备注
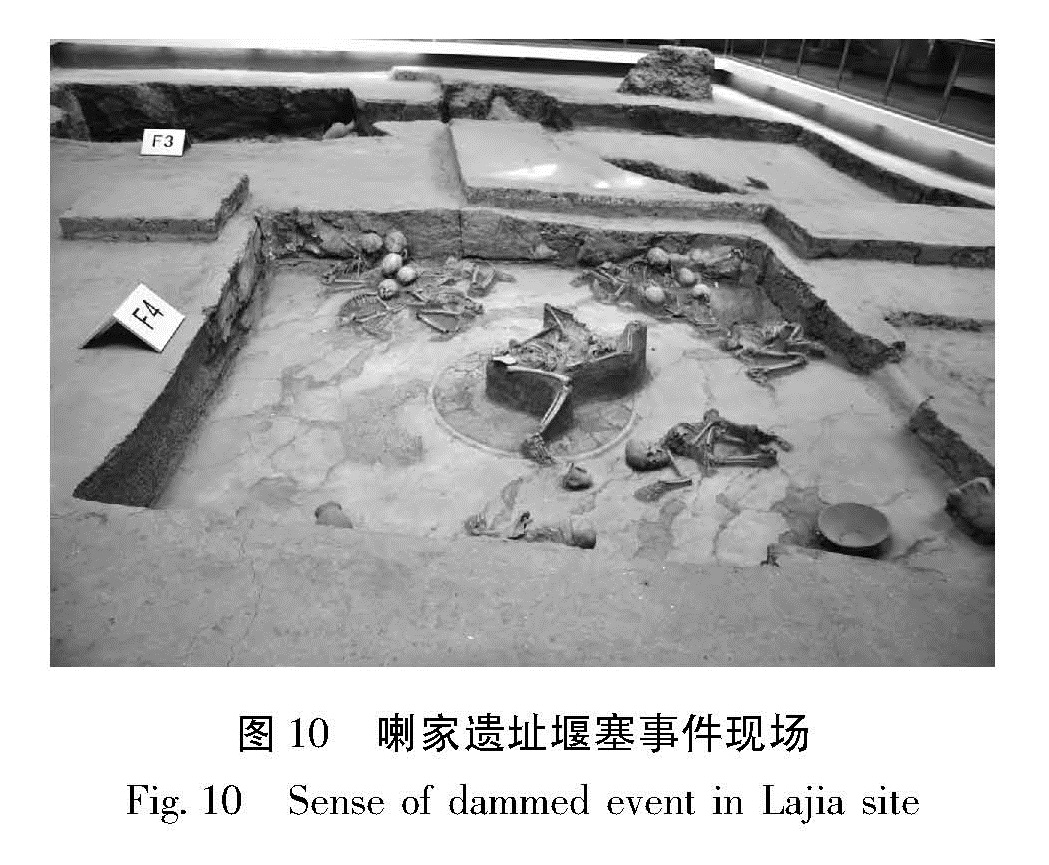
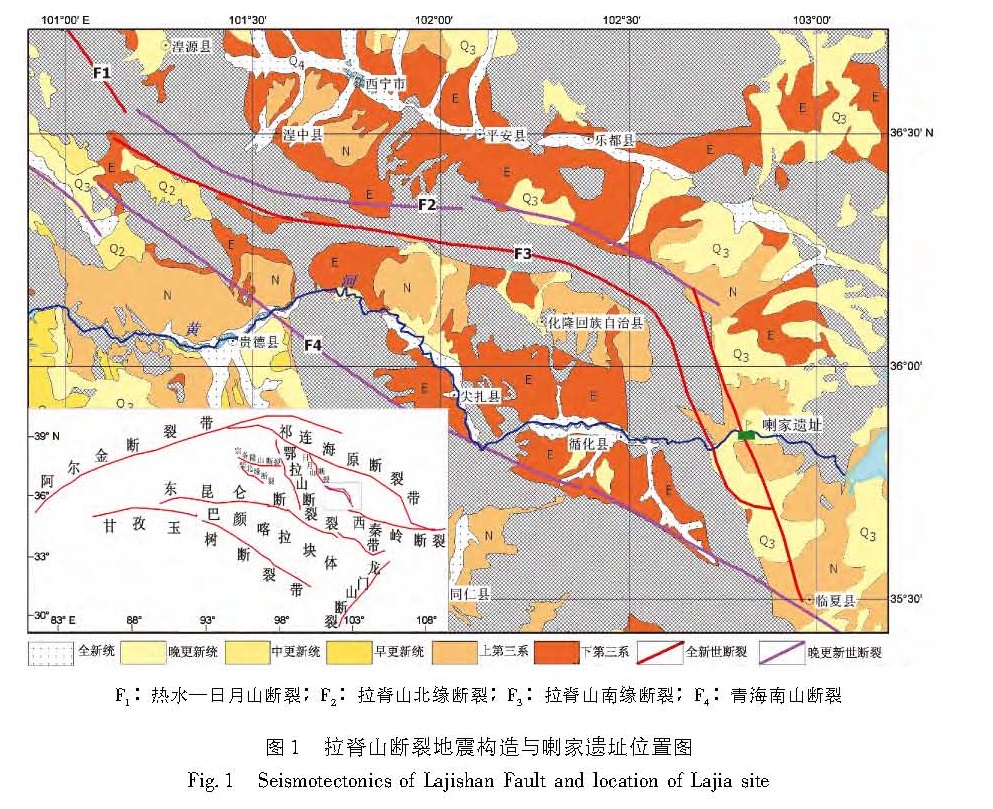
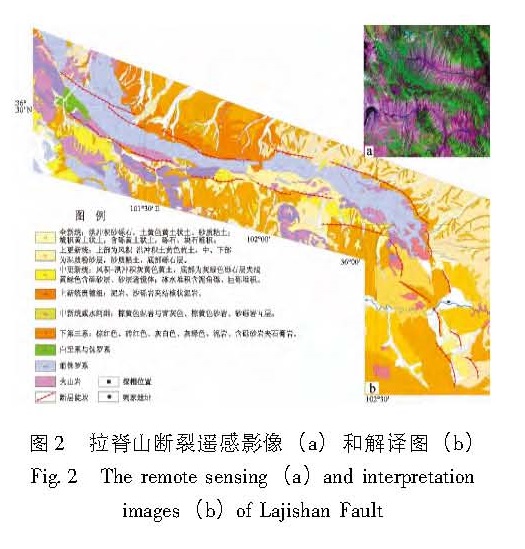
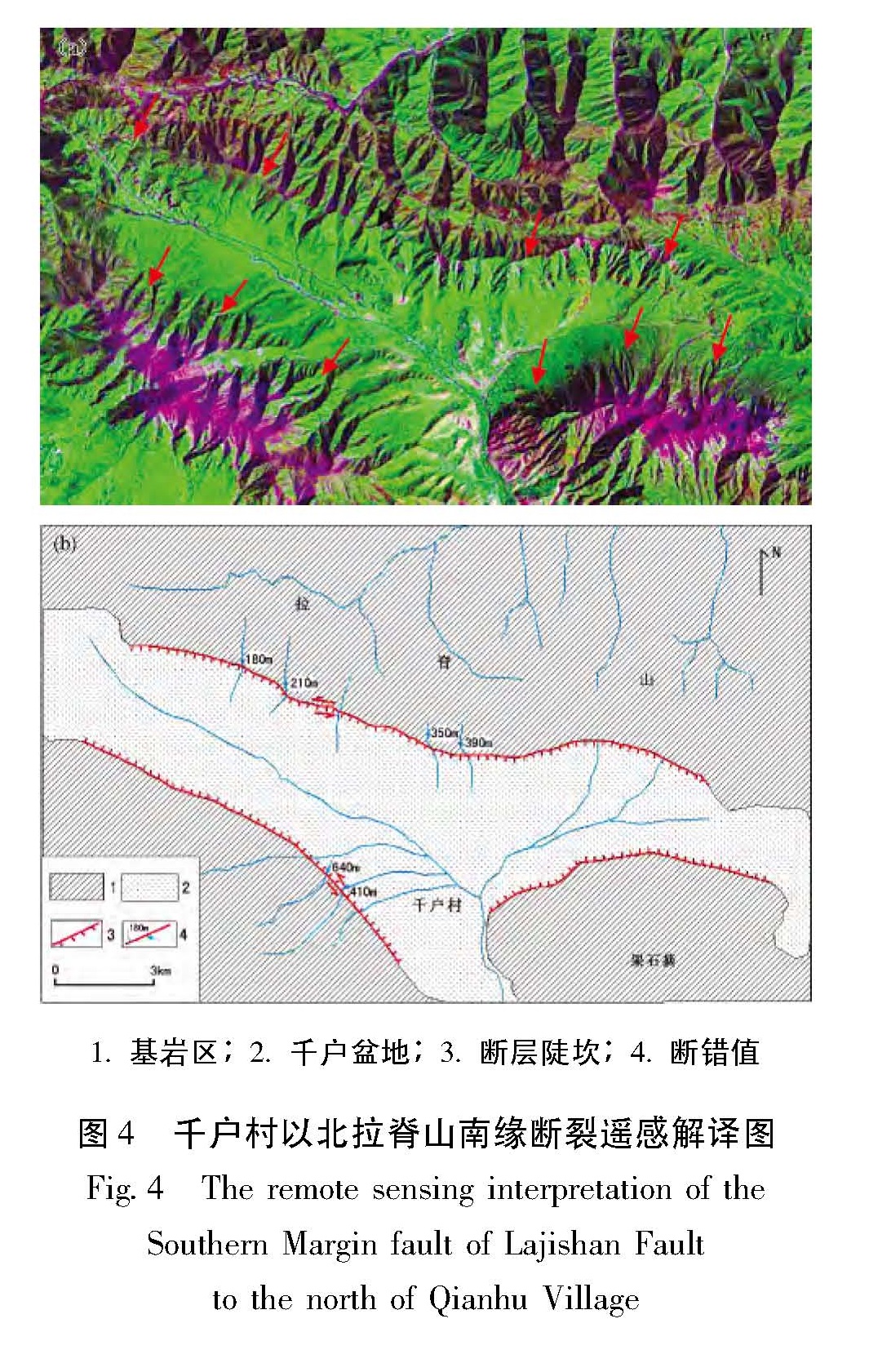
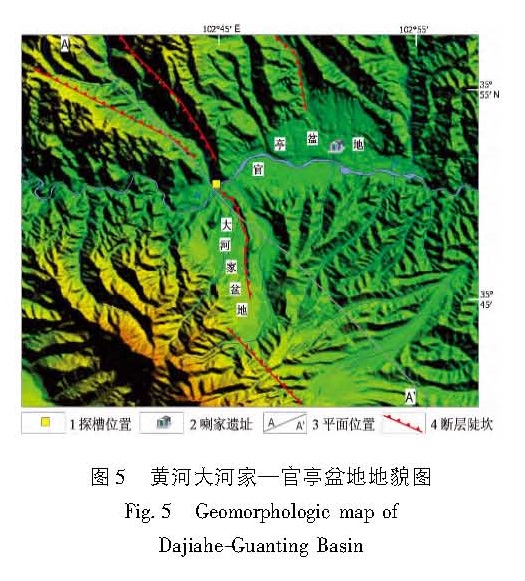
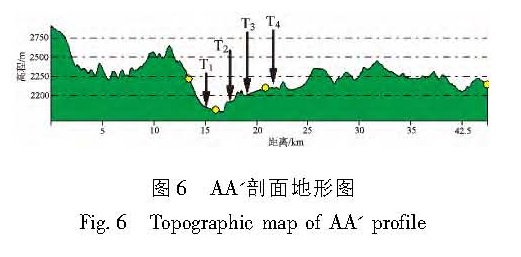
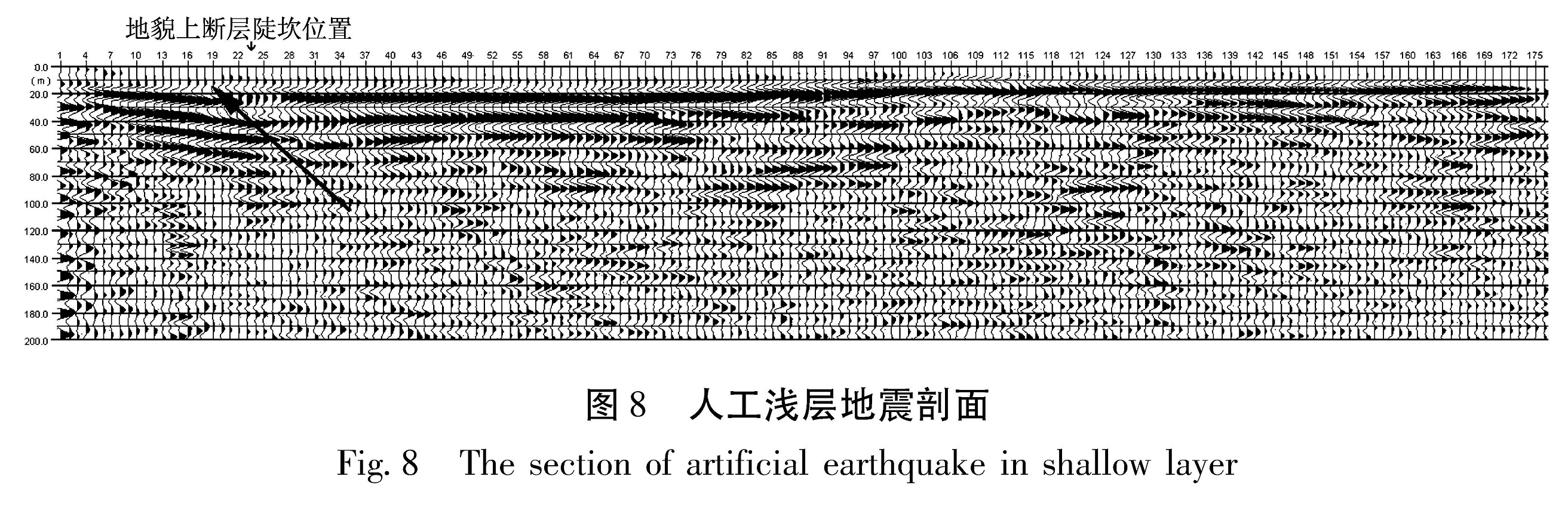
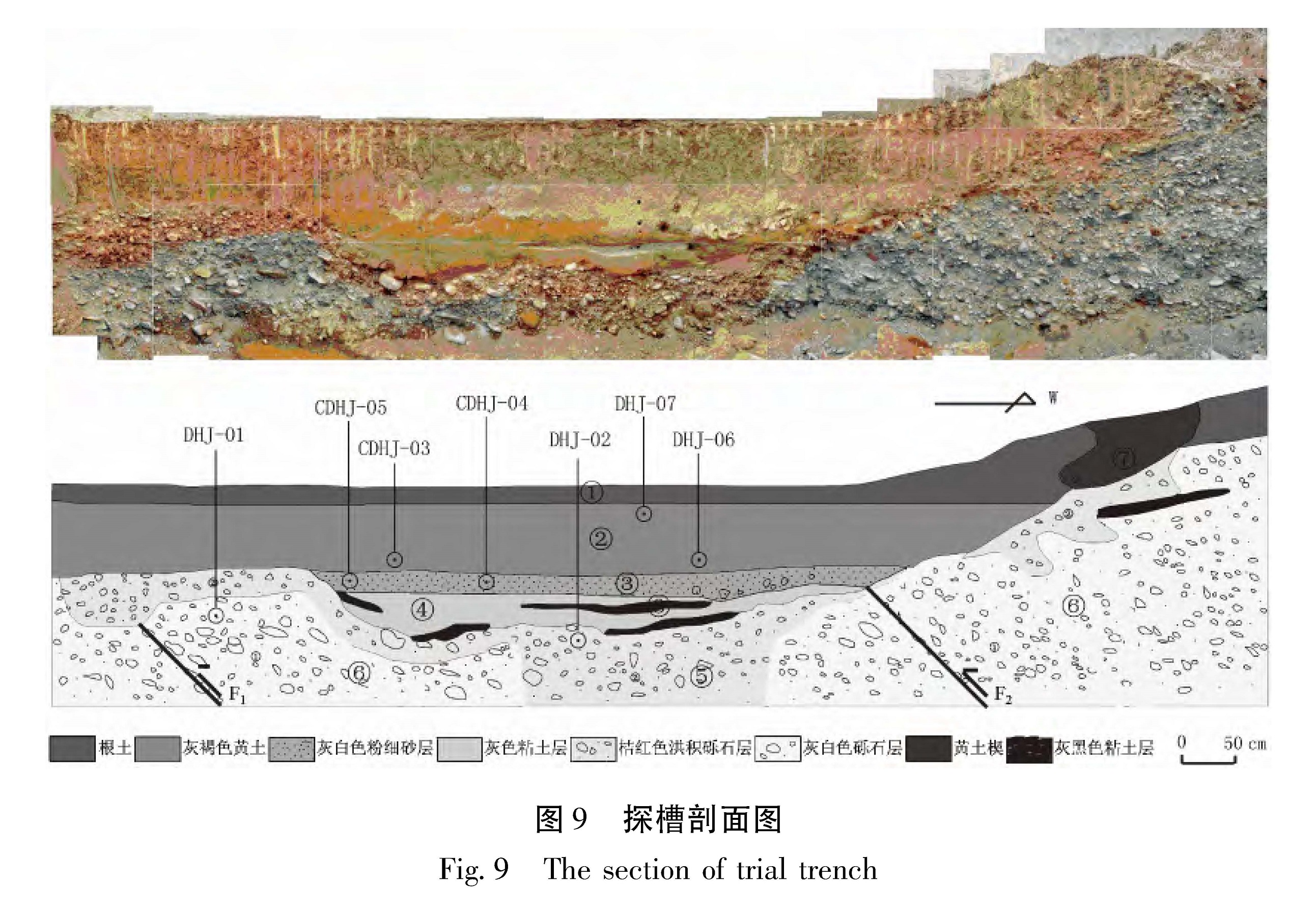
