基金项目:中国地震局地震科技星火计划项目(XH18066Y)、中国地震局震情跟踪青年项目(2018010206)、国家自然科学基金面上项目(41674015)和国家自然科学基金青年项目(41704010)联合资助.
(The First Monitoring and Application Center,China Earthquake Administration,Tianjin 300180,China)
the Nepal earthquake; Himalayan structural belt; GPS; BERNESE
备注
基金项目:中国地震局地震科技星火计划项目(XH18066Y)、中国地震局震情跟踪青年项目(2018010206)、国家自然科学基金面上项目(41674015)和国家自然科学基金青年项目(41704010)联合资助.
利用2015年尼泊尔MW7.8地震发生前后喜马拉雅构造带中段地区境内外的GPS连续站及流动站资料,以优化后的BERNESE解算策略进行数据解算,通过同震位移场分析、典型基线的时间序列分析、速度场动态变化分析等多种手段分析地震发生前后的地壳形变特征。结果 表明:该次地震并没有完全释放应力积累能量,震后印度板块推挤作用并未减缓,该区域构造应力积累仍处于较高水平,震情形势值得关注。
In this paper,we collect the GPS data in the middle section of the Himalayas structural belt before and after the 2015 25th April MW7.8 Gorkha,Nepal earthquake,including observation data from continuous and regional stations,and the data is solved using the BERNESE software.To study the crustal deformation before and after the Nepal earthquake,the coseismic displacement field,the typical baseline time series,and the velocity field analysis are carried out.The results show that the earthquake did not completely release the accumulated stress energy,and the push of the Indian plate did not slow down after the earthquake.Energy accumulation is still at a relatively high level,and we should pay more attention to the seismic risk.
引言
喜马拉雅构造带历史地震活动强度大,对中国大陆构造环境影响深刻,特别是2015年4月25日位于此区域的尼泊尔发生MW7.8地震,引起我国西藏日喀则等地区强烈余震,此次大震引起的动力调整过程无疑会对中国大陆(特别是中国大陆中西部地区,青藏高原及其东部、北部临近地区)的震情形势产生深远影响(杜方等,2016; 徐晶等,2016)。地震发生后,国内外专家学者利用GPS和InSAR资料迅速给出了同震位移及地表破裂结果(Wu et al,2016; 单新建等,2015; 占伟等,2015,Lindsey et al,2015),取得了一定的认识。
