基金项目:深部探测技术与实验研究专项SinoProbe-06-03(国土资源部公益性行业科研专项201311181),中央级科研院所基本科研任务专项(ZDJ2013-22)和2015年地震监测台网运行经常性项目联合资助.
(1.中国科学院计算地球动力学重点实验室, 北京100049; 2.中国科学院大学地球科学学院, 北京100049; 3.中国地震局地壳应力研究所, 北京100085)
(1. Key laboratory of Computational Geodynamics of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China)(2. College of Earth Science, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 10004, China)(3. Institute of Crustal Dynamics, CEA, Beijing 100085, China)
Nepal MW7.9 earthquake; coulomb stress change; stress triggering; nearby faults
备注
基金项目:深部探测技术与实验研究专项SinoProbe-06-03(国土资源部公益性行业科研专项201311181),中央级科研院所基本科研任务专项(ZDJ2013-22)和2015年地震监测台网运行经常性项目联合资助.
基于EDGRN/EDCMP程序,计算了尼泊尔MW7.9地震引起的库仑应力变化对强余震的触发作用和对周边断层的加/卸载作用。结果 显示:4月25日MW6.7和4月26日MW6.8强余震均受到明显触发作用,地震产生的应力场扰动有利于2015年5月12日MW7.2强余震的发生。单独反演破裂模型和联合反演破裂模型的计算结果均显示:余震的分布和库仑应力变化的正值区有很好的对应关系,分别有85.5%和75.8%的余震落在库仑应力变化正值区。雅鲁藏布江缝合带西段的西侧受到超过10 kPa的库仑应力加载。喀喇昆仑断裂、班公错怒江缝合带、格林错断裂的库仑应力加载约为1 kPa。龙木错—邦达错断裂、玛尼玉树断裂以及嘉黎断裂受本次地震的影响较小。在震中的西北和东北方向,藏南典型南北向伸展构造受到了库仑应力加载作用,量值约为1 kPa。
Based on the EDGRN/EDCMP codes, we calculated the effect of the coulomb stress change induced by Nepal MW7.9 earthquake on strong aftershocks triggering and stress loading/unloading effect on nearby faults. The results show that the MW6.7 strong aftershock on Apr.25, and MW6.8 strong aftershock were significantly triggered, the co-seismic perturbed stress field contributes to the occurrence of MW7.2 aftershock on Apr.12. The calculation result by using signal earthquake inversion rupture model and joint inversion rupture model of signal earthquake both show that there were good corresponding relation between the positive zone of coulomb stress variation and the distribution of aftershocks, 85.5% and 75.8% of aftershocks located at the positive coulomb stress zone respectively. The coulomb stress loading on west side of Western Segment of Yarlung Zangbu River Suture Zone was larger than 10 kPa. The Karakoram Fault, Bangong Nujiang Suture Zone and Gelincuo Fault were mainly under stress loading of about 1 kPa. The Nepal MW7.9 earthquake has little influence on Longmucuo-Bangda, Mani-Yushu and Jiali Faults. In the northwest and northeast direction of the epicenter, the coulomb stress loading on typical S—N extensional structure in Southern Tibet was about 1 kPa.
