基金项目:科技支撑项目(2012BAK19B01-02)、地震行业科研专项(201308009)和中国地震局“强化华北地区强震监视跟踪”专项联合资助.
备注
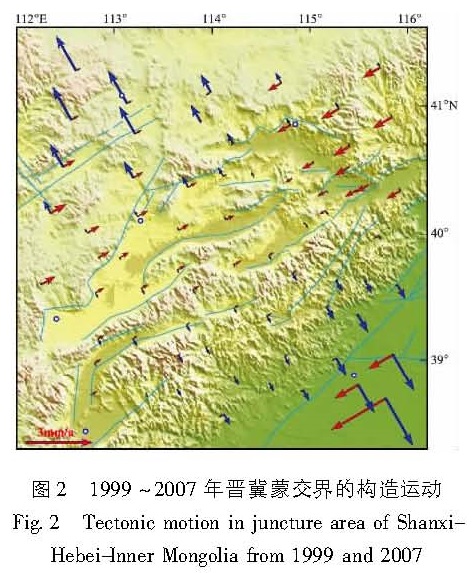
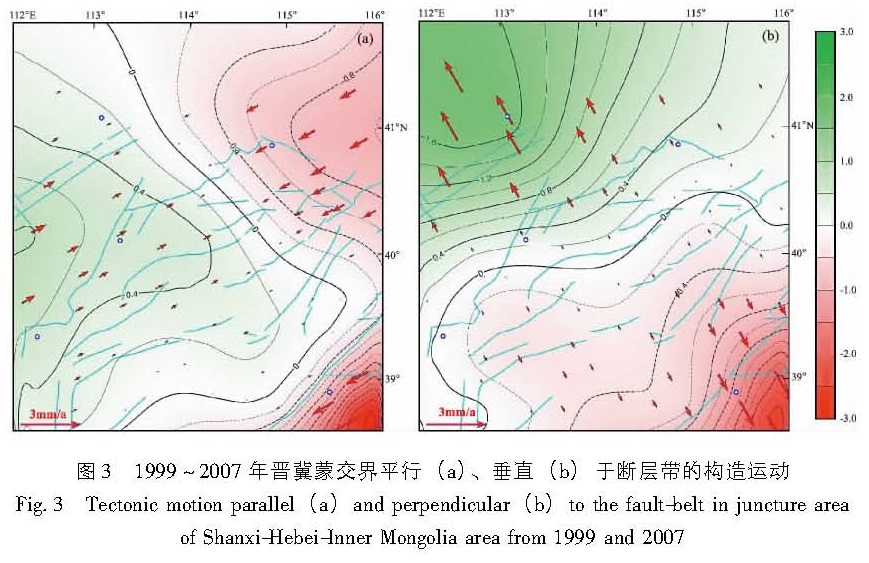
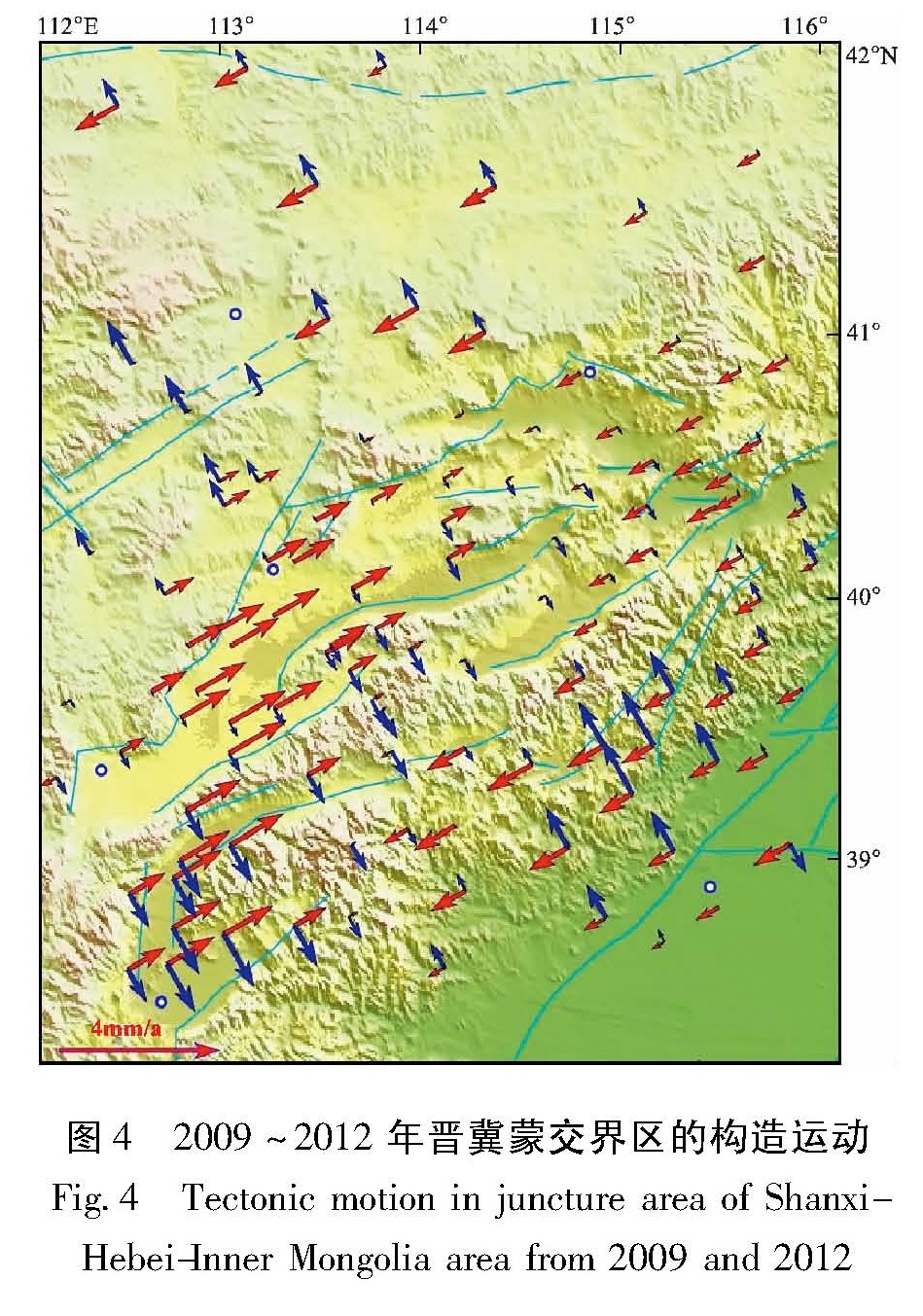
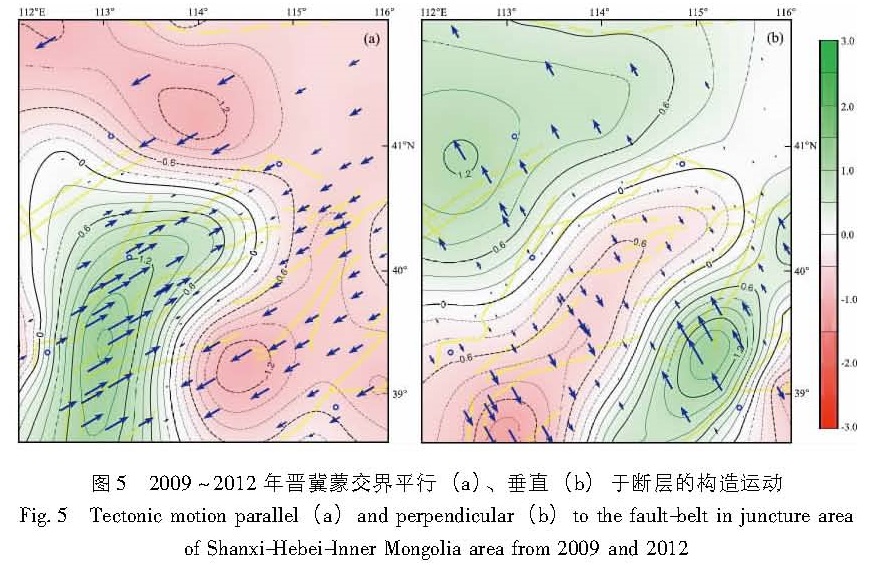
利用1999~2007和2009~2012年GNSS资料,在形变场连续变化的条件下,借助多核函数解析与水平运动滤波及利用坐标系转换公式获得平行和垂直于断裂带的运动结果,给出了晋冀蒙交界区现今水平构造活动的方式与大小:(1)1999~2007年的垂直于断裂带的水平构造活动呈明显的张性活动状态,在约400 km范围内年均张性活动量3 mm左右,且基本上是以渐变的活动方式而均匀地过渡; 但沿断裂走向上却看不到显著的走滑活动,在400 km的范围上仅观察到年均约1 mm的相对挤压量;(2)2009~2012年平行于断裂构造的活动仍为压性活动,垂直于断裂构造的活动则为张、压相间的空间变化活动。这种动态变化可能受控于环境应力场的动态调整。
Based on the GNSS observation data from 1999 to 2007 and from 2009 to 2012,we analyzed the mode and intensity of the present horizontal tectonic motion in Shanxi-Hebei-Inner Mongolia area,by using the method of multi-kernel function analysis,horizontal movement filtering,and the arithmetic about the tectonic motion result parallel or perpendicular to the fault-belt obtained by coordinate transform formula. The results show as follows:(1)From 1999 to 2007,the horizontal tectonic activity perpendicular to the fault-belt showed tensional activity and basically uniformly transited in gradual active manner,and the maximal value was 3 mm/a in the range of about 400 km. However,there were no apparent strike-slip activity along the fault-belt,and the relative compression amount was about 1 mm/a in the range of 400 km.(2)From 2009 to 2012,the tectonic activity parallel to the fault-belt still showed compressive activity,and the tectonic activity perpendicular to the fault-belt showed the space activity of tensional and compressive alternately. This dynamic variation may be dominated by dynamic adjustment of environment stress field.