基金项目:云南省应用基础研究计划项目——云南地区温泉CO2释放与地震活动关系初步研究(2011FB129)和财政部公益性行业科研专项——氡、汞观测方法技术标准语地下流体学科标准体系表研究(201308006)联合资助.
(1.云南省地震局,云南 昆明 650224; 2.中国地震局地壳应力研究所 地壳动力学重点实验室,北京 100085)
(1. Earthquake Administration of Yunnan Province,Kunming 650224, Yunnan, China)(2. Key Laboratory of Crustal Dynamics,Institute of Crustal Dynamics, CEA, Beijing 100085,China)
crustal fluid; carbon dioxide; earth degassing; deep-source fluid; earthquake
备注
基金项目:云南省应用基础研究计划项目——云南地区温泉CO2释放与地震活动关系初步研究(2011FB129)和财政部公益性行业科研专项——氡、汞观测方法技术标准语地下流体学科标准体系表研究(201308006)联合资助.
介绍了地壳流体CO2的3个主要成因:有机成因、变质成因及幔源成因,并着重讨论了CO2气体的稳定同位素13C的示踪性能; 总结了由地壳释放CO2的主要方式、上升通道及其存在形态。在回顾地壳流体CO2等释放在目前地震监测、预报及相关研究中的主要研究进展的同时,指出地壳深部流体(CO2、He、CH4等)在同位素地球化学、深源流体运移与地震活动、深源流体对震源介质的影响等。此外,提出对深源流体监测不能仅限单一组分(CO2)的监测,需多种深源成分(He、Ne、Ar、H2、CH4)同时监测。
Three main causes of crustal fluid CO2 which includes organic origin, metamorphic genesis and mantle origin are introduced, the tracing performance of stable isotope tracer 13C of CO2 are discussed emphatically, and the release rule, the rising channel and the existence form of CO2 released from crust are also summarized. Based on the main research progress of the releasing of crustal fluids CO2 on seismic monitoring, earthquake prediction and other relative research, we point out the future hot fields of the research is that the isotope geochemistry of fluids, the relationship between migration of deep-seated fluids and seismic activity, the influence of deep-seated fluids to media of hypocenter etc.. In addition, we put forward that monitoring the deep-source fluid cannot use a single component(CO2), it need a variety of deep-source components(He、Ne、Ar、H2、CH4)monitor simultaneously.
引言
地球在形成和演化过程中的分异作用使地球排气至今未止。随着新观测技术的应用,对地球内部气体的赋存状态、迁移、逸出及其作用的观测研究也取得了很大进展。地球排气可形成CO2气藏和有机烃类天然气藏等重要的气体矿产资源(戴金星,1993),且与若干金属矿床的形成有着密切联系。同时,地球排气还可引发灾害,1986年中非喀麦隆尼奥斯(Nyos)湖区发生CO2爆发式排放导致近2000人死亡(上官志冠,武成智,2008)。现已查明著名的“魔鬼三角”百慕大沉船、空难事件与海底排出的CH4气体而形成水合甲烷冰山有关。此外,温室气体排放、南极臭氧层空洞、大气异常增温、森林大火、厄尔尼诺现象、干旱等自然灾害不只限于单纯的人为因素或气象因素,还必须考虑地球深部大规模向地表排放气体的影响(杜乐天,1996)。大量资料表明,几乎所有MS≥7.0地震在临震或发震时都伴随着冒烟、冒火、发光、或伴有硫磺气味等现象发生,并且这些现象沿构造带(断层)展布。1966年邢台6.8级地震、1975年海城7.3级地震、1976年唐山7.8级地震,仍至2008年汶川8.0级地震,在震前均有大量气体释放(张景廉等,2011)。此外,印尼苏门答腊地区2004年和2005年两次M>8.0地震前也发现震区有明显的排气现象和气体地球化学异常(高建国等,2007; 孙玉涛等,2014)。
无论是现代火山喷出气体,还是中下地壳加热脱气,或者大洋中脊新洋壳形成处水热流体中,CO2是地球排出气中的主要成分(Gerlach,1991; Kerrick,Caldeira,1998,Mörner,Etiope,2002)。在气体地球化学研究中,地下流体CO2在地震监测、隐伏断裂探测和地裂缝的现场定位等方面都有着广泛的应用。王基华等(1998)研究表明断层土壤气CO2动态监测对中强地震有较好的映震效能。然而CO2的动态变化受多重因素的影响,如断层气CO2受夏高冬低的季节性变化影响,土壤中逸出量也与气压有很大关系(官致君等,2003); CO2化学性质活泼,易溶于水,因此受降雨或地表水的渗入溶解影响较大; 在深部温压条件下,CO2可能与别的气体或新破裂的岩石产生反应(方震等,2012); 成因及来源复杂,地壳深部CO2向地表迁移过程中可能会有地表CO2的混入。由此种种因素的影响,很难识别地震异常,CO2作为地震预测指标效果不明显。究其原因在于逸出气CO2的来源、运移机制及映震机理还没有真正搞清楚。气体地球化学领域发展起来的同位素示踪技术,有助于判断CO2气体的来源与运移机制,辨识地下流体动态变化异常,理解地震前兆形成的机理,为地震预测提供更科学的判定依据。