引言
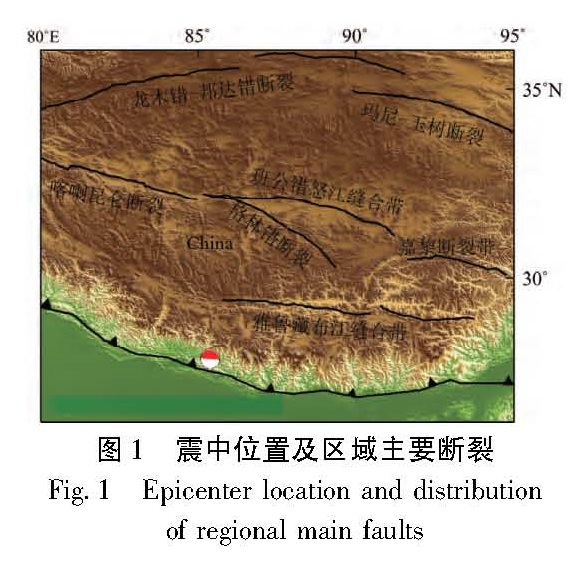
2015年4月25日14时11分26.3秒,在尼泊尔境内发生MW7.9强烈地震,震中位置(28.2°N,84.7°E),震源深度为15 km。根据中国地震局地球物理研究所(2015)发布的快速反演结果,断层面上最大滑动量约2.1 m,而根据Hayes(2015)的结果,断层面上最大滑动量约为3.1 m。张勇等(2015)后续又增加了GSN全球台网中震中距更近的资料和2个GPS台站的同震位移数据,进行了地震波资料单独反演与联合反演,得到的断层面上的最大滑动量分别为3.2 m和5.2 m。4月26日我国西藏自治区日喀则地区的吉隆县、定日县以及聂拉木县发生了多次地震,其中最大震级为MS5.9, 给日喀则地区造成了一定的经济损失。4月25日14时45分和4月26日15时9分尼泊尔陆续发生了MW6.7和MW6.8强余震,5月12日在尼泊尔主震的西南部又发生了MW7.2强余震。
2015年尼泊尔MW7.9地震发生于青藏高原南部喜马拉雅构造带上,该带在印度板块与欧亚板块的陆陆俯冲碰撞和推挤下,发生过多次大地震,如1934年Bihar MS8.2地震(Sapkota et al, 2013),1950年察隅MS8.7地震(Gupta, Gahalaut, 2014)和2005年KashmirMS7.6地震(Avouac et al, 2006)。印度板块相对于欧亚板块以约46 mm/a的速度向北运动,使得青藏高原内部产生南北向的缩短和东西向的拉张,在喜马拉雅构造带上应力高度集中,尼泊尔MS7.9地震是由欧亚板块与印度板块持续的南北向俯冲挤压造成的,深入研究该地震邻近区域及周围断层的库仑应力加/卸载作用,对于理解青藏高原的动力学模型以及青藏高原内部的地震危险性分析具有重要意义。
目前地震应力触发与断层相互作用的研究多以库仑破裂应力变化为基础。Stein和Lisowski(1983)首次提出库仑应力概念,发现1979年加州Homestead Valley大地震的余震集中在库仑应力大于3 bar的区域。这类研究的广泛开展始于1992年美国Landers MS7.3地震,King等(1994)计算Landers地震对后续Big Bear地震产生的库仑应力增量为2.2~2.9 bar,认为Landers地震加速了Big Bear地震发生。Jaumé和Sykes(1996)计算发现旧金山湾地区的许多断层位于1906年旧金山大地震产生的应力影区,使下一次大地震的发生延迟数十年。万永革等(2000,2002)讨论我国几次复杂地震中的应力触发问题, 并对地震静态应力触发模型做了全球检验。沈正康等(2003)讨论了东昆仑活动断裂带大地震之间的粘弹性应力触发。汶川地震后,许多学者(Parsons et al, 2008; 万永革等,2009; 单斌等,2009; 石耀霖,曹建玲,2010; 李玉江等,2013)给出了汶川地震对周围断层活动的影响。
Okada(1992)的弹性半空间位错解析解,具有数学上的解析性和简洁性,但只能计算半无限空间均匀介质的同震形变。Wang等(2003)发展的EDGRN/EDCMP程序,可以计算考虑自重的层状均匀介质中点源位错产生的位移的格林函数,把破裂面离散成许多离散的点位错, 通过线性叠加的方法计算同震形变。本文采用EDGRN/EDCMP程序,计算了尼泊尔MS7.9地震在后续3次强余震破裂面上的静态库仑应力变化,并定量分析本次地震对周边活动断裂带的应力加/卸载作用,从而判断尼泊尔MW7.9地震对周围断层地震活动性的影响。
1 研究区域及数据
1.1 研究区域与构造背景青藏高原南缘的喜马拉雅构造带是印度板块与欧亚板块的俯冲、碰撞边界,这一过程开始于距今约55~65 Ma,至今仍处于强烈推挤过程中。喜马拉雅构造带由MCT(主中央断裂)、MBT(主边界断裂)和MFT(主前缘断裂)3个巨大逆断裂系组成,其南部最新活动边界的MFT活动性最强(邓起东等,2014),此次地震发生在MFT或者邻近的位置(USGS, 2015)。青藏高原次级块体拉萨块体、羌塘块体距离此次地震震中位置较近,块体之间被活动断裂系所分割,历史记录显示在这些活动断裂上发生了多次7级以上地震。由于Okada(1992)弹性位错表达式基于平面假设,未能考虑地球曲率影响,因此选择的研究区域不宜过大,本文的研究区域和区域内主要断层见图1。
