基金项目:中国地震局地震科技星火计划——基于InSAR的东昆仑断裂玛沁玛曲段地震危险性分析(XH17059)、汶川地震对川滇地区震后影响与观测异常研究(XH16058Y)、国家自然科学基金——基于三维地壳形变研究黄河断裂灵武段现今活动状态(41604015)和山西省科技攻关项目——基于InSAR技术的山西地震重点监视防御区现今地壳形变场监测与研究(20140313023-1)联合资助.
(The Second Crust Monitoring and Application Center,China Earthquake Administration,Xi'an 710054,Shaanxi,China)
the Anninghe-Zemuhe fault; slip distribution; steepest descent method; GPS
备注
基金项目:中国地震局地震科技星火计划——基于InSAR的东昆仑断裂玛沁玛曲段地震危险性分析(XH17059)、汶川地震对川滇地区震后影响与观测异常研究(XH16058Y)、国家自然科学基金——基于三维地壳形变研究黄河断裂灵武段现今活动状态(41604015)和山西省科技攻关项目——基于InSAR技术的山西地震重点监视防御区现今地壳形变场监测与研究(20140313023-1)联合资助.
基于约束条件下最小二乘原理及最速下降法,采用最小二乘配置拟合后的震间期GPS速度场作为约束,对安宁河—则木河断裂断层面滑动分布进行了反演。研究结果表明:由GPS资料计算所获取的断层面滑动分布,与地震地质研究中得到的断层面凹凸体分布具有较好的一致性,即安宁河断裂(西昌至冕宁以北)闭锁深度较深,强震危险性较大; 而则木河断裂闭锁深度较浅,近期发生强震的可能性较小。
Based on the least squares principle with constraint conditions and the steepest descent method(SDM),the slip distribution on the fault plane was inversed along Anninghe-Zemuhe fault plane using the interpolated GPS velocity field from observation by the least squares principle.The results indicate that it is consistent between the fault plane slip and the location of asperity defined by seismic geological