基金项目:2014年度中国地震局“三结合”课题(142503)和2012年度中央级公益性科研院所基本科研业务专项《川滇菱形地块北端地下磁化率结构研究》(DQJB12C11)共同资助.
(1.云南省地震局,云南 昆明 650224; 2.中国地震局地球物理研究所,北京 100081)
(1.Yunnan Earthquake Agency,Kunming 650224,Yunnan,China)(2.Institute of Geophysics,China Earthquake Administration,Beijing 100081,China)
magnetic susptibility; earthquake prediction; the Eryuan earthquake
备注
基金项目:2014年度中国地震局“三结合”课题(142503)和2012年度中央级公益性科研院所基本科研业务专项《川滇菱形地块北端地下磁化率结构研究》(DQJB12C11)共同资助.
以2013年3月3日云南洱源M5.5地震为对象,研究地震孕震过程中地下介质的磁化率变化,分析其发震前的显著变化特征,为地震预测寻找磁学的短期预测指标。应用ModelVision软件,反演了2011—2013年6期滇西地磁场总强度测网中4条测线的地下磁化率结构及其变化。结果 表明:在维西—乔后与无量山断裂之间,磁化率在深度10~15 km和15~20 km同时减小,之后仅在深度15~20 km转为增大,之后发生洱源地震。
The subject of this paper is based on the March 3,2013 Eryuan M5.5 earthquake occurred in Yunnan.We study on the variation characteristic of underground medium magnetic susceptibility during the seismogenic process,and we analyze the significant change characteristic before the Eryuan earthquake.This study searches short term prediction index of magnetism for earthquake prediction.We apply the ModelVision software to invert the underground magnetic susceptibility structure and its variations of 4 survey lines in the magnetic field total intensity network in the western Yunnan during the 6 periods from 2011 to 2013.The results show that the magnetic susceptibility decreases in the depth of 10~15 km and 15~20 km simultaneously,after that it only becomes increase in the depth of 15~20 km.Meanwhile,the Eryuan earthquake took place.
