基金项目:国家重大研发计划“地震应急全时程灾情汇聚与决策服务技术研究(2018YFC1504504)”和中国地震局地震应急专项“云南省地震局地震应急指挥系统改造试点”联合资助.
(Yunnan Earthquake Agency,Kunming 650224,Yunnan,China)
the social media; Lushan earthquake; Jiuzhaigou earthquake; emotional analysis
备注
基金项目:国家重大研发计划“地震应急全时程灾情汇聚与决策服务技术研究(2018YFC1504504)”和中国地震局地震应急专项“云南省地震局地震应急指挥系统改造试点”联合资助.
社会感知技术是研究重特大地震事件中灾区民众行为反应时空特征的一种有效手段。采用情感词典和规则相结合的方法,以2013年四川芦山7.0级和2017年九寨沟7.0级地震为例,用震后24 h微博数据分析了地震灾区民众微博数量特征、情感极性特征、情绪时间序列特征、情绪反应空间分布特征。研究结果表明:芦山地震灾区民众负面情绪大于正面情绪,而九寨沟地震后民众正面情绪大于负面情绪,微博活跃数量程度与人口密度、生命线破坏程度、震中距离和烈度密切相关,微博活跃数量呈现空间分布不均衡特征。分析认为,2次地震后,灾区民众情感行为反应差异主要与灾区人口密度、房屋抗震性能、当地民众防震减灾意识、地震知识了解程度等密切相关。
Social perception technology is an effective means to study the temporal and spatial characteristics of people's behavior response in earthquake-strichen areas. Taking Lushan M7.0 earthquake in 2013 and Jiuzhaigou M7.0 earthquake in 2017 in Sichuan as examples,we obtain the 24 hours Weibo data after the earthquake by emotional dictionary and rules,and analyze the quantitative characteristics,the emotional polarity characteristics,temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of emotional response in the earthquake-stricken area. The results show that the negative emotions of the people in Lushan earthquake-stricken area are greater than the positive ones,and the positive ones in Jiuzhaigou earthquake are greater than the negative ones. The degree of microblog activity is closely related to population density,lifeline damage,epicenter distance and intensity and the spatial distribution of it is unbalanced. The main reasons for the difference of people's emotional and behavioral responses in the two earthquake-stricken areas are closely related to the population density,the seismic performance of buildings,the awareness of earthquake prevention and disaster reduction of local people,and the awareness of earthquake science popularization.
引言
