(1.青海省地震局,青海 西宁 810001; 2.中国地震局地壳应力研究所,北京 100085)
大柴旦—托素湖带断裂; 遥感解译; 发震构造; 逆冲断层; 构造类别法
(1. Earthquake Administration of Qinghai Province,Xining 810001,Qinghai,China)(2. The Institute of Crustal Dynamics,CEA,Beijing 100085,China)
Dachaidan-Tuosu Lake Fault belt; remote sensing; seismogenic structure; thrust fault; structural category method
备注
通过对大柴旦—托素湖断裂进行遥感解译、野外地质调查,认为该断裂遥感迹象清晰、断层三角面发育、线性陡坎明显,分为东、中、西三段。断裂在东、西两段晚更新世以来活动强烈,中段晚更新世以来活动较弱。根据构造类别法认为该断裂具有发生中强地震的发震构造,很可能是德令哈至大柴旦多次中强地震的发震构造。
According to the remote sensing interpretation and field geological investigation etc. of Dachaidan-Tuosu Lake Fault belt,we find that the remote sensing sign of the fault is clear,the fault facet is develop,and the linear scarp is obvious. The fault belt could be divided into three segments of east,central and west. The activity of east and west segment of Dachaidan-Tuosu Lake Fault was very strong,however the central part of it was weak since late Pleistocene. It shows that the fault has the seismogenic structure of mid-strong earthquake by the structural category method,which could be the seismogenic structure of several strong earthquakes in Delingha-Dachaidan region.
引言
青藏高原在新生代逆冲推覆构造变形、地壳缩短增厚和高原隆升过程中具有自高原腹地向周边地区扩展趋势。新生代晚期逆冲推覆构造运动主要发生于青藏高原周缘地区,如青藏高原南侧喜马拉雅山前中新世早期发育主中央逆冲断裂、中新世中晚期发育主边界逆冲断裂、第四纪发育主前缘逆冲断裂(吴珍汉等,2007b)。大量观测资料表明,青藏高原北侧柴达木盆地北缘地区发育多期逆冲推覆构造,新生代逆冲推覆构造运动对柴达木盆地形成演化具有重要的控制作用(吴珍汉等,2007a)。