基金项目:国家自然基金项目(51208411,51408453)、陕西省文物局重点科技项目(2011-K-008)和陕西省教育厅专项科技项目(12JK0899,2010JK635)联合资助.
(西安建筑科技大学 土木工程学院,陕西 西安 710055)
(Civil Engineering Department, Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, Xi'an 710055, Shaanxi, China)
multi-layer wooden structure; ancient architecture; damage model; total energy consumption of destruction; earthquake damage assessment; damage coefficient
备注
基金项目:国家自然基金项目(51208411,51408453)、陕西省文物局重点科技项目(2011-K-008)和陕西省教育厅专项科技项目(12JK0899,2010JK635)联合资助.
以西安城墙永宁门箭楼为研究对象,评估震后多层木结构古建筑的破坏程度,根据各主要耗能构件在低周水平反复荷载作用下的滞回耗能特性,计算其构件破坏总耗能; 根据地震模拟振动台试验,计算不同地震工况下各耗能构件所耗散的能量,在此基础上建立主要耗能构件相应的破坏模型。对三个主要耗能部位:柱架榫卯节点、斗栱结构层和柱础进行地震破坏状态评估; 引入能量分配系数建立主要耗能构件破坏状态与整体结构破坏状态之间的关系,继而得出整体结构的破坏系数以反映整体结构在不同地震作用下的破坏状态,研究结果可为多层木结构古建筑的抗震加固提供参考借鉴。
Take Embrasure watchtower of Yongning Gate of Xi'an City Wall as a research subject, we made a reasonable assessment for the extent of damage to the ancient architecture with multilayer wooden structure after the earthquake. Based on the hysteretic energy properties of the major energy-dissipation components under low-cycle levels cyclic loading, we calculated the damage total energy consumption of the component. According to the seismic simulation shaking table test, we calculated the dissipated energy induced by each energy-dissipation component under different seismic conditions. And on the basis of it, we established the damage model of major energy-dissipation component under different seismic action. We also made the earthquake damage