基金项目:云南省应用基础研究计划项目—云南地区温泉CO2释放与地震活动关系初步研究(2011FB129)和地震科技星火计划攻关项目—强震的深源流体源兆捕捉——以云南宁洱为例(XH12042)联合资助.
(Earthquake Administration of Yunnan Province,Kunming 650224,Yunnan,China)
Xiaojiang Fault zone; thermal spring; geochemical characteristics; moderate-strong earthquake
备注
基金项目:云南省应用基础研究计划项目—云南地区温泉CO2释放与地震活动关系初步研究(2011FB129)和地震科技星火计划攻关项目—强震的深源流体源兆捕捉——以云南宁洱为例(XH12042)联合资助.
小江断裂带属现今仍在活动的断裂,同时也是一条破坏性地震多发带。为探究特定地区的地球化学场与地震的耦合关系,寻找特定的前兆观测组分,笔者选取并计算了小江断裂带及邻近地区的95处温泉的热储温度。利用温泉的水化学数据(K+、Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+、SO2-4、Cl-、HCO-3),结合该区域的构造特征及地震活动规律,对温泉的水化学、水温、热储温度、稳定同位素(δ13C,3He/4He)等地球化学特征进行了研究。结果 表明温泉中主要离子含量、TDS含量、水温及热储温度的高值区域在空间上主要沿小江断裂带展布,且呈北高南低的分布特征。水温和热储温度高值区内中强地震(M≥4.7)分布少; 相反,低值区内中强震活动频繁,且强度相对较大。碳、氦同位素特征显示,CO2气体的碳同位素(δ13C)组成具有明显的生物成因特征; 幔源氦(百分含量)同素所占比例相对较低,表明小江断裂带中南段壳幔连通程度低,脱气作用几乎都发生在地壳范围。
The Xiaojiang Fault is not only a still-active fault nowadays but also a destructive earthquake-prone zone.In order to explore the coupling relationship between geochemical field and earthquake in specific areas and look for the specific precursor observational component,the geothermal reservoir temperatures of 95 thermal springs was selected and calculated in Xiaojiang fault zone and its adjacent areas.Using the hydrochemistry data(K+,Na+,Ca2+,Mg2+,SO2-4,Cl-,HCO-3)in the thermal springs,integrated with the regional tectonic features and regular pattern of seismic activity,the geochemical characteristics of hydrochemistry,water temperature,geothermal reservoir temperature and stable isotopes(δ13C,3He/4He)was studied. The results show that the high values area of main ion content,TDS,water temperature and geothermal reservoir temperatures mainly spatially distributed along the Xiaojiang Fault,and had the distribution characteristic of decreasing from north to south gradually. The moderate-strong earthquakes(M≥4.7)occurred less in high-value region of water temperature and geothermal reservoir temperature,however the activity of the moderate-strong earthquakes was frequent and the intensity of it was relatively high in the low-value region. Stable isotope characteristics of carbon and helium showed that carbon isotope composition(δ13C)of CO2 gas had obvious biogenic features,and the proportion of mantle-derived helium(percentage of mantle-derived He)was relatively low,which indicated that connectivity between crust and mantle was not well in the middle and south segment of Xiaojiang Fault,so the degasification almost occurred in the crust.
引言
近年来,地震学界越来越重视活动断层地球化学特征的研究(张春山等,2003; Claesson et al,2007; Famin et al,2008; Süer et al,2008; Plastino et al,2011; Tanikawa et al,2012)。此项研究的开展不仅有助于更深入了解该断层的活动方式、活动强度以及切割深度等断层运动特征,而且对探索断层带深部,特别是震源区附近介质的物理化学环境,搞清楚各类地球化学组分的地震前兆机制,寻找特定地区的前兆观测组分有着十分重要的意义(Thomas,1988; Virk,Stagh,1994; King et al,1995; Wakita,1996; Biagi et al,2000; Inan et al,2012; Woith et al,2012)。
在地震的孕育和发生过程中,地球深部会产生很多物理化学现象。特别是地下水的化学组分,除受地下水来源、储水层介质、循环条件等因素的影响(Thomas,1988; Toutain et al,1997; Tokunaga,1999)而引起水化学成分及含量不同之外,还受地质构造和地壳运动的影响,特别是在现今构造活动强烈的断裂带,常常出现地下水某些组分和化学类型的异常变化,从而形成新的、特殊的水文地球化学场(张春山等,2004)。正在活动的断层是构造运动最突出的部位,现今仍在活动的断裂带是地球内部与地表发生沟通的主要通道,它可使地球内部组分(深源流体)向上迁移,同时也可使地表水渗入地壳深部,经地热或其它方式的加热作用逐渐升温,形成对流循环(张炜等,1988)。在此过程中,地壳中不同层位的化学物质会相继溶于地热流体中,该流体在特定的构造条件下,将以温泉的形式返回地面。
