基金项目:江苏省地震局青年科学项目(201510QX)资助.
(1.江苏省地震局,江苏 南京210014; 2.中国地震局地震预测研究所,北京100036)
(1. Earthquake Administration of Jiangsu Province, Nanjing 210014, Jiangsu, China)(2.Institute of Earthquake Science, CEA, Beijing 100036, China)
soil gas; geochemical feature; anomaly concentration contrast; Tanlu Fault Zone
备注
基金项目:江苏省地震局青年科学项目(201510QX)资助.
为讨论郯庐断裂带江苏段土壤气体CO2、Rn以及Hg的地球化学特征,在重岗、晓店、桥北和何庄4个地点跨断层测量了土壤气中CO2、Rn以及Hg的浓度。测量结果表明:郯庐断裂带江苏段上土壤气CO2、Rn和Hg的浓度异常衬度分别为2.74~3.75, 2.05~5.73和1.84~3.96。土壤气中CO2、Rn和Hg的浓度异常主要集中分布在断裂带内及附近,且与活动断裂带地震活动性有很好的一致性。
In order to discuss the geochemical features of soil gas CO2, Rn and Hg in Jiangsu section of Tanlu Fault Zone, we measured the concentration of CO2, Rn and Hg across the fault in Chonggang, Xiaodian, Qiaobei and Hezhuang. The measurement results show that the anomaly concentration contrasts of soil gas CO2, Rn and Hg are 2.74~3.75, 2.05~5.73 and 1.84~3.96 respectively in Jiangsu section of Tanlu Fault Zone. The distribution of anomaly concentration of soil gas CO2, Rn and Hg concentrated within the fault zone and its nearby, and there had good consistency between the seismic activity of the active fault zones and the concentration anomaly of soil gas CO2, Rn and Hg.