assessment of three major energy-dissipation parts: the column frame straight mortise tenon joint, brackets structure layer and column bases layer. Then introducing the energy distribution coefficient, we built the relationship of damage state between major energy component and overall structure to obtain destroy coefficients of the whole structure to reflect the damage state of overall structure under different earthquake. The obtained results can provide the reliable theoretical basis for the seismic reinforcement of ancient architecture with multi-layered wood structure.
引言
中国古建筑是世界建筑体系中的独立系统,主要以木构架作为承重体系,自其诞生、演变与发展至今,已有近七千年的历史,承载着丰富的历史文化信息(刘致平,1987)。随着国家对古建筑保护力度的不断加强,有关古建筑的研究,已从过去着重于历史、考古和建筑规制等方面扩展到结构与抗震性方面。相关的研究(方东平等,2001; 薜建阳等,2004)以及现残存的许多木结构古建筑,均已证明其具有优良的抗震性能。以往的专家学者对古建筑的抗震性能进行研究,为其在震后的损坏评估和修缮加固提供科学参考依据,是古建筑保护的重要工作。李铁英等(2004)对山西应县木塔的结构残损机制,静、动力特性以及结构加固修缮方面进行了全面系统的研究,提出了结构双参数地震损坏准则,并对其结构震害等级进行了划分和评估。方东平等(2001)通过对西安城墙安远门(即北城门)箭楼的现场测试,得出其结构动力特性和在地震作用下的动力响应规律,并对木结构古建筑的维修加固提出了科学建议。薛建阳等(2004)基于宋《营造法式》的规制,制作了缩尺比为1:3.52的古建筑木结构及其构件模型,进行了相应的地震模拟振动台试验和拟静力试验研究,探索了古建筑木结构在地震动环境中的减隔震机理。李鹏等(2010)对藏式古建筑多柱式结构的力学性能进行了研究,分析了导致其破坏的主要因素、结构破坏的顺序和形式。谢启芳等(2010)和周乾等(2009)基于汶川地震后木结构古建筑震害的实际考察,综合分析了古建筑木结构震害的基本特征,总结了相应的教训和启示。以上这些研究工作,均从不同的广度和深度探究了中国木结构古建筑的抗震机制、破坏等级及具体的损坏评估方法,但都未从结构能量耗散减震的角度评估其抗震性能及破坏状况。现行的《古建筑木结构维护与加固技术规范》(GB50165 —1992)也是根据结构的“残损点”定性地给出结构或构件残损界限,而没有给出定量的评估标准和方法。为弥补该方面研究工作的不足,同时也作为对古建筑木结构抗震能力评估手段的一种探索和尝试,本文以西安城墙永宁门箭楼复建工程为背景,建立古建筑木结构损坏与其耗能的内在关系,并基于能量的原则和标准对其损坏等级作出评估。根据试验设备负载能力,按荷载配重相似关系制作了1:6的箭楼结构中部三间木构架模型及其结构构件模型,进行了相应的地震模拟振动台试验和拟静力试验的研究,对其结构各个部分吸收或耗散的能量进行量化,继而建立能量耗散与结构损坏之间的对应关系,并据此建立木结构古建筑基于能量耗散标准评判其破损等级的模式。