本文选取云南中部小江断裂带及邻近地区为研究区,分析了该区域内95处温泉水文地球化学特征和部分温泉的稳定同位素特征,其中温泉坐标、水温、水化学组分(K+、Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+、SO2-4、Cl-、HCO-3、SiO2)及其含量等数据来源于《云南省志:卷二十五 温泉志》和《横断山区温泉志》,稳定同位素(δ13C,3He/4He)来自于赵柯等(2005)的数据。笔者利用SiO2温标计算了温泉的热储温度,再结合该区域的构造特征及地震活动规律,对温泉的水化学组分、水温、热储温度的空间分布以及同位素组成等进行了研究,最后阐述了地震活动与水文地球化学场的耦合关系。这些问题的研究对地震危险区划和潜在震区的判定具有重要的理论意义和实用价值,对地震观测孔的布置,以及开展地震前兆探索提供了重要的理论依据。
1 研究区概况
本文研究区包括云南中部和四川南部部分地区(23.42°~27.12°N,102°~104°E),是一个长约420 km、宽约200 km 的矩形区域(图1a)。由于印度板块向北挤压,使得川滇地块向东南滑动,同时受到东部稳定的华南地块及南部印支地块阻挡,形成了顺时针旋转的楔形断块构造格局(图1b)(王二七等,1995; 闻学泽等,2011)。
F1:小江断裂带; F2:普渡河断裂; F3:罗茨—易门断裂; F4:曲江断裂; F5:石屏—建水断裂;
F6:红河断裂带; F7:师宗—弥勒断裂; F8:寻甸—宣威断裂
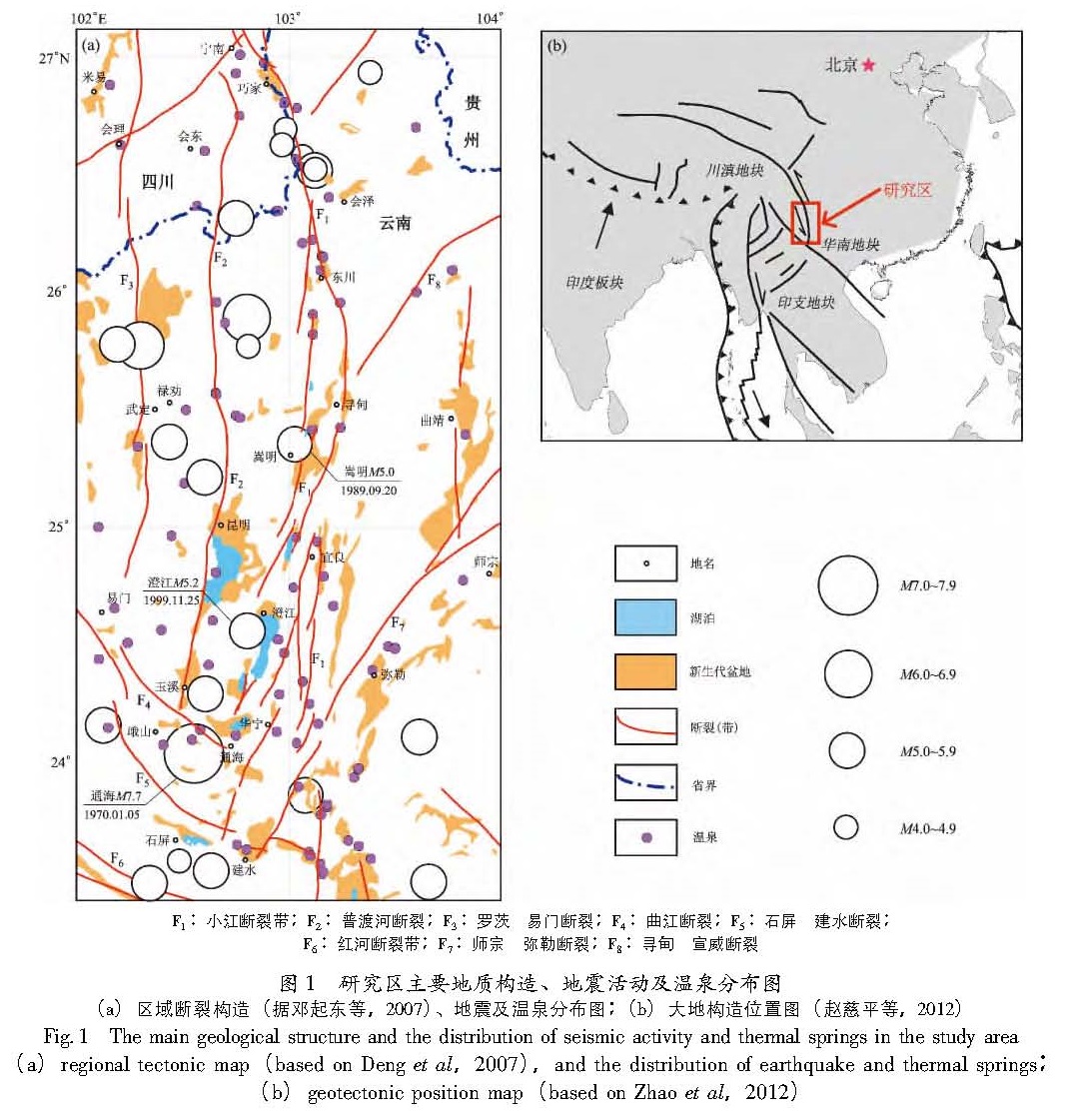
图1 研究区主要地质构造、地震活动及温泉分布图
(a)区域断裂构造(据邓起东等,2007)、地震及温泉分布图;(b)大地构造位置图(赵慈平等,2012)
Fig.1 The main geological structure and the distribution of seismic activity and thermal springs in the study area(a)regional tectonic map(based on Deng et al,2007),and the distribution of earthquake and thermal springs; (b)geotectonic position map(based on Zhao et al,2012)在云南中东部地区,近南北向的小江断裂带(F1)以及北西向曲江断裂和石屏断裂带(F4、F5)活动强烈。小江断裂自中更新世以来以左旋走滑运动为主,是川滇活动块体的东南边界,与之平行的还有发育于古生代沉积岩层中的普渡河断裂(F2)和汤郎—易门断裂(F3)。小江断裂沿走向分成北、中、南三段:北段展布于巧家—东川之间,为单一断层; 中段为东川至通海、华宁,分为东、西两支; 华宁以南至红河断裂为南段。该断裂主要发育在古生界沉积岩层中,部分地段发育在中生界、新生界地层中(唐文清等,2006)。曲江—石屏断裂带展布于小江断裂带南段的西侧,由北支曲江断裂(F4)和南支石屏—建水断裂(F5)组成,全长约120 km,向东止于小江断裂带的南段,形成于古生代,新生代以来由于川滇块体南南东向的挤出运动,表现出以右旋走滑为主、兼挤压逆冲的运动特征(闻学泽等,2011),且与其南侧的红河断裂带(F6)共同构成该块体的最南边界(张培震等,2003)。小江断裂带东侧发育有滇东南褶皱区与扬子准地台的分界—师宗—弥勒大断裂(F7)和北东向寻甸—宣威断裂(F8)。
小江断裂带现今仍在活动,是我国南北地震带的一个重要组成部分,也是一条强烈破坏性地震多发带,断裂带及周围地区构造环境复杂,历史上曾发生多次大地震,地震以频度低、强度大为特征,自1500年以来共发生M≥6强震22次,如云南省最强地震——1833年的嵩明8.0级大地震就发生在该断裂(钱晓东,秦嘉政,2009; 沈娅宏等,2012)。由于本文采用的温泉水化数据大部分来源于20世纪80年代初期的检测分析结果,为了与这些数据有一致的时间对应关系,本文收集了研究区1970~2012年M≥4.7中强震资料并列于图1a中,其中1970~1990年的地震目录来源于《中国近代地震目录》(国家地震局震害防御司,1999),1990年以后的地震则使用中国地震台网中心测定的地震目录。从图中可以看出,该区近40余年来共发生M≥4.7中强震23次,其中大部分地震发生在小江断裂带北段(巧家至会泽)以及汤郎—易门断裂中段(武定—禄劝一带),其中段近40年发生中强地震频率较低,仅发生过1989年嵩明5.0级和1999年澄江5.2级地震,曲江—石屏断裂带与小江断裂带南段的交汇处地震发生表现出频度高、强度高的特点,如1970年通海7.7级地震发生于曲江断裂上。而与小江断裂近似平行的普渡河断裂发生地震频度不高,且强度也不大。
从图1a中可以看出,区内温泉分布不均匀,大部分沿小江断裂带出露,尤其在断裂的复合部位曲江—石屏断裂带与小江断裂带南段的交汇处形成集中出露,多出露于中生代、古生代及震旦系地层中,而其围岩多为碳酸盐岩、灰岩、砂岩等沉积岩。小江断裂以东地区温泉分布较少,表明区内地下热水的生成与运移严格受构造活动的控制,并且与断裂的现代活动强度与规模密切相关。绝大部分温泉水温都低于60℃,属中低温热水,高温热水较少,最高仅76℃。
2 数据来源及处理方法
2.1 温泉地球化学资料及选取《云南省志·温泉志》(云南省地方志编纂委员会,1999)和《横断山区温泉志》(佟伟,章铭陶,1994)记录研究区内温泉共有166处,记述了每一处水热活动区的每个温泉的基本要素(地名、经纬度)和现象,但并非每个泉点中的水化学数据或水化指标是完整的,如某些温泉没有水化学分析,或者某组分未检测(na)、未检出(nd)等。因此,在对水化学数据后续处理过程中,必须对研究区范围内的温泉资料进行选取及相应处理。
资料选取及处理的原则是:(1)温泉水样必须有水化学分析数据,包括K+、Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+、SO2-4、Cl-、HCO-3、SiO2等组分的含量;(2)温泉必须有与水化学分析样取样时同时测量的泉口温度;(3)温泉在空间上尽量满足均匀分布;(4)对于CHD6(吉鲁热水塘)这样的热田区和由多个相距很近的温泉组成的水热活动区,由于温泉在小范围内分布很密,从空间代表性而言,只选取1个即可,即选择泉口温度和由温泉水地球化学温标计算的热储温度同时最高者;(5)由于《云南省志:温泉志》中对每个温泉都无具体的编码,笔者按《横断山区温泉志》资料中的编码方法对相应的温泉进行编号,如云南省峨山彝族自治县的第二个温泉是美党村温泉,相应的编码为DES2。为作区分,巧家代码为DQJ,曲靖代码为DQJG;(6)组分未检测(na)和数据不明(数据<1.74)等情况一律视为该组分数据缺失(-),未检出(nd)的组分含量视为0;(7)新田盐场温泉Na+和Cl-含量远高于平均值(CHD5:Na+:2 350 mg/L,Cl-:3 737 mg/L; 平均值:Na+:78.6 mg/L,Cl-:75.9 mg/L),为了清晰、客观地反应离子浓度区域特征,该点Na+、Cl-含量不参与水岩平衡及空间分布的讨论;(8)TDS为水溶固体物质总量,用水化软件AqQa计算得到。
根据上述原则,研究区范围内共选取了95处有水化学分析资料的温泉,其中有3个泉点水化数据参考赵柯等(2005)考察的数据(DYL2、DCJ3、DJS1)。每个温泉水化学数据经过筛选并汇总((K++Na+):92组; Ca2+:94组; Mg2+:93组; SO2-4:85组; Cl-:68组; HCO-3:94组; SiO2:76组)列入表1。
注:温泉编号带“*”的3组数据来源于赵柯等(2005),带“#”的11组数据来源《横断山区温泉志》(佟伟,章铭陶,1994),其余数据均来自《云南省志:温泉志》(云南省地方志编纂委员会,1999).
