基金项目:国家自然科学基金(41604056)、国家重点研发计划“深地资源勘查开采”重点专项(2016YFC0600402)和中国地震局2017年度震情跟踪课题(2017010206)联合资助.
(1.中国科学院测量与地球物理研究所,湖北 武汉 430077; 2.中国科学院大学,北京 100049; 3.陕西省地震局,陕西 西安 710068; 4.江苏省地震局,江苏 南京 210014)
(1. Institute of Geodesy and Geophysics,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Wuhan 430077,Hubei,China)(2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China)(3. Shaanxi Earthquake Agency,Xi'an 710068,Shaanxi,China)(4. Jiangsu Earthquake Agency,Nanjing 210014,Jiangsu,China)
Shaanxi Qianling observatory; thermoelastic deformation; air temperature inside tunnel; temperature of surrounding rock; infrared thermography
备注
基金项目:国家自然科学基金(41604056)、国家重点研发计划“深地资源勘查开采”重点专项(2016YFC0600402)和中国地震局2017年度震情跟踪课题(2017010206)联合资助.
以陕西乾陵台为例,采用红外热像仪对引硐、NS和EW向硐室衬砌的温度进行测量和热成像。结果 表明:引硐为高温段,随着不断深入,温度以近线性的趋势从20.7℃下降至14.8℃; NS向硐室温度比EW向略高,平均分别为13.5℃和13.1℃,但二者整体变化皆稳定均匀。各区段内温度存在小幅的波动现象,某些局部区域个别测点的温度较离散; 而同一测点处衬砌和空气的温度并不一致,存在较大差异。硐室E端处的热像图显示顶拱的温度普遍高于侧壁。
Taking the Shaanxi Qianling Observatory as an example,we systematically detect and image the temperature in lining for the front,NS,and EW parts of the tunnel using the powerful infrared thermal camera. The results show that lining temperature in the front is much higher,varying