research.The locking depth of the Anninghe fault(Xichang to the north of Mianning)is big,with a high seismic risk.However,for the Zemuhe fault,the locking depth is small,with a low seismic risk in the short-term.
引言
安宁河—则木河断裂带作为青藏地块与华南地块的边界断裂,自新生代以来发生了强烈的构造运动,在晚第四纪反复经历多次断裂活动和强震活动。地震危险性趋势研究和古地震研究结果均表明安宁河断裂带冕宁—西昌段存在一个较大尺度的凹凸体,区域应力场显示该段呈高应力背景下的闭锁状态,是未来川滇地块发生大地震的潜在危险段之一(易桂喜等,2004; 冉勇康等,2008; 闻学泽等,2008)。
以GPS为代表的空间大地测量技术在地壳形变监测领域应用十分广泛,它能够为科研人员提供高精度、大尺度、多维的地壳形变监测数据。就一般意义而言,断层附近震间期地壳形变,能够反映震间期断层面滑动分布特征。进一步将震间期断层滑动分布和断层长期滑动速率进行比较,就可以得到断层面闭锁特征,利用闭锁特征可以圈定断层面凹凸体位置,为强震地点预测提供依据。借助GPS、InSAR等大地形变资料,不少学者对安宁河—则木河断裂断层长期滑动速率,断层面滑动分布及断层闭锁程度进行了深入研究(申重阳等,2002; Shen et al,2005; 方颖等,2005; 张希等,2005,2007,2009,2013; 赵静等,2015,2018; Jiang et al,2015),但受限于研究资料和研究方法,不同学者研究结果存在显著差异。如赵静等(2015)研究结果显示安宁河—则木河断裂整段闭锁程度均较高,而Jiang等(2015)研究显示则木河断裂除了北端和安宁河断裂交汇的西昌附近,以及南端和小江断裂交汇的巧家附近之外,闭锁程度均不高。
目前,在研究震间期断层面运动时,大多采用基于弹性回跳理论的负位错模型,其基本原理是,将震间期观测位移场描述为块体旋转、块体内部形变与断层运动的集合。这就需要对研究区进行块体划分,而分块方式则依赖于研究区的地质背景,具有很大的不确定性,许多地块内部依然存在很多次级断裂。因此,在描述块体运动和内部形变时,依然存在很多不确定性。本文将断层附近震间期地表形变场表述为断层浅部孕震层运动引起的相对近场形变,和深部断层蠕滑层引起的相对远场变形之和。