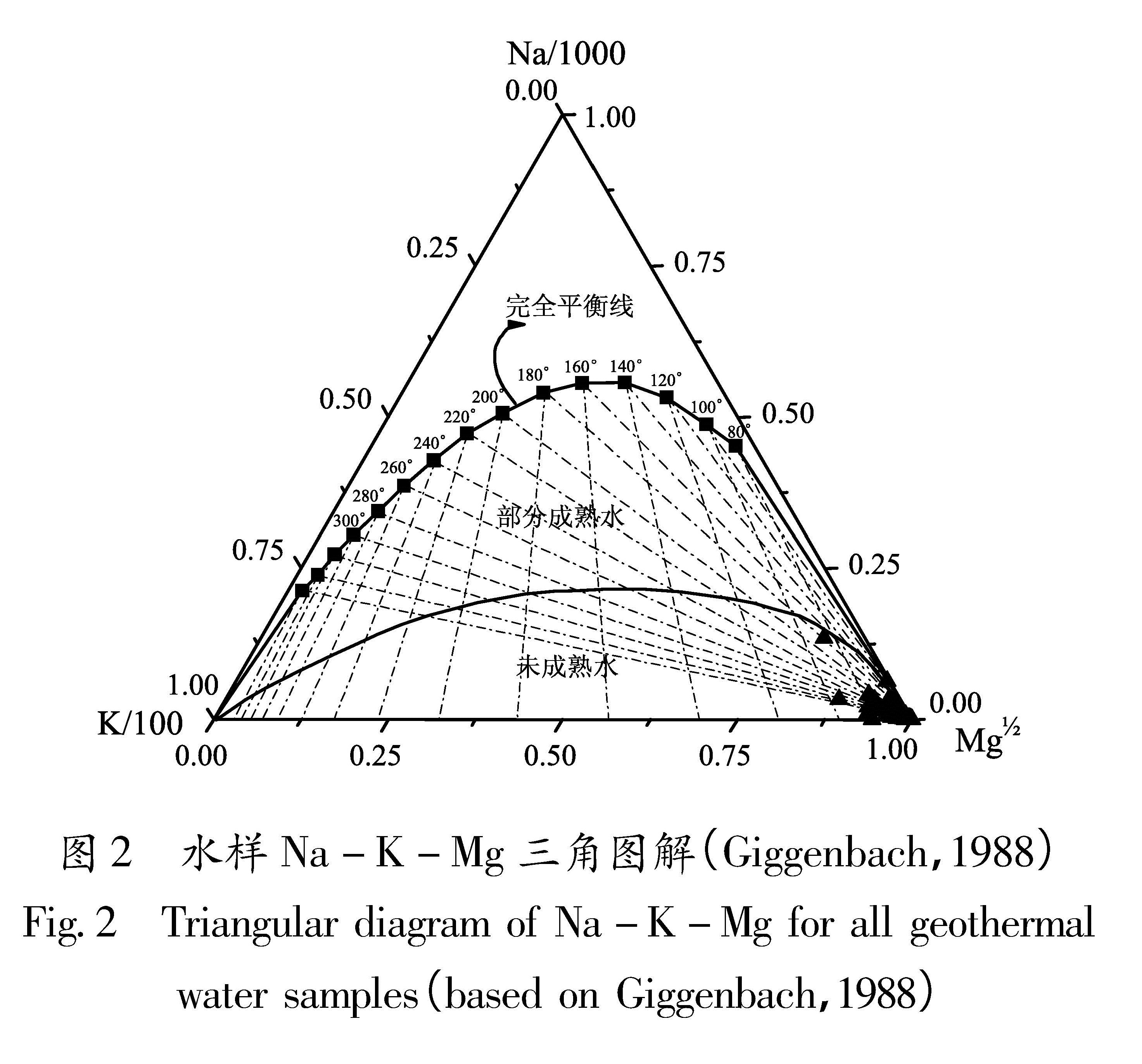
2.2 水—岩反应平衡的判定Na-K-Mg三角图解(Giggenbach,1988)是一种用来判断地热流体中水岩反应是否达到平衡的简便方法(图2),图中分为完全平衡、部分成熟水和处于岩石溶解淋滤过程中的未成熟水3个区域。该方法常被用来评价水—岩平衡状态和区分不同类型的水样,其优点为可在同一幅图上同时判断出大量水样的平衡状态,能把混合水和平衡水很好地分开。将区内有Na+、K+、Mg2+含量的温泉63件水样投到Na-K-Mg三角图上,用▲表示,可以发现绝大部分温泉水均靠近部分成熟水或属未成熟水,由于温度较低并且Mg2+含量较高,图中水样均落在Mg1/2一侧,这表明水—岩反应的平衡温度较低,地下热水有可能接受大气降水补给或者冷水混入。由于处于未成熟状态,一些在高温环境下能达到平衡的反应在此水样中不能达到平衡,也可能是由于温泉水可能来自较热的环境,在由热水向地表上升的过程中,流经碳酸盐岩地层,受到浅层冷水混入影响较大,从而使温泉水中元素的含量变低。
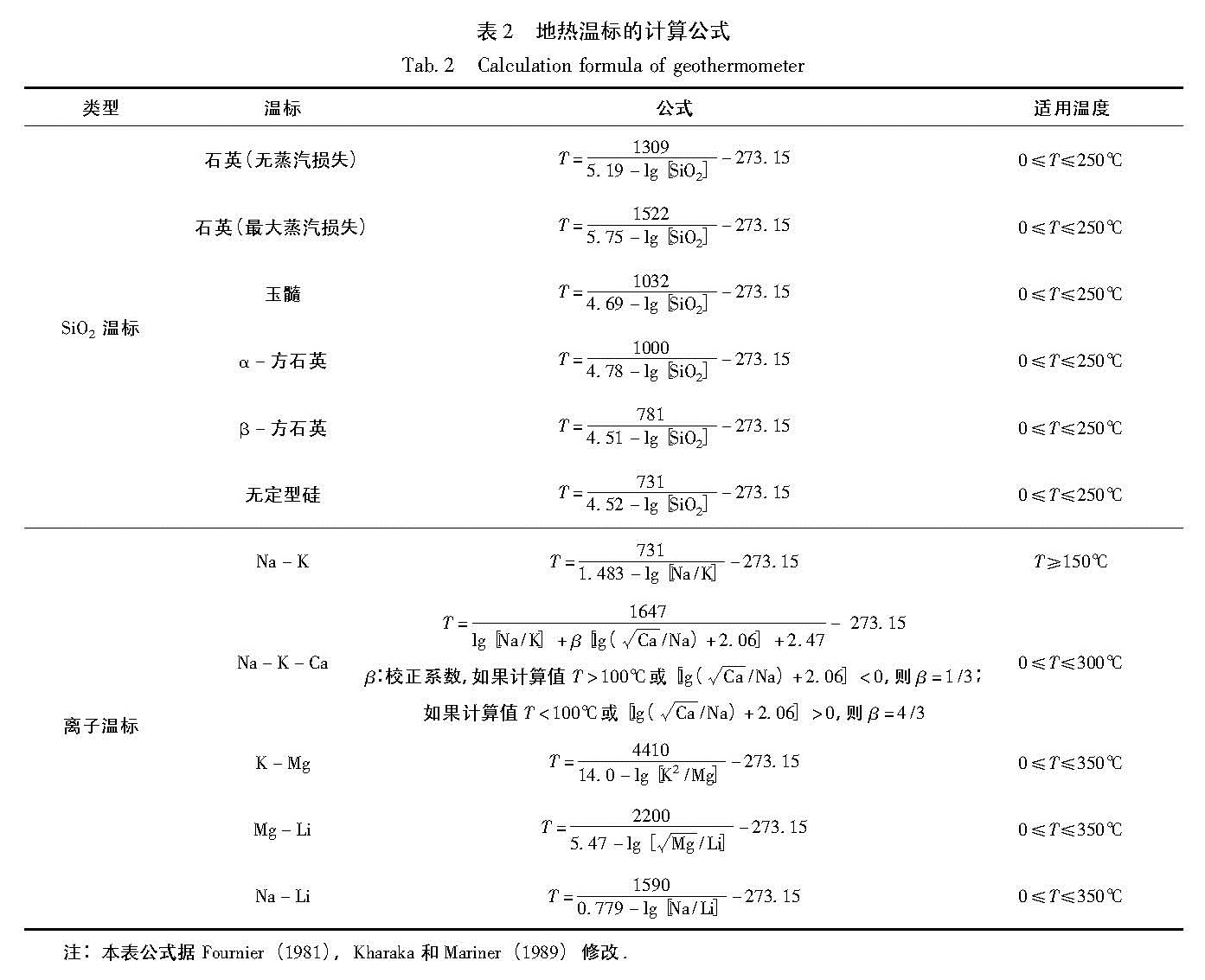
2.3 地热温标目前常用的地热温标大体可以分为两类(表2)(Fournier,1981; Kharaka,Mariner,1989):一类是SiO2温标(包括石英温标、玉髓温标等); 另一类是阳离子温标(如Na-K、Na-Li、Na-K-Ca 等温标)。SiO2温标是应用最早也是最常用的地球化学温标,其原理是基于地热流体中SiO2矿物的溶解度与温度呈函数关系。试验表明,天然水中溶解SiO2一般不受其他离子、复合物及挥发组分散失的影响,且SiO2的沉淀在热流冷却过程中,随温度的下降而沉淀速率减慢,因此在地热流体中SiO2的浓度能很好地指示地下热储的
温度。SiO2温标适用热水温度范围为0~250 ℃。阳离子地热温标是基于热水与溶解矿物间的K+、Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+等阳离子的交换与温度的关系而建立的经验公式,该公式在热储温度估算方面有着广泛的应用。Mitrofan等(2010a,b)研究表明在地震孕育或发生的过程中,离子型地热温标有着明显的响应。
注:本表公式据Fournier(1981),Kharaka和Mariner(1989)修改.研究区内绝大部分温泉水样没有达到水岩平衡,表明该区温泉不适合用阳离子温标方法估算地下热储的温度(王皓,柴蕊,2009),而且水温不高,基本上无蒸汽损失或有的泉点蒸汽损失量很小。因此,本文利用SiO2温标(无蒸汽损失)计算区内76个泉点的热储温度,计算结果列入表1。DAN3(温水河村热水塘)和CHD5(新田盐场温泉)的热储温度计算值低于泉口温度且出现负值,证明该结果不可用。分析原因可能为水样中SiO2含量在分析检测中出现偏差,含量过小; 且温标计算方法的选择不当等也会导致热储温度计算值小于泉口温度,甚至出现负值的情况。
3 结果与讨论
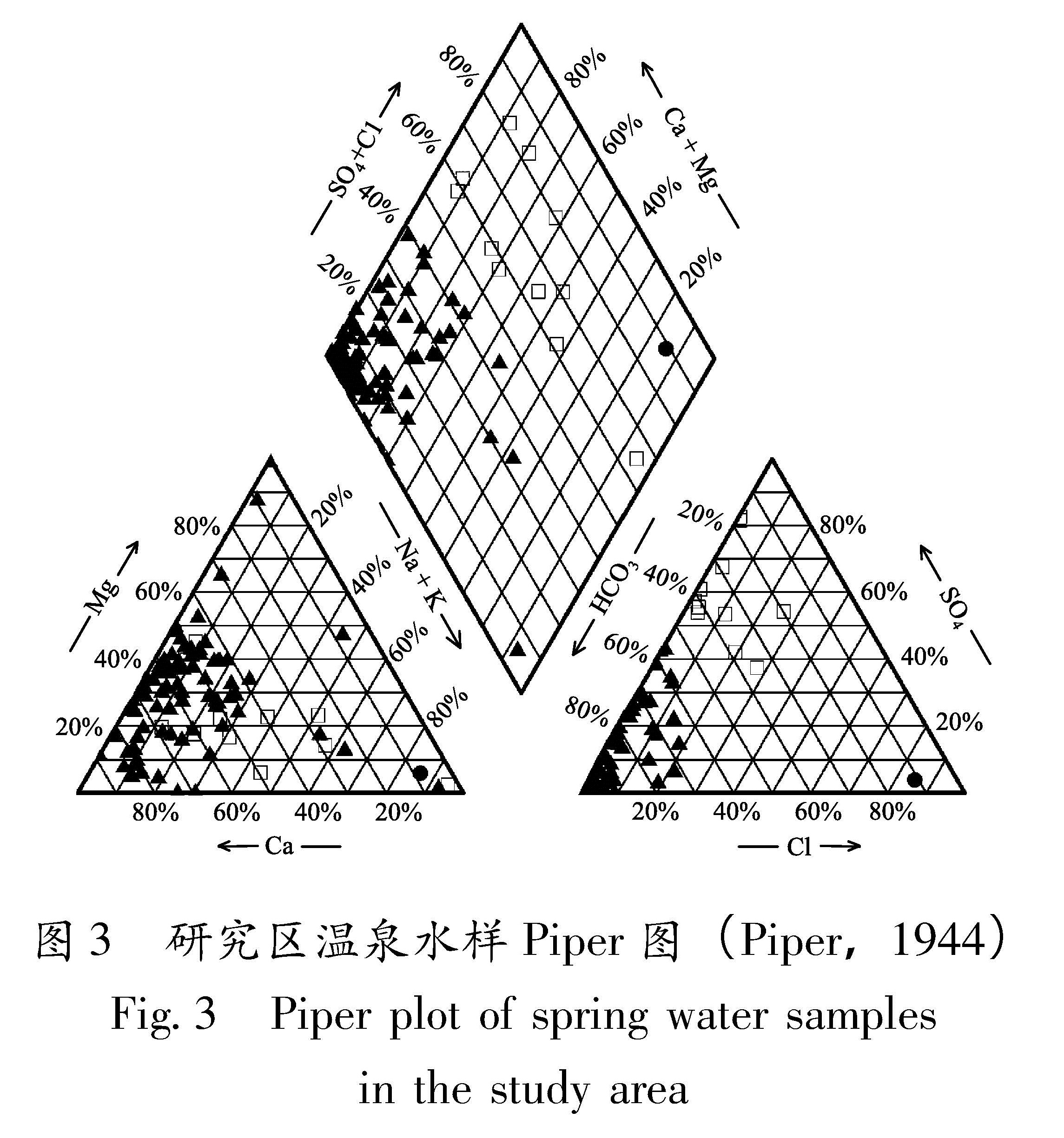
3.1 水化学特征研究区内95件温泉水样中,各离子的浓度差异很大,水质复杂。其中有1处温泉水样主要阴离子缺失(DYS1),其余94件温泉化学数据绘制成Piper图(Piper,1944)(图3),大致可划分成以下3种水化类型:
Ⅰ型:阴离子SO2-4占优势,位于阴离子三角图的上角,用□符号表示(图3),共11件水样,编号是:DYL1、DYL2、DYL7、DCJ2、DCJ3、DHZ2、CNN3、CNN4、CNN5、CHD4、CMY2,水化类主要为HCO3-SO4-Ca(Na)型,矿化度相对较高。Ⅰ型水样主要分布于小江断裂带的北段(四川宁南)和中南段(宜良、澄江)地区。地下水中的SO2-4可能来自沉积岩中夹杂的石膏(CaSO4·2H2O)或其它硫酸盐。沿小江断裂混杂第三纪煤层(褐煤),褐煤的主要挥发分为CO2以及硫化物,硫化物被氧化后,使本来难溶于水的S以SO2-4形式大量进入地下水中(赵珂等,2005),因此流经这类地层的地下水往往以SO2-4为主,表现出酸性地热水的特点。
Ⅱ型:阴离子Cl-占优势,位于阴离子三角图的右角,用●符号表示(图3),该型水比较特殊,仅CHD5(会东县新田盐场温泉)水样1件,矿化度最高,水化类型为:Cl-Na型。据资料记录,该温泉含有较高的Na+和Cl-,水温仅24℃,属于含盐低温温泉,当地居民曾用泉水制盐,盐味苦涩,其原因是该泉水含有一定量的Ca2+、Mg2+离子。利用γNa/γCl特性系数法可以对泉水的来源进行初步判定,标准海水的γNa/γCl系数的平均值为0.85,海相沉积地层中,如果水中Na与地层中的交换性Ca产生阳离子交换,则Na的含量降低,γNa/γCl<0.85(李学礼等,2010)。CHD5温泉的γNa/γCl系数为0.63,由此可以推断,新地质构造运动以后,封闭的海相沉积水可能随大气降水的径流而排泄。