综合国内外研究,本文系统阐述了地表逸出气CO2的成因类型、来源判别、运移机制及赋存形态等物理化学机制。其目的之一是在今后的地震监测中,能进一步判断监测气CO2的成因以及不同来源CO2的映震效能; 二是结合地球化学动力学、构造地质学、地震地球化学等领域的理论知识,探讨逸出气CO2的映震机理。同时,本文还回顾了CO2气体及其存在形态(超临界态、水合离子型态)在地震研究领域的主要成果与进展。这将有助于全面了解CO2等流体地球化学在未来地震监测预报中的研究热点和发展方向,为探索地震前兆信息与地震预测提供新的技术途径。
1 地壳流体CO2成因及来源识别
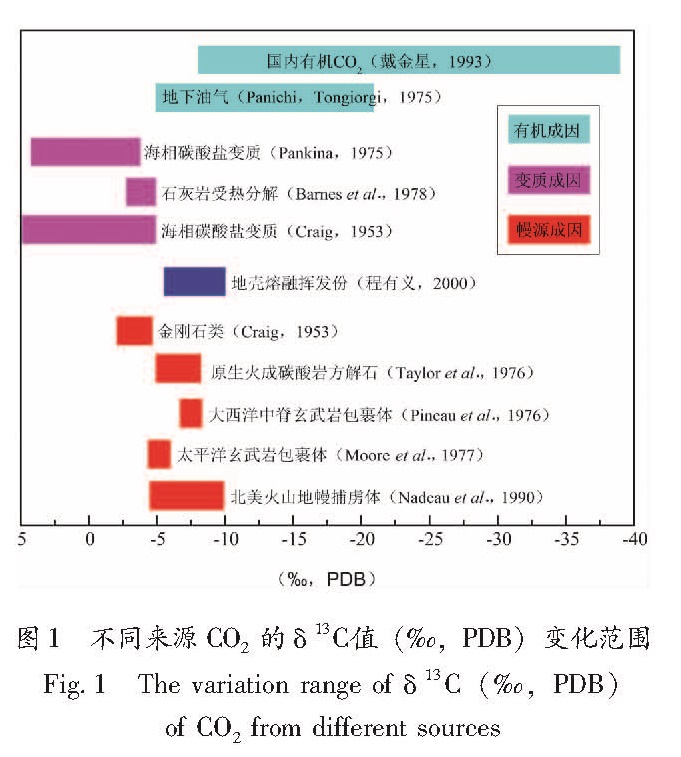
CO2是排气过程中普遍存在的气体。在地壳内部CO2的分布表现出随深度的增加而增多的趋势(杜乐天,2007)。据前苏联科拉半岛CK-3号超深钻和德国巴伐利亚州KTB超深钻的研究资料(车用太,鱼金子,2006)显示,地壳气体成分中CO2含量居首位。有人把从地球内部排出的CO2(包括深部地幔和浅部地壳)成因归为有机成因和无机成因两类。Barnes等(1978)则认为有3种来源:有机物来源、海相碳酸盐岩的变质和地幔岩浆脱气。本文将CO2的3种成因归纳为:有机生物成因、变质成因和幔源成因。由于地壳流体CO2有可能存在以上一种成因或多种成因的混合,在没有近地表来源证据的情况下,碳的稳定同位素组成大致可以说明其来源(图1)。本文所指的深源流体,主要是来自于地壳多震层以下的流体,即来自地壳脆—延性过渡带及其以下的流体,主要为幔源成因,但也不排除变质成因的混入。一般而言,也就是中地壳及其以下的流体。
1.1 有机生物成因通常,有机成因CO2的产生过程为有机物的氧化、裂解、热降解、微生物降解,但其来源可能较为广泛。例如,在富含有机质的煤、泥、页岩中,含氧官能团(如羧基、羟基等)有机质的缩聚作用或脱基团作用; 阶地或冲积沉积层中的有机物氧化分解; 古植物纤维质在成煤过程; 褐煤转化为沥青煤和无烟煤的变质过程等,在一定的温压条件下均可产生大量CO2(Sugisaki et al.,1983; Evans et al.,2001)。这些有机物来源的CO2是贫13C的,Panichi和Tongiorgi(1975)根据北美和意大利南部的油田资料分析,认为这个来源的CO2的δ13C变幅很宽(-5‰~-22‰),而且与碳酸盐源CO2相比,油田的CO2样品的碳同位素组成总是很轻。Barnes等(1978)也认为,以煤、石化木和石油等形式存在的有机物质,其13C含量很小,δ13C值也低于-20‰。Shapiro等(1982)测定了圣安德烈斯断层附近的测孔中CO2的δ13C值为-22‰,推断CO2来源于有机物质的氧化。我国有机成因的CO2的δ13C区间值在-8‰~-39‰,主频率段在-12‰~-17‰,最轻的是安徽省繁昌三山街第四系生物气为-39.14‰(戴金星,1993)。因此,一般有机成因CO2中δ13C通常小于-12‰,主δ13C平均值约为-25‰。
1.2 变质成因变质成因CO2从产生的动力源主要可以归纳成两类(李振生等,2011):一是接触变质作用,侵入体与围岩(碳酸盐岩)相互作用分解产生CO2,其释放量与接触变质级别成正比; 二是断裂变质作用。断裂带可作为岩浆或高温热液的侵位通道,而且剪切热效应也可使断裂带明显增温,都为碳酸盐岩热变质提供热源。在地下深部高温热源的作用下,含有灰岩、白云岩等碳酸盐矿物的岩石产生分解生成CO2:
CaCO3〖FY(〗400℃〖FY)〗CaO+CO2↑
含硅质的大理石、白云石等沉积碎屑岩在600~700 ℃高温下,经区域变质作用或解除变质作用,生成硅灰石、镁橄榄石,释放出CO2气体,反应如下:
CaCO3+SiO2〖FY〗CaSiO3(硅灰石)+CO2↑
2CaMg(CO3)2+SiO2〖FY〗Mg2SiO4(镁橄榄石)+2CaCO3+2CO2↑
侵入体的接触带上存在镁橄榄石和硅灰石便是CO2生成的直接证据(Panichi,Tongiorgi,1975)。此外硅酸盐(高岭石、蒙脱石和钾云母)在成岩环境温度超过100 ℃时,与碳酸盐岩矿物水解生成大量CO2(Hutcheon,Abercrombie,1990)。如高岭土与碳酸盐的水解:
5FeCO3+SiO2+Al2Si2O5(OH)4+2H2O〖FYKN*〗Fe5Al2Si3O10(OH)8+5CO2↑
程有义(2000)研究认为,地壳岩石的熔融脱气也可产生CO2。在深部流体的参与下,由于局部地热梯度异常,中下地壳可以产生含有一定挥发分的熔融岩浆,该挥发分主要成分为CO2,与未脱气的地幔岩浆相比,其丰度较低,δ13C值一般在-6‰~-10‰之间。海相碳酸盐岩是碳源的主要组成部分,在有水参与时,其分解所需温度大大降低,高于70℃便可分解产生CO2,如方解石和白云石等矿物组成的沉积岩在地下深部高温热源下,发生变质脱碳作用而生成CO2; 碳酸盐岩在岩石破裂或有酸性水的溶蚀作用下,也会产生大量CO2气体。此类CO2最大限度地继承了其母源碳酸盐的碳同位素组成,δ13C值一般在+3.5‰~-3.5‰之间(Pankina,1979)。Craig(1953)海相沉积碳酸盐岩变质的CO2其δ13C值为+5‰~-5‰,而许多来自欧洲、小亚细亚、日本等地的含海相沉积碳酸盐岩的CO2同位素分析显示其δ13C值接近于0‰(Irwin,Barnes,1980)。
图1 不同来源CO2的δ13C值(‰,PDB)变化范围
Fig.1 The variation range of δ13C(‰,PDB) of CO2 from different sources1.3 幔源成因在地幔来源的气体中,无论是在熔岩喷出气、大洋中脊喷出气、还是温泉逸出气中,CO2含量总是占主要气体成分的第一位。火山喷出气中,CO2是最常见、含量较高的气体组分,而且也是下地壳与上地幔中存在着流体活动的首要证据。岩浆是CO2气体的重要源体,岩浆中溶解或游离着大量的CO2气体(周晓成,2011)。对全球大部分火山喷出气研究可知,绝大部分火山气体中CO2占气体总量的50%以上,最高可达98%(鱼金子,车用太,1998)。地幔流体中CO2为主要成分的其它证据来自上地幔岩的流体包裹体(被玄武岩浆喷溢带到地表),研究结果显示,CO2含量约占总气体量的50%以上(夏林圻,徐培苍,1990; 张铭杰,王先彬,1999)。
幔源碳的δ13C值主要是通过金刚石、岩浆碳酸岩以及幔源岩石的气液包裹体的研究获得的。Craig(1953)测定了6个采自南非金伯利矿的透明八面体金刚石的δ13C值,得到的结果在-2.4‰~-4.7‰之间。据Taylor等(1967)报道原生火成碳酸盐方解石的δ13C值在-5.0‰~-8.0‰,其它幔源CO2的同位素组成的直接证据来自地壳扩张中心和地幔柱。来自大西洋中脊的拉斑玄武岩样品的CO2包裹体的δ13C变化范围为(-7.6±0.5)‰(Pineau et al.,1976); 来自太平洋玄武岩样品中的流体包裹体中CO2的δ13C变化范围为-4.7‰~-5.8‰,太平洋海隆排放的CO2气体δ13C变化范围为-5.4‰~-5.8‰(Moore et al.,1977)。国外一些学者(Nadeau et al.,1990,Pineau,Mathez,1990)还测定了北美大陆火山岩中地幔岩捕虏体中的δ13C变化范围介于-4‰~-10‰之间,夏威夷火山岩的δ13C变化范围介于-1.6‰~-10.8‰和-22‰~-26‰之间。