引言
1960—2000年期间,美国在圣安德列斯断层及其临近地区(Johnston,1997; Johnston,Mueller,1987; Mueller,Johnston,1998)、 日本在东海地震活动区(Rikitake,Honkura,1985; Sumitomo,Noritomi,1986; Sasai,Ishikawa,1991)、 前苏联与俄国在中亚地震活动区(Shapiro et al,1978,1982,1994)、中国在地震活动区(国家地震局科技监测司,1988,1991; Gu et al,2006; Zhan et al,1989,1999)等都积极开展了震磁观测与研究(Nagata,1969),并探索地震预测,获得了很大的进展。自2000年以来,由于各种原因,许多国家的震磁观测与研究已不如以前了,例如美国地质调查局(USGS)自2004年帕克费尔德发生M6地震(Johnston et al,2006)后,由于缺乏经费,已终止了在美国的构造磁∕震磁监测与模拟的计划。与其他国家不同,近年来我国加强了震磁观测与研究,在地震活动区开展了地磁总强度与三分量相互配合的地磁监测工作,分析与研究岩石圈磁场异常变化的前兆信息,探索地磁预测地震方法并应用于实际的地震监测预报工作,取得了很大的进步(顾左文等,2006; 顾春雷等,2010,2012; 倪喆,2014a,b,c; Chen,et al,2016; Yuan,2016; Ni,2016)。
目前,我国的震磁观测与研究表明,应用地表的磁测资料所总结的岩石圈磁场异常特征已不能满足当前地震预测的分析和解释,拓展地磁异常“场”分布向“源”分布的认识,进一步挖掘其在地下介质磁性结构中的分布规律和演变特点,应当成为地磁预测地震研究可持续发展的主要方向之一。为此,应用重磁反演软件,对地磁场总强度数据进行反演计算,根据实验室已测定的岩石磁化率和地下垂直岩性之间的关系,以反演结果来分析与研究地震孕育和发震过程中地下介质的磁性变化,可以深入地了解构造活动过程中温度、应力等多种因素使地下介质的磁性产生改变,从而揭示地下“源”的变化引起地表“场”分布的地磁异常现象,使地磁方法用于地震预测研究更具物理性与合理性。为获得地下介质的磁化率结构及其变化与地震之间的关系,本文以2013年3月3日云南洱源M5.5地震为研究对象,以滇西地震预报实验场流动地磁场总强度测网观测资料为基础,以先验信息地下垂直岩性磁化率和深度之间的关系作为约束条件,借鉴了已经开展的地磁剖面计算的具体技术流程,获得了该地震孕育和发生与相应区域地下磁化率结构之间的变化特征,表明开展地下介质磁化率结构变化的研究在地震预测中具有良好的应用前景。
1 观测资料
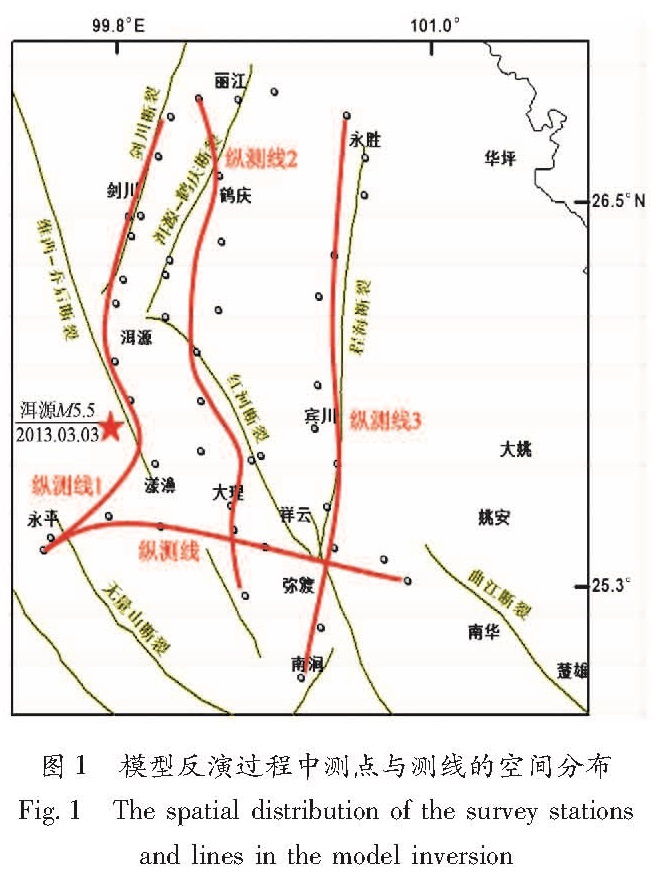