1 试验概况
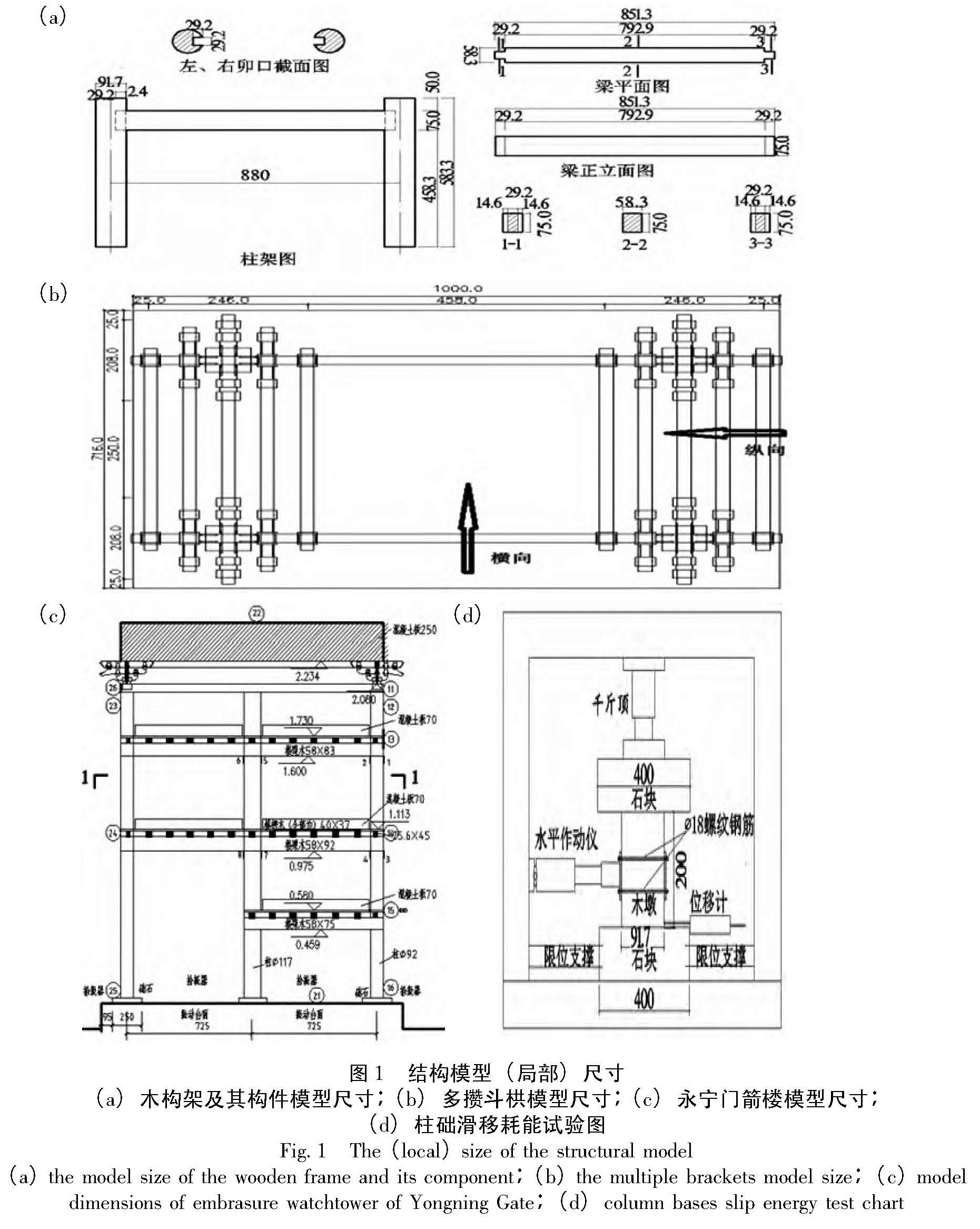
1.1 试验内容试验研究分为拟静力试验和动力试验两个部分。拟静力试验包括:柱底面与础石之间低周水平循环作用下的摩擦耗能试验、木构架榫卯节点模型、斗栱铺作层模型在低周水平反复作用下的拟静力试验; 动力试验部分为永宁门箭楼中间部位三间木结构柱架模型(缩尺比为1:6)的地震模拟振动台试验(图1),其尺寸单位为mm。
(a)
(b)
(c)(d)
图1 结构模型(局部)尺寸(a)木构架及其构件模型尺寸;(b)多攒斗栱模型尺寸;(c)永宁门箭楼模型尺寸; (d)柱础滑移耗能试验图
Fig.1 The(local)size of the structural model(a)the model size of the wooden frame and its component;(b)the multiple brackets model size;(c)model dimensions of embrasure watchtower of Yongning Gate;(d)column bases slip energy test chart1.2 整体模型设计试验模型以西安城墙永宁门箭楼为原型,根据试验设备的大小及负载能力,确定缩尺比为1:6。根据清工部《工程做法则例》(梁思成,2006)中有关楼面荷载的规定,以及试验模型与原型间荷载相似关系设计确定混凝土配重板(模拟屋盖),三层、二层及一层楼板的配重分别为64 kN、4 kN、4 kN、2 kN(图1c)。
模型按其结构组成,沿竖向可分为柱础层、柱架层、屋盖层。柱础层的础石为青石板,用螺栓固定于振动台台面上; 柱脚平摆浮搁于础石上,柱架结构由柱、梁、枋组成,屋盖结构部分则由RC配重板模拟。
2 多层木结构古建筑地震作用下的耗能分析
通过永宁门箭楼模型振动台试验可知,在地震作用下其整体结构主要依靠斗栱铺作层滑移摩擦,柱架榫卯节点摩擦转动,柱础滑移等部位的耗能来减小地震作用对其所造成的损坏。对于以上3个耗能构件,为简化计算,根据在水平地震作用下结构的水平位移,通过各工况模拟地震作用下各层间的剪力—层间位移试验滞回曲线求得相应各构件所耗散的能量。根据地震模拟振动台试验结果,将模型结构简化为多质点体系,其各层的总剪力r(ti)(邱法维等,2000)为
r(ti)=Σnj=kmjx··j(ti).(1)
式中,j代表层号; x··j(ti)为ti时刻第j层质心的绝对加速度值(mm/s2); mj为第j层的质量(kg)。结构模型在n工况地震作用下的层间累积滞回耗能(邱法维等,2000)为
Enk=Σni=11/2[tk(ti)+rk(ti-1)][Δx(ti)-Δx(ti-1)].(2)
式中,Enk为第k层的滞回耗能(N·m); rk(ti)为ti时刻第k层的剪力(N),Δxk为第k层的层间位移(mm),求和上限m为振动持时段内的全部采样点数。图2反映了不同工况地震作用下的各耗能构件的累积滞回耗能量随时间ti的变化。
通过以上分析,并按照式(1)、(2)计算,可分别得出柱础、木柱架以及斗栱铺作层相应的地震剪力和累积滞回耗能。
图2 不同地震工况下模型的累积滞回耗能
(a)Ⅷ度基本地震烈度;(b)Ⅷ度罕遇地震烈度