利用二维均匀弹性半空间位错模型剖面分析法,确定目标断层的长期滑动速率、闭锁深度(孕震层深度)作为先验约束,然后考虑断层浅部孕震层和深部蠕滑层进行几何模型设置,再采用基于约束条件下最小二乘原理及最速下降法(Steepest Descent Method,简称SDM)(Wang et al,2013)进行震间期断层面滑动分布的反演,避免了块体划分对研究结果的影响。在资料方面,安宁河—则木河断裂作为中国地震局强震危险性主要跟踪地区之一,多年来积累了丰富的GPS观测数据,这些GPS观测资料获得的川滇地区长期地壳水平运动速度场,亦为本文研究提供了支持。因此,本文将利用Reinoza等(2015)提出的研究方法,以川滇地区长期地壳水平运动速度场作为约束,对安宁河—则木河断裂震间期的断层面滑动分布进行反演,并结合已有地震地质研究成果,评价未来可能发生强震的具体位置。
1 GPS资料来源及处理说明
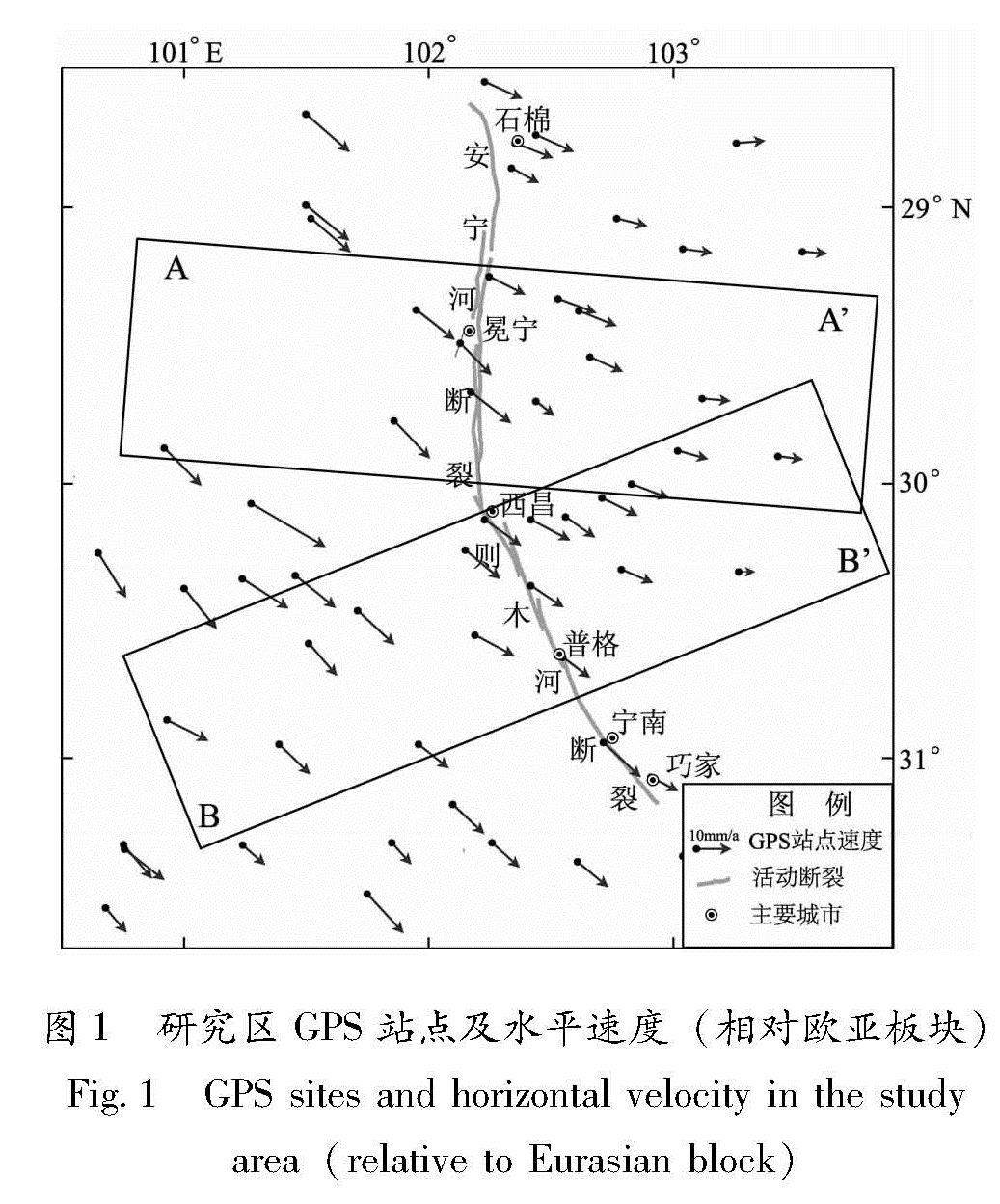
GPS观测提供了高精度、大范围的地壳运动定量数据,这些数据所形成的地壳运动速度场是进行断层运动研究的重要基础。借助中国地壳运动观测网络I期和II期观测结果,利用国内外多种数据处理软件(GAMIT/GLOBK,BERNESE,PANDA,GIPS)可以得到中国大陆地壳水平运动速度场。在这些速度场成果中,Wang等(2017)、Zheng等(2017),Pan和Shen(2017)分别采用BERNESE软件、PANDA软件和GIPSY软件进行了数据处理,其处理过程中采用的IGS提供的卫星轨道精密星历、潮汐模型(固体潮、极潮、海潮)、大气折射模型(电离层折射改正、气象模型及映射函数)、天线相位中心等参数基本相同,后期参考框架的实现也基本一致。在单日解计算方面,Zheng等(2017)采用精密单点定位技术,Wang等(2017),Pan和Shen(2017)采用双差定位技术得到的结果差异不大。为了获得反映构造形变的长期地壳水平运动速度场,在数据处理过程中不仅需要扣除仪器、人为因素等对站点观测时间序列的影响,还需要扣除在观测时间段内,显著地震同震及震后形变的影响。通过比较,我们认为Zheng等(2017)研究得到的速度场更加符合本文研究需要,它不仅更好地考虑了非构造因素对速度场的影响,对于站点仪器、人为因素的影响,也在处理过程中通过记录手簿查对加以改正; 还考虑了在资料观测时间段内的所有显著地震,主要包括2004年苏门答腊MW9.1地震,2011年日本MW9.0地震以及研究区内所有MW≥5.9地震。Zheng等(2017)还借助最小二乘原理对站点时间序列用线性函数来估计长期速度,并将速度场统一到欧亚框架之下(图1),为我们的计算提供了便利。
2 二维均匀弹性半空间位错模型剖面分析