1.4 地壳流体CO2来源识别一般认为,有机成因的δ13C值在-12‰或者更低,海相沉积碳酸岩变质成因的CO2的δ13C值在+3.5‰~-3.5‰左右,幔源成因的CO2的δ13C值在-4.7‰~-8.0‰。然而,能否直接根据CO2相应δ13C值的变化范围判识其来源呢?如若不能,又有什么方法可以识别呢?下面笔者将针对这两个问题展开论述。
地幔存在大规模的碳同位素组成的不均一性(Pineau,Mathez,1990),这就存在生物有机碳下沉与均一的原始碳源混合的可能。如图1所示,深部流体与地壳熔融挥发分的混合作用也可使δ13C值在0~-12‰之间变化,该范围显然覆盖了幔源碳δ13C值的变化范围(-4.7‰~-8.0‰)。此外,沉积碎屑岩中的钙质胶结物和泥质岩石中的一些碳酸盐矿物,主要是方解石、白云石或菱铁矿,由于其形成环境特殊,其δ13C值明显小于海相碳酸盐的δ13C(-3.7‰~+3.7‰),一般认为在-9‰~-15‰范围变化(程有义,2000)。由此可见,碳同位素组成具有多解性,不能简单地根据δ13C变化范围判断其来源。
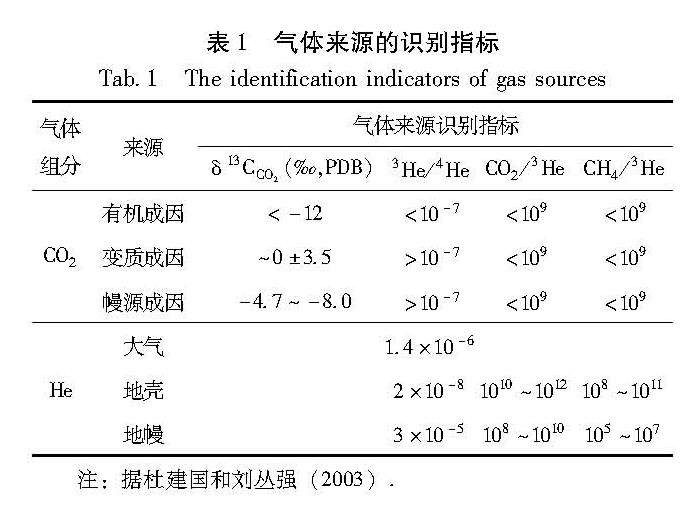
为了准确地判断地壳流体CO2的真正来源,常借助于稀有气体氦同位素3He/4He比值、复合气体含量(CO2/3He、CH4/3He比值等)地球化学指标进行综合判识。通常来自于壳源CO2中的R/Ra<1(R为样品的3He/4He比值,Ra为大气3He/4He比值,其值为:1.4×10-6),而来自于幔源CO2中的R/Ra>1。对全球范围内有关样品的测试与研究表明,幔源流体中CO2/3He值的分布范围数量级为108~1010,CH4/3He值数量级为105~107; 壳源流体的CO2/3He值则远高于地幔值,数量级达1010~1012,CH4/3He值分布于108~1011范围,也显著高于幔源值(陶明信等,2005)。但幔源气体在地壳中运移和聚集过程中,其CO2/3He比值会受到各种因素的影响而发生不同程度的变化。Poreda等(1988)研究发现,壳源流体以具有高CH4/3He值(1012)、高CO2/3He值(1011)和低R值(0.01Ra)的特征; 幔源流体以具有低的CH4/3He值(<106)的高R值(0.6~3.9Ra)和低CO2/3He(<109)和高R值(2Ra~4Ra)的特征。表1中列出了判断各种气体组分来源的近似参量,对于多来源的混合气体,表1内的指标数值会发生改变。
注:据杜建国和刘丛强(2003).
2 排放与运移
地壳流体CO2的释放与现今基本构造过程密切相关,特别是构造板块俯冲带和洋中脊伸展构造带存在着大量的新生代火山、喷气孔。大陆地壳的排气过程按区域大致可划分火山区排气和非火山区排气。在火山区,火山通道及附近的断层成为排气的主要通道; 而非火山区,各种规模的断裂、裂谷等都是地球内部向地球表面和大气排放气体的通道(杨玉荣,2000)。气体排放的“驱动力”,除自身的浮力而外,还有沉积压实作用、成岩作用、变质作用、岩浆脱气作用、构造变形、热对流和热扩散及流体密度梯度等(易立新等,2003)。CO2排放的时空分布上存在非常不均一现象。时间上,排放量以显生宙早古生代为最高,中生代白垩纪次之,排放量最低出现于石炭纪—二叠纪和包括第四纪在内的晚新生代,前寒武纪末期也很可能具有低CO2排放(中国科学院地球化学研究所,1998)。空间分布上,全球CO2排放点集中于板块缝合带、年轻的造山带及高热流值的地区,主要包含两个地区,一个是比较狭窄的环太平洋地区,其延伸长度超过30 000 km; 另一条CO2富集带包括中欧、南欧以及小亚细亚的广阔地区(Barnes et al.,1978)。同时还有大洋中脊和海底薄弱部位,CO2随海底热液排出。
火山区和地热异常区是CO2排放活动的主要集中区域,通常在火山喷发期会喷出大量火山气体,而在火山休眠期没有熔浆喷出地表,也同样会排出大量火山气体,主要表现形式为火山喷气孔和火山热泉。美国黄石公园火山地热区每年向现今地球大气圈中输送的CO2气体高达1.5×105 t(Werner,Brantley,2003); 意大利火山学者对希腊爱琴岛上由陆内俯冲形成的、规模较小的Methana和Sousaki两个休眠活火山研究表明:CO2气体排放量分别为1600 t/a和2.0×104 t/a(D'Alessandro et al.,2008)。国内学者对腾冲火山区温泉逸出气做了许多深入的研究(高清武,范树全,1992; 王先彬等,1993; 上官志冠等,2004),温泉逸出气中CO2最高可达96.6%。成智慧等(2012)利用数字皂膜通量仪测量了腾冲新生代火山区温泉中CO2的排放通量达3.58×103 t/a。对长白山火山区温泉气体成分进行研究(高清武,2004; 高玲等,2006)表明气体成分均以CO2为主,其含量变化范围为73.55%~97.59%。火山区内的CO2气体释放通量为6.9×104 t/a(张茂亮等,2011)。海底火山喷发释放的CO2,至今还没有较为可靠的数据。
在大陆非火山区,现今仍在强烈活动的深大断裂是地球排气的主要通道。Sugisaki等(1983)将与断裂活动有关的从断裂散发出来的气体定义为“断层气”,按照断层气体的排出方式,可将其分为两类,一类主要是从断裂带的岩石排出或以土壤微渗漏的方式排出,该类气体也称作“土壤气”。土壤气以垂直向排气为主,常用于隐伏断裂和地裂缝的定位及断层活动性的研究(Wang et al.,2006)。同时,土壤气也是研究火山及其活动性的主要手段(Rizzo et al.,2009; Camarda et al.,2012); 另一类则主要由深循环的地热水携带并通过温泉出露点释放的“温泉气”,该类气体常用于地下热源识别(Yokoyama et al.,1999)及火山区岩浆囊探测(赵慈平等,2011),也应用于全球性气候变暖、海平面上升、碳循环等(赵珂等,2005; 张茂亮等,2011; 成智慧等,2012)。但无论是土壤气还是温泉气,在地震研究领域的应用都较为广泛。
地下气体运移、富集与储存是一个复杂的物理化学过程,受诸多因素的影响,在其运移过程中,既有物理作用,也有化学作用。一些学者提出了扩散模式、对流模式、接力传递作用等分析深部气体运移的理论机制,用于解释地球排气以及地震、火山事件中气体的异常观测结果(方震等,2012)。近年来有学者(Walia et al.,2010; Li et al.,2013)提出CO2、N2、CH4等气体在向地表运移过程中可作为载气,能将一些地壳中衰变速度较快或扩散系数较低的气体(如222Rn、He等)载流运移至地表,为捕捉这些气体地震异常提供可能。