from 20.7 ℃ to 14.8 ℃,and exhibits a linearly decrease with an increase in distance from the entrance. The lining temperature in the NS part is slightly higher than the EW part,the mean temperatures are approximately 13.5 ℃ and 13.1 ℃ respectively,but each of which is basically uniform and stable. Generally,slight temperature fluctuations widely exist in three main parts of tunnel,the dispersions are larger at a few individual points among them. Furthermore,temperatures in lining and air are significantly discrepant at the same point,this means the difference is drastic. Additionally,infrared thermograms of the eastern end of tunnel show that the temperature in ceiling is clearly larger than that in the sidewalls.
引言
GPS、重力、地形变和断裂蠕变等观测手段可以为相关地球动力学研究提供重要的观测数据,但其观测值往往是构造运动、地潮、地震、气象、水文和环境等诸多因素影响下的综合物理量。其中,温度动态变化(以下简称温变)导致物质的热胀冷缩,是影响观测仪器和地壳形变的重要因素之一(Harrison,Herbst,1977; 刘冠中等,2014; 谭伟杰等,2017)。2009年意大利L'Aquila MW6.1地震前约2个月,气温在两周内持续下降近2.5℃,导致震源区80 km范围内29个GPS测站的水平向产生形变,最大达2.97 mm。若不考虑温变对地表形变的影响,该瞬时形变异常则被误判为主震前的MW5.9慢地震事件(Borghi et al,2016; Amoruso et al,2017a)。因此,定量分析温变的准确影响量,对进一步厘清和理解上述物理信号的物理本质具有十分重要的现实意义。