21世纪初以来,我国西南地区相继发生了四川汶川8.0级、四川芦山7.0级、云南鲁甸6.5级、四川九寨沟7.0级等多次重特大地震灾害事件,大地震发生后,政府部门迫切需要了解地震破坏、人员伤亡等情况。通过对带有地理位置标记的社交媒体大数据进行充分挖掘和分析,可以快速获取整个地震灾害事件及灾害链中民众的情绪反应,帮助政府部门有效开展舆情疏导、科学施救和民众情绪的安抚工作,提高救灾效率。
在地震灾区民众行为认知社会调查研究方面,传统的调查方式主要是在震后通过访谈或问卷调查来分析人对灾害事件的反应和行为,获取的数据往往是总体样本的一个子集,存在着样本代表性、典型性、时效性和空间范围等方面问题(吴志峰等,2015)。随着互联网、物联网技术的快速发展,特别是带有定位功能的移动设备、智能手机等的广泛使用,由社交媒体签到数据、带位置的照片、微视频、移动轨迹数据等构成的位置大数据已经成为当前用来感知人类社群活动规律最有效的手段之一(刘经南等,2014; 李德仁,2016)。社会感知可以提取人的时空行为特征,还可以从带有时空标记的社交媒体数据获取个体认知的情绪反应(Liu et al,2015; 刘瑜,2016)。特别是在重大地震事件发生后,灾区大量民众在微博、微信、QQ空间等社交媒体平台上发布对本次地震的情感、心情、观点、评论等,这些数据成为反映社会行为活动和灾害特征的一种重要的数据源(王艳东等,2016)。因此,对这些带有地理位置标记的社交媒体大数据进行充分挖掘和分析,能够在一定程度上克服传统社会调查数据获取不足的问题。尤其是在大地震发生后,灾情的时空变化是“黑箱-灰箱-白箱”的一个演变过程,通过社会感知方式获取灾情,对于政府震后初期进行舆情引导、灾民救助等有重要的意义。
近年来,在全球范围内重大地震事件发生后,国内外学者纷纷利用灾害前后发布的社交媒体数据,围绕地震舆情信息分析监控(赵金楼,成俊会,2015; 曹彦波,2018; Li et al,2018),地震灾害监测预警(Sakaki et al,2013; Crooks et al,2013; 苏晓慧等,2013),地震灾情挖掘分析(徐敬海等,2015; 褚俊秀,徐敬海,2016; Comunello et al,2016; Thapa,2016; 曹彦波等,2017a,b)等方面做了大量的研究工作。在地震舆情信息分析方面,不同学者利用社交媒体数据分析地震公众行为模式、通行行为、情感反应等,如Onook等(2010)利用twitter数据分析了在海地地震后谣言对人们情绪的影响,焦虑的人对负面消息更敏感,很容易受到谣言影响; Qu等(2011)利用新浪微博分析了2011年玉树7.1级地震后,人们利用社会平台传播震情灾情、救灾物资需求、救援处置等信息,以及公众对地震事件的抑郁、愤怒、悲伤等情绪表达; Bengtsson等(2011)使用海地最大手机公司的用户身份模块(SIM)卡的位置数据估计2010年1月12日海地7.3级地震后及随后的霍乱暴发后人口流动的规模和趋势; Lu等(2012)在海地地震后也使用同样的数据确定由于避难行为和人口移动,导致首都太子港的人口大量减少,灾害期间的人口流动显著; 王昊等(2012)利用基于情感的HITS算法分析了2011年日本9.0级地震发生后一周内,人们在社交媒体上对地震的评论和情绪反应特征; Yusuke(2015)通过Twitter数据,分析了2011年日本东部9.0级大地震发生后东京地区由于地震导致新干线停运,人们无法回家的原因及通勤行为的时空特征; Cheng等(2016)以2011年日本大地震为例,调查了社会媒体如何影响人们对灾难的看法及其在灾后恢复活动方面的行为意图,分析人们对灾难感知产生的不同影响; Li等(2017)通过分析在线设计媒体(Twitter)研究了海地地震和日本地震震后公众在不同阶段的情绪反应模式。上述研究成果为基于社交媒体的地震灾区民众情感分析提供了重要的参考和理论基础。
2013年四川芦山7.0级地震和2017年九寨沟7.0级地震是近年来川滇地区发生的2次大地震,对灾区民众影响广泛而深远,目前利用新媒体手段对2次地震事件进行社会影响数据源获取、情感反应分析等方面的研究存在一定不足。本文基于新浪微博数据,这2次地震为例,获取震后24 h微博数据,探索在地震灾害事件初期灾区民众情感行为和反应的时空模式。
1 研究方法
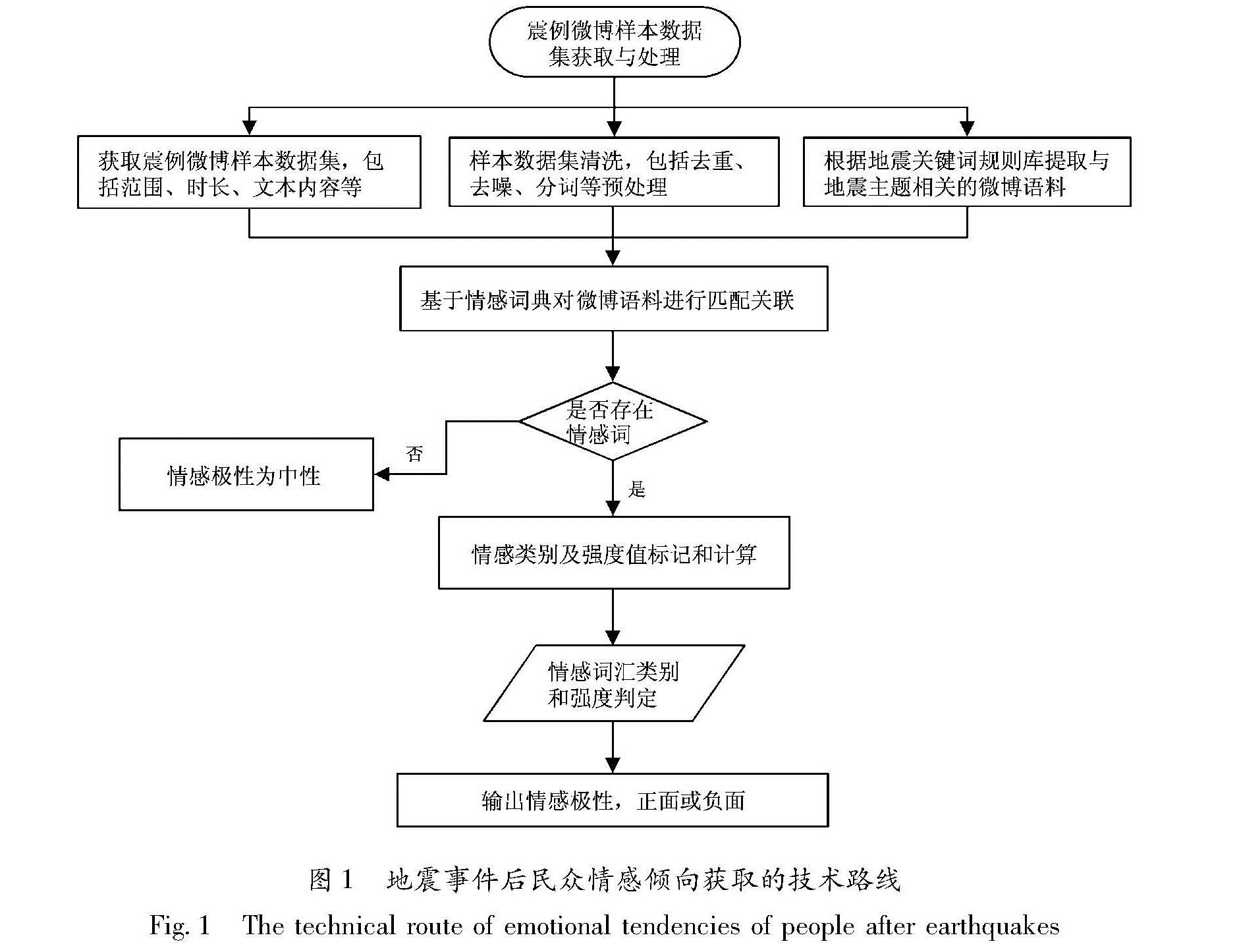