滇西地震预报实验场流动地磁场总强度测网简称滇西测网(图1),由“三纵一横”的4条测线49个测点构成,每年2或3月、8或9月各进行1期地磁场总强度的观测。纵测线1由北向南沿剑川断裂、穿过维西—乔后和无量山断裂; 纵测线2由北向南分别穿过了洱源—鹤庆和红河断裂北段; 纵测线3由北向南平行于程海断裂,其南段穿过红河断裂北段; 横测线由西向东分别穿过无量山、维西—乔后和红河断裂。本文采用了2011—2013年滇西测网6期资料,其中第1~5期资料在洱源地震之前观测,第6期资料在地震之后观测。这6期总强度观测数据均为主副桩观测,每个测点观测6组,在主副桩上每组观测10个总强度测值,相邻组间差不超过3 nT。由于楚雄2个测点远离滇西测网,故未采用这2个测点。横测线利用13个测点,纵测线1、2、3分别也有13个测点。
2 数据处理
本研究借鉴了攀枝花—会泽、屏山—盐源地磁剖面数据处理的技术路线 袁洁浩,顾左文,高金田,等.2016.蒙古S-D 剖面的岩石圈磁异常观测与研究. 陈斌.2013.川滇菱形地块北端地下磁化率结构研究分析报告.。主要流程大致有三步:一是对原始观测数据进行地磁日变通化、长期变化改正; 二是利用IAGA公布的主磁场模型IGRF11将岩石圈磁场从地磁场中剥离出来; 三是对岩石圈磁场进行分解,为磁化率结构模型反演进行数据准备。本文采用了通海地磁基准台的总强度分钟值数据进行日变通化,日变通化时间选取原则为各期野外观测当月磁情最为平静一天的00:00~03:00(北京时),6期49测点的日变通化的标准方差在 0.01~1.00 nT。长期变化改正使用 “1995.0—2014.5年中国地区地磁场非线性变化模型(NOC)”(顾左文等,2009),将6期日变通化后的数据统一归算至2010.0年。岩石圈磁场的分解采用向上延拓方法(管志宁,2005),分别在30 km、10 km处分解成基底和中间层部分,而浅表部分为岩石圈磁场与基底、中间层部分的差值。向上延拓方法计算的数学公式如下:
ΔT'(Xi,-h)=h/(π)∑n-1k=1((Xk-Xi))/((Xk-Xi)2+h2)·
ΔT(Xk,0)(1)
其中:ΔT和 △T'分别为延拓前后的岩石圈磁场值,单位均为nT; h为向上延拓高度; Xi和Xk为各测点的投影距离,Xi为给定的,而Xk为可变的; n是测点总数。
3 模型反演
从岩石圈磁场中剥离出来的三部分,即基底部分、中间层部分和浅表部分,用澳大利亚Encom Technology Pty Ltd公司开发的ModelVision Pro 11.0专业重磁软件分别对这三部分进行磁化率的反演。磁化率是指表征磁介质属性的物理量,感应磁化强度和剩余磁化强度是构成岩石圈磁场的两大成
分。剩余磁化强度与现代磁场无关,而感应磁化强度与地质构造、构造活动、应力、温度等多种因素的变化有关。感应磁化强度与磁场强度的比值为磁化率,磁化率大于零,即顺磁质; 磁化率小于零且值很小,即逆磁质。对于铁磁介质,磁化率很大,且还与磁场强度有关。对于各向同性磁介质,磁化率为标量。对于各向异性磁介质,磁化率是一个二阶张量。
反演时,基于不同深度地下垂直岩性的先验信息,对于基底部分从地表往下按照顺磁性、铁磁性和逆磁性的顺序以给定磁化率初始值进行分层反演,而中间层和浅层部分进行磁化率的自由反演,最后将这三部分的反演结果进行合并。反演磁化率模型中,6期横测线的基底反演标准方差为0.450~2.925,纵测线1的标准方差为0.494~3.308,纵测线2的标准方差为0.448~2.925,纵测线3的标准方差为0.464~2.768。
4 磁化率变化与地震