自北西向南东主要包括大柴旦—宗务隆山断裂、柴达木盆地北缘断裂、大柴旦—托素湖断裂、宗务隆山南缘断裂等(袁道阳,2003),众多的逆冲推覆构造晚更新世以来活动强烈,曾发生多次破坏性地震。自2003年德令哈西6.6级地震以来,德令哈至大柴旦地区发生3次6级以上地震,青海省地震局等相关单位进行了震后地质调查,认为其发震断裂为大柴旦—宗务隆山断裂①(孙洪斌等,2003; 李智敏等,2010),但2003年德令哈6.6级地震的余震分布与大柴旦—托素湖断裂带方向基本一致。本文通过遥感解译、野外地质调查等,在大柴旦—托素湖一带发现第四纪最新活动的重要证据,认为大柴旦—托素湖断裂晚更新世以来活动强烈,可能是发生多次破坏性地震的发震构造。
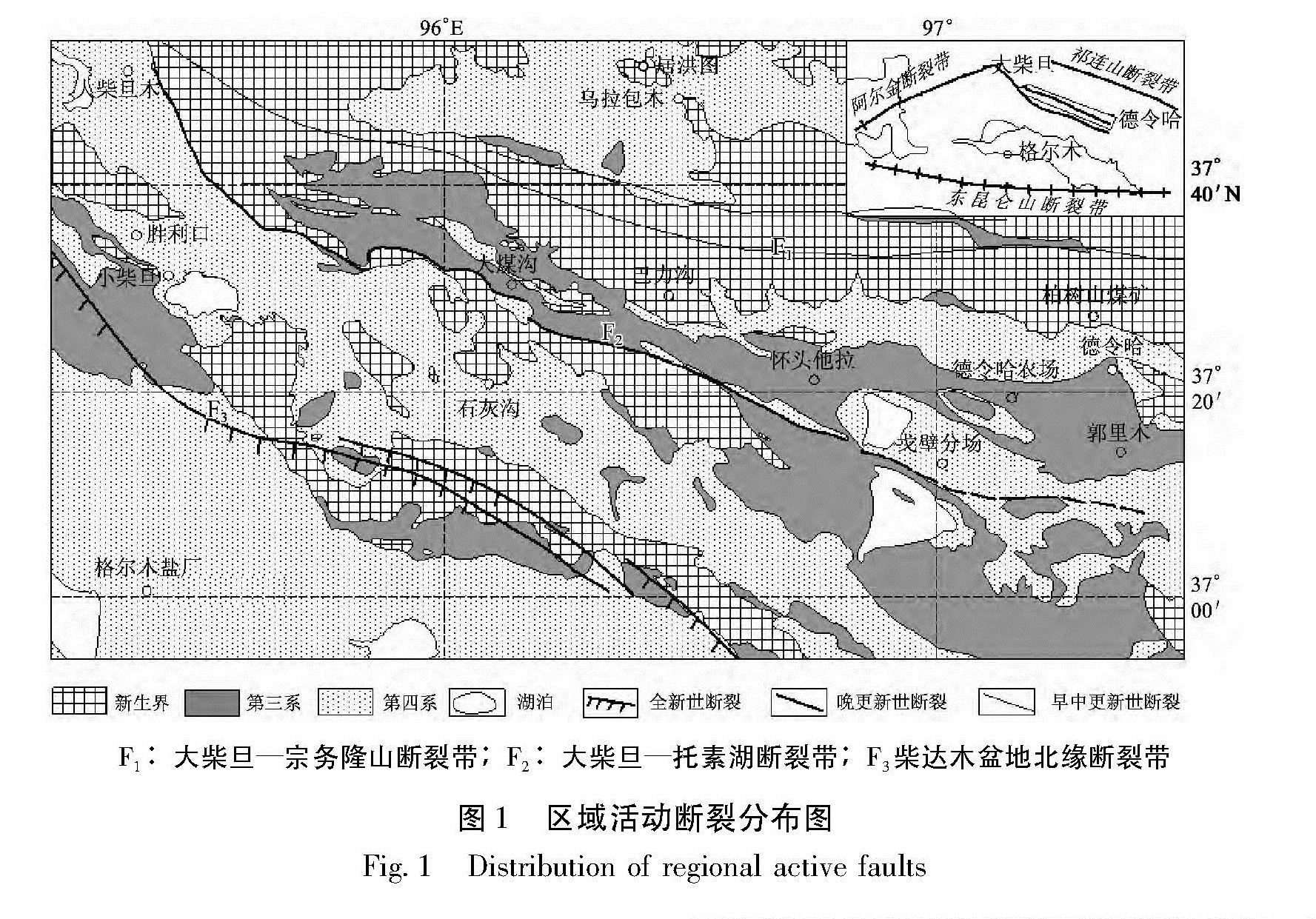
1 大柴旦—托素湖断裂带概述
大柴旦—托素湖断裂带西起大柴旦北部山前地带,向东南方向延伸经莫和滩南缘、石底泉槽地、可鲁克湖东南,全长210 km左右,总体走向呈北西—东西—南东,为一平卧的反“S”型,走向呈舒缓波状,贯穿并利用了柴北缘褶带、欧龙布鲁克台隆中原有的凹陷和断裂形迹而具有新构造运动特点(青海省地质矿产局,1991)。
大柴旦—托素湖断裂带西段起始于大柴旦东北部山前地带,向东南方向延伸经莫和滩南缘,由多条不连续的次级断层组成,主要控制前白垩(AnK)系的分布。断裂中段西起大煤沟附近,向南东经羊肠子沟口的无名泉、雷达站,沿欧龙布鲁克山北缘向东延伸,经俄博山、怀头他拉煤矿、南泉水梁,终止于托素湖东南。东段由一条基本连续的骨干断裂组成,主要发育在中新统及上新统之中,局部隐伏于第四系之下(青海省地质局,1978a,b)(图1)。
