基金项目:2019年中国地震局监测预报司地震大形势项目子课题《云南地区地震精确定位》和中国地震局星火计划(XH18042Y)联合资助.
(1.云南省地震局,云南 昆明 650224; 2.四川省地震局,四川 成都 610041)
(1. Yunnan Earthquake Agency,Kunming 650224,Yunnan,China)(2. Sichuan Earthquake Agency,Chengdu 610041,Sichuan,China)
b-value; consistency parameter of focal mechanism; stress tensor variance; strong earthquake risk; Northwestern Yunnan
备注
基金项目:2019年中国地震局监测预报司地震大形势项目子课题《云南地区地震精确定位》和中国地震局星火计划(XH18042Y)联合资助.
利用1965年1月—2018年11月云南地震台网提供的月报目录和1999年1月—2018年10月中小地震震源机制解,对滇西北地区主要断裂的b值和震源机制一致性参数进行了空间扫描,结合历史强震空区,分析了滇西北地区的强震危险性。结果 表明:①2000年1月以来程海断裂、龙蟠—乔后断裂及维西—乔后断裂南段b值显著降低,而中甸断裂地震空区两端、程海断裂及邻区则为低b值(b<0.7)主体区域。②震源机制一致性较好的区域分布于程海断裂中部、龙蟠—乔后断裂及维西—乔后断裂南段及邻区。分析认为,低b值和震源机制一致性好可能是区域应力水平增强所致,据此判断程海断裂、龙蟠—乔后断裂及维西—乔后断裂南段及邻区可能是滇西北地区未来发生强震的潜在危险区。
Using the monthly report catalog provided by Yunnan Seismic Network from Jan.,1965 to Nov.,2018 and the focal mechanisms of small-moderate earthquakes from Jan.,1999 to Oct.,2018,we calculated the spatial distribution characteristics of b-value and focal mechanism consistency parameters in the Northwest Yunnan. And then combined with the seismic gap of historical strong earthquakes,we analyzed the strong earthquake risk in northwest Yunnan. The results show that:①Since Jan.,2000,b-value in the Chenghai fault,southern sections of the Longpan-Qiaohou fault and Weixi-Qiaohou fault has been significantly reduced. And the main area of the low b-value(b<0.7)in the research area is at both ends of Zhongdian fault seismic gap,Chenghai fault zone and its adjacent areas. ②The regions with good consistency in the source