3 存在形态及检测方法
CO2气体的物理化学性质具有其特殊性,常温常压条件下,是一种无色、弱酸性气体。但在地壳深部的高温高压下,CO2有可能呈超临界状态(临界温度为31.1 ℃,临界压力为7.4 MPa)(张晓东,2003)。超临界流体存在形式既不是液相,也不是气相,而是介于两者之间的一种特殊状态,具有较强的扩散率和渗透率,迁移能力较强; 一些难溶物质在临界流体(CO2和H2O)的作用下很容易溶解,该流体有一定的侵蚀性。根据地温增温率和静压梯度,可推测中、下地壳以下水和CO2流体呈超临界状态,在上地壳中局部高温异常地段也可存在超临界流体(徐有生等,1995)。当深部的CO2气体上升到地表的过程中,必然会溶解于上地壳流体中,特别是由断裂、裂隙等下渗的地表水。CO2的溶解度与压力成正比,随着含有CO2的流体出露至地表,由于流体压力的减小,一部分游离的CO2以气态的形式逸出,最终CO2气体随地下水排出地表。
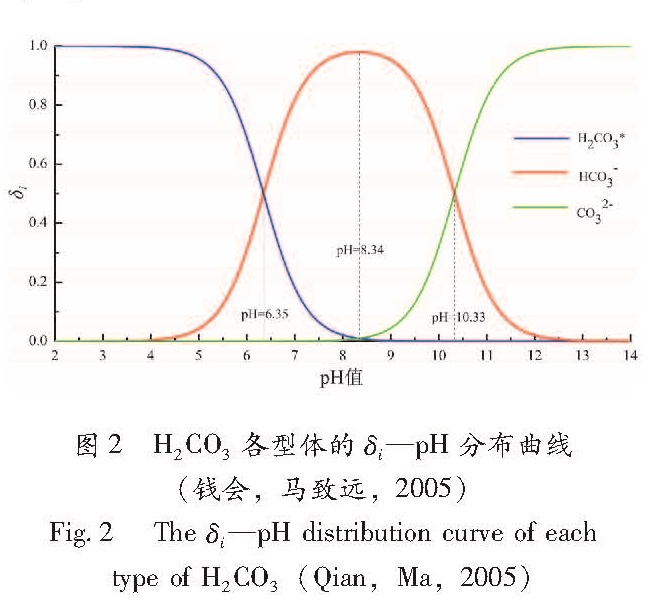
地下水中的CO2以HCO3-、CO32-和游离CO2 3种型体存在,3种型体之间的比例关系主要取决于温泉水的pH值。常温常压下到达平衡时(1 atm,25 ℃),绘制出碳酸各型态的分布分数(δi)与pH值的函数关系如图2所示,图中游离CO2用H2CO3*表示。
目前对CO2气体含量的分析检测方法主要有:酸碱滴定法、气相色谱法、红外光谱法、电化学传感法等。实验室常用的分析方法是气相色谱法,该方法有检测灵敏度高、选择性高、分析检测速度快等优点,而对于野外CO2现场分析检测一般采用红外光谱法或电化学传感法,因为这两种方法分析仪器相对简单,便于携带。目前应用于地震野外断层气CO2监测的一种简便方法——CO2快速测定管(林元武,王基华,1998),该方法实质是一种化学反应法,直接把测定管置于观测孔中,经过24小时的连续反应,便可获得CO2释放量。与气相色谱法测定的结果对比,其结果有很好的一致性,且测定法具有简便、价廉、可靠有效和干扰少等特点,在地震前兆监测、隐伏断裂和地裂缝的现场定位等应用中具有更好的推广价值。图2 H2CO3各型体的δi—pH分布曲线(钱会,马致远,2005)
Fig.2 The δi—pH distribution curve of each type of H2CO3(Qian,Ma,2005)4 CO2释放在地震预测研究中的应用
国外对地壳流体CO2释放的研究在一些多地震和火山活动的国家开展比较普遍,如美国、日本及欧洲中南部地中海沿线等国家开展研究较早。我国自20世纪90年代开始便注意到断层中CO2释放可能是地震预测研究的一种有效途径。经过多年的探索,地壳流体CO2释放在地震研究领域成功应用于地震活动性、遥感探测、地震预测、映震机理解释、流体触(诱)发震等方面的研究。结合国内外相关研究发现,应用深源流体同位素地球化学研究地震已成为现今的热点。
4.1 在地震活动性方面的应用地壳流体CO2的释放空间分布与主要地震区(带)分布基本一致。从CO2排放点的环球分布上看,其排放条带的走向均与板块缝合带、历史上主要地震带相重合。同时,CO2排放条带也是大地震发生的集中区域。条带以外的孤立CO2排放点也是趋于和局部性地震区相重合。在世界上绝大部分比较古老的造山带和克拉通地区,CO2排放点和地震活动同样稀缺。这种地理上分布的重合现象说明CO2的产生与现代广泛存在的基本构造活动过程紧密相关(Irwin,Barnes,1980)。国内相关研究也表明,富含CO2流体出露点或出露带的分布与强震震中相吻合,且CO2释放强度与地区强震活动正相关,地震活动不太强烈的地区CO2释放强度明显偏低(石慧馨,1979; 上官志冠,刘桂芬,1993; 康来迅等,1999)。然而,在我国的地震活动带上,有一大部分区域地下流体不是很发育,深循环水的出露也十分少见。应用CO2空间释放特征圈定地震区(带)具有一定局限性。换句话说,该方法只能作为地震区划的一种辅助手段。
小区域与大区域的CO2释放特征有所差别。王永才和孙香荣(1992)讨论了河北及邻近地区CO2富集带与地热异常带、地震震中的分布关系。结果显示,CO2富集带与地热异常带在空间上重合,但与M≥5地震震中分布并不重合,这些地震多发生在CO2富集带的边沿附近。地热异常带、CO2富集带和地震活动带之间空间分布的这种依存关系不是偶然的。地热异常带地下流体也异常发育,促进了碳酸盐的变质作用,产生CO2富集带。地热异常区呈带状断续分布,从而在地温梯度变化大的地段容易积累热应力,进而引起地震发生。从地震小区划角度看,地壳流体CO2释放或富集空间分布可以大致确定未来破坏性地震的潜在震源位置。
4.2 在遥感探测方面的应用许多观测实例表明,地震前CO2、CO、CH4等温室气体排放量的增加可使地表或近地表的温度升高3~5 ℃(Tronin,2006)。卫星热红外图像作为一种新的遥感探测手段,可以监测这些气体异常排放现象。强祖基等(1997)实验发现,不同比例的气体(CO2、CH4、He等)与空气混合后在外加瞬变电场的作用下可引起高达6.1 ℃的增温,太阳辐照也可引起上述混合气体增温4~5 ℃。这些模拟结果与临震前卫星热红外增温幅度(5~6 ℃)基本一致。2004年印尼苏门答腊MW9.3地震前观测到了间断性的、不连续的气体释放,震前7 d的卫星热红外图像显示,在安达曼海和南海南部存在增温12 ℃孤立异常区,异常区东南端已覆盖到MW9.3巨震的震中(高建国等,2007)。利用高分辨率卫星遥感数据不仅可以反演亮温、大气温度、地表温度,还可以反演一些气体组分(CO、CH4、CO2、H2O、O3等)含量等化学参数数据,进而提取与地震有关的遥感信息。2001年印度Gujarat地区MS7.8地震前,卫星遥感数据也显示CO含量有异常,且该异常与热红外异常相吻合(Singh et al.,2010)。2008年汶川MS8.0地震前后均有水汽含量异常增高的现象(崔丽华,2009),同时也伴随热红外异常(魏乐军等,2008)。2012年芦山MS7.0地震前龙门山地区观测到震前地下甲烷的释放,且受断裂带控制明显,雅安市气温出现明显增温异常,增温幅度最高为6.2 ℃,研究表明,芦山地震前甲烷的释放与气温异常升高有良好的对应关系(王杰等,2013)。不同地区发生的地震,地球化学特征和气象特征不同。通过研究遥感数据未发现CO2气体含量异常,并不能判定地震前后就没有CO2的释放,它可能受气象因素干扰、传感器对CO2的敏感度、反演精度低和CO2的背景含量较高等因素影响。总而言之,利用遥感数据监测地震有关的气体前兆异常与传统的定点取样检测方法相比,具有实时监测、组分快速分析、取样手续简便、可获得地面或高空大区域三维空间数据等优点。