Ⅲ型:阴离子HCO-3占优势,位于阴离子三角图的左角,用▲符号表示,共82件水样(图3),矿化度较低。主导阳离子为Na+的有4件水样(CMY2、DJS1、DQJG2、DDC5),其中CMY2为CO3-Na型水,依据《横断山区温泉志》(佟伟,章铭陶,1994)记录,其pH值变化较大,野外测量值为7.5,实验室测量值为9.1,造成水样中HCO-3离子大部分转化为CO2-3离子。DJS1、DQJG2、DDC5水化类型为HCO3-Na型。主导阳离子为Mg2+的有8件水样(CHD3、CHD6、DHN2、DHN3、DHN5、DHZ3、DKY3、DML3),水化类型都为HCO3-Mg-Ca型。其余的水样以Ca2+为主导阳离子,共70件,占全部水样的近74%,水化类型为HCO3-Ca-Mg(Na)型。该类型水比较复杂,从元古界地层到第四系的沉积盆地都有出露,温泉中HCO-3主要来源于碳酸盐类,Ca2+和Mg2+主要是地下水溶解了可溶性的灰岩(CaCO3)与白云岩(MgCO3)的结果,化学类型以HCO3-Ca(Mg)型为主。
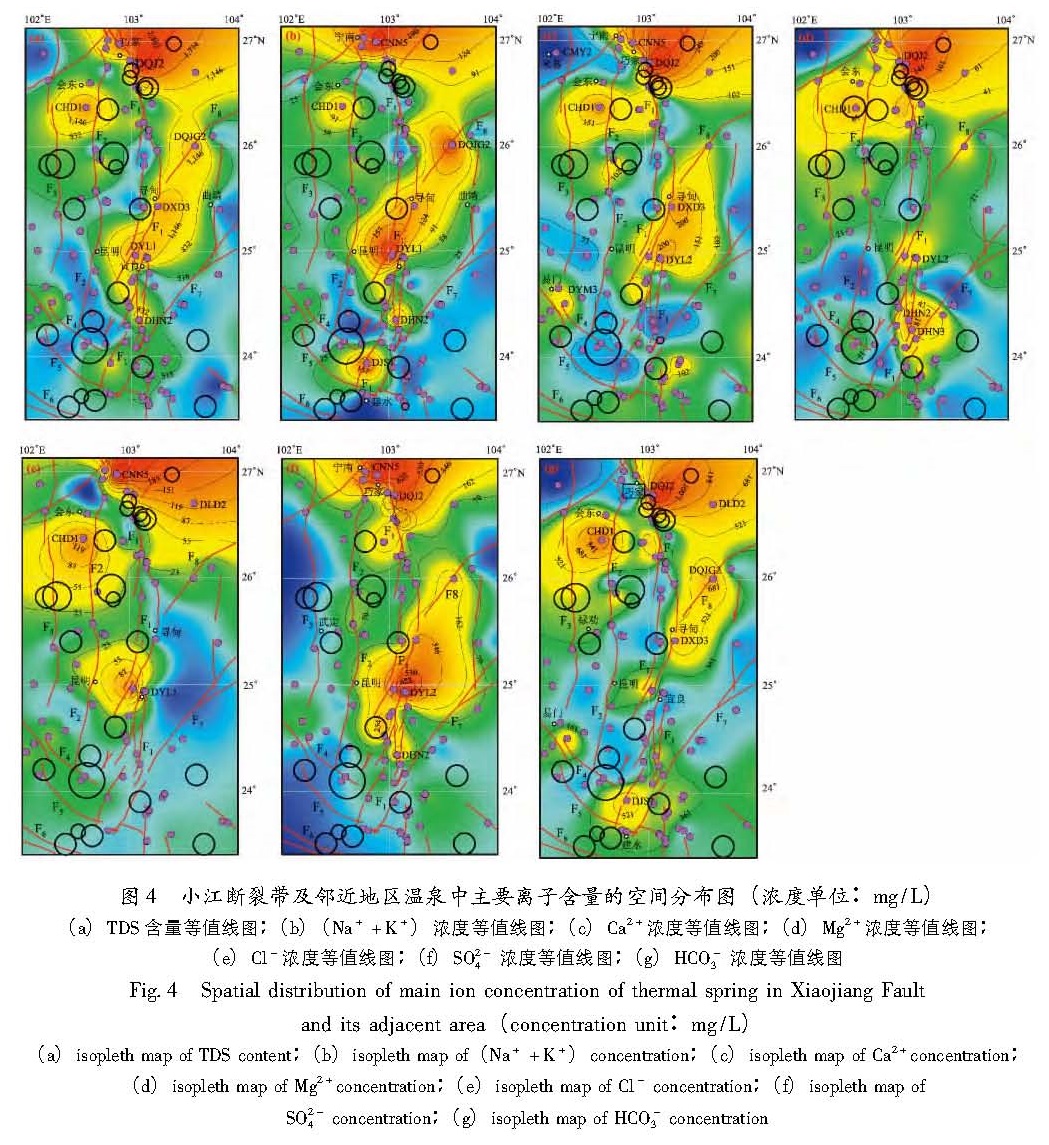
综合Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ型水发现,低矿化水中以HCO-3及Ca2+、Mg2+为主; 高矿化水则以Cl-及Na+为主; 中等矿化的地下水中,阴离子常以SO2-4为主,主要阳离子可以是Na+或Ca2+,这主要是由各种矿物在水中的溶解度不同而造成的; 氯盐的溶解度最大,硫酸盐次之,碳酸盐较小; 钙的硫酸盐,特别是钙、镁的碳酸盐,溶解度最小; 随着矿化度增大,钙、镁的碳酸盐首先达到饱和并沉淀析出,矿化度继续增大时,钙的硫酸盐也饱和析出。因此,高矿化水中以易溶的氯和钠占优势。3.2 离子空间分布为了进一步了解温泉水样主要离子在研究区内的分布特征,利用Surfer 7.03中的Kriging空间插值方法,绘制小江断裂带及邻近地区泉点分布、各泉点的TDS及7种主要离子的浓度等值线图(图4)。
根据TDS的高低可以将地下水划分为淡水(TDS<1 g/L),微咸水(1 g/L<TDS<2g/L),咸水(2 g/L<TDS<35 g/L)和卤水(TDS>35 g/L)4类(李学礼等,2010)。研究区内有81个泉点属于淡水,占全部泉点的85%; 11个属于微咸水,占12%; 3个为咸水,占3%。由图4a可知,高矿化度的泉点主要分布在小江断裂带北段(巧家至会泽一带)和中段(沿北北东向昆明—寻甸—曲靖北一带展布),最高点为北段的DQJ2(3 163.9 mg/L),中段最高值为DYL1(1 664.2mg/L),南段最高值为DHN2(1 109.6 mg/L)。总体上看,TDS变化趋势为沿小江断裂带(F1)由北向南逐渐减弱,特别是南段,几乎所有的温泉水都属淡水。其余寻甸—宣威断裂(F8)上的DQJG2
(1 477.8 mg/L)和普渡河断裂上(F2)的CHD1(1 704.5 mg/L)属于微咸水。值得一提的是,其它几条断裂(F4、F5、F6、F7)上及其附近温泉的矿化度都很低,属于淡水。
Na+和K+性质相似,在地下水中K+含量一般很小,在研究地下水成分时,将K+浓度归并到Na+浓度中,不另区分(陈南祥,2008)。研究区内的钠、钾含量(Na++K+)变化为0.43~308 mg/L,平均值为40.72 mg/L。由图4b可以看
图4 小江断裂带及邻近地区温泉中主要离子含量的空间分布图(浓度单位:mg/L)
(a)TDS含量等值线图;(b)(Na++K+)浓度等值线图;(c)Ca2+浓度等值线图;(d)Mg2+浓度等值线图;
(e)Cl-浓度等值线图;(f)SO2-4浓度等值线图;(g)HCO-3浓度等值线图
Fig.4 Spatial distribution of main ion concentration of thermal spring in Xiaojiang Fault and its adjacent area(concentration unit:mg/L) (a)isopleth map of TDS content;(b)isopleth map of(Na++K+)concentration;(c)isopleth map of Ca2+concentration; (d)isopleth map of Mg2+concentration;(e)isopleth map of Cl- concentration;(f)isopleth map of SO2-4 concentration;(g)isopleth map of HCO-3 concentration出,钠、钾高值点主要分布在小江断裂带(F1)的北段CNN5(307.4 mg/L)和中段DLY1(308 mg/L),寻甸—宣威断裂(F8)上的DQJG2(240 mg/L),小江断裂带南段除了DHN2(183 mg/L)外,其余泉点的钠、钾值都很低,一般不超过33 mg/L。钠、钾含量在低矿化水中的含量一般很低,但在高矿化水中则是主要的阳离子。因此,钠、钾含量总体趋势与TDS的分布极其相似,都呈北高南低,由北向南逐渐减弱。