1.1 技术路线本文采用基于情感词典和规则相结合的方法,首先获取用于震例研究的微博样本数据集,对数据集进行清洗、去重、去噪、分词等预处理,根据地震关键词规则库提取与地震主题相关的微博语料; 然后基于情感词典对微博语料逐一进行分类标记和对比,若该句子无情感词,则确定该条微博无情感倾向,为中性情绪反应; 若有情感词,根据情感词的分类和强度判定该条微博情感极性属于正面或负面,对震例样本集所有微博语句进行判定,最终确定此次地震事件民众情感倾向性(图1)。
1.2 地震主题微博提取方法2013年4月20日四川发生芦山7.0级地震,时隔4年后的2017年8月8日,又发生了九寨沟7.0级地震,2次地震共造成202人死亡,11 995人受伤,27人失踪。2次地震是继2008年5月12日汶川8.0级地震后川滇地区发生的震级最高的地震事件,社会影响广泛。震后数天里,大量与地震相关的信息广泛传播,互联网社交媒体高度关注,成为最热议话题。地震发生后,灾区民众第一时间在微博、微信、QQ空间等社交媒体平台上发布了大量博文、图片、微视频等,其中含有大量与本次地震相关的评论、观点、感悟、心情、情感等社会感知信息。
本文采用新浪微博开放平台提供的数据接口服务功能,获取2次地震发布的带有地理位置信息的微博(廉捷等,2011),震例样本数据集获取内容如下:①采集范围:以芦山(30.3°N,103°E)7.0级地震、九寨沟(33.2°N,103.82°E)7.0地震震中为圆心,250 km为半径,采集研究区约20万km2范围内民众发布的微博数据; ②采集时长:地震发生后24 h微博用户发布的数据; ③采集内容:微博创建时间、ID、发布内容、来源、图片、地理位置。
获取微博原始震例样本数据集后,如何提取
与地震主题相关的微博是进行情感分析的关键。笔者采用北京理工大学张华平研发的NLPIR汉语分词系统(又名ICTCLAS 2016)分别对获取到的2次地震微博原始数据进行去重、分词等预处理。同时,在前人对景谷6.6级、永善5.0级、九寨沟7.0级、通海5.0级地震微博主题特征词分类研究基础上(表1),参考地震行业相关标准和地震专业术语逐条将微博原始信息与地震主题特征词汇进行关联匹配,结合人工解译和判读,提取与2次地震主题相关的微博语料数据。
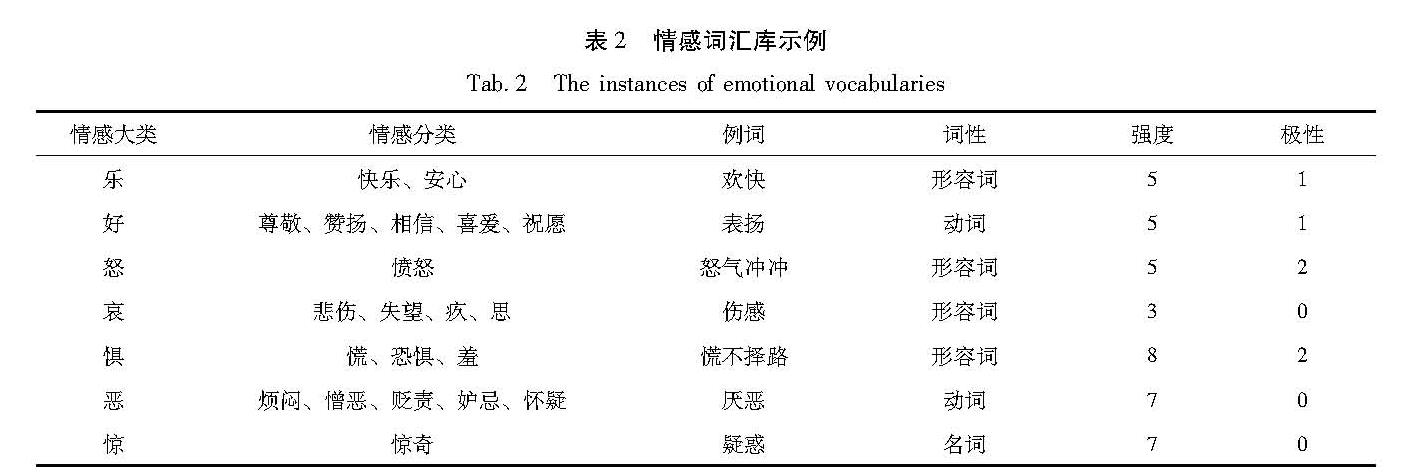
1.3 情感分析方法随着社交媒体软件平台的广泛应用,自然语言处理技术(NLP)也成为国内外学者和研究机构关注的热点,情感分析是自然语言分析处理技术的关键应用之一,目前与主题相关的情感分析技术有基于词典的规则方法、基于表情符号的规则方法、基于词典与规则结合的公式方法、基于机器学习方法和基于语义的分析方法(姚天昉,娄德成,2007; 庞磊等,2012; 李清敏,张华平,2014; 王磊,2018; 钮成明等,2018; 王华,2018)。构建较为完善的情感词典是进行情感分析研究的基础,本文结合了众多情感字典和情感词资源,以大连理工大学情感词汇本体为基础(徐琳宏等,2008),将情感分为7大类、21小类,情感强度分为1,3,5,7,9共5档,9表示强度最大,1为强度最小(表2)。笔者根据地震情感分析的需要,加入近年地震事件中出现的一些网络新词、连词、程度副词和表情符号等,补充和完善情感词典,便于下一步对微博样本数据集进行情感分析。
传统的情感分析主要是基于情感词典将文本情感极性划分为正面、负面、中性3类,本文基于词典与规则结合的公式方法对震例样本数据集进行情感分析,除传统三分法外,还对民众发布的微博短文本进行更细粒度的情感分类,识别出民众对于地震事件的行为反应所表达的情感:“髙兴” “喜欢” “生气” “厌恶” “恐惧” “悲伤”“无情感”等,再根据每一条博文语料中“正面”和“负面”情感词汇数据最终判定该条微博的情感极性。具体算法如下:
E=∑i=1Wpi+∑j=1Wnj(1)
式中:E表示一条微博语句的情感值; Wp表示负面情感词汇数量,赋值为-1; Wn表示正面情感词汇数量,赋值为1。逐一计算微博语料中出现的“正面”和“负面”的情感值,最终求解得出整条微博语句的情感极性,若E>0,则判定为正面情感; E<0,判定为负面情感。
九寨沟7.0级地震后8 min(2017-08-08 21:27:08),一位微博网友发布了信息“深深地感受到无力,无处可逃[失望][失望][失望]地震吓得腿都软了”。该条语句中,“无处可逃”的情感极性为-1,“[失望]”为-1,“吓”为-1,利用式(1)计算得出该条微博情感值E=-6,判定为负面情感。
2 结果分析与讨论
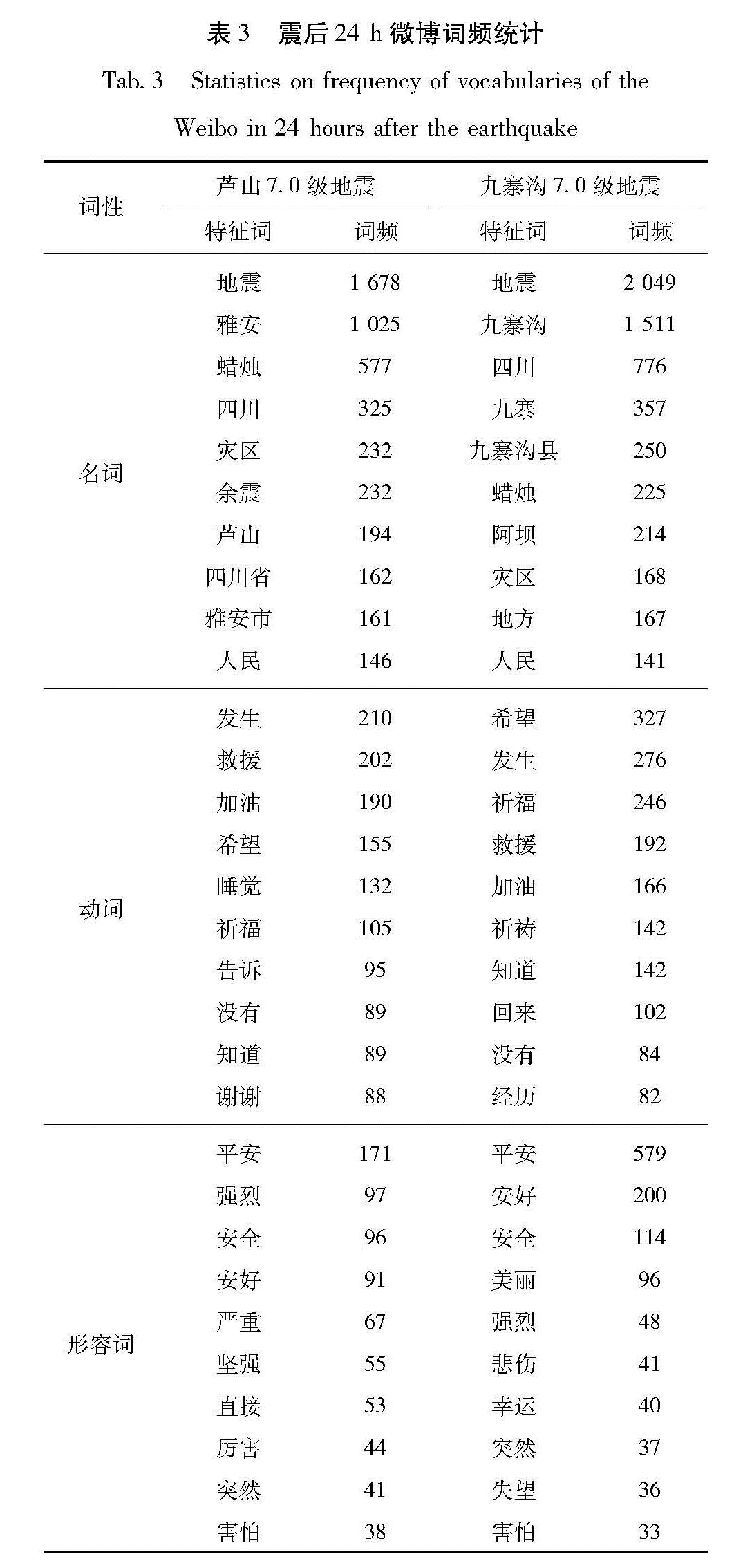
