基金项目:地震行业科研专项(201508009)、科技部基础性工作专项(2015FY210400)和中国地震局三结合课题(CEA-JC/3JH-163702)联合资助.
备注
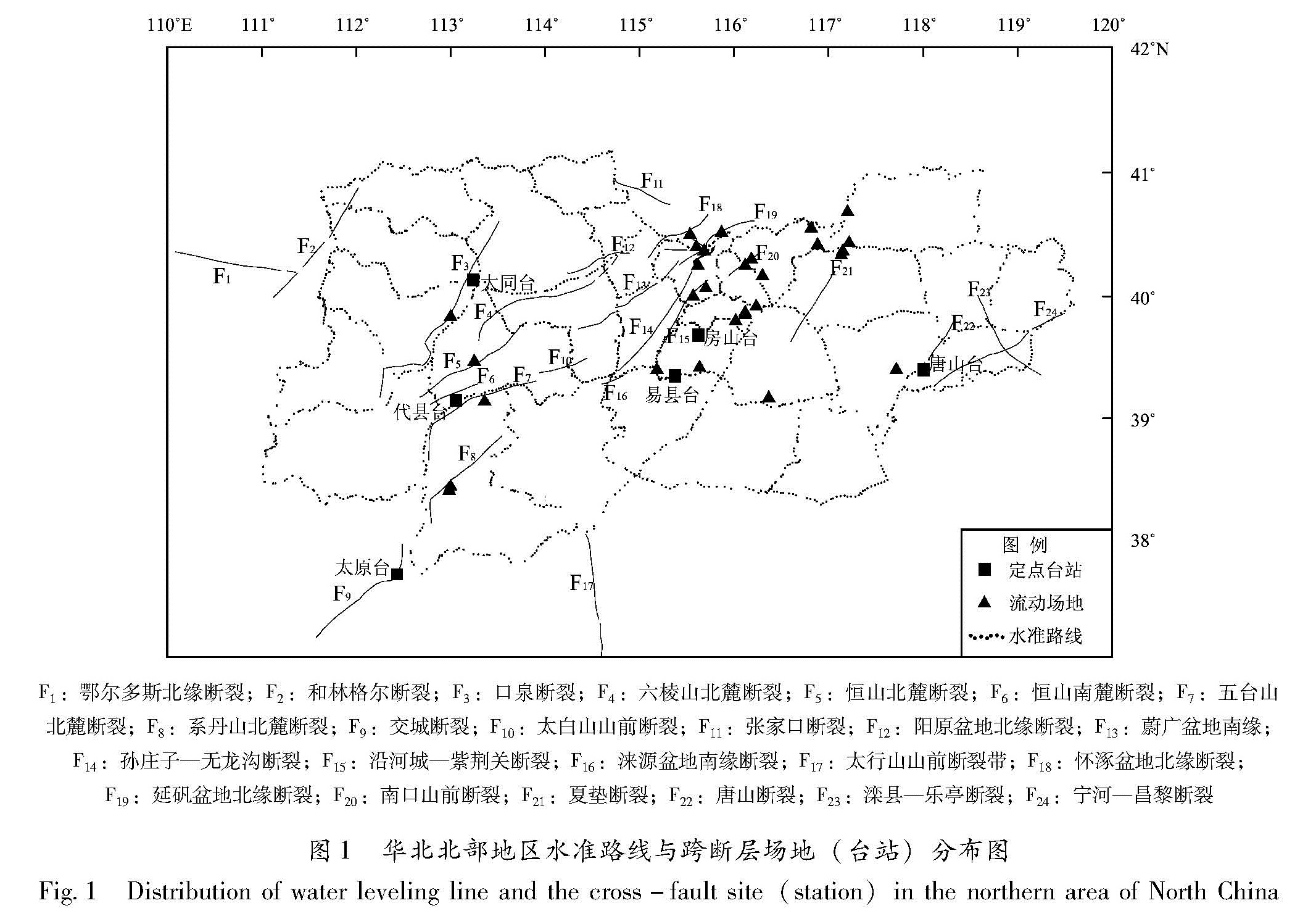
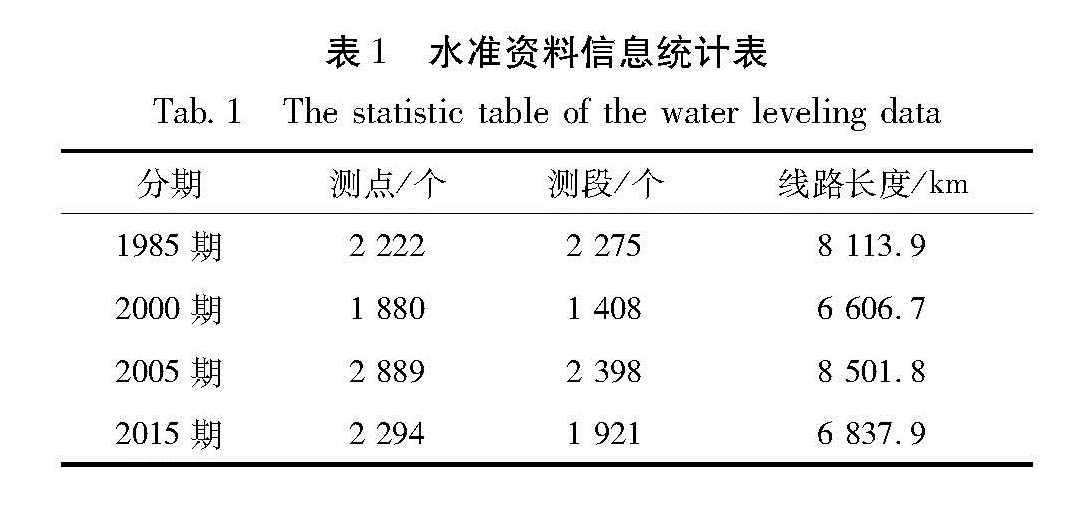
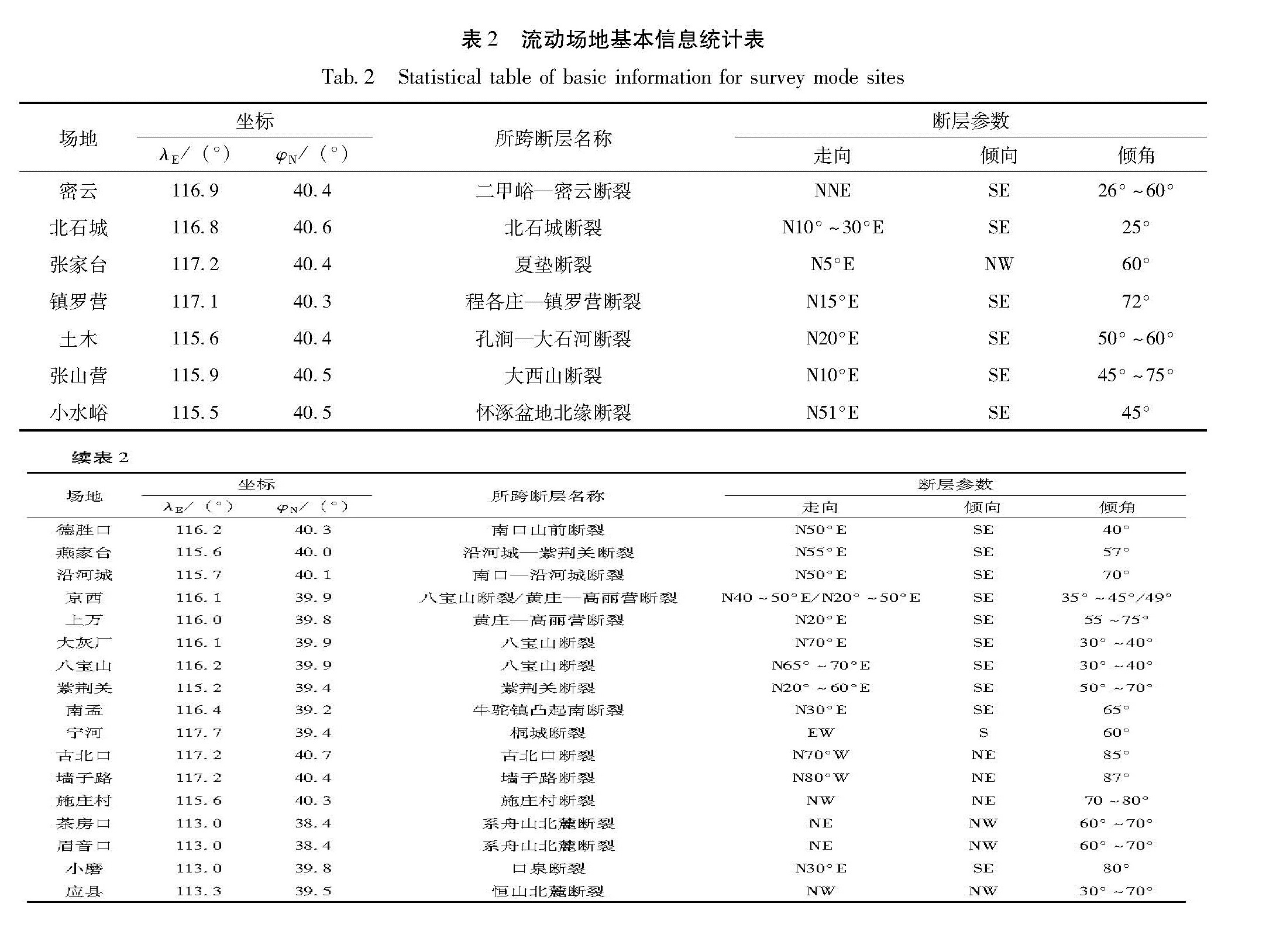
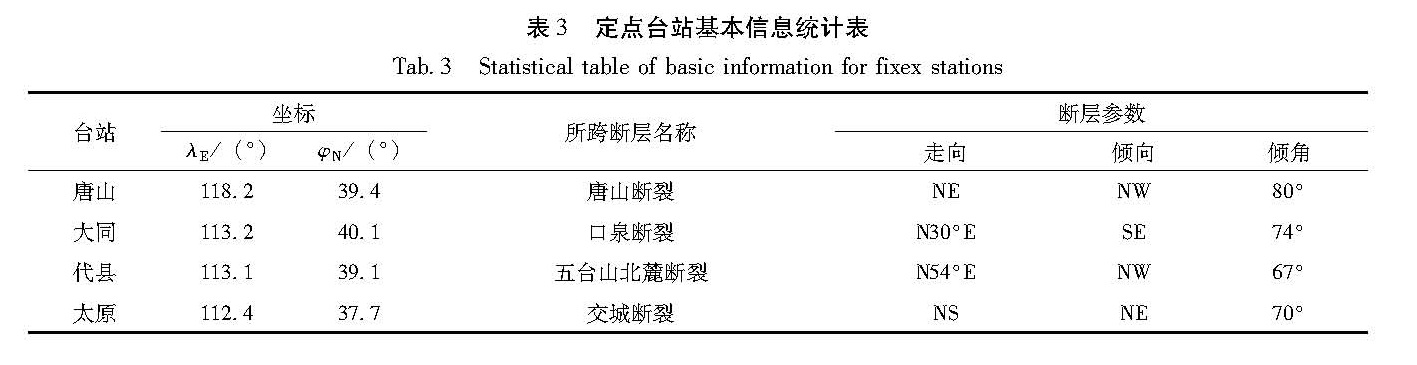
