基金项目:国家自然科学基金—基于三维地壳形变研究黄河断裂灵武段现今活动状态(41604015)和中国地震局地震科技星火计划—基于InSAR的东昆仑断裂玛沁玛曲段地震危险性分析(XH17059)联合资助.
备注
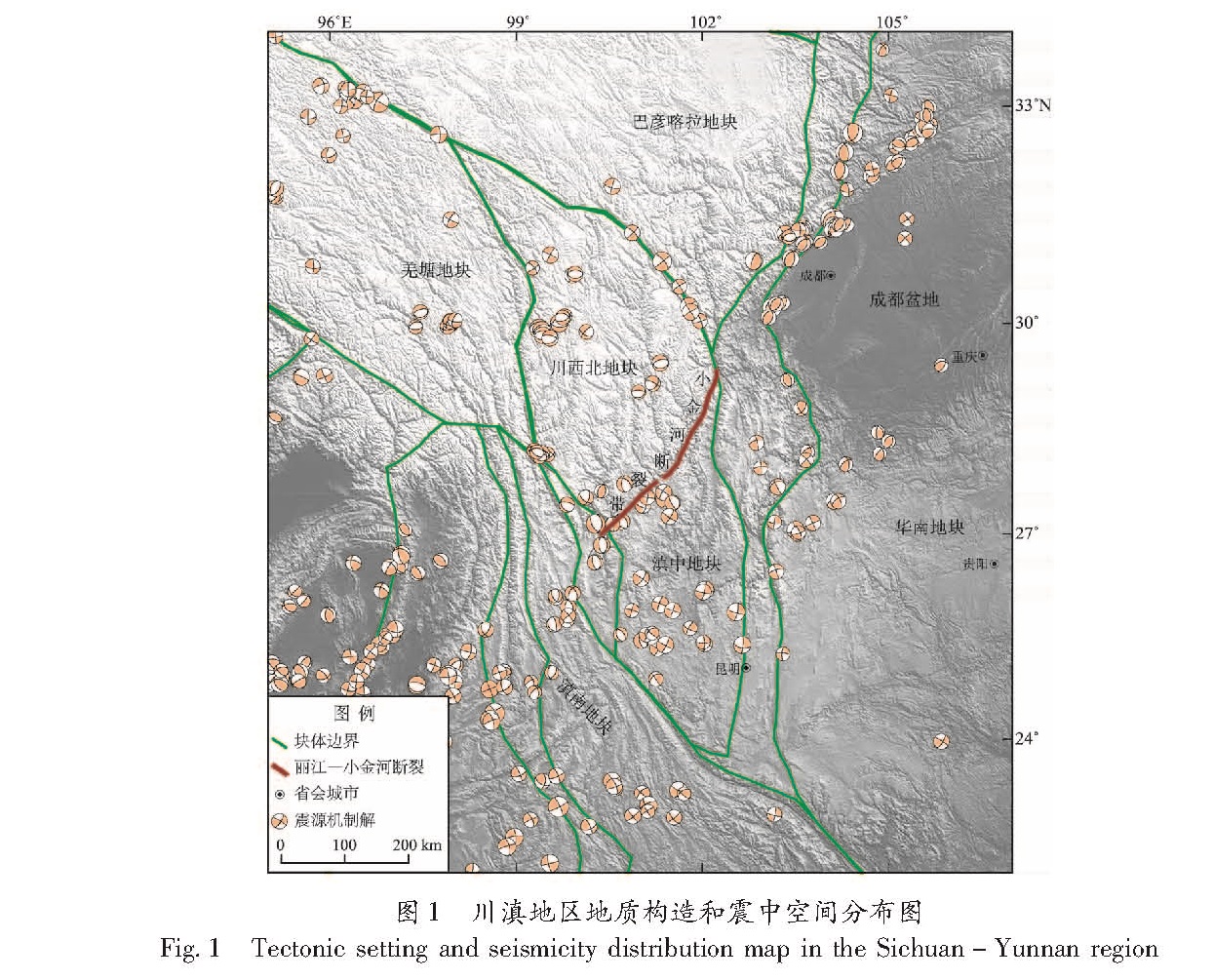
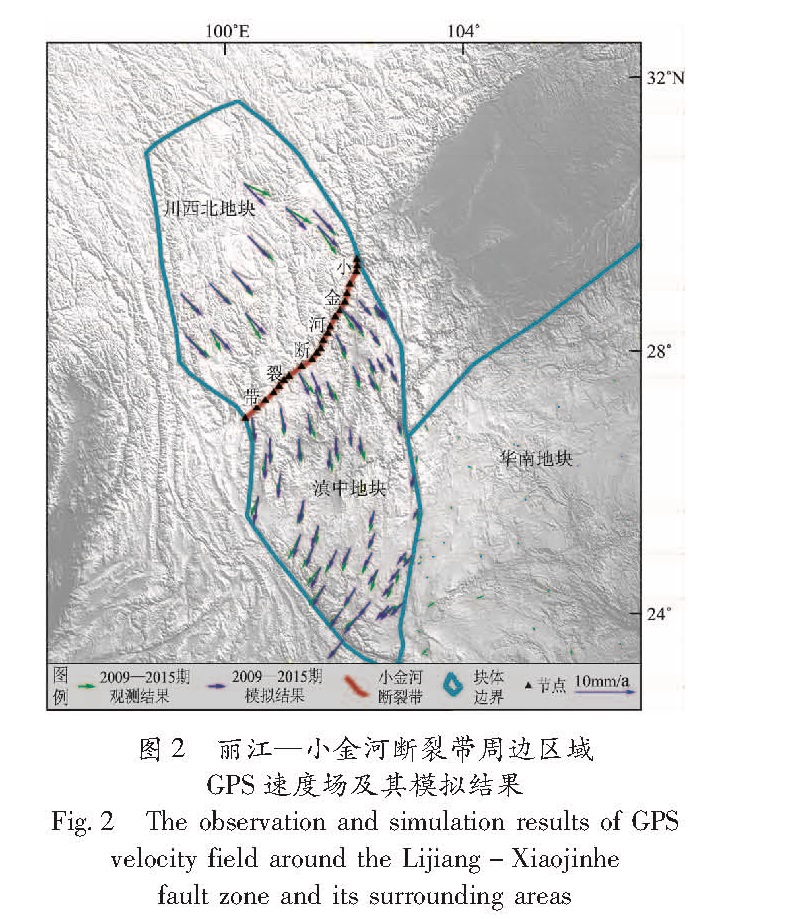
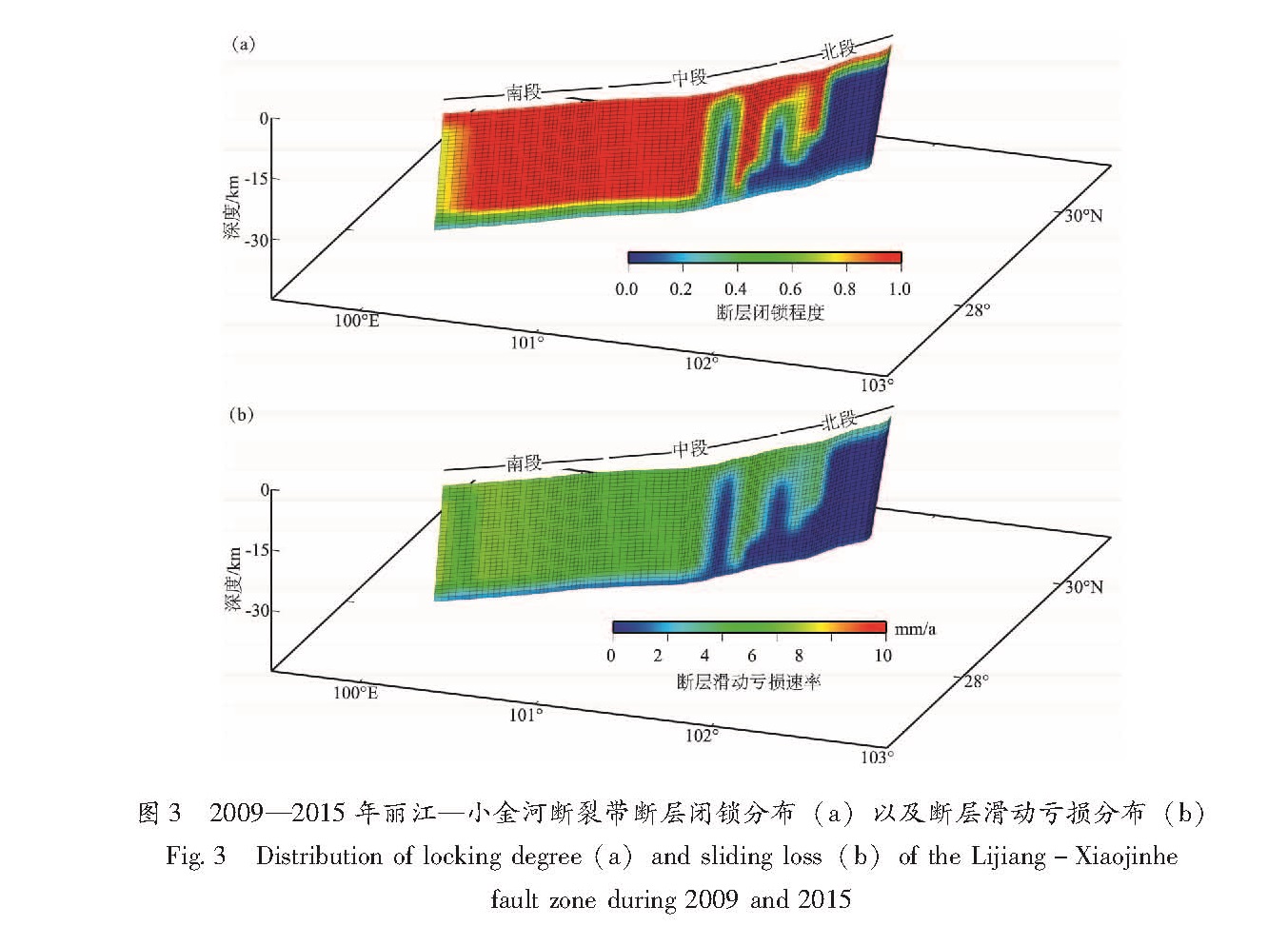
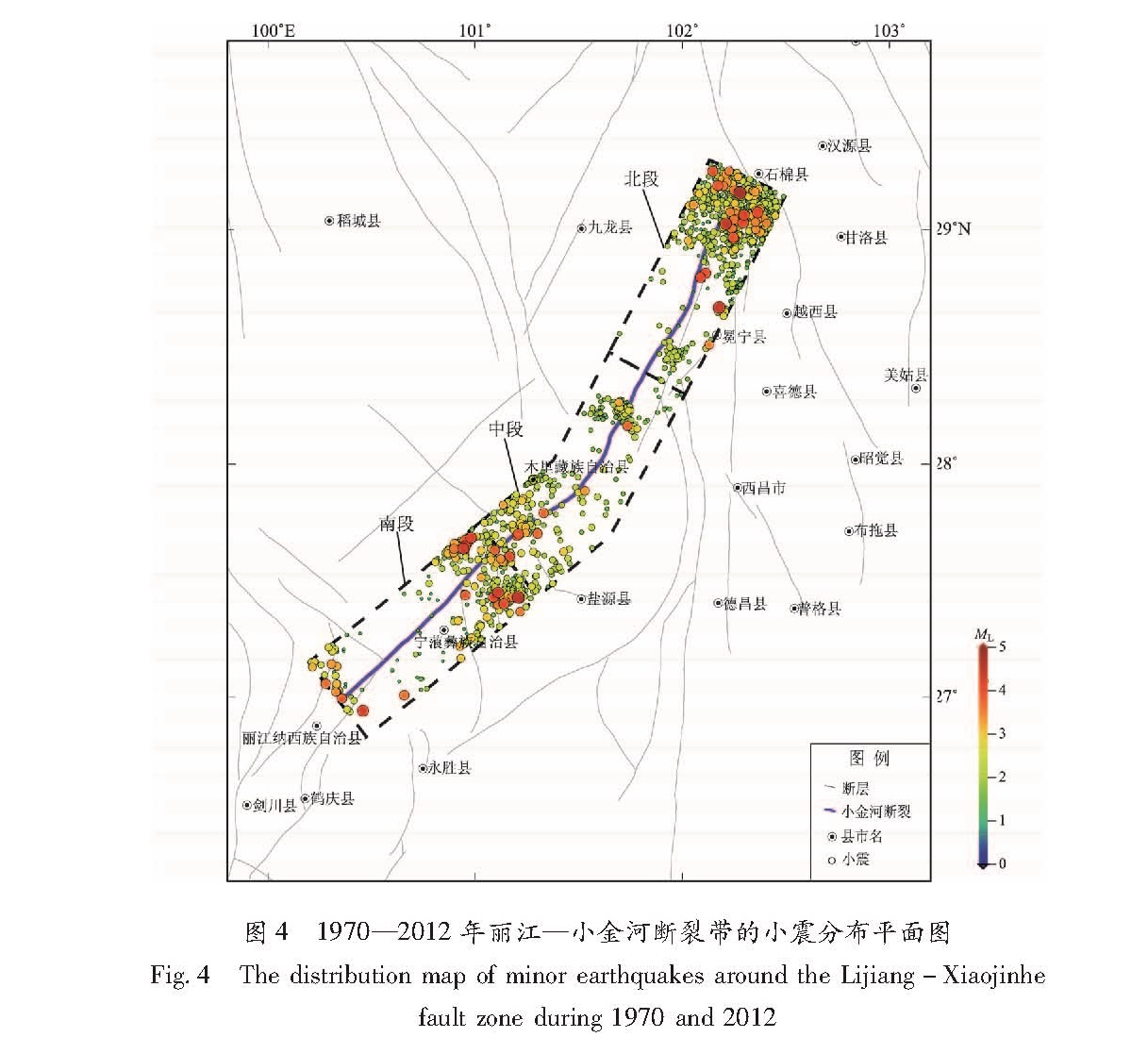
基于2009—2015年中国大陆GPS水平速度场数据,采用DEFNODE负位错反演程序计算了丽江—小金河断裂带的断层闭锁程度和滑动亏损速率特征,并结合小震精定位结果分析了该断裂带的强震危险性。结果 表明,GPS水平观测值与模型值的拟合结果较好,小震分布与闭锁程度结果存在一定的相关性,丽江—小金河断裂的南段—中段南部(丽江—宁蒗)除最南端外基本完全闭锁,断层的滑动亏损速率也相对较大,该段落具有发生较大地震的潜在危险性; 