2.1 数量统计分析芦山7.0地震、九寨沟7.0地震发生后的24 h内,分别采集到研究区约20万km2范围内带位置信息的原始微博数据3 498条、5 906条。对2次地震微博原始数据进行去重、分词等预处理后,九寨沟地震中2 396条微博与地震事件相关,占总数68%,芦山地震有2 802条,占总数47%。经过分词解析,统计对比2次地震后微博词频和词云可以看出(表3,图2),2次地震后排名前10位的名词中,“地震”高居首位,其余如“雅安”“余震”“九寨沟”“灾区”等高频词,全部均与地
表3 震后24 h微博词频统计
Tab.3 Statistics on frequency of vocabularies of the Weibo in 24 hours after the earthquake词性 芦山7.0级地震 九寨沟7.0级地震 特征词 词频 特征词 词频 地震 1 678 地震 2 049 雅安 1 025 九寨沟 1 511 蜡烛 577 四川 776 四川 325 九寨 357名词 灾区 232 九寨沟县 250 余震 232 蜡烛 225 芦山 194 阿坝 214 四川省 162 灾区 168 雅安市 161 地方 167 人民 146 人民 141 发生 210 希望 327 救援 202 发生 276 加油 190 祈福 246 希望 155 救援 192动词 睡觉 132 加油 166 祈福 105 祈祷 142 告诉 95 知道 142 没有 89 回来 102 知道 89 没有 84 谢谢 88 经历 82 平安 171 平安 579 强烈 97 安好 200 安全 96 安全 114 安好 91 美丽 96形容词 严重 67 强烈 48 坚强 55 悲伤 41 直接 53 幸运 40 厉害 44 突然 37 突然 41 失望 36 害怕 38 害怕 33
震相关。从解析出来的排名前10位的动词也可以看出,震后频频提及“发生”“救援”“祈福”“祈祷”等词汇。从2次地震微博中也大量出现针对地震的个人感悟、心情、情感等词汇,如“平安”“安好”“害怕”“悲伤”“失望”等。
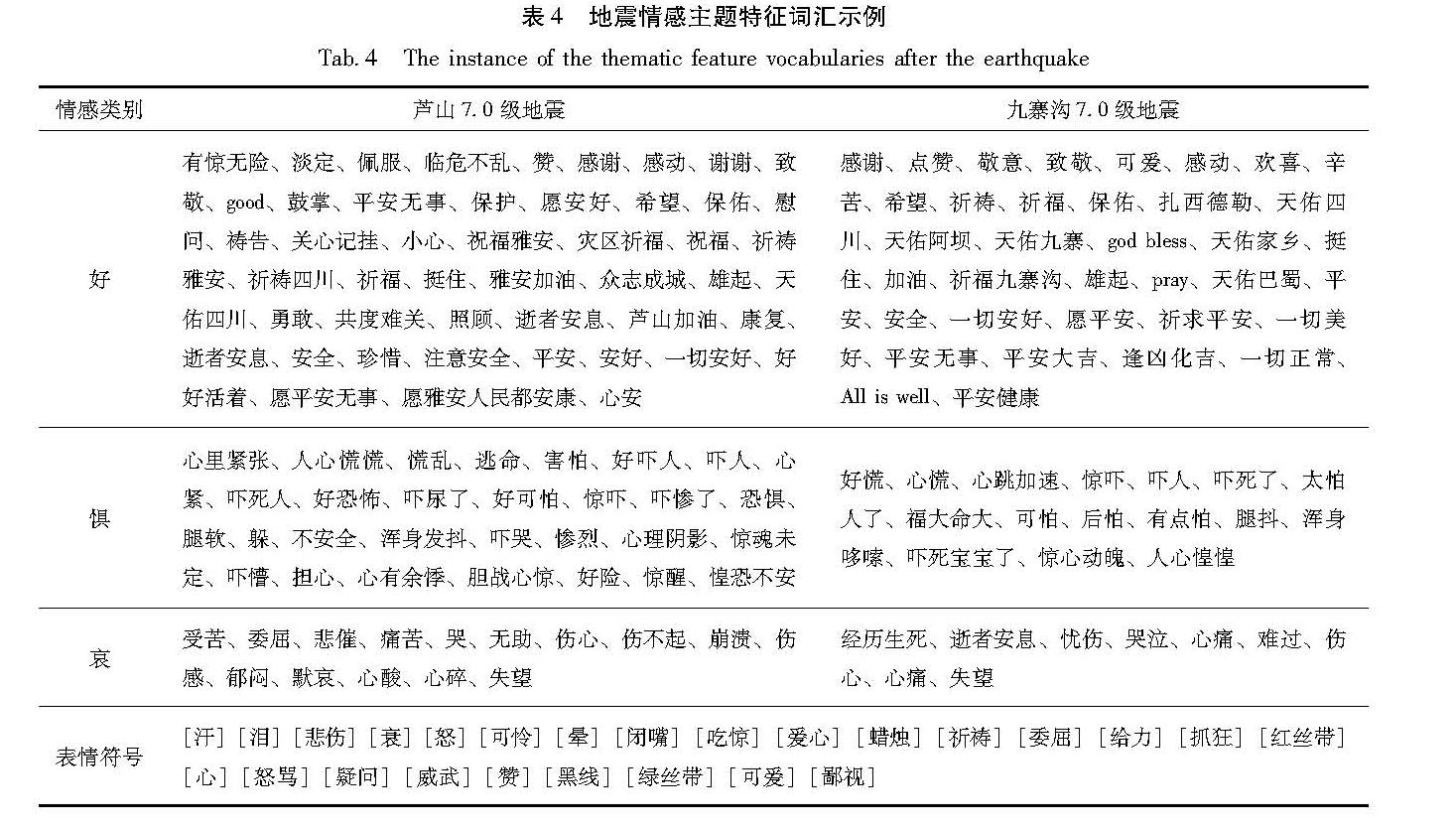
基于扩展后的中文情感词汇库,笔者对2次地震事件中与地震相关的5 198条微博进行了关联和匹配,结合人工标记判定,提取微博样本数据集中反映地震情感的主题特征词汇,其中博文里还出现了大量表达情绪的表情符号(表4)。
2.2 情感极性分析2次地震发生后,震区民众反应强烈,在社交媒体平台纷纷发布和转发与地震相关的信息。芦山7.0级地震发生在2013年4月20日8时2分,正值周六早晨,灾区大部分民众尚未外出,部分
还在睡觉。震后4 min(2013-04-20 08:05:48),震中附近一位微博网友就发布了一条对地震事件的情绪表达和反应:“尼玛,摇了这么久,瞌睡都吓来没有了[抓狂][抓狂][抓狂][抓狂]”。距离震中30 km的网友分享了一张地震灾情照片,照片反映出该区域震感强烈,“器物反应”明显,屋内花盆、塑料瓶翻到。九寨沟7.0级地震发生在21时19分,震中九寨沟景区是全球著名旅游景点,恰逢暑假,大量国内外游客聚集,震后3 min(2017-08-08 21:22:12),距离震中49 km的一位微博网友就发布了信息:“吃饭的时候桌子在晃,吓得饭店一条街的人都跑出去了。”从这条信息可以看出该区域震感强烈,“器物反应”明显。
震后微博网友发布的内容随意性强,口语化程度高,一条博文中会反应多种情绪表现。根据中文情感词汇本体库,对照“乐”“好”“怒”“哀”“惧”“恶”“惊”7类情感词汇,对2次地震后24 h内发布的5 198条微博进行解析和标记。在芦山地震中,博文中提及“乐好”情感表达词汇的微博有855条、“生气”96条、“恐惧”468条、“悲伤”336条、“疑惑”157条; 在九寨沟地震中,“乐好”有1 397条、“生气”6条、“恐惧”283条、“悲伤”246条、“疑惑”77条。
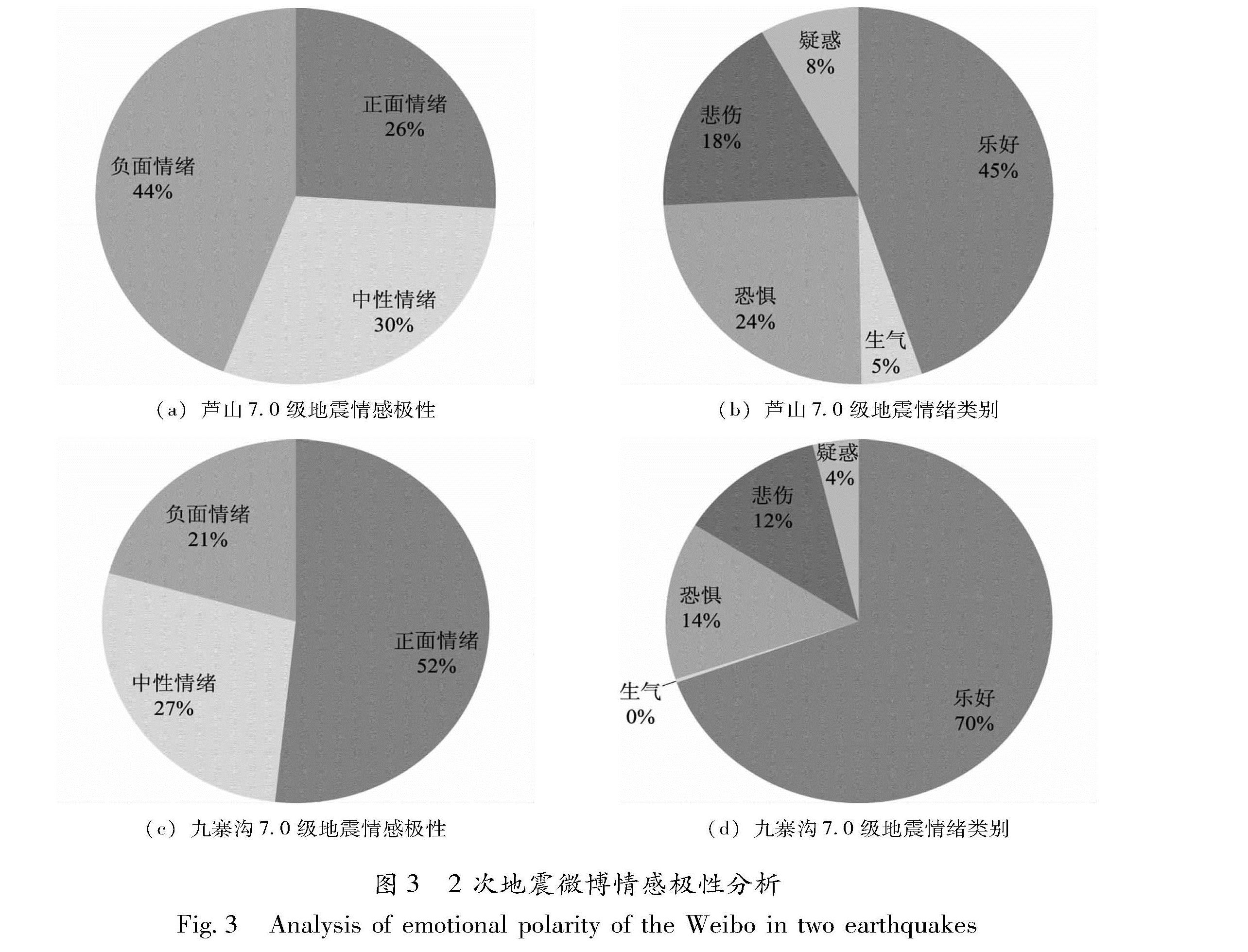
根据式(1)计算了2次地震每条微博的情感极性,从图3a可以看出,芦山地震中民众以负面情绪为主,730名微博网友对此次地震事件的情绪反应为正面,1 236条微博为负面情绪,836条未提及情感词汇,为中性情绪。而在九寨沟地震中,民众正面情绪大于负面,有1 239名网友表达了正面情绪,496条微博负面情绪,661条为中性情绪(图3b)。从图3c,d可看出,芦山地震中乐好情绪占45%,负面情绪以恐惧和悲伤为主,分别占24%和18%; 九寨沟地震中以乐好情绪为主,占70%,其余负面情绪中提及到“恐惧”的情感词汇占到14%。