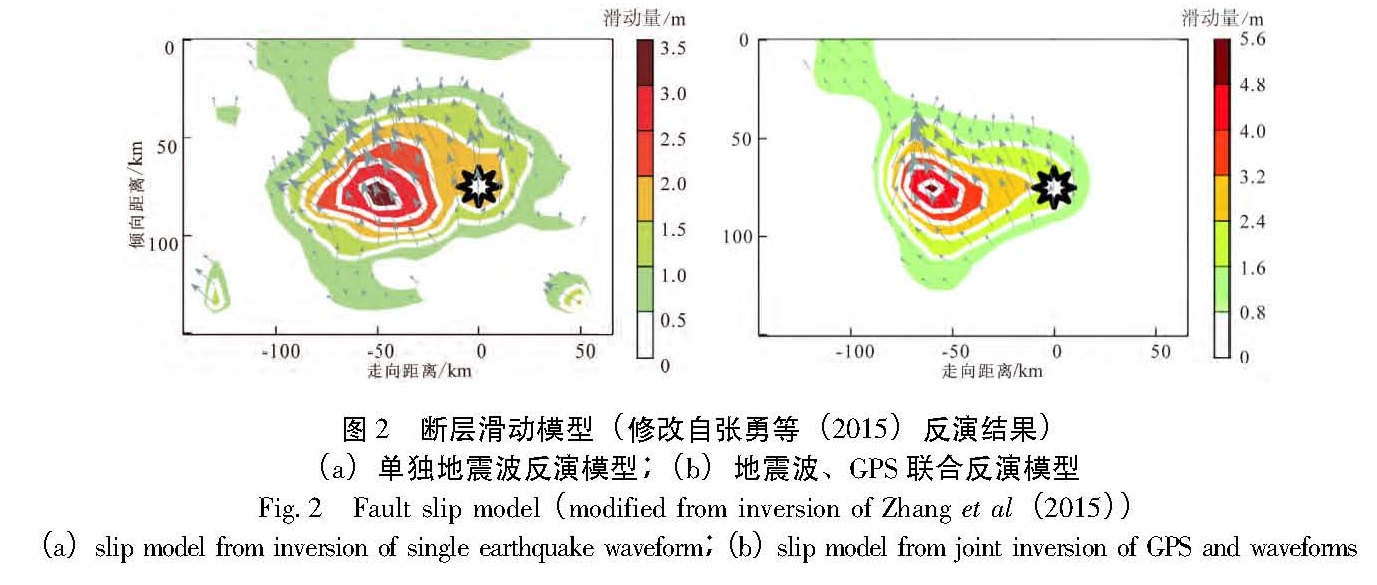
1.2 震源模型及计算参数尼泊尔地震发生后的2小时9分,张勇等(2015)利用远震地震波数据快速确定和发布了此次地震的破裂过程模型,此后又根据更丰富的资料,增加了GSN全球台网中震中距更近的数据以及同震位移明显的两个台站的GPS数据对破裂模型进行了更新(图2)。联合反演得到的静态滑动量分布比地震波单独反演结果的滑动分布范围有所缩小,但滑动量幅度增加,最大滑动量由地震波单独反演的3.2 m提高到联合反演的5.2 m。此外,Hayes(2015)利用波形反演也给出有限断层模型,但其使用的是远震的数据,考虑到近场信息对于确定震源破裂过程意义重大,本文的计算采用张勇等(2015)用单独地震波反演和地震波、GPS联合反演得到的两个破裂模型。
图2 断层滑动模型(修改自张勇等(2015)反演结果)(a)单独地震波反演模型;(b)地震波、GPS联合反演模型
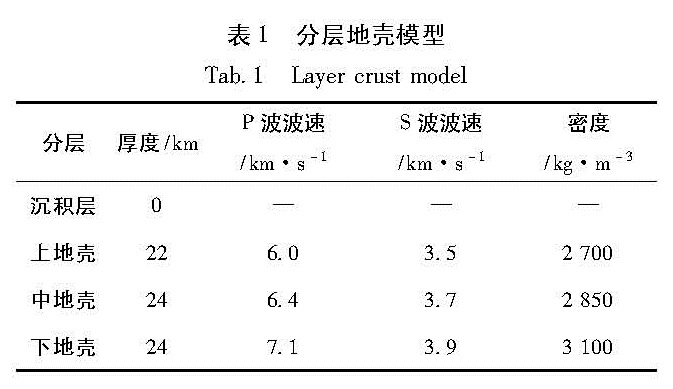
Fig.2 Fault slip model(modified from inversion of Zhang et al(2015))(a)slip model from inversion of single earthquake waveform;(b)slip model from joint inversion of GPS and waveforms本文的分层地壳模型参数参考自Crust2.0(Bassin et al, 2000)给出的研究区沉积层、上地壳、中地壳和下地壳分层的地震波速和密度数据,参数如表1所示。
2 库仑应力变化计算原理
根据库仑破裂准则,岩石趋于破裂时库仑破裂应力增量为(Harris, 1998)
Δσf=Δτ+μ'Δn.(1)
式中,μ'为视摩擦系数, Δτ为剪应力变化量,Δσn为法向正应力变化量。
笔者采用(1)式计算静态库仑应力变化,对应力符号规定如下:Δτ与破裂滑动方向一致为正,Δσn以拉为正。μ'的选取,一般认为滑动速率比较大的走滑断层、正断层等具有较小的摩擦系数,常取0.2~0.4,滑动速率较小的逆冲断层具有较大摩擦系数,常取0.6~0.8(Parsons et al, 1999)。地震引起的扰动应力张量的6个独立分量(Δσxx,Δσyy,Δσzz,Δσxy,Δσyz,Δσxz),可以通过二阶张量坐标变换(陈连旺等,2008)计算任意断层面上Δσn,和该断层面上任意滑动方向的Δτ,代入(1)式得到库仑应力变化Δσf。如果Δσf为正,认为有利于断层的滑动或后续地震的发生,Δσf为负则认为不利于断层的滑动或后续地震的发生。
3 尼泊尔MW7.9地震与后续余震的关系
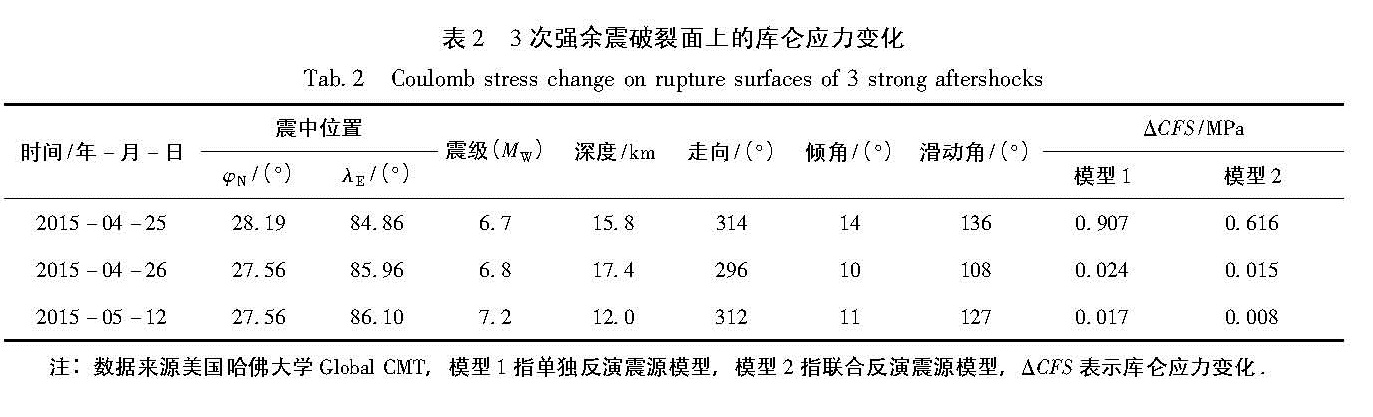
3.1 对3次强余震的触发作用2015年4月25日和4月26日在主震震中附近陆续发生了MW6.7和MW6.8强余震,5月12日在尼泊尔主震的西南部又发生了MW7.2强余震。表2给出了这3次强余震的破裂信息,笔者据此计算了余震破裂面上的库仑应力变化。需要说明的是,大地震发生后的大量余震会产生可以观测到的地表位移场(万永革等,2005),因此余震会对周围区域的应力场产生扰动,所以笔者在计算中考虑了4月25日MW6.7强余震对后续两余震的影响以及4月26日MW6.8强余震对5月12日MW7.2强余震的影响。计算中,MW6.7和MW6.8强余震的错动方向按照表2给出,位错大小、破裂长度、破裂宽度按照经验公式(Wells,Coppersmith,1994)给出。
表2显示,2015年4月25日MW6.7和4月26日MW6.8地震破裂面上库仑应力变化均超过0.01 MPa; 5月12日MW7.2地震破裂面上的库仑应力变化均为正值,但独立反演模型计算的库仑应力变化大于一般认为的库仑应力触发阈值0.01 MPa,而联合反演模型计算的库仑应力变化低于0.01 MPa。表2仅给出了取视摩擦系数为0.6的库仑应力值,笔者还测试了视摩擦系数分别为0.4和0.8的情况,结果类似。两种震源模型的计算结果都支持尼泊尔MW7.9地震触发了4月25日MW6.7和4月26日MW6.8余震,单独反演模型的计算结果支持MW7.9地震触发了5月12日MW7.2余震,联合反演模型的计算结果显示MW7.9地震产生的应力场扰动有利于2015年5月12日MW7.2余震的产生。
3.2 库仑应力变化与余震分布的关系尼泊尔MW7.9地震发生后,截至6月3日,
注:数据来源美国哈佛大学Global CMT,模型1指单独反演震源模型,模型2指联合反演震源模型,ΔCFS表示库仑应力变化.