F1:大柴旦—宗务隆山断裂带; F2:大柴旦—托素湖断裂带; F3 柴达木盆地北缘断裂带
2 大柴旦—托素湖断裂带遥感解译特征
大柴旦—托素湖断烈带航卫片解译表明,沿断裂带岩体破碎,山缘高差界线平直,断层三角面、垭口、断层谷地发育。断裂西段弯曲,中、东段延伸相对舒展,总体呈NWW向展布,倾向SW,倾角74°左右,具有强烈的挤压逆冲特征。
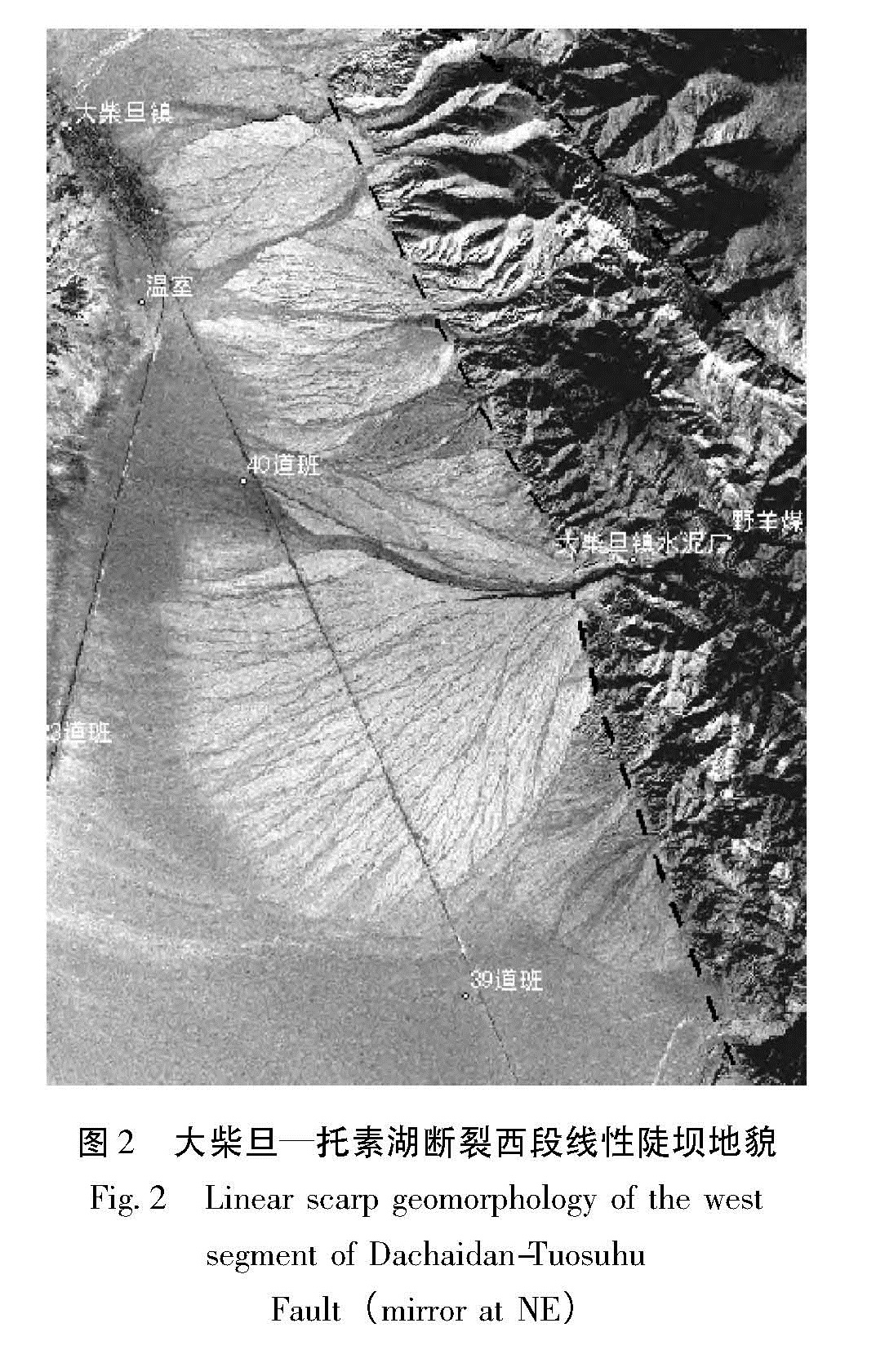
大柴旦—托素湖断裂西段西起大柴旦镇东北附近,向东南经大柴旦水泥厂向东至绿草山煤矿,断裂带转为近东西向展布。在大柴旦镇东北,该断裂断错山前冲洪积扇,形成高约0.8~1.2 m的断层陡坎,陡坎走向NW,垂直于山前洪积扇,但未能在冲沟内发现断错迹象(图2)。
在大柴旦东南山前地带出现平直断层陡坎地貌(图3),河流发生下切侵蚀,而侧向侵蚀作用较弱,因而谷坡较陡,河谷成深切“V”字型,反映了该区段构造活动性比较强烈。
大柴旦—托素湖断裂断裂中段西起大煤沟附近,向南东经羊肠子沟口的无名泉、雷达站,沿欧龙布鲁克山北缘向东延伸,经俄博山、怀头他拉煤矿、南泉水梁,终止于连湖东南。在绿草山煤矿至新生煤矿附近,断裂走向转为北西向,遥
感影像中山前线性断层三角面非常清晰(图4)。图2 大柴旦—托素湖断裂西段线性陡坝地貌
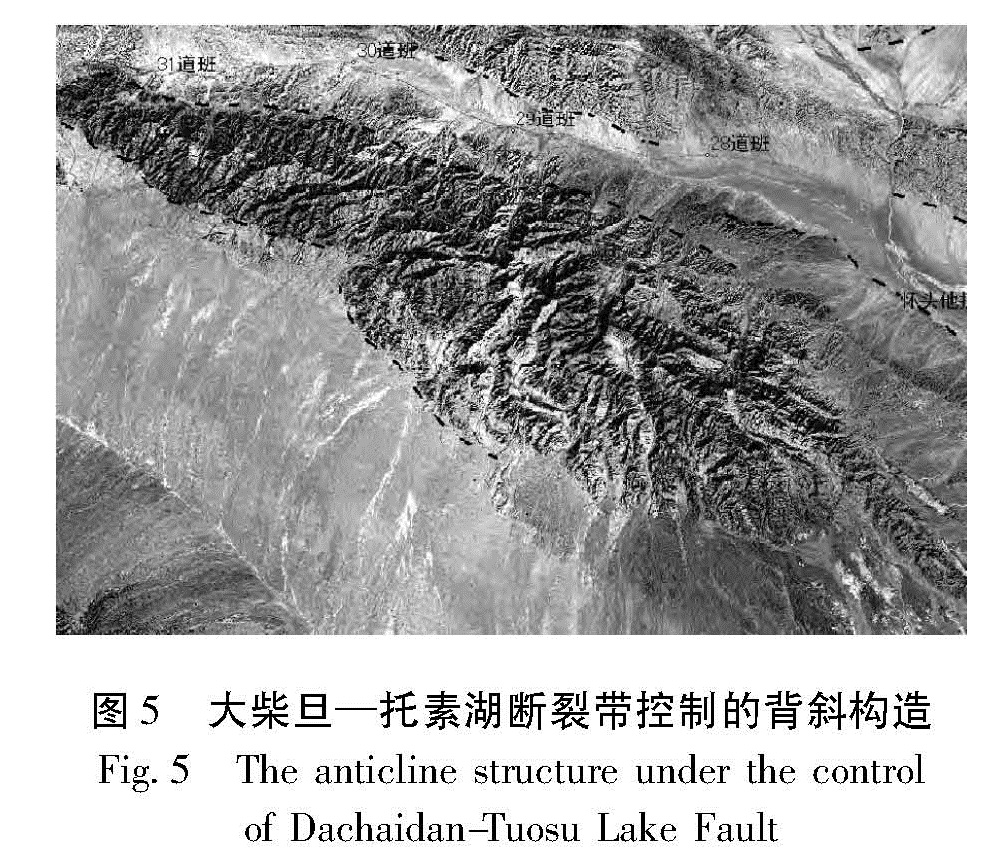