相比地表,温变较小的硐室是较为理想的观测场地。目前,根据《地震台站建设规范地形变台站》(DB/T8.1—2003)的要求,地球动力学观测硐室的建设规范要求硐室覆盖层厚不小于40 m,室温的年变和日变幅度分别不超过0.5 ℃和0.03 ℃。然而满足了该要求,是否就能消除温变所引起的热弹性形变呢?针对这一问题,近年来国内外许多学者开展了不少定量的分析工作。对于观测仪器,温变有直接的不利影响(Beavan,Bilham,1977; 古澤保等,1993; Lee et al,2001; Amoruso et al,2017b)。以硐体应变仪为例,尽管其铟钢棒的热膨胀系数小于等于2×10-7/℃,但0.5 ℃的温变最大仍能引起1×10-7的干扰(李家明等,2009)。而温度对硐室围岩影响的量级则更加显著(寺石眞弘等,2009; Ben-Zion,Allam,2013; 狄樑等,2017),在周年尺度上,孙玉军等(2008)利用热固耦合方法,通过数值模拟得出硐室温度年变0.2 ℃便可导致围岩1×10-7量级的形变; 在年际尺度上,Venedikov等(2006)采用贝叶斯方法,分析了西班牙兰萨罗特(Lanzarote)地球动力学观测台硐室气温长期变化对围岩的影响,结果显示硐室温度上升1 ℃就会引起约3.6×10-7的张应变,反之压缩。由上可见,即使微小的硐室温变,对仪器和围岩的综合干扰也不容忽视。
由于许多硐室覆盖层的实际厚度远小于40 m,且不同部位覆盖层的厚度不尽相同(寺石眞弘等,2009),而硐室末端还具有热汇聚和热扩散效应; 外界气象等干扰因素在不同时间尺度上,会出现非规律性的剧烈变化。这些客观因素,会导致硐室温度的分布不均和大幅变化,同时也进一步加剧了温度影响的复杂度。而在实际观测中,通常只在硐室内架设一个温度计,这显然无法真实反映整个硐室的温度场及其动态变化。虽然可以根据硐室的布局对热传导模型进行相应简化,并将硐室内单点实测的温度数据作为参考,计算得到硐室的理论温度场,但该方法需要硐室内多个测点的温度数据以对比实证(Yamazaki,2013)。因此,要合理约束并进一步完善硐室温度场的数学、物理和数值模型等,就需要实测硐室不同区段的温度分布,这对准确计算热弹性的形变量至关重要。
传统的硐室温度观测方法局限性很大,难以对硐室进行超密集温度台阵观测,因此不足以揭示硐室温度分布及变化的全貌。而红外热成像技术可以将物体发射的红外信号转换成直观的温度云图,具有测量速度快、精度高、密度大和非接触等优点,已被广泛应用于隧道围岩、岩土体和火山等温度场测量领域(田宝柱等,2016; Bonaccorso,Calvari,2017; 夏浩等,2017; Liu et al,2018),但在地球动力学观测硐室的温度测量方面还鲜有开展。
陕西乾陵台位于鄂尔多斯块体西南缘,其观测数据有助于区内构造运动、地潮和震源过程等地球动力学问题研究。然而,该台硐室覆盖层的最大厚度仅约20 m,硐室温度变化较不稳定,且仅能观测硐室内一点的气温变化。鉴于以上不足,本文尝试采用红外热成像技术对硐室温度进行系统全面的实测,从不同视角揭示其温度的分布特征,以期为该台热弹性形变效应的准确改正和抑制外界干扰因素措施的优化等,提供更详实的观测依据。