共记录到其周边发生124次MW>4.0余震,余震的平均震源深度约15 km,几次震级较大的余震震源深度也接近15 km,因此本文采用15 km作为库仑应力变化的计算深度。有研究采用最优破裂面来计算库仑应力变化与余震的对应关系,但最优破裂面的取向取决于区域背景应力场和地震破裂扰动应力场的迭加(King et al, 1994),而往往只能通过震源机制解或者实测应力获得区域背景应力场的方向,对背景应力场大小的获取也局限于浅表的地应力测量(周龙寿等,2013)。因此,对区域背景应力场的估计往往很粗略,故本文仅采用主震破裂面作为库仑应力变化的投影面,计算结果见图3。
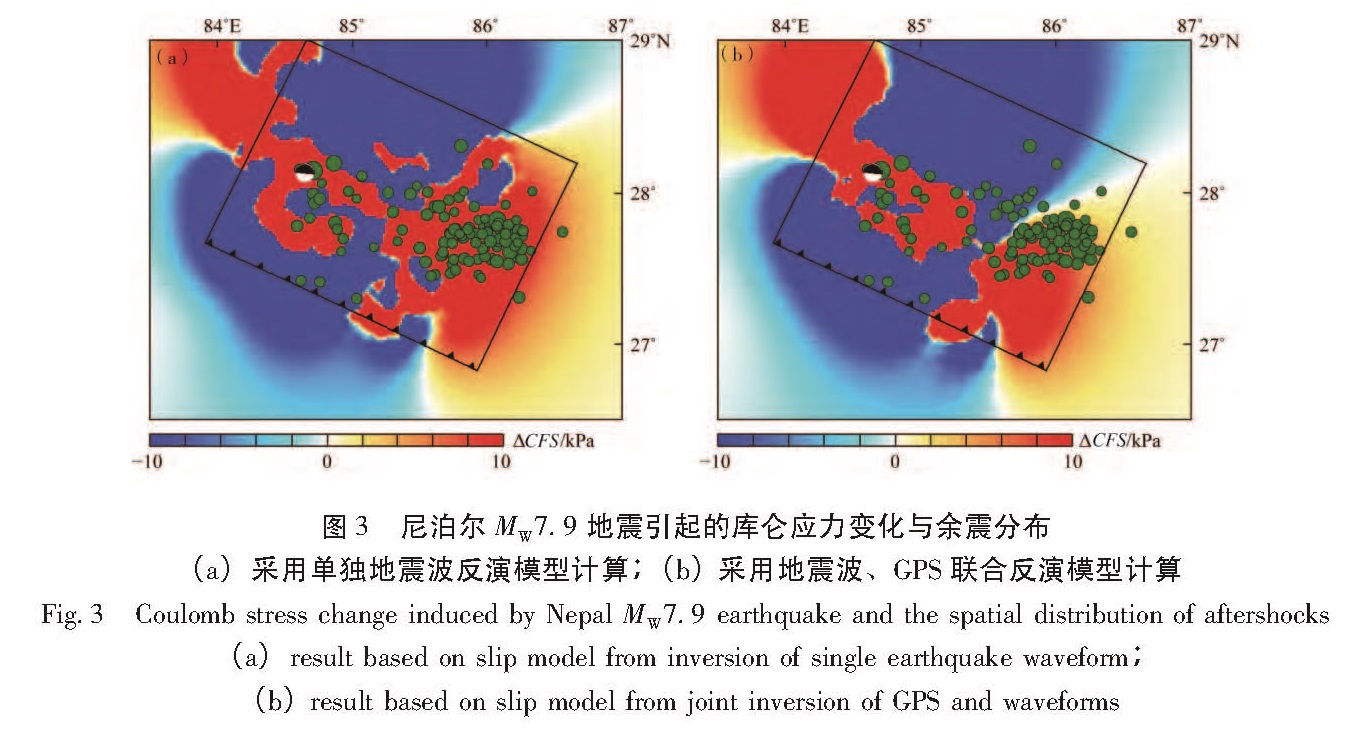
图3a显示,有85.5%的余震落在库仑应力变化正值区,其中78%的余震落在变化大于0.01 MPa的区域。图3b显示,有75.8%的余震落在库仑应力变化正值区,其中32.3%的余震落在变化大于0.01 MPa的区域。两震源破裂模型均显示,余震的分布和库仑应力变化的正值区有很好的对应关系,图3b所示的库仑应力变化正值区面积比图3a小,这可能与联合反演破裂模型的滑动分布范围小于独立反演破裂模型有关。
图3仅给出了取视摩擦系数为0.6的库仑应力值,笔者还测试了视摩擦系数分别为0、0.4、0.8的情况,库仑应力变化与余震分布的对应关系没有发生大的改变,例如,采用图3a的震源破裂模型取视摩擦系数为0和0.8进行计算,分别有81.5%和80.7%的余震落在变化正值区,其中分别有75.8%和76.6%的余震落在变化大于0.01 MPa的区域。
图3 尼泊尔MW7.9地震引起的库仑应力变化与余震分布(a)采用单独地震波反演模型计算;(b)采用地震波、GPS联合反演模型计算
Fig.3 Coulomb stress change induced by Nepal MW7.9 earthquake and the spatial distribution of aftershocks (a)result based on slip model from inversion of single earthquake waveform; (b)result based on slip model from joint inversion of GPS and waveforms4 尼泊尔MW7.9地震对周边断层的影响
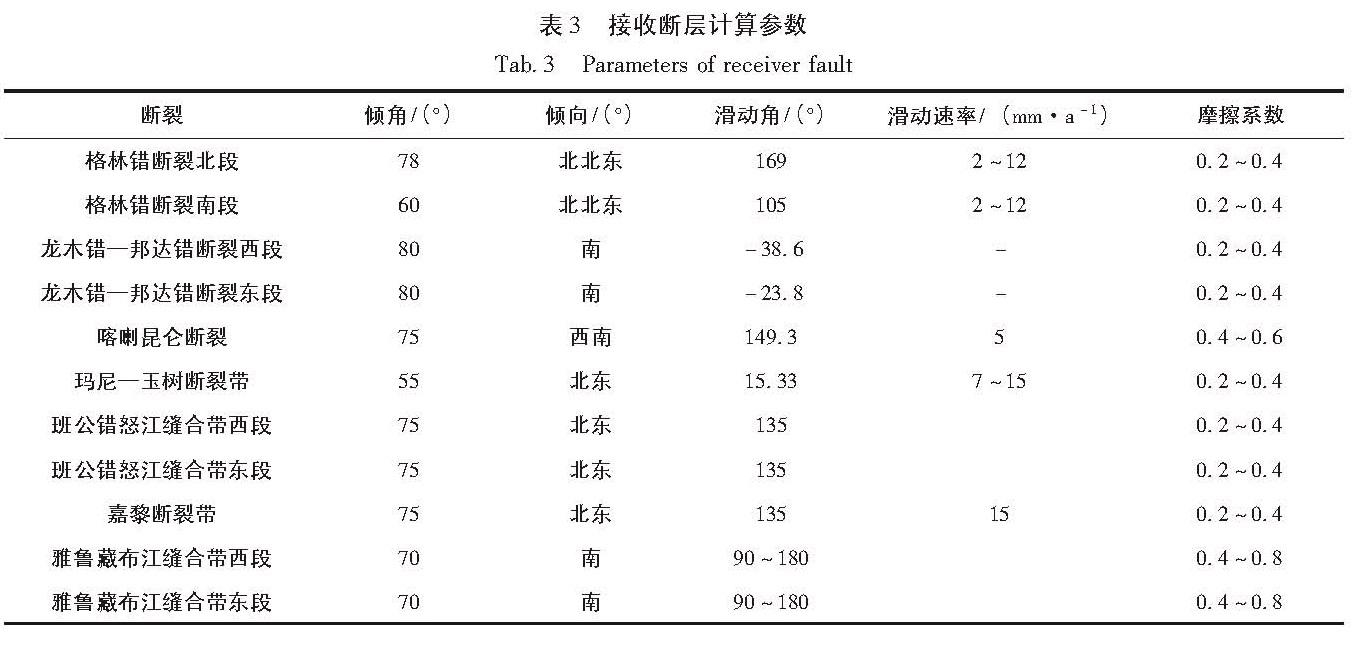
为研究尼泊尔MW7.9地震的发生对附近断裂构造的影响,选取图1中的8条主要活动断裂,计算尼泊尔MW7.9地震震源破裂在这些断层面上产生的库仑应力变化。断层面的走向、倾向、滑动角规定了库仑应力变化计算中的“接收断层”,通过对震源机制解取平均,并根据
参考文献(万永革等,2010; 马杏垣,1989; 彭小龙,王道永,2013; 邓起东,张培震,2002; 肖根如等,2010; 张培震等,2003)得到具体的断层参数,见表3。雅鲁藏布江断裂沿印度与欧亚板块碰撞的缝合带发育,该区海拔高、生存环境恶劣,并且该区可用的地震资料稀少、研究程度很低,尹安(2001)在雅鲁藏布江缝合带发现了大量逆冲推覆构造及其相伴产生的韧性剪切变形带,但张培震等(2003)根据横跨青藏高原南部的GPS观测发现了该断裂活动的迹象,其运动方式为右旋,滑动速率为(5±3)mm/a,因此本文中其滑动角范围为90°~180°。
按照表3各条断层的走向、倾向和滑动角以及
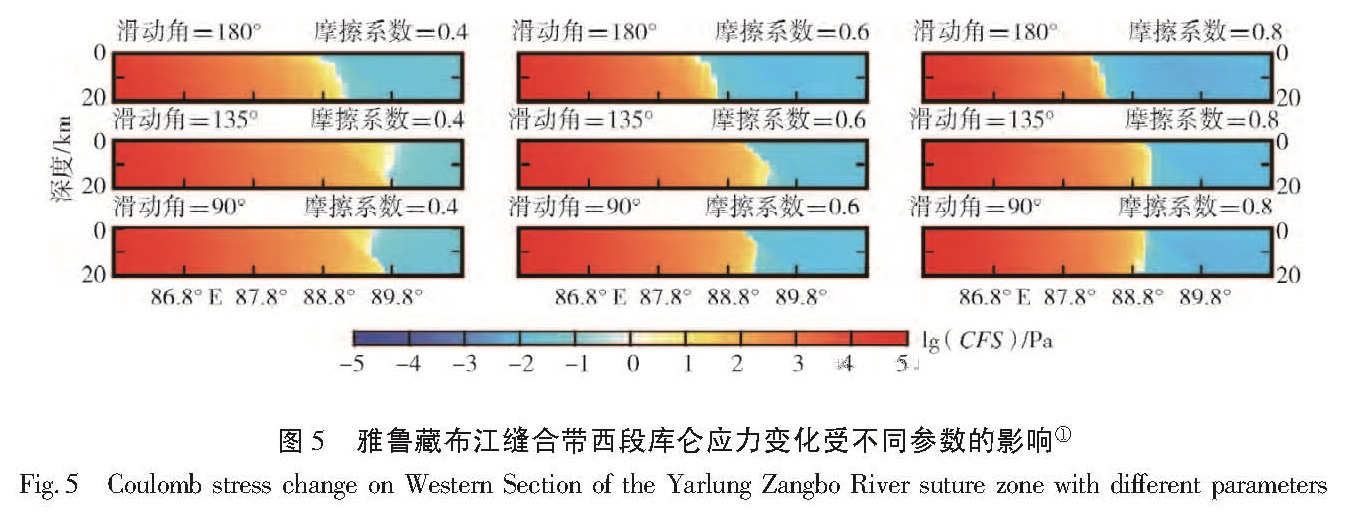