Fig.2 Linear scarp geomorphology of the west segment of Dachaidan-Tuosuhu Fault(mirror at NE)由绿草山煤矿向东至可鲁克湖西,断裂出现分支现象,分别为南部的山前断裂及北侧的断裂,共同控制了中间的背斜构造(图5)。在可鲁克湖西,遥感影像中构造地貌特征比较清晰,沿断裂带发育有洪积扇、断层陡坎、破裂带等微地貌特征,并多处呈现一定的负地形沉积盆地,对盆地的形成和发展具有强烈的控制作用; 断裂在地貌上产生了非常清晰的洪积扇陡坎地貌,沿北西方向展布(图6),陡坎前缘洪积扇规模较小。在可鲁克湖与托素湖之间,断层控制了两湖之间的分界线,形成了线性陡坎地貌,断裂两侧湖泊沉积环境及地形地貌具有明显的差异(图7)。
图3 大柴旦—托素湖断裂山前陡坎地貌
Fig.3 Piedmont scarp geomorphology of the western segment of Dachaidan-Tuosu Lake Fault图4 大柴旦—托素湖断裂中段山前陡坎地貌
Fig.4 Piedmont scarp geomorphology of the middle segment of Dachaidan-Tuosu Lake Fault大柴旦—托素湖断裂东段由一条基本连续的骨干断裂组成,主要发育在中新统及上新统之中,局部隐伏于第四系之下。在托素湖和尕海湖之间,由于湖相沉积所覆盖而呈半隐伏状态,断裂带遥感影像线性不是很明显。不过断裂带的发育对所经区域的水系边界有比较明显的控制作用,特别是控制了几个小型湖泊的分布,呈串珠状发育。断裂带基本隐伏于第三系和第四系湖相沉积层之下,但是仍然控制了托素湖与可鲁克湖之间水系的发育,并沿倾覆褶皱的边界分布(图8)。图7 可鲁克湖与托素湖之间陡坎地貌
