基金项目:国家自然科学基金(41604015)、国家科技基础性工作专项(2015FY210400)和中国地震局监测预报司青年震情跟踪课题(2018010213)联合资助.
(The Second Crust Monitoring and Application Center,China Earthquake Administration,Xi'an 710054,Shaanxi,China)
Tonghai MS5.0 earthquake; crust deformation; GPS; strain rate field
备注
基金项目:国家自然科学基金(41604015)、国家科技基础性工作专项(2015FY210400)和中国地震局监测预报司青年震情跟踪课题(2018010213)联合资助.
利用1991—2015年GPS观测地壳长期水平运动速度场,研究了2018年8月13,14日云南通海2次5.0级地震前附近区域地壳水平形变背景特征,结合构造分析认为:(1)通海地震发生在区域地壳水平运动受阻,应变快速积累部位,即面应变率和最大剪应变率的高值区。该部位亦是小江断裂带和曲江—石屏断裂带的交汇部位,从背景形变特征来看,该区域及其附近未来稍长一段时间再次发生中强地震的危险性依然存在。(2)个旧与弥勒之间为另一个应变快速积累部位,应警惕未来发生中强地震的可能。
According to crustal long-term horizontal movement field of GPS observation from 1991 to 2015,we studied the deformation features of crustal horizontal movement in epicenter area before two Yunnan Tonghai MS5.0 earthquakes occurred on Aug.13 and Aug.14 in 2018.Combined with the tectonic,the results show that:(1)The Tonghai earthquakes occurred in the region where the crustal horizontal movement was hindered and the strain energy accumulated rapidly,that is,the high value area of the plane strain rate and the maximum shear strain