从芦山地震到九寨沟地震,地震灾区民众情绪反应有了很大变化,以从负面情绪为主导转化以为正面情绪为主导。影响2次地震情绪转化的原因与地震震害、地震地质灾害、人口分布、房屋抗震性能、民众防震减灾意识、地震知识了解程度、自救互救能力等密切相关。例如:2次地震共同特点是震级大、烈度高,极震区烈度都达到Ⅸ度,但造成的震害破坏程度不一样,芦山地震造成196人死亡,21人失踪,13 484人受伤;
九寨沟地震造成25人死亡,525人受伤。芦山地震死亡人数是九寨沟地震的9倍左右,受伤人数约26倍。芦山地震后,灾区生命线系统破坏严重且范围广,震后一周重灾区供水、供电系统仍未能恢复功能,很多偏远灾区通讯困难,震中宝兴县、天全县一度成为“信息孤岛”,且震后余震频繁、震级相对较高,地震当天共发生16次4级以上余震,继2008年汶川8.0级大地震后,民众心理又再次遭受大震冲击,恐惧、悲伤情绪蔓延。而在九寨沟地震的震区,特别是经过汶川地震恢复重建后的房屋建筑达到设防标准,震区房屋建筑抗震性能总体较好。九寨沟景区及城镇建筑物多采用了框架结构,抗震性能较强,大大减轻了人员伤亡。且在经过汶川和芦山地震后,九寨沟地震灾区民众防震减灾意识和自救互救能力有了进一步提高,当地民众对地震心理承受能力明显强于芦山地震。因而,在同样震级的2次地震事件中,民众反应有了较大变化。
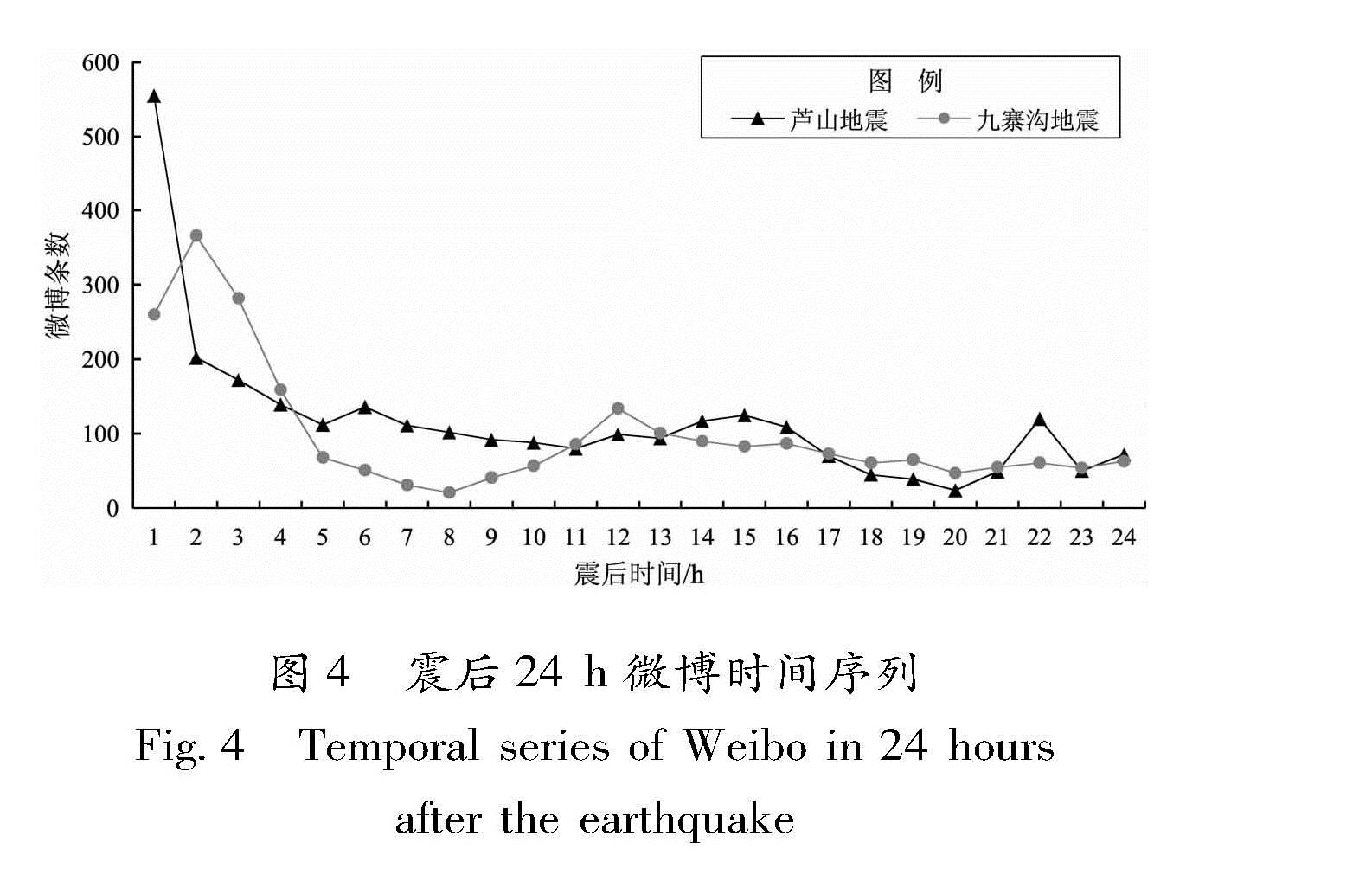
2.3 时空特征分析从图4可以看出:2次地震后微博数量均比平常有激增,震后2 h是微博发布高峰期,芦山地震后2 h里发布了755条,九寨沟地震后2 h发布了626条,占24 h发布微博总量的1/3。震后5 h数量逐级降低,期间出现多次波动,震后12 h和22 h出现小的峰值。
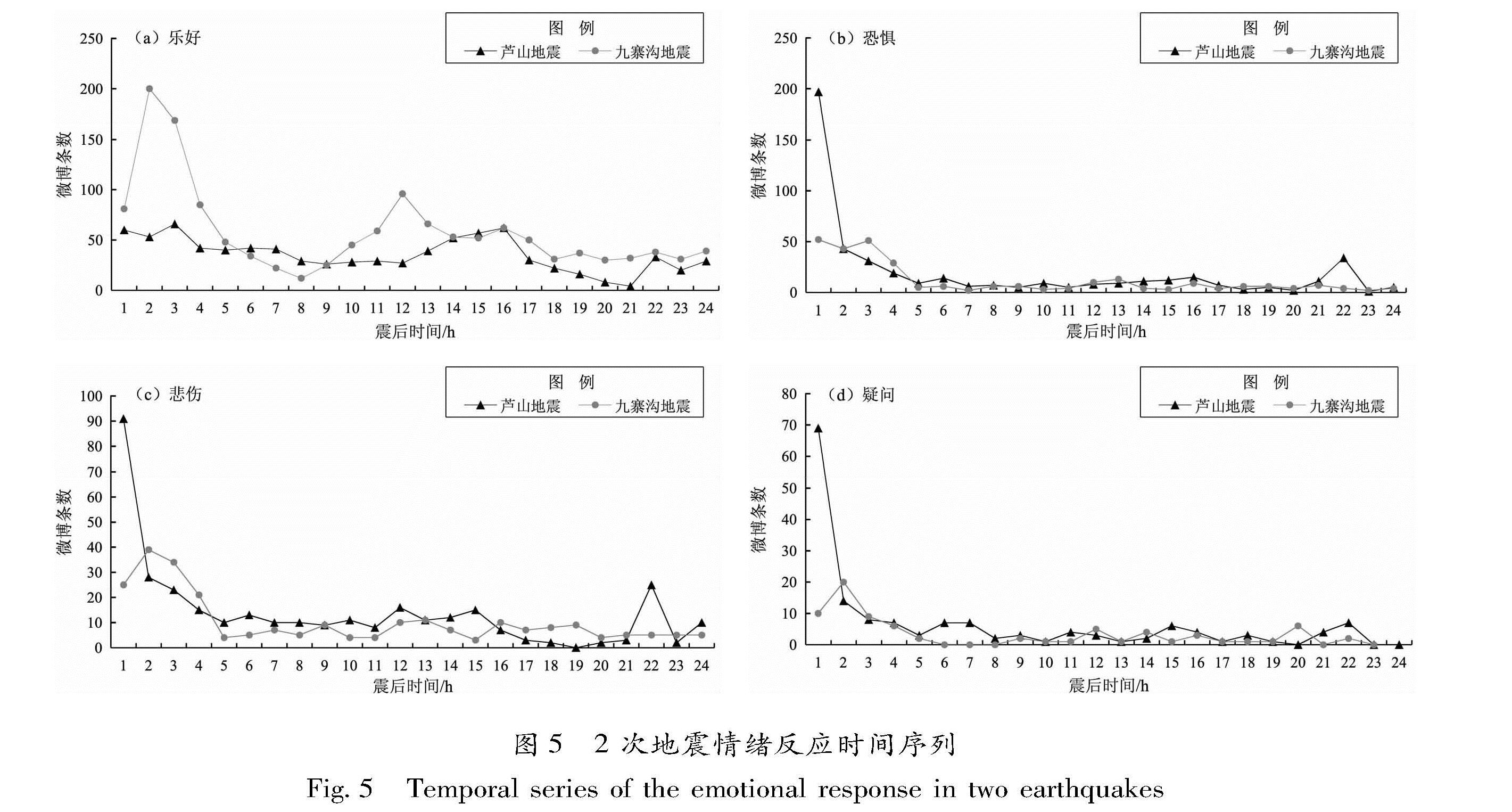
从图5可以看出:震后2 h是网友情绪表达比较集中的时段,与地震相关的“乐好”“恐惧”“悲伤”“疑问”“生气”等各种情绪反应达到高峰。在震后10 h,网友开始对抗震救灾、救援行动、医疗救助、救援人员点赞、致敬和正面评论,表达了“高兴”“喜欢”等正面情绪。例如:距离震中26 km的微博网友于震后3 h发布了地震救援相关信息和图片(2013-04-20 11:03:52):“正在赶往灾区的救援车辆!雅安!加油”。九寨沟地震后,距震中约10 km的漳扎镇荷叶社区一位网友(2017-08-09 03:41:40)发布了信息:“救护车、救援车都在进入,愿一切都好”。芦山地震发生在8时,震区部分人员还在睡觉,被地震摇醒、吓醒、震醒,恐慌、害怕、伤心等情绪较重,博文里出现了大量表达了以“恐惧”“悲伤”情绪为主的特征词汇。在九寨沟地震中,地震对世界自然遗产九寨沟的诺日朗瀑布、五花海等旅游景观和旅游基础设施造成较严重破坏,部分网友表达了伤感情绪,对景点破坏感到可惜。2次地震后余震不断,部分微博网友关注了中国地震台网中心、四川省地震局等地震部门官方微博,多次转发地震信息,同时私信地震部门,提出未来是否还有大地震等问题。
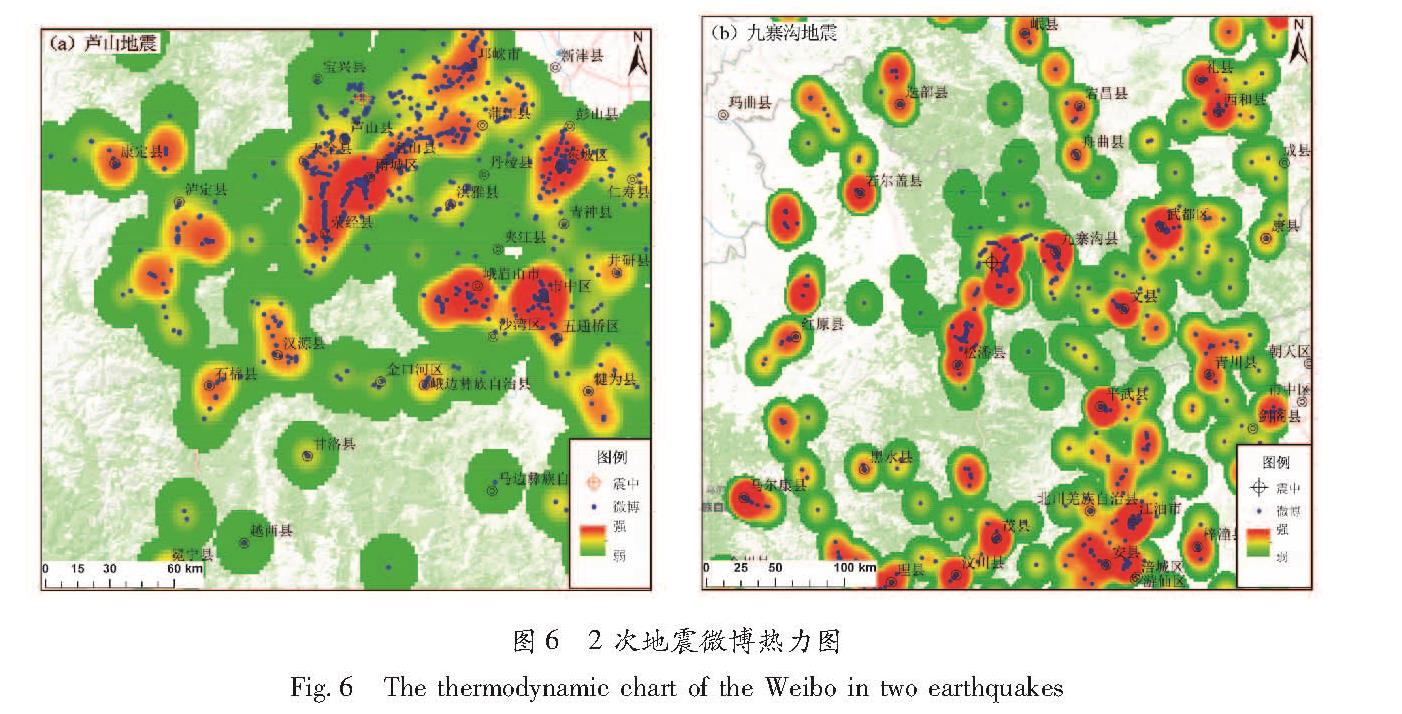
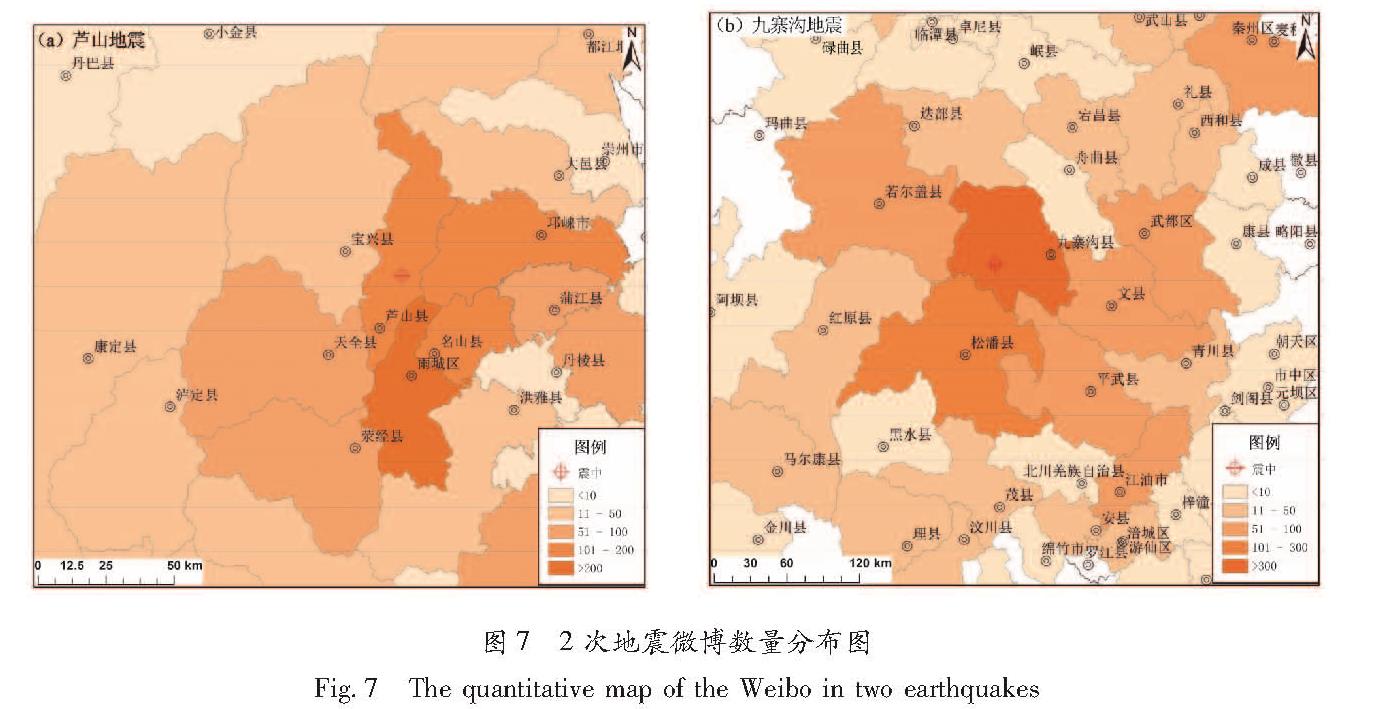
从2次地震微博空间分布图可以看出(图6,7):在芦山地震中,微博用户发布地点主要集中在震中附近的芦山县、宝兴县、天全县、荣经县、雅安市的雨城区等人口密集的县城、乡镇以及交通沿线区域,主要呈点状和条带状分布。震中250 km范围内,发布与地震有关的微博涉及到74个县(市、区),发布数量排名前5的分别是雨城区361条,涪城区244条,旌阳区143条,市中区142条,邛崃市140条,芦山县110条。在九寨沟地震中,微博发布空间分布相对聚集,沿九寨沟县城—九寨沟景区—松潘县城呈线状分布,主要集中在交通沿线的景区、景点、城区和乡镇的人口密集区域。研究区内发布的微博涉及47个市(县、区),数量最多的是九寨沟县,共发布了1 260条,占总数的53%,其余松潘县262条,平武县80条。总体来说,2次地震微博活跃数量程度与人口空间分布、震中距离相关性显著,2次地震微博发布地点大部分集中在县城周边、交通沿线以及景区、景点等人口比较密集的区域,微博活跃数呈现空间分布不均衡特征。
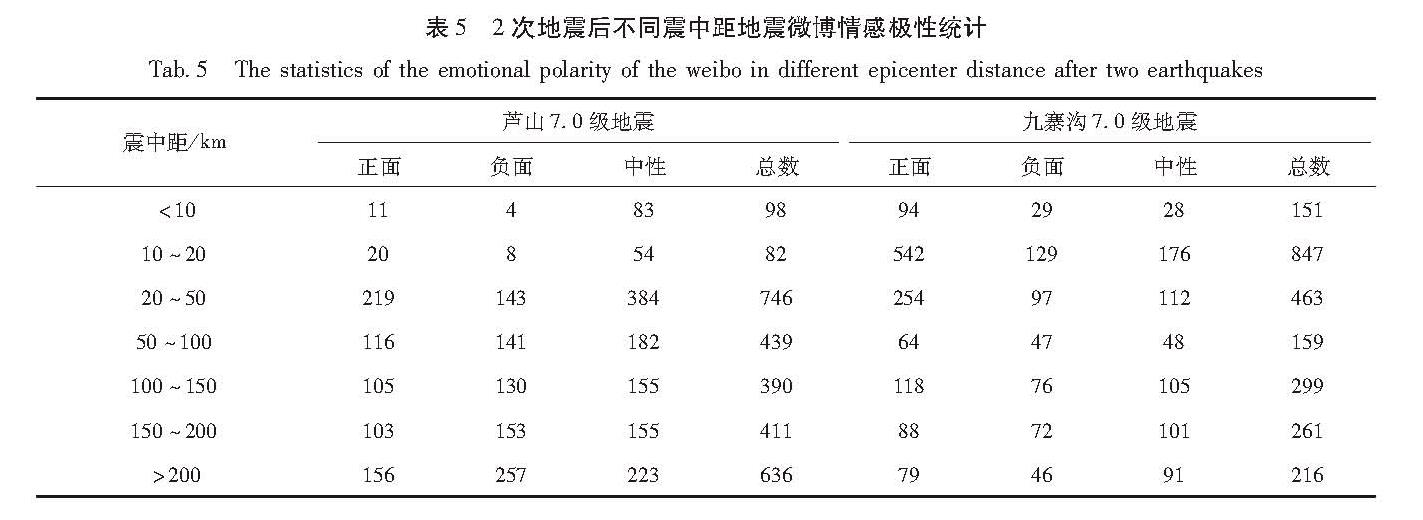
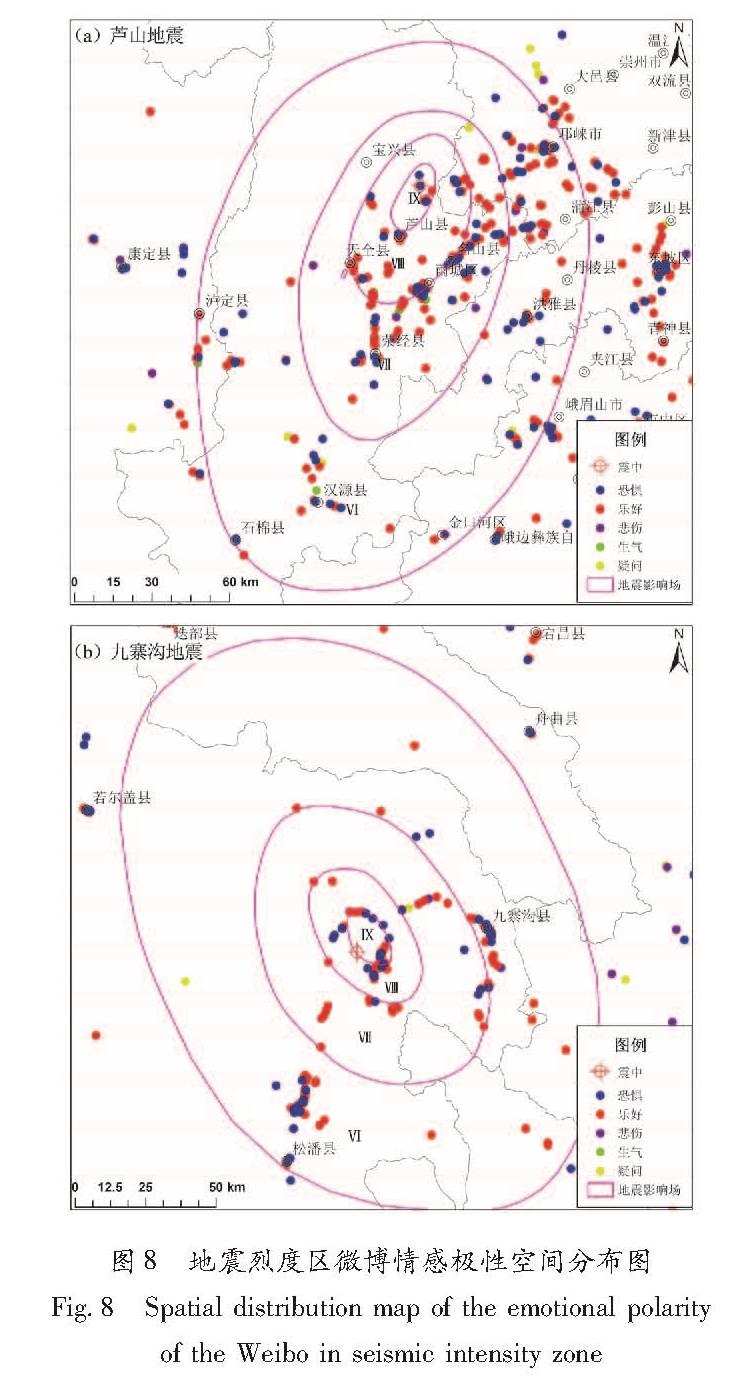