Fig.2 Cumulative hysteretic energy dissipation of the model under different seismic working condition(a)basic seismic intensity of Ⅷ degrees;(b)intensity of rare earthquake with Ⅷ degrees在地震作用下,结构的主要耗能能力依次为柱架的榫卯节点耗能,柱础以及斗栱铺作层的摩擦滑移耗能,其中柱架耗能占结构总滞回耗能的65%以上,而且随着地震作用的增强,柱架榫卯节点在整体结构中的耗能增加较快,斗栱铺作层和柱础的摩擦滑移耗能则增加较慢。
3 永宁门箭楼主要耗能构件地震破坏
5 结论
通过对西安永宁门箭楼结构模型的振动台试验及其构件模型的拟静力试验并进行基于能量的分析研究,可得出以下结论:
(1)多层古建筑木结构的主要耗能方式是柱架榫卯节点的变形与摩擦滑移耗能。随着地震作用强度的增大,在整体结构耗能中榫卯节点耗能所占比例减小,而斗栱和柱础的耗能比例增加,说明在小震作用下柱架榫卯节点起主要的耗能减震作用,在中震作用下斗栱层和柱础发生摩擦滑移而共同隔震减振。
(2)利用耗能构件地震破坏评估模型可定量计算出柱架、斗栱铺作层和柱脚层在各工况地震作用下的破坏系数,并据此评估结构的破坏状态。
(3)基于能量分配系数并根据斗栱、榫卯节点以及柱脚这3个主要耗能构件建立了西安永宁门箭楼多层木结构地震破坏评估模型,通过理论计算与试验结果的对比分析,两者基本相符合,由此证明了本文基于能量标准的木结构古建筑破坏评估模型的合理性。
(4)本文的研究方法与结论,可为永宁门箭楼以及同类多层木结构古建筑的复建与抗震加固提供参考和借鉴。
评估
通过模型振动台试验可知,木结构古建筑在水平地震作用下的破坏主要发生在柱架的榫卯节点,斗栱铺作层和柱础部位。结构的破坏主要缘于其在地震作用下所吸收地震能量超过了其所能承受的限度; 其中结构耗散能量是由榫卯节点中榫头与卯口的因摩擦、滑移变形、斗栱铺作层榫头的剪切变形和摩擦滑移,以及柱、础间的摩擦滑移组成。在此过程中,结构各个构件的变形不断增大并导致其先后出现不同程度的破坏,即结构或构件最终的破坏过程实质上是其能量的吸收和耗散达到极限的过程(于琦等,2011)。
3.1 破坏模型结构耗能能力为结构受力与变形达到极限状态时所能吸收的能量,即结构在低周反复荷载作用下丧失承载力或承载力急剧降低时所能耗散的累积滞回能量(建筑抗震试验方法,JGJ 101—1996); 笔者将“构件破坏总耗能”定义为对应于构件达到承载力与变形极限状态时刻的累积损伤耗能量,由于往复的地面运动使结构(构件)材料性能逐步退化并最终导致其丧失承载与变形能力的结果。低周反复荷载作用下结构构件在第j循环的受力状态所能耗散的能量公式为
Ekj=Skj,(3)
则有,Ek=Σmj=1Ekj.(4)
式中,Ekj为第k构件经正反向位移±δj循环作用后所耗散的能量,m为构件发生破坏时低周反复循环作用次数,Ek为第k构件经m个循环作用后所耗散的总能量。
图2为各构件在不同工况地震作用下的累积滞回耗能随时间的变化曲线。根据构件的“构件破坏总耗能”和“各工况地震作用下的累积滞回耗能”,今定义构件k在n工况地震作用下的破坏系数Dkn为该构件在n工况地震作用下的累积滞回耗能与地震作用下“构件破坏总耗能”的比值(薛建阳等,2012),即
Dkn=(Enk)/(Ek).(5)