利用高分辨率的遥感资料,获得了拉脊山断裂带的几何学特征,通过野外调查和开挖探槽,对拉脊山断裂带上古地震进行了研究。认为拉脊山断裂在大河家地区逆冲活动造成黄河阶地上形成断层陡坎,在陡坎位置开挖探槽,揭露出了3 700 a.BP以来至少发生过2次中强以上古地震事件,并造成了黄河阶地变形,最晚一次古地震事件发生在(3 136±51)a.BP左右,估算断层全新世中晚期以来的滑动速率为0.51 mm/a。形成于3 650~2 750 a.BP前后的喇家遗址位于该探槽剖面6.4 km处,因此得出拉脊山断裂带上强烈的古地震事件与喇家文化的毁灭存在密切的联系。该研究对认识拉脊山断裂带的地震危险性和确定形成喇家遗址的古地震证据具有重要的科学价值。
The geometric features of the Lajishan Fault Zone are got by remote sensing data in high resolution. According to the field investigation and excavation trenches,we do the research of paleoseismics on Laji Mountain Fault. The result obtained as follow:The fault scarps were formed in stage terrace of Yellow River,because of the thrusting activity of Lajishan Fault in the Dajiahe Region. Through the excavation trenches on the location of scarps,there were at least two medium-strong paleoseismic in the study region,which made the stage terrace of Yellow River formed. The last paleoseismic occurred on about(3 136±51)a.BP,the slip rate along Lajishan Fault Zone is estimated to be about 0.51 mm/a since late Holocene. The Lajia site which formed in about 3650~2750 aBP is 6.4 km far from the trench profiles,so the strong paleoseismic on Lajishan Mountain Fault Zone is closely related to the destroy of Lajia culture. The research has the important scientific value to recognize the seismic risk of Lajishan Mountain Fault Zone and determine the paleoseismic evidence of forming the Lajia site.