Ca2+的浓度等值线图如图4c所示,高值区都位于小江断裂带北段,会泽以北到巧家一带,泉点DQJ2的Ca2+浓度高达469.88 mg/L,小江断裂(F1)中段的DXD3和南段北端DYL7也相对较高,分别是250 mg/L,247.29 mg/L。普渡河断裂(F2)北段附近的CHD1泉点Ca2+(231.5 mg/L)含量相对较高,而小江断裂南段到曲江断裂、建水断裂一带,各泉点的Ca2+含量较低,一般不超过150 mg/L,基本上呈现由北向南,Ca2+含量逐渐降低的趋势。与Ca2+类似,Mg2+高值点也出现在小江断裂北段的DQJ2泉点,浓度高达193.49 mg/L(图4d)。尽管Ca2+、Mg2+来源及其在地下水中的分布相近,但Mg2+在小江断裂带的中段的含量较低,而南段的DHN2、DHN3的值相对较高,都在90 mg/L以上。同样,CHD1泉点的Mg2+含量(76.1 mg/L)也明显高于小江断裂带以外的其他泉点。其他几条断裂上及其附近的泉点的Mg2+值都较低,最低点位于汤郎—易门断裂北段附近的CMY2泉点,Mg2+的含量仅0.81 mg/L。Ca2+、Mg2+含量相比,Mg2+在地下水中含量通常较Ca2+少,不成为地下水中的主要阳离子。
阴离子Cl-、SO2-4、HCO-3在地下水中广泛分布。研究区内3种阴离子的等值线分布(图4e~g)可以看出,3种阴离子的高值点都分布在小江断裂(F1)的北段,Cl-和SO2-4的最高值都位于CNN5泉点,分别为302 mg/L和852 mg/L,而HCO-3的最高值点位于DQJ2(1 565.8 mg/L),该点的Cl-和SO2-4的值也仅次于最高值。小江断裂带中段上的泉点DYL1,Cl-和SO2-4也表现出相对较高的值,分别为156.38 mg/L、458.82 mg/L; 而中段的HCO-3值较北段低。小江断裂带南段,除了DLY7上的SO2-4含量(787.12 mg/L)相对较高以外,Cl-和HCO-3含量都很低。在研究区内,除普渡河断裂附近泉点CHD1的Cl-(149.79 mg/L)和HCO-3(1 052.67 mg/L)含量以及寻甸—宣威断裂上(F8)的泉点DQJG2的SO2-4含量(242.36 mg/L)相对较高外,其它几条断裂带上及其附近泉点的Cl-、HCO-3和SO2-4的含量都很低。导致小江断裂带上3种阴离子的含量要比其他断裂上泉点的含量高。
综合图4分析可知,总矿化度(TDS)的分布与7种主要离子含量分布非常相似,空间上基本是沿断裂带展布,受断裂控制明显,特别是小江断裂带上泉点各化学组分含量较高。小江断裂与其它几条断裂相比,切割较深,断裂开启程度高,热水的循环深度大,与断裂带两盘岩石进行了充分的水—岩反应(杨雷等,2011)。构造活动控制了温泉的运移速度及部分物理化学条件,使得水岩反应更容易达到平衡,其矿物质含量就越高,水化学类型越复杂。对比7种主要离子、TDS以及近40余年M≥4.7破坏性地震分布可以看出,离子浓度较高的区域地震分布较少,而离子浓度较低的区域地震分布较多,TDS与地震分布的这种关系尤为明显,小江断裂带北段(巧家至会泽)TDS的高值与低值过渡区域和普渡河断裂(F2)、汤郎—易门断裂(F3)中段的TDS低值区地震较多,此外,小江断裂带(F1)与曲江—建水断裂带(F4、F5)的交汇处,TDS值也较低,但地震活动频度高,强度相对较大,1970年通海7.7级大地震就发生在该处,震源深度较浅(国家地震局震害防御司,1999; 张四昌,刘百篪,1978)。温泉水样主要离子与地震活动性之间的这种分布规律,表明地下流体特征与地震活动存在着某种内在联系,特别是与断层活动有紧密的联系(王基华等,2000)。这意味着离子成分浓度高,循环深度大,“水—岩”作用加剧,地下流体对断裂的弱化程度高,在该部位应力不会积累很大; 相反,离子成分浓度低,循环深度浅,地下流体运移过程中“水—岩”作用程度低,也反映了断裂闭合性较好,容易造成应力累积。因此,地下流体离子成分浓度的高低能反映出断裂活动强度的大小、地震活动性的强弱。
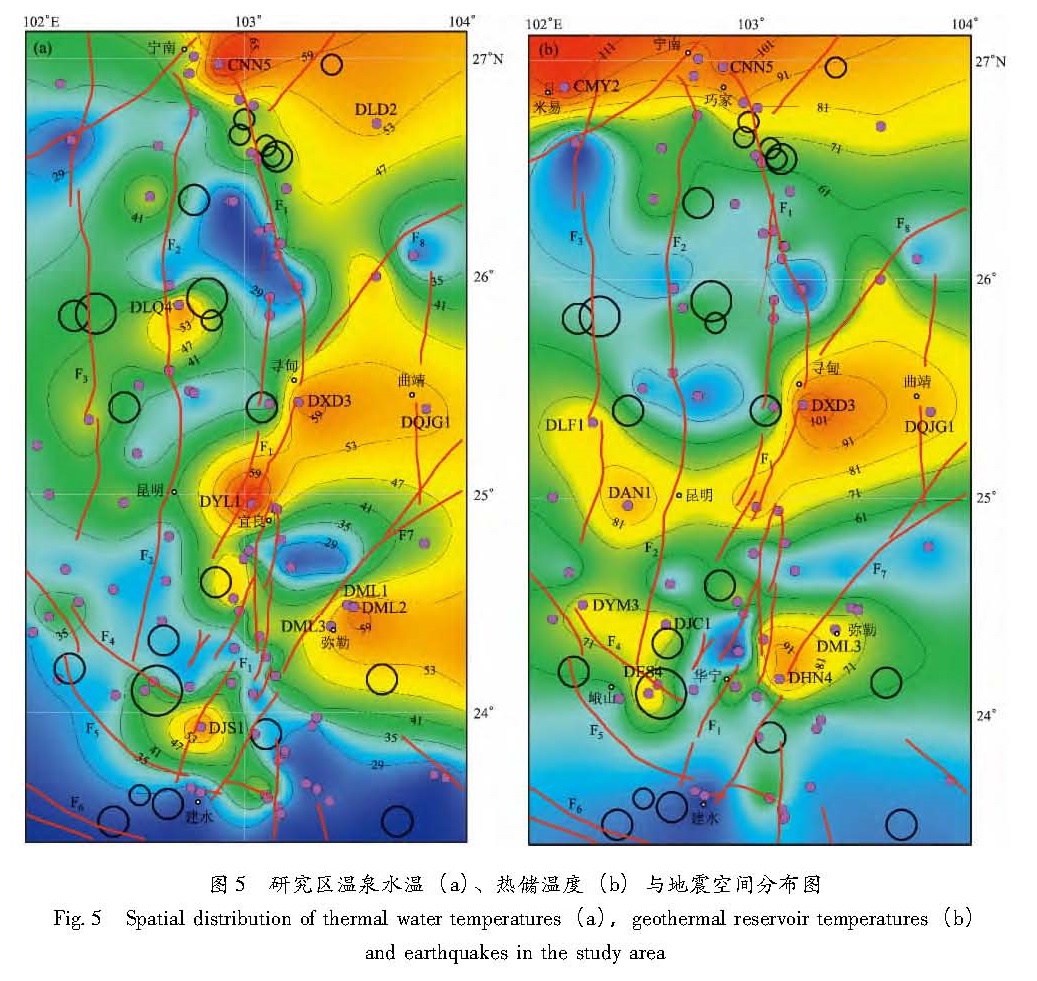
3.3 水温分析及热储温度估算根据研究区95处温泉水温分析,平均水温为37.2 ℃。地下热水主要为低温热水,其中高温热水(60 ℃~100 ℃)共7处,约占7%; 中温热水(40 ℃~60 ℃)共27处,约占29%; 低温热水(20 ℃~40 ℃)61处,约占64%。
图5a是研究区温泉水温的空间分布图,水温最高的泉点是小江断裂带上两个Ⅰ型水样(CNN5、DLY1温度分别是75 ℃、76 ℃)。从整体上看,小江断裂以东温泉(DLD2、DQJG1、DML1、DML2、DML3)水温较高,都在50 ℃以上,而小江断裂以西的温泉水温较低,除个别泉点外(DLQ4),均不超过50 ℃。小江断裂带中北段(东川附近)和南部温泉较为特殊,水温一般低于40 ℃,这主要是由于温泉出露点位于两大断裂交汇处,可能自身循环度较浅,且出露地层为灰岩地层,表层岩溶作用强烈,溶隙或裂隙等较