3.2 地震破坏评估根据结构模型振动台试验以及构件模型的拟静力试验,并考虑古建筑木结构的抗震性能特点,将直榫柱架的榫卯节点、斗栱铺作层和柱础看成结构的3个耗能构件,依据其相应的破坏评估系数对永宁门箭楼整体结构中的直榫柱架榫卯节点、斗栱铺作层和柱础做水平地震作用下的损坏评估,得到其主要耗能构件在不同地震加速度作用下的破坏程度,为永宁门箭楼及类似结构的复建和加固提供了科学的理论依据。
(1)直榫柱架榫卯节点的破坏评估
以永宁门箭楼为结构原型,按缩尺比1:6设计了3个尺寸相同的木构架模型,其节点连接方式均是半榫节点。根据模型与原结构的荷载相似关系,在16.2 kN的竖向集中力作用下,进行了拟静力试验。得出了相应6个榫卯节点的节点弯矩转角曲线(高大峰等,2014a),如图3所示。柱架结构因其榫卯节点的榫头与卯口间互相挤压导致其局部残余变形不断累积、连接能力不断下降,以致于成为机构而破坏。
根据式(3)并借助于Origin 8.0软件对上述36个榫卯节点的构件破坏总耗能进行计算,结果如表1所示。
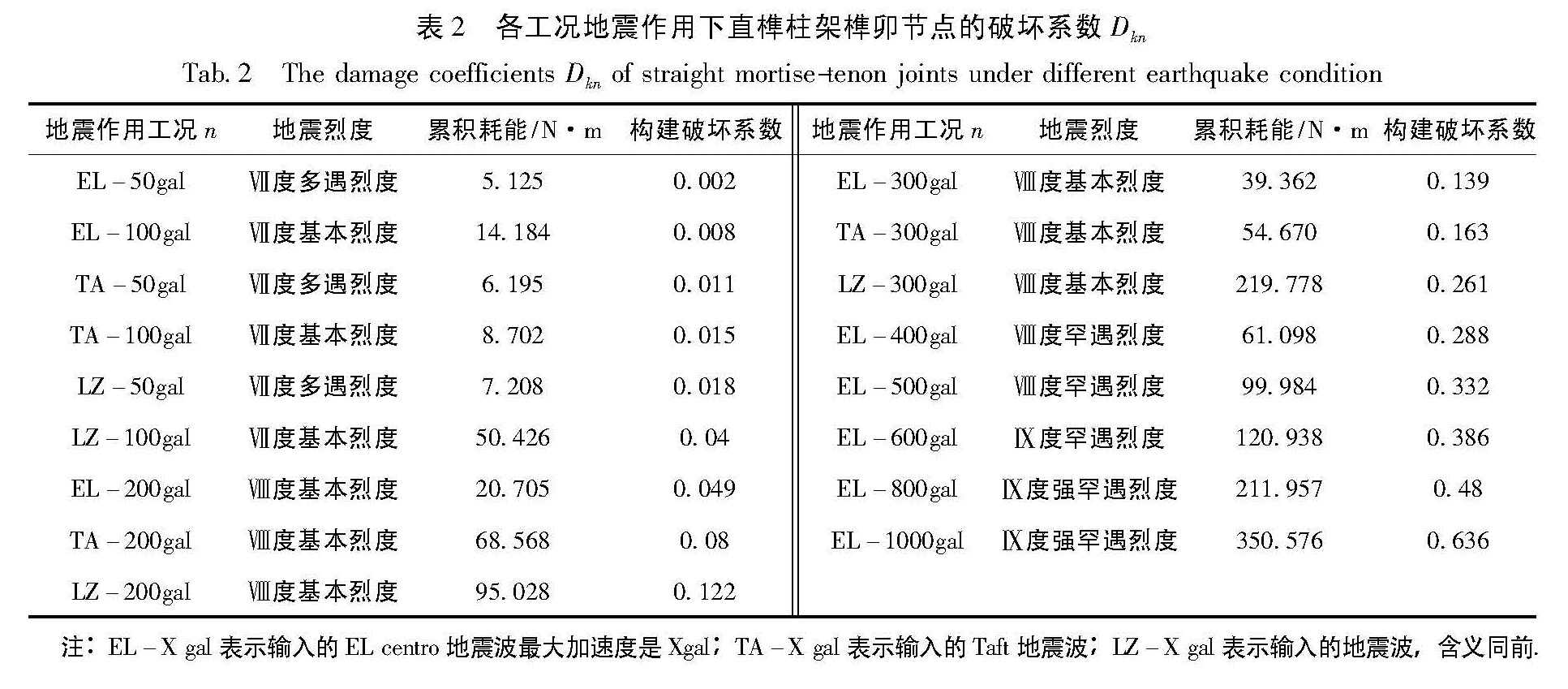
根据图2得出的各地震工况下的直榫柱架榫卯节点的累积耗能,表1列出相应的构件破坏总耗能,并结合隋龑等(2010)对古代殿堂式木结构古建筑当心间缩尺模型的振动台试验研究,得到在地震作用过程中,单层殿堂式古建筑木结构主要通过柱架层榫卯节点的转动变形滞回耗能; 由张锡成(2013)对古建筑木结构抗震能力的分析可知,由榫卯连接的柱架耗能占其结构总耗能的主要部分。简化计算,将模型结构所有榫卯节点的耗能求和,今将模型结构在水平地震作用下的总耗能等效为柱架模型24个榫卯节点的耗能之和(注,这里因构件本身弹塑性变性所耗能量占的比例小而忽略之),按照式(5)并根据地震加载工况逐级累积计算出榫卯节点破坏系数(表2)。
on the right joint;(c)hysteretic energy curve of wooden frame 2 on the left joint;(d)hysteretic energy curve of wooden frame 2 on the right joint;(e)hysteretic energy curve of wooden frame 3 on the left joint; (f)hysteretic energy curve of wooden frame 3 on the right joint图3 直榫柱架滞回耗能曲线
(a)木构架1左侧节点滞回耗能曲线;(b)木构架1右侧节点滞回耗能曲线;(c)木构架2左侧节点
滞回耗能曲线;(d)木构架2右侧节点滞回耗能曲线;(e)木构架3左侧节点滞回耗能曲线; (f)木构架3右侧节点滞回耗能曲线
Fig.3 Hysteretic energy curves of straight tenon-mortise joints(a)hysteretic energy curve of wooden frame 1 on the left joint;(b)hysteretic energy curve of wooden frame 1表2 各工况地震作用下直榫柱架榫卯节点的破坏系数Dkn
Tab.2 The damage coefficients Dkn of straight mortise-tenon joints under different earthquake condition注:EL-X gal表示输入的EL centro地震波最大加速度是Xgal; TA-X gal表示输入的Taft地震波; LZ-X gal表示输入的地震波,含义同前.