引言
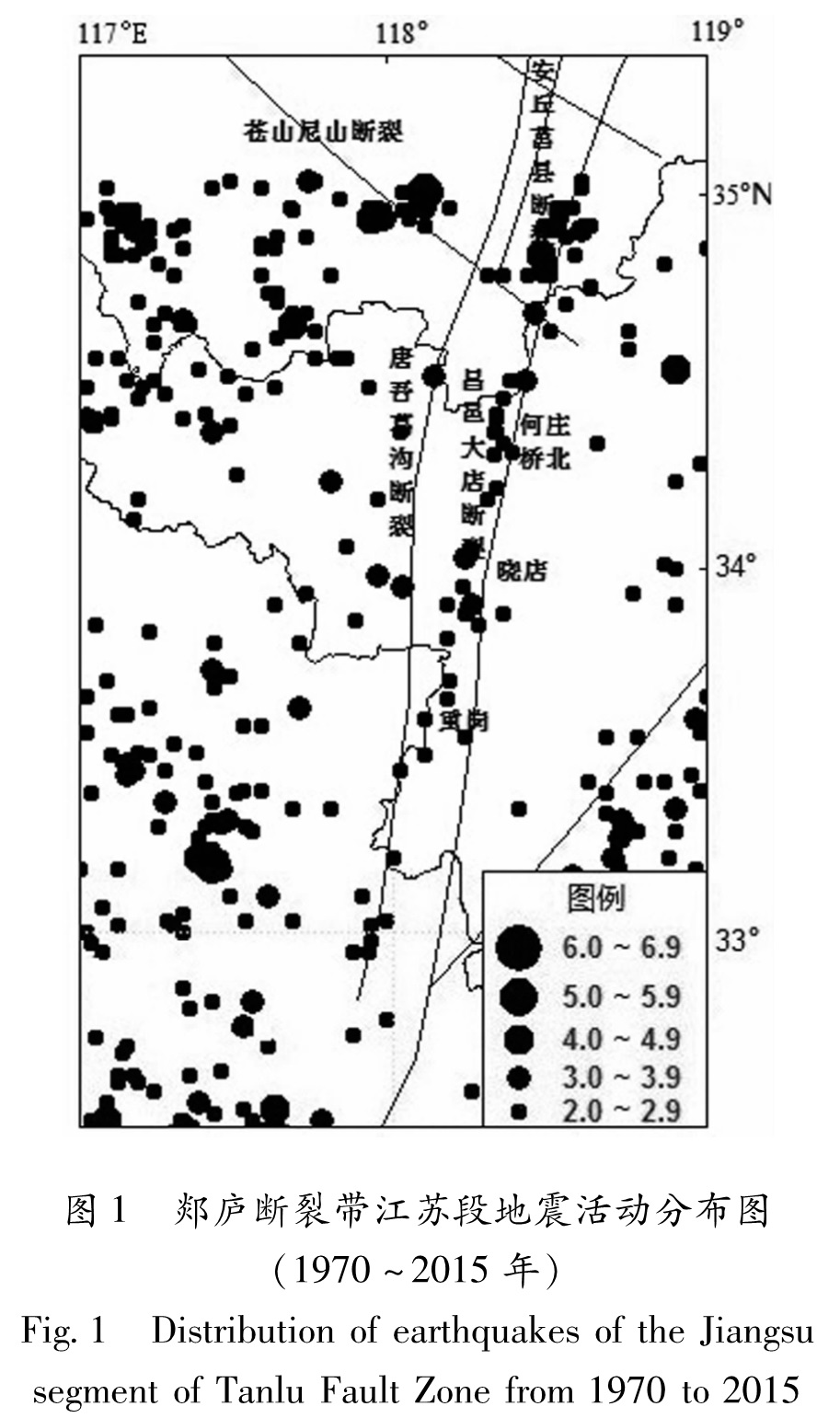
大断裂带及其附近常发生大地震,而大地震往往造成大规模的地表破裂带。郯庐断裂带江苏段主要形成于三叠纪末期,最初是一条走滑断层,位于中朝板块和扬子板块之间的秦岭—大别碰撞带的东侧(黄耘等,2011)。在第四纪时期,郯庐断裂带进一步发展为右行走滑—逆冲断层(张鹏等,2011)。历史上该断裂带发生过多次大地震,如1668年7月28日山东郯城8.5级大地震、1975年2月24日辽宁海城7.3级大地震等(郑颖平等,2012)。汶川地震之后,该地震带又成为新的研究热点。随着地壳运动对地表环境的破坏,地下的大量气体物质,如二氧化碳、氡气、汞气、甲烷、氢气、微量一氧化碳、氦气、硫化氢和苯系列等,能够通过断裂或滑坡边界所产生的裂缝向地表方向迁移释放出来(周晓成等,2012a,李营等,2009)。因此,通过解读地震活动断层土壤气体的地球化学特征,能够反映出其活动情况(周晓成等,2011)。在美国的圣安德烈斯断裂、日本的跡津川和牛首断层、意大利的Pernicana断裂与中国的福州隐伏断裂上,都观测到了土壤气体中CO2、Rn、Hg、CH4、H2和He等浓度的显著异常变化(King et al,1996)。
土壤气CO2、Rn和Hg等浓度异常是寻找地震活动断裂带非常有效的方法,且在活动断裂带附近对地震发生具有非常敏感的响应性。土壤是由岩石风化而生成的,与岩石相比,其结构较为疏松,表面积较大,孔隙度较高,因此土壤中所含气体易于扩散逃逸到大气环境中。土壤气体的地震前兆异常资料表明,地震的震级越大,土壤气体地震前兆异常的幅度越明显,且与震中距成反比分布,距离震中越近的土壤气体测点的前兆异常数目越多。
地震活动断裂带土壤气CO2是地球内部生成的众多流体组分中最有可能大量迁移至地表并在地表某点集中释放的气体之一,它的异常浓度和通量,可以很好地反映地震活动和断裂带的活动情况(周晓成等,2012b)。Rn的浓度分布异常和下层的断裂带内部岩石破裂有非常大的关联。Rn气体主要来源于断裂层中富含放射性铀、钍系列元素的岩石,因此,断裂带的破裂强度越大,破裂产生的裂隙越多,生成的Rn气体就越多。土壤Rn气体浓度高值测点主要分布在断裂点附近,与断层走向基本一致。理论上,由于Rn的迁移与扩散作用,土壤覆盖层的Rn浓度的分布会以断层面破碎点为中心,向周围不断地递减,这导致断层面上的Rn浓度较高,而四周较低。Rn元素的成因主要是断层岩层破碎以及地震活动,土壤母岩的类型与部分垃圾污染对Rn浓度的影响性较为有限。