为发育,热水在向上运移过程中掺入了大量的地表冷水,导致水温较低(杨雷等,2011)。总的看来,小江断裂带上出露温泉水温普遍较高,位于小江断裂带上的温泉水温要比其余温泉的水温平均值高出3 ℃~4 ℃。这表明热水成因受断裂活动控制明显,热水的循环深度大,表现出水温较高,同时也说明小江断裂要比云南中东部地区其他几条断裂的切割深度较深。换句话说,水温的高低与断裂深浅、断裂带的规模、破碎程度具有相关性。
图5b是表1中地热储温度利用Kriging 插值法绘制的空间分布图,从图上可以看出,北部地区米易—巧家一带的地热储温度最高,大部分泉点计算的热储温度在80℃以上; 小江断裂的中段寻甸—曲靖地区的热储温度次之,其中昆明地区
图5 研究区温泉水温(a)、热储温度(b)与地震空间分布图
Fig.5 Spatial distribution of thermal water temperatures(a),geothermal reservoir temperatures(b)and earthquakes in the study area(富民、安宁、宜良)热储温度也较高,一般都在70 ℃以上; 南部分为东西两块,分别是玉溪—峨山和华宁—弥勒地区,热储温度也在70℃以上。向才英和周真恒(2000)研究表明四川米易地区的大地热流值在66~90 mW/m2之间,中部昆明地区大地热流值高达105 mW/m2; 玉溪—峨山地区,大地热流值达92 mW/m2,而东川地区属于低热区,大地热流值≤60 mW/m2。区内大地热流值分布与地热储温度分布特征基本吻合,这说明了SiO2地热温标(无蒸汽损失)计算热储温度的合理性。
结合水温、热储温度与地震分布图(图5)可以发现,并不是温泉的热储温度越高,其水温也越高。如CMY2、DAN1、DES4、DHN4等计算出热储温度较高,但温泉水温较低,这主要是因为深部热液沿断裂上升过程中,冷水混入的比例不同所致,还与泉水流量、热储埋深有关。无论是水温还是热储温度,高值区域中强地震(M≥4.7)分布较少。然而,小江断裂带(F2)以西(自巧家以南,经会泽至嵩明)到汤郎—易门断裂(F3)地区(米易南至武定),还有小江断裂带南段、曲江—石屏断裂带(F4、F5)及这两条断裂带的交汇处,水温和地热储温度较低,却是破坏性地震的高发区域,1970年以来,M>4.7级中强地震主要发生在这几个区域内。这种变化关系表明水在地震孕育或发生过程中起着重要作用。首先,水温升高,水的空隙压力也随之升高,水的空隙压力升高又将大大降低活动断层面的正压力(陆明勇等,2007)。其次,水温升高,水热蚀变作用越强烈,地下热水与围岩的物理化学作用更加明显,使沿断裂面的岩石产生泥化、水化和溶蚀作用,岩石的抗压强度约降低20%~80%,断层面的摩擦力下降约30%~90%(宋贯一等,2000)。此外有研究表明,岩石的破裂强度、弹性模量、剪切破裂能、断裂韧性和抗张强度等力学参数随环境水温的升高而降低(荣代潞等,1992)。由此可以推断在水温、热储温度高值区,地下热水活动越强烈,对断裂及其围岩弱化程度越高。断层不断发生滑移,断面上很难积累应力而发生地震,这就造成该地区缺震少震的现象明显; 相反,水温或热储温度低的地区,地下热水对断裂弱化作用的强度则较低,可积累较大不易释放的构造应力,在这些地区断裂强度也较大,在累积一定的构造应力下,断裂发生错动而发震。
3.4 同位素在固体地球内部尤其是地幔中含有大量活跃的、易运移的气体或挥发成份,如He、CO2、H2、CH4等,它们包含着丰富的地球化学信息,这些气体或挥发成份在发生地幔脱气作用后可运移到壳内或地表(陶明信等,2005)。因此动态监测这些深源气体有可能反映深部的地质构造问题,如断裂深度、开启性、活动性和壳幔的连通性等,从而可为地震预报研究提供有科学价值的信息和新的研究途径。然而,地幔气体上升至地表后,必然会被壳源或大气源气体混染,所以在近地表采集的气体样品为幔源、壳源或大气源的复合气体。因此,如果要了解断裂带的深度及其壳幔连通程度等特征,我们应研究断裂带及其附近的气体样品中是否含幔源气体及其多少的问题。气体样品同位素示踪可用来追溯物质来源和揭示物质循环过程。
在地壳深部运移的流体组分中,CO2是分布最广、含量最丰富的气体组分之一,它不仅在中上地壳相对富氧的环境条件下大量存在,在下地壳,甚至在上地幔流体中,也是最重要的挥发性组分(上官志冠,刘桂芬,1993)。目前比较公认的是δ13C值的来源及变化范围(上官志冠,高松升,1987),大气CO2的δ13C值变化范围从-8.5‰~-6‰; 生物成因CO2的δ13C平均值约为-25‰; 变质成因的CO2的δ13C平均值约为0‰; 幔源CO2的δ13C值的变化范围为-8.0‰~-4.7‰。