根据永宁门箭楼木结构模型振动台试验结果,并结合表2中直榫柱架在各级地震作用力下的破坏系数可知:在水平地震激励作用下,当设计地震波输入为600 gal(对应九度罕遇地震作用),直榫柱架的破坏系数为0.386,榫卯节点出现轻微拔榫现象,在三层东南梁东侧榫头拔出4 mm,如图4b所示; 地震波输入为800 gal时,因为直榫榫头与卯口之间的挤压作用,榫头最大拔出达到10 mm(占榫头的总长度的1/3),结合破坏系数约为0.5,判断直榫(柱架)已达到中等破坏,但仍具有较好的承载力和稳定性; 当地震波输入增至1 000 gal时,在西南柱三层横向卯口部位出现劈裂缝,此时榫卯节点已达到其极限承载力(构件其他部件的受力仍处于弹性范围),破坏系数达到0.7,构件破坏严重但结构尚未达到极限承载力。由此可知,多层木结构由于其榫卯节点耗能特性,即使在结构破坏严重的情况下,仍能保持一定的承载力。
图4 模型榫卯节点损伤情况(a)中框架东跨梁榫头拔出;(b)东南梁榫头拔出
Fig.4 The damage state of the model mortise-tenon joint(a)the east span beam tenon in the framework was drawn;(b)southeast beam tenon was drawn(2)斗栱结构层的破坏情况
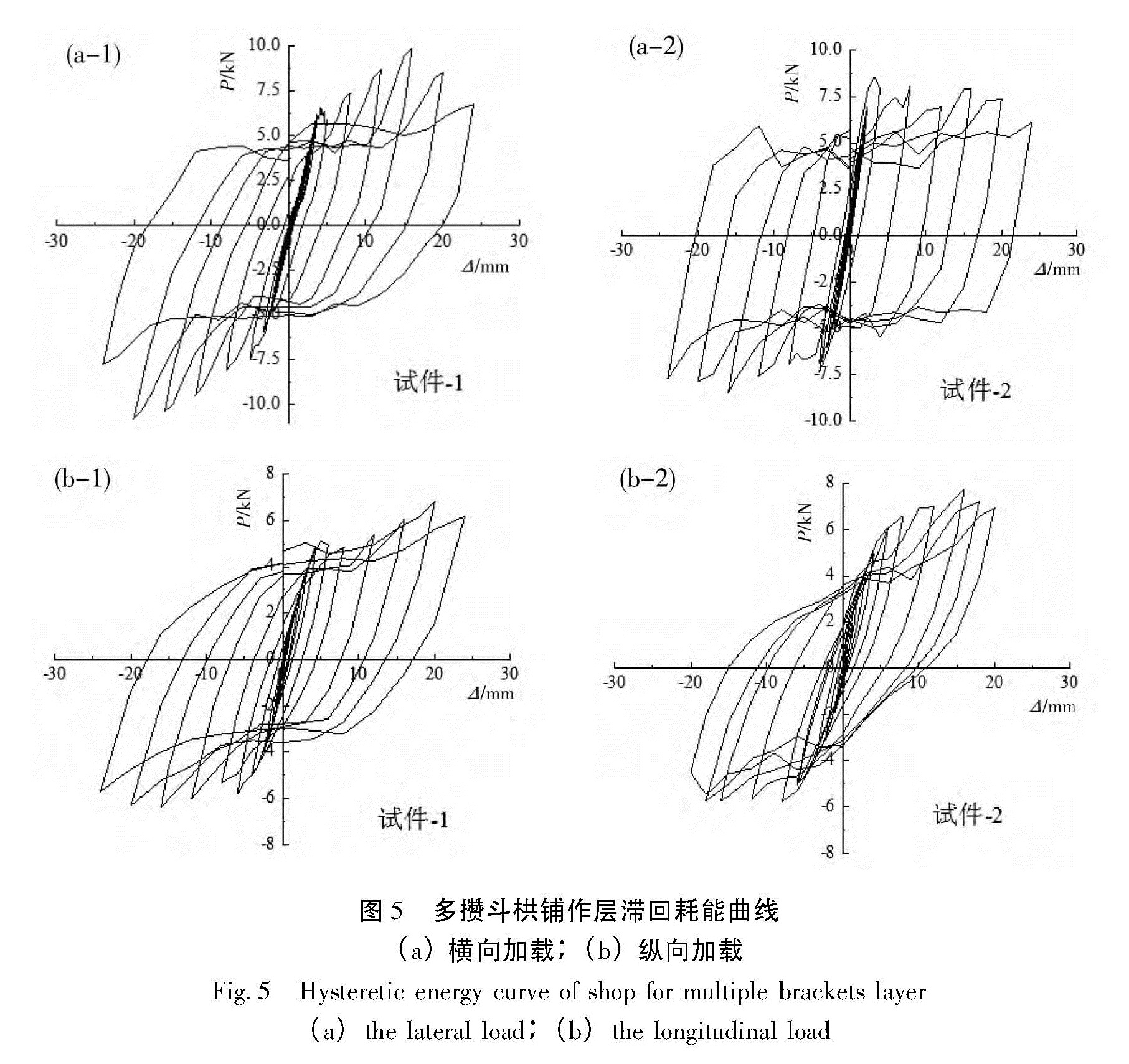
依据模型与原型的结构荷载相似关系,需在斗栱铺作层施加32 kN的竖向荷载,进行低周水平反复作用下的拟静力试验,得到了两组相应的滞回耗能曲线(高大峰等,2014b),利用Origin 8.0软件对该两组斗栱铺作层进行构件破坏总耗能计算。根据《古建筑木结构维护与加固技术规范》(GB50165-92)以及拟静力试验的结果,规定当坐斗滑移量超过其底面边长的一半时,即认为斗栱铺作层发生极限破坏,试验结果如表3、图5所示。
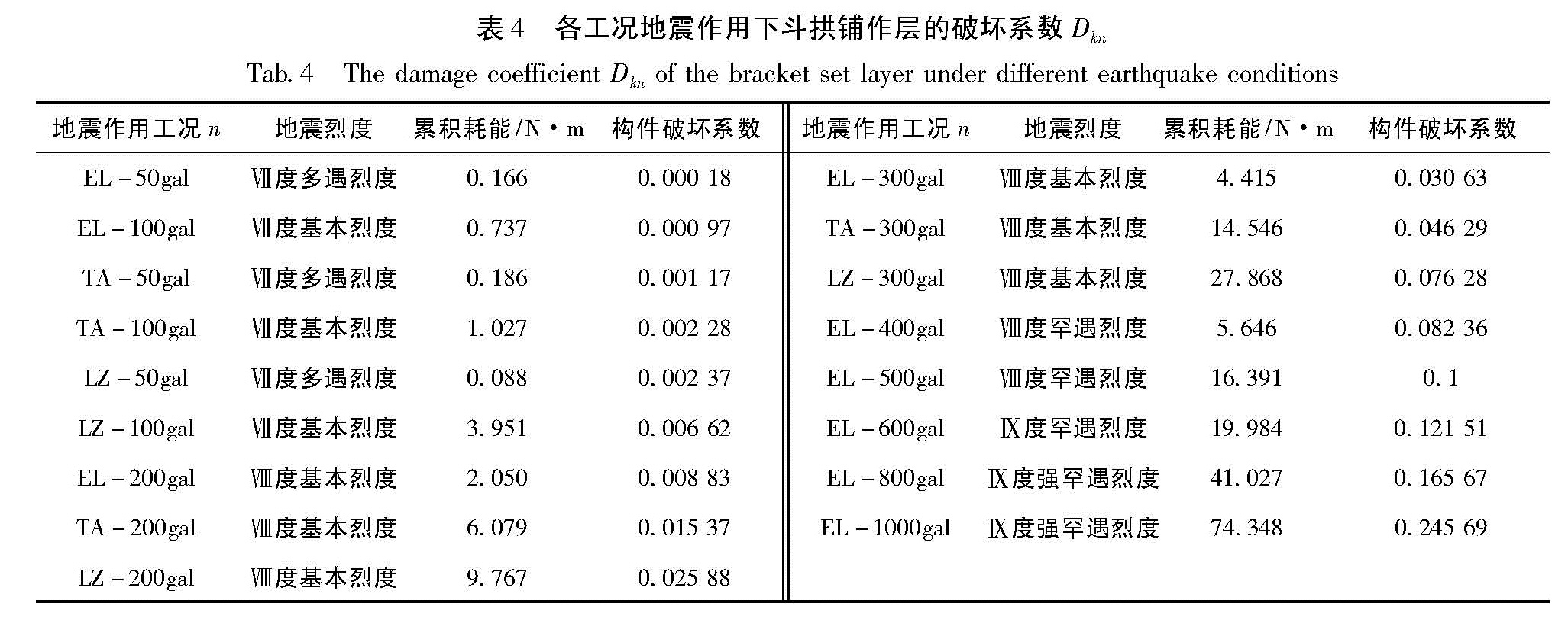
根据图2计算出的各地震工况作用下斗栱铺作层的累积滞回耗能以及斗栱铺作层的构件破坏总耗能,按照式(5)并根据地震加载工况逐级累积计算出斗栱铺作层在各工况地震作用下的破坏系数(表4)。
从表4看出,当斗栱铺作层在模拟地震作用达到1 000 gal时所耗散的能量不多,计算得破坏系数仅为0.246,属于轻微破坏。这与木结构古建筑设计强度裕度大的特点相符。观察斗栱铺作层变形损伤状况发现,其栌斗底部因摩擦滑移而呈弧形光滑面(图6a),栌斗底部与普拍枋相连榫卯的卯口沿振动方向发生较大的塑性变形(图6b),由榫头挤压导致,破坏系数仅为0.246,说明地震作用下斗栱铺作层会整体滑移但其构件本身并未发生严重变形破坏,仍具有良好的承载力和整体性。
(3)柱脚的滑移破坏状况
为研究地震作用下箭楼结构柱脚的滑移隔震性能,依据模型与原型结构的几何与荷载相似关系制作两个缩尺比1:6的短柱模型,在竖直方向施加7.8 kN的力。进行低周水平反复作用下的拟静力试验,得出相应的滞回耗能曲线(图7),根据Origin8.0计算得到柱脚的构件破坏总耗能进行计算。根据《古建筑木结构维护与加固技术规范》(GB50165-92),并考虑木结构古建筑的结构特征,规定当柱脚侧向滑移达半个柱径时,结构即失去稳定性发生破坏。
图5 多攒斗栱铺作层滞回耗能曲线(a)横向加载;(b)纵向加载