Hg元素具有电离势较高、穿透能力极强以及挥发性较高的特点,Hg蒸汽可以通过破碎带或裂隙挥发到地表上部。而当岩石在构造应力作用下发生破裂的过程中,岩石在受到挤压之后,压力与温度会迅速增大,使岩石中的Hg化合物迅速地完成一系列化学反应。生成的Hg蒸汽在热力与压力同时作用下,沿着构造裂隙向地表上方扩散,因此Hg元素对断裂活动及温度变化反应非常灵敏。
一般而言,断裂及其附近土壤,气体浓度测值较高,随着到断裂距离的增加,其浓度测值逐渐降低,趋于背景值或在背景值上下浮动(周晓成等,2012a)。郯庐断裂带为地下气体逃逸提供了良好的通道。目前,对郯庐断裂带江苏段上跨断层土壤气体的测量研究还相对较少,因此,本文选取该段为研究区域,通过分析横跨断裂走向观测土壤气Rn、Hg与CO2的含量大小,综合判定郯庐断裂带江苏段的地球化学特征及其活动性。通过对郯庐断裂带江苏段跨断层土壤气体测量,确定断层位置、贯通和应力集中情况,并考察开展断层气测量与地震危险区确定的可能性。
1 地震地质概况
郯庐断裂带是在第四纪时期新构造运动强烈复活之后,在中国华北、东北的东部地区形成的一条显著的右旋走滑断裂带,是一条以岩石圈为尺度而划分的构造边界带。郯庐断裂带在江苏重岗一桥北段为白垩纪红色砂岩逆冲覆于晚更新世粘土地层之上(施炜等,2003)。
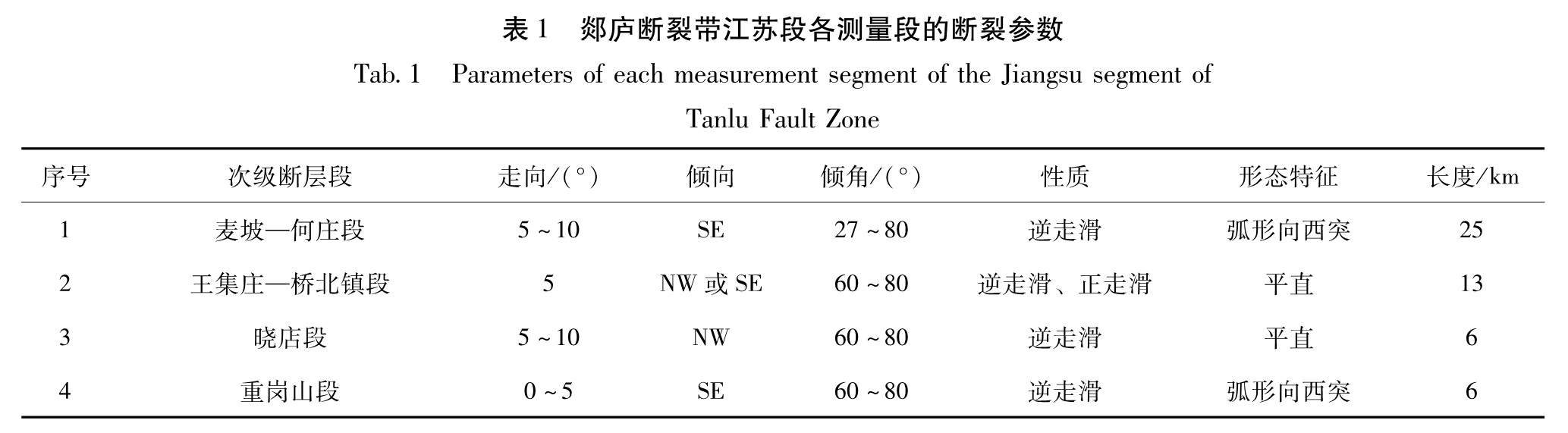
安丘—莒县断裂(F5)发育于昌邑—大店断裂(F1)和白粉子—浮来山断裂(F2)之间,北起莒县小土岭,南至泗洪峰山,全长约260 km,走向10°N—20°E。该断裂控制一系列串珠状北东走向的小山包,自北而南有西北岭、左山、中华山、芨山、马陵山、南马陵山、嶂山、赤山、重岗山、峰山等。地表破裂带往往沿这些小山包的一侧发育,也并非是一条完整的断裂,而是由一系列自然的断层呈斜列展布构成(图1)。本文研究所在的区段的断裂参数如表1所示。
segment of Tanlu Fault Zone from 1970 to 2015表1 郯庐断裂带江苏段各测量段的断裂参数