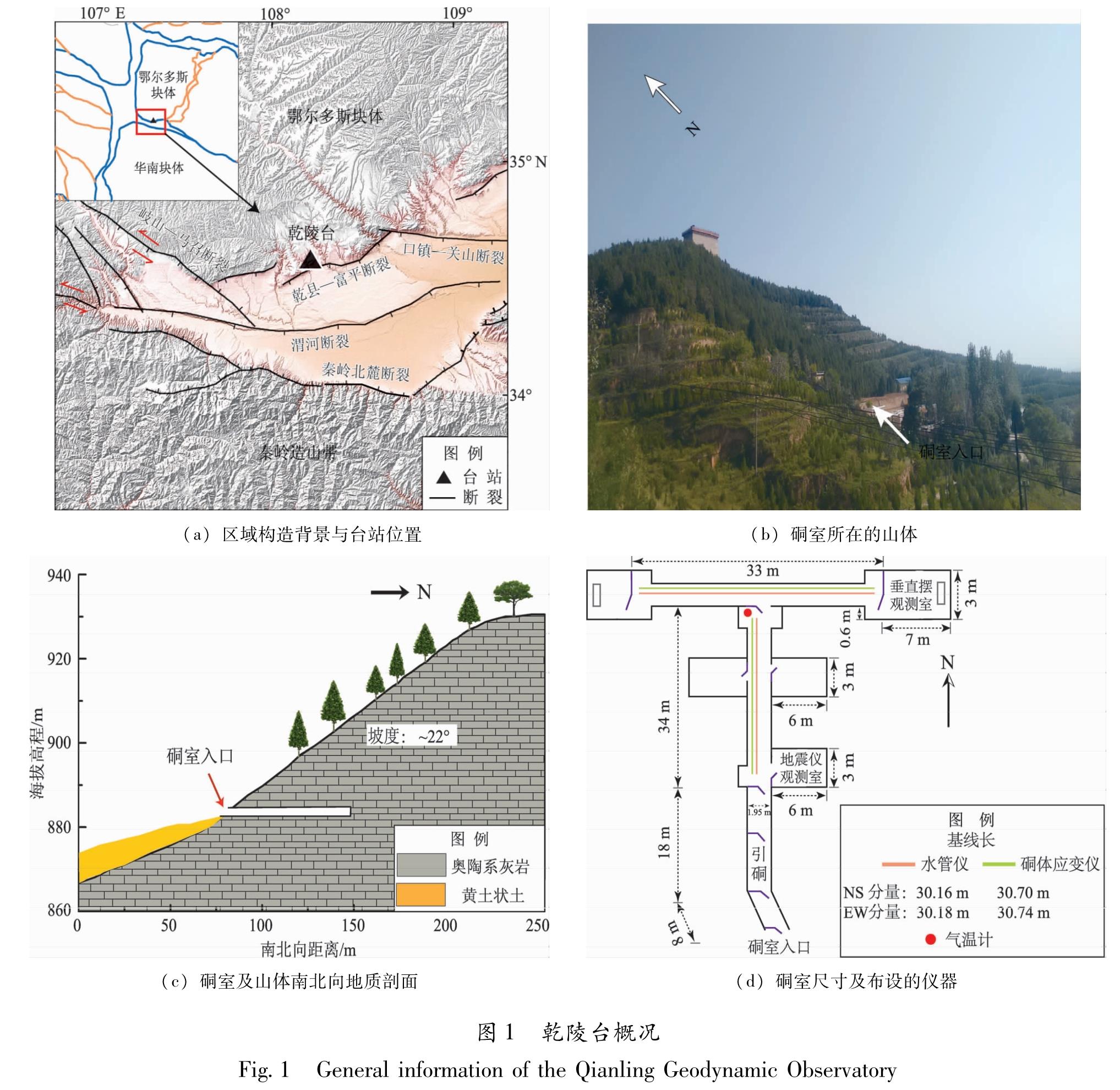
1 区域构造背景和台站概况
鄂尔多斯块体西南缘是青藏块体、秦岭造山带和鄂尔多斯块体的交汇区,也是青藏高原向NE向扩展的最前缘。区内构造活动强烈,主要发育有岐山—马召、渭河、秦岭北麓、乾县—富平和口镇—关山等断裂(图1a)。因此,该区是研究构造变形、断裂活动和限定青藏高原扩展模式等动力学问题的理想场所(李新男,2017)。
陕西乾陵台始建于1977年,位于渭河断陷盆地中段和鄂尔多斯块体南缘的接触带,并处于乾县—富平断裂的下盘(图1a)。台站所在区域的年均降雨量约为545 mm,地下水埋深大于10 m(俱战省等,2012)。台基为奥陶系灰岩,产状近水平,裂隙较少,山体坡度约为20°,植被覆盖良好。观测硐室高2.5 m,进深约60 m,硐室混凝土衬砌厚约20 cm,室内空气相对湿度约90%,顶拱覆盖层最厚约20 m(图1b,c)。目前,该台主要架设有SS-Y型铟钢棒硐体应变仪、VS型垂直摆、DSQ型水管仪、地震仪和数字式气温计。图1d为硐室尺寸和仪器基线参数的示意图,实景照片如图2所示。
2 硐室温变及其典型干扰
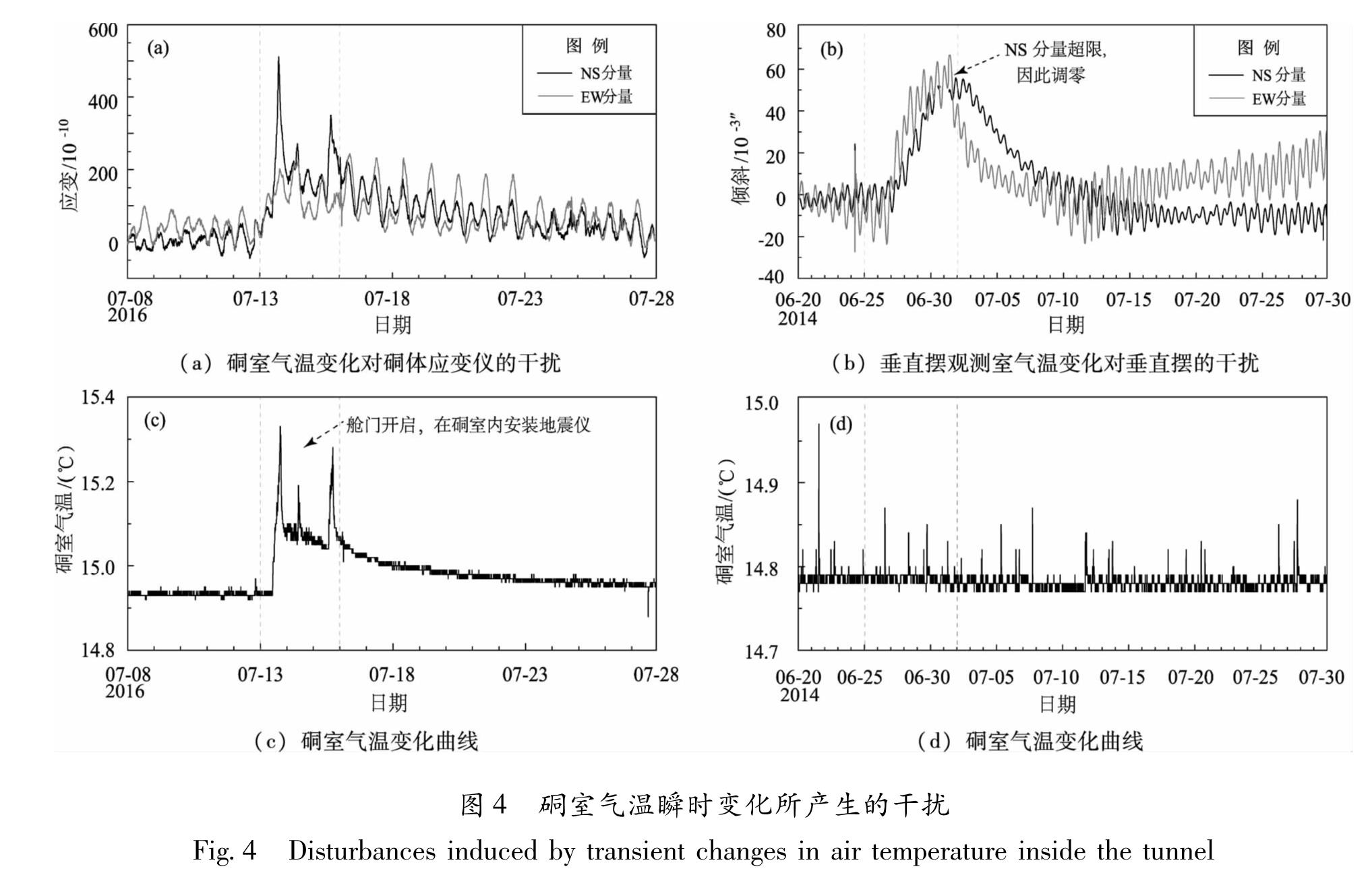
乾陵台覆盖层厚度较小,所以硐室温度的长期变化并不恒定。如图3所示,2015年至2018年9月10日温变的分钟值曲线具有明晰的年变形态,年变幅约0.20 ℃,年均气温约为15.00 ℃。但冷空气、降雨和人为等诸多干扰因素所导致的瞬时温变幅度,往往远大于年变幅。如2017年10月26日,因维修硐体应变仪而开启舱门,由此与外界空气进行对流并产生热传导,导致硐室快速升温高达1.2 ℃(图3)。
硐室温度瞬时大幅变化,会造成仪器系统和硐室的“显著变形”。2016年7月13—15日,工作人员在地震仪观测室安装地震仪,由于开启硐室舱门的时间较长,引起硐室快速升温,高达0.4 ℃。硐体应变仪NS,EW分量产生的张应变分别约为450×10-10和200×10-10,二者相差近2.3倍(图4a,c)。同样的温变对二者的干扰有如此显著的差异,主要是因为温度计布设在NS和EW向硐室的交汇处,故该点的气温测值难以真实反映硐室NS,EW向等不同区段的温变。尤其是距温度计较远处,很难观测到局部瞬时的温变。2014年6月25日至7月1日,EW向硐室东端的垂直摆观测室内40 W的白炽灯一直未关,垂直摆柔丝等热敏感器件,因室内温度上升而变形,导致NS和
EW分量分别向N,E倾斜达60×10-3″,以致超出量程,但温度计并未观测到相应的升温变化(图4b,d),这无疑增加了正确判定该倾斜异常性质的难度。
由上可见,仅通过单点的温度测量难以满足实际的观测需求。因此,全面观测硐室内不同区段的温变,对厘清因热弹性形变所引起的测值异常非常关键。
