基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展规划资助项目“中国地壳运动观测网络”(G1998040703)资助.
备注
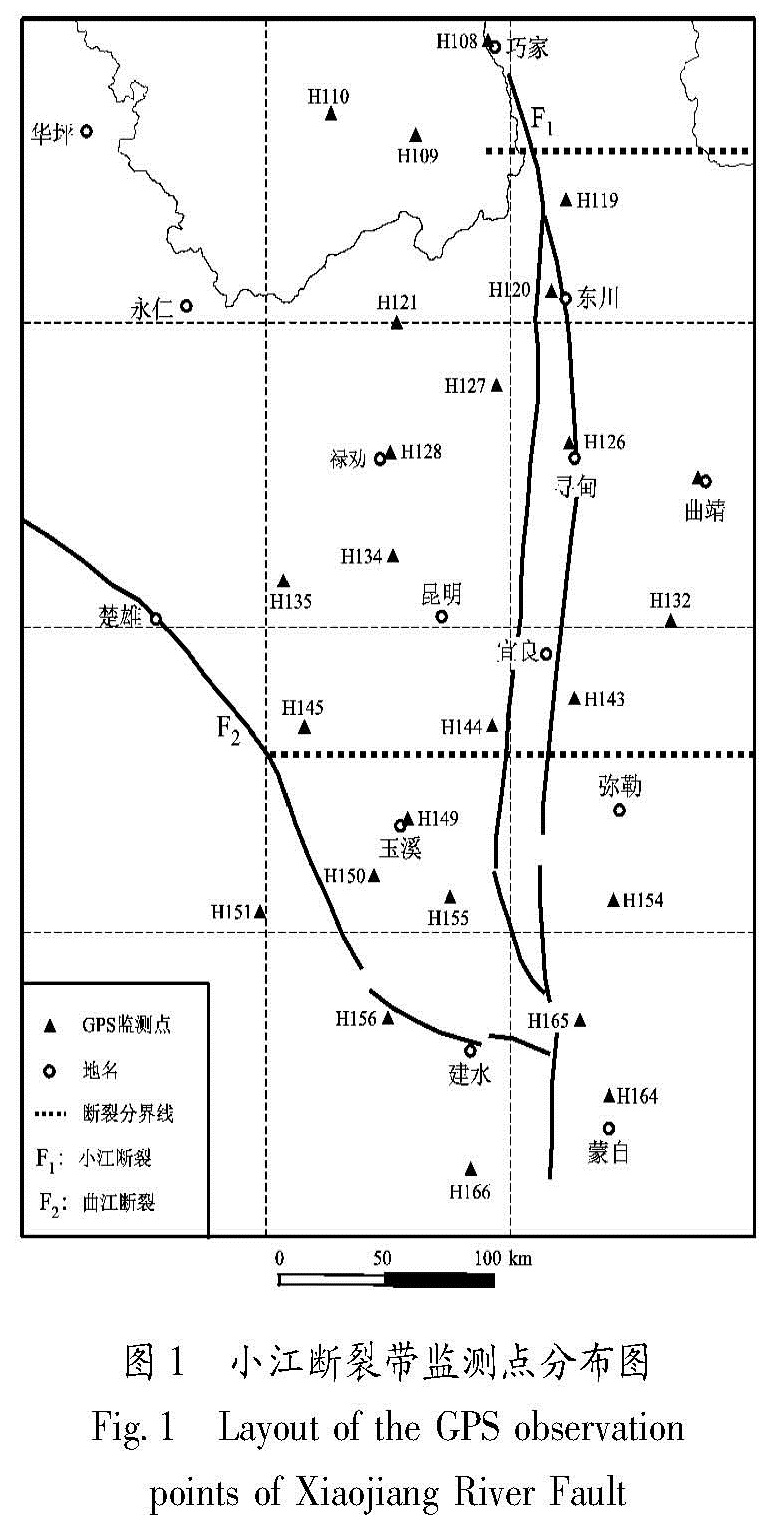
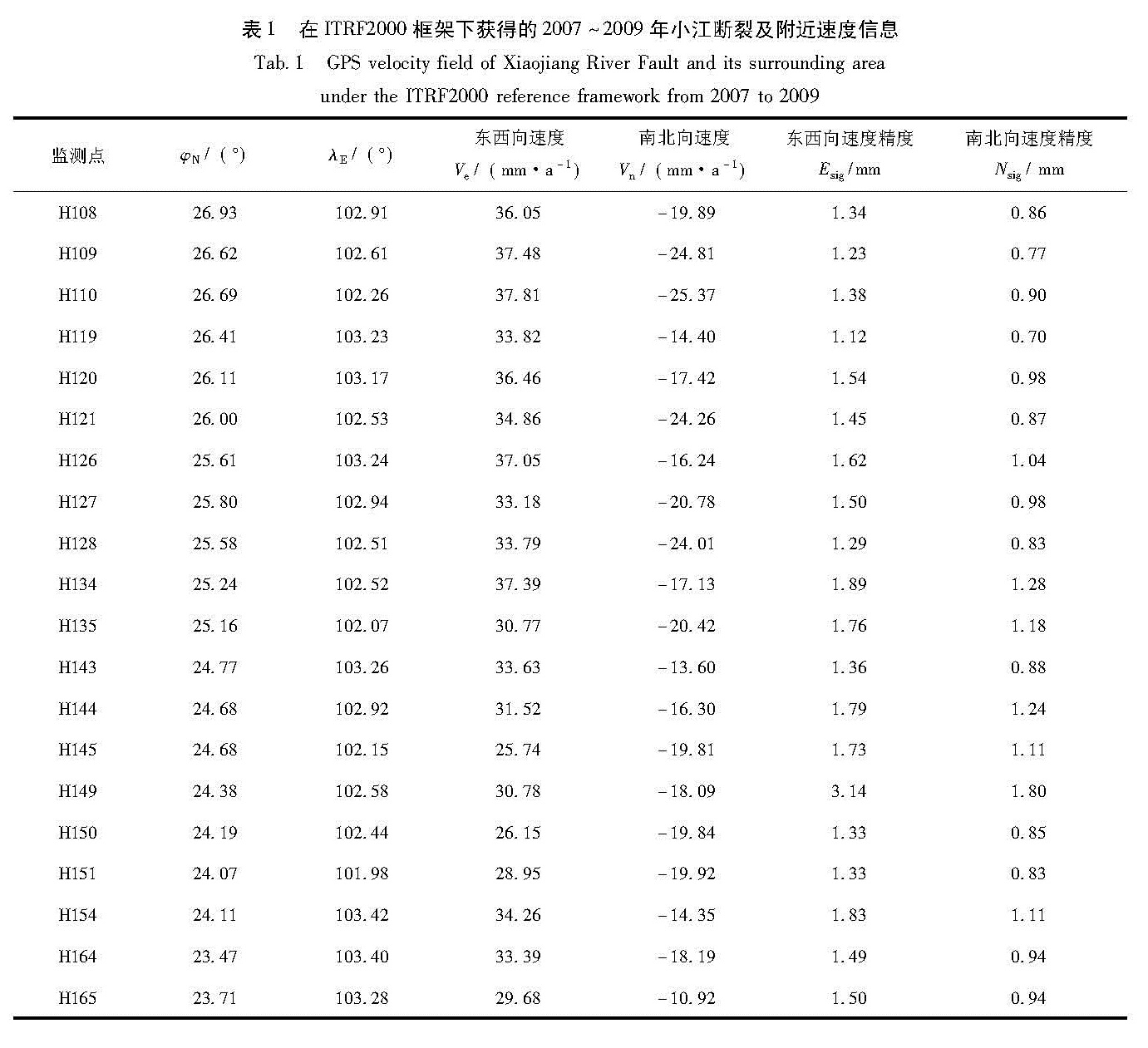
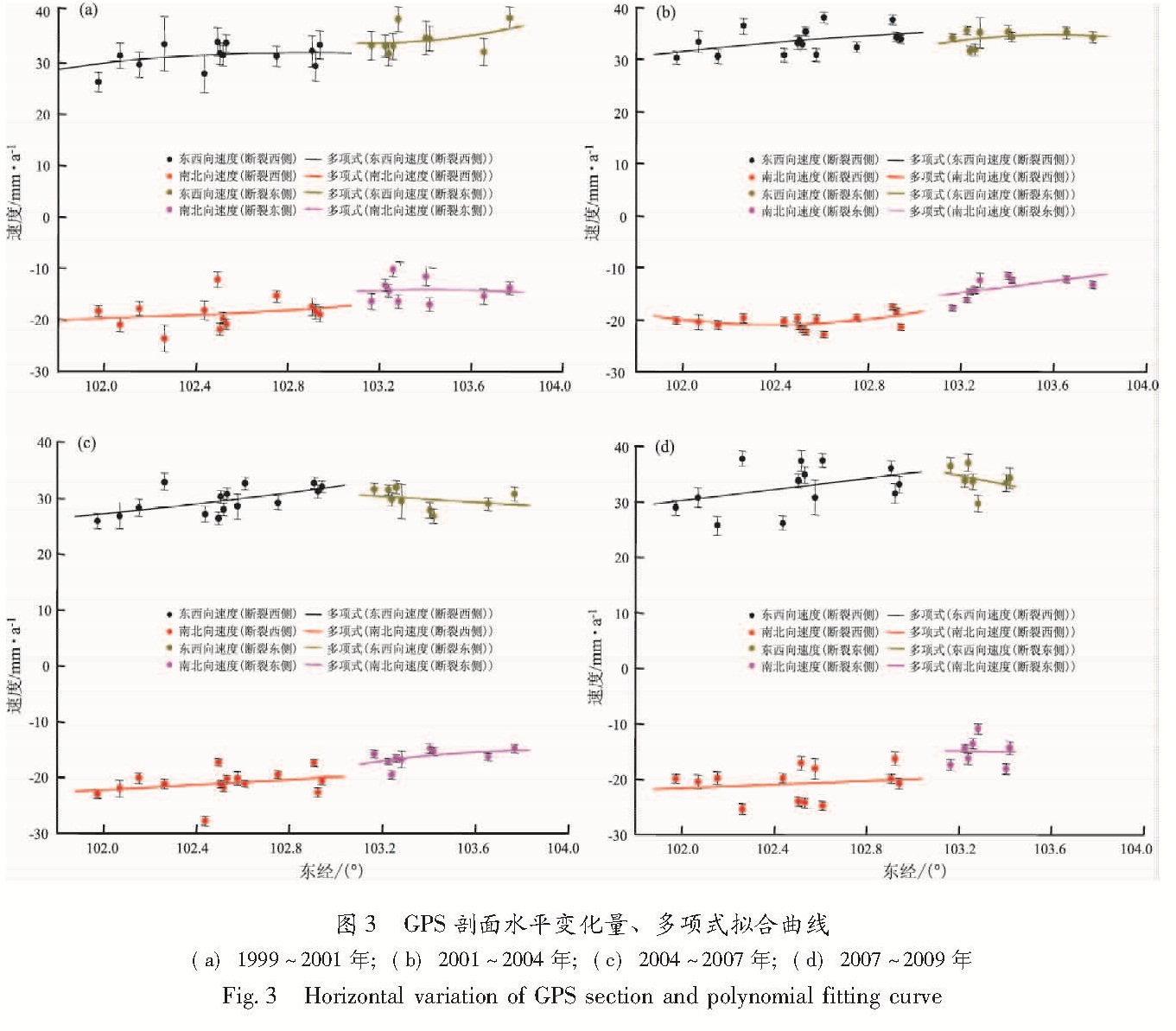
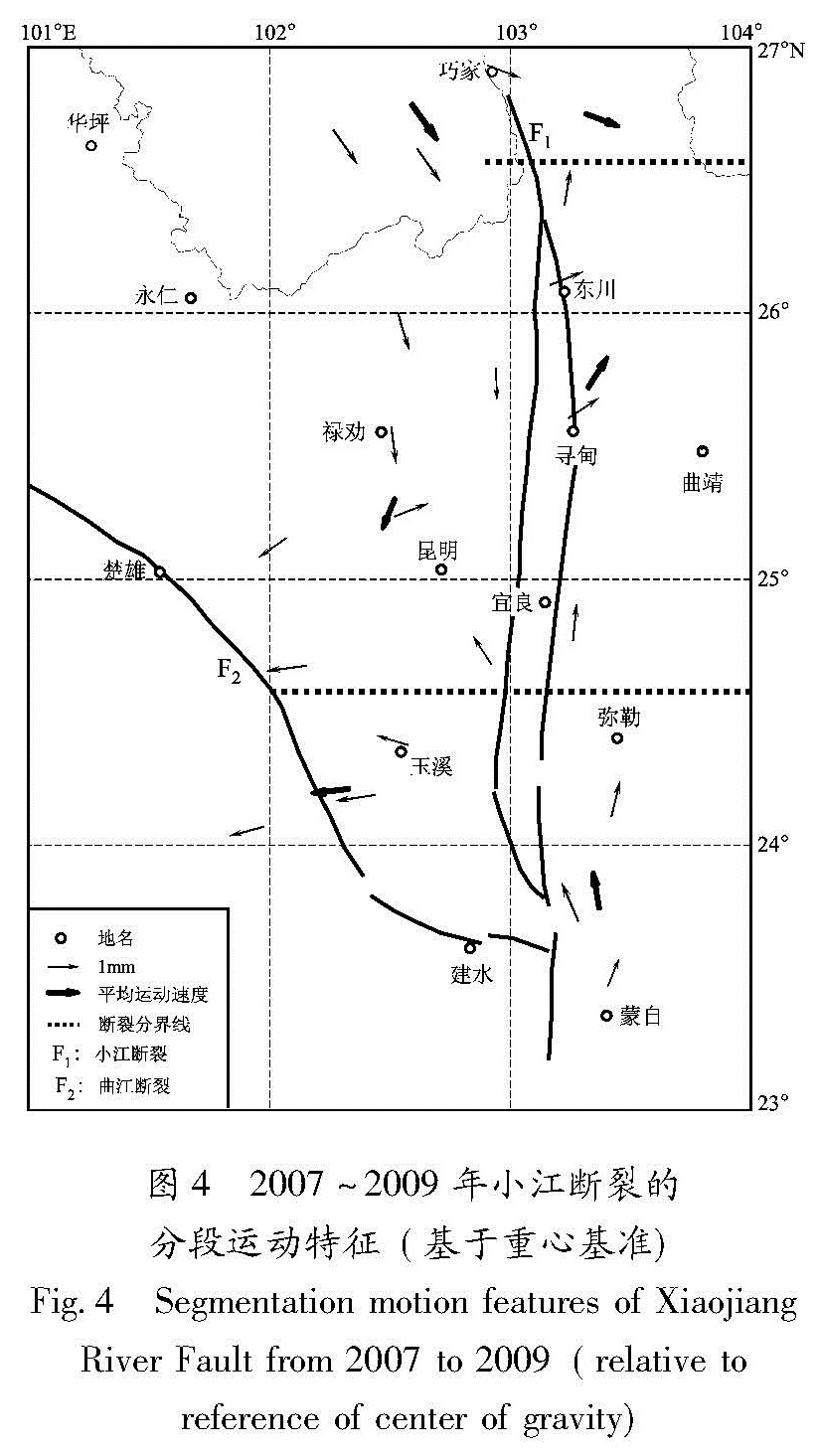
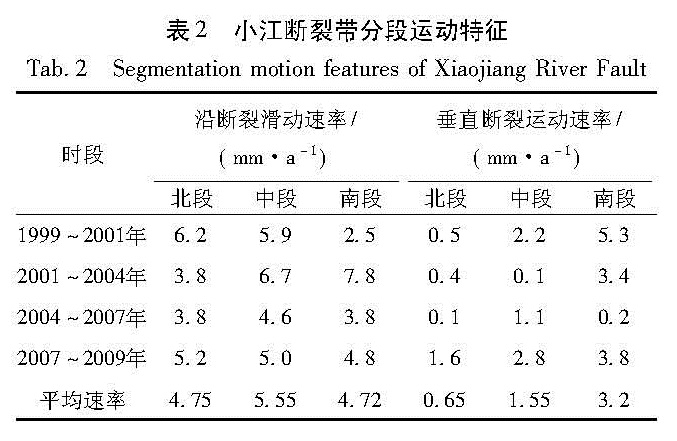
利用中国地壳运动观测网络1999~2009年5期的GPS观测数据,选择以区域重心基准为参考的方法,从大地形变测量的角度分析和研究了小江断裂近期及其各段的地壳形变信息。