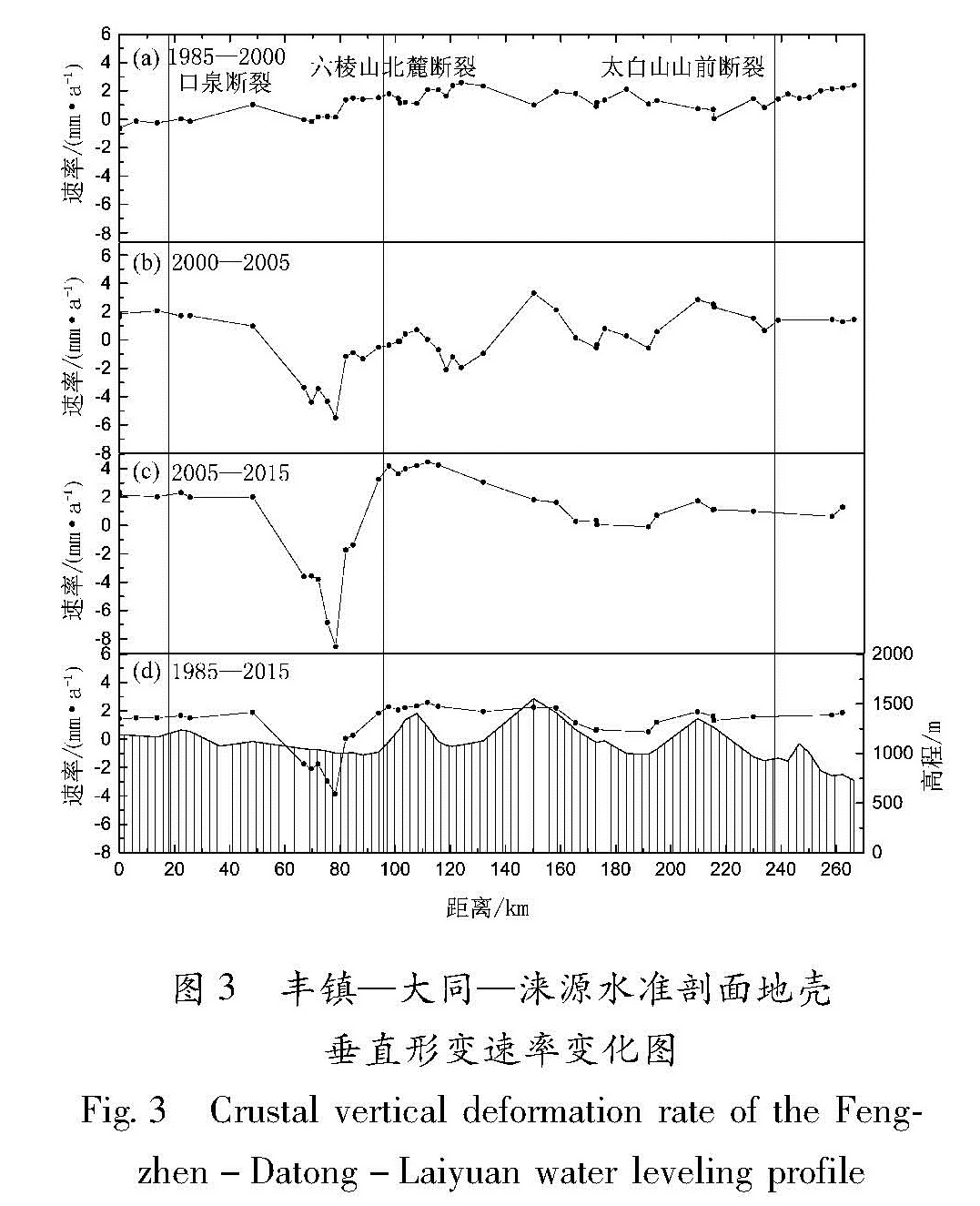
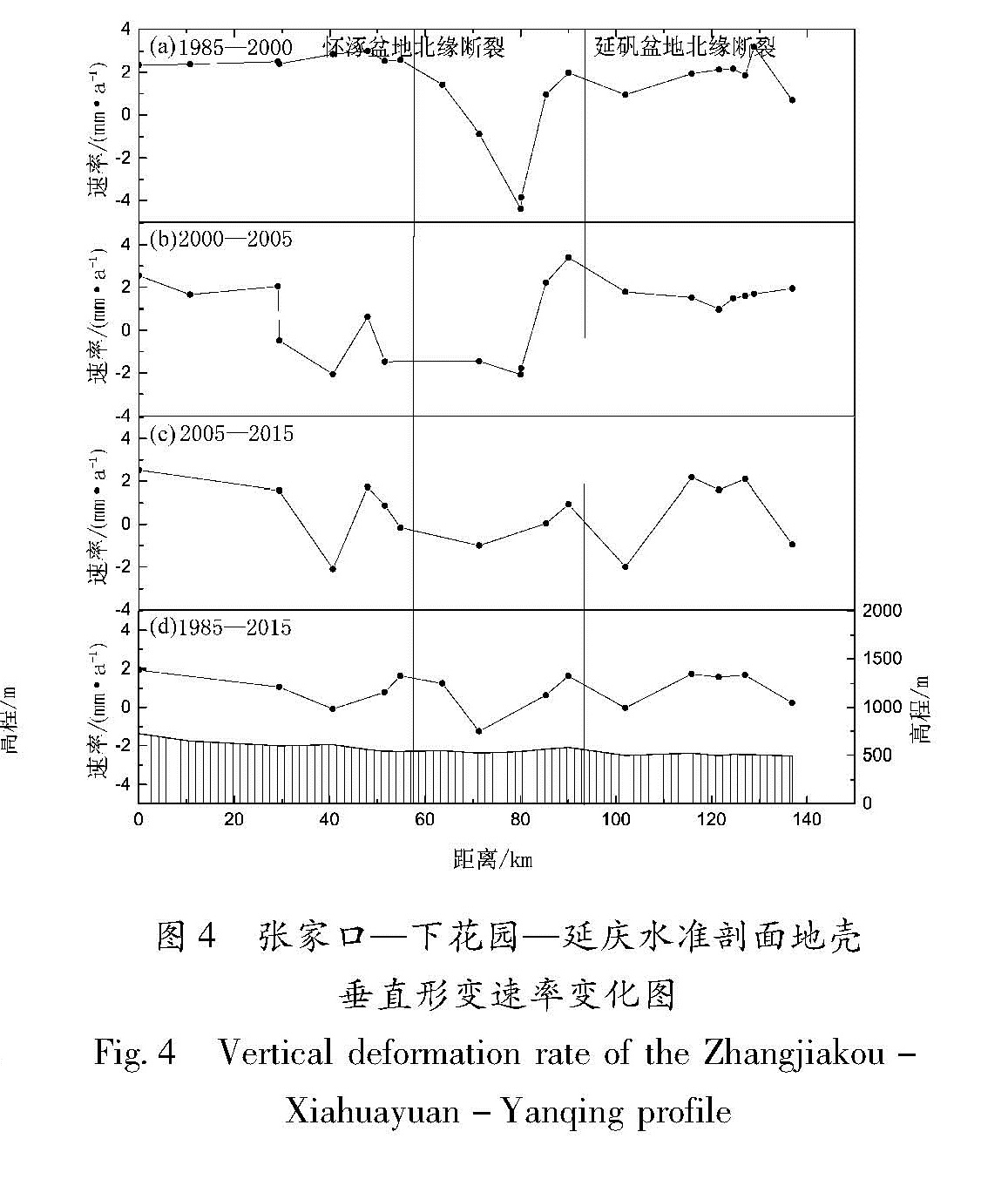
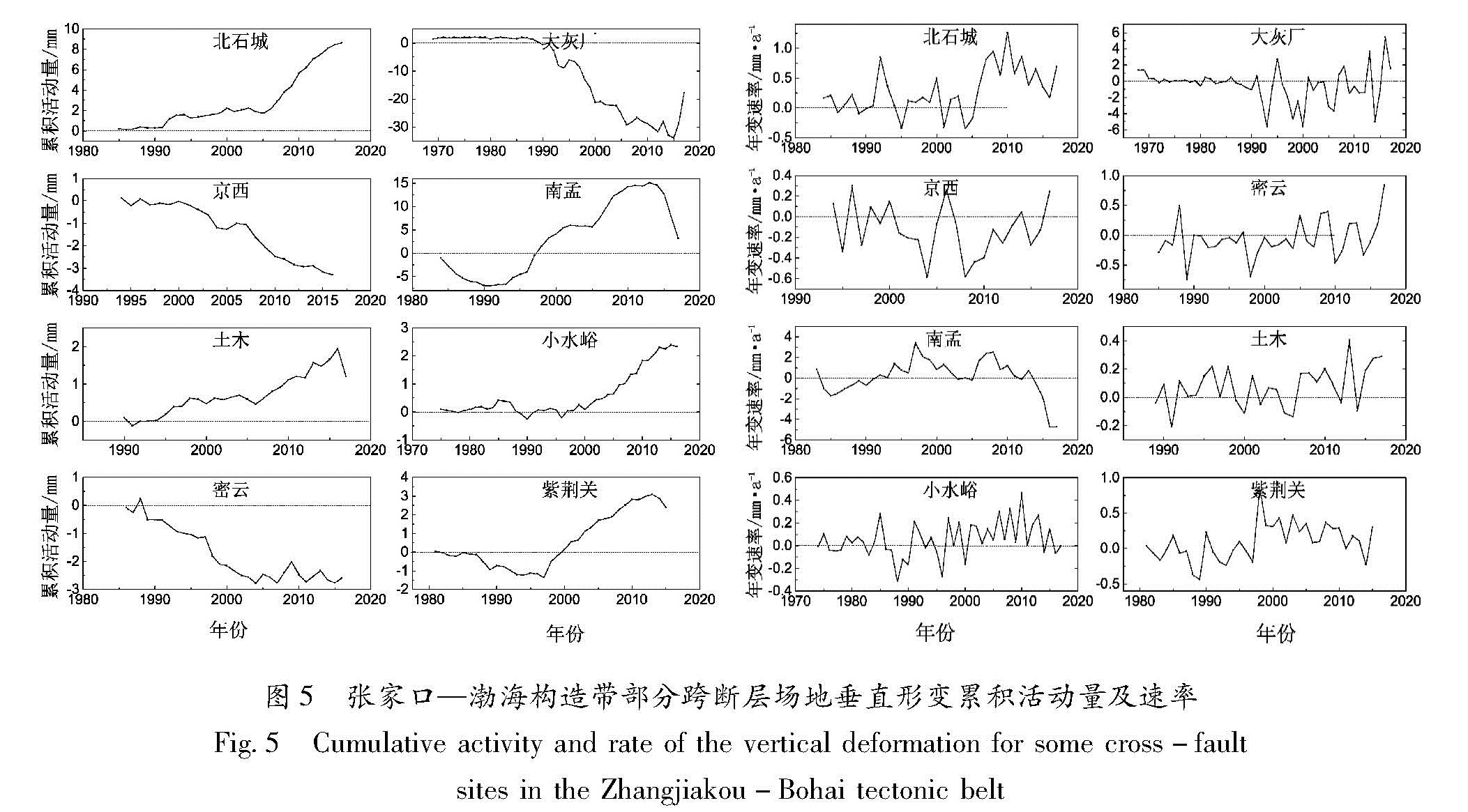
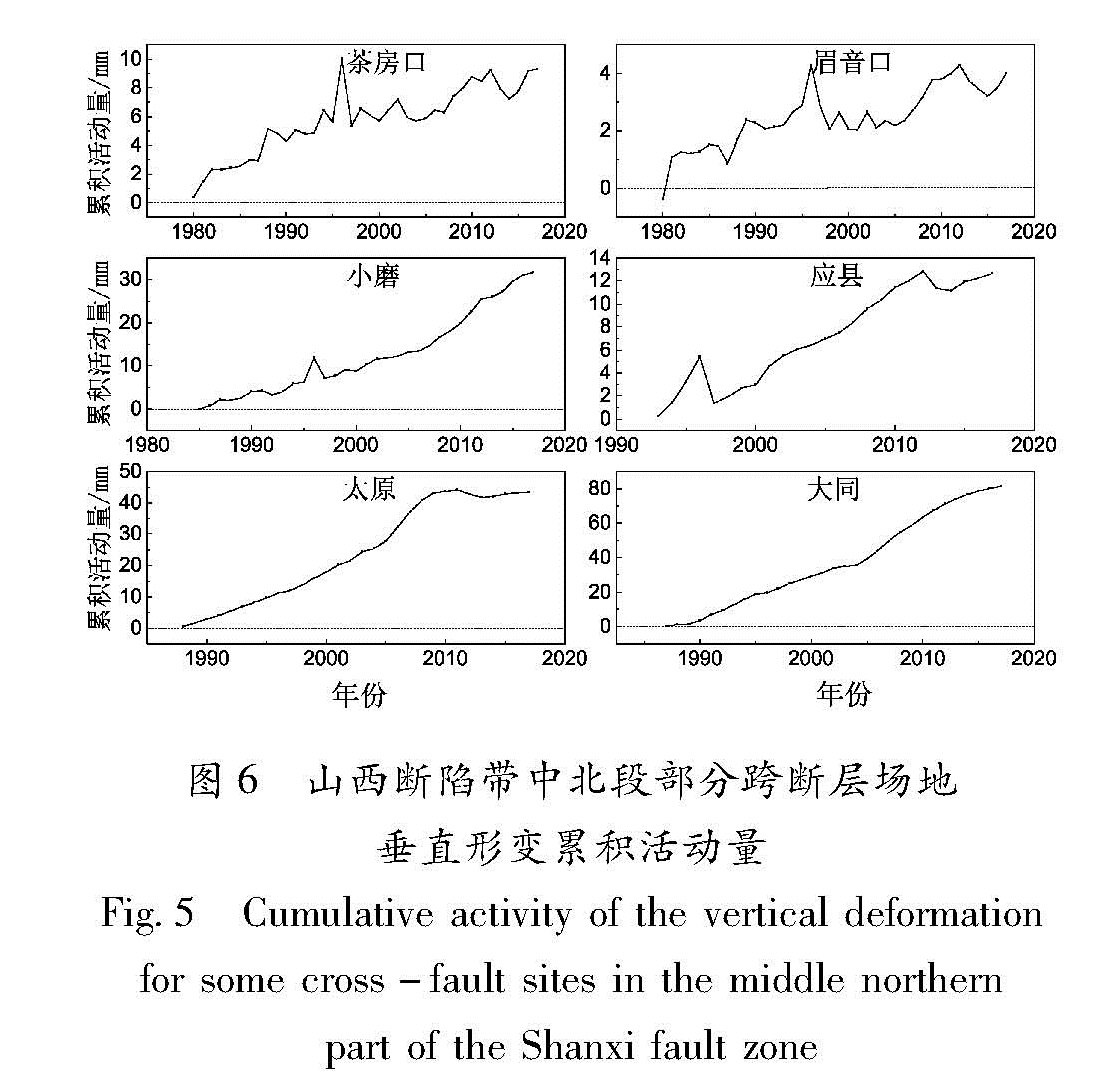
基于华北北部地区3期复测区域精密水准及跨断层形变测量资料,计算得出1985—2015年多个时间段的地壳垂直形变速率。并结合跨断层形变观测资料,分析区域内主要断裂的活动性,明确该区域的整体地壳垂直形变演化趋势及地震危险性。