基金项目:国家创新研究群体科学基金(41521002)和地质灾害与地质环境保护国家重点实验室基金资助项目(SKLGP2017Z016)联合资助.
(成都理工大学 地质灾害防治与地质环境保护国家重点实验室,四川 成都 610059)
(State Key Laboratory of Geohazard Prevention and Geoenvironment Protection,Chengdu University of Technology,Chengdu 610059,Sichuan,China)
collapse; geological hazard assessment; frequency ratio; risk zoning; Jiuzhaigou MS7.0 earthquake
备注
基金项目:国家创新研究群体科学基金(41521002)和地质灾害与地质环境保护国家重点实验室基金资助项目(SKLGP2017Z016)联合资助.
以九寨沟MS7.0地震为例,分析同震形变及地震前后地质灾害(崩塌、滑坡、不稳定斜坡)分布规律,提取地震前后崩滑地质灾害影响因子,统计各个因子各个等级的频率比,根据频率比进行危险性与地质灾害易损性评价,最终完成九寨沟地震前后地质灾害风险区划。研究结果表明:九寨沟地震前地质灾害主要集中于沟道中,震后地质灾害主要集中于同震形变区域; 震后九寨沟县地质灾害风险范围提高至震前水平的120%,增加的风险区主要为漳扎镇和九寨沟景区。
Taking Jiuzhaigou earthquake as an example,we study the distribution law of co-seismic deformation and post-earthquake collapse geological disasters(collapse,landslide,unstable slope),and extract the influence factors of post-earthquake collapse geological disasters,and count the frequency ratio of each grade of each factor.Finally,according to the frequency ratio,we take the risk and geological disaster vulnerability assessment to complete the risk zoning before and after the Jiuzhaigou earthquake. The results show that the pre-earthquake geological disasters were mainly concentrated in the channel,and the post-earthquake geological disasters were mainly concentrated in the coseismic deformation zone.After Jiuzhaigou earthquake,the geological disaster risk range in Jiuzhaigou County increased to 120% before the earthquake level,and the increased risk zone was mainly Yuzha Town and Jiuzhaigou Scenic Area.
引言
2017年8月8日21时19分46秒,四川省阿坝州九寨沟县(103.82°E,33.20°N)发生MS7.0地震,震源深度20 km。地震发生后,众多学者进行了地质灾害方面的相关研究。姚鑫等(2017)对九寨沟地震InSAR同震形变场及发震构造进行了探讨,揭示了控震构造是巴颜喀拉地块北缘边界断裂弧形旋转体系的尾端构造,发震断层是该断裂系中塔藏断裂的南段; 李渝生等(2017)从地质调查、测试与震源构造动力学理论分析相结合的角度阐明九寨沟地震断层破裂机制; 戴岚欣等(2017)通过遥感技术进行震区地质灾害解译,统计出地质灾害与各类因素的关系,进行地质灾害分布规律研究(Fan et al,2018; Wu et al,2018; Wang et al,2018); 刘甲美等(2017)、陈晓利等(2018)利用灾前地形、区域地质等资料,运用Newmark累积位移模型提出了九寨沟地震应急快速地质灾害评价方法; 许冲等(2018)、邓飞等(2018)、张孝奎等(2018)通过无人机和现场调查对九寨沟地震触发滑坡进行详细描述; 王志一等(2018)以九寨沟地震为例提出了光学与SAR遥感影像相结合的地震地质灾害快速解译方法; Zhao等(2018)、Nie等(2018)根据应急调查和遥感解释结果分析了同震滑坡大多为浅层滑坡、崩塌等,规模较小。