3 红外热成像方法
依据斯蒂芬—玻尔兹曼定律(Stefan-Boltzmann Law),物体红外辐射的总功率与自身绝对温度关系如下:
E=εσT 4(1)
式中:E为辐射出射度; 发射率ε为实际物体与同温度下黑体辐出度的比值,理想黑体的ε为1,ε与物体的材质等相关,如灰岩为0.90~0.95,混凝土为0.62~0.94,水泥为0.65~0.96; σ为斯蒂芬—玻尔兹曼常数,自然界中σ=5.669 7×10-10W/(m2·K4); T为物体的热力学温度(李云红等,2007),只要物体温度高于0 K,即绝对零度-273 ℃,都能辐射红外能量。
式(1)的指数形式表明,物体表面发生微小温变便可产生较大的红外辐射能。红外热像仪通过接收物体发射的红外辐射,将其转换为物体表面温度分布的热图像。因此,红外热像仪能通过非接触的方式,实时并准确测量物体表面的温度场。
4 硐室红外热成像特征
本文采用Fluke TiS20便携式红外热像仪,其红外光谱带为7.5~14.0 μm,温度灵敏度为0.1 ℃,空间分辨率IFOV为5.2 mRad,图像分辨率为120像素×90像素,视场为35.7°×26.8°,最小焦距0.45 m,最小检测目标尺寸为IFOV×最小焦距,即2.3 mm,则最小能对应热图像每个像素的面积为(2.3×2.3)mm2,需指出的是,热图像的每个像素代表一个监测点的温度值,因此监测密度取决于热图像的分辨率; 成像清晰度则由IFOV值决定,IFOV值越小成像越清晰。目前,高精度热像仪的IFOV可低至0.6 mRad。
硐室温度主要由硐室气温和围岩温度构成,二者既相互作用又互相反馈,在衬砌表面的边界值一致,因此,测量衬砌表面的温度就可有效计算二者的温度场(何春雄等,1999)。由于乾陵台所在地区秋冬季的降雨量较少,该时段硐室衬砌表面附着的入渗雨水也相对较少,硐室内相对湿度较小,因此在该时段进行测温,可有效减小衬砌表面水体和空气中水汽所导致的测温误差(苏美亮等,2013)。2018年9月21日9时,依次对引硐、NS和EW向硐室3个主体区段的衬砌进行了系统测温,期间户外气温约22 ℃,天气晴朗、静风。为避免与外界空气对流,在进入硐室后就立即关闭舱门,同时也未开启硐室内的照明设施,以防止其生热。
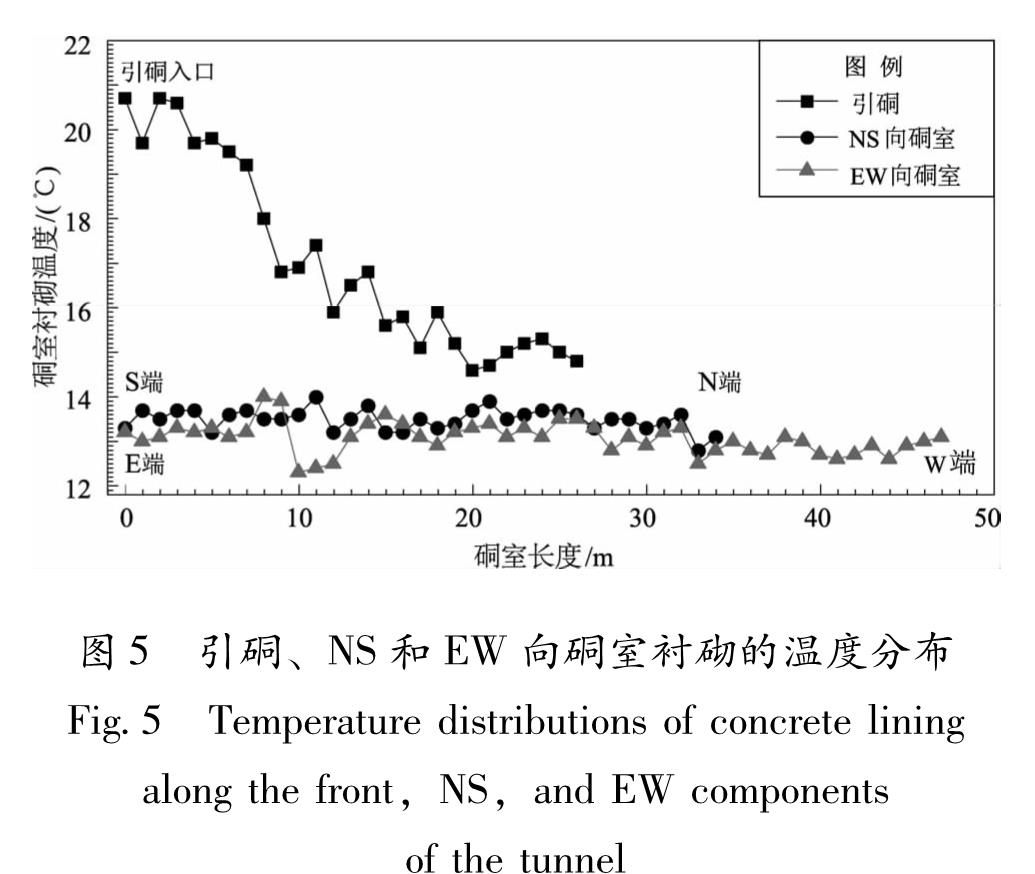
为了解硐室温度分布的概况,同时也考虑到临近仪器侧壁的温变,更易直接影响硐体应变等观测,首先沿靠近仪器的侧壁且距底板约1.4 m的水平测线,以1 m为间隔进行“台阵式”逐点观测,具体位置如图2a中的红色圆环所示。整体而言,侧壁的材质较一致,粗糙度一般,表面较平整,反光程度低,且裂隙较少,这些因素可以有效确保各被测目标表面具有较一致的发射率,从而降低测温误差。测量中拍摄焦点都准确校准,考虑到衬砌主要为混凝土和白水泥,将ε设置为0.92,测温结果如图5所示。从图中可以看出,引硐部分是高温段,随着向N端的深入,其温度从20.7 ℃逐渐下降至14.8 ℃,呈现出近线性的降温趋势,这也从侧面反映出外界气象、人为等因素对硐温有直接且较强的不利影响; NS向硐室的温