rate.The region is also located at the intersection of Xiaojiang Fault system and Qujiang Shiping fault system.According to the characteristics of background deformation,the study area still has a high risk of moderate-strong earthquake in the future.(2)Another rapid strain accumulation zone is lying at the area between Gejiu and Mile,we should pay attention to the possibility of moderate-strong strong earthquakes in the future.
引言
以GPS为代表的空间大地测量技术在地壳形变监测与地震预测研究领域的应用已十分广泛,能够为科研人员提供高精度、大尺度、多维的地壳形变监测数据。许多学者和专家利用这些数据,对区域地壳形变与强震孕育之间的关系展开了研究,取得了一些认识:江在森等(2003)对GPS 水平面应变率及最大剪应变率的震例进行分析总结,认为与构造背景相一致的面应变、剪应变的高值区及其边缘梯度带是未来可能发生强震的危险区域; 江在森等(2009)利用GPS等观测资料研究了2008年汶川8.0级地震前的区域地壳运动与构造变形,结果表明汶川地震前龙门山以西地壳存在显著应变积累特征; 武艳强等(2013)利用龙门山断裂带及其附近的GPS观测资料,分析了2013年四川芦山7.0级地震震前形变场,发现其发震断裂龙门山断裂带南段震前一直处于闭锁状态; 占伟等(2015)利用GPS观测资料研究了2015年尼泊尔8.0级地震的形变孕震特征,发现震前喜马拉雅主边界断裂存在大范围挤压应变积累,震源区处于近南北向应变积累高值过渡区。以上研究结果为利用GPS水平形变资料研究地震震前区域地壳形变特征提供了参考。
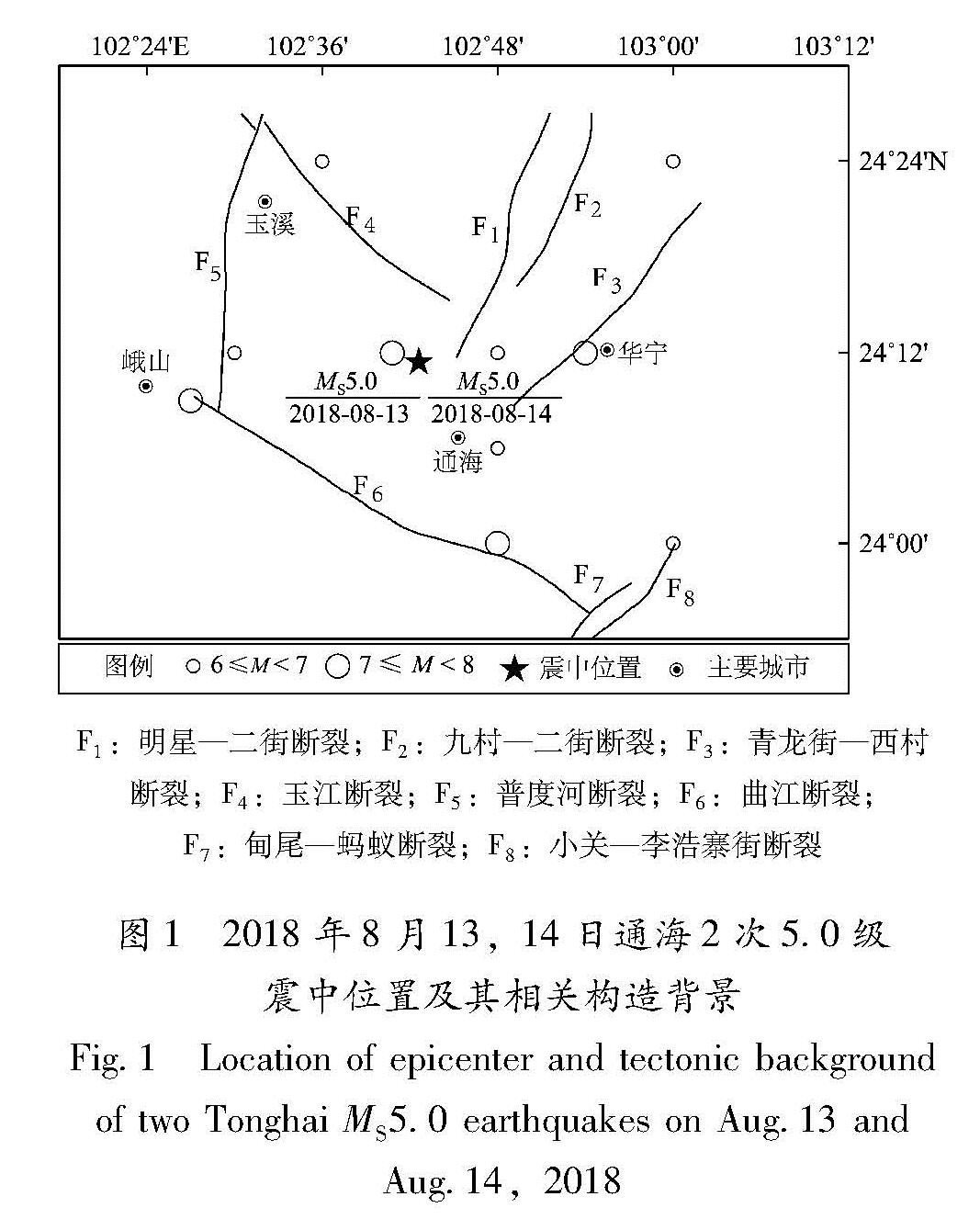
2018年8月13日1时44分、8月14日3时50分,云南省玉溪市通海县(24.19°N,102.71°E)先后发生2次5.0级地震。这2次地震发生部位处于什么样的构造环境,震前地壳水平形变、应变场有何特点?进行此方面的研究对于认识该地震发震机理及未来相关构造区域震情判定具有重要的意义。因此,本文拟借助Zheng等(2017)1991—2015年地壳水平运动速度场结果,利用Shen等(2015)计算连续形变、应变场的方法,对通海2次地震震前所在区域的地壳水平形变、应变场进行分析。