从2次地震微博距震中距离统计表可以看出(表5):在芦山地震中,由于震后初期震中附近的芦山县、天全县、宝兴县等地通信中断,加之震中人口密度低,震中距20 km内震后24 h内发布了180条微博,仅占总数的6%,震中距大于20 km范围则发布了2 622条,占94%,负面情绪微博数量与距离震中远近密切相关,总体负面情绪数量大于正面情绪。而在九寨沟地震中,震中九寨沟景区人口高度密集,20 km内就发布了998条微博,占总量的42%,在民众情感反应上以正面情绪为主。将2次地震烈度图与微博情绪反应空间分布图进行了叠加(图8),在芦山地震中,IX度区发布了90条微博,VIII度区370条,VII度区292条,VI度区376条,VI度区以外1 674条,VI度以上区域占总数的40%。九寨沟地震VI度以上区域共发布了1 532条微博,占总数64%。芦山地震VI度以上区域,“恐惧”“悲伤”“生气”“疑问”等负面情绪多于“乐好”等正面情绪,而九寨沟地震中,VI度以上区域以正面情绪为主导。
表5 2次地震后不同震中距地震微博情感极性统计
Tab.5 The statistics of the emotional polarity of the weibo in different epicenter distance after two earthquakes图8 地震烈度区微博情感极性空间分布图
Fig.8 Spatial distribution map of the emotional polarity of the Weibo in seismic intensity zone2次地震情感极性的数量和空间分布与震中距和地震烈度值高低差异较大,芦山地震微博情感极性与震中距呈正相关关系,与烈度值高低呈负相关关系; 而九寨沟地震与震中距呈负相关关系,与烈度值高低呈正相关关系。导致这种差异的主要原因是地震生命线破坏和灾区的人口密度,九寨沟地震极震区是全球著名的九寨沟风景区,当地人口和大量外来人口集聚,震后通讯电力等生命线工程未遭受重大破坏,微博数量相对较多。在芦山地震震中附近人口密度低,加之生命线破坏严重,震后微博数量少,发布地点大量来自通信未受影响的雅安市区。
3 结论
本文基于新浪微博数据,采用情感词典和规则相结合的方法,以四川芦山7.0级地震和九寨沟7.0级地震为例,分析了震后24 h灾区民众情感行为和反应的时空特征,取得的主要结论如下:
(1)从微博数量统计分析看:基于扩展后的中文情感词汇本体库,对2次地震事件微博进行了关联和匹配,提取出微博样本数据集中反映地震情感的主题特征词汇,情感词汇类别包括乐、好、怒、哀、惧、恶、惊等7个类别以及新浪微博表示心情的表情符号。
(2)从地震情感极性分析看:芦山地震灾区民众负面情绪大于正面情绪,负面情绪以恐惧和悲伤为主,分别占24%和18%。而九寨沟地震中正面情绪大于负面情绪,负面情绪中提及到“恐惧”的情感词汇占到14%。
(3)从地震情绪时间序列特征分析看:2次地震发生后24 h里,震区民众反应强烈,微博日活跃量激增,震后初期2小时是微博发布高峰期,是与地震相关的“乐好”“恐惧”“悲伤”“疑问”“生气”等情绪表达比较集中的时段。“乐好”情绪主要是网友对抗震救灾、救援行动、医疗救助、救援人员进行点赞、致敬和正面评论等方面的情感表达。
(4)从地震情绪反应空间分布特征看:微博活跃数量与人口密度、生命线破坏程度、震中距和烈度高低密切相关,微博活跃数量呈现空间分布不均衡特征。芦山地震微博主要集中在震中附近的芦山县、宝兴县、雅安市区及交通沿线人口密集区域,呈点状和条带状分布。九寨沟地震微博空间分布相对聚集,沿九寨沟县城—九寨沟景区—松潘县城呈线状分布,主要集中在交通沿线的景区、景点、城区和乡镇的人口密集区域。
通过对2次地震事件分析,灾区民众从芦山地震的负面情绪为主转化为九寨沟地震以正面情绪为主,灾区民众情感行为反应特征发生了变化,这与民众防震减灾意识、地震知识了解程度、自救互救能力、人口分布、房屋抗震性能等有很大关系。经过汶川和芦山地震灾后恢复重建、防震减灾工作的强化,九寨沟灾区房屋抗震性能大幅度提高,民众防震减灾意识和自救互救能力进一步提高,民众对地震的心理承受能力强于芦山地震,因此以正面情绪为主导。但是,由于社交媒体手段也存在使用对象、覆盖面、城乡差异等问题,实际地震事件中需多技术手段、多源数据融合进行综合分析,以帮助抗震救灾相关部门更好地了解民众在地震事件不同阶段情绪状态反应,有的放矢,提高救灾效率。
- 曹彦波,毛振江.2017a.基于微博数据挖掘的九寨沟7.0级地震灾情时空特征分析[J].中国地震,33(4):613-625.