笔者首先根据实际观测资料对断层附近形变场进行二维均匀弹性半空间位错模型剖面分析,以获取断层孕震层深度(闭锁深度)和蠕滑层滑动速率(滑动速率)。Savage和Burford(2012)给出了走滑断层震间形变曲线位移公式; Fruend和Barnett(1976)通过“刃型”位错给出倾滑断层震间形变数学表达式; 邹镇宇等(2015)对上述公式进行了改进,获得了考虑断层地表位置的一般倾角断层的震间期数学表达式。考虑到安宁河—则木河断裂晚第四纪以来主要以左旋运动为主,倾滑分量相对较小,以GPS水平位移平行断裂方向分量作为约束,借助带倾角的走滑断层二维均匀弹性半空间位错模型数学表达式(邹镇宇等,2015),在断层倾角确定的情况下,反演断层闭锁深度和滑动速率。参数估计采用网格搜索算法,在滑动速率和闭锁深度构成的二维模型空间内,计算其加权残差平方和并使其最小,目标函数为:
∑[(v0-vc)/σ]2/n(1)
式中:v0为实测速率; vc为拟合速率; σ是其中误差; n为观测值数目。
由于GPS实际观测站点比较稀疏,对安宁河—则木河断裂无法做到分段剖面分析,只能根据速度场分布,划分了2个剖面(图1 中AA'和BB'),其中AA'主要通过安宁河断裂西昌至石棉段,BB'主要通过则木河断裂普格至西昌段。
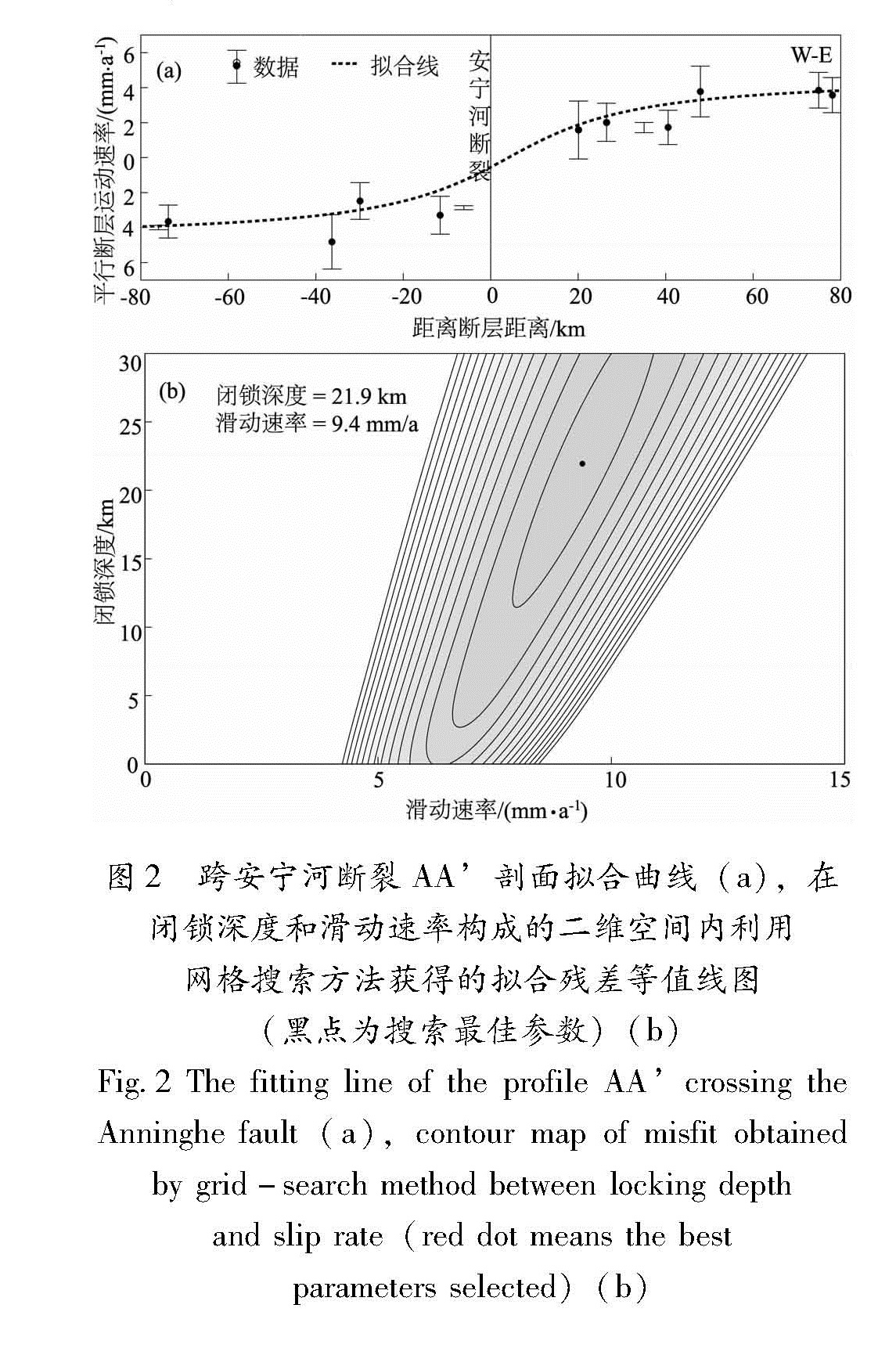
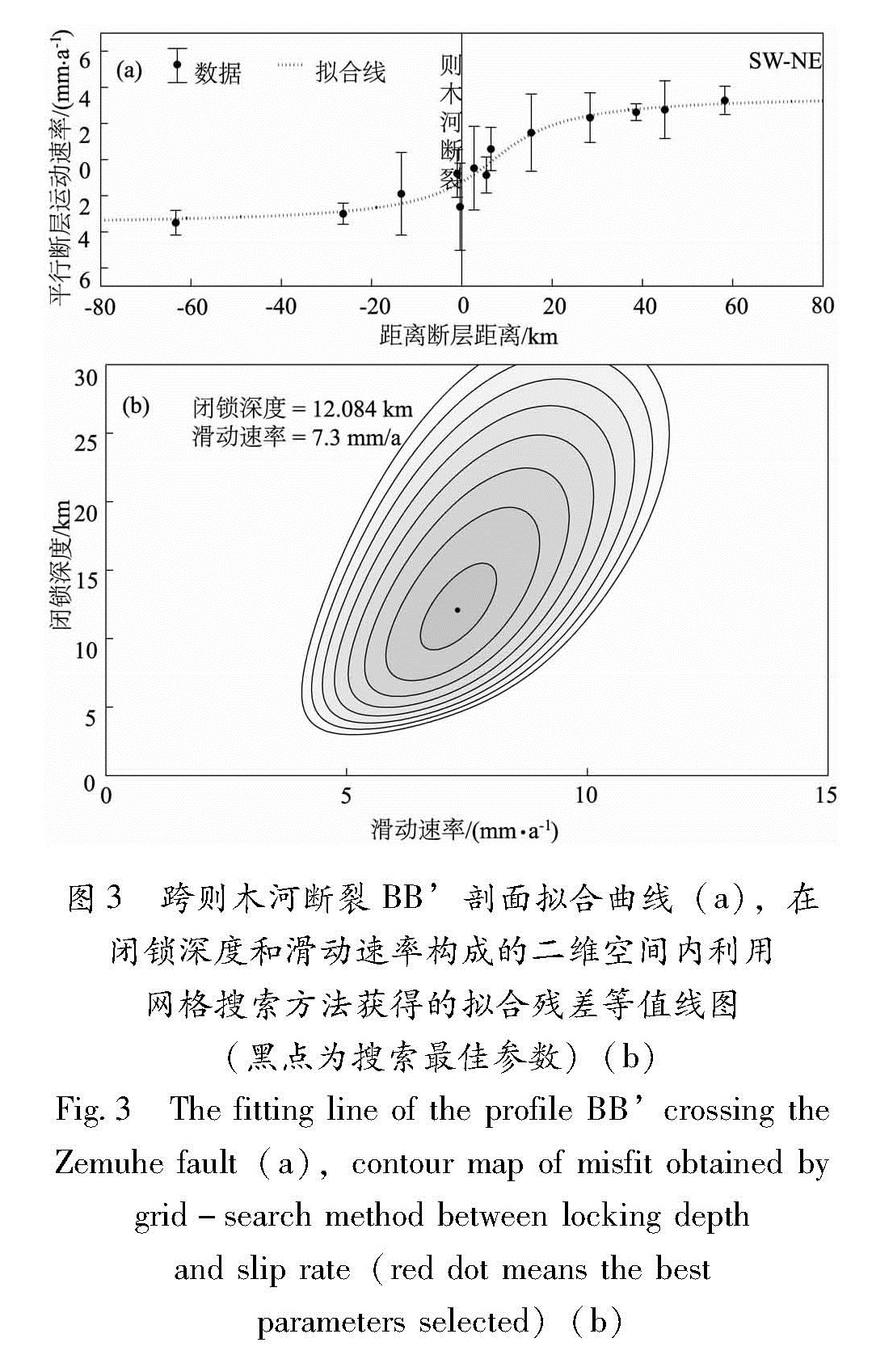
根据已有的断裂几何产状的研究(闻学泽,2000; 杨卓欣等,2011),给定安宁河断裂断层倾向E,倾角80°; 则木河断裂断层倾向NE,倾角60°。剖面长度为断层两侧各80 km左右,资料选取的时候应尽可能避开构造较为复杂的过渡带和转换区。反演结果显示(图2,3),在给定的搜索范围内,2个剖面参数估计均具有较好的收敛性。安宁河断裂深部蠕滑层左旋走滑速率为9.4 mm/a,断层闭锁深度为21 km。则木河断裂深部蠕滑层左旋走滑速率7.3 mm/a,断层闭锁深度为12 km,和相关利用形变资料研究结果接近。这表明安宁河断裂西昌至冕宁段未来强震危险性更高。需要说明的是,除了主干断裂安宁河—则木河断裂之外,附近其他次级断裂对震间形变场也会产生影响。但从反演的拟合曲线(图2a、图3a)来看,形变差异主要来自安宁河—则木河断裂,周围其他次级断裂贡献较小。因此,不会对分析结果产生大的影响。
图2 跨安宁河断裂AA'剖面拟合曲线(a),在闭锁深度和滑动速率构成的二维空间内利用网格搜索方法获得的拟合残差等值线图(黑点为搜索最佳参数)(b)
Fig.2 The fitting line of the profile AA' crossing the Anninghe fault(a),contour map of misfit obtained by grid-search method between locking depth and slip rate(red dot means the bestparameters selected)(b)3 震间期断层面滑动分布反演