Tab.1 Parameters of each measurement segment of the Jiangsu segment of Tanlu Fault Zone(1)麦坡—何庄段
在麦坡一带,断裂呈直线状,变现为王氏组二段(K2w2),以高角度逆冲到王氏组三段(K2w3)之上,同时兼有走滑运动量。由于王氏组三段(K2w3)地层很软,被强烈侵蚀,加上断层两侧地层颜色对比明显,所以野外所见断裂地貌非常壮观。
在大尚庄—何庄一带,断层线呈向西突出的弧形,由王氏组(K2w)逆冲于晚更新世(Qp3)地层形成的地台之上,并错断了全新世(Qh)地层,断裂地貌明显,断层崖发育,冲沟显示出右旋变位现象。
(2)王庄集—桥北镇段
该段位于王庄集与桥北镇间,全长13 km,控制南马陵山的东边界。断裂走向N5oE,断层面倾向SE或NW,为高角度断裂。断裂西侧南马陵山与东侧冲积平原形成明显对照,断层线平直,断裂变现为东盘下降,西盘上升。在北部王庄集一带断裂剖面表现为逆冲性质,南部桥北镇一带断裂剖面表现为正断性质。如桥北镇探槽剖面,揭示断层面近直立,断裂西侧为紫红色砂岩(K2w),断层破碎带,挤压片理、构造透镜体发育明显; 断裂东侧为第四纪土层,下部晚更新世(Qp3)浅黄褐色黏土,较板实; 上部为全新世(Qh)黄色含砂土层,内含少量石英砾石,较松软。第四纪土层与断层泥之间边界清渐,也有部分混染现象。跨断裂冲沟具有明显的右旋变位,反映出断裂的走滑运动性质。
(3)晓店段
该段断裂长6 km,走向N10°E,倾向NW,是西侧山体与东侧平原的分界断裂。控制山体发育,表现为西盘王氏组(K2w)逆冲于上更新统(Qp3)之上,断层线平直。
(4)重岗山段
该段位于重岗山的西侧,断层线略具弧形,向西突出。断裂走向0°N—5° E,倾向SE,全长12 km,地貌上表现清晰,构成了低山与平原的分界线,断层崖明显。在剖面上,断裂东侧为紫红色砂岩(K2w),近断裂处为紫红色砂岩破碎带,夹有断层泥。断裂西侧为第四纪沉积,下部为灰绿色、深灰色黏土,上部为黄褐色砂土、亚黏土和粉砂层。
2 土壤气测量方法
首先选择郯庐断裂江苏段重岗、晓店、桥北和何庄4个断裂层进行土壤气测量,通过在土壤中打孔,实时地抽取土壤气体,然后测量其中CO2、Rn和Hg的浓度值测量示意图见图2。测量线是跨越断层的,测点之间平均间隔为10~30 m,测点主要位于断裂带上。测量步骤为:(1)仪器放置在采样点处,选择潮湿度不大的测点进行测量,打
开仪器电源开关,预热仪器;(2)选用打孔钢钎,用锤子在土壤中打约70 cm深的孔,拔出钢钎,迅速插入土壤气体取样器,顶端地表土壤部分用土壤密封压实,以防止抽气时空气进入孔中;(3)用软橡胶皮管将仪器与取样器连接,中间接好干燥塔,进行浓度测量。其中仪器抽取气体的流速大概为1.2 L/min,测量时间为5 min。气汞用RA-915+型塞曼效应汞分析仪现场抽气测量,检测限1 ng/m3; CO2使用便携式红外线CO2分析仪现场抽气测量,CO2的检测限是10 ppm; 气氡是用RAD7测氡仪进行现场抽气测量。跨断层土壤气CO2、Rn和Hg的浓度测值的误差都在10%以内。由于土壤气体的浓度测量过程是一个不够稳定的数据,为测量其土壤含量结果,应取最大值进行读数。在实际测量过程中,测氡仪采取3次读数,每次持续5 min,最后采用数据录入取最大值(Zhou et al,2010)。CO2仪与气汞仪也是在15 min内读取最大测值进行录入。
在重岗剖面布置了2条平行测线,剖面方向尽量与断裂走向垂直,测点间距为10 m,测线间距为8 m。在野外测量过程中,为了避免偶然因素对测量结果的影响,对浓度较高的异常点进行了重复测量,其中Rn的重复检测点占总测点数的11.5%,Hg和CO2的重复检测点占总测点数的7%。每条剖面都具备1~2条平行测线,对于测线的选择,遵循测线尽量垂直于断层的走向这一条基本原则,通过比较同一剖面上不同平行测线的测量浓度,保证了数据的可信度。此外,由于土壤气容易受其他因素影响,因而测量多种土壤气体组分比单一组分更可靠。在断裂发育部位,容易引起多种土壤气体组分聚集,呈现一致的浓度异常; 反之,当构造不发育时,各土壤气体组分呈现一致异常的几率较小,这样可以有效识别与断裂无关的异常。本次测量工作客观地反映了各土壤气体组分在郯庐断裂带的分布特征。
3 土壤气测量结果分析
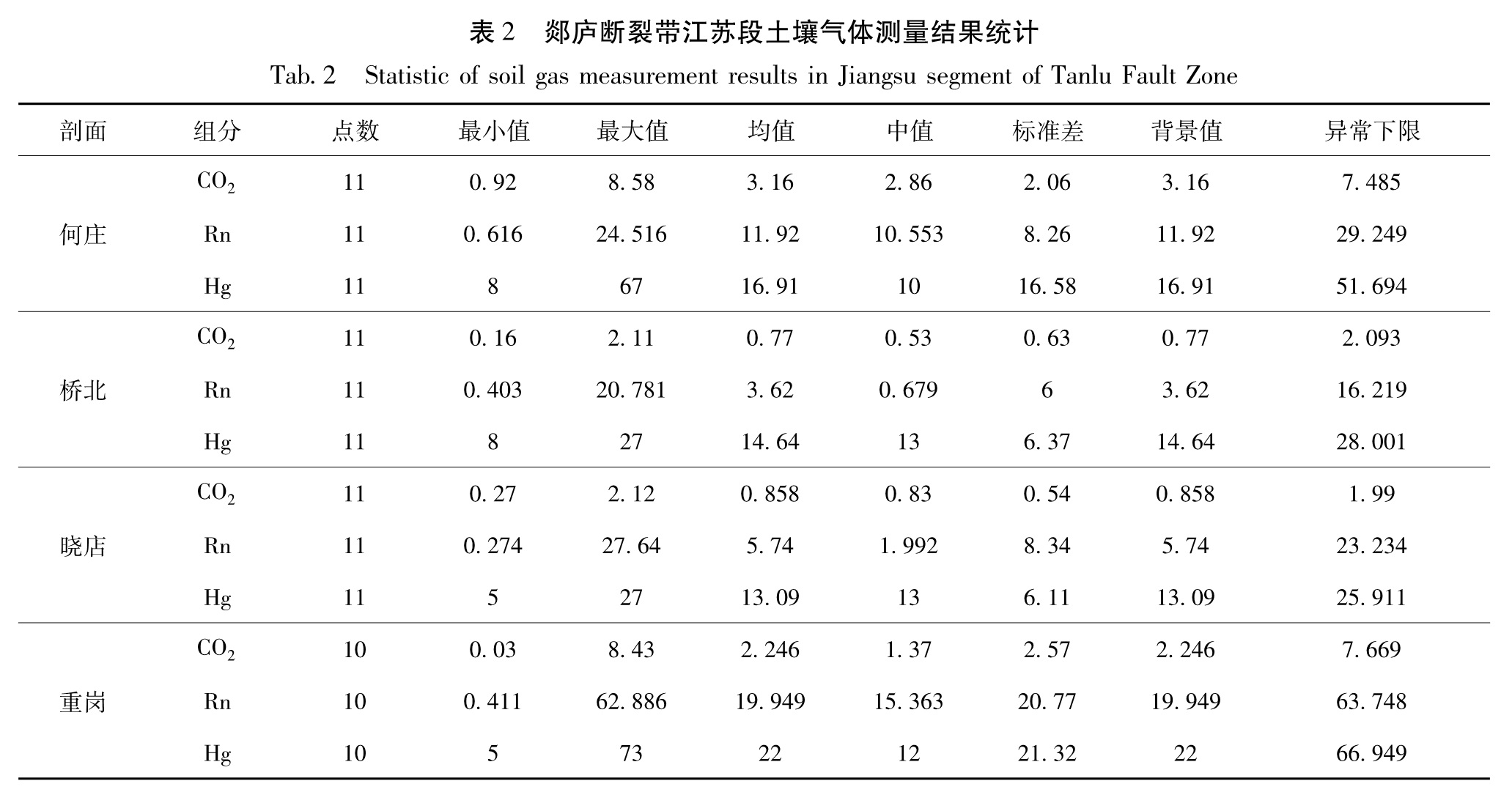
在郯庐断裂带江苏段,测点总共有43个。通过柯尔莫可洛夫-斯米洛夫检验来分析测量数据是否符合正态分布,采用显著性水平默认值α=0.05,通过Matlab编程对测量数据进行分析,最终均符合正态分布。因此,背景值等于平均值,异常下限的结果等于背景值加上2倍标准差。异常强度可用衬度来表示,即用土壤气CO2、Rn和Hg浓度测值与其背景值的比值来表示。
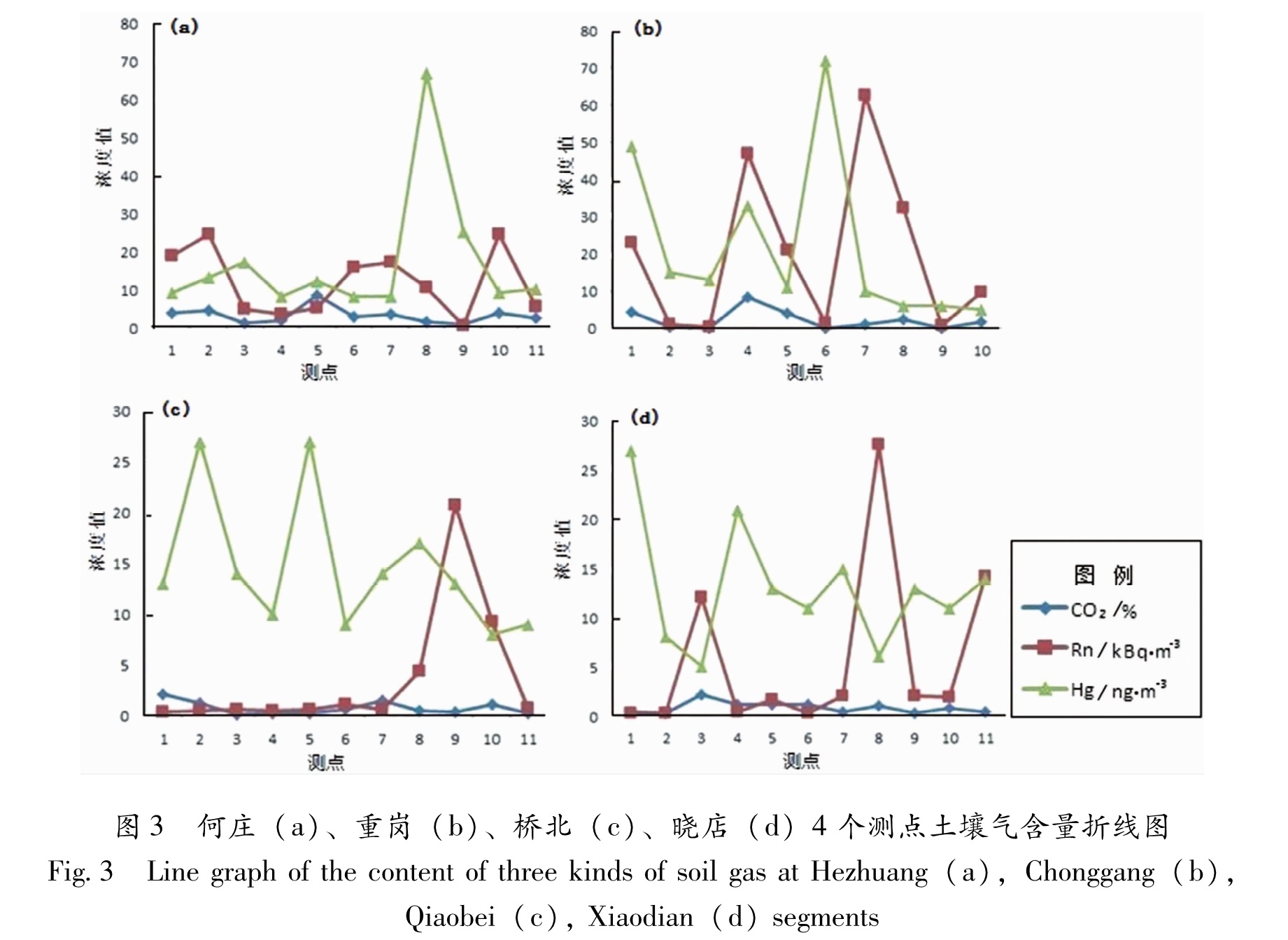
土壤气体浓度异常特征如下:在重岗段测点CO2、Rn和Hg异常点数分别占该剖面的10%。其中CO2异常点在第4测点,距离断裂73.25 m,衬度为3.75; Rn异常点位于第7测点,距断裂21.48 m; Hg异常点在第6测点,距断裂44.36 m。异常主要集中在距断裂21.48~73.25 m之间。
在晓店段测点,CO2、Rn和Hg异常点数分别占该剖面的9.1%。其中CO2异常点在第3测点,距离断裂21.39 m; Rn异常点位于第8测点,距断裂81.48 m; Hg异常点在第1测点,距离断裂298.95 m。异常数据的分布不是很均匀。
在桥北段测点,CO2、Rn和Hg异常点数分别占该剖面的9.1%、9.1%、18.2%。其中CO2异常点在第1测点,距离断裂174.73 m; Rn异常点位于第9测点距断裂33.07 m; Hg异常点在第2、5测点,分别距离断裂155.99 m、108.11 m。异常数据的分布不是很均匀。在大量的降雨之后,土壤中的孔隙几何形状、大小都没有恢复到被堵塞或切断前的状态,这样就会大幅度的影响土壤气中Rn、Hg元素向地表扩散与迁移。因此,Rn、Hg浓度的测量结果会高出背景值较多。
在何庄段测点CO2、Rn和Hg异常点数分别占该剖面的9.1%、18.2%、9.1%。其中CO2异常点在第5测点,距离断裂33.08 m; Rn异常点位于第2、10测点,距断裂分别为12.82 m、134.74 m; Hg异常点在第8测点,距离断裂74.4 m。异常数据的分布不是很均匀。表2为郯庐断裂带江苏段土壤气体测量结果统计,图3为何庄、桥北、晓店、重岗段土壤气体含量折线图。
图3 何庄(a)、重岗(b)、桥北(c)、晓店(d)4个测点土壤气含量折线图
Fig.3 Line graph of the content of three kinds of soil gas at Hezhuang(a),Chonggang(b),Qiaobei(c), Xiaodian(d)segments4 讨论
活动断裂带是深部气体主要的释放通道,通过对海原断裂带东南段和汶川MS8.0地震破裂带的土壤气体地球化学特征分析研究,发现断裂带土壤气CO2、Rn和Hg浓度与断裂的破裂(垂直位移和水平位移)大小和地震活动性相关,并在一定程度上能反映断裂裂隙发育程度(周晓成等,2011; Zhou et al, 2010)。虽然在活动断裂带土壤气体地球化学测量中土壤气会受到地下水位、气象条件、沉积物的差异和仪器测量误差的影响,但在活动断裂附近,活动断裂深部脱气强弱是控制断层气强度的主要因素。
断层活动性的研究是活断层探测工作的任务之一。对不同地区断层的研究表明,同一条断层活动性强的部分断层气测值高,活动性弱的部分测值低。断层带上土壤气CO2,Rn和Hg浓度值分别在0.03%~8.58%, 0.274~62.886 kBq·m-3和 5~73 ng·m-3之间。距断裂带越近,浓度值结果高的测点数目越集中,随着距断裂带距离增大,浓度异常测点的数量逐渐降低,而且浓度值也随之下降。尤其在晓店段,土壤气体浓度异常数量最多,断裂活动性最强,明显高于其他3个测点。这与晓店段地震活动性强具有很好的一致性,而桥北段土壤气体浓度异常数量较少,也与其地震活动性相对较弱呈现对应关系。
土壤气中CO2、Rn和Hg浓度的地球化学特征总结如下:
(1)断裂所有剖面的背景值和最大值:断裂4个剖面土壤气中CO2、Rn和Hg的浓度背景值分别是0.8%、14.7 kBq·m-3和11.6 ng·m-3。土壤气中CO2,Rn和Hg浓度最高达到8.58%、62.886 kBq·m-3和73 ng·m-3,土壤气中CO2和Rn的浓度是相当高的。
(2)断裂各剖面的平均值和最大值的空间变化:CO2浓度最大值和平均值的高值主要集中于何庄测线,Rn的浓度最大值和平均值的高值主要集中在何庄和重岗段,Hg的浓度最大值和平均值的高值主要集中何庄和桥北段。
(3)断裂各剖面的异常空间变化:本文研究断裂土壤气CO2,Rn和Hg浓度各个剖面采用统一异常界,具体有以下几个原因:①断裂岩性的复杂性、断裂性质和分布的多样性; ②对于断裂深部结构的了解很少; ③数据信息提取中减少人为干预,CO2、Rn和Hg的浓度异常分别是2.06%、24.5 kBq·m-3和27 ng·m-3,且分别主要集中分布在何庄段、重岗段和何庄段。
5 结论
通过对郯庐断裂4个剖面土壤气中CO2、Rn和Hg的浓度异常进行分析,得出如下结论:
(1)土壤气CO2、Rn和Hg的浓度异常主要集中分布在断裂带内及附近。由各剖面土壤气浓度异常空间分布可以得出,CO2、Rn和Hg的浓度异常分布在断裂左右两侧50 m范围之内,这主要与活动断裂内裂隙的发育有直接的关系。断层带土壤气CO2、Rn和Hg异常衬度分别为2.74~3.75、2.05~5.73和1.84~3.96,因此把异常衬度最大的测点定为隐伏断层所在的位置。对跨断裂土壤气CO2、Rn和Hg的浓度测量发现,断裂上及其附近的CO2、Rn和Hg浓度异常明显,随着距离断裂距离增大,异常幅度逐渐减少。
(2)活动断裂带地震活动性和土壤气中CO2、Rn和Hg的浓度异常有很好的一致性。通过对郯庐断裂带江苏段跨断层土壤气CO2、Rn和Hg浓度的测量分析,确定了各剖面上土壤气体的地球化学特征的背景值和异常下限值。郯庐断裂上的多种土壤气体组分异常表明,利用多种土壤气体组分可以有效地勘探隐伏断裂。
在此特向中国地震局地震预测研究所周晓成老师、防灾科技学院陈志伟和范安庆在郯庐断裂带江苏段土壤气体测量中给予的多方面的支持和帮助表示感谢。
- 黄耘,李清河,张元生等. 2011.郯庐断裂带鲁苏皖段及邻区地壳速度结构[J]. 地球物理学报,54(10):2549-2559.
- 李营,杜建国,王富宽等. 2009.延怀盆地土壤气体地球化学特征[J]. 地震学报,31(1):82-91,117.
- 施炜,张岳桥,董树文.2003.郯庐断裂带中段第四纪活动及其分段特征[J]. 地球学报,24(1):11-18.
- 张鹏,李丽梅,张景发等.2011.郯庐断裂带江苏段第四纪活动特征及其动力学背景探讨[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,31(4):389-396.
- 郑颖平,翟洪涛,李光等. 2012.郯庐断裂带江苏新沂—安徽宿松段地震危险性分析[J]. 华北地震科学,30(2):48-51.
- 周晓成,杜建国,陈志等. 2012a.地震地球化学研究进展[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,31(4):340-346.
- 周晓成,易丽.2012b.张北县北部土壤气中氡浓度和土壤表面氡的析出率[J]. 北方环境,25(3):104-105.
- 周晓成,王传远,柴炽章等.2011.海原断裂带东南段土壤气体地球化学特征[J]. 地震地质,33(1):123-132.
- King C Y, King B S, Evans W C, et al.1996.Spatial radon anomalies on active faults in California[J]. Applied Geochemistry,11(4):497-510.
- Zhou X, Du J, Chen Z, Cheng J, et al. 2010. Geochemistry of soil gas in the seismic fault zone produced by the Wenchuan MS 8.0 earthquake[J]. southwestern China. Geochemical Transactions, 11(1),doi.10.1186/1467-4866-11-5.