- 曹彦波,吴艳梅,许瑞杰,等.2017b.基于微博舆情数据的地震有感范围提取研究[J].地震研究,40(2):185-192.
- 曹彦波.2018.基于新浪微博的通海5.0级地震舆情时空特征分析[J].地震研究,41(4):525-533.
- 褚俊秀,徐敬海.2016.地震灾情位置微博抓取与展示[J].地理空间信息,14(5):38-40.
- 李德仁.2016.展望大数据时代的地球空间信息学[J].测绘学报,45(4):379-384.
- 李清敏,张华平.2014.面向话题的中文微博观点倾向性分析研究[J].科学技术与工程,14(12):227-231.
- 廉捷,周欣,曹伟,等.2011.新浪微博数据挖掘方案[J].清华大学学报(自然科学版),51(10):1300-1305.
- 刘经南,方媛,郭迟,等.2014.位置大数据的分析处理研究进展[J].武汉大学学报:信息科学版,39(4):379-385.
- 刘瑜.2016.社会感知视角下的若干人文地理学基本问题再思考[J].地理学报,71(4):564-575.
- 钮成明,詹国华,李志华.2018.基于深度神经网络的微博文本情感倾向性分析[J].计算机系统应用,27(11):205-210.
- 庞磊,李寿山,周国栋.2012.基于情绪知识的中文微博情感分类方法[J].计算机工程,38(13):156-158.
- 苏晓慧,张群燕,张晓东,等.2013.基于微博的芦山地震前后宏观异常信息筛选与分析[J].震灾防御技术,8(4):451-458.
- 王昊,杨亮,林鸿飞.2012.日本地震的微博热点事件分析[J].中文信息学报,26(5):7-13.
- 王华.2018.基于主题模型和支持向量机的文本情感分类方法[J].宁德师范学院学报(自然科学版),30(3):246-254.
- 王磊.2018.基于最大熵的中文词语情感分析研究[J].计算机时代,(12):7-11.
- 王艳东,李昊,王腾,等.2016.基于社交媒体的突发事件应急信息挖掘与分析[J].武汉大学学报(信息科学版),46(3):290-297.
- 吴志峰,柴彦威,党安荣,等.2015.地理学碰上“大数据”:热反应与冷思考[J].地理研究,34(12):2207-2221.
- 徐敬海,褚俊秀,聂高众,等.2015.基于位置微博的地震灾情提取[J].自然灾害学报,24(5):12-18.
- 徐琳宏,林鸿飞,潘宇,等.2008.情感词汇本体的构造[J].情报学报,27(2):180-185.
- 姚天昉,娄德成.2007.汉语语句主题语义倾向分析方法的研究[J].中文信息学报,21(5):73-79.
- 赵金楼,成俊会.2015.基于SNA的突发事件微博舆情传播网络结构分析——以“4.20四川雅安地震”为例[J].电子商务与管理,27(1):148-157.
- Bengtsson L,Lu X,Thorson A,et al.2011.Improved Response to Disasters and Outbreaks by Tracking Population Movements with Mobile Phone Network Data:a Post-Earthquake Geospatial Study in Haiti[J].PLoS Medicine,8(8).doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1001083.
- Cheng J W,Mitomo H,Otsuka T,et al.2016.Cultivation Effects of Mass and Social Media on Perceptions and Behavioural Intentions in Post-Disaster Recovery-the Case of the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake[J].Telematics and Informatics,33(3):753-772.
- Comunello F,Parisi L,Lauciani V,et al.2016.Tweeting after an earthquake:User localization and communication patterns during the 2012 Emilia seismic sequence[J].Annals of geophysics = Annali di geofisica,59(5).doi:10.4401/ag-6945.