mechanism are located in the middle of the Chenghai fault,the southern sections of Longpan-Qiaohou fault and the Weixi-Qiaohou fault and their adjacent areas. It is concluded that the low b-value and the best consistency of the source mechanisms may be due to the increase of regional stress. Based on this,it can be judged that Chenghai fault,the southern sections of Longpan-Qiaohou fault and Weixi-Qiaohou fault and their adjacent areas are the potential seismic hazard areas for strong earthquakes in Northwestern Yunnan in future.
引言
强震活动往往发生在活动断裂带上具有高应力积累的凹凸体段或者闭锁段(Aki,1984; Wiemer,Wyss,1997; Wyss et al,2000)。地震一旦成核,破裂将会在高应力环境下扩展,并穿过凹凸体及其附近的非凹凸体的断裂段(Wyss et al,2004)。古登堡-里克特所提出的震级-频度关系(Gutenber,Richter,1944)中的b值与介质的非均匀度、有效剪应力等参数有关,并与应力呈反比关系,这一现象早已在岩石破裂实验(Scholz,1968)、与流体抽取有关的地震活动(Wyss,1973)以及地下矿山岩石破裂(Urbancic et al,1992)中被观测到。特定岩体内构造应力的大小与b值成反比,因此低b值可作为评判高有效剪应力的一个指标(Wyss et al,2000)。目前,利用b值的空间分布揭示和推断一个区域内活动断裂带不同段落的相对应力水平,已成为分析不同断裂段现今活动习性与强震(大震)潜在危险地段的重要手段之一(Wyss et al,2000; Wyss,Stefansson,2006; 钱晓东,秦嘉政,2008; 易桂喜等,2008,2010,2013; 邵延秀等,2015; 吴萍萍等,2015; 毛燕等,2016; 韩晓明等,2016; 张广伟,2016)。
震源机制一致性参数(陈颙,1978; 刁桂苓等,2004; 王俊国,刁桂苓,2005; 程万正等,2006; 泽仁志玛等,2010)在震情跟踪工作中已经成为判断地震危险性的一个有效判据,基于震源机制解反演应力场的时空变化捕捉强震前兆信息的方法也被广泛运用。
滇西北地区处于青藏高原东南缘、川滇菱形块体西南部,受印度板块与欧亚板块碰撞作用(Dewey,Sun,1988; Rowley,1996)的影响,新构造活动显著,发育了众多受近南北向断裂控制的地堑或半地堑盆地,构成了“Z”字形的滇西北裂陷带(吴中海等,2008; 黄小巾等,2014; 罗睿洁等,2015)。该区域历史上M≥6.0地震频发,且大多发生在主要断裂及其附近区域,但M7专项工作组(2012)研究表明,在M≥6.0地震主体活动断裂上仍存在3个地震空区,分别为中甸断裂地震空区、小金河断裂地震空区和宾川地震空区。1996年2月3日丽江M7.0地震后,滇西北地区M≥6.0地震活动较弱,仅发生2组6级地震,最大震级MS6.2,可见该区自1996年丽江地震后强震进入弱活动状态,地震空区持续发展。2013年3月以来,滇西北地区ML≥4.0地震显著增强,且主要集中分布在维西—乔后断裂、程海断裂及其附近地区。2013年3月—2018年11月共计发生ML≥4.0地震20次,其中4.0~4.9级16次、5.0级以上4次,最大为2013年3月3日洱源5.5级地震。因此,探讨滇西北地区的强震危险性具有重要意义。本文结合滇西北地区历史强震空区,计算b值与震源机制一致性参数,分析该区域主要断裂和历史强震空区现今应力状态和强震危险性。
