基金项目:中国博士后基金项目(20090460403)、江苏省普通高校研究生科研创新计划资助项目(CXZZ11_0878)和南京师范大学研究生科研创新计划资助项目联合资助.
(1.南京师范大学 虚拟地理环境教育部重点实验室,江苏 南京 210046; 2.中国地震台网中心,北京 100045; 3.浙江大学 计算机学院,浙江 杭州 310058)
(1.Key Laboratory of Virtual Geographic Environment,Ministry of Education,Nanjing Normal University,Nanjing 210046,Jiangsu,China)(2.China Earthquake Networks Center,Beijing 100045,China)(3.College of Computer Science and Technology,Zhejiang University,Hangzhou 310058,Zhejiang,China)
Yushu earthquake; astro-tidal-triggering; NCEP remote sensing data; abnormal temperature rise
备注
基金项目:中国博士后基金项目(20090460403)、江苏省普通高校研究生科研创新计划资助项目(CXZZ11_0878)和南京师范大学研究生科研创新计划资助项目联合资助.
利用天体引潮力周期变化计算模型和NCEP多源综合温度数据资料,分析了2010年4月14日青海玉树MS7.1地震的诱因。结果 表明:在玉树地震前,天体引潮力经历低谷—高峰—低谷—高峰的连续变化,NCEP遥感数据呈现出起始增温—加强增温—高峰增温—增温衰减的规律,由此证明以NCEP温度为主导,以天体引潮力构造附加应力变化为参考,是一种有希望的预测思路。
Using the cycle process model of the astro-tidal-triggering and according to the NCEP integrated multi-source temperature data,we analyzed the triggering factors of Yushu MS7.1 earthquake in Qinghai occurred on Apr.14 in 2010.The result indicated that astro-tidal-triggering went through a continuous change between peak and trough,such as “trough-peak-trough-peak”,and the NCEP remote sensing data showed the law of “original temperature rise-enhancement-reaching peak-attenuation” before Yushu MS7.1 earthquake.Thus,under the dominant of temperature variation in the NCEP remote sensing data and taking the tectonic additional stress variation of astro-tidal-triggering as the reference is a promising idea to predict the earthquake.