3.1 断层几何模型设置根据断层几何产状和已有的地震地质研究结果(闻学泽等,2000,2008),将安宁河—则木河断裂划分为4段,即将安宁河断裂分为冕宁至石棉段和西昌至冕宁段,则木河断裂划分为宁南至普格段和普格至西昌段。参考小震精定位剖面投影结果,设定模型上层孕震层深度为20 km,下层蠕滑层深度为30 km。断层倾角和之前二维均匀弹性半空间位错模型剖面分析一致,安宁河断裂倾向E,倾角80°,则木河断裂倾向NE,倾角60°,且断层上下倾角一致。将断层面上层以较密网格划分,断层面下层以较粗网格划分。
3.2 地表水平形变约束对于断层面精细化研究而言,现有GPS站点空间分布显得过于稀疏,特别是在断裂两侧较近的范围内,站点分布更少。最小二乘配置方法能够一定程度上弥补这种不足,可以对观测资料进行较好的空间拟合与推估(武艳强等,2009),但也有可能会滤掉一些局部信息,但对于较大尺度的断层构造运动研究而言,仍然具有优势。通过对比利用最小二乘配置拟合水平速度场作为约束的反演结果,以及利用实际观测作为约束的反演结果,可以发现利用最小二乘配置拟合水平速度场作为约束得到的结果更为合理,反演过程中收敛也较快。因此,本文将详述利用最小二乘配置拟合水平速度场进行反演的数据处理过程及反演结果。
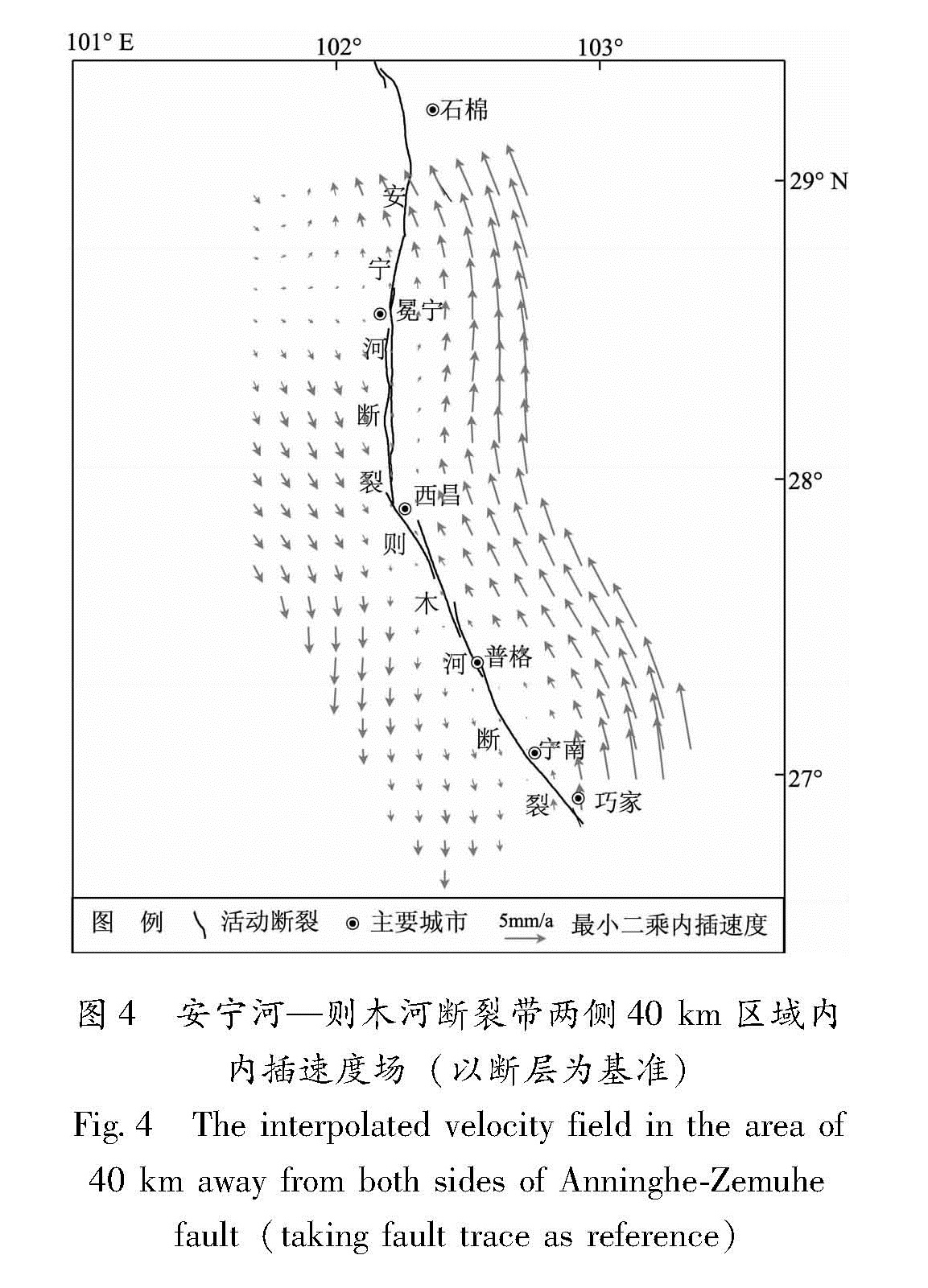
要进行震间期断层面滑动分布反演研究,就必须得到由断层运动引起的地表形变场,而实际观测得到的地表形变场,采用的框架并不是以断层为基准,而是相对于某一稳定的框架,在反演之前需要对资料进行框架转换。本文GPS速度场是相对欧亚板块框架的,为了得到以研究断层为基准的水平形变场,采用如下方案:首先将研究区相对欧亚板块GPS速度场进行最小二乘配置拟合,获得相对欧亚板块均匀分布的水平运动速度场; 其次,为了尽可能减少研究区域其他次级断裂的影响,参考相关研究结果(Jiang et al,2015),选取断裂两侧40 km以内的速度场,并将速度场扣除整体欧拉旋转矢量,得到反映断层附近区域相对运动的速度场; 最后,选取断层两侧5 km以内的点计算欧拉旋转矢量,并将所有速度转换到以断层为基准的框架下。通过上述步骤处理得到的速度场(图4),可以近似认为是由于断层震间期运动引起的形变场。
3.3 SDM反演方法介绍Wang等(2013)的研究是基于分层介质模型中,地震位错造成的地表形变的正反演程序PSCMP及SDM。本文采用其反演程序SDM进行震间期断层面滑动分布的反演。根据地表形变资料建立震间期断层模型,公式为:
y=f(x)+ε(2)