摩擦系数范围计算了各条断层0~20 km深度范围的库仑应力变化,以深度范围里的极值(深度的采样间隔为2 km)来表示断层应力状态的改变,图4仅给出各断层取各自摩擦系数范围中间值的结果,其中雅鲁藏布江缝合带滑动角取中间值135°。为了考察不同滑动角、摩擦系数带来的不确定性,图5给出了单独反演模型计算的雅鲁藏布江缝合带西段断层面在不同滑动角和摩擦系数条件下的库仑应力变化,可以看出不同滑动角、摩擦系数会影响断层上的库仑应力正值区的面积大小。
由图4可以看出,2种震源模型计算的断层面上的库仑应力变化整体特征较为一致。雅鲁藏布江缝合带西段的库仑应力变化正负交替,其西侧的最大库仑应力加载超过了10 kPa,其东侧的最大库仑应力卸载约为0.1 kPa。龙木错—邦达错断裂西段的西侧受到轻微库仑应力卸载作用,龙木错—邦达错断裂西段的东侧、龙木错—邦达错断裂东段、玛尼玉树断裂的库仑应力加载约为0.1 kPa。喀喇昆仑断裂、班公错怒江缝合带、格林错断裂的库仑应力加载约为1 kPa。嘉黎断裂的库仑应力变化正负交替,加/卸载量值均小于0.1 kPa,受本次地震的影响较小。
图4 尼泊尔MW7.9地震引起的青藏高原内部断层的库仑应力变化库仑应力变化的表示采用对数坐标,如果ΔCFS>0则取为lg(CFS),如果ΔCFS<0,则取为-lg(-CFS).(a)采用单独地震波反演模型计算;(b)采用地震波、GPS联合反演模型计算
Fig.4 Coulomb stress change on fault planes induced by Nepal MW 7.9 earthquake (a)result based on slip model from inversion of single earthquake waveform; (b)result based on slip model from joint inversion of GPS and waveform图5 雅鲁藏布江缝合带西段库仑应力变化受不同参数的影响库仑应力变化的表示采用对数坐标,如果ΔCFS>0则取为lg(CFS),如果ΔCFS<0,则取为-lg(-CFS).
Fig.5 Coulomb stress change on Western Section of the Yarlung Zangbo River suture zone with different parameters青藏高原一个最显著的地质特征是在藏南及高原腹地广泛发育的南北向伸展构造如藏南拆离系(STDS)。在先前的讨论中,表3并未给出藏南内部南北向的正断层,根据张进江和丁林(2003)获取了藏南南北向伸展构造的大致产状,作为简化计算了走向北东,倾角、滑动角的典型正断层的库仑应力变化,以此来代表本次地震对藏南的南北向伸展构造的影响,结果见图6。可以看出,在尼泊尔MW7.9地震的西北和东北方向,藏南的南北向伸展构造受到了库仑应力加载作用,量值约为1 kPa。
图6 尼泊尔MW7.9地震引起的藏南伸展构造库仑应力变化(a)采用单独地震波反演模型计算;(b)采用地震波、GPS联合反演模型计算
Fig.6 Coulomb stress on extensional structure in South Tibet induced by Nepal MW 7.9 earthquake (a)result based on slip model from inversion of single earthquake waveforms; (b)result based on slip model from joint inversion of GPS and waveforms5 不确定性讨论