Fig.7 Scarp geomorphology between Keluke Lake and Tuosu Lake(red dotted line is the location of interpret fault)
遥感解译表明:大柴旦—托素湖断裂西段主要发生在侏罗系与第三系之中或之间; 中段发生在震旦系与上第三系之间,或者石炭系与上第三系之间; 断裂东段发生在上第三系之中,局部被第四系覆盖。3 新活动特征研究
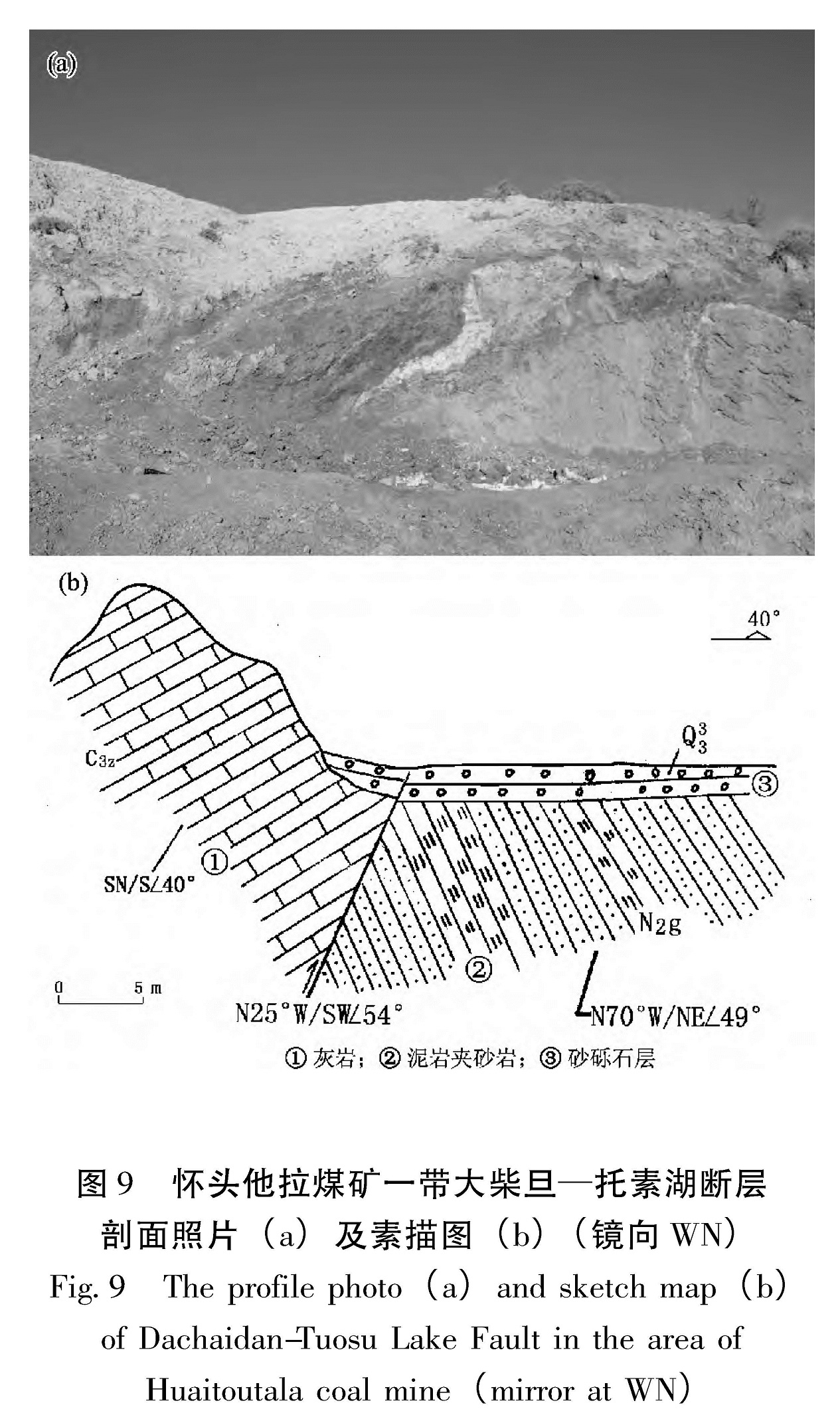
野外考察发现,大柴旦—托素湖断裂活动的微地貌显示具有较好的连续性,如怀头他拉煤矿一带(37.428°N,96.225°E)可见石炭系中、上统灰岩夹页岩、煤线地层逆冲于第三系泥质岩之上,形成较大的山缘高差(图9),该处可见基岩崩塌极为发育。大柴旦—托素湖断裂沿线呈现槽状、坑状凹地地貌,泉水发育,并且覆盖于第三系之上的砾石层已被断错。
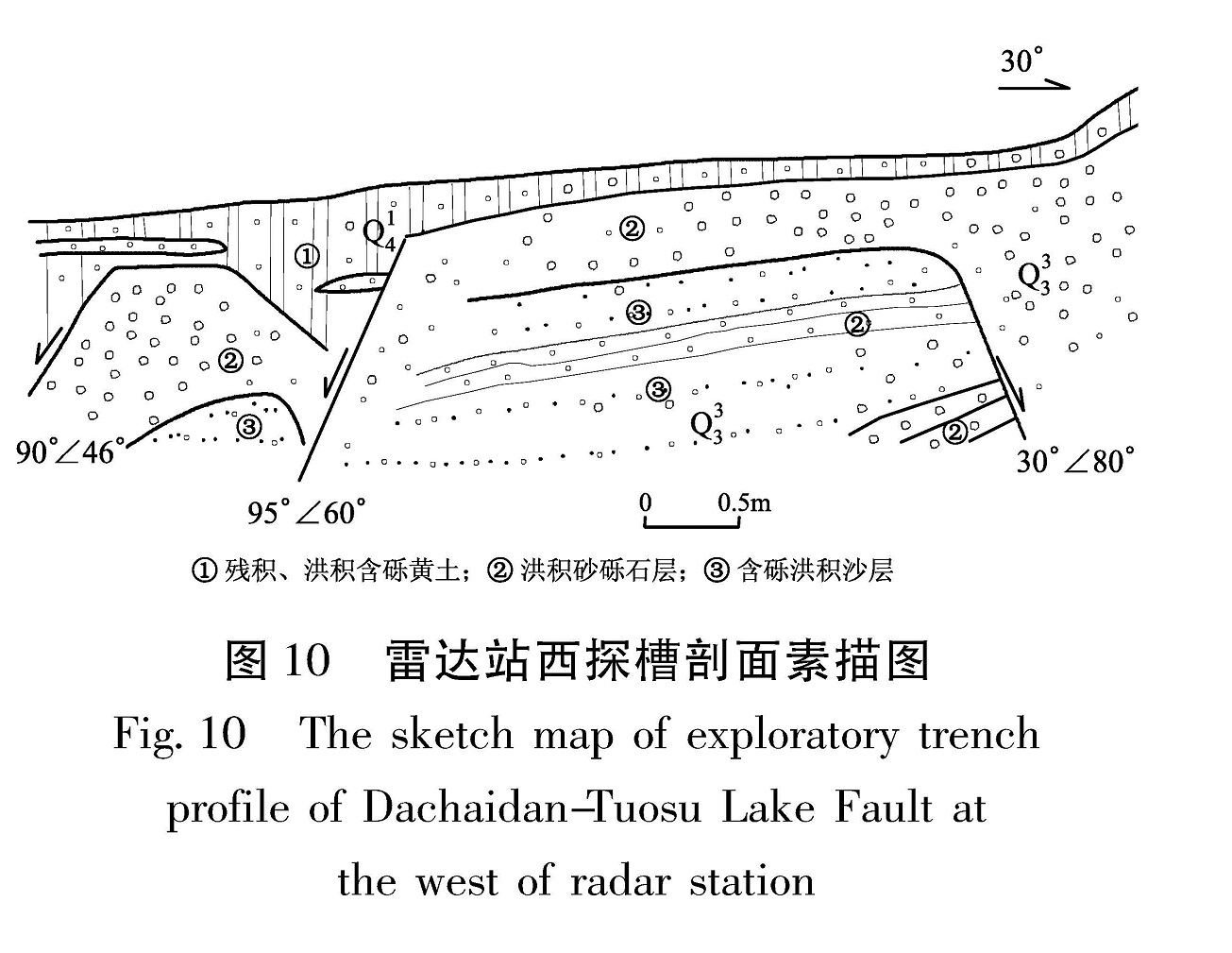
大柴旦—托素湖断裂在雷达站附近,地貌显示大柴旦—托素湖断裂存在两个平行的断面,两者相距约40 m,表现为断层三角面连续展布,断坎、断层谷发育。其中南侧一条断层坎发生在砾石层上,断坎高度稳定,一般在1.7 m左右。在断层陡坎下开挖的探槽证实了断层的存在,并且发育3个次级断面(图 10),其中3个断面倾向南,倾角46°~60°。
图9 怀头他拉煤矿一带大柴旦—托素湖断层剖面照片(a)及素描图(b)(镜向WN)