式中:x为与断层有关的参数,包括断层长度、宽度、位置、走向、倾角、滑移量; ε为误差; y为地表观测值。
在断层几何参数确定后,位错模型的反演问题就可以转换为一般的线性反问题,公式为:
y=Gb+ε(3)
式中:G为格林函数,是运用位错理论根据弹性半无限空间或分层地球模型计算的; b为地下断层面的滑动量; y代表地表观测。
为了获取高分辨率断层面精细滑动分布,将断层面划分为很多小块,b为每个子断层面上的滑动量。根据整个断层的位错分布得出剪切应力降,公式为:
F(s)=〖JB<1=〗Gs-y〖JB>1=〗2+α2〖JB<1=〗IIs〖JB>1=〗2(4)
式中:II为相关位移幅度的权重因子与拉普拉斯算子有限差分近似; s为地下断层面的滑动量; y代表地表观测值; α为平滑因子。
3.4 反演结果及其分析利用上述断层几何模型,用处理后的以断层为基准的GPS水平运动速度场作为约束,采用SDM反演程序包(Wang et al,2013),进行震间期断层面滑动分布的反演。对反演参数的约束,参照二维反正切剖面分析结果,对安宁河断裂设置10 mm的最大约束,则木河断裂设置8 mm的约束。为了保证反演结果的稳定性,引入滑动因子进行约束,最佳滑动因子一般通过权衡粗糙度和拟合残差确定。本文选取的最佳滑动因子为0.15。为了尽可能提高反演结果的可靠性,利用Crust2.0将地壳处理成层状介质模型。
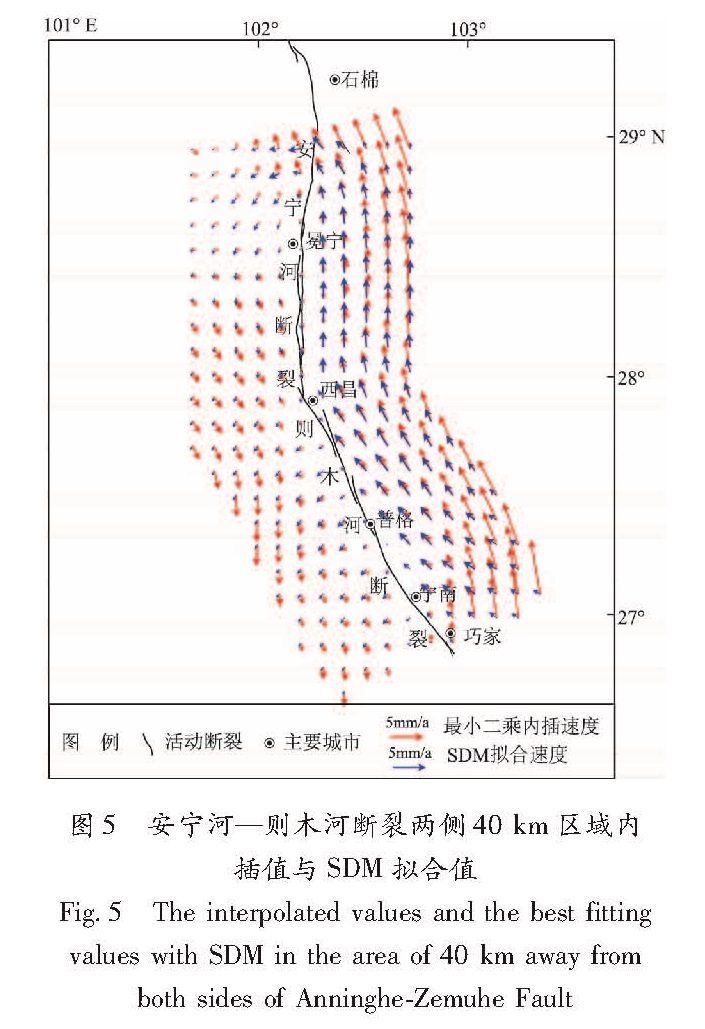
从水平速度场拟合效果来看(图5),SDM反演给出的拟合度达到了75.8%,相对于同震形变而言,拟合度过低,但对于微小量的震间形变而言,在可接受范围之内。大部分站点拟合残差在2 mm以下,越靠近断层拟合残差越小,而远离断层拟合残差较大,断层两端拟合残差相对较大。其主要原因除了与数据本身有关之外,也可能与断层模型的设置单一有关。尽管如此,本文的反演较为收敛,断层面运动的主要特征得到了反映。
图6为SDM反演得到的断层面滑动分布,上部分色块图代表震间期断层面滑动量大小分布。为了更好地和小震精定位结果进行比较,将1999—2015年断层两侧20 km以内大于2级的精定位小震投影到断层面上(色块图中灰色圆形)。为了更好显示断层的运动性质,在图6下部分给出了断层面每个网格滑动矢量(蓝色箭头,沿着断层走向为左旋走滑,反向为右旋走滑,向上为逆冲,向下为拉张)。由于安宁河断裂与则木河断裂的断层倾角不同,断层面的宽度也不同,因此在左右两侧分别给出其纵坐标。从反演断层面滑动分布来看:(1)断层面滑动矢量,特别是闭锁深度以下,安宁河断裂和则木河断裂存在显著差异,