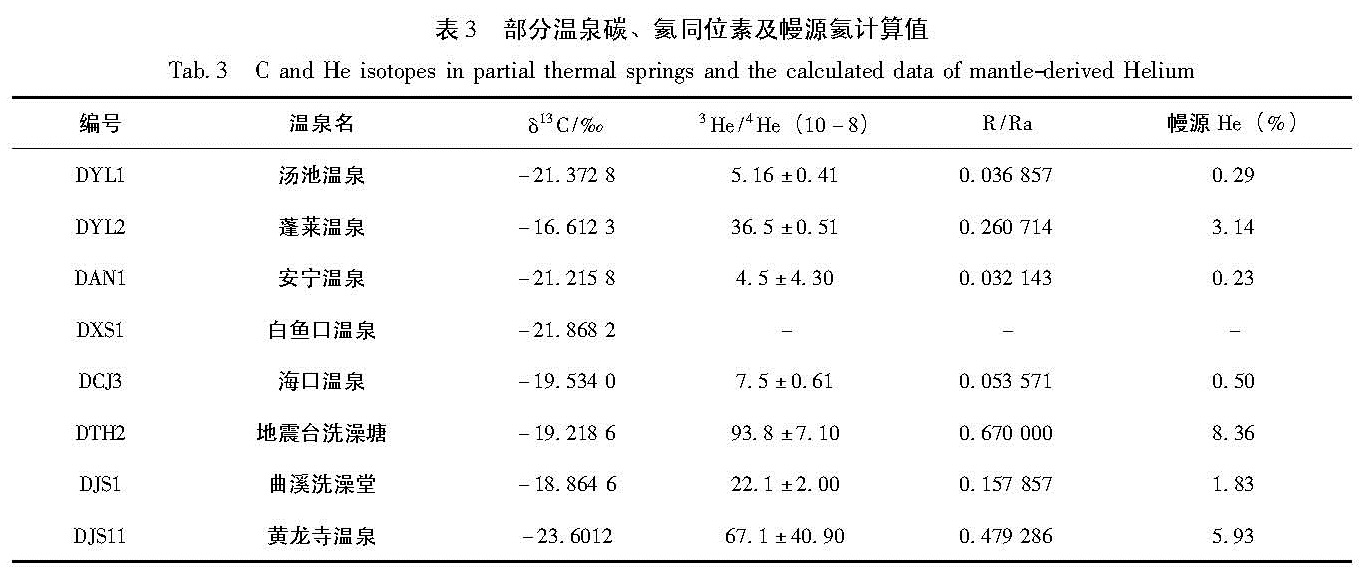
本文收集了研究区内8个泉点的溶解和逸出CO2的稳定碳同位素和He同位素组成(赵柯等,2005)(表3)。由表3可以看出,小江断裂带中南部的温泉CO2的δ13C值集中在-16.6‰~-23.6‰之间,介于纯生物成因(δ13C=-25 ‰)和其它三种成因之间。由此可见,这8个温泉CO2气体的稳定碳同位素组成生物成因占了很大的比重,具有明显的生物成因特征。据赵柯等(2005)分析研究,造成δ13C这种特征的原因可能与沿小江断裂混杂第三纪煤层(褐煤)有关。滇东主要断裂带的温泉出露地层主要以灰岩为主,地下水在循环过程中,除溶解吸收在土壤中的CO2外,还接受混杂在地层中的第三纪煤层(褐煤)挥发
表3 部分温泉碳、氦同位素及幔源氦计算值
Tab.3 C and He isotopes in partial thermal springs and the calculated data of mantle-derived Helium出的CO2,并溶解其周围的碳酸盐岩后再出露地表释放CO2。较低的δ13C值意味着温泉中的微量碳主要来源于生物成因CO2的溶解作用。
He是一种既不参与化学反应过程又具有显著分馏特征的惰性气体,其同位素被证明是一种获取深部物质信息的灵敏示踪剂,所以氦同位素是用来判断地下流体起源与构造活动的又一个有效示踪标志(Hoke et al,2000)。周晓成等(2012)研究指出,活动断裂带地区的温泉、深井气体同位素比值(3He/4He、21Ne/22Ne、4He/20Ne、40Ar/36Ar)与组分浓度(He、H2、CH4、Ne、Ar和N2)及其比值(He/Ar、N2/Ar、CH4/Ar)均在地震前后或者同时出现明显异常。大量研究表明(徐永昌,1992; 李圣强,杜建国,1998; 上官志冠等,2000; 杜建国,刘丛强,2003; Pérez et al,2008),不同成因的氦同位素组成明显不同:大气氦、壳源氦和幔源氦的端元值分别为1.4×10-6、2.0×10-8和1.1×10-5。通常以R/Ra来表示氦同位素组成特征(R为样品的3He/4He比值,Ra为大气3He/4He比值)。一般认为,当R/Ra<1时,氦同位素组成表现为壳源特征,当R/Ra >1时,氦同位素组成表现为幔源特征。根据壳源和上地幔源氦同位素的两端元复合模式(Andrews,1985)估算幔源He百分含量:
He幔源(%)=((3He/4He)样品-(3He/4He )壳源)/((3He/4He)幔源-(3He/4He)壳源)×100%.
计算值列入表3,除DXS1数据缺失外,其余7个点的幔源氦比例的变化范围0.23%~8.36%,平均值约为2.9%,沈立成等(2007)对小江断裂带中南部温泉气体也进行了采样分析,结果表明样品中的幔源氦平均约占总氦的2.27%,最高也才8.9%,这与我们用赵柯等(2005)数据处理后的结果相吻合,进一步说明数据的来源的可靠性。同时,沈立成等(2007)研究数据还给出滇西南地区幔源氦平均约占总氦的26.15%,最大值大于48%; 怒江断裂幔源氦含量平均值约为26.2%,最大值大于48.8%。小江断裂带幔源氦释放与之相比强度明显小很多,且与同处于南北地震带上的鲜水河断裂幔源氦(平均约占总氦的8.1%)相比释放强度也较弱。综上所述,反映出小江断裂带中南深部的壳幔连通程度较低,而地壳闭合性程度相对较高,所能观测到的脱气作用几乎都发生在地壳范围内,故而其幔源氦同素所占比例相对较低。
4 结论
通过对小江断裂带及邻近地区的温泉地球化学数据收集、汇总,对每一处水化学特征及水文地球化学场进行对比研究,得出以下结论:
(1)区内温泉水化学类型差异较大。其中碳酸型大部分为:HCO3-Ca-Mg(Na),共70件,其余水样化学类型为:HCO3-Mg-Ca或HCO3-Na; 硫酸型温泉共11件水样,水化类型主要为SO4-HCO3-Ca(Na); 氯型水样只有1件,Cl-Na型。应用Na-K-Mg三角图解模型对水样进行分析,绝大部分样品均未达到水—岩平衡。
(2)区内温泉中TDS含量、主要离子含量、水温及热储温度的空间分布特征研究结果表明,在空间分布上受活动构造控制明显,主要沿小江断裂带北高南低展布; 与近40余年的地震活动关系表现为高值区域中强地震(M≥4.7)分布较少,而低值区域中强地震发生频度较高,且强度较大,该对应关系在水温和热储温度空间分布上尤为明显。
(3)小江断裂带中南部部分泉点溶解或逸出CO2的碳同位素分析结果表明,CO2气体的碳同位素(δ13C)组成具有明显的生物成因特征; 氦同位素(幔源He百分含量)研究结果表明,小江断裂带中南深部的壳幔连通程度较低,而地壳闭合性程度相对较高,所能观测到的脱气作用几乎都发生在地壳范围。
本文在撰写和修改过程中得到周挚、毕玉洁以及云南财经大学张春生的帮助,在此向他们表示衷心感谢。
- 陈南祥.2008.水文地质学[M].北京:中国水利水电出版社,73-74.