1 资料选取与预处理
1.1 地震目录及最小完整性震级本文利用云南地震台网提供的1965年1月—2018年11月月报目录计算滇西北地区(25.0°~28.5°N,99.0°~101.5°)b值。为避免统计结果 受资料选取的影响,余震的删除、小震群去丛和地震目录的完整性分析非常重要。本文在利用k-k法初步去除余震的基础上,人工进行了二次核对,最终获得0级以上地震94 148次。再采用EMR方法(基于G-R关系基础上的完整性震级范围法)计算研究区地震目录最小完整性震级MC值。由图1a可见,MC值随时间呈减小趋势,这与地震台网的扩展、地震分析方法的不断改进和监测能力的不断提高有关; 2000年前后MC值大幅度降低,这是因为该时段云南地区台站实现了从模拟记录向数字化记录的转变(皇甫岗,李忠华,2010)。为了减弱MC的大幅变化和研究区内发生的1996年2月3日丽江M7.0地震对b值计算结果的影响,分2个时段分别计算b值,即1965年1月—1995年12月(Ⅰ时段)、2000年1月—2018年11月(Ⅱ时段)。图1b,c显示,MC在Ⅰ时段为2.2±0.03,在Ⅱ时段为1.3±0.03。
图1 MC时序图(a)和Ⅰ(b),Ⅱ(c)时段MC图
Fig.1 The variation of MC with time(a)and MC diagrams inⅠ(b),and Ⅱ(c)periods1.2 震源机制解本文根据2002年立项的国家重大基础研究前期研究专项“新一代地震参数目录测定”、专著(徐彦,2013)、2016年立项的地震监测预报专项和中国地震局滇西地震预报实验场小孔径台网给出的相关结果整理了研究区1999年1月—2018年10月绝大部分中小地震震源机制参数。为了排除序列的余震对震源机制一致性参数的影响,剔除了余震的震源机制解,最终获得1 158次ML≥2.5地震的震源机制解,其中2.5~2.9级地震456次、3.0~3.9级地震576次、4.0~4.9级地震107次、5.0~5.9级地震15次、6.0~6.9级地震4次。
2 研究方法
2.1 b值计算古登堡-里克特提出的震级与对应频度的对数线性关系为:
lgN=a+bM(1)
式中:N代表震级M以上地震的频度; a值表示统计区域内的地震活动水平; b值既反映了小地震与大地震的比例关系,又可以反映介质的应力状态。
式(1)已被广泛用来研究地震活动性(李永莉等,2002; 易桂喜等,2008,2010,2013; 王辉等,2012; 毛燕等,2016)。本文采用zmap程序包(Wiemer,Malone,2001)中的默认方法(最大似然法)计算b值。最大似然法是一种常用的点估计方法,其本质在于选取能使观测到的地震样本出现的概率最大的那个参数值作为未知参数的估计(陈阳等,2013)。计算公式(Aki,1965)为:
b^=(Nlge)/(∑Ni=1(Mi-M0))(2)
式中:b^代表b值的估计量; N为地震总个数; Mi代表第i个地震的震级; M0为起算震级。