引言
地震是地球内部快速而剧烈的构造运动,是一种力学过程。不同学者从天体引潮力的诱震作用(Tramutoli et al,2005)和震前温度变化角度对地震进行了大量的研究(Gorny et al,1988; Friedemann,2002; Qiang et al,1999; Tronin et al,2002; Milne,John,1913),结果表明:当震源系统岩石中的构造应力达到临界状态时,天体引潮力变化是触、诱发地震的重要外部因素之一(马未宇等,2006,2008; Ma et al,2007)。Heaton(1975)从理论上证实:由于地球介质的不均匀性,潮汐应力在地球内部的分布也是不均匀的,地壳中的实际潮汐应力值往往大于平均值,而潮汐应力的积累速度通常比构造应力大两个数量级,当构造应力处于临界状态时,迭加上这样快速的脉冲应力,从力学观点来看完全有可能加速破裂过程而触发地震。但天体引潮力具有明显的周期性,不是每个周期都会发生地震,如何判断地应力强度是否达到发震的临界状态,是这一问题的关键(马未宇等,2008)。另一方面,早期地面站点记录向卫星遥感技术观测发展,大震前地温的异常变化研究而更趋广域、快捷、高效,但存在许多问题(Kalnay et al,1996),如:红外线不能有效穿透云层,无法获得云下地面温度; 地震引起的增温过程和气象增温叠加,直接、单一利用卫星红外技术将无法有效获取异常增温信息; 尤其是采用统计方法获取异常温度,长期平均温度可能掩盖地震引起的短临增温波动,而且由于不同研究者采用的统计年时间域长短不一样等原因也会造成增温背景选择的不确定性,引起异常增温判识的歧义性。探究震前增温与天体引潮力变化,其所揭示的物理特性与地震活动表现出的增温异常现象,在本质上是一致的,反映的都是构造运动达到一定程度发生突变—短临地震活动发生这一临界点的判定问题,二者具有明显的互补性。天体引潮力作为目前唯一能够预先计算出的地球形变现象,在时间域上具有一定指示作用,而热异常表现的构造运动为地应力强度判识提供支持。因此本文将天体引潮力计算和多源遥感数据结合提取异常增温信息,对青海玉树地震进行初步研究。
1 天体引潮力附加构造应力的作用分析
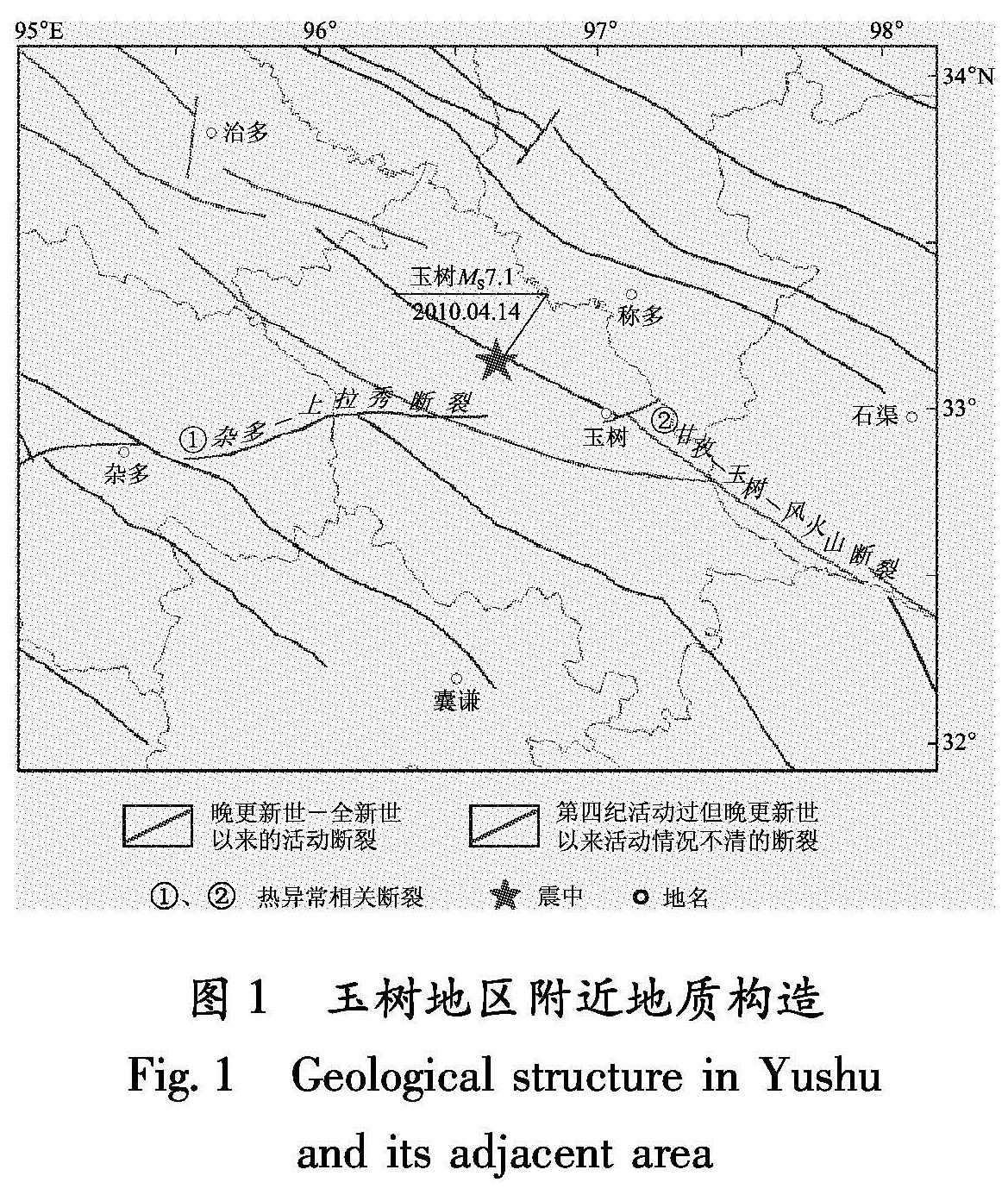
2010年4月14日青海省玉树县(33.1°N,96.6°E)发生MS7.1地震,该地震发生在印度板块向北东方向运动的前缘和受欧亚板块、扬子板块阻挡形成的断裂破碎带前沿,为构造应力集中区域(钱晓东,秦嘉政,2010)。图1所示为中国西南地区的地壳断裂图。从图中可以看到,玉树MS7.1地震发生于甘孜—玉树—风火山断裂上。在一系列近SEE走向的平行断裂中,甘孜—玉树—风火山断裂是一条走向南偏东约70°的走滑断裂,断层倾角较陡,为晚更新世—全新世、距今约10~20万年的活动断裂,该断裂以左旋水平运动为主(闻学泽等,2003),伴有各处不等但量值较小的垂直运动,且断裂的南西侧地块相对抬升(张希等,2010)。