1 研究区构造背景及数据选取
2018年通海地震的宏观震中位于通海县四街镇境内,且2次地震发生在同一位置上。震中距NW走向的曲江断裂约18 km,距NW走向的玉江断裂约8 km,距NE走向的明星—二街断裂约4 km。通海2次地震余震序列分布主要呈NE走向,分析认为,这2次地震与NE走向的明星—二街断裂相关。活断层探测表明,明星—二街断裂NE由抚仙湖西岸明星以北延入抚仙湖内,向SW经牛摩村、孤山、螺蛳铺、水箐沟,至二街西延入杞麓湖内,长约78 km,总体走向15°左右,倾向SE,倾角较陡,达70°。沿该断裂可见宽度大于15 m的断层破碎带,为全新世活动断裂。2次通海地震震中附近区域没有发生过更大地震的痕迹,也没有更大地震的历史记载(云南网,2018)。从大区域构造来看,这2次地震发生于川滇块体东南端,处于小江断裂带、曲江—石屏断裂带的交汇部位。该区域构造变形复杂,历史强震极其活跃,曾发生过多次6级以上强震(闻学泽等,2011),其中距离最近的最大地震为在曲江断裂发生的1970年通海7.8级地震,距此次地震震中仅3 km 左右(图1)。
近年来,由中国地震局负责的网络工程和陆态网络项目先后实施,通海地震震中附近及其邻近区域在震前积累有十多年的多期流动GPS观测资料,Zheng等(2017)利用这些资料,使用PANDA软件,采用精密单点定位技术,获得了反映构造变形的1991—2015年地壳长期水平运动速度场,其在数据处理过程中不仅扣除由于仪器、人为因素等对站点观测时间序列的影响,还扣除了观测时间段内,显著地震同震及震后形变的影响。同时,借助最小二乘原理对站点时间序列用线性函数来估计长期速度,并将速度场统一到欧亚框架之下,为本文的研究提供了便利。图1 2018年8月13,14日通海2次5.0级震中位置及其相关构造背景
Fig.1 Location of epicenter and tectonic background of two Tonghai MS5.0 earthquakes on Aug.13 and Aug.14,2018鉴于形变场空间分辨率的限制,对于通海地震发震构造而言,本文研究范围相对较大,主要以地震震中为中心,向其外围扩展了约100 km,主要包括川滇块体南部滇中地块及其附近区域(23°~26°N,101°~104°E)。研究范围内共有63个GPS站点,平均间隔约为30 km,大部分区域站点分布相对较为均匀,相对密集和均匀分布的站点会使研究结果具有较高的可靠性。