按照一定间隔将研究区进行网格化处理,采用最大似然法计算出ML≥MC地震的各统计单元的b值; 再根据每一单元的b值得到相应区域的b值; 最后基于应力与b值呈反比关系(Wyss et al,2000)分析滇西北主要断裂带和M7专项工作组(2012)提出的历史强震空区的地震危险性。易桂喜等(2008)研究指出,b>1.0的区域表明区域内断层具有以频繁小震活动为主要特征的蠕滑性质,未来发生强震的可能性相对较小,反之,则区域整体应力水平相对较高,而Wyss等(2004)所获得的凹凸体b<0.7,因此一般b<0.7的区域为低b值异常区。
2.2 震源机制一致性计算已有研究提出多种表征震源机制一致性的参数,如单个地震震源机制解的P,T,B轴和构造应力场的3个正交应力主轴在三维空间的夹角之和(刁桂苓等,2004; 赵英萍等,2004)、单个地震的滑动矢量与在平均剪切应力作用下产生的滑动矢量之间的夹角misfit角(Michael,1984,1987)、应力张量方差(Michael et al,1990; Lu et al,1997)和体波谱振幅相关系数(朱航等,2006; 段云歌等,2018)等。本文采用Michael等(1990)反演研究区的应力张量方差,并用此表征震源机制一致性。Michael等(1990)的方法是按照剪应力方向与断层滑动方向相一致的原则提出的将非线性问题转化为线性反演应力张量的算法。计算过程中,由于无法区分震源机制解的断层面和辅助面,因此在反演应力张量时将2个节面等同看待,通过节面与假定应力张量的拟合函数关系选取其中拟合误差较小的节面作为震源机制断层面。基于研究区每个网格节点及其周围一定范围内的多个震源机制解,用每个震源机制解给激发断层运动的应力张量1个限制,通过若干个解的逼近则可以得到作用于该节点的应力张量解的方向,在应力张量结果的基础上求取应力张量方差和misfit角。
Michael等(1990)认为misfit角大小或应力张量方差高低均能表征震源机制一致性程度,其低值反映震源机制一致性好,应力场是均匀的; 高值则反映震源机制一致性差,应力场是非均匀的。Lu等(1997)研究指出当应力张量方差大于0.2时,说明该区域的应力场在时空分布上都是非均匀的,震源机制一致性程度低,可解释为研究区区域应力水平不高; 当应力张量方差小于0.1时,说明震源机制一致性程度高,且可以用统一的应力张量解释在该区域观测到的震源机制解,也可以理解为研究区域统一受控于较高的区域应力场。通过反演震源机制一致性参数的空间分布特征,可确定相对高应力区,再对相对高应力区的一致性参数进行时间扫描,根据变化形态可分析区域内的强震危险程度和紧迫性。综上,misfit角或应力张量方差的时空变化特征可以用来分析研究区未来强震的可能发生地点和时间。
3 结果分析
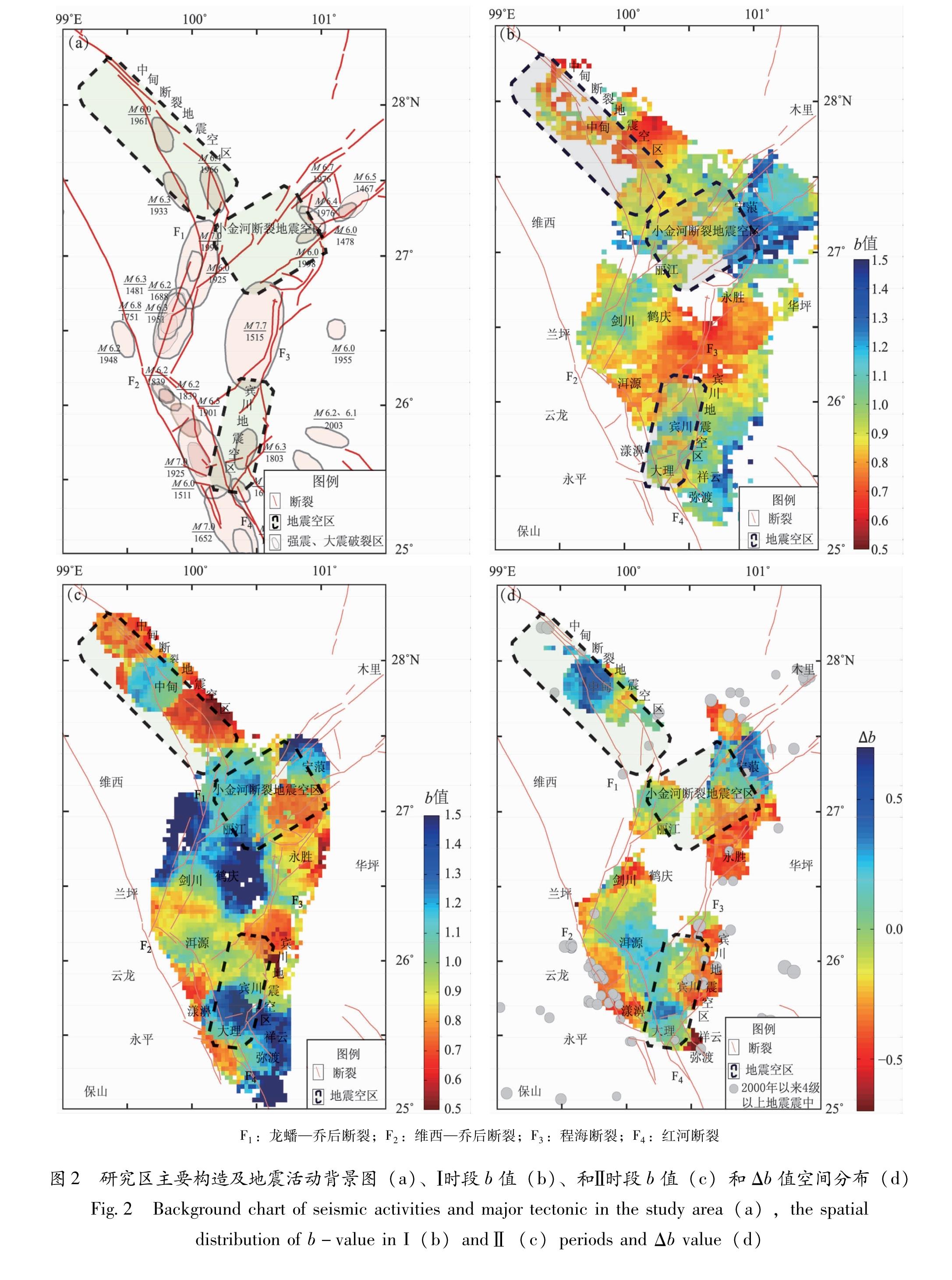
3.1 b值空间变化特征本文研究区构造复杂,展布有龙蟠—乔后断裂、维西—乔后断裂、中甸断裂、小金河断裂、程海断裂和红河断裂等(图2a),历史强震几乎都发生在这些断裂带上,而宾川地震空区、小金河断裂地震空区和中甸断裂地震空区分别位于SN向的程海断裂中南段、NE向的小金河断裂带南段和NW向中甸断裂带上。因此将断裂带附近的中小地震密集区以0.03°的间隔进行网格化,以每个网格节点为圆心,在半径20 km的范围内进行地震统计并估算b值。计算条件要求每个网格的地震数量不少于30个,参与拟合的有效震级分档数不低于5档,不满足条件的网格在图中用空白显示,即没有b值计算结果。
图2 研究区主要构造及地震活动背景图(a)、Ⅰ时段b值(b)、和Ⅱ时段b值(c)和Δb值空间分布(d)