4.3 在地震预测、机理解释方面的应用地下流体地球化学变化特征能很好的反映地震断层的活动情况。CO2作为断层流体中的主要成份,是地震前兆异常的主体,可应用于地震监测、预测。土壤气CO2前兆异常用于预测地震的比较成功的实例是林元武和王基华(1998)对河北怀来后郝窑断层土壤气体CO2动态观测。结果表明,CO2异常一般出现在震前15~47 d,特别是1996年包头西MS6.4地震和1998年张北—尚义MS6.2地震,异常峰值高出背景值的10倍左右,大多数地震发生在CO2异常达到峰值后的转折性下降过程之中。在火山区,土壤气CO2不但能辨别火山地区的脱气构造和指示火山活动(Melián et al.,2014),且CO2释放通量变化与地震活动强弱有较好的响应关系(Baubron et al.,2002; Rizzo et al.,2009; Giammanco et al.,2010)。地震活动带上的泥火山逸出气,是区域构造应力集中的结果。在地震前后,逸出气中CO2含量有着明显异常(Tanikawa et al.,2010; 杜建国等,2013)。
温泉逸出气CO2动态监测不仅可以指示断裂活动情况,且对于地震也有较好的响应关系。流体在上升至地表过程中,可能与地壳岩石广泛接触并经流体—岩石相互作用,温泉逸出气在地下环境中可能比土壤气更具有代表性(Toutain,Baubron,1999)。上官志冠和高松升(1990)在对云南下关、江干等典型温泉中溶解CO2总量动态的观测表明,在5级左右地震前,热动力变质成因和深源CO2成因的碳酸泉释放CO2总量既有一定的趋势异常,又有明显的临震突变异常,但其映震特征各有不同。李志鹏和刘仕锦(2012)对四川龙头沟温泉逸出气CO2的含量长期(1988~2010年)监测结果整理、分析发现,M≥5地震前CO2百分含量有多次突降异常。
无论断层上的土壤气或是温泉逸出的温泉气,它们对地震响应的机理是什么?究竟是热动力变质产生CO2,还是深部幔源CO2释放,亦或是其它原因(有机成因CO2混入、深部吸附CO2扰动释放)致使土壤气、温泉气中释放的CO2发生变化?深源流体在地壳深部是如何运移的?现目前的办法唯有通过深源气体同位素的变化得以解释。大量研究显示,出露在断裂带上释放的CO2组分的稳定同位素及相关参数(CO2%、δ13CCO2、3He/4He、CO2/3He)在震前或震后都出现明显的异常(Hilton,1996; Shangguan,1996; Toutain,Baubron,1999; Italiano et al.,2001; Salazar et al.,2002; Biagi et al.,2006; Troll et al.,2013; Pierotti et al.,2014)。应用深源气体同位素地球化学监测、识别地震异常、预测地震、解释地下流体的映震机理等已成为国际上热门研究领域。
通过监测温泉CO2同位素组成来研究流体运移与地震响应关系已有很多成果。Sorey等(1998)在加利福尼亚Mammoth Mountains火山区,应用1989年5月的地震群首发时间作为壳内气体(2~4 km)的开始释放时间,在1990年3月观察到CO2的累积释放和3He/4He比值的升高,这表明地震导致地幔组分的释放到达地表,并计算了从岩浆房释放的气体的运移速率大约为10~40 m/d。Weise等(2001)观测了Bad Brambach地区富含CO2的矿泉(Eisenquelle)逸出气,期间发生约500次小震群(M≤2.2)。发现地震后1个月左右出现He含量的同震漂移,而3He/4He比值和δ13CCO2值异常出现在震后220 d,同位素漂移被解释为由震中区破裂岩石所释放的壳源流体的混入而造成的,并根据震中到泉点出露点的距离(约14 km)推算出壳源流体的运移速率至少为50 m/d。在同一地区(Bad Brambach)的另一矿泉(Wettinquelle),Bräuer等(2007)也对逸出气及同位素组成(3He/4He、δ13CCO2、δ13CCH4、δ15N)进行动态监测。在观测期内也出现了小震群活动(5次地震震级超过3.0级),许多研究者认为通过孔隙压力作用导致地幔流体上涌触发了此次地震活动(Parotidis et al.,2003; Hainzl,2004)。结果表明所有监测的气体(CO2、CH4、He)及同位素组成(3He/4He、δ13CCO2、δ13CCH4、δ15N)在震时和震后都发现了壳源流体混合引起的漂移,漂移持续时间大约为2 a。在此次地震开始活动的前6周左右,发现3He/4He和δ13CCO2有明显降低的趋势异常,同时伴随有附近钻孔水位下降的现象。Bräuer等(2007)将这些异常解释为震前地壳形变和同震破裂过程两种效应造成岩石渗流参数的改变而导致壳源流体的释放。壳源流体与幔源流体的混合、迁移造成了持续近2年的地球化学异常。由此可见,深部流体同位素已成为研究地球动力学的重要手段。对深源流体监测也不能仅限单一组分的监测,需多种深源成分的同时监测。特别是对深部来源的稀有气体(He、Ne、Ar、H2)同位素以及各种气体的比值(3He/4He、CO2/3He、CH4/3He等)监测,更能说明地壳深部的变化情况。
4.4 在深源CO2触(诱)发地震研究中的应用从动力学角度看,导致地震活动的主要因素还是在地球内部。Gold和Soter(1984)认为:地球深部高压流体在向地表运移过程中,有效地抵消部分上覆岩石的压应力,从而降低地壳岩石抗剪强度并诱发地震,另外他还强调地表观测的地震前兆效应可能是地球深部流体运移到地表而产生的,并非区域构造应力显著增大引起。车用太和鱼金子(2006)提出板内地壳硬夹层孕震与流体促震的假设,认为浅源地震震源多分布于上地壳流体活动系统与中下地壳高导低速层之间的硬夹层中。当集中在硬夹层内的地壳应力累积到一定程度时,硬夹层薄弱带首先屈服而发生微破裂并膨胀,形成震源体。处于真空状态的微破裂空隙能使深部流体被吸入膨胀体内,而深部流体起着岩石强度弱化作用。当剪应力与抗剪强度相等时,岩石破裂并发生地震。CO2的构造意义就是在地壳深部它能造成高孔隙压力,断层附近存在高孔隙压流体主要是基于震源附近观测到的低波速高泊松比异常、低电阻率异常、正磁异常、负重力和低密度异常区、剪切波分裂、地球化学异常区等得到的认识(晏锐等,2011)。Agosta等(2008)研究了欧洲中部和南部不同地区富含CO2流体的同位素组成,认为在地震成核过程中断层内部存在高压CO2流体,为地下存在高压流体提供了证据。