本文收集了该区域“中国大陆构造环境监测网络(CMONOC,以下简称陆态网络)”、尼泊尔监测网络(境外)2010—2017年GPS连续站和流动站观测资料,特别是尼泊尔地震前后应急观测数据,通过更为丰富和精确的GPS观测资料,分析了震前、同震、震后该区域的地壳形变特征。首先,利用BERNESE软件,采用改进后的GPS数据解算策略对“陆态网络”和尼泊尔监测网络2010—2017年GPS观测数据进行解算,得到该区域连续站的时间序列及震前、震后速度场结果; 然后,利用更加精确的GPS连续观测资料计算同震位移,得到较为准确的同震位移场结果; 最后,通过“陆态网络”和尼泊尔监测网络最新的数据进行基线时间序列分析以及喜马拉雅构造带中段速度场的动态变化分析,基于上述结果,对喜马拉雅构造带中段区域的地壳形变进行综合分析。
1 GPS同震位移场
1.1 资料收集与数据处理本文共收集到2010—2017年西藏地区15个“陆态网络”连续站数据、中国地震局第一监测中心(以下简称一测中心)3个新建连续站数据、ARIA团队建立的尼泊尔连续监测网络(由NASA UNAVCO网站提供原始观测数据)28个连续站和一测中心在尼泊尔地震前后观测得到的震前震后20个流动站数据(观测时间分别是震前40 d和震后30 d内),如图1所示。基于以上丰富的GPS连续和流动观测数据,采用BERNESE软件进行处理,分别计算了同震位移场、跨喜马拉雅构造带2侧典型基线时间序列以及震前、震后2期速度场,以此分析喜马拉雅构造带中段近期地壳形变特征和趋势。
在数据处理策略方面,本文利用BERNESE软件,将所有流动站、连续站数据放在一起进行不分区模式处理,同时选取全球框架下较为稳定的约37个IGB08核心站在统一框架下进行整体平差,这样避免了GAMIT软件因为每次只能处理不超过100个站而必须进行分区造成的精度损失,提高了数据解算精度。2种软件和解算策略的精度及优缺点对比郭炳辉等(2016)有所提及。
1.2 同震位移场图2为同震水平位移场结果,图中显示:主前山断裂带(MFT)以北区域首先具有整体向南运动的趋势,靠近震中区域的站点水平位移方向与主前山断裂带MFT走向近垂直,且最大水平位移达到1.84 m(KKN4站点,该站点位于震中东边40 km处); 西藏南部地区的流动站点的水平位移方向相对于尼泊尔境内的连续站点的位移方向,发生一定角度的改变,且呈现两侧向最大位移区域汇聚的趋势。
因此,从GPS同震水平位移场可以看出该地震断层运动以逆冲倾滑为主,与USGS提供主震震源机制解的断层几何参数及震间GPS地壳形变场特征相吻合,属于典型的喜马拉雅型(低角度逆冲型)地震。这也与国内外学者得到的GPS和InSAR联合解算的同震位移结果基本一致(赵斌等,2015; 占伟等,2015; 单新建等,2015)。
图3为同震垂直位移场结果,由图可知,主震震中与最大余震震中连线以南变形位移区域具有较大的垂直向上运动,最大位移达1.25 m左右(KKN4站点); 主震震中与最大余震震中连线以北具有垂直向上和向下2种运动趋势,KKN4站点以北的CHLM站点具有近60 cm垂直向下运动,CHLM站点以东的J041站点具有近8 cm垂直向下位移; 然而远离最大变形区的西藏南部具有垂直向上运动的趋势,最大形变量可达1~2 cm。
同时,主前山断裂带MFT的南部区域的站点GPS垂直位移几乎为零,表明该地震并没有破裂到地表引起地表形变,这也与国内外测震科学研究小组基于远场地震波资料快速获得震源机制解及滑动分布模型中显示的该地震纯逆冲、低倾角、没有破裂至地表的基本特征相吻合(赵斌等,2015)。
表1给出的GPS同震位移场结果,全部为实际解算结果利用时间序列分析方法去除了趋势变化得到的结果,利用更长时间的数据积累拟合出更优的时间序列模型,从而得到较为准确的同震位移场结果(Wu et al,2016)。
图2 GPS获得的尼泊尔MW7.8地震同震水平位移场
Fig.2 Coseismic horizontal displacements caused by the 2015NepalMW7.8,earthquake,inferred from GPS observations图3 GPS获得的尼泊尔MW7.8地震同震垂直位移场
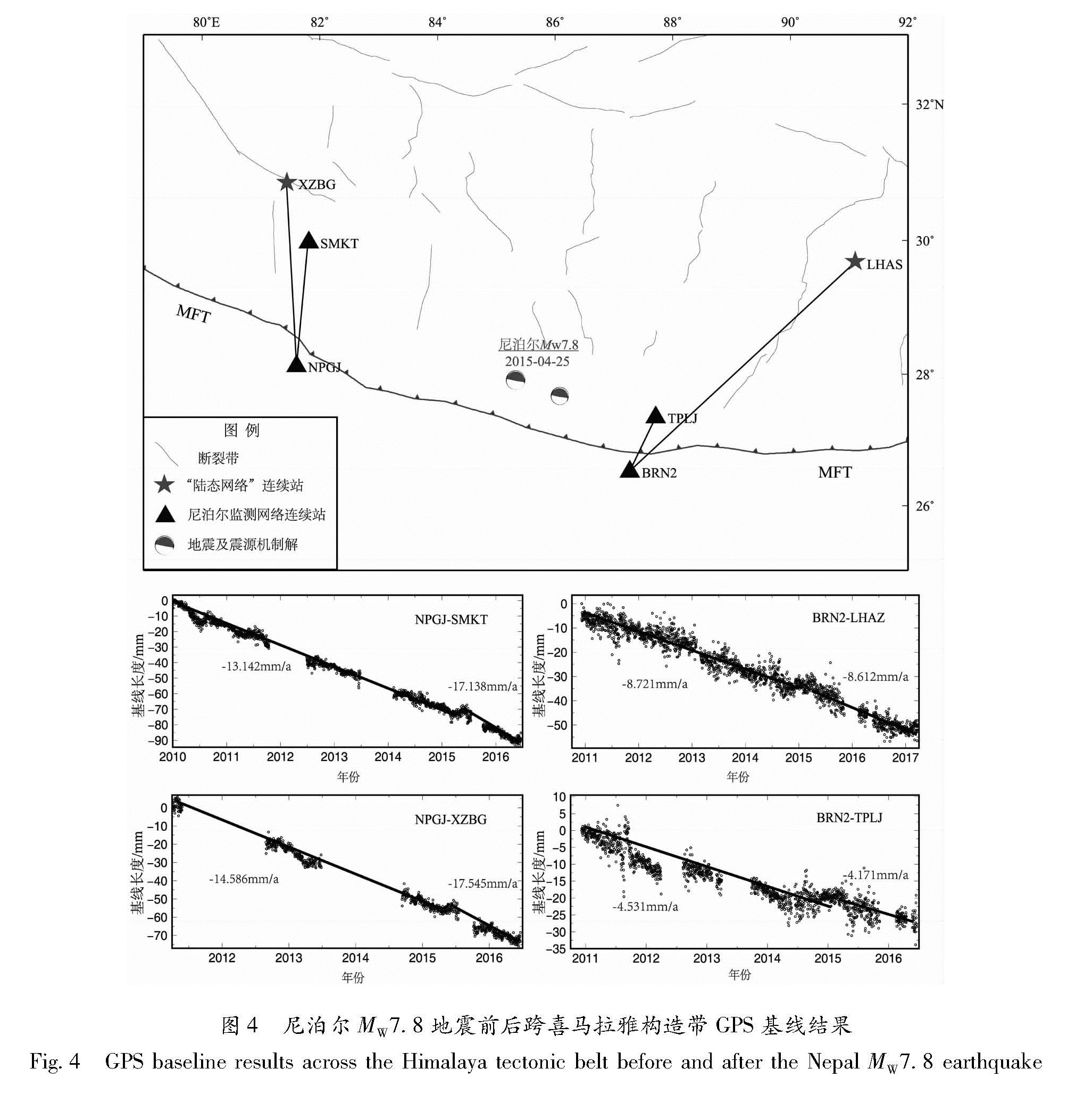