安宁河断裂整体表现为左旋逆冲,而则木河断裂表现为左旋拉张,且安宁河断裂深部滑动速率大于则木河断裂;(2)则木河断裂整段闭锁程度不高,闭锁深度和二维反切剖面反演断层闭锁深度接近,最大为10 km左右,西昌至普格段滑动亏损相对较大,但闭锁深度并未下达到小震动活动稀疏的分界线。参考易桂喜等(2004)研究结果,可能与该段处于1850年大地震时释放的应力尚未得到恢复阶段有关,处于应变能积累的中早期。而宁南至普格之间滑动亏损深度较浅,小震活动相对比较频繁,可能断层应变积累以小震形式得到释放;(3)安宁河断裂(西昌至冕宁以北)整体上闭锁程度较高,整段在孕震层基本完全闭锁,闭锁深度最大处在冕宁附近,接近20 km,从小震活动分布来看,滑动速率较小,也就是滑动亏损较大的地方,小震活动比较稀疏,可能反映该断裂处于强闭锁状态,这和闻学泽等(2008)利用地震地质资料所得研究结果基本一致。因此,未来安宁河断裂强震危险性要显著高于则木河断裂,应加强观测与跟踪。图5 安宁河—则木河断裂两侧40 km区域内插值与SDM拟合值
Fig.5 The interpolated values and the best fitting values with SDM in the area of 40 km away from both sides of Anninghe-Zemuhe Fault4 结论与讨论
本文采用Reinoza等(2015)的研究方法,以最小二乘配置方法拟合得到的GPS地壳水平运动速度场作为约束,借助基于约束条件下最小二乘原理及最速下降法(SDM)模型,反演了安宁河—则木河断裂震间期断层面深浅部运动特征。研究结果表明,计算得到的断层面滑动亏损与地震地质研究得到的断层面凹凸体分布具有较好的对应,安宁河断裂西昌至冕宁以北之间强震危险性程度更高,则木河断裂强震危险性较低。需要解释的是:(1)本文研究结果与地震地质研究结果吻合,与以往利用GPS、InSAR得到的研究结果存在一定差异,可能是由于来源资料的使用和处理上的不一致;(2)文中利用经过最小二乘配置拟合后的速度场做为约束,虽然突出了断层整体运动特征,但也可能过滤掉了与断层局部运动有关的形变信息,甚至可能放大了周围其他次级断裂对速度场的影响。但我们根据前人的经验(Savage,Burford,1973),将计算范围控制在断层两侧40 km以内,以尽可能减小这种影响;(3)安宁河—则木河断裂的深浅部几何构造非常复杂,仅用1个断面去反演太过近似,可能与实际出入较大,这可能也是速度场拟合残差有些大的原因,我们将在未来的模型中继续予以完善。
感谢德国波茨坦地学研究中心汪荣江老师提供的SDM程序包,感谢中国地震局地球物理研究所房立华研究员提供小震重新定位目录。
- 方颖,江在森,牛安福,等.2005.川滇菱形块体东边界地壳形变研究[J].大地测量与地球动力学,25(3):81-85.