深部CO2等高压流体对地震的孕育和发生起着重要的作用,它不仅可以间接地反映地下应力(变)场的变化,而且在地震孕育过程中起到断层弱化和促(诱)震的作用(Chiodini et al.,2004; Pérez et al.,2008; Weinlich,2014)。Di Luccio等(2010)在研究2009年拉奎拉MW6.3地震时发现,流体孔隙压力扩散控制了余震的时空演化。富含CO2的流体(来自于20 km深处已发生交代作用的地幔楔)向上运移至中下地壳时,在裂隙或岩性不连续面形成超压气储构造。随着孔隙压力的增加,有效正应力和内聚力随之减小,就造成先前存在的裂缝滑移和新的破裂开始。在亚平宁地区,垂直向的断裂很可能切割整个地壳,这种超压构造很容易产生伸展运动,而要造成走滑运动则很困难。因此,Di Luccio指出深源流体可能激发断层活动而发震,且深源流体比构造应力更可能控制增生楔的发震构造。不仅含有CO2的深源流体会触发地震,相反,强地震也会造成断层面上产生大量CO2。Famin等(2008)应用傅里叶变换红外微量分析研究了日本Nojima断层中假玄武玻璃,结果显示在地震发生的同时,两盘岩石排出气中近99%的气体为CO2,利用外推法估算了日本1995年神户地震(MJMA7.2,MW6.9)在几秒钟内就产生了(1.8~3.4)×103 t的CO2,如此大量的CO2释放可能造成断层面上瞬时流体压力增大,这就可能造成断层滑动或诱发余震。Miller等(2004)认为意大利北部Umbria-Marche地下存在的前(主)震释放CO2高压流体,并利用流体压力脉冲解释了余震的分布规律。由此可见,深部CO2的释放与地震活动具有相互依存、促进的辩证统一关系。
5 结语
地球内部存有大量的气体在学术界已得到广泛认同,排气作用与各种自然灾害的关系也十分密切。从动力学角度看,地球内部的气体是地球化学场中反应最为敏感、迁移性最强的流体物质,是可以直接将地球深部信息直接带出地表的载体。地壳流体CO2是地球内部浅层气体和深部流体的重要组成部分,在地震预测与研究中有着广泛的应用。通过CO2的空间释放特征,可以研究地震的活动规律和圈定震中的潜在位置。大量的CO2等温室气体释放可引起区域温度异常,使红外遥感探测地震异常成为可能。对地表逸出气CO2含量动态监测可获得地震异常信息,而深部CO2等深源流体的活动也可触发地震。总之,深入开展CO2释放规律的研究,对于识别地震异常、预测地震、解释地下流体的孕震机理有着广泛的科学和现实意义。
目前,CO2在地震监测中的主要手段有断层土壤气的动态监测,也有水化学中溶解CO2的相关参数的监测(如HCO3-离子、总溶解碳等)。经过十几年的实践表明,CO2作为地震预测指标效果不是很明显。原因在于地下流体CO2的干扰因素诸多,既有物理因素,也有化学因素,且CO2含量动态观测也不能说明地震的孕育与发生过程,这就给地震异常识别带来了困难。传统的地下流体观测面临着严重的挑战,开展深部流体的观测与研究是一个非常重要的研究领域。许多学者研究从浅层流体转向深部流体,希望能从深部流体的来源与运移机制研究中得到可靠的地震前兆信息。国际上,深部流体同位素示踪技术已成为研究物质来源与运移规律一种成熟的技术方法。CO2的碳同位素结合深部稀有气体同位素可识别其来源、判断运移规律,不仅有助于全面理解CO2的映震机理,且能判识地震前兆异常。在探寻流经震源区深度的地震流体“源兆”特征观测组分或观测量方面,深源CO2的观测有可能成为干扰因素少、映震效果较好的特征观测方法。此外,结合地球物理的深部探测方法(如层析成像等技术),深源CO2等气体的观测研究有可能揭示地震孕育、发生过程中深源流体与震源体的相互作用关系。
本文在撰写和修改过程中得到云南财经大学张春生助教的帮助,审稿过程中获得专家提出的建设性修改意见,在此向他们表示衷心感谢。
- 车用太,鱼金子.2006.地震地下流体学[M].北京:气象出版社.
- 成智慧,郭正府,张茂亮,等.2012.腾冲新生代火山区温泉CO2气体排放通量研究[J].岩石学报,28(4):1217-1224.
- 程有义.2000.含油气盆地二氧化碳成因研究[J].地球科学进展,15(6):684-687.
- 崔丽华.2009.汶川地震前的遥感信息异常及其机理研究[D].唐山:河北理工大学.
- 戴金星.1993.天然气碳氢同位素特征和各类天然气鉴别[J].天然气地球科学,4(2):1-40.
- 杜建国,刘丛强.2003.同位素地球化学在地震研究方面的作用[J].地震,23(2):99-107.
- 杜建国,周晓成,陈志,等.2013.北天山泥火山对2012年6月30日新源—和静MS6.6地震的响应[J].地震学报,35(6):876-887.
- 杜乐天.1996.自然灾害可能的深部流体肇因[J].地学前缘,3(4):298-305.
- 杜乐天.2007.固体地球观向流体地球观的概念更新[J].地球物理学进展,22(4):1220-1224.
- 方震,刘耀炜,杨选辉,等.2012.地震断裂带中气体来源及运移机制研究进展[J].地球物理学进展,27(2):483-495.
- 高建国,郭增建,王涌泉,等.2007.苏门答腊大地震印度洋震区放气现象研究[J].气象与减灾研究,30(2):28-32.
- 高玲,上官志冠,魏海泉,等.2006.长白山天池火山近期气体地球化学的异常变化[J].地震地质,28(3):358-365.
- 高清武,范树全.1992.腾冲现代火山活动区地热流体的地球化学特征[J].西安地质学院学报,14(3):40-44.
- 高清武.2004.长白山天池火山水热活动及气体释放特征[J].地球学报,25(3):345-350.
- 官致君,闻学泽,程万正.2003.断层气CO2快速测定方法在四川地震预测中的应用[J].地震研究,26(增刊):22-27.
- 康来迅,张新基,黄杏珍,等.1999.西秦岭北缘断裂带排气活动的比较研究[J].地震学报,21(6):657-664.
- 李振生,张文俊,吴小奇,等.2011.松辽盆地二氧化碳的气源及其脱气模式[J].天然气地球科学,22(1):29-37.
- 李志鹏,刘仕锦.2012.四川康定龙头沟温泉CO2突降异常与地震活动关系[J].地震地磁观测与研究,33(2):80-83.
- 林元武,王基华.1998.断层气CO2测定新方法与张北—尚义6.2级地震预报[J].地震,18(4):353-357.
- 钱会,马致远.2005.水文地球化学[M].北京:地质出版社,50-54.
- 强祖基,孔令昌,郭满红,等.1997.卫星热红外增温机制的实验研究[J].地震学报,19(2):197-201.
- 上官志冠,高清武,赵慈平.2004.腾冲热海地区NW向断裂活动性的地球化学证据[J].地震地质,26(1):46-51.
- 上官志冠,高松升.1990.滇西地区二氧化碳的释放与地震[J].地震学报,12(2):186-193.