Fig.2 Background chart of seismic activities and major tectonic in the study area(a),the spatial distribution of b-value in I(b)andⅡ(c)periods and Δb value(d)分别以2.2,1.3为起始震级扫描计算研究区Ⅰ,Ⅱ时段的b值,空间分布如图2b,c所示。由图2b明显可见,Ⅰ时段的b值在中甸断裂地震空区、小金河断裂地震空区和程海断裂中段普遍低于1.0,表明该时段这些区域应力水平相对于宁蒗—盐源(b>1.0)和弥渡—祥云地区(b>1.0)要高,而在中甸断裂地震空区东南端和永胜—鹤庆一带的低b值异常尤为显著(b<0.7); 图2c所示,Ⅱ时段b值在中甸断裂地震空区、程海断裂中北段和剑川—洱源—漾濞地区低于1.0,而中甸断裂地震空区南端、宾川地震空区北端与永胜地区、程海断裂北段与小金河断裂地震空区东南角交汇区域b值低于0.7,几个局部地区b值甚至低于0.6。
对比Ⅱ时段与Ⅰ时段b值空间分布可看出,中甸地区低b值(b<0.7)区域有所扩展,永胜—鹤庆地区低b值(b<0.7)区域明显向程海断裂方向收缩,在程海断裂北段新增一个低b值(b=0.5~0.7)区域。而丽江地区b值从Ⅰ时段低于1.0显著升高为1.1~1.5,宾川地震空区南部的b
值也从Ⅰ时段的0.8~1.0显著升高为1.3以上。因此,统一以2.2(Ⅰ时段的最小完整性震级)为起始震级计算Ⅱ时段相对于Ⅰ时段的b值变化量Δb(图2d)。图2d显示,Ⅱ时段宁蒗南部—永胜—宾川一带和鹤庆—剑川—洱源—漾濞一带b值降低(Δb<0)。由此可见,2000年以来,b值显著降低的区域几乎沿着程海断裂、龙蟠—乔后断裂和维西—乔后断裂南段展布,这与2000年以来滇西地区4级以上地震空间分布格局相吻合。
3.2 震源机制一致性参数空间变化特征本文收集的1999年1月—2018年10月滇西北地区的1 158次ML≥2.5地震震源机制空间分布如图3a所示,为了便于与b值计算结果进行对比,震源机制一致性参数扫描区域与b值扫描区域一致。将拟扫描区域按照0.05°×0.05°进行网格化,选取每个网格节点及其周围至少15个地震的震源机制解反演每个节点的应力张量方差。研究区应力张量方差空间分布特征如图3b所示,从图中可见,永胜—鹤庆—剑川—洱源—宾川一带、小金河断裂
图3 研究区震源机制解(a)和应力张量方差(b)空间分布图
Fig.3 Focal mechanism of study area(a)and spatial distribution about variance of stress tensor(b)地震空区的中部和中甸断裂地震空区南北两端存在应力张量方差小于0.2的区域,而应力张量方差的主体低值区域(应力张量方差为0.10~0.15)为永胜仁和地区、宾川—鹤庆—剑川—洱源地区。
4 结论与讨论
本文利用1965年1月—2018年11月云南地震台网提供的月报目录和1999年1月—2018年10月中小地震震源机制解,分析了滇西北主要断裂带和3个历史地震空区的强震危险性,主要得出以下结论:
(1)2000年1月以来,研究区的低b值(<0.7)主体区域为中甸断裂地震空区南端、宾川地震空区北端与永胜地区、程海断裂中北段与小金河断裂地震空区交汇地区,上述区域应力水平较高,具备发生强震的条件,而丽江地区b值较高,发生强震的可能性不大。