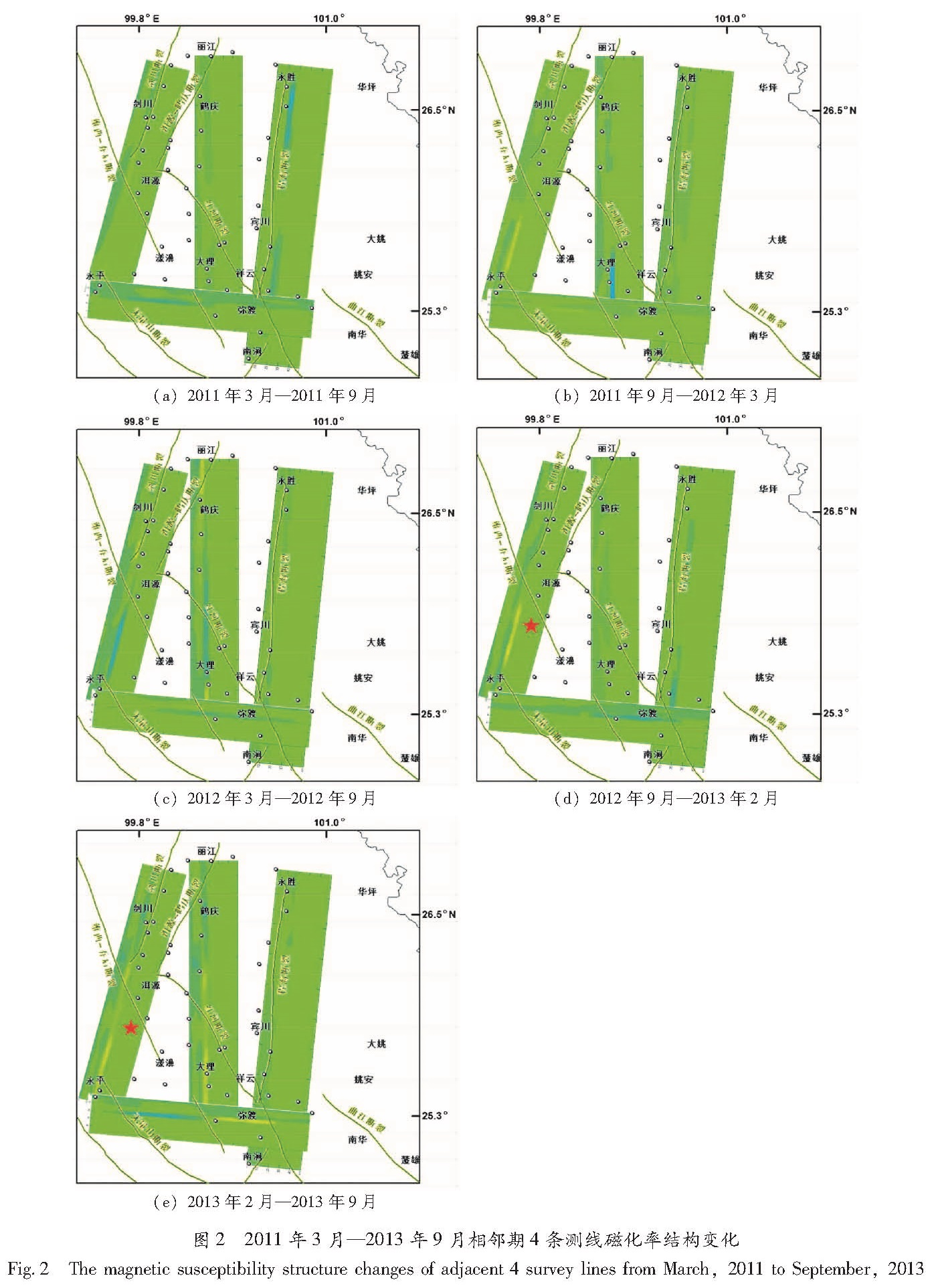
经模型反演之后分别得到了这4条测线的磁化率结构及其变化图,为更加清晰直观地了解磁化率结构变化在时间和空间上的演化过程,本文分别将4条测线2011年3月—2013年9月共5期的相邻期时间变化投影到测点分布的空间位置上(图2)。
从图2a中可以看出,该相邻期磁化率结构变化主要以减小为主,其显著变化出现在纵测线1、纵测线3和横测线、纵测线2无明显变化。纵测线1在维西—乔后断裂和无量山断裂之间出现了磁化率减小的变化,深度约为0~5 km。纵测线3在南北两段永胜—期纳、海哨—云南驿段出现了磁化率减小,并且北段减小的速率高于南段,深度约为10~20 km。整条横测线均有磁化率减小,无量山断裂到维西—乔后断裂之间深度为15~20 km,其它部分深度约为0~15 km。由此可见,该相邻期磁化率变化从空间位置上集中在无量山断裂北端、维西—乔后与剑川断裂交汇处、程海与红河断裂交汇处围成的区域。
与2011年3—9月相邻期(图2a)相比,图2b中磁化率结构变化在横测线和纵测线1开始显现出了增大,纵测线2出现了显著的减小,纵测线3的减小变化趋于零。纵测线1在维西—乔后断裂和无量山断裂之间深度为10~15 km、15~20 km分别出现了磁化率的减小和增大。纵测线2在维西—乔后和红河断裂之间深度为15~20 km出现了磁化率的增大。纵测线3的磁化率减小变化趋于零,横测线在无量山断裂与维西乔后断裂之间深度15~20 km出现磁化率的增大,其余范围和不同深度依然存在磁化率的减小。由此可见,该相邻期磁化率变化从空间位置上集中在无量山断裂北端和维西—乔后、红河断裂围成的区域。
与2011年9月—2012年3月相邻期(图2b)相比,图2c中磁化率结构变化依然存在增大和减小,只是空间位置发生了改变。横测线、纵测线1的维西—乔后断裂以南、纵测线2的红河断裂以南均呈现出显著的减小且深度为15~20 km,纵测线1的维西—乔后断裂以北沿剑川断裂、纵测线2的洱源—鹤庆断裂南北两侧呈现出明显的增大且深度为10~15 km,纵测线3无变化。由此可见,该相邻期磁化率减小变化从空间位置上集中在维西—乔后、红河断裂以南区域,增大变化集中在剑川和洱源—鹤庆断裂周边。
与2012年3—9月相邻期(图2c)相比,图2d中纵测线1的维西—乔后断裂以北沿剑川断裂、纵测线2的洱源—鹤庆断裂南北两侧呈现出的增大变化趋于零,纵测线1的维西—乔后断裂以南深度为15~20 km的减小演化成深度为10~15 km、15~20 km分别出现了磁化率的减小和增大。与2011年9月—2012年3月相邻期相比,图2d中磁化率结构变化具有高度的相似性,纵测线1在维西—乔后断裂和无量山断裂之间深度为10~15 km、15~20 km分别出现了磁化率的减小和增大,纵测线2、纵测线3无显著的变化,整条横测线依然显现出减小趋势。由此可见,该相邻期磁化率变化从空间位置仍然集中在维西—乔后、红河断裂以南区域。
与2012年9月—2013年2月相邻期(图2d)相比,图2e中纵测线1在维西—乔后断裂和无量山断裂之间深度为10~15 km、15~20 km出现的磁化率减小和增大趋于减缓,纵测线2分别在深度为10~15 km、15~20 km出现的磁化率减小和增大、纵测线3无显著的变化,横测线在无量山、维西—乔后断裂之间深度15~20 km呈现出减小,红河、维西—乔后断裂之间深度15~20 km呈现出增大。