结果 表明:除强下沉区外,华北北部地区以继承性运动为主,太行山山前构造带以西总体上升,华北平原下沉,燕山块体较为稳定。张家口—渤海构造带西段总体活动水平较低,山西断陷带中北段断裂总体以张性正断层活动为主,两条断裂相交错区域是垂直形变高梯度集中区,且中强地震发生频次相对较高,需持续和重点监测。
Based on the repeated measurement data and cross-fault data in the northern area of North China,we calculate the vertical strain rate during 1985-2015 for several periods.The results reflect deformation characteristics and seismicity by contour line and gradient of vertical deformation.Combining the observation data of cross-fault deformation,the activity of the main faults in the region is analyzed.Then we identify the overall trend of deformation,and to require critical attention in the region and areas.The results show that the northern part of North China is dominated by the succession movement,at the same time the west of the Taihang Mountain front tectonic zone is generally raising,and the North China plain subsidence and the Yanshan block is steady.The overall activity of the western section of the Zhangjiakou-Bohai tectonic belt is low,and the main faults in the middle northern section of the Shanxi fault depression zone mainly present as normal fault activity.The interlaced area of the two fault phase is a high gradient concentrated area with high vertical deformation and the frequency of moderate strong earthquakes is high,and these areas need sustained and focused attention in the future.