2 连续形变场、应变场计算方法
由于实际地壳运动观测站点分布往往是不均匀的,而且还有非连续的构造变形在其中。因此利用观测形变场进一步计算连续形变、应变场就显得尤为重要。Shen等(2015)提出了一种对于离散的空间大地测量观测数据进行内插的最佳方法,并且将这种方法应用到美国南加州地区水平应变率场的计算中,获得了很好的结果。该方法依赖于具有先验约束的权重平滑因子来获得对观测数据的最佳拟合。对于任一站点,在它附近区域内插点的水平位移场通过双线性函数插值方法来实现,在球面上需要反演的模型参数包括块体平移、旋转及应变率。借助最小二乘方法,采用相邻区域加权GPS速度场来估计待求站点模型参数,并使得速度场拟合残差最小。对于最佳权重的选择,采用距离相关权重:
Li=exp((ΔR2i)/(D2))(1)
W=∑iLiVi(2)
式中:Li是高斯函数; Vi是依赖于Voronoi单元的面积; ΔRi为计算点与GPS站点的距离; D为空间平滑距离参数,对不同站点采用不同的数值(Shen et al,2015)。
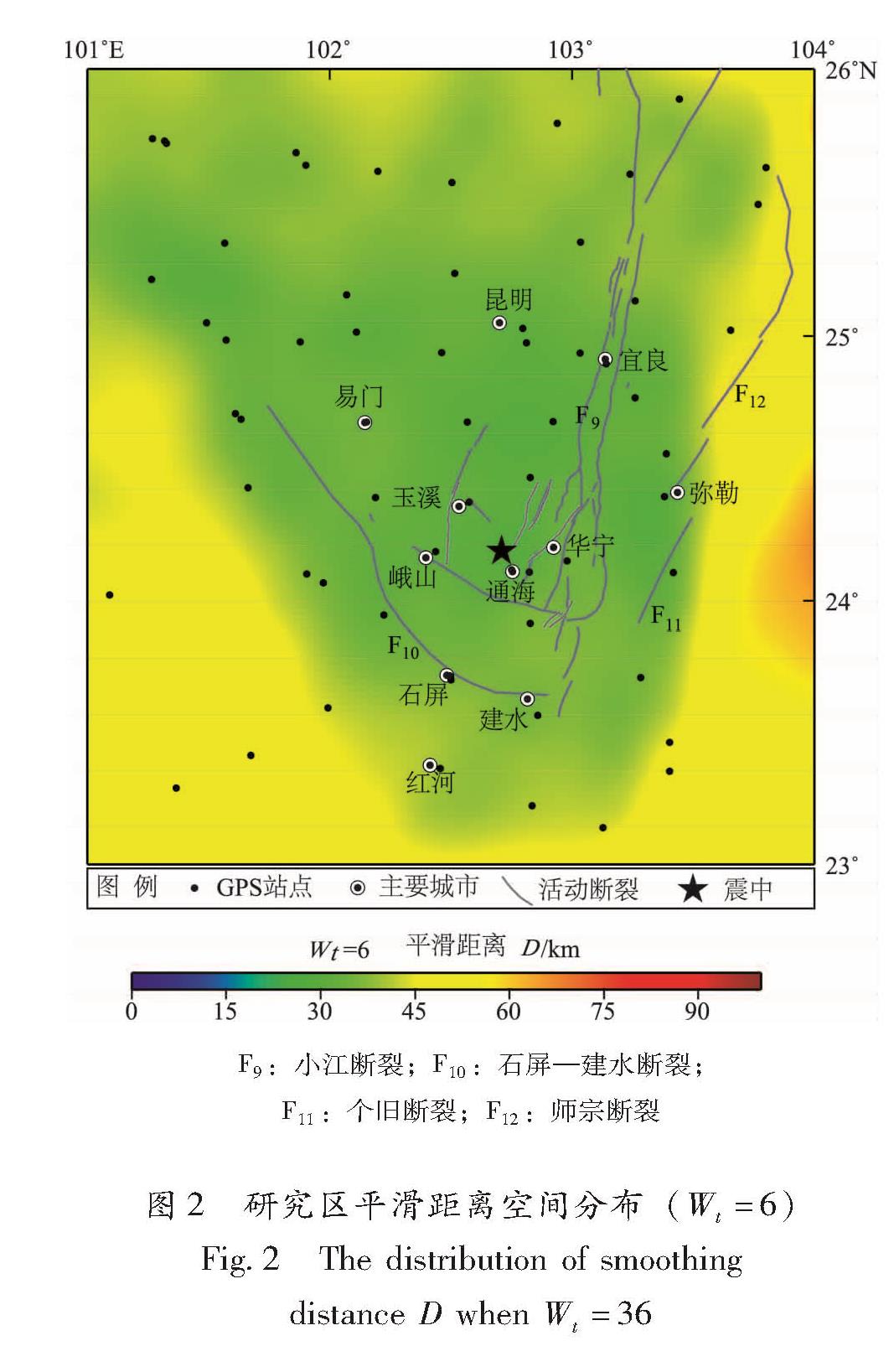
为了确定最佳平滑距离D,笔者引入一个参数来表示重定权系数和的阈值,并设置W(D)=Wt,随着Wt增大,更多的GPS数据被包含进来; 反之,Wt越小,所涉及的站点越少。不同于已有的研究(Shen et al,2015; Ge et al,2015),本文研究范围较小,参考已有的研究结果,采用较小的Wt=6计算,获得研究区平滑距离的空间分布(图2)。从图2可以看出,研究区大部分区域平滑距离约为30 km。按照上述参数设置,采用形变场、应变率场内插程序的更新代码(Shen et al,2015)计算了研究区连续的形变场和应变率场。
图2 研究区平滑距离空间分布(Wt=6)
Fig.2 The distribution of smoothing distance D when Wt =363 水平形变场分析
从相对欧亚板块速度场(图3)来看,研究区存在显著的整体运动,内部差异变形表现不太明显。为了更清楚地反映区域内部相对变形特征,在对原始速度场借助Shen等(2015)程序进行了连续形变场的计算之后,对连续形变相对欧亚板块速度场进行了整体无旋转基准转换(杨国华等,2005),获得了反映区域内部变形的连续速度场(图4)。需要说明的是,受到GPS流动站点分布的影响,对于站点较为稀疏的研究区域东南和西南角没有获得连续形变场,而这2个部位相对远离发震构造中心部位,并不影响计算结果的可靠性。