- 冉勇康,陈立春,程建武,等.2008.安宁河断裂冕宁以北晚第四纪地表变形与强震破裂行为[J].中国科学:地球科学,38(5):543-554.
- 申重阳,王琪,吴云,等.2002.川滇菱形块体主要边界运动模型的GPS数据反演分析[J].地球物理学报,45(3):352-361.
- 闻学泽,范军,易桂喜,等.2008.川西安宁河断裂上的地震空区[J].中国科学:地球科学,38(7):797-807.
- 闻学泽.2000.四川西部鲜水河-安宁河-则木河断裂带的地震破裂分段特征[J].地震地质,22(3):239-249.
- 武艳强,江在森,杨国华,等.2009.利用最小二乘配置在球面上整体解算GPS应变场的方法及应用[J].地球物理学报,52(7):1707-1714.
- 杨卓欣,王夫运,段永红,等.2011.川滇活动地块东南边界基底结构——盐源—西昌—昭觉—马湖深地震测深剖面结果[J].地震学报,33(4):431-442.
- 易桂喜,闻学泽,范军,等.2004.由地震活动参数分析安宁河—则木河断裂带的现今活动习性及地震危险性[J].地震学报,26(3):294-303.
- 张希,郝明,贾鹏,等.2013.全国主要构造区GPS水平运动负位错反演与应变积累特性[J].地震研究,36(1):1-8.
- 张希,江在森,王双绪,等.2005.川滇地区地壳水平运动的弹性块体边界负位错模型与强震地点预测[J].地震研究,28(2):119-124.
- 张希,江在森,王双绪,等.2007.青藏块体东北缘 GPS 与水准资料的三维负位错联合反演[J].国际地震动态,(7):61-66.
- 张希,张四新,王双绪.2009.汶川与攀枝花地震前地壳垂直运动的负位错模型与孕震背景[J].大地测量与地球动力学,29(3):16-23.
- 赵静,江在森,牛安福,等.2015.川滇菱形块体东边界断层闭锁程度与滑动亏损动态特征研究[J].地球物理学报,58(3):872-885.
- 赵静,任金卫,江在森,等.龙门山断裂带西南段闭锁与变形特征[J].地震研究,41(2):209-215.
- 邹镇宇,江在森,武艳强,等.2015.针对一般倾角的走滑/倾滑位移理论公式的改进[J].大地测量与地球动力学,35(3):460-463.
- Freund L B,Barnett D M.1976.A two-dimensional analysis of surface deformation due to dip-slip faulting[J].Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America,66(3):667-675.
- Jiang G,Xu X,Chen G,et al.2015.Geodetic imaging of potential seismogenic asperities on the Xianshuihe-Anninghe-Zemuhe fault system,southwest China,with a new 3-D viscoelastic interseismic coupling model[J].Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth,120(3):1855-1873.
- Pan Y,Shen W B.2017.Contemporary crustal movement of southeastern Tibet:Constraints from dense GPS measurements[J].Scientific Reports,7,doi:10.1038/srep45348.
- Reinoza C,Jouanne F,Audemard F A,et al.2015.Geodetic exploration of strain along the El Pilar Fault in northeastern Venezuela[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,120(3):1993-2013.
- Savage J C,Burford R O.1973.Geodetic Determination of Relative Plate Motion in Central California[J].Journal of Geophysical Research,78(5):832-845.
- Savage J C,Burford R O.2012.Geodetic Determination of Relative Plate Motion in Central California[J].Journal of Geophysical Research,78(5):832-845.
- Shen Z K,Lü J,Wang M,et al.2005.Contemporary crustal deformation around the southeast borderland of the Tibetan Plateau[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,110,doi:10.1029/2004 JB003421.
- Wang R,Diao F,Hoechner A.2013.SDM-A geodetic inversion code incorporating with layered crust structure and curved fault geometry[C].Austria EGU General Assembly 2013.
- Wang W,Qiao X,Yang S,et al.2017.Present-day velocity field and block kinematics of Tibetan Plateau from GPS measurements[J].Geophysical Journal International,208(2):1088-1102.
- Zheng G,Wang H,Wright T J,et al.2017.Crustal Deformation in the India-Eurasia Collision Zone From 25Years of GPS Measurements[J].Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth,122(11):9290-9312.