而中段中北部—北段闭锁程度要弱得多,尤其在断裂带的北段,闭锁程度很弱,除了南部有部分闭锁,其余地方无强闭锁状态,且在5 km左右深度处断裂基本由闭锁状态转化为蠕滑状态特征,断层的滑动亏损速率也相应很小,该段发生较大地震的可能性较小。
Based on the GPS horizontal velocity field of 2009-2015 and the back-slip dislocation model of DEFNODE,we inverted for fault locking degree and fault slip deficit of the Lijiang-Xiaojinhe fault zone,and analyzed the potential seismic danger combining with the results of relocated small earthquakes. The results show that the fit results of GPS horizontal observation value and the simulated value are consistent,and there is also a certain correlation between the distribution of minor earthquakes and the degree of fault locking. The inversion results show that the southern part of the Lijiang-Xiaojinhe fault zone is basically completely locked except the southernmost,and the fault slip deficit rate is relatively large,which has the potential danger of a large earthquake. The middle section of the Lijiang-Xiaojinhe fault is different from the south to north,and the southern is locked seriously,which is also almost completely locked,and the degree of locking of the northern fault is much weaker. And for the northern part of the Lijiang-Xiaojinhe fault zone,the locking degree is very weak. Besides the partial locked in the south,there is no strong locking state in other parts,and the fracture is basically transformed from the locking state to the creep state at a 5 km depth,and the fault slip deficit rate is relatively small,while the possibility of larger earthquakes in this section is much smaller.