Fig.3 Coseismic vertical displacements caused by the 2015 Nepal MW7.8,earthquake,inferred from GPS observations图4 尼泊尔MW7.8地震前后跨喜马拉雅构造带GPS基线结果
Fig.4 GPS baseline results across the Himalaya tectonic belt before and after the Nepal MW7.8 earthquake2 基线时间序列
GPS站间大地线(椭球面上连接两点的最短弧线)弧长作为基线长度,对 GPS三维定位信息只取N(南北向)、E(东西向)信息而避免了精度较低的U向(椭球面法向)误差影响,且GPS基线长度不受参考框架本身漂移、旋转等因素影响,可以较为客观地反映地壳相对运动变化信息(江在森等,2009)。利用BERNESE软件解算得到的中国大陆“陆态网络”连续站、一
测中心连续站时间序列以及尼泊尔监测网络连续站时间序列,进行粗差剔除、阶跃修复,并通过去除线性和周期变化得到的测站坐标时间序列文件。在跨喜马拉雅带中段两侧典型测站筛选了一些连续站基线时间序列,以分析地震前后该区域地壳形变特征。
2.1 尼泊尔地震前后GPS基线结果对比2015年尼泊尔MW7.8地震同震和震前形变结果显示:尼泊尔地震导致了青藏高原中部地区显著的拉张应变释放,但高原东、西部应变释放量值有限。为了进一步研究该地震对青藏高原的影
图5 跨喜马拉雅构造带与构造带两侧GPS基线结果对比
Fig.5 Comparison of GPS baseline results of crossing the Himalaya tectonic belt and two sides of the tectonic belt响,给出了震源区东西两侧跨喜马拉雅构造带GPS基线结果(如图4所示,所选测站在尼泊尔同震过程中变形均不显著)。结果显示,震源区西侧基线在尼泊尔地震前后表现出明显的缩短增强作用,主要反映了青藏高原内部2个测点在尼泊尔地震后指向震源区运动增强,震后调整过程明显。震源区东侧基线表现出稳定的地壳缩短效应,尼泊尔地震前后动态变化不明显,反映了该区域受尼泊尔地震影响较小,为强震调整过程中的不变区,预示该区的构造应力积累可能处于较高水平。尼泊尔地震震源区附近断层发生了较大范围解锁,震源区东侧受该地区震后影响不明显,维持稳定的应变积累特征,有利于强震孕育过程。
2.2 跨喜马拉雅构造带与构造带两侧GPS基线结果对比为了研究地震前后跨喜马拉雅构造带与构造带两侧GPS基线不同变化趋势,选取了紧靠构造带两侧的尼泊尔境内连续观测站点,将以上站点和喜马拉雅构造带南侧到中国西藏境内连续站之间不同的几条GPS基线进行对比。
如图5所示,尼泊尔境内紧靠构造带的GRHI站(南侧)到西藏仲巴站的基线时间序列呈缩短态势,约12 mm/a,喜马拉雅构造带中部东侧的BRN2(南侧)到西藏日喀则站的基线时间序列也呈现约12 mm/a的缩短趋势。紧靠构造带两侧的GRHI(南侧)和PYUT(北侧)站也是一直呈现缩短趋势,但量级较小,约4 mm/a,喜马拉雅构造带中段东侧的BRN2(南侧)与北侧的TPLJ站基线时间序列也呈约4 mm/a的压缩趋势。说明构造带北侧到西藏南部地区吸收了很大一部分印度板块的推挤作用(有些研究表明大约是1/2(Ader et al,2015; 谭凯等,2016),同时,震后的基线时间序列显示,此应力积累过程并未减缓。构造带中部由于位于尼泊尔地震震中区域,断层发生了较大范围的解锁,但是构造带东部地区受到的影响较小,应力积累一直在持续,有利于强震孕育。
3 速度场变化
通过连续站时间序列拟合出了尼泊尔地震前后研究区域2期速度场,通过速度场对比可以发现,总体来说有变缓趋势,特别是中国西藏地区内部,大部分测站速度有变缓趋势。但构造带南侧站点普遍表现出速度不变或变大,说明印度板块的运动并没有因为此次地震有所减缓,该地区未来的震情趋势值得持续关注。因为目前2015—2017年数据大约只有1~1.5 a,与2010—2015年近5年的数据拟合的速度场还有一定差距,所有结果值得进一步讨论,特别是对于尼泊尔地区连续站,因为震后进行了仪器更新和新站建设,还需要积累数据进行重新评估。