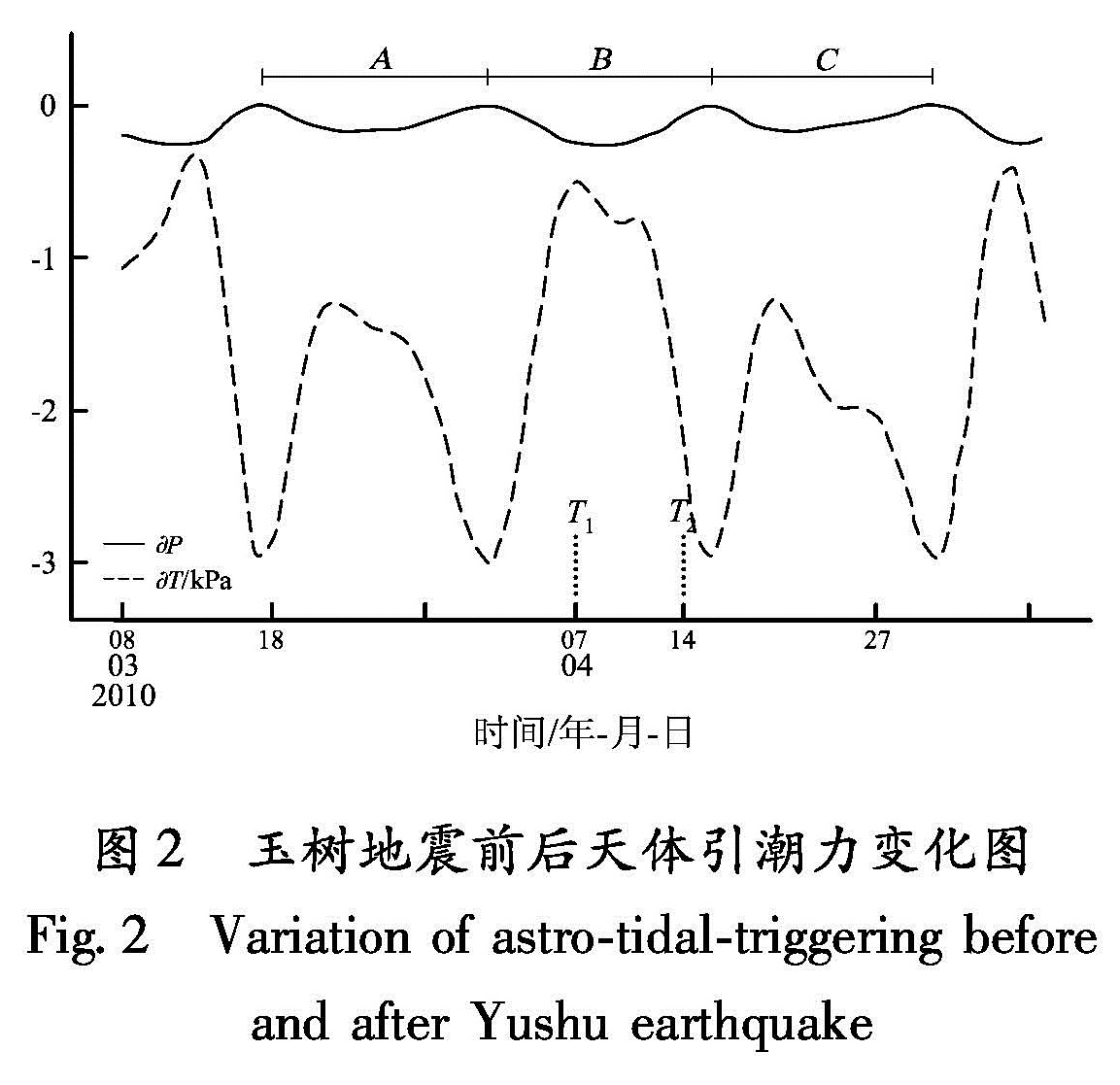
本文根据美国USGS提供震源机制解,采用Ma等(2007)的方法,计算了天体引潮力沿发震构造主压应力轴P与主张应力轴T的引潮力分量并绘制成图2,图中T1表示热异常起始观测时间,T2表示玉树地震发震时间。由图2可以看出,玉树地震过程中,引潮力沿主压应力轴方向分量变化不明显,而其沿主张应力轴分量变化剧烈,且有很强的周期性:每个周期经历低谷—高峰—低谷的过程。地震发生的周期B中,天体引潮力由高向低连续变化接近最低值,表明此次地震过程中引潮力对发震构造的作用主要表现为加速断层面的滑动,与该地区构造滑动为主的左旋走滑运动特征吻合,使断层失稳,释放已有的构造应变能而诱发地震。2 NCEP增温异常状况分析
为了解决红线外不能穿透云层、以及地震引起的增温过程和气象增温叠加干扰而无法有效获取异常增温信息的问题,消减干扰因子的作用,本文采用NCEP全球再分析温度数据(由Global Rawinsonde Data、COADS Surface Marine Data、Aircraft Data、Surface Land Synoptic Data、Satellite Sounder Data、SSM/I surface wind speeds 6类数据组成),并对几乎所有的观测资料进行同化处理,能够较综合、准确反映多因素作用下的实际温度状况。
同时为了避免由统计算法可能带来背景选择时间域的不确定性问题,本文根据天体引潮力周期提取时间信号,以2010年4月8日(天体引潮力主张应力分量开始减小)为背景温度,对2010年4月8~16日共9天的NCEP逐日数据减背景温度,获得了玉树地震前后的地区逐日增温图像,如图3所示。
玉树附近地区于2010年4月8日出现异常增温现象,较背景值高5 ℃~6 ℃,4月9日震中持续增温,甘孜—玉树断裂带方向增温明显,增温6 ℃~7 ℃,表明温度场在空间上正在朝东特别是东南方向,且孕震体中变形的范围正在变大; 4月10日异常增温面积有所缩小,但异常增温幅度明显,且主要向甘孜—玉树断裂迁移汇集,在震中以东方向增温幅度高达9 ℃,异常在空间上呈现间断分布; 4月11日震中附近保持7 ℃~8 ℃增温,而震中往东方向异常增温带沿甘孜—玉树断裂走向继续扩大并沿断裂连续贯通; 4月12日,震中增温达到峰值接近10 ℃,此时由于羌塘地块向东运动的速率加大而巴颜喀拉地块速率不变,故2个地块交汇处的甘孜—玉树—风火山断裂表现为带有左旋性质的走滑断裂,且增温带面积达到最大,与东南方向的增温带合并; 4月13日,震中附近出现异常减温现象,与前一天相比减温达到5 ℃~6 ℃。增温面积迅速减小; 4月14日异常增温面积减小到震中附近,温度保持在前一天的异常减温温度,表明最终的断层破裂起始点集中在一个较小的空间范围内,此时天体引潮力张力方向分量达到低谷,对板块运动起促滑作用,地震爆发; 4月15日和16日,异常增温趋于正常化并逐渐消失。玉树地震前异常增温过程与遥感岩石力学试验中岩石受力破裂的红外热像变化过程(Wu,Cui,2000)相似(加载初期红外辐射上升—加载