图5 引硐、NS和EW向硐室衬砌的温度分布
Fig.5 Temperature distributions of concrete lining along the front,NS,and EW components of the tunnel度则略高于EW向,但二者整体差异较小且趋于均匀稳定,平均温度分别约为13.5 ℃和13.1 ℃,均有别与硐室气温观测值。上述现象表明,随着硐室的不断深入,硐外气温对衬砌温度的影响逐渐减小; 另一方面,也意味着在保温较好的深部硐室,衬砌温度并不恒定为硐内气温(王明年等,2016)。
在各区段内,温度均起伏波动,引硐的波动最为显著。但在某些局部区域,个别测值呈离散分布。如图5所示,引硐和EW向硐室的第13,11个测点,它们分别与之前的测点值相差1.2 ℃和1.6 ℃。出现如此大的温度异常点,可能主要受以下因素影响:(1)低温水渗入衬砌局部区域,使得温度降低;(2)该区域表面红外热辐射存在大幅波动;(3)测温目标表面的发射率较低;(4)测温区域衬砌围岩中含有裂隙;(5)硐室覆盖厚度不均匀、硐室上部山体覆盖物存在差异等。由此也表明,衬砌表面的温度分布存在较大的不均匀性。
硐室N端温度计当天观测的气温约为15.02℃,而此处衬砌的温度约为13.1℃,说明硐室气温和衬砌表面温度有一定差别。究其原因,可能主要是由于衬砌(混凝土和白水泥构成)比空气的导热系数更大,而下渗的低温雨水,会导致衬砌热量更易流失,使衬砌表面温度偏低; 硐室内部相对密闭,对空气的保温效果较好,因此气温相对偏高。需要说明的是,此次仅对比了一个测点处的差异,后期还需测量更多区域的气温,以供进一步的对比分析。
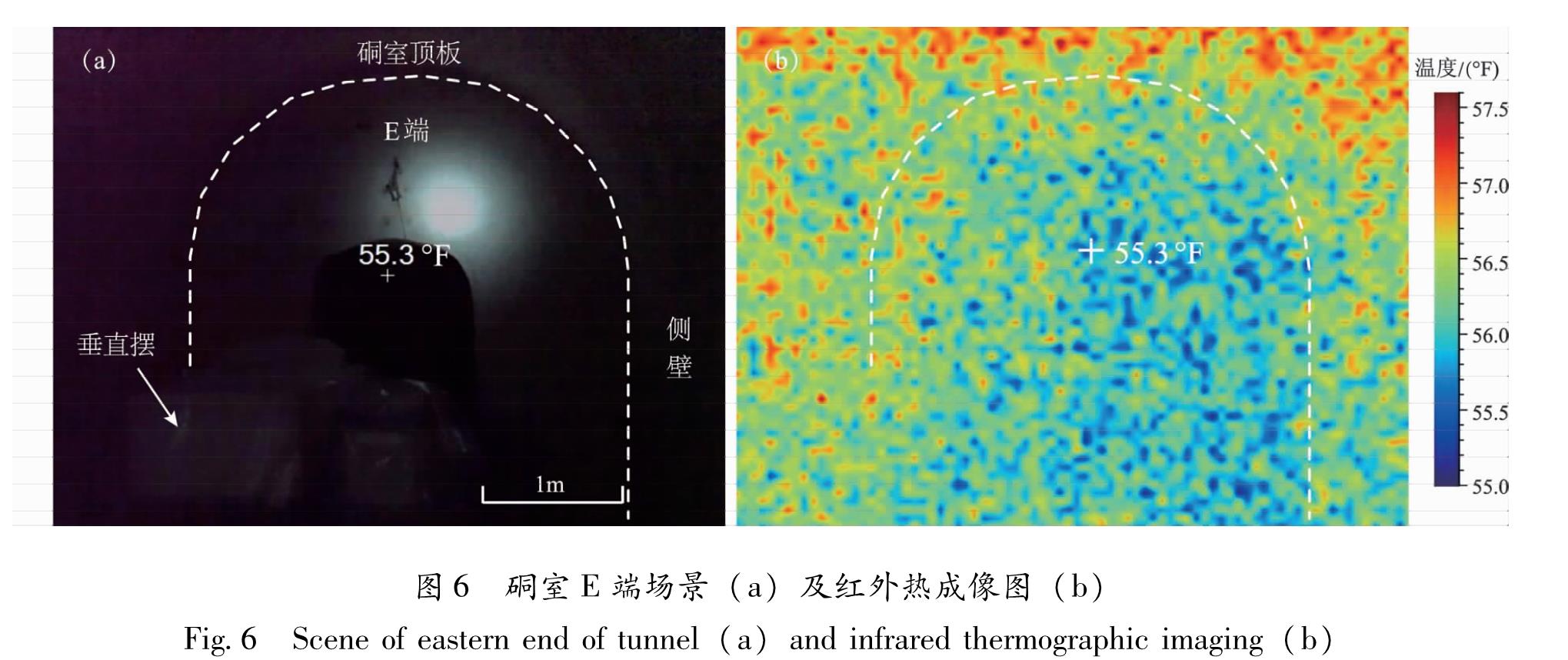
由于硐室端部的几何形态较复杂,所以更容易产生热汇聚和热扩散效应(孙玉军等,2008)。针对这一特殊的“热点”区域,将硐室E端作为试点,在景深约6 m处进行了初步红外热成像,结果如图6所示。从图6b中可以看出,端面校准点的温度为55.3 °F(12.9℃),视场内温度分布范围为12.8 ℃~14.2 ℃,温度分异区明显,即顶拱的温度要略高于端面。而在细观尺度上,红外热成像图出现许多“噪点”,即局部小区域内冷热值混沌分布的特征,显然不能由此揭示更小空间尺度内更精确的温度分布规律。这主要由于IFOV值较大,加之在上述视场内,所能检测最小目标的尺寸高达31 mm。因为该热像仪的温度灵敏度仅为0.1 ℃。所以热像图的分辨率被大大降低,导致细节信息不够明晰。