4 讨论和结论
4.1 同震位移场基于BERNESE解算得到的同震位移场结果与目前的认识和结论基本相符。根据前人研究成果,1934年Bihar-Nepal MW8.1地震与1905年Kangra MW7.8 地震之间存在一个沿喜马拉雅造山带走向长约700~800 km的地震空区,正好2015年尼泊尔地震主破裂区位于该地震空区的东段(约200 km)区域。1833年距今,即2015年尼泊尔MW7.8 地震之前的近2个世纪的时间内,该地震空区没有发生8级以上的大地震(Stevens et al,2015)。同时,该区域的西段上一次发生8级以上的地震的时间是公元1505年,根据地质调查结果及经验公式计算,该次地震的破裂滑移亏损可达10 m。然而根据2015年尼泊尔地震地震波及大地测量的反演破裂结果显示,此次地震的平均滑移量只有4 m左右(Fan,Shearer,2015; 张勇等,2015; 赵斌等,2015),这反映了该次地震并没有完全释放应力积累能量,诱发的震级要比预测的小。因此,该地区后期震情形势值得持续关注。
4.2 基线时间序列基线时间序列基本能够反映断层两侧运动趋势,构造带北侧到西藏南部地区吸收了很大一部分印度板块的推挤作用,反映出在震前相当长一段时间的应力积累。通过密集的跨喜马拉雅构造带GPS监测网络数据,国内外很多专家获得了该区域的运动趋势,印度板块以40 mm/a的速度持续沿北北东方向下插入欧亚板块,印度与藏南间跨喜马拉雅山的地壳汇聚速率约为20 mm/a,吸收了约一半的汇聚速率(Bilham et al,1997;
图6 尼泊尔MW7.8地震前后两期速度场对比图(基于欧亚大陆基准)
Fig.6 Two periods GPS velocity field before and after the 2015 Nepal MW7.8,earthquake(with respect to Eurasian plate)Tapponnier et al,2001; 赵斌等,2015),这与震前的基线时间序列结果基本一致。震后跨喜马拉雅构造带两侧的基线时间序列虽然存在一定的震后余滑和粘弹性松弛,但本文特别筛选了远离震中区域的喜马拉雅带中段西侧和东侧,在充分考虑震后效应的同时分析了其变化趋势,发现其应力积累过程并未减缓。同时,也需要通过境内外连续站数据的积累,对该区域的基线变化进行持续关注。
震源区西侧基线在尼泊尔地震前后表现出明显的缩短增强作用,主要反映了青藏高原内部2个测点在尼泊尔地震后指向震源区运动增强,震后调整过程明显。震源区东侧基线表现出稳定的地壳缩短效应,尼泊尔地震前后动态变化不明显,反映了该区域受尼泊尔地震影响较小,为强震调整过程中的不变区,预示该区的构造应力积累可能处于较高水平。
4.3 速度场变化从2010—2015年与2015—2017年2期速度场变化可以看出,尼泊尔地震之后该区域地壳形变总体来说有变缓趋势,特别是中国西藏地区内部,但喜马拉雅构造带南侧站点普遍变现出速度不变或变大,说明印度板块的推挤运动并没有因为此次地震有所减缓。
国内外很多专家也在尼泊尔地震发生后进行了较为详细的研究,特别是震后趋势方面,从孕震断层多锁固段脆性破裂理论(李培等,2015)、震后库伦应力及粘弹性介质模型(徐晶等,2016)等多个方面分析了该区域的震后形变趋势,大部分专家认为该地区仍处于临界状态,应力积累仍处于较高水平。结合本文的研究成果,该区域的震情趋势值得持续关注。
感谢AIRA团队及NASA UNAVCO网站提供的尼泊尔监测网络GPS连续站原始观测数据,本文在撰写过程中得到了占伟博士等一测中心GPS数据解算小组成员的大力支持。同时感谢审稿专家提出的宝贵修改意见和编辑部老师的热心帮助,在此表示由衷的感谢!