Fig.5 Hysteretic energy curve of shop for multiple brackets layer(a)the lateral load;(b)the longitudinal load表4 各工况地震作用下斗拱铺作层的破坏系数Dkn
Tab.4 The damage coefficient Dkn of the bracket set layer under different earthquake conditions图6 斗栱铺作层模型损伤情况(a)栌斗底部呈弧形;(b)卯口挤压变形
Fig.6 The damage state of bracket set layer model(a)the curved bottom of big bucket set; (b)the mortise extrusion deformation图7 柱础层滞回耗能曲线(a)短柱1;(b)短柱2
Fig.7 The hysteretic energy dissipation curve of the plinth level(a)short column 1;(b)short column 2根据计算出的地震作用下柱脚滑移的累积滞回耗能(图2)以及柱脚破坏总耗能(表5),按式(5)并根据地震加载工况逐级累积计算出斗栱铺作层在各工况地震作用下的破坏系数(表6)。
表6 各工况地震作用下柱础层的破坏系数Dkn
Tab.6 The damage coefficient Dkn of column bases layer under different earthquake conditions从表6可知,在地震作用过程中柱脚所耗散的能量并不多,说明柱脚层破坏不严重,在1 000gal地震波激励下其破坏系数在0.10左右,属于轻微破坏。这与木结构古建筑设计强度裕度大的特点相符。柱脚是平摆浮搁于础石上,其水平反力主要由柱底与础石之间的摩擦力来提供。其能与小震时的地震水平作用相平衡而保证结构稳定。在遇到大震时,即地震水平作用超过此摩擦力时,柱架即发生滑移而隔震,其与现代抗震理论中典型的被动控制-摩擦隔震作用相似。柱脚层的摩擦滑移并不大。试验观察发现:在50~200 gal地震激励时,柱脚无相对滑移,但有扭转现象; 在200~300 gal地震激励时,西北角柱滑移11 mm,北面中柱滑移4 mm,西面中柱滑移7 mm; 在400~600 gal地震激励时,西北角柱滑移3 mm,西南中柱滑移23 mm,其滑移量均未超过柱径的1/3,这样的摩擦滑移耗能可以减轻结构震害,且古建筑柱础做法规定“方倍柱之径”,给柱脚滑移留出有相当的滑移区以免其滑移到础石之外而发生失稳破坏(姚侃等,2007)。
4.永宁门箭楼结构整体地震破坏评估
4.1 破坏模型的建立古建筑木结构的破坏主要发生在柱架的榫卯节点、斗栱铺作层和柱脚部位。随着地震作用的加强,柱架结构榫卯节点的榫、卯节点之间相互挤压,其局部残余变形不断增加,连接能力不断下降以至于结构变成机构,但梁柱构件其他部位仍基本完好。因此为了简化计算,可忽略梁柱构件的局部损伤对结构性能的影响,结合前面对3个主要耗能构件地震作用下的破坏评估分析。根据3个耗能构件的不同能量分配,计算出其相应的能量分配系数,并据此得到主要耗能构件破坏状态与整体结构破坏等级的关系。
由于3个耗能构件的质量、刚度等性能参数不同,故在工况n地震作用下各自所耗散的能量不同,求出三个耗能构件所耗散的能量之和并视其为结构整体发生破坏时的总耗能
En=Σ3k=1Enk.(6)
通过分析各构件耗能对结构整体耗能所贡献的比例,特引入耗能构件的能量分配系数.