从图4结果来看,整个研究区域,速度场大小和量值变化最为剧烈、运动受阻最明显部位位于小江断裂带和曲江—石屏断裂带。小江断裂带表现为明显的左旋变形,且在其中南段西侧几十千米范围内,与汶川地震之前龙门山断裂带西侧地壳形变变化类似,同样表现出大范围小变形的地震孕育晚期断层闭锁特征,这和张勇等(2018)对小江断裂带强震危险性分析是一致的。而通海地震正是发生在与小江断裂带走向一致、处于能量积累部位的NE走向的明星—二街断裂上。曲江—石屏断裂带更多表现为逆冲特征,兼具一定的右旋变形分量,从量值大小上看,在其北侧也存在运动受阻、应变积累特征。图3 研究区GPS站点及速度分布(相对欧亚板块)
Fig.3 Distribution of the GPS site and velocity in study region(relative to the Eurasia Plate)从整个研究区域M≥6.0历史强震活动分布(图4)来看,速度场差异显著、运动受阻部位和强震历史活跃区域具有很好的一致性。因此,未来及稍长一段时间,在小江断裂南段和曲江—石屏断裂之间(图4中粉红色椭圆形区域)具有发生中强、乃至更大地震的形变背景特征。区域无旋转基准仅作为参考基准的变换,无法增大或者缩小内部变形,而仅仅使内部变形看起来更为明显。为了进一步验证无旋转基准结果的可靠性,笔者对研究区跨过通海2次地震震中部位垂直小江断裂走向剖面,进行了GPS原始速度场和连续无旋转基准速度场剖面分析(图5)。图5显示跨小江断裂带GPS剖面平行断层运动速度、无旋转基准连续速度场和实际观测具有一致性,从侧面也证明本文分析方法的可靠性和有效性。从图中还可以看出,小江断裂南段处于左旋应变积累部位,其远场滑动速率约8~9 mm/a,而近场要小得多,存在明显的位移亏损特征。图4 研究区内插速度场及M≥6.0历史强震活动分布(区域无旋转基准)
Fig.4 Distribution of interpolation velocity field and historic seismic activity(M≥6.0)in study region(no rotation relative to the study region)4 水平应变率场分析
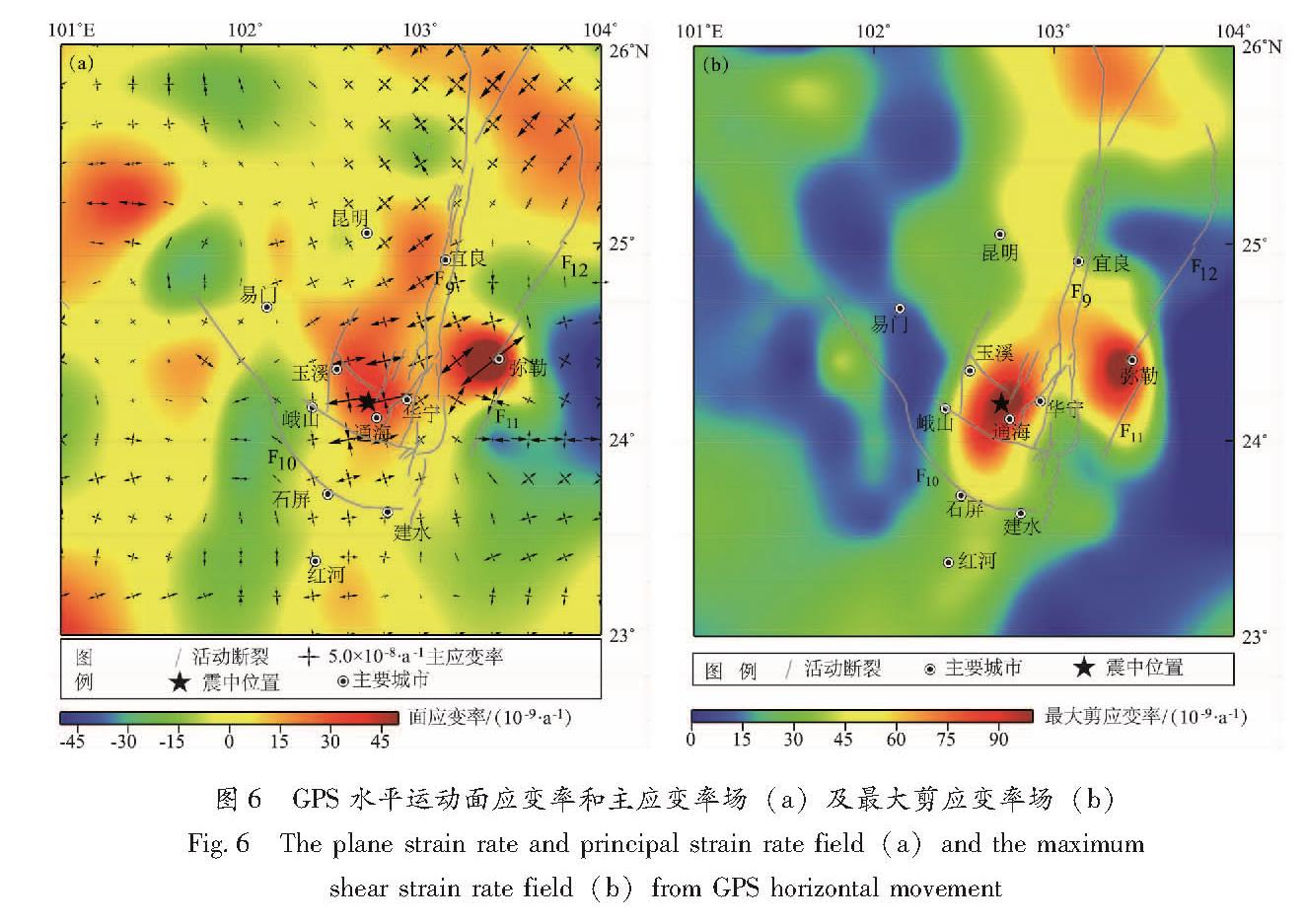