- 单新建,张国宏,汪驰升,等.2015.基于InSAR和GPS观测数据的尼泊尔地震发震断层特征参数联合反演研究[J].地球物理学报,58(11):4266-4276.
- 杜方,旦增,朱德富.2016.2015年尼泊尔8.1级地震与喜马拉雅弧的历史地震研究[J].地震研究,39(2):177-186.
- 郭炳辉,吕志鹏,党学会,等.2016.基于BERNESE的GNSS连续站坐标时间序列解算策略研究[J].华北地震科学,34(2):7-12.
- 江在森,武艳强,方颖,等.2009.汶川8.0级地震前区域地壳运动与应变场动态特征[J].地震,29(1):68-76.
- 李培,秦四清,薛雷,等.2015.2015年4月25日尼泊尔MW7.8地震孕育过程分析与震后趋势研判[J].地球物理学报,58(5):1827-1833.
- 谭凯,赵斌,张彩红,等.2016.GPS和InSAR同震形变约束的尼泊尔MW7.9和MW7.3地震破裂滑动分布[J].地球物理学报,59(6):2080-2093.
- 徐晶,李海艳,邵志刚,等.2016.基于库仑应力变化分析2015年尼泊尔MS8.1地震对中国大陆的影响[J].地震,36(1):69-77.
- 占伟,武艳强,梁洪宝,等.2015.GPS观测结果反映的尼泊尔MW7.8地震孕震特征[J].地球物理学报,58(5):1818-1826.
- 张勇,许力生,陈运泰.2015.2015年尼泊尔MW7.9地震破裂过程:快速反演与初步联合反演[J].地球物理学报,58(5):1804-1811.
- 赵斌,杜瑞林,张锐,等.2015.GPS测定的尼泊尔MW7.9和MW7.3级地震同震形变场[J].科学通报(S2):2758-2764.
- Ader T,Avouac J P,Jing L Z,et al.2012.Convergence rate across the Nepal Himalaya and inter-seismic coupling on the Main Himalayan Thrust:Implications for seismic hazard[J].J Geophys Res,17(B04403),1-16.
- Bilham R,Larson K,Freymueller J T.1997.GPS measurements of present-day convergence across the Nepal Himalaya[J].Nature,386(6620):61-64.
- Fan W,Shearer P M.2015.Detailed rupture imaging of the 25 April 2015 Nepal earthquake using tele-seismic P waves[J].Geophys Res Lett,42(14):5744-5752.
- Lindsey E O,Natsuaki R,Xu X H,et al.2015.Line-of -sightdisplacement from ALOS-2 Interferometry:MW7.8 Gorkha earthquake and MW7.3 aftershock[J].Geophys Res Lett,42(16):6655-6661.
- Stevens V L,Avouac J P.2015.Inter-seismic coupling on the main Himalayan thrust[J].Geophysical Research Letters,42(14):5828-5837.
- Tapponnier P,Xu Z Q,Roger F,et al.2001.Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet plateau[J]. Science,294(5547):1671-1677,doi:10.1126/science.105978.
- Wu Y Q,Jiang Z S,Liang H B,et al.2016.Coseismic deformations of the 2015 MW7.8 Gorkha earthquake and interseismic strain accumulation in the Himalayan tectonic belt and Tibetan plateau[J].Tectonophysics,670:144-154,doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2015.12.028.