现有的观测资料还不足以对静态库仑应力变化计算提供足够的约束,如介质的纵向分层和横向的不均匀性、初始应力场的未知、震源破裂过程反演的不确定性、孔隙水压力的差异以及断层摩擦性质的差异。单斌等(2009)讨论了断层参数不确定性较高的岷江断裂取不同倾角和滑动角对计算的影响,石耀霖和曹建玲(2010)采用修正的库仑应力计算方法,比较了不同地震破裂模型和视摩擦系数条件下的库仑应力分布差异。王力伟和陈棋福(2010)分析了不同计算模型、断层位置、走向、倾角、摩擦系数等因素对库仑应力变化计算的影响。
地震产生的库仑应力变化强烈依赖于震源模型,如图3a、b所示,在近场库仑应力变化正值区与余震的对应程度存在一定差异。此外,Hayes(2015)在震后1小时发布了震源破裂模型,该模型与张勇等(2015)模型的方法和使用的数据都不一样,笔者在相同的程序和相同的摩擦系数和分层介质参数条件下计算了Hayes模型的库仑应力变化,发现仅49.2%的余震落在库仑应力变化正值区。由于没有足够的同震形变资料,也没有直接的标准判断不同破裂模型的优劣,如果仅以应力变化与后续地震直接的对应性作为标准,张勇等(2015)利用地震波独立单独反演的破裂模型更优。
石耀霖和曹建玲(2010)发现不同的视摩擦系数虽然有一定影响,但不会对库仑应力整体分布图像有太大影响。视摩擦系数的变化改变了正应力变化在库仑应力变化计算中的权重,对于断层面上的库仑应力变化,按照表3中各断层的摩擦系数变化范围做了测试,发现视摩擦系数的影响主要体现在库力应力量值的变化,也可能会导致库仑应力正值区面积的变化,如图5所示,随着视摩擦系数的增加,断层上库仑应力正值区面积增加。此外,滑动角的不确定性对库仑应力的变化影响也较大,对于雅鲁藏布江缝合带西段,当滑动角为135°时库仑应力正值区面积最大。因此,想要获得对地震活动性有指示意义的结果,需要结合更多资料缩小断层参数和视摩擦系数的不确定范围。
研究区域包含了拉萨、羌塘和板块边界等构造块体,EDGRN/EDCMP软件只能计算横向均匀、纵向分层模型的格林函数,因此比较不同地壳模型对库仑应力变化的影响,根据Crust2.0给出的拉萨块体、羌塘块体和板块边界的地壳模型参数,计算不同的分层地壳模型的同震形变。采用不同地壳模型,结果的差异主要体现在库仑应力变化的量值,例如对于雅鲁藏布江缝合带,不同地壳模型的计算结果的平均相对变化量不超过12.8%。此外,由图5可以看出,地壳模型差异对计算结果的影响较断层面上滑动角的不确定性产生的影响要小,因此作为一级近似,本文采用横向均匀、纵向分层的模型进行计算是可以接受的。需要指出的是,真实地壳具有很强的横向不均匀性,地表和莫霍面等圈层也具有较大的起伏,需要在将来采用数值方法建立更为接近真实的模型,更精确地计算库仑应力变化。
6 结论与讨论
本文根据地震静态触发原理,利用已发布的有限断层模型,计算了尼泊尔MW7.9地震引起的同震库仑应力变化对余震的触发作用,并分析了对邻近主要活动断层的影响。主要结论如下:
(1)尼泊尔MW7.9地震对4月25日MW6.7和4月26日的MW6.8强余震有显著触发作用,MW7.9地震产生的应力场扰动有利于5月12日MW7.2余震的产生。
(2)单独反演和联合反演两个震源破裂模型均显示,余震的分布和库仑应力变化的正值区有很好的对应关系,分别有85.5%和75.8%的余震落在库仑应力变化正值区。
(3)雅鲁藏布江缝合带西段的西侧受到超过10 kPa的库仑应力加载,地震活动性增强。喀喇昆仑断裂、班公错怒江缝合带、格林错断裂的库仑应力加载约为1 kPa。龙木错—邦达错断裂、玛尼玉树断裂以及嘉黎断裂的库仑应力加/卸载小于0.1kPa,受本次地震的影响较小。