采用上文方法,进一步计算研究区域连续应变率场。主应变率能清晰反映地壳应变状态特征,从图6a可以看出,研究区主要断裂运动特征和地质构造背景具有较好的一致性,即小江断裂带整体表现为左旋特征,曲江—石屏断裂带整体表现为右旋兼逆冲特征,进一步印证了闻学泽等(2011)关于这2条断裂带构造动力学认识,即它们共同承担了川滇块体S向、SSE向运动,吸收了该区域地壳大部分应变能,也是历史强震显著活跃区域。通海5.0级地震就发生在这2条断裂带的交汇部位,该部位主应变率尤为显著,1970年通海7.8级大震也发生在该部位。因此,未来及其稍长一段时间,该区域再次发生中强地震的危险性依然存在。从面应变率(图6a)还可看出,整个研究区域除个别位置外,面应变率整体以张性应变为主,2个显著的面应变高值区为通海—峨山—华宁—玉溪一带和个旧—弥勒之间,面应变率达到5.0×10-8/a。通海5.0级地震正是发生在面应变高值区之一的通海附近。值得关注的是,在个旧断裂与师宗断裂交汇部位,面应变高值区历史强震并不突出,考虑到近年来个旧断裂附近有较强的地震活动(2016年连续发生几次中小地震),未来一段时间应该注意个旧至弥勒之间发生中强地震的危险性。
最大剪应变率(图6b)和面应变率分布类似,有2个高值区,其位置和面应变率高值区大体一致,分别分布在石屏—建水以北、玉溪以南、峨山以东、华宁以西和个旧至弥勒之间,其量值接近10×10-8/a,通海地震也发生在最大剪应变率的高值区之一的通海附近。总体来看,本次通海地震发生于研究区应变积累显著部位,未来稍长一段时间在该区域及其附近具有再次发生中强地震的应变背景特征。
5 结论及讨论
本文利用1991—2015年GPS速度场,研究了2018年8月13,14日通海2次5.0级地震相关构造区域地壳水平形变、应变背景特征。研究结果表明,以现有的站点密度,长期流动GPS观测水平形变、应变场,能够较好反映中强地震发震地点。本次通海地震就发生在区域地壳水平运动受阻、应变快速积累部位,即面应变率和最大剪应变率的高值区。最大剪应变高达9.0×10-8/a,面应变达到5.0×10-8/a。从研究区域形变、应变空间分布来看,未来及稍长一段时间,在小江断裂带南段和曲江—石屏断裂带,以及小江断裂带南段东侧个旧至弥勒之间2个应变快速积累部位,发生中强地震的可能性较大,应该加强跟踪观测。
由于GPS实际观测站点较为稀疏,本文采用内插后区域地壳形变、应变场进行分析,而数学处理并不能完全代替实际观测,因此本文得到的结论还有待进一步的实际观测来证明和修正。另外,笔者也尝试对通海5.0级地震震中及邻近区域的震前地壳形变动态特征展开研究,可能由于5.0级地震孕震形变场相比汶川8.0级、芦山7.0级、尼泊尔8.0级地震而言要小的多,研究结果并不理想。
感谢沈正康老师提供速度场、应变场内插程序最新代码及云南省地震局提供震中附近相关断裂位置。
- 江在森,方颖,武艳强,等.2009.汶川8.0级地震前区域地壳运动与变形动态过程[J].地球物理学报,52(2):505-518.
