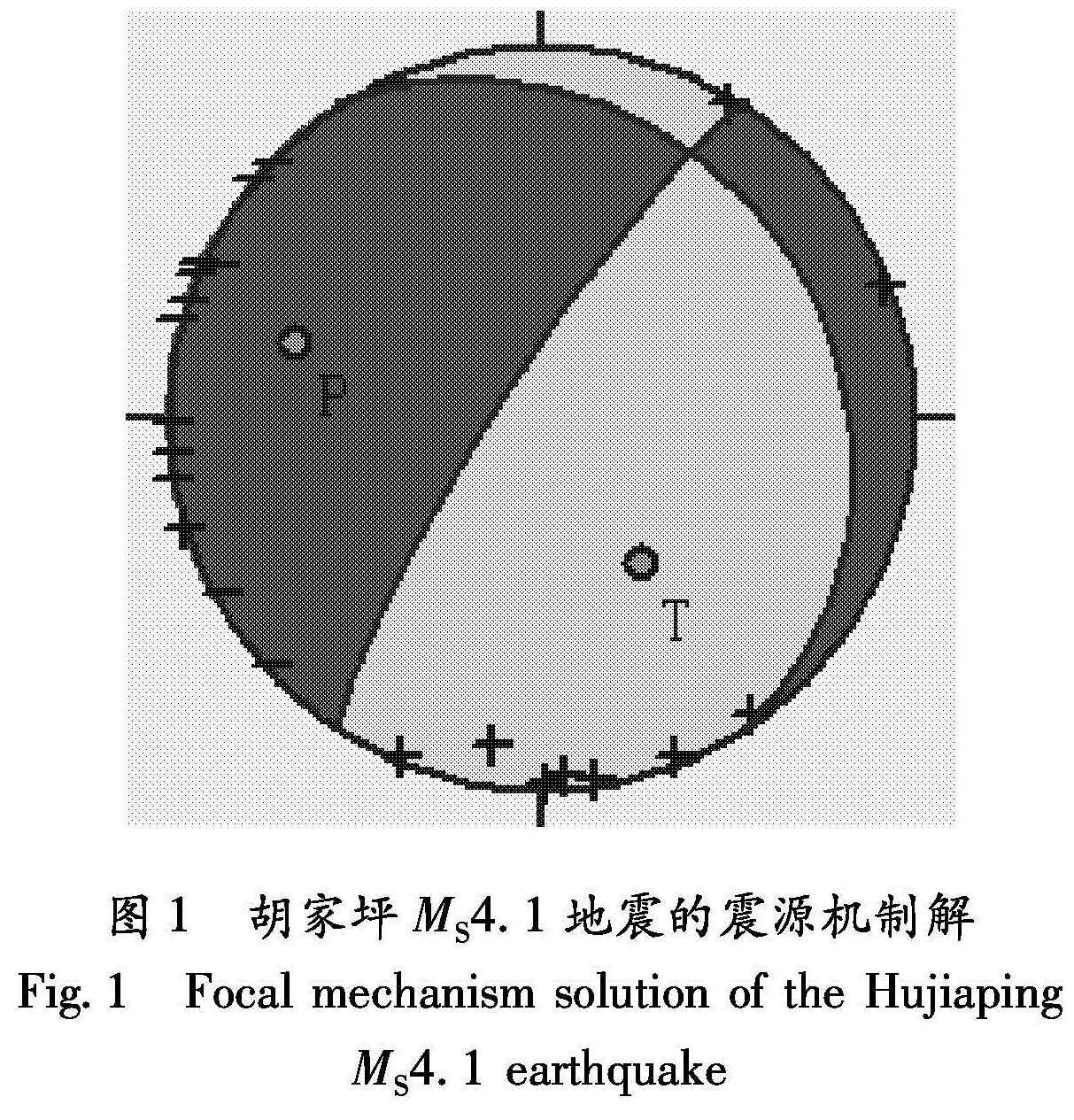
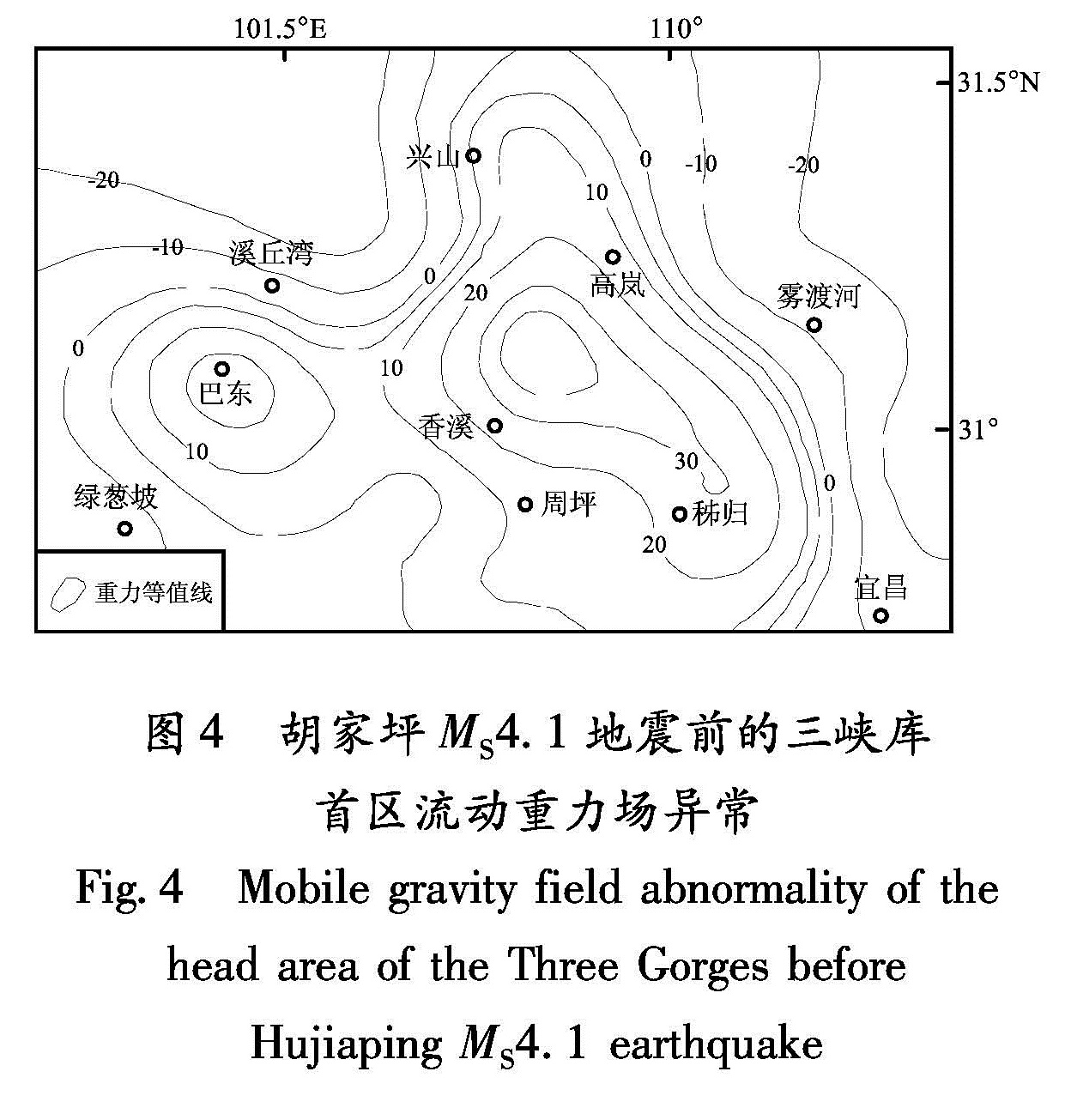
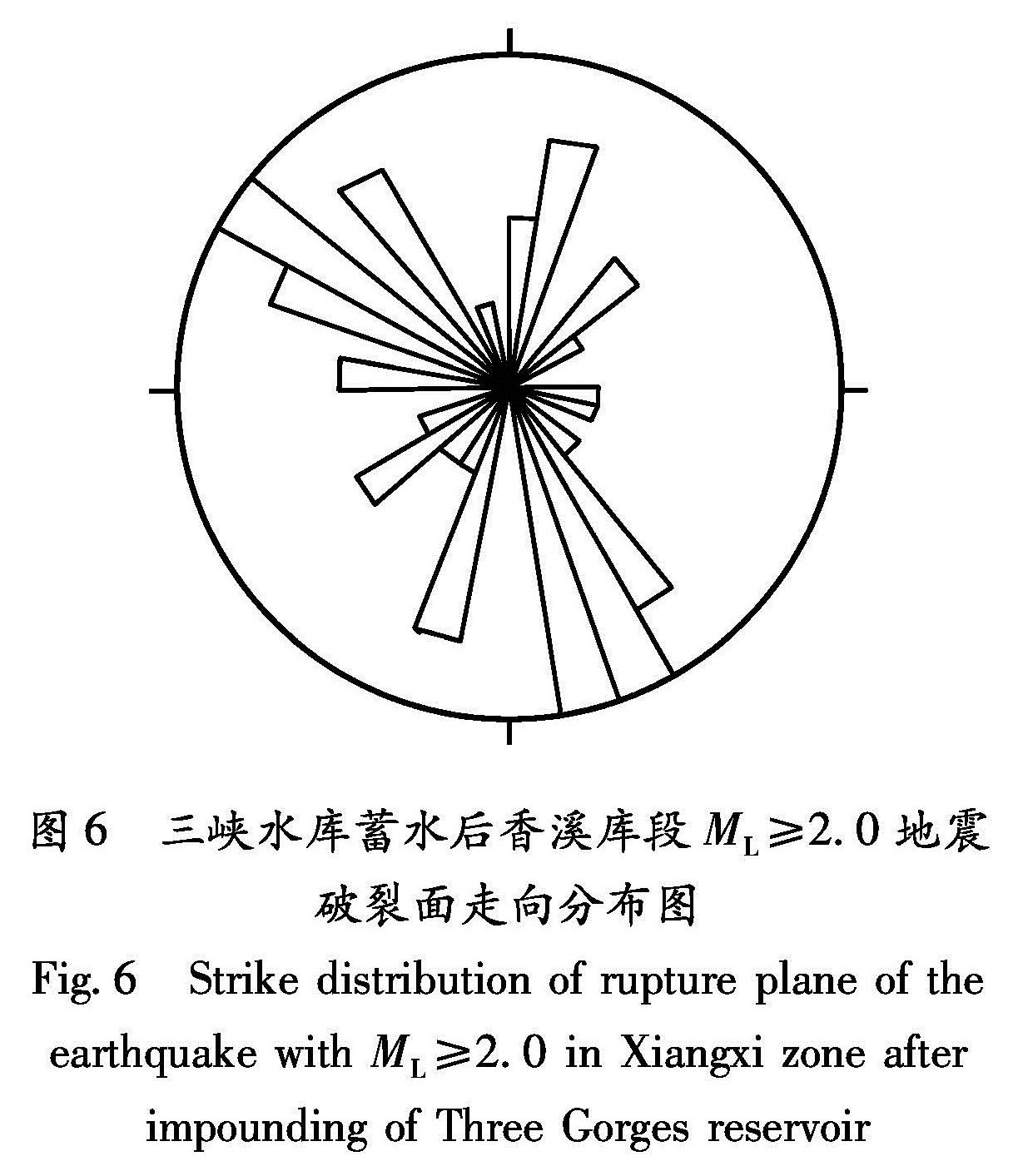
利用有限元方法,在三峡水库172 m试验性蓄水后发生胡家坪MS4.1地震的大背景中,建立了三峡库首区三维线弹性有限元模型。计算得到了172 m水位相对于蓄水前库首区地壳8 km深度处的等效应力场,与该地区同期流动重力场异常分布特征基本一致。在此基础上,将蓄水后等效应力场的变化与胡家坪MS4.1地震对比后发现,本次地震发生在等效应力递增区与递减区的梯度带上。分析认为,这样的地段等效应力变化明显,是应力应变积累和构造活动强烈的部位,加之处于仙女山断裂的北端段,容易促
Using finite element method,we established a 3D linear elastic finite element model of the head area of the Three Gorges Reservoir after the Hujiaping MS4.1 earthquake occurred after the 172 m level experimental impoundment.Then we calculated and obtained the equivalent stress field under 172 m water level and that in 8 km depth in the head area of the Three Gorges before impoundment,which are consistent with the distribution characteristics of contemporaneous flowing gravity field abnormality in this area.On this basis,we compared the equivalent stress field changes after the impoundment with the Hujiaping MS4.1 earthquake,and found that this earthquake occurred in the gradient zone between the increasing zone and decreasing zone of the equivalent stress.We analyzed that the equivalent stress varied distinctly in the gradient zone,where the stress and strain was accumulated and tectonic activity was intense.In addition,the gradient zone is located in the north section of the Xiannushan Fault,which is easy to make fault instable and move to induce the seismic activity.