图2 2011年3月—2013年9月相邻期4条测线磁化率结构变化
Fig.2 The magnetic susceptibility structure changes of adjacent 4 survey lines from March,2011 to September,2013综上所述,云南洱源M5.5地震前维西—乔后断裂、红河断裂以南是地下磁化率结构变化显著地区; 在维西—乔后与无量山断裂之间,磁化率在深度10~15 km和15~20 km同时减小,之后仅在深度15~20 km转为增大,此时洱源地震发生了。
5 结论与讨论
2013年3月3日在云南洱源发生了M5.5地震,震中位于滇西的维西—乔后断裂。对滇西地区地磁资料的分析研究表明,洱源M5.5地震前存在地磁场总强度与岩石圈磁场的前兆信息,根据该地磁前兆信息,倪喆(2014a)对这个地震的地点作出了较好的预测。
岩石圈磁场是由地下介质的感应磁化强度和剩余磁化强度两者所产生的磁场构成的。剩余磁化强度是表示剩余磁性大小的物理量,它是岩石和矿石在形成时所产生的磁性,历经地质变动后保留下来的部分磁性,它的大小和方向与现代地磁场无关,而是决定于形成时的环境及所经历的地质变动。感应磁化强度是表示感应磁性大小的物理量,它是岩石和矿石受地磁场磁化所产生的磁性,其数值等于磁化率x与磁化磁场之磁场强度T的乘积。顺磁性物质的方向与现代地磁场方向一致,而逆磁性物质则方向相反。
磁化率是表征地下介质磁性强弱的磁学量。实验室观测结果表明,岩石的磁化率与温度有着密切的关系。一般来说,温度上升,磁化率减小; 温度下降,磁化率上升。因此,分析2011年3月—2013年9月滇西测区5个相邻期地下介质磁化率结构的变化,得到了洱源地震前在维西—乔后和无量山断裂之间深度10~20 km的区域内,温度的上升和下降经历过了2个周期的变化,最终洱源M5.5地震发生在维西—乔后和无量山断裂之间深度10~15 km为温度上升和15~20 km温度下降的区域。
观测与研究表明,有些地震主要是由地下介质的不均匀性而不是由地壳应力增加所控制的。对于这些地震而言,分析与研究地下介质磁化率的不均匀性及其变化,对于发震的地点、时间、震级的预测探索是很有意义的。由于磁化率与温度具有密切的关系,故磁化率变化的分析结果可以研究地下温度的变化,进而探讨震源区的地热变化。因此,地震孕育过程中地下介质磁化率结构变化的分析研究是很有意义的,有助于推进地震预测的探索研究。
本文在撰写过程中,中国地震局地球物理研究所詹志佳研究员和顾左文研究员给予了大力的指导与支持,在此表示感谢!
- 顾春雷,张毅,顾左文,等.2012.华北地震区岩石圈磁异常场零值线与中强震震中分布关系[J].西北地震学报,25(2):174-179.
- 顾春雷,张毅,徐如刚,等.2010.地震前后岩石圈磁场变化特征分析[J].地球物理学进展, 25(2):472-477.
- 顾左文,陈斌,高金田,等.2009.应用NOC方法研究中国地区地磁时空变化[J].地球物理学报,52(10):2602-2612.
- 顾左文,张毅,姚同起,等.2006.九江—瑞昌MS5.7地震地磁异常的观测与分析[J].地震学报,28(6):611-621.