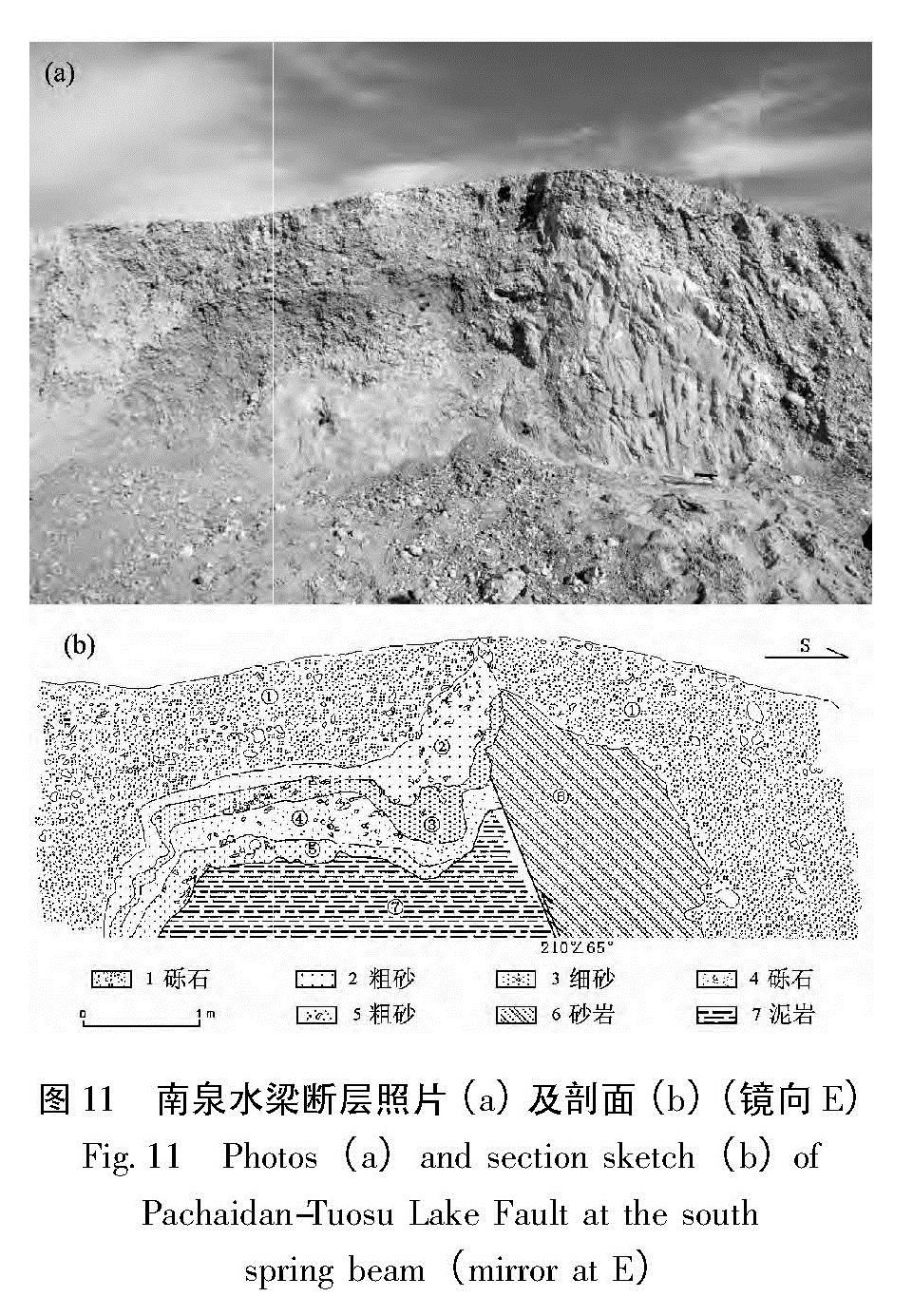
Fig.9 The profile photo(a)and sketch map(b)of Dachaidan-Tuosu Lake Fault in the area of Huaitoutala coal mine(mirror at WN)大柴旦—托素湖断裂在南泉水梁(37.205°N,96.70°E)形成近东西向高约7 m的鼓梁,沿泉水出露形成约40~50 m的断裂破裂带(图 11)。图 10 雷达站西探槽剖面素描图
Fig.10 The sketch map of exploratory trench profile of Dachaidan-Tuosu Lake Fault at the west of radar station断层特征:(1)断层产状:210°∠65°。(2)断裂最新活动沿第三系泥岩岩与第四系砾石层之间发育,第三系泥质砂岩逆冲于第四系砾石层之上,形成约1.5 m断距。(3)断面处上盘砾石层定向排列,砾石层层理杂乱不清,松散未胶结。(4)断层沿线形成高约10 m断层陡坎,断层沿线泉水出露。图 11 南泉水梁断层照片(a)及剖面(b)(镜向E)
Fig.11 Photos(a)and section sketch(b)of Pachaidan-Tuosu Lake Fault at the south spring beam(mirror at E)初步分析认为,该断裂晚更新世—全新世活动明显。
4 结论
