基金项目:科技部科技基础性工作专项(2015FY210400)和中国地震局地震行业科研专项(201508009)共同资助.
备注
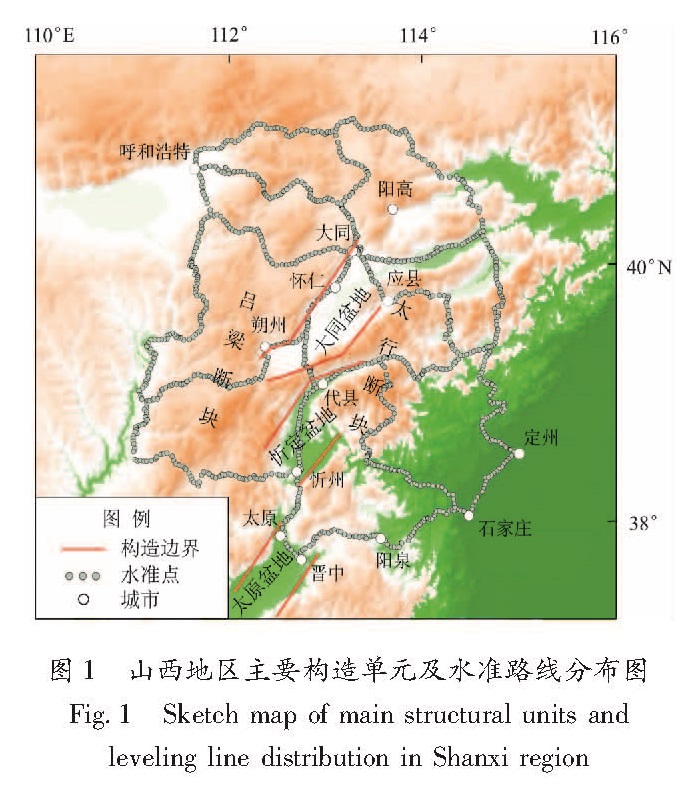
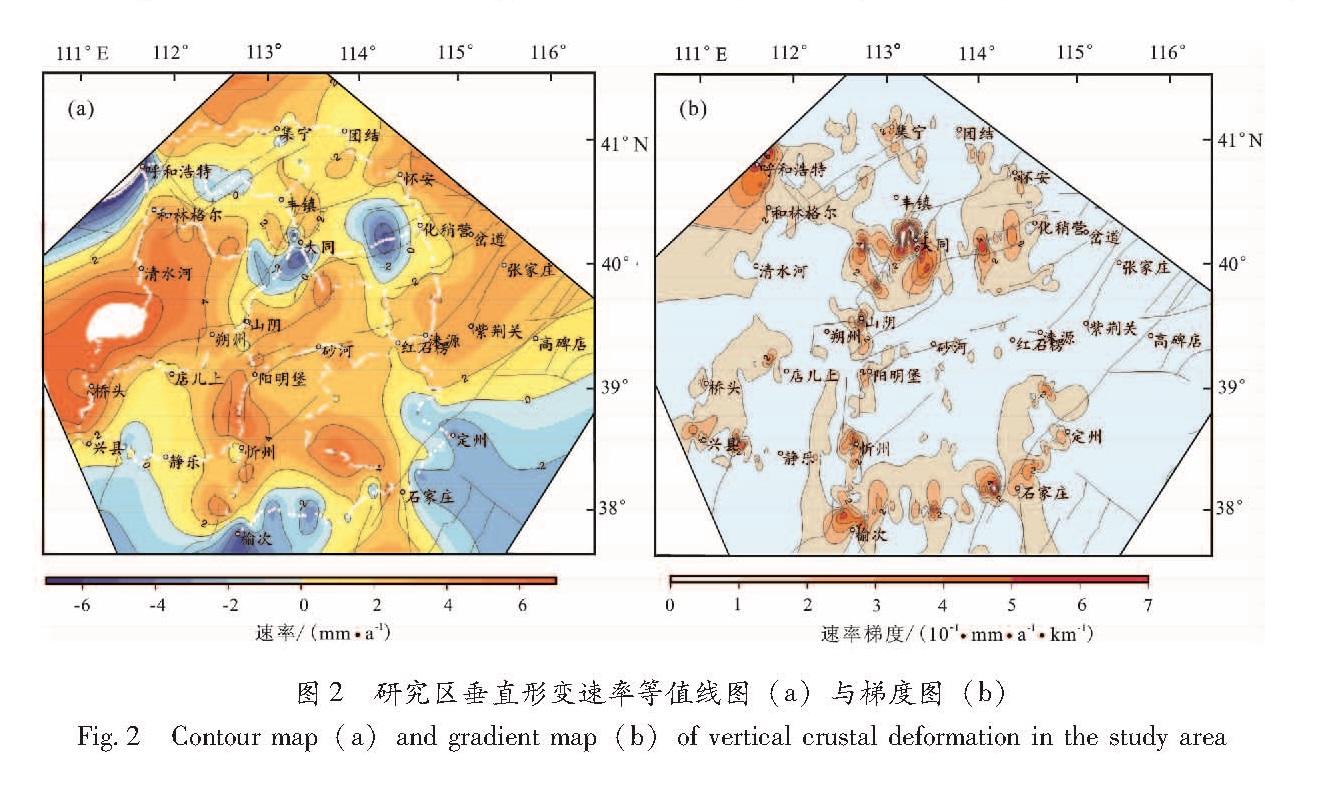
采用山西中北部地区2006期和2015期一等精密水准测量资料,利用经典动态平差方法,对区域近期地壳垂直形变时空演化特征进行了研究。结果 表明:(1)山西中北部地区近期整体表现为山地隆升,盆地下沉的特点,以继承性运动为主,但局部也存在差异性。吕梁断块和太行断块表现为隆升,活动速率分别为2~8 mm/a和2~6 mm/a; 山西断陷带的系列盆地表现出相对下沉,沉降速率为-3~-10 mm/a;(2)汶川地震显著影响了区域地壳垂直运动形变场。震前区域地壳运动表现为显著拉张特点,震后张性减弱,挤压增强;(3)大同—化稍营、呼和浩特和榆次—石家庄一带存在地壳垂直形变高梯度带,中长期尺度上存在地震危险性背景。
Based on two periods of 2006 and 2015 first-order leveling data in central and northern Shanxi,the temporal and spatial evolution characteristics of the crustal vertical deformation was studied by using the classical dynamic adjustment method.The conclusions are as follows:①The recent overall performance in central and northern Shanxi shows uplift in the mountainous region and the subsidence in basins,which were mainly based on the inheritance movement,accompanied by differential movement.The Lvliang block and Taihang block are uplifting,with the rate of 2~8 mm/a and 2~6 mm/a,respectively.The basins in the Shanxi fault depression zone show relative subsidence and the rate is-3~-10 mm/a.②Before and after the Wenchuan earthquake,the crustal movement in the study area changed.Before the earthquake,the regional crustal movement was characterized by tension,and after the earthquake the tension became weaken and the extrusion enhanced.③There is a high gradient zone of vertical crustal deformation in the Datong-Huashaoying,Huhehaote and Yuci-Shijiazhuang region,and it shows a seismic risk background in medium and long term.