此外,该型号的热像仪也无法对硐室进行全断面的三维观测。因此,更精细的硐室红外热像全貌很难得以真实和清晰呈现,这不利于端部和其他区域的合理对比。对于端部的热汇聚和热扩散问题,本文暂不做进一步的分析和讨论,在后续的工作中将采用更高精度的热像仪,通过更精细和更长时间的观测来加以重点探讨。要说明的是,由于泡沫保温板较好地密封了垂直摆(图6a),所以其热异常在图6b中并不显著。
从以上初步结果来看,硐室系统内衬砌表面的温度分布很不均匀,并且在空间上的差异也非常明显。
5 结论与讨论
本文采用红外热像仪,对乾陵台硐室的衬砌进行温度观测和热成像,并得到结论如下:
(1)该台硐室衬砌的温度分布特征总体上呈现出:引硐为高温段,随着硐室的不断深入,温度以近线性的趋势由20.7℃逐渐下降至14.8℃; NS向硐室温度略高于EW向,但二者均趋于均匀恒定,平均分别为13.5℃和13.1℃; 硐室入口处与硐室最内侧的温差高达8.4℃,整体而言,引硐温度最高且温差最大,NS向硐室次之,EW向最小。
(2)温度的波动幅度以引硐最显著,NS和EW向硐室则相对平缓,但在某些局部区域,个别测点的温度明显离散。
(3)相同测点处,硐室气温明显高于衬砌温度,二者差异明显。
(4)硐室E端顶拱的温度略高于端面,最大温差可达1.4 ℃,但由于热像图分辨率有限,因此无法获取更精细的细观特征。
乾陵台硐室衬砌温度分布具有显著的不均匀性,局部差异非常明显,其复杂度超乎预判。上述特征对更好理解和准确改正该台的热弹性形变效应等,具有重要的现实意义。同时,也能为合理构建和计算硐室围岩和气温系统热传导的数学或数值模型,提供更可靠的边界值约束依据。由于本文的主要目的是测探红外热成像方法在地球动力学观测硐室测温方面的可行性和应用潜力,所以暂未深入分析温度分布非均匀特征背后的物理机制,这将在后续工作中进一步开展。
相比传统定点单一的硐室气温观测方法,红外热成像虽然不能连续直接观测气温,但却能以“超密集台阵”的方式,对衬砌进行精确、快捷的温度成像; 也能有效填补目前气温观测模式下的“空白”区。鉴于该方法所特有的诸多优点,值得进一步开展相关研究,今后或可作为一种不同视角和有效的辅助测温手段。
特别需要说明的是,鉴于该台硐室温度的时变性及分布的复杂程度; 加之本文所使用红外热像仪的精度有限,若要揭示其更系统精细的三维时变温度分布特征,尚需采用更高精度的红外热像仪并进行更长时间的观测和资料分析。
在硐室几何尺寸测量和红外热成像过程中,陕西省地震局张国强工程师、乾陵地球动力学观测台的张创军高级工程师、陈嘉选和杨晓东工程师给予了很大帮助,中国科学院测量与地球物理研究所危自根博士与笔者进行了有益的讨论,两位评审专家提出诸多有益建议,对稿件质量的提升帮助很大,在此一并表示诚挚的感谢。
- 狄樑,陆德明,丁建国,等.2017.气象因素对倾斜仪观测干扰特征分析[J].大地测量与地球动力学,37(8):870-875.
