基金项目:地震行业专项《2016-2025年中国大陆强震危险区预测》01-03子专题“大地形变在2016-2025年中国大陆强震危险区预测中的应用研究”与“十二五”国家科技支撑计划课题(2012BAK19B01-07)联合资助.
备注
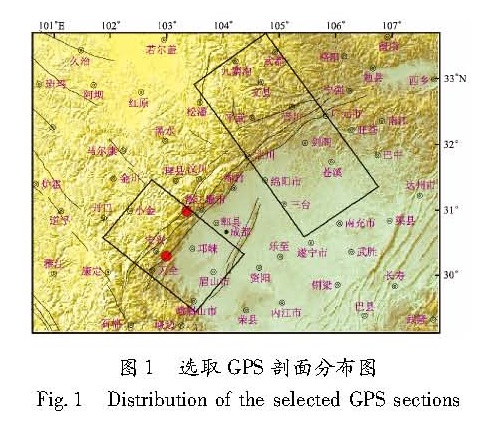
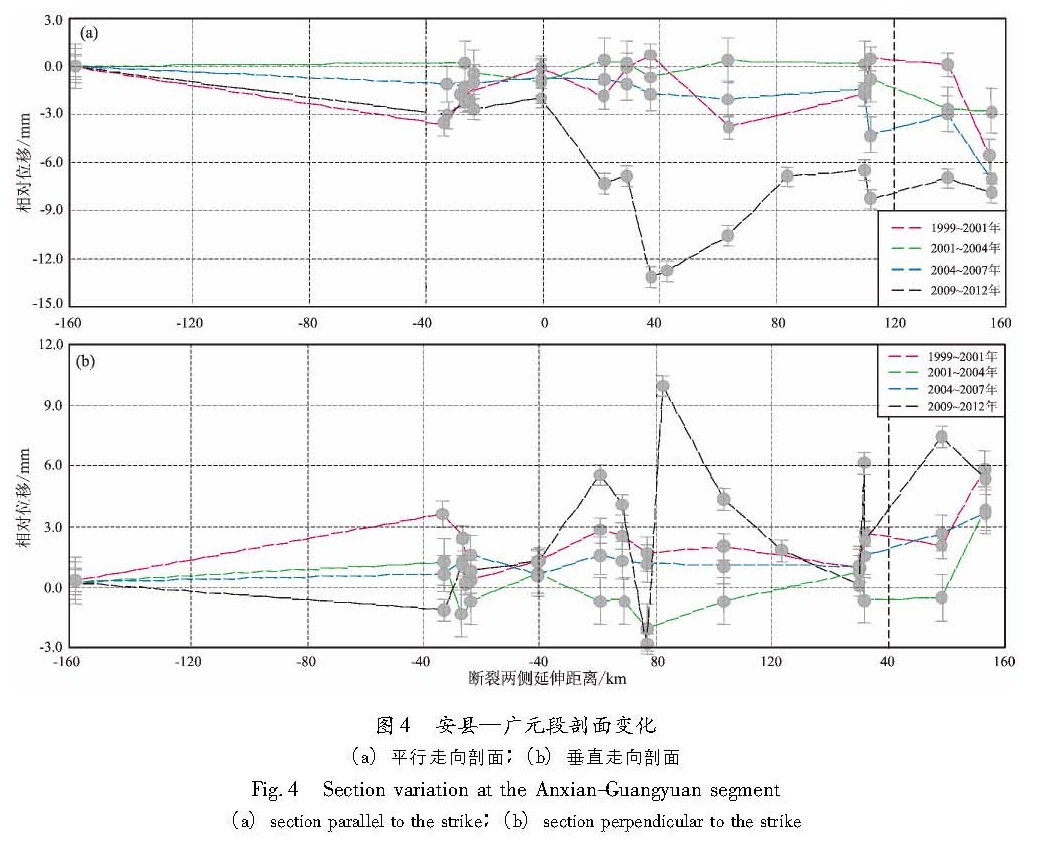
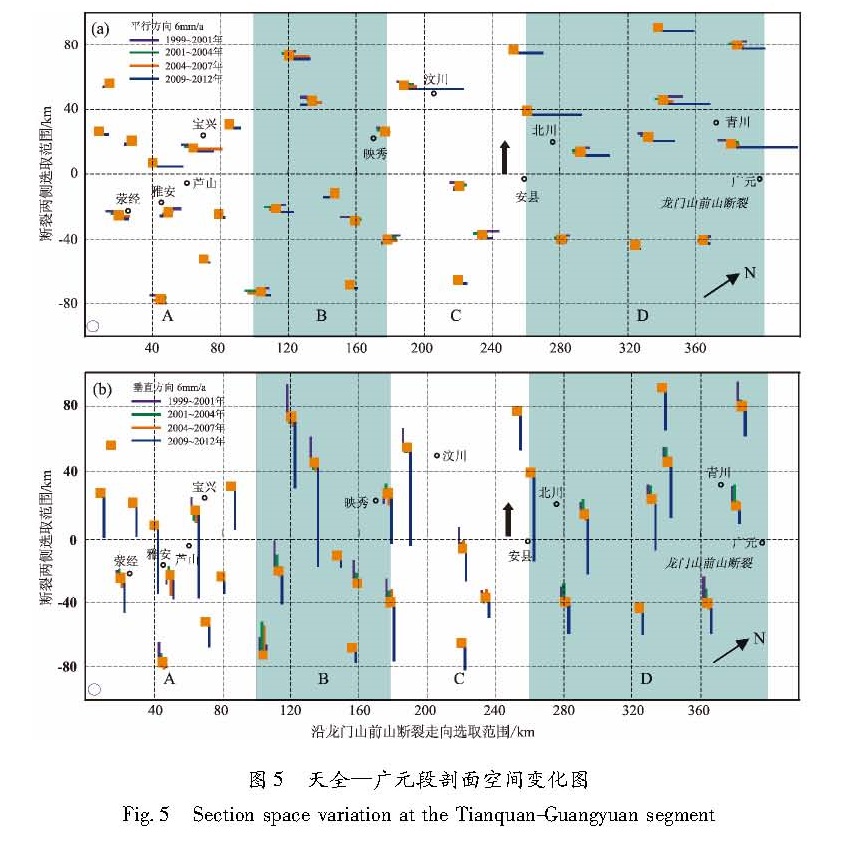
利用1999~2012年4期GPS速度场数据,对龙门山断裂天全—映秀段及安县—广元段的GPS剖面变形与应变积累作了探讨。在剖面应变积累对地震触发成因及程度方面,将芦山MS7.0与汶川MS8.0地震进行了对比分析。结果 表明:(1)芦山地震之前,该地区压性速率远高于1999~2007年,它是汶川大震后的应力调整过程;(2)汶川MS8.0、芦山MS7.0两次强震间隔如此之短,不排除是汶川地震之后龙门山断裂西南段应力场高值压应力的调整过程对此次芦山地震起到触发作用的可能性。
Using the four periods of GPS velocity field data from 1999 to 2012,we discuss the GPS section deformation and strain accumulation of segments from Tianquan to Yingxiu and from Anxian to Guangyuan of Longmenshan Fault. In the respect of GPS section strain accumulation on the cause and degree of earthquake triggering,we compare the Lushan MS7.0 earthquake and Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake. The results show that:(1)The pressure rate before Lushan MS7.0 earthquake is much higher than that of 1999~2007 in this region,which is the stress adjustment process after Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake.(2)The interval of Wenchuan MS8.0 and Lushan MS7.0 earthquakes is so short,the Lushan MS7.0 earthquake might be affected by the adjustment process of high pressure stress along the southwest section of Longmenshan Fault after Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake.