基金项目:中国地震局地震研究所所长基金(IS201326127、IS201506204)和国家自然科学基金项目(41404016、41504011、41574017、41541029)联合资助.
(1.中国地震局地震研究所 中国地震局地震大地测量重点实验室,湖北 武汉430071; 2.地壳运动监测工程研究中心,北京 100036)
(1. Key Laboratory of Earthquake Geodesy,Institute of Seismology,CEA,Wuhan 430071,Hubei,China)(2. National Earthquake Infrastructure Service,Beijing 100036,China)
high rate GNSS; sampling rate; aliasing; shake table simulation experiment
备注
基金项目:中国地震局地震研究所所长基金(IS201326127、IS201506204)和国家自然科学基金项目(41404016、41504011、41574017、41541029)联合资助.
利用振动台实验,通过设置多个采样频率监测仿真的正弦波形及天然地震波形,研究高频GNSS出现的频率混叠现象及其时频特征,并讨论合理的规避混叠现象的采样率设置方法。结果 表明:混叠效应在时域和频域中均有所体现,混叠频率的幅度若高于GNSS的误差水平,其导致的失真将不能忽略; 震级与震中距是导致混叠现象的主要因素,活动断裂的孕震能力与地震危险性及站点与断层面距离是决定高频GNSS监测站采样频率的重要依据。
High rate GNSS measuring the kinematic displacements caused by earthquake with discrete and equal interval sampling rate. According the Nyquist Law,if analog signals have resolve energy at the frequencies higher than the half of sampling rate,the higher frequency signals masquerading as the low frequency signal in the time and frequency domains will contaminate the sampled data. This effect is called aliasing. In this paper,we investigate the aliasing of high rate GNSS by using shake table tests. First we used the sinusoids as input signals to confirm the aliasing effects in the high rate GNSS. Then we used an acceleration record of real earthquake as the input signal to study the mechanism of aliasing effects in the high rate GNSS.The results show that the aliasing occurs both in time domain and frequency domain,and shows non-negligible effect if the masqueraded amplitude is greater than the uncertainty of GNSS positioning. The earthquake magnitude and epicenter distance of GNSS site are two major factors which determine the amplitude of the aliasing effect. Therefore, sampling rate of GNSS should be set according to the seismogenic ability of monitoring fault and the distances between the fault plane and GNSS sites.
引言
逐历元解算使GNSS能够捕获瞬时动态变形信号,也使得空间大地测量形变监测从传统的“零频”(如静态GPS、InSAR)扩展至地震学观测窗口。自Larson等(2003)成功利用1 Hz采样的GPS数据恢复了2002年Denali地震的远场地震波形后,高频GNSS数据被大量用于大地震研究中,如快速确定大震矩震级及地震预警(Blewitt et al,2009; Yang et al,2011; Wright et al,2012; Melgar et al,2012),为大震的破裂过程提供近场的强地面运动约束(Delouis et al,2010; Yue,Lay,2011; Galetzka et al,2015),开展远场地震波面波震相的捕获及其频散特性研究(Davis,Smalley,2009; Hung,Rau,2013)。
高频GNSS被誉为一种新的“地震仪”(Bilich et al,2008; 方荣新等,2011),与传统地震仪在监测方式上具有显著的不同:高频GNSS的直接观测对象为卫星发射的载波信号,具体定位方法是以动态解算站-星间的位置关系获取不同历元的点位坐标,并最终通过历元间坐标差分获取包含地震动信号的点位运动轨迹,但其本质是以地震动信号为实际观测对象、等步长采样的数字化传感器,其应用必须遵守采样定理(Nyquist's Law)。依据采样定理,数字信号中所包含的被采集模拟信号的最高频率小于采样率一半时,可完整重构被采集模拟信号,而当被采集模拟信号的最高频率超过仪器采样率一半时,高出部分的信号将折叠至正常的低频部分,造成采集信号不可逆转的失真,即频率混叠现象(万永革,2007)。频率混叠发生的必要条件为等步长、离散采样的数字记录,并且考虑到具体地震信号频率的未知性,高频GNSS既满足混叠现象发生的条件,也存在发生的风险。Smalley(2009)曾利用已有的强震记录重采样至部分低采样率,借以说明高频GPS若以类似低频采样观测也可能产生混叠现象,但并未对真实的高频GPS数据进行分析,因此高频GPS存在的频率混叠现象仅停留在理论分析层面,尚无实例佐证。强震加速度记录与高频GPS位移记录两者直接观测的物理量不同,两种仪器相互补充而无法取代彼此,且转化的积分过程中亦存在不可忽略的误差,利用前者作为后者的近似也有其局限性。
通过观测卫星信号解算出位置的瞬时坐标以得到地震信号的“间接”观测方式决定了高频GNSS必须存储中间观测量(载波相位),而目前的存储、传输手段尚难以支持高频GNSS以绝对高于地震信号频率范围的采样率(如强震仪设计的200 Hz)进行连续观测。目前大量的GNSS观测网络的高频采样率设置在1~5 Hz之间,远低于地震仪器的采样率,从而导致未能覆盖地震信号频率的可能性大大增加,若产生混叠现象将对以近场高频GNSS为数据基础的研究,如破裂模型反演、矩震级的快速确定等,产生难以忽略的影响。本文主要以高频GNSS中采样率设计为主要研究内容,以振动台仿真实验为主要方法,分析高频GNSS中频率混叠现象的时频特征。
1 振动台仿真实验及数据处理
刘刚等(2014)以振动台实验研究高频GNSS捕捉的震相,本文实验设置与之相似,即将高频GNSS天线设置于GSK-166单向线性振动台上以驱动GNSS扼流圈天线发生位移,GNSS接收机分别以1、2、5、10、20和50 Hz的等间隔采样率同步记录。由于室外条件难以满足垂直向振动,我们仅在水平轴向进行实验(图1)。此次实验设计为2个部分:(1)将振动信号频率固定为2 Hz的正弦波作为振动台输入;(2)将1999年Izmit MW7.4地震震中距20 km的YPT强震仪的加速度记录作为振动台输入。
我们采用动态精密单点定位策略解算高频GNSS数据,其原理为利用卫星轨道和钟差对单台接收机相位数据逐历元进行非差定位处理,获取测站相对于全球参考框架、以历元间隔的高精度位移(Larson et al,2003)。具体实现采用武汉大学研发的高精度数据处理软件PANDA,能够处理采样率高达50 Hz的GPS动态数据(Fang et al,2013)。卫星轨道和钟差选用IGS发布的精密产品,处理得到的瞬时坐标精度水平向优于1 cm,垂直向优于3 cm。
2 实验结果及分析
采样定理是数字信号处理学的基本理论,即
被采集信号的频率范围不能高于采样率一半,否则采集信号将因频率混叠而失真,这个频率的限制被称为Nyquist频率。频率混叠现象具体表现为高出Nyquist频率部分的信号将伪装成低频部分,并折叠至低于Nyquist频率的信号部分,从而导致采集数据记录为两部分信号能量的叠加而无法恢复出真实的信号。混叠部分的能量造成的影响还依赖于记录仪器所能达到的精度范围,若高于Nyquist频率部分的能量所造成的影响小于仪器的误差水平,则可因记录仪器无法分辨而忽略,若高于仪器的误差水平,则将对信号产生不可忽略的影响。本文处理的高频GNSS位移时序水平向精度为毫米级,因此我们将对仪器记录产生影响的位移阈值设计为1 mm,高于Nyquist频率部分产生的位移大于此阈值时,则认为混叠效应产生的影响不可忽略。
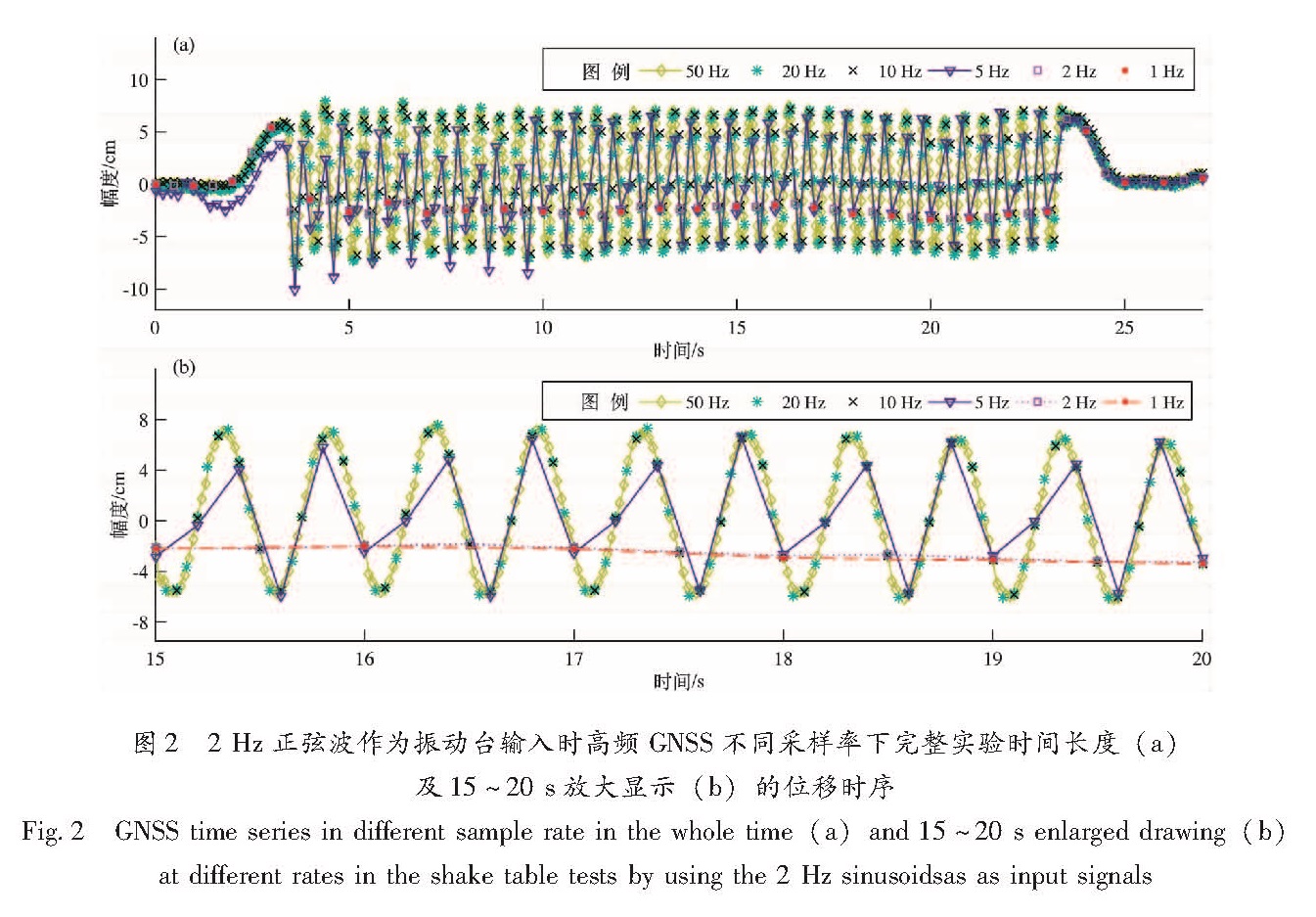
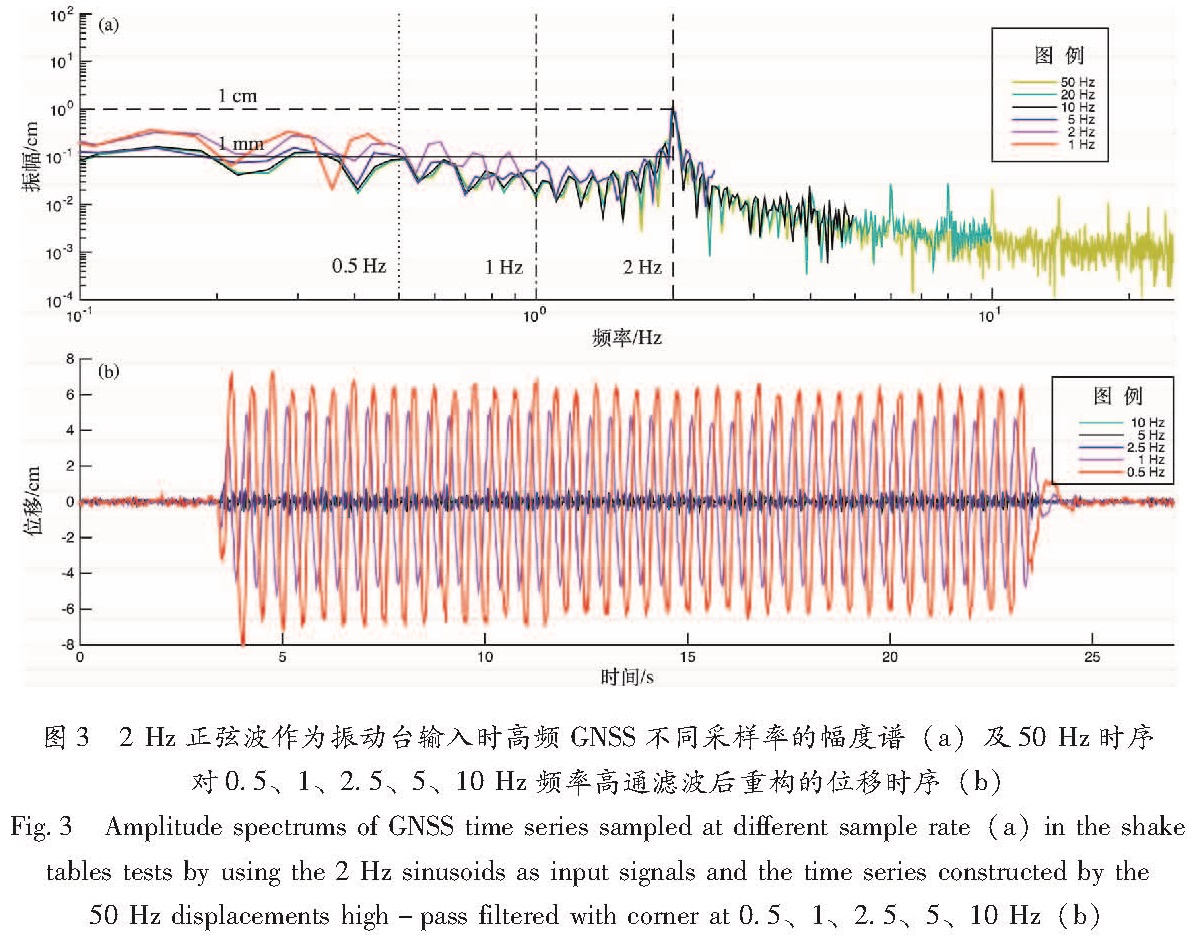
图2给出了信号卓越频率为2 Hz的正弦波作为振动台输入时高频GNSS不同采样率下的位移时序:10 Hz及以上采样率时序完整地恢复了正弦波形,5 Hz时序则基本上刻画出了正弦波形的轮廓,而2 Hz及1 Hz时序近似显示为直线。依据采样定理,2 Hz及1 Hz时序因出现频率混叠而导致采集信号失真。从时域上看,造成2 Hz及1 Hz采样率失真的直接原因是相邻采样点间存在高于观测精度的、可分辨的细节变化,而粗糙的采样率不能记录到这些变化。从频率上看(图3a),输入信号卓越频率为2 Hz时,5 Hz及以上采样率时序覆盖了此频率,而2 Hz及1 Hz采样率的Nyquist频率分别为1 Hz及0.5 Hz,明显低于2 Hz,并且高于Nyquist频率的部分可造成位移大于1 mm并接近1 cm的幅度。高频部分伪装成低频成分并折叠至低于Nyquist频率部分的信号中,且产生的幅度值高频GNSS完全可分辨时,可使得2 Hz及1 Hz采样率的时序在低频部分(低于2 Hz的频带内)与5 Hz及以上采样率时序有所差别(幅度值偏高),因此2 Hz及1 Hz高频GNSS时序中包含了不可忽略的混叠效应。为进一步研究混叠产生的影响,我们对50 Hz采样时序进行了0.5、1、2.5、5、10 Hz(对应1、2、5、10、20 Hz采样率)以上的高通滤波(图3b)。对0.5 Hz及1 Hz(对应1、2 Hz采样率)进行高通滤波后重构的时序基本上呈现了整个正弦波形; 对2.5、5及10 Hz(对应5、10、20 Hz采样率)进行高通滤波后重构时序在GPS观测噪声以下,且无正弦波特征。
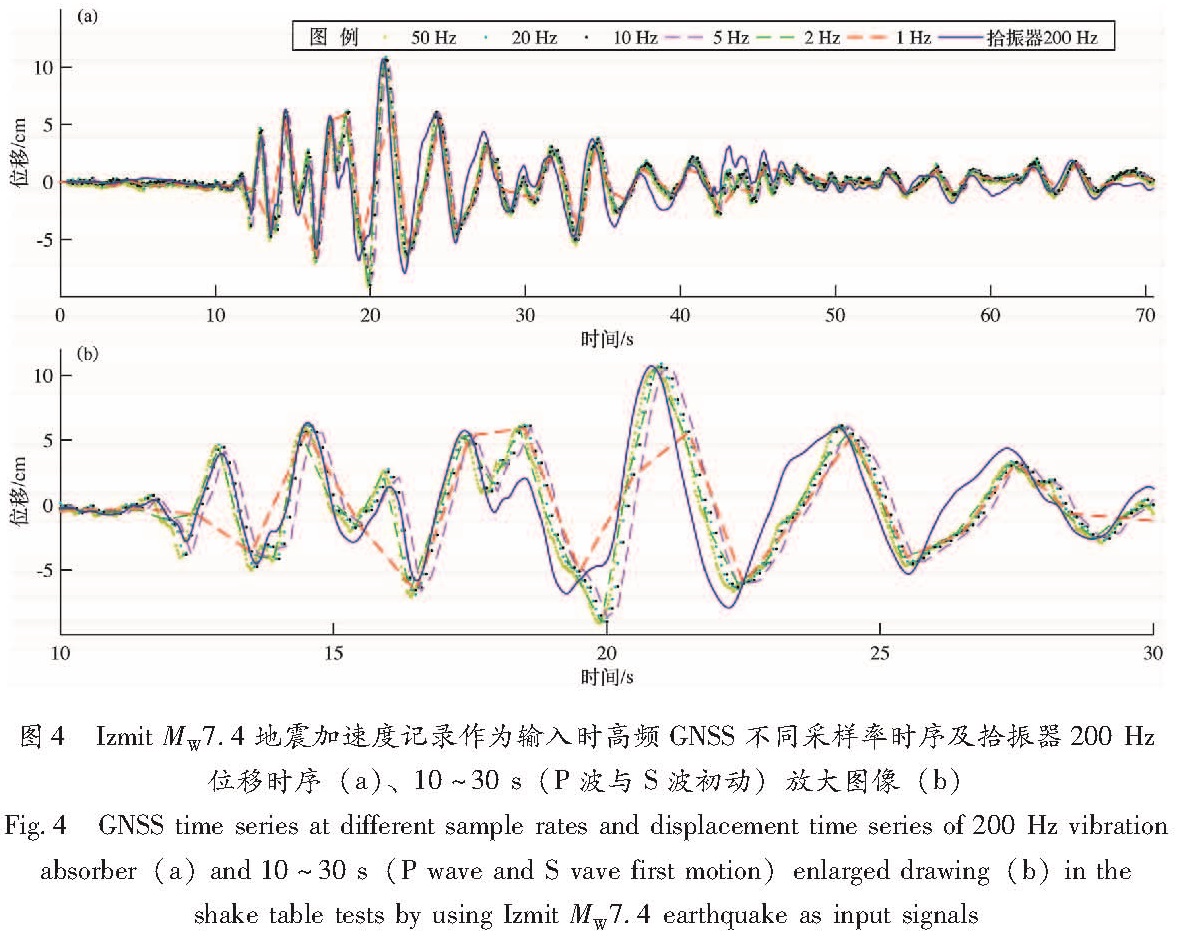
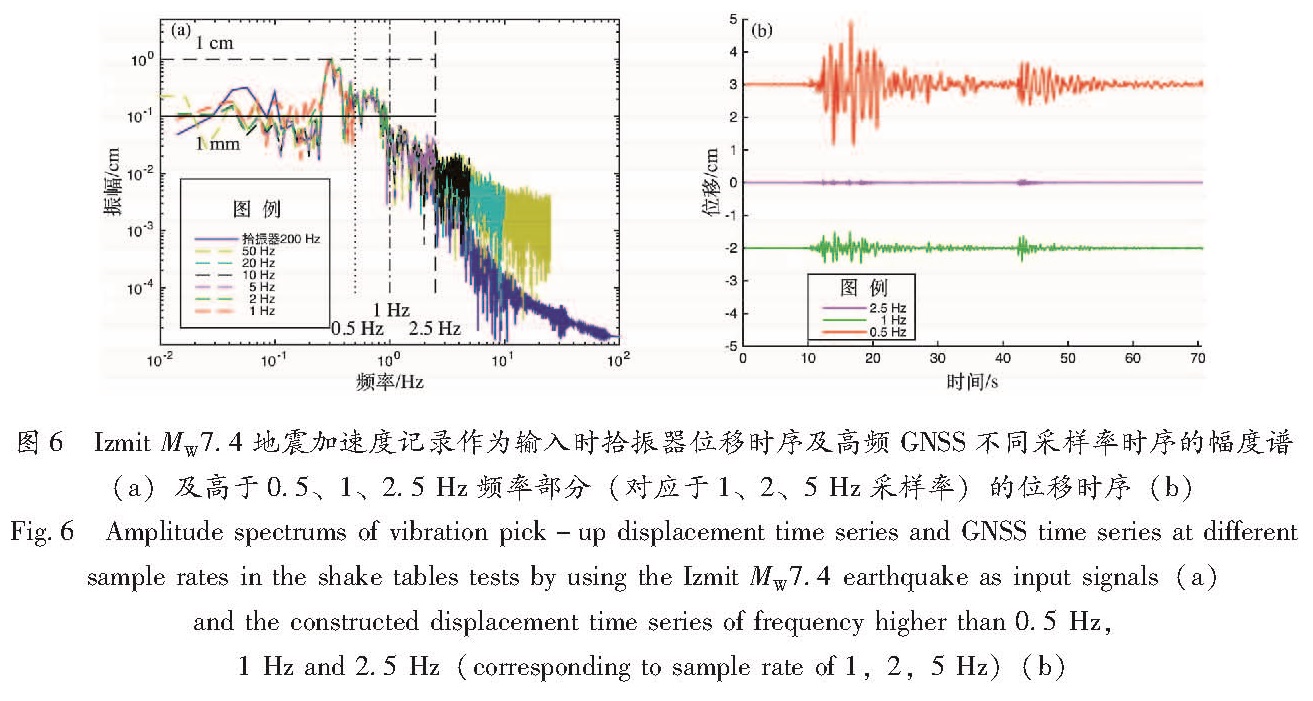
上述的正弦波振动台实验验证了高频GNSS出现频率混叠的可能性。为进一步研究高频GNSS在实际地震监测中的混叠现象,以1999年Izmit MW7.4地震震中距20 km的YPT强震仪的加速度记录为输入数据进行振动台实验。考虑到振动台对复现YPT加速度记录存在难以避免的畸变,将振动台自带的以200 Hz采样的拾振器记录作为此次试验的真值(与YPT采样率相同),并对其进行校正(Li et al,2012),积分至位移后与高频GNSS时序进行比较(图4中蓝色曲线)。积分后的位移时序在70 s后基本回落至零值,与实验结尾振动平台归位于初始位置相对应,表明此次试验仅包含了地震产生的波动效应,振幅为GNSS完全可分辨的厘米级。
实验结果表明:在时域中,10 Hz及其以上的采样率的GNSS时序与拾振器时序拟合的很好,二者的互相关系数达90%(图4a),完整地恢复了振动台产生的位移变化。5 Hz及2 Hz采样率时序较好地拟合了拾振器记录,但1 Hz采样率时序则缺失了振动中某些剧烈的变化:在10~30 s的P波震相和S波初动区间中,部分脉冲出现了遗漏(图4b)。
图2 2 Hz正弦波作为振动台输入时高频GNSS不同采样率下完整实验时间长度(a)及15~20 s放大显示(b)的位移时序
Fig.2 GNSS time series in different sample rate in the whole time(a)and 15~20 s enlarged drawing(b) at different rates in the shake table tests by using the 2 Hz sinusoidsas as input signals图3 2 Hz正弦波作为振动台输入时高频GNSS不同采样率的幅度谱(a)及50 Hz时序对0.5、1、2.5、5、10 Hz频率高通滤波后重构的位移时序(b)
Fig.3 Amplitude spectrums of GNSS time series sampled at different sample rate(a)in the shake tables tests by using the 2 Hz sinusoids as input signals and the time series constructed by the 50 Hz displacements high-pass filtered with corner at 0.5、1、2.5、5、10 Hz(b)图4 Izmit MW7.4地震加速度记录作为输入时高频GNSS不同采样率时序及拾振器200 Hz位移时序(a)、10~30 s(P波与S波初动)放大图像(b)
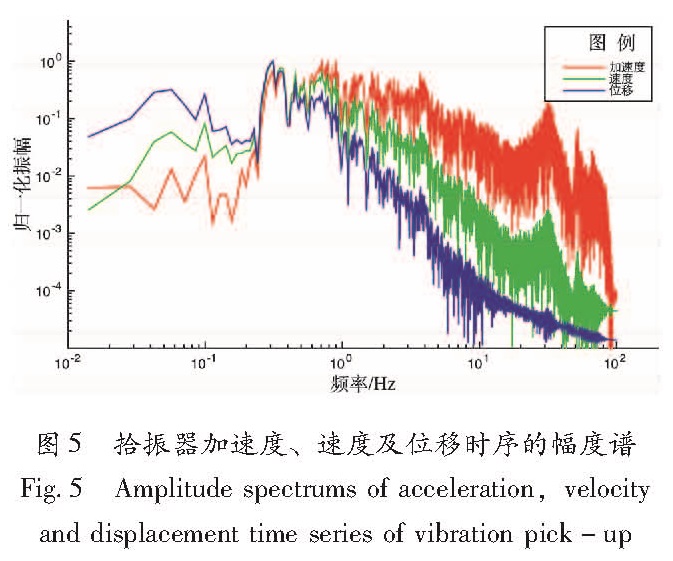
Fig.4 GNSS time series at different sample rates and displacement time series of 200 Hz vibration absorber(a)and 10~30 s(P wave and S vave first motion)enlarged drawing(b)in the shake table tests by using Izmit MW7.4 earthquake as input signals谱分析表明相同的地震波信号,其加速度谱、速度谱及位移谱的特征不尽相同(图5),加速度谱的高频部分的能量丰富,卓越频率集中在0.2~5 Hz区间,且在10 Hz以上的高频部分依然存在较大的幅度; 速度谱相对于加速谱,其卓越频率有所降低,集中在0.2~1 Hz左右,高于1 Hz的高频部分幅度相对较低; 位移谱的卓越频率为0.3 Hz,高于0.3 Hz频率的幅度相对于速度谱及加速度谱为最低,表明位移时序以低频为主,包含的高频能量较少,因此直接以位移为观测量的高频GNSS与加速度计或速度计相较,其采样率可设置为相对较低值。在位移时序上,输入信号的卓越频率在0.3 Hz左右,幅度大于1 mm阈值的频带为0.02~1 Hz(图6a)。采样率为1 Hz的GNSS时序无法捕捉0.5~1 Hz频带范围的信号,而此范围内的信号可产生GNSS能分辨的频率混叠效应,因此采样率1 Hz时序受到频率混叠效应影响而出现失真现象。大于1 Hz采样率的其他采样率数据虽然也受到高频混叠效应的影响,但混叠产生的幅度值低于GNSS的观测误差,因此产生的影响可忽略。此外,我们对拾振器记录分别进行了0.5、1、2.5 Hz的高通滤波(分别对应1、2及5 Hz采样率)(图6b),重构高频信号结果表明高于2.5 Hz频率的信号产生的幅度值小于阈值1 mm,高于1 Hz频率信号产生的幅度值为小于5 mm,而高于0.5 Hz频率信号产生的幅度则大于1 cm,基本显示了地震波的轮廓。
图5 拾振器加速度、速度及位移时序的幅度谱
Fig.5 Amplitude spectrums of acceleration,velocity and displacement time series of vibration pick-up图6 Izmit MW7.4地震加速度记录作为输入时拾振器位移时序及高频GNSS不同采样率时序的幅度谱(a)及高于0.5、1、2.5 Hz频率部分(对应于1、2、5 Hz采样率)的位移时序(b)
Fig.6 Amplitude spectrums of vibration pick-up displacement time series and GNSS time series at different sample rates in the shake tables tests by using the Izmit MW7.4 earthquake as input signals(a) and the constructed displacement time series of frequency higher than 0.5 Hz,1 Hz and 2.5 Hz(corresponding to sample rate of 1,2,5 Hz)(b)3 讨论
高频GNSS出现频率混叠现象的根本原因是由采样率决定的Nyquist频率低于地震信号频率,因此调高GNSS采样率成为避免混叠现象有效办法之一。然而在哪些条件下需要调高采样率是需要讨论的问题,可从仪器接收到的地震信号位移谱频带特征方面考虑(相对于速度谱和加速度谱,位移谱的特征频率更低)。Smalley(2009)提出震级是影响GNSS混叠现象的重要因素,6~7.5级地震频谱特征包含较多可被高频GNSS观测到的高频分量,这些高频分量将导致距离震中较近且采样率不高(如1 Hz)的站点产生混叠现象; 此外,震中距亦是另一个重要因素,震中距越小,地下介质滤除的高频信息越少,仪器接收到的信号频率相对越高,则要求采样率设置越高。我国大陆强震频发,6级以上地震分布具有明显的规律性,7级以上强震基本分布于大型活动断裂上(张培震等,2013)。因此活动断裂的孕震能力与地震危险性及站点与断层面距离是决定高频GNSS监测站采样频率的主要因素,而依据活动断裂分布来布局具有不同采样率的GNSS监测网络亦具有重要意义。
本文对Izmit地震的实验结果支持Smalley(2009)给出的10~20 km内站点需要采样5 Hz的结论。同时依据芦山地震SCTQ(震中距29 km)站点1 Hz与50 Hz GPS位移序列的异同(Lou et al,2013),认为距离断层50 km以内的站点的采样率亦应高于1 Hz。
提高采样率将会对数据储存和传输产生压力。最为合理的解决方法为实时处理,用数据流的方式将原始数据存储至数据心以降低传输压力。考虑到实时处理方法暂未成熟,且震时可能导致数据传输中断,因此有必要增加接收机本身的存储能力。
4 结论
通过振动台实验,本文展示了高频GNSS出现的频率混叠现象并分析了其特征。与定位方式无关,高频GNSS离散化等间隔的采样方式满足频率混叠产生的条件,一旦信号频率高于Nyuist频率将导致混叠现象产生。混叠效应在时域和频域中均有所体现,混叠频率的幅度若高于GNSS的误差水平,其导致的失真将不能忽略,这对震源物理过程、地震预警等基于近场数据的研究领域具有重大的影响。
感谢武汉地震科学仪器研究院对仿真实验的协助,感谢两位匿名审稿专家的建设性修改意见和编辑的辛勤工作。
- 方荣新,施闯,陈克杰,等.2011.GPS地震仪:PANDA软件测试结果与验证[J].武汉大学学报(信息科学版),36(4):453-456.
- 刘刚,聂兆生,方荣新,等.2014.高频GNSS形变波的震相识别:模拟实验与实例分析[J].地球物理学报,57(9):2813-2825,doi:10.6038/cjg20140908.
- 万永革.2007.数字信号处理的MATLAB实现[M].北京:科学出版社.
- 张培震,邓起东,张竹琪,等.2013.中国大陆的活动断裂、地震灾害及其动力过程[J].中国科学:地球科学,43(10):1607-1620.
- BILICH A,CASSIDY J,LARSON K M.2008.GPS Seismology:Application to the 2002 MW7.9 Denali Fault Earthquake[J].Bull Seismol Soc Am,98(2):593-606.
- BLEWITT G,HAMMOND W C,KREEMER C,et al.2009.GPS for real-time earthquake source determination and tsunami warning systems[J].Geod,83(3):335-343.
- DAVIS J P,SMALLEY J R.2009.Love wave dispersion in central North America determined using absolute displacement seismograms from high-rate GPS[J].Geophys Res Lett,114(B11):292-310,doi:10.1029/2009JB006288.
- DELOUIS B,NOCQUET J-M,VALLÉE M.2010.Slip distribution of the February 27,2010 MW8.8 Maule Earthquake,central Chile,from static and high-rate GPS,InSAR and broadband teleseismic data[J].Geophys Res Lett,37(17),L17305,doi:10.1029/2010GL043899.
- FANG R,SHI C,SONG W W,et al.2013.Determination of earthquake magnitude using GPS displacement waveforms from real-time precise point positioning[J].Geophys J Int,196(1):461-472,doi:10.1093/gji/ggt378.
- GALETZKA J,MELGAR D,GENRICH J F,et al.2015.Slip pulse and resonance of the Kathmandu basin during the 2015 Gorkha earthquake,Nepal[J].Science,349(6252):1091-1095.
- HUNG H K,RAU R J.2013.Surface waves of the 2011 Tohoku earthquake:Observations of Taiwan's dense high-rate GPS network[J].J Geophys Res,118(1):332-345,doi:10.1029/2012JB009689.
- LARSON KM,BODIN P,GOMBERG J.2003.Using 1-Hz GPS Data to Measure Deformations Caused by the Denali Fault Earthquake[J].Science,300(5624):1421,doi:10.1126/science.1084531.
- LI H,WANG D,CAI Y J,et al.2012.Baseline Correction of Digital Strong-Motion Data-Examples from the 2008 Wenchuan,China,Earthquake[J].Adv Mater Res,378-379,247-250.
- LOU Y,ZHANG W,SHI C,et al.2013.High-rate(1-Hz and 50-Hz)GPS Seismology:Application to the 2013 MW6.6 Lushan earthquake[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,79:426-431,doi:http://dx.doi.rog/10.1016/j.jseases.2013.10.016.
- MELGAR D,BOCK Y,CROWELL W B.2012.Real-time centroid moment tensor determination for large earthquakes from local and regional displacement records[J].Geophys Res Lett,188(2):703-718.
- SMALLEY R.2009.High-rate GPS:How High do We Need to go?[J].Seismol Res Lett,80(6):1054-1061.
- WRIGHT T J,HOULIÉ N,HILDYARD M,et al.2012.Real-time,reliable magnitudes for large earthquakes from 1Hz GPS precise point positioning:The 2011 Tohoku-Oki(Japan)earthquake[J].Geophys Res Lett,39(1),L12302,doi:10.1029/2012GL051894.
- YANG S M,NIE Z S,JIAZ G,et al.2011.Co-seismic displacements of 2011 Japan MW9.0 earthquake recorded by far-field GPS stations[J].Geodesy and Geodynamics,2(3),12-15,doi:10.3724/SP.J.1246.2011.00012.
- YUE H,LAY T.2011.Inversion of high-rate(1 sps)GPS data for rupture process of the 11 March 2011 Tohoku earthquake(MW9.1)[J].Geophys.Res Lett,38(7):752-767,doi:10.1029/2011GL048700.