(4)在尼泊尔MW7.9地震的西北和东北方向,藏南典型南北向伸展构造受到了库仑应力加载作用,量值约为1 kPa。
震源滑动模型对同震应力变化的计算影响较大,尤其在离震源较近的近场区域。本文采用的两个震源破裂模型在近场的库仑应力变化有较大差别,但远场断层面上库仑应力变化的整体特征比较一致。此外,Hayes(2015)利用远场地震波数据反演得到了一个震源破裂模型,由于缺乏近场的地震波数据约束,使用该模型在实际计算中得到的近场库仑应力变化与余震对应的并不好,仅有不超过半数的余震落在库仑应力变化正值区。特别地,本文使用的两个震源模型来源于同一作者,它们的差别仅在于反演过程中是否考虑GPS数据,因此只是在滑动量的幅值和分布面积上有一些差别。但每次大地震发生后,不同作者给出的破裂模型往往具有很大差异,如2010年Mentawai MW7.8地震反演工作中,不同研究得到的最大滑动量可介于3.5~20 m之间(Lay et al, 2011; Yue et al, 2014)。因此,为了提高计算结果的可靠性,将来需要使用基于更多近场地震波数据和大地测量数据反演得到的断层破裂模型。
断层的视摩擦系数、滑动角具有较大的不确定性,在地震活动性分析中,应该重视参数的不确定性引起的库仑应力变化正值区的改变。本文采用了横向均匀、纵向分层模型,真实地球介质的横向不均匀性对库仑破裂应力变化的计算结果有一定影响,需要在未来利用数值手段建立更接近真实的模型来计算库仑应力变化。此外,在研究库仑应力变化与余震分布的对应关系时,将来建立在余震精定位和更完整的地震序列基础上的分析工作将更具可靠性。
受限于目前还没有可以利用的大量余震的震源破裂信息,本文仅考虑了二次强余震对库仑应力变化的影响,大量的余震活动对该区域的应力变化产生多大影响?根据万永革等(2005)的研究结果,Landers地震后发生大量余震活动,产生的位移场方向与主震大体一致达到厘米量级,不足主震产生位移场的10%。据此可推论,大量余震对库仑应力变化的空间模式改变不会很大,但对绝对量值会有一定改变。下地壳、上地幔的黏弹性松弛效应,也对库仑破裂应力变化结果产生一些影响,但本文讨论的是地震发生后短期内的弹性响应,时间尺度远低于流变介质松弛时间。另外,本文未考虑背景应力场,动态应力触发,流体作用等因素,相关内容需继续深入研究,本文的研究仅从一个角度提供一个有意义的参考。
-
陈连旺,张培震,陆远忠等. 2008. 川滇地区强震序列库仑破裂应力加卸载效应的数值模拟[J]. 地球物理学报, 51(5): 1411-1421.
单斌,熊熊,郑勇等. 2009. 2008年5月12日MW7. 9汶川地震导致的周边断层应力变化[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 39(5): 537-545.
邓起东,程绍平,马冀等. 2014. 青藏高原地震活动特征及当前地震活动形势[J]. 地球物理学报, 57(7):2025-2042.
邓起东,张培震. 2002. 中国活动构造基本特征[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 32(12): 1020-1030.
李玉江,陈连旺,陆远忠等. 2013. 汶川地震的发生对周围断层稳定性影响的数值模[J]. 中国地质大学学报:地球科学, 38(2): 398-410.
马杏垣. 1989. 中国岩石圈动力学图集[M]. 北京:中国地图出版社.
彭小龙,王道永. 2013. 雅鲁藏布江断裂带活动构造特征与活动性分析[J]. 长江大学学报(自然版),10(9):41-44.