(2)对比Ⅱ时段与Ⅰ时段b值空间分布可知:中甸地区低b值区域有所扩展,这可能与Ⅱ时段MC降低,该地区参与计算的地震相对增多有关; 永胜—鹤庆地区低b值区域往程海断裂方向大幅收缩,且在程海断裂北段新增一个低b值区域,而在其南段b值升高且空间上明显出现扩展,这表明程海断裂中北段的强震危险性在不断增加; 丽江中东部和鹤庆北部地区b值显著升高,这可能与1996年丽江7级地震能量强释放有一定关系。Δb计算结果显示,Ⅱ时段永胜—宾川一带和鹤庆—剑川—洱源—漾濞一带b值相对于Ⅰ时段降低。由此可见2000年以来,b值显著降低的区域几乎沿着程海断裂、龙蟠—乔后断裂和维西—乔后断裂南段分布,这与2000年以来滇西地区4级以上地震空间分布格局基本一致。
(3)应力张量方差低值主体区域为永胜仁和地区、宾川—鹤庆—剑川—洱源地区,其值为0.10~0.15。这表明上述地区应力是相对均匀的,震源机制一致性较好,应力水平较高,发生强震的可能性较大。
综上,滇西北地区b值和应力张量方差的空间扫描结果显示程海断裂、龙蟠—乔后断裂和维西—乔后断裂南段及邻区低值变化特征相对显著,这可能是区域应力水平增强的表现。因此分析认为,未来滇西北地区的强震发生在程海断裂、龙蟠—乔后断裂和维西—乔后断裂南段及其邻区的危险性较大。
根据b值和震源机制一致性参数结果可判别出强震的相对危险地点,但在时间尺度上属于中-长期类,如果要在时间判断方面给出更明确的结论,需要结合其它地震学参数和地球物理观测资料开展进一步的研究后再进行综合判定。
- 陈阳,吕悦军,谢卓娟,等.2013.地震活动性参数b值的研究[C].北京:地壳构造与地壳应力所,38-47.
- 陈颙.1978.用震源机制一致性作为描述地震活动性的新参数[J].地球物理学报,21(2):142-159.
- 程万正,阮祥,张永久.2006.川滇次级地块震源机制类型与一致性参数[J].地震学报,28(6):561-573.
- 刁桂苓,赵英萍,啜永清,等.2004.大同晚期强余震前震源机制解的一致性特征[J].内陆地震,18(4):202-206.
- 段云歌,陈天长,苏金蓉,等.2018.2013年芦山MS7.0地震余震序列震源机制一致性的时空变化[J].地震研究,41(2):252-257.
- 韩晓明,张文韬,王树波.2016.河套地震带的b值时空变化特征分析[J].中国地震,32(3):522-532.
- 皇甫岗,李忠华.2010.20世纪云南地区地震记录完整性评价[J].地震研究,33(1):1-6.
- 黄小巾,吴中海,李家存,等.2014.滇西北裂陷带的构造地貌特征与第四纪构造活动性[J].地质通报,33(4):578-593.
- 李永莉,蔡静观,曹刻.2002.云南地区强震活动过程中的调制比b值[J].地震研究,25(1):25-30.
- 罗睿洁,吴中海,黄小龙,等.2015.滇西北宾川地区主要活动断裂及其活动构造体系[J].地质通报,34(1):155-170.
- 毛燕,刘自凤,叶建庆.2016.小江断裂带强震危险性分析[J].地震研究,39(2):213-217.
- 钱晓东,秦嘉政.2008.小江断裂带及周边地区强震危险性分析[J].地震研究,31(4):354-361.
- 邵延秀,袁道阳,梁明剑.2015.滇西南地区龙陵—澜沧断裂带地震危险性评价[J].地震学报,37(6):1011-1023.
- 王辉,曹建玲,荆燕,等.2012.川滇地区强震活动前b值的时空分布特征[J].地震地质,34(3):531-543.
- 王俊国,刁桂苓.2005.千岛岛弧大震前哈佛大学矩心矩张量(CMT)解一致性的预测意义[J].地震学报,27(2):178-183.
- 吴萍萍,李振,叶庆东.2015.郯庐断裂带南段及邻区地震b值的空间分布特征[J].中国地震,31(2):372-381.
- 吴中海,张永双,胡道功,等.2008.滇西北哈巴玉龙雪山东麓断裂的晚第四纪正断层作用及其动力学机制探讨[J].中国科学:地球科学,38(11):1361-1375.