- 上官志冠,刘桂芬.1993.川滇块体边界断裂的CO2释放及其来源[J].中国地震,9(2):146-153.
- 上官志冠,武成智.2008.中国休眠火山区岩浆来源气体地球化学特征[J].岩石学报,24(11):2638-2646.
- 石慧馨.1979.中国碳酸水出露带分布特征简介[J].地震地质,1(2):86-93.
- 孙玉涛,崔月菊,刘永梅,等.2014.苏门答腊两次M>8.0地震前后CO和O3卫星遥感气体地球化学异常与地面验证[J].地震研究,37(2):222-227.
- 陶明信,徐永昌,史宝光,等.2005.中国不同类型断裂带的地幔脱气与深部地质构造特征[J].中国科学(D辑),35(5):441-451.
- 王基华,林元武,高松升.1998.怀来断层气CO2监测及张北尚义地震的短临预报[J].地震地质,20(2):113-116.
- 王杰,张雄,潘黎黎,等.2013.芦山地震(MS7.0)前甲烷释放与大气增温异常[J].地学前缘,20(6):29-35.
- 王先彬,徐胜,陈践发,等.1993.腾冲火山区温泉气体组分和氦同位素组成特征[J].科学通报,38(9):814-817.
- 王永才,孙香荣.1992.河北及邻近地区地下水溶解二氧化碳,氢和氦分布的地震地质特征[J].华北地震科学,10(2):58-66.
- 魏乐军,郭坚峰,蔡慧,等.2008.卫星热红外异常——四川汶川MS8.0级大地震的短临震兆[J].地球学报,29(5):583-591.
- 夏林圻,徐培苍.1990.岩浆包裹体挥发组发的研究[J].地球化学,(2):108-116.
- 徐有生,侯渭,郑海飞,等.1995.超临界水的特性及其对地球深部物质研究的意义[J].地球科学进展,10(5):445-449.
- 晏锐,蒋长胜,邵志刚,等.2011.关于震源附近流体,热和能量分配问题的研究进展[J].中国地震,27(1):14-28.
- 杨玉荣.2000.浅议地下气体逸出总量的观测与研究[C]//中国地震学会第八次学术大会论文摘要集.
- 易立新,车用太,王广才.2003.地壳中流体动力学模型研究[J].地震,23(2):108-114.
- 鱼金子,车用太.1998.地壳中的CO2及其释放与地震短临预测[J].国际地震动态,(8):8-12.
- 张景廉,杜乐天,曹正林,等.2011.再论汶川大地震与深部气体的关系[J].西北地震学报,33(1):96-101.
- 张茂亮,郭正府,成智慧,等.2011.长白山火山区温泉温室气体排放通量研究[J].岩石学报,27(10):2898-2904.
- 张铭杰,王先彬.1999.中国东部新生代碱性玄武岩及幔源捕虏体中的流体组成[J].地质学报,73(2):162-166.
- 张晓东.2003.中国东北地区CO2气藏成因及聚集规律分析[J].石油学报,24(6):13-17.
- 赵慈平,冉华,陈坤华.2011.腾冲火山区壳内岩浆囊现今温度:来自温泉逸出气体 CO2、CH4间碳同位素分馏的估计[J].岩石学报,27(10):2883-2897.
- 赵珂,姜光辉,杨琰,等.2005.滇东主要断裂带温泉CO2成因浅析[J].地球与环境,33(2):11-15.
- 中国科学院地球化学研究所.1998.高等地球化学[M].北京:科学出版社.
- 周晓成.2011.汶川MS8.0地震后川西地区的气体地球化学[D].合肥:中国科学技术大学.
- Agosta F.,Mulch A.,Chamberlain P.,et al..2008.Geochemical Traces of CO2-rich Fluid Flow Along Normal Faults in Central Italy[J].Geophysical Journal International,174(2):758-770.
- Barnes I.,Irwin W.P.,White D.E..1978.Global Distribution of Carbon Dioxide Discharges and Major Zones of Seismicity//USGS.Water-Resources Investigations[M].Virginia,United States:Open-File Report,78-89.
- Baubron J.C.,Rigo A.,Toutain J.P..2002.Soil Gas Profiles as a Tool to Characterise Active Tectonic Areas:the Jaut Pass Example(Pyrenees,France)[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,196(1):69-81.
- Biagi P.,Castellana L.,Minafra A.,et al..2006.Groundwater Chemical Anomalies Connected with the Kamchatka Earthquake(M= 7.1)on March 1992[J].Natural Hazards and Earth System Science,6(5):853-859.
- Bräuer K.,Kämpf H.,Koch U.,et al..2007.Seismically Induced Changes of the Fluid Signature Detected by a Multi-isotope Approach(He,CO2,CH4,N2)at the Wettinquelle,Bad Brambach(central Europe)[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth(1978–2012),112(B4).
- Camarda M.,De Gregorio S.,Gurrieri S..2012.Magma-ascent Processes during 2005-2009 at Mt Etna Inferred by Soil CO2 Emissions in Peripheral Areas of the Volcano[J].Chemical Geology,330:218-227.
- Chiodini G.,Cardellini C.,Amato A.,et al..2004.Carbon Dioxide Earth Degassing and Seismogenesis in Central and Southern Italy[J].Geophysical research letters,31(7):L07615.
- Craig H..1953.The Geochemistry of the Stable Carbon Isotopes[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,3(2):53-92.
- Di Luccio F.,Ventura G.,Di Giovambattista R.,et al..2010.Normal Faults and Thrusts Reactivated by Deep Fluids:The 6 April 2009 MW6.3 L'Aquila Earthquake,Central Italy[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth(1978-2012),115(B6).DOI:10.1029/2009JB007190.
- D'Alessandro W.,Brusca L.,Kyriakopoulos K.,et al..2008.Methana,the Westernmost Active Volcanic System of the South Aegean Arc(Greece):Insight from Fluids Geochemistry[J].Journal of Colcanology and Geothermal Research,178(4):818-828.
- Evans W.,Sorey M.,Kennedy B.,et al..2001.High CO2 Emissions through Porous Media:Transport Mechanisms and Implications for Flux Measurement and Fractionation[J].Chemical Geology,177(1):15-29.
- Famin V.,Nakashima S.,Boullier A.M.,et al..2008.Earthquakes Produce Carbon Dioxide in Crustal Faults[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,265(3):487-497.
- Gerlach T.M..1991.Present-day CO2 Emissions from Volcanos[J].Eos,Transactions American Geophysical Union,72(23):249-255.
- Giammanco S.,Bellotti F.,Groppelli G.,et al..2010.Statistical Analysis Reveals Spatial and Temporal Anomalies of Soil CO2 Efflux on Mount Etna Volcano(Italy)[J].Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research,194(1):1-14.
- Gold T.,Soter S..1984.Fluid Ascent through the Solid Lithosphere and its Relation to Earthquakes[J].Pure and Applied Geophysics,122(2-4):492-530.
- Hainzl S..2004.Seismicity Patterns of Earthquake Swarms due to Fluid Intrusion and Stress Triggering[J].Geophysical Journal International,159(3):1090-1096.
- Hilton D.R..1996.The Helium and Carbon Isotope Systematics of a Continental Geothermal System:Results from Monitoring Studies at Long Valley Caldera(California,USA)[J].Chemical Geology,127(4):269-295.
- Hutcheon I.,Abercrombie H..1990.Carbon Dioxide in Clastic Rocks and Silicate Hydrolysis[J].Geology,18(6):541-544.
- Irwin W.P.,Barnes I..1980.Tectonic Relations of Carbon Dioxide Discharges and Earthquakes[J].Journal of Geophysical Research,85(B6):3115-3121.