结果 显示:小江断裂近期具有明显的左旋走滑运动特征,并具有一定的张扭性质,这种运动性质在汶川地震前后具有很好的继承性,这也说明了汶川大地震对小江断裂的总体运动趋势并未造成太大的影响。2007~2009年的GPS资料显示小江断裂北段的平均滑动速率为4.75 mm/a,平均张扭速率为0.65 mm/a; 中段的平均滑动速率为5.55 mm/a,平均张扭速率为1.55 mm/a; 南段的平均滑动速率为4.72 mm/a,平均张扭速率为3.2 mm/a。
Using GPS observation data of five periods recorded in the crustal movement observation network of China from 1999 to 2009,we selected the regional gravity center as reference datum to study the recent crustal movement characteristics of Xiaojiang River Fault and its segmentation motion characteristics from geodetic deformation survey aspect.The results showed that the movement of Xiaojiang Fault featured characteristics of left-lateral strike slip and tension-shear,and these characteristics was the same before and after Wenchuan M8.0 earthquake,which showed that the Wenchuan earthquake had no influence on the total movement of Xiaojiang River Fault.Using GPS data from 2007 to 2009,we obtained the average slip rate was 4.75mm/a and the average tension-shear was 0.65mm/a in the northern section of the Xiaojiang River Fault.In the middle section of it,the average slip rate was 5.55mm/a and the average tension-shear was 1.55mm/a.In the southern section of it,the average slip rate was 4.72mm/a and the average tension-shear rate was 3.2mm/a.