- 徐彦.2013.云南地区ML3.0以上中小地震震源机制解汇编[M].昆明:云南科技出版社,168-186.
- 易桂喜,闻学泽,苏有锦.2008.川滇活动地块东边界强震危险性研究[J].地球物理学报,51(6):1719-1725.
- 易桂喜,闻学泽,辛华等.2013.龙门山断裂带南段应力状态与强震危险性研究[J].地球物理学报,56(4):1112-1120.
- 易桂喜,闻学泽,张致伟.2010.川南马边地区强震危险性分析[J].地震地质,32(2):282-293.
- 泽仁志玛,刁桂苓,李志雄,等.2010.大震前显示的地震震源机制趋于一致的变化[J].地震,30(1):108-114.
- 张广伟.2016.云南地区地震的重新定位及b值研究[J].中国地震,32(1):54-62.
- 赵英萍,刁桂苓,高景春,等.2004.张北强余震前震源机制解的一致性特征[J].华北地震学报,22(1):1-4.
- 朱航,刘杰,陈天长.2006.采用体波谱振幅相关系数方法研究地震序列的震源机制变化过程[J].地震,26(2):1-11.
- M7专项工作组.2012.中国大陆大地震中-长期危险性研究[M].北京:地震出版社,234-235.
- Aki K.1965.Maximum likelihood estimate of in the formula logN=a-bM and its confidence limits[J].Bull Earthquake ResInst Univ Tokyo,43:237-239.
- Aki K.1984.Asperities,barriers,characteristic earthquakes and strong motion prediction[J].J Geophys Res,89(B7):5867-5872.
- Dewey J F,Sun Y.1988.The tectonic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau[J].Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B Biological Sciences,327(1594):379-413.
- Gutenberg B,Richter C F.1944.Frequency of earthquakess in California[J].Bulletin of the seismological Society of America,34:185-188.
- Lu Z,Wyss M,Pulpan H.1997.Detail of stress directions in the Alaska subduction zone from fault plane solutions[J].J Geophys Res,102(B3):5383-5402.
- Michael A J,Ellsworth W L,Oppenheimer D H.1990.Coseismic stress changes induced by the 1989 Loma Prieta,California earthquake[J].Geophys Res Letter,17(9):1441-1444.
- Michael A J.1984.Determination of stress from slip data:Faults and folds[J].J Geophys Res,89(B13):11517-11526.
- Michael A J.1987.Use of focal mechanisms to determine stress:A control study[J].J Geophys Res,92(B1),357-368.
- Rowley D B.1996.Age of initiation of collision between India and Asia:A review of stratigraphic data[J].Earth& Planetary Science Letters,145(1/4):1-13.
- Scholz C H.1968.The frequency-magnitude relation to microfracturing in rock and its relation to earthquakes[J].Bull Seism Soc Am,58(1):399-415.
- Urbancic T I,Trifu C I,Long J M,et al.1992.Space-time correlation of b values with stress release[J].Pure Appl Geophys,139(3):449-462.
- Wiemer S,Malone S.2001.A software package to analyze seismicity:ZMAP[J].Seism Res Lett,72(2):374-383.
- Wiemer S,Wyss M.1997.Mapping the frequency-magnitude distribution in asperities:An improved technique to calculate recurrence times[J].J Geophys Res,102(B7):15115-15128.
- Wyss M,Sammis C G,Nadeau R M,et al.2004.Fractal dimension and b-value on creeping and locked patches of the San Andreas fault near Parkfield,California[J].Bull Seism Soc Am,94(2):410-421.
- Wyss M,Schorlemmer D,Wiemer S.2000.Mapping asperities by minima of local recurrence time:San Jacinto-Elasinore fault zone[J].J Geophys Res,5(B4):7829-7844.
- Wyss M,Stefansson R.2006.Nucleantion points of recent mainshocks in Southern Iceland,mapped by b-values[J].Bull Seism Soc Am,96(2):599-608.
- Wyss M.1973.Towards a physical understanding of the earthquake frequency distribution[J].Geophys J R Astr Soc,31(4):341-359.