- Italiano F.,Martelli M.,Martinelli G.,et al..2001.Significance of Earthquake-related Anomalies in Fluids of Val D'Agri(southern Italy)[J].Terra Nova,13(4):249-257.
- Kerrick D.M.,Caldeira K..1998.Metamorphic CO2 Degassing from Orogenic Belts[J].Chemical Geology,145(3):213-232.
- Li Y.,Du J.,Wang X.,et al..2013.Spatial Variations of Soil Gas Geochemistry in the Tangshan Area of Northern China[J].Terrestrial,Atmospheric & Oceanic Sciences,24(3):323-332.
- Mörner N.A.,Etiope G..2002.Carbon Degassing from the Lithosphere[J].Global and Planetary Change,33(1):185-203.
- Melián G.,Hernández P.A.,Padrón E.,et al..2014.Spatial and Temporal Variations of Diffuse CO2 Degassing at El Hierro Volcanic System:Relation to the 2011-2012 Submarine Eruption[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,119:1-16.
- Miller S.A.,Collettini C.,Chiaraluce L.,et al..2004.Aftershocks Driven by a High-pressure CO2 Source at Depth[J].Nature,427(6976):724-727.
- Moore J.G.,Batchelder J.N.,Cunningham C.G..1977.CO2-filled Vesicles in Mid-ocean Basalt[J].Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research,2(4):309-327.
- Nadeau S.,Pineau F.,Javoy M.,et al..1990.Carbon Concentrations and Isotopic Ratios in Fluid-inclusion-bearing Upper-mantle Xenoliths along the Northwestern margin of North America[J].Chemical Geology,81(4):271-297.
- Panichi C.,Tongiorgi E..1975.Carbon Isotopic Composition of CO2 from Springs,Fumaroles,Mofettes and Travertines of Central and Southern Italy:a Preliminary Prospection Method of Geothermal Area[C]//Second United Nations Symposium on the Development and Use of Geothermal Resources.1:815-825.
- Pankina R.G.1979.Origin of CO2 in Petroleum Gases(from the Isotopic Composition of Carbon)[J].International Geology Review,21(5):535-539.
- Parotidis M.,Rothert E.,Shapiro S..2003.Pore-pressure Diffusion:A Possible Triggering Mechanism for the Earthquake Swarms 2000 in Vogtland/NW-Bohemia,Central Europe[J].Geophysical research letters,30(20):2075-2086.
- Pierotti L.,Facca G.,Gherardi F..2014.Anomalous CO2 Content in the Gallicano Thermomineral Spring(Serchio Valley,Italy)before the 21 June,2013 Alpi Apuane Earthquake(M=5.2)[C]//EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts,16:14051.
- Pineau F.,Javoy M.,Bottinga Y..1976.13C/12C Ratios of Rocks and Inclusions in Popping Rocks of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and their Bearing on the Problem of Isotopic Composition of Deep-seated Carbon[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,29(2):413-421.
- Pineau F.,Mathez E..1990.Carbon Isotopes in Xenoliths from the Hualalai Volcano,Hawaii,and the Generation of Isotopic Variability[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,54(1):217-227.
- Poreda R.J.,Jeffrey A.W.A.,Kaplan I.R.,et al..1988.Magmatic Helium in Subduction-zone Natural Gases[J].Chemical Geology,71(1):199-210.
- Pérez N.M.,Hernandez P.,Igarashi G.,et al..2008.Searching and Detecting Earthquake Geochemical Precursors in CO2-rich Groundwaters from Galicia,Spain[J].Geochemical Journal,42(1):75-83.
- Rizzo A.,Grassa F.,Inguaggiato S.,et al..2009.Geochemical Evaluation of Observed Changes in Volcanic Activity during the 2007 Eruption at Stromboli(Italy)[J].Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research,182(3):246-254.
- Salazar J.,Pérez N.,Hernández P.,et al..2002.Precursory Diffuse Carbon Dioxide Degassing Signature Related to a 5.1 Magnitude Earthquake in El Salvador,Central America[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,205(1):81-89.
- Shangguan Z.G..1996.Earthquake-precursory Characteristics of Variation in Total Content of Dissolved CO2(TCD-CO2 parameter)in Geothermal Fluid[J].Chinese science bulletin,41(19):1626-1630.
- Shapiro M.,Melvin J.,Tombrello T.,et al..1982.Correlated Radon and CO2 Cariations near the San Andreas Fault[J].Geophysical Research Letters,9(5):503-506.
- Singh R.P.,Mehdi W.,Gautam R.,et al..2010.Precursory Signals using Satellite and Ground Data Associated with the Wenchuan Earthquake of 12 May 2008[J].International Journal of Remote Sensing,31(13):3341-3354.
- Sorey M.L.,Evans W.,Kennedy B.,et al..1998.Carbon Dioxide and Helium Emissions from a Reservoir of Magmatic Gas Beneath Mammoth Mountain,California[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth(1978–2012),103(B7):15303-15323.
- Sugisaki R.,Ido M.,Takeda H.,et al..1983.Origin of Hydrogen and Carbon Dioxide in Fault Gases and its Relation to Fault Activity[J].The Journal of Geology:239-258.
- Tanikawa W.,Sakaguchi M.,Wibowo H.T.,et al..2010.Fluid Transport Properties and Estimation of Overpressure at the Lusi mud Volcano,East Java Basin[J].Engineering Geology,116(1):73-85.
- Taylor Jr.H.P.,Frechen J.,Degens E.T..1967.Oxygen and Carbon Isotope Studies of Carbonatites from the Laacher See District,West Germany and the Alnö District,Sweden[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,31(3):407-430.
- Toutain J.P.,Baubron J.C..1999.Gas Geochemistry and Seismotectonics:a Review[J].Tectonophysics,304(1):1-27.
- Troll V.R.,Chadwick J.P.,Jolis E.M.,et al..2013.Crustal Volatile Release at Merapi Volcano; the 2006 Earthquake and Eruption Events[J].Geology Today,29(3):96-101.
- Tronin A..2006.Remote Sensing and Earthquakes:A Review[J].Physics and Chemistry of the Earth,parts A/B/C,31(4):138-142.
- Walia V.,Lin S.J.,Fu C.C.,et al..2010.Soil-gas Monitoring:A Tool for Fault Delineation Studies along Hsinhua Fault(Tainan),Southern Taiwan[J].Applied Geochemistry,25(4):602-607.
- Wang G.,Liu C.,Wang J.,et al..2006.The Use of Soil Mercury and Radon Gas Surveys to Assist the Detection of Concealed Faults in Fuzhou City,China[J].Environmental Geology,51(1):83-90.
- Weinlich F.H.2014.Carbon Dioxide Controlled Earthquake Distribution Pattern in the NW Bohemian Swarm Earthquake Region,Western Eger Rift,Czech Republic-gas migration in the Crystalline Basement[J].Geofluids,14(2):143-159.
- Weise S.M.,Bräuer K.,Kämpf H.,et al..2001.Transport of Mantle Volatiles through the Crust Traced by Seismically Released Fluids:a Natural Experiment in the Earthquake Swarm Area Vogtland/NW Bohemia,Central Europe[J].Tectonophysics,336(1):137-150.
- Werner C.,Brantley S..2003.CO2 Emissions from the Yellowstone Volcanic System[J].Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems,4(7):1061-1087.
- Yokoyama T.,Nakai S.I.,Wakita H.1999.Helium and Carbon Isotopic Compositions of Hot Spring Gases in the Tibetan Plateau[J].Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research,88(1):99-107.