- 江在森,马宗晋,张希,等.2003.GPS初步结果揭示的中国大陆水平应变场与构造变形[J].地球物理学报,46(3):352-358.
- 闻学泽,杜方,龙锋,等.2011.小江和曲江-石屏两断裂系统的构造动力学与强震序列的关联性[J].中国科学:地球科学,41(5):713-724.
- 武艳强,江在森,王敏,等.2013.GPS监测的芦山7.0级地震前应变积累及同震位移场初步结果[J].科学通报,58(20):1910-1916.
- 杨国华,江在森,武艳强,等.2005.中国大陆整体无净旋转基准及其应用[J].大地测量与地球动力学,25(4):6-10.
- 云南网.2018.云南省地震局:通海震区发生更大地震的可能性不大[EB/OL].(2018-08-15)[2018-08-24].http://news.ycwb.com/2018-08/15/content_30065692.htm.
- 占伟,武艳强,梁洪宝,等.2015.GPS观测结果反映的尼泊尔MW7.8地震孕震特征[J].地球物理学报,58(5):1818-1826.
- 张勇,洪敏,崔兴平,等.2018.小江断裂带近场活动特征分析[J].地震研究,41(3):375-380.
- Ge W P,Molnar P,Shen Z,et al.2015.Present‐day crustal thinning in the southern and northern Tibetan Plateau revealed by GPS measurements[J].Geophysical Research Letters,42(13):5227-5235.
- Shen Z K,Wang M,Zeng Y,et al.2015.Optimal Interpolation of Spatially Discretized Geodetic Data[J].Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America,105(4):2117-2127.
- Zheng G,Wang H,Wright T J,et al.2017.Crustal Deformation in the India-Eurasia Collision Zone From 25 Years of GPS Measurements[J].Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth,122(11):9290-9312.