- 管志宁.2005.地磁场与磁力勘探[M].北京:地质出版社.
- 国家地震局科技监测司.1991.中国地震预报方法研究[M].地震出版社.
- 国家地震局科技监测司.1988.地震监测与预报方法清理成果汇编.地下水分册[M].地震出版社.
- 倪喆,陈双贵,袁洁浩,等.2014b.芦山7.0级地震前后岩石圈地磁变化异常研究[J].地震研究,37(1):61-65.
- 倪喆,闫万生,袁洁浩.2014c.鲁甸地震与永善地震前岩石圈磁场局部异常的特征分析[J].地震研究,37(4):537-541.
- 倪喆.2014a.洱源5.5级地震前后地磁场变化异常特征分析[J].地震研究,37(3): 426-432.
- CHEN B,NI Z,YUAN J,et al.2016.Anomalous variations of lithospheric magnetic field before several earthquakes[J].Abstracts of International 2016 EMSEV Workshop,Lanzhou,China, August 25-29,183.
- GU Z,ZHAN Z,GAO J,et al.2006.Seismomagnetic research in Beijing and its adjacent area, China.Physics and Chemistry of the Earth[J].physics & chemistry of the Earth Parts A/b/c,31(4-9):258-267.
- JOHNSTON M,MUELLER R.1987.Seismomagnetic observation with July 8,1986,ML5.9 North Palm Springs earthquake[J].Science,237:1201-1203.
- JOHNSTON M,SASAI Y,EGBERT G,et al.2006.Seismomagnetic effects from the long-awaited 28 September 2004 M6.0 Parkfield earthquake[J].Bull Seism Soc Am,96(4B):S206-S220.
- JOHNSTON M.1997.Review of electric and magnetic fields accompanying seismic and volcanic Activity[J].Surveys in Geophysics,18(1):441-475.
- MUELLER R,JOHNSTON M.1998.Review of magnetic field monitoring near active faults and volcaniccalderas in California[J].Phys Earth Plan Int,105(3-4):131-144.
- NAGATA T.1970.Basic magnetic properties of rocks under the effect of mechanical stresses[J].Tectonophysics,9(2-3):167-195.
- NI Z.2016.Geomagnetic survey and anomalies related to earthquake activity in the North-South belt of China[R].Technical Program of International 2016 EMSEV Workshop,Lanzhou,China,August 25-29.
- RIKITAKE T,HONKURA Y.1985.Solid Earth Geomagnetism[M].Tokyo:Tarra Scientific Publishing.
- SASAI Y,ISHIKAWA Y.1991.Tectonomagnetic signals related to the seismo-volcanic activity in the Izu Penisula[J].Phys Earth,39:299-319.
- SHAPIRO V,ABDULLABEKOV K.1982.Anomalous variations of the geomagnetic field in east Fergake-magnetic precursor of the Alay earthquake with M=7.0(1978,November 2)[J].Geophys J R Atron Soc,68(1):1-5.
- SHAPIRO V,MIMINOV M,ABDULLABKOV K.1994.High precision magnetomery for earthquake prediction in Uzbekistan[M].Ninety-one forcasts between 1982 and 1992//Hayyakawa M,Fujinawa Y.Electromagnetic Phenomena Related to Earthquake Prediction, Tokay:Terra Scientific Publlishing Company,37-42.
- SHAPIRO V,PUSHKOV A,ABDULLABEKOV K,et al.1978. Geomagnetic investigations in the seismoactive regions in Middle Asia[J].Geomag Geoelectr,30:503-509.
- SUMITOMO N,NORITOMI K.1986.Synchronous precursors in the electrical earth resistivity and geomagnetic field in relation to an earthquake near the Yamasaki fualt,Southwest Japan[J].Geomag Geoeletr,38:971-989.
- YUAN J.2016.Analysis on the anomaly of mobile geomagnetic monitoring in the North-South seismic belt and North China in 2016[R].Lanzhou:Technical Program of International 2016 EMSEV Workshop.ZHAN Z,GAO J,ZHANG H,et al.1999.Seismomagnetic signals observed in China[J]//Hayakawa M Atmospheric and Ionospheric Electromagnetic Phenomena Associated with Earthquakes. Tokyo,Japan:Terra Scientific Publishing Company.185-196.
- ZHAN Z.1989.Investigations of tectonomagnetic phenomena in China[J].Physics of Earth and Planetary Interiors,57(1):11-22.