- 邓起东,冉永康,杨晓平,等.2007.中国活动构造图(1:400万)[M].北京:地震出版社.
- 杜建国,刘丛强.2003.同位素地球化学在地震研究方面的作用[J].地震,23(2):99-107.
- 国家地震局震害防御司.1999.中国近代地震目录(公元1912年—1990年)[M].北京:地震出版社.
- 李圣强,杜建国.1998.氡,氦等气体地球化学在地震科学研究中的进展[J].地球科学进展,13(3):238-245.
- 李学礼,孙占学,刘金辉.2010.水文地球化学(第三版)[M].北京:原子能出版社.
- 陆明勇,牛安福,刘耀炜,等.2007.流体力与构造应力相互关系的探讨[J].地震,27(1):55-62.
- 钱晓东,秦嘉政.2009.小江断裂带及周边地区强震危险性分析[J].地震研究,31(4):354-361.
- 荣代潞,金发辉,贺玉亭,等.1992.水的临界温度对大震孕育和发生的作用的模拟实验研究[J].地震学报,14(2):156-163.
- 上官志冠,白春华,孙明良.2000.腾冲热海地区现代幔源岩浆气体释放特征[J].中国科学(D辑),30(4):407-414.
- 上官志冠,高松升.1987.滇西实验场区温泉碳同位素地震地球化学特征[J].地震,(6):25-35.
- 上官志冠,刘桂芬.1993.川滇块体边界断裂的 CO2释放及其来源[J].中国地震,9(2):146-153.
- 沈立成,袁道先,丁悌平,等.2007.中国西南地区CO2释放点的He同位素分布不均一性及大地构造成因[J].地质学报,81(4):475-487.
- 沈娅宏,张建国,毛燕,等.2012.小江断裂带及其周边地区构造应力场特征[J].云南大学学报(自然科学版),34(3):308-314.
- 宋贯一,易立新,宋晓冰.2000.地下热水对断裂活动与地震活动的影响研究[J].地震学报,22(6):632-636.
- 唐文清,刘宇平,陈智梁,等.2006.云南小江断裂中南段现今活动特征[J].沉积与特提斯地质,26(2):21-24.
- 陶明信,徐永昌,史宝光,等.2005.中国不同类型断裂带的地幔脱气与深部地质构造特征[J].中国科学(D辑),35(5):441-451.
- 佟伟,章铭陶.1994.横断山区温泉志[G].北京:科学出版社.
- 王二七,Burchfiel B.C.,Rogden R.H.,等.1995.滇中小江走滑剪切带晚新生代挤压变形研究[J].地质科学,30(3):209-219.
- 王皓,柴蕊.2009.地热温标在地热系统中的应用研究[J].河北工程大学学报:自然科学版,26(3):54-58.
- 王基华,林元武,刘成龙.2000.地下流体在地震孕育与发生中的作用—以张家口南部地热活动区为例[J].地震,20(增):l16-119.
- 闻学泽,杜方,龙锋,等.2011.小江和曲江—石屏两断裂系统的构造动力学与强震序列的关联性[J].中国科学:地球科学,41(5):713-724.
- 向才英,周真恒.2000.云南地震活动与岩石圈热结构的关系[J].中国地震,16(3):263-272.
- 徐永昌.1992.我国80年代气体地球化学研究[J].沉积学报,10(3):57-69.
- 杨雷,肖琼,沈立成,等.2011.不同地质背景地热系统水—岩作用下温泉水的地球化学特征—以重庆市温塘峡背斜温泉、滇东小江断裂带温泉为例[J].中国岩溶,30(2):209-215.
- 云南省地方志编纂委员会.1999.云南省志:温泉志[G].昆明:云南人民出版社.
- 张春山,张立海,吴满路,等.2004.中国大陆水文地球化学—构造地震危险区划研究[J].地质力学学报,10(3):213-226.
- 张春山,张业成,吴满路.2003.南北地震带南段水文地球化学特征及其与地震的关系[J].地质力学学报,9(1):21-30.
- 张培震,邓起东,张国民,等.2003.中国大陆的强震活动与活动地块[J].中国科学(D辑),33(增刊):12-20.
- 张四昌,刘百篪.1978.1970年通海地震的地震地质特征[J].地质科学,(4):323-335.
- 张炜,罗光伟,邢玉安,等.1988.气体地球化学方法在探索活断层中的应用[J].中国地震,4(2):121-123.
- 赵慈平,冉华,王云.2012.腾冲火山区的现代幔源氦释放:构造和岩浆活动意义[J].岩石学报,28(4):1189-1204.
- 赵珂,姜光辉,杨琰,等.2005.滇东主要断裂带温泉CO2成因浅析[J].地球与环境,33(2):11-15.
- 周晓成,杜建国,杨志,等.2012.地震地球化学研究进展[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报,31(4):340-346.
- Andrews J.N..1985.The isotopic composition of radiogenic helium and its use to study groundwater movement in confined aquifers[J].Chemical Geology,49(1):339-351.
- Biagi P.F.,Ermini A.,Cozzi E.,et al.2000.Hydrogeochemical precursors in Kamchatka(Russia)related to the strongest earthquakes in 1988–1997[J].Natural Hazards,21(2):263-276.
- Claesson L.,Skelton A.,Graham C.,et al.2007.The timescale and mechanisms of fault sealing and water-rock interaction after an earthquake[J].Geofluids,7(4):427-440.
- Famin V.,Nakashima S.,Boullier A.M.,et al.2008.Earthquakes produce carbon dioxide in crustal faults[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,265(3):487-497.
- Fournier R O. 1981. Application of water geochemistry to geothermal exploration and reservior engineering[M]. Geothermal Systems:Principles and Case Histories, 109-143.
- Giggenbach W.F..1988.Geothermal solute equilibria.Derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca geoindicators[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,52(12):2749-2765.
- Hoke L.,Lamb S.,Hilton D.R.,et al.2000.Southern limit of mantle-derived geothermal helium emissions in Tibet:implications for lithospheric structure[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,180(3):297-308.
- Inan S.,Baldererf W.P.,Leuenberger-west F.,et al.2012.Springwater chemical anomalies prior to the MW=7.2 Van Earthquake(Turkey)[J].Geochemical Journal,46:e11-e16.
- Khrarka Y K, Mariner K H. 1989.Chemical gethermometers and their application to formation waters from sedvmentry basins//Naeser N D, McCulloh T H. Thermal history of sedimentary basins[M]. Berlin:Springer,99-117.
- King C.Y.,Koizumi N.,Kitagawa Y..1995.Hydrogeochemical anomalies and the 1995 kobe earthquake[J].Science,269(5220):38-39.
- Mitrofan H.,Chitea F.,Anghelache M.A.,et al.2010a.Subsurface temperature signatures related to particular focal mechanisms,in Romania(Vrancea)and Northern Italy seismic regions[J].Romanian Reports in Physics,62(4):854-864.
- Mitrofan H.,Marin C.,Zugrávescu D.,et al.2010b.Persistent pre-seismic signature detected by means of Na-K-Mg geothermometry records in a saline spring of Vrancea area(Romania)[J].Nat.Hazards Earth Syst.Sci.,10:217-225.
- Piper A.M..1944.A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses[J].Transactions,American Geophysical Union,25:914-928.
- Plastino W.,Panza G.F.,Doglioni C.,et al.2011.Uranium groundwater anomalies and active normal faulting[J].Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry,288(1):101-107.
- Pérez N.M.,Hernández P.,Igarashi G.,et al.2008.Searching and detecting earthquake geochemical precursors in CO2-rich groundwaters from Galicia,Spain[J].Geochemical Journal,42(1):75-83.
- Süer S.,Güleç N.,Mutlu H.,et al.2008.Geochemical monitoring of geothermal waters(2002-2004)along the North Anatolian Fault Zone,Turkey:spatial and temporal variations and relationship to seismic activity[J].Pure and Applied Geophysics,165(1):17-43.
- Tanikawa W.,Mukoyoshi H.,Tadai O..2012.Experimental investigation of the influence of slip velocity and temperature on permeability during and after high-velocity fault slip[J].Journal of Structural Geology,38:90-101.
- Thomas D..1988.Geochemical precursors to seismic activity[J].Pure and Applied Geophysics,126(2):241-266.
- Tokunaga T..1999.Modeling of earthquake-induced hydrological changes and possible permeability enhancement due to the 17 January 1995 Kobe Earthquake,Japan[J].Journal of Hydrology,223(3):221-229.
- Toutain J.P.,Munoz M.,Poitrasson F.,et al.1997.Springwater chloride ion anomaly prior to a ML =5.2 Pyrenean earthquake[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,149(1):113-119.
- Virk H.S.,Stagh B..1994.Radon recording of Uttarkashi earthquake[J].Geophysical research letters,21(8):737-740.
- Wakita H..1996.Geochemical challenge to earthquake prediction[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,93(9):3781-3786.
- Woith H.,Wang R.J.,U.Maiwald U.,et al.2012.On the origin of geochemical anomalies in groundwaters induced by the Adana 1998 earthquake[J].Chemical Geology,339:177-186.