沈正康,万永革,甘卫军等. 2003. 东昆仑活动断裂带大地震之间的粘弹性应力触发研究[J].地球物理学报, 46(6):786-795.
石耀霖,曹建玲. 2010. 库仑应力计算及应用过程中若干问题的讨论——以汶川地震为例[J]. 地球物理学报, 53(1):102-110.
万永革, 沈正康, 兰从欣. 2005. 兰德斯地震断层面及其附近余震产生的位移场研究[J]. 地震学报, 27(2):139-146.
万永革,沈正康, 盛书中等. 2009. 2008年汶川大地震对周围断层的影响[J]. 地震学报, 31(2): 128-139.
万永革,沈正康, 盛书中等. 2010. 2008年新疆于田7. 3级地震对周围断层的影响及其正断层机制的区域构造解释[J]. 地球物理学报, 53(2):280 -289.
万永革,吴忠良,周公威等.2000. 几次复杂地震中不同破裂时间之间的"应力触发"问题[J].地震学报, 22(6):568-575.
万永革,吴忠良,周公威等.2002. 地震静态应力触发模型的全球检验[J]. 地震学报, 24(3):301-315.
王力伟,陈棋福. 2010. 以2008年汶川8.0级地震为例分析地震触发的静态库仑应力计算的不确定性[J]. 中国地震, 26(3):251-264.
肖根如,甘卫军,陈为涛等. 2010. 青藏高原班公—怒江缝合带现今运动状况的GPS观测研究[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 40(6):1496 -1502.
尹安. 2001. 喜马拉雅—青藏高原造山带地质演化[J]. 地球学报, 22(3):194 -230.
张进江,丁林. 2003. 青藏高原东西向伸展及其地质意义[J]. 地质科学, 38(2): 179-189.
张培震,王敏, 甘卫军等. 2003. GPS观测的活动断裂滑动速率及其对现今大陆动力作用的制约[J]. 地学前缘,(S1):82 -92.
张勇,许力生, 陈运泰. 2015. 2015年尼泊尔MW7.9地震破裂过程:快速反演与初步联合反演[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(5):1804 -1811.
周龙寿,丁立丰,郭啟良.2013.不同压裂介质影响下绝对应力测值的试验研究[J].岩土力学,34(10):2870-2876.
中国地震局地球物理研究所.2015.2015年4月25日尼泊尔8.1级地震[EB/OL].(2015-04-25)[2015-05-02].http://www.cea-igp.ac.cn/tpxw/272110.shtml
Avouac J P, Ayoub F, Leprince S. 2006. MW 7.6 Kashmir earthquake: Sub-pixel correlation of ASTER images and seismic waveforms analysis [J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 249(3): 514-528.
Bassin C, Laske G, Masters, G. 2000. The Current Limits of Resolution for Surface Wave Tomography in North America[C].Los Angeles:EOS Trans AGU, 81, F897.
Gupta H, Gahalaut V K. 2014. Seismotectonics and large earthquake generation in the Himalayan region [J]. Gondwana research, 25(1): 204-213.
Harris R A. 1998. Introduction to Special Section: Stress Triggers, Stress Shadows, and Implications for Seismic Hazard[J]. J. Geophys. Res, 103: 24347-24358.
Hayes.2015.Updated Finite Fault Results for the Apr 25, 2015 MW 7.9 35 km E of Lamjung, Nepal Earthquake(Version 2)[EB/OL].(2015-04-25)[2015-05-02]. http://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/eventpage/us2002926#scientific_finitefault.
Jaumé S C, Sykes L R.1996. Evolution of moderate seismicity in the San Francisco Bay region, 1850 to 1993: Seismicity changes related to the occurrence of large and great earthquakes[J]. J Geophys Res, 101(B1): 765-789.
King G C, Stein R S, Lin J. 1994. Static stress changes and the triggering of earthquakes[J]. Bull seismol Soc Am, 84(3): 935-953.
Lay T, Ammon C J, Kanamori H, et al. 2011. The 25 October 2010 Mentawai tsunami earthquake(MW 7.8)and the tsunami hazard presented by shallow megathrust ruptures [J]. Geophys Res Lett, 38(6): 514-528.
Okada Y. 1992. Internal deformation due to shear and tensile faults in a half-space[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 82(2): 1018-1040.
Parsons T, Ji C, Kirby E. 2008. Stress changes from the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake and increased hazard in the Sichuan basin[J]. Nature, 454: 509-510.
Parsons T, Stein R S, Simpson R W, et al. 1999. Stress sensitivity of fault seismicity; a comparison between limited-offset oblique and major strike-slip faults [J]. J Geophys Res, 104: 20183-20202.
Sapkota S N, Bollinger L, Klinger Y, et al. 2013. Primary surface ruptures of the great Himalayan earthquakes in 1934 and 1255[J]. Nature Geoscience, 6(1): 71-76.
Stein R S, Lisowski M. 1983. The 1979 Homestead Valley earthquake sequence, California: Control of aftershocks and postseismic deformation[J]. J Geophys Res, 88(B8): 6477-6490.
USGS.2015.General summary, 2015 MW 7.9 35 km E of Lamjung, Nepal Earthquake(Version 2)[EB/OL].(2015-04-25)[2015-05-02]. http://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/eventpage/us20002926#general_summary
- ] Wang R, Martín F L, Roth F. 2003. Computation of deformation induced by earthquakes in a multi-layered elastic crust-FORTRAN programs EDGRN/EDCMP[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 29(2): 195-207. Wells D L,Coppersmith K J. 1994. New empirical relationships among magnitude,rupture width,rupture area,and surface displacement[J]. Bull Seism Soc Am, 84(4):974 -1002. Yue H, Lay T, Rivera L, et al. 2014. Rupture process of the 2010 MW 7.8 Mentawai tsunami earthquake from joint inversion of near-field hr-GPS and teleseismic body wave recordings constrained by tsunami observations[J]. J Geophys Res, 119(7): 5574-5593.