- 古澤保,大谷文夫,寺石眞弘,等.1993.線膨張率の異なる2種のスーパー·インヴァー棒伸縮計の比較観測[J].測地学会誌,39(4):363-376.
- 何春雄,吴紫汪,朱林楠.1999.严寒地区隧道围岩冻结状况分析的导热与对流换热模型[J].中国科学:地球科学,29(增刊1):1-7.
- 俱战省,刘文兆,郑粉莉,等.2012.陕西省乾县地下水位动态变化特征分析[J].水土保持通报,32(2):178-181.
- 李家明,姚植桂,张卫华,等.2009.超短基线伸缩仪的研制[J].大地测量与地球动力学,29(4):144-147.
- 李新男.2017.鄂尔多斯西南缘活动构造几何图像、运动特征及构造变形模式[D].北京:中国地震局地质研究所,12-19.
- 李云红,孙晓刚,原桂彬.2007.红外热像仪精确测温技术[J].光学精密工程,15(9):1336-1341.
- 刘冠中,马瑾,杨永林,等.2014.川西地区长周期气温变化对跨断层位移观测的影响及芦山地震前的异常断层活动[J].地球物理学报,57(7):2150-2164.
- 寺石眞弘,大谷文夫,竹内文朗,等.2009.地殻変動連続観測における季節変化[R].京都:京都大学防災研究所年報,52(B):285-291.
- 苏美亮,方云,周伟强,等.2013.千手观音凝结水的红外热成像检测技术[J].物探与化探,37(2):295-300.
- 孙玉军,李杰,曹建玲,等.2008.深部洞室中微小温度年度变化足以造成地应变年度变化[J].地震学报,30(5):464-473.
- 谭伟杰,许雪晴,董大南,等.2017.温度变化对中国大陆三维周年位移的影响[J].测绘学报,46(9):1080-1087.
- 田宝柱,刘善军,张艳博,等.2016.花岗岩巷道岩爆过程红外辐射时空演化特征室内模拟试验研究[J].岩土力学,37(3):711-718.
- 王明年,唐兴华,吴秋军,等.2016.高岩温隧道围岩—支护结构温度场演化规律[J].铁道学报,38(11):126-131.
- 夏浩,胡新丽,唐辉明,等.2017.红外热像技术在滑坡物理模型试验中的应用[J].岩土力学,38(1):291-299.
- Amoruso A,Crescentini L,Chiaraluce L.2017a.Surface temperature and precipitation affecting GPS signals before the 2009 L'Aquila earthquake(Central Italy)[J].Geophys J Int,210(2):911-918.
- Amoruso A,Crescentini L,Bayo A,et al.2017b.Two high-sensitivity laser strainmeters installed in the Canfranc Underground Laboratory(Spain):instrument features from 100 to 0.001mHz[J].Pure Appl Geophys,175(5):1727-1737.
- Beavan J,Bilham R.1977.Thermally induced errors in fluid tube tiltmeters[J].J Geophys Res,82(36):5699-5704.
- Ben-Zion Y,Allam A A.2013.Seasonal thermoelastic strain and postseismic effects in Parkfield borehole dilatometers[J].Earth Planet Sci Lett,379:120-126.
- Bonaccorso A,Calvari S.2017.A new approach to investigate an eruptive paroxysmal sequence using camera and strainmeter networks:lessons from the 3-5 December 2015 activity at Etna volcano[J].Earth Planet Sci Lett,475:231-241.
- Borghi A,Aoudia A,Javed F,et al.2016.Precursory slow-slip loaded the 2009 L'Aquila earthquake sequence[J].Geophys J Int,205(2):776-784.
- Harrison J C,Herbst K.1977.Thermoelastic strains and tilt revisited[J].Geophys Res Lett,4(11):535-537.
- Lee J C,Angelier J,Chu H T,et al.2001.Continuous monitoring of an active fault in a plate suture zone:a creepmeter study of the Chihshang fault,eastern Taiwan[J].Tectonophysics,333(1):219-240.
- Liu X X,Liang Z Z,Zhang Y B,et al.2018.Experimental study on the monitoring of rockburst in tunnels under dry and saturated conditions using AE and infrared monitoring[J].Tunn Undergr Space Technol,82:517-528.
- Venedikov A P,Arnoso J,Cai W,et al.2006.Separation of the long-term thermal effects from the strain measurements in the Geodynamics Laboratory of Lanzarote[J].J Geodyn,41(1):213-220.
- Yamazaki K.2013.An attempt to correct strain data measured with vault-housed extensometers under variations in temperature[J].Tectonophysics,599:89-96.
- DB/T8.1—2003,地震台站建设规范地形变台站[S].