- Crooks A,Croitoru A,Stefanidis A,et al.2013.Earthquake:Twitter as a Distributed Sensor System[J].Transactions in GIS,17(1):124-147.
- Li L F,Zhang Q P,Tian J,et al.2018.Characterizing Information Propagation Patterns in Emergencies:a Case Study with Yiliang Earthquake[J].International Journal of Information Management,38(1):34-41.
- Li X H,Wang Z,Gao C,Shi L.2017.Reasoning Human Emotional Responses from Large-Scale Social and Public Media[J].Applied Mathematics and Computation,310:182-193.
- Liu Y,Liu X,Gao S,et al.2015.Social sensing:a New Approach to Understanding Our Socio-Economic Environments[J].Annals of the Association of American Geographers,105(3):512-530.
- Lu X,Bengtsson L,Holme P.2012.Predictability of Population Displacement after the 2010 Haiti Earthquake[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,109(29):11576-11581.
- Onook O,Kyounghee H K,Rao H R.2010.An Exploration of Social Media in Extreme Events:Rumor Theory and Twitter During the Haiti Earthquake[C].Saint Louis,VSA:Proceedings of Thirty-first International Conference on Information Systems,231.
- Qu Y,Huang C,Zhang P Y,et al.2011.Microblogging after a Major Disasterin China:a Case Study of the 2010 Yushu Earthquake[C].Hangzhou,China.Proceedings of the ACM Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work(CSCW11).25-34.
- Sakaki T,Okazaki M,Matsuo Y.2013.Tweet Analysis for Real-Time Event Detection and Earthquake Reporting System Development[J].IEEE Transactions on Knowledge And Data Engineering,25(4):919-931.
- Thapa L.2015.Spatial-Temporal Analysis of Social Media Data Related to Nepal Earthquake.The International Archives of the Photogrammetry[J].Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences,XLI(B2):567-571.
- Yusuke H.2015.Behaviour Analysis Using Tweet Data and Geo-Tag Data in a Natural Disaster[J].Transportation Research Procedia,(11):399-412.