通过对大柴旦—托素湖断裂带较详细的航片解译及野外的追踪考察,对断裂带的新活动特征取得了初步的认识:大柴旦—托素湖断裂带卫星影像断裂迹象清晰、明显,沿线发育线性陡坎、断层三角面发育。该断裂带为区域性断裂,具有明显的逆冲性质,属于本区NNW —NWW 向的柴达木盆地北缘活动断裂系内的一条次级挤压构造。断裂带长约210 km,走向NE,在地貌上形成了明显的线性延伸的断层陡坎,沿线断层泉发育,初步推测该断裂为晚更新世一全新世活动断裂。依据该断裂的长度、活动性,根据构造类比,判断该断裂具备发生7.0~7.5级地震的构造条件。
- 李智敏,屠泓为,田勤俭,等.2010.2008年青海大柴旦6.3级地震及法阵背景研究[J].地球物理学进展,(03):768-774.
- 青海省地质局.1978a.区域地质调查报告,德令哈旧址幅(10-47-26).
- 青海省地质局.1978b.区域地质调查报告,托素湖幅(10-47-25).
- 青海省地质矿产局.1991.青海省区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社.
- 孙洪斌,张铁军,都昌庭.2003.德令哈6.6级地震的地震地质灾害及发震构造分析[J].高原地震,(3):33-41.
- 吴珍汉,叶培盛,胡道功,等.2007a.青藏高原北部风火山花岗斑岩锆石U-Pb同位素测年及其地质意义[J].现代地质,21(3):435-442.
- 吴珍汉,叶培盛,赵文津,等.2007b.东昆仑南部晚新生代逆冲推覆构造系统[J].地质通报,26(4):448-456.
- 袁道阳.2003.青藏高原东北缘晚新生代以来的构造变形特征与时空演化[D].北京:中国地震局地质研究所.