ξk=(Enk)/(En).(7)
对于整体结构而言,能量分配系数ξk的大小表明构件耗能对结构总耗能贡献的大小。在每一个工况地震作用后,结构整体破坏系数Dn可定义为各耗能构件的破坏系数Dkn与能量分配系数ξk乘积的总和
Dn=Σ3k=1Σmn=1ξkDnk.(8)
根据式(6)~(8),可计算出在地震作用下永宁门箭楼结构整体地震破坏系数Dn(表7)。
表7 各工况地震作用下永宁门箭楼多层木结构的破坏系数Dkn
Tab.7 Damage coefficient Dkn of multilayer wood structure of Yongning Gate Embrasure watchtower under different earthquake conditions注:EL-X gal表示输入的EL centro地震波最大加速度是X gal; TA-X gal表示输入的Taft地震波最大加速度是Xgal; LZ-X gal表示输入的兰州地震波最大加速度是X gal.
4.2 地震破坏评估依据箭楼结构各构件的耗能及破坏系数(表7),并结合相应的试验现象可知,永宁门箭楼在经历了九度罕遇地震后,其整体结构的破坏系数为0.292,柱架榫卯节点少量拔出,斗栱铺作与普拍枋连接榫卯节点发生挤压变形,但结构仍具有良好的承载力和整体性; 当地震激励为1000 gal时,整体结构的破坏系数约为0.5,结构处于中等破坏状态; 这恰与现在的抗震设防的三原则:“小震不坏,中震可修,大震不倒” 相符。这充分体现出中国木结构古建筑科学的抗震设防理念。
- 方东平,俞茂宏,宫本裕等.2001.木结构古建筑结构特性的计算研究 [J].工程力学,18(1):137-144.
- 高大峰,邓红仙,刘静等.2014a. 明清木结构榫卯节点拟静力试验研究[J]. 世界地震工程,(4):8-16.
- 高大峰,李飞,刘静等.2014b. 木结构古建筑斗栱结构层抗震性能试验研究[J]. 地震工程与工程振动,1:131-139.
- 李鹏,杨娜,杨庆山等. 2010.藏式古建筑木梁柱节点力学性能研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 43(增刊):263-268.
- 李铁英,魏剑伟,张善元等.2004.木结构双参数地震损坏准则及应县木塔地震反应评价[J].建筑结构学报,25(2): 91-98.
- 梁思成.2006.清工部《工程做法则例》图解[M].北京:清华大学出版社.
- 刘致平. 1987.中国建筑类型及结构[M]. 北京:中国建筑工业出版社,35-40.
- 邱法维,钱稼茹,陈志鹏.2000.结构抗震实验方法[M].北京:科学出版社.
- 隋龑,赵鸿铁,薛建阳等.2010.古代殿堂式木结构建筑模型振动台试验研究[J].建筑结构学报,31(2):35-40.
- 谢启芳,薛建阳,赵鸿铁. 2010.汶川地震中古建筑的震害调查与启示[J]. 建筑结构学报,(增刊2):18-23.
- 薛建阳,张风亮,赵鸿铁等. 2012.古建筑木结构基于结构潜能和能量耗散准则的地震破坏评估[J]. 建筑结构学报, 33(8):127-134.
- 薛建阳,赵鸿铁,张鹏程. 2004.中国古建筑木结构模型的振动台试验研究[J]. 土木工程学报,37(6):6-11.
- 姚侃,赵鸿铁,薛建阳等. 2007.木结构古建筑的抗震性能分析[J]. 建筑科学,(7):47-50.
- 于琦,孟少平,吴京. 2011.基于变形与能量双重准则的钢筋混凝土结构地震损伤评估[J]. 土木工程学报, 44(5):16-23.
- 张锡成.2013.地震作用下木结构古建筑的动力分析[D].西安:西安建筑科技大学.
- 周乾,闫维明,杨小森等. 2009.汶川地震古建筑震害研究[J]. 北京工业大学学报,35(3):330-337.GB 50165—1992.古建筑木结构维护与加固技术规范[S].
- GB 50165—1992,古建筑木结构维护与加固技术规范[S].
- JGJ 101—1996,建筑抗震试验方法[S].