另一端迁移扩展—主破裂发生前增温衰减—破裂—趋于平静),体现了构造运动挤压—岩石微破裂—能量积累—岩石破裂加强—能量释放—发震的物理过程。更值得一提的是异常前端,西藏自治区那曲地区聂荣县(32.5° N,92.8°E),在北京时间2010年4月17日发生MS5.2地震,该区域也是热异常延伸的最西端,再次表明震前热异常区域可能是强构造运动的一种热表现。
天体引潮力变化A、C周期相同但未出现与B周期类似的温度变化过程,也说明天体引潮力是使压应力处于高临界状态的构造带诱发地震的外部因素,温度变化的过程正是天体引潮力使岩石连续积累地应力的过程。而临失稳前出现了短暂的降温,是岩石破裂失稳的重要晚期前兆,其出现意味岩石即将发生宏观破裂和失稳灾变,可以做出临期灾变预报。
3 结论和探讨
(1)通过对反映地应力强度的NCEP增温异常与天体附加构造应力时序变化关系的研究,可以得出地应力是内因根据,天体引潮力附加构造应力是触发地震外因条件的发震机理。
(2)震前异常增温一般呈现起始—加强—高峰—衰减—发震—平静的过程,与岩石受力破裂的过程具有相似性。尤其当地震不是发生在异常增温达到高峰时,而是发生在异常增温衰退的时段,将对地震的短临预测具有积极作用。
(3)从玉树地震的发生时段与天体引潮力附加构造应力时序变化图的所在位置看,该次地震发生在低谷时段。表明天体引潮力触发、诱发高应力活动断裂带的地震机理有减压促滑现象存在,其本质是使处于高应力状态的活动断层失稳破裂,说明研究引潮力与地震关系不能脱离构造环境。
(4)地震短临期间,红外增温异常实质是地应力急剧增加的表现,通过红外增温异常可较直观地显示地震构造活动状况,圈定增温异常区; 根据天体引潮力附加构造应力在不同方向、深度的断裂带上的大小和时间演变与发震时刻的关系,可以推断可能发震的断裂和发震时间。因此以NCEP温度为主导,以构造附加应力变化为诱导,以地震地质为基础这种面中求线、线中求点的地震捕捉战术,是一种很有价值的预测思路。
- 马未宇,徐秀登,徐保华.2006.印度尼西亚9.0地震序列与增温异常和天体引潮力的相关关系研究[J].西北地震学报,28(2):129-133.
- 马未宇,赵虎,周波.2008.汶川8.0地震天体引潮力和温度变化过程[J].国际地震动态,(11):104.
- 钱晓东,秦嘉政.2010.2010年青海玉树地震及震后青藏高原强震趋势分析[J].地震研究,33(4):255-264.
- 闻学泽,徐锡伟,郑荣章,等.2003.甘孜—玉树断裂的平均滑动速率与近代大地震破裂[J].中国科学(D辑:地球科学),33(S1),199-208.
- 张希,张晓亮,张四新.2010.青藏块体东北缘近期GPS水平运动特征与汶川大震影响[J].地震研究,33(4):265-268.
- Friedemann F.2002.Charge generation and propagation in igneous rocks[J].Journal of Geodynamics,33(4),543-570.
- Gorny V I,Salman A G,Tronin.1988.The earth outgoing IR radiation as an indicator of seismic activity[J].Sci USSR,30(1):67-69.
- Heaton T H.1975.Tidal triggering of earthquakes[J].Geophys J R astr Soc,43(307):307~326.
- Kalnay E,Kanamitsu M,Kistler R,et al.1996.The NCEP/NCAR 40 years reanalysis project[J].Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society.77(3):437-471.
- Ma W Y,Zhang X C,Dai X F,et al.2007.A preliminary study on the use of NCEP temperature images and Astro-Tidal-Triggering to forecast short-impending earthquake[J].Earthquake Research in China,21(1):85-93.
- Milne,John.1913.Earthquakes and Other Earth Movements[M].New York:DAppleton.
- Qiang ZJ,Dian CG,Li LZ.1999.Satellite thermal infrared brightness temperature anomaly image-short-term and impending earthquake precursors[J].Science in China(Science D),42(3):313-324.
- Tramutoli V,Cuomob V,Filizzolab C.2005.Assessing the potential of thermal infrared satellite surveys for monitoring seismically active areas:The case of Kocaeli(I·zmit)earthquake,August 17,1999[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,96(3),409-426.
- Tronin,Hayakawa M,Molchanov O A.2002.Thermal IR satellite data application for earthquake research in Japan and China[J].Geodyn,33(4-5),519-534.
- Wu L,Cui C.2000.Remote sensing rock mechanics(RSRM)and associated experimental studies[J].International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,37(6):879-888.