现有研究成果往往集中于地震后地质灾害评价预测,或对地震前后地质灾害发育特征进行分析,而对地震前后地质灾害易发性(危险性、风险等)的对比分析少有提及。地震前后地质灾害风险对比分析可对震后地质灾害防治工作有重要的指导意义。因此,本文在对以往典型文献分析的基础上,选取地质灾害易发性评价因子进行易损性评价,最终完成2017年九寨沟MS7.0地震前后地质灾害风险对比分析。
1 地质灾害分布规律
1.1 研究区概况及数据选取九寨沟县位于四川省阿坝州东北部、青藏高原东北缘、岷山山脉的东部以及龙门山山脉的西北部,地处青藏高原与四川盆地的大地貌单元过渡的深切割高山峡谷地带。境内山脉纵横,峰峦重叠,相对高差悬殊,形成以高山深切河谷为主的地貌类型。由于地形陡峻,前缘临空条件发育,坡体表面松散物质沿与完整基岩接触面下滑的下滑分力较大,坡体稳定性较差,因此易在斜坡部位形成滑坡; 在地形切割形成陡崖的地段,由于岩体卸荷常形成崩塌、危岩,危及住户安全; 区内支沟沟域面积较大,沟道纵坡较陡,两侧岸坡高陡,泥石流物源发育。
本次地震发震区位于龙门山断裂带、塔藏断裂带、岷江断裂带和虎牙断裂带的交汇处,发震断裂带为虎牙断裂,地震破裂面走向NW,倾向WS,倾角70°~80°,最大滑动距离85 cm,主破裂长约30 km(李渝生等,2017; 刘华国等,2018)。根据中国地震台网中心数据可知,近百年内此次地震震中500 km范围内发生过多次6.5级以上地震。
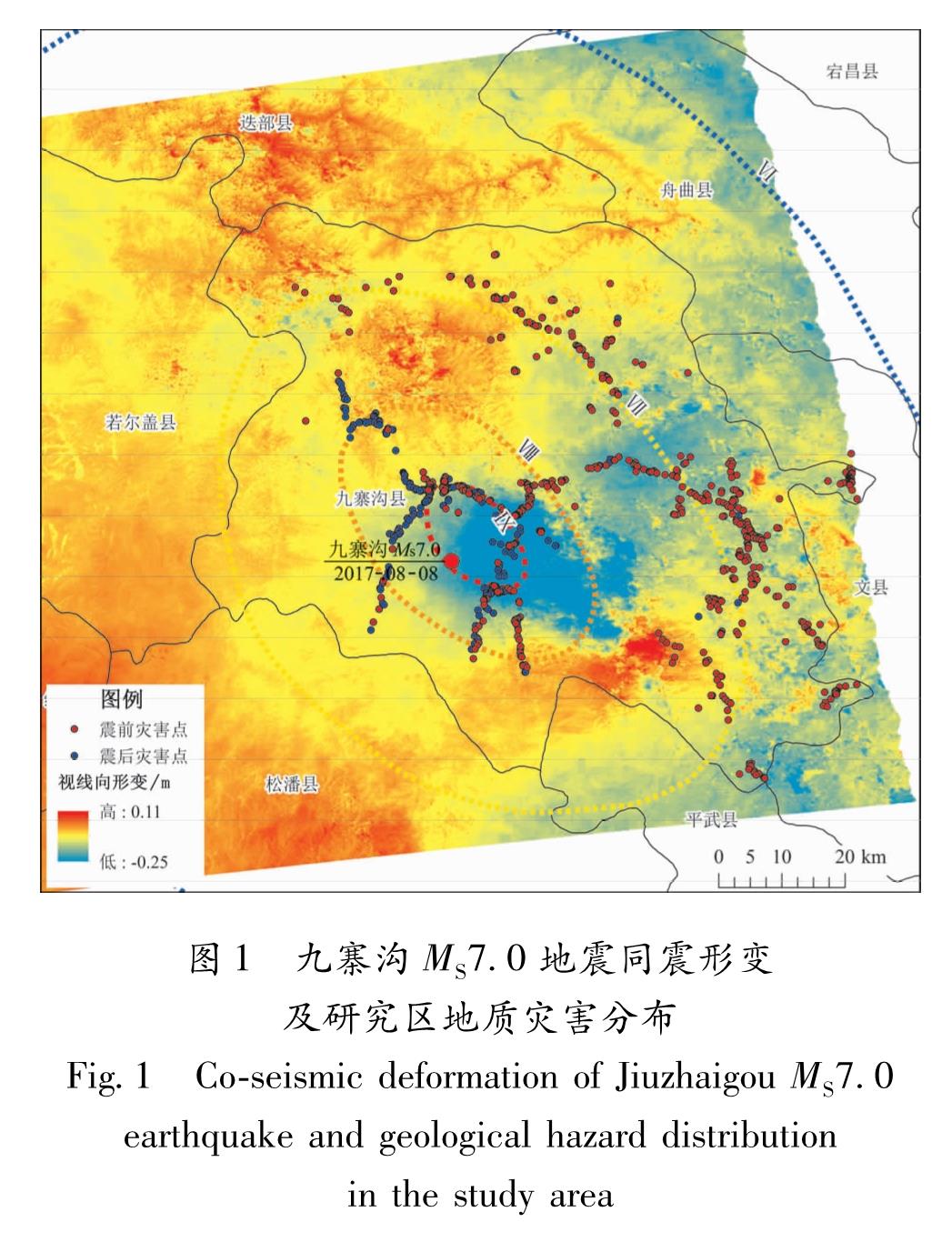
采用2017年8月6日和8月18日的Sentinel-1A SAR雷达数据,入射角43.8°,水平照射方位南东12.9°,垂直基线距+35.7 m,利用DInSAR技术进行干涉处理获取地震后研究区形变场(视线向形变)。同震地表形变的视线向绝对量值如图1所示,形变量值为-25~11 cm,这一结果是水平形变与垂直形变在视线向投影的结果,负值代表远离卫星形变,正值代表靠近卫星形变。通过对比其它研究人员成果(姚鑫等,2017; 孟庆筱,党学会,2018),升轨数据与降轨数据结果完全相反,再次证明九寨沟地震为走滑断层诱发的地震。形变分布主要在震中1 km范围内,呈“果核状”。
地震后,九寨沟县地质灾害调查结果显示,震后地质灾害主要以崩塌地质灾害为(图1),发育有主崩塌144处、不稳定斜坡59处、滑坡57处。对比震前地质灾害调查结果(崩塌163处、不稳定斜坡43处、滑坡78处),不稳定斜坡数量明显增多,如图2所示。将地震前后地质灾害叠加至同震形变图与九寨沟县行政区划图(图1),可发现震前地质灾害均匀分布于九寨沟县各个区域,主要分布于沟道中; 而震后地质灾害集中分布于同震大形变区域内(Ⅷ烈度区内),且同样主要分布于沟道中。在同震大形变区外分布有一定量地质灾害,其原因在于地震会诱发不稳定斜坡,且会演化为崩塌、滑坡、泥石流等地质灾害。对比现有成果,本研究调查得出的震后地质灾害少于其他研究成果,分析其原因为所选用数据为现场调查结果,而其他成果是遥感影像解译的成果,但现场调查结果对于震后地震灾害成果有一定代表性。
图1 九寨沟MS7.0地震同震形变及研究区地质灾害分布
Fig.1 Co-seismic deformation of Jiuzhaigou MS7.0 earthquake and geological hazard distribution in the study area图2 九寨沟MS7.0地震前后研究区地质灾害统计
Fig.2 Statistics of geological hazard before and after the Jiuzhaigou MS7.0 earthquake in the study area1.2 地质灾害诱发因子选取震前地质灾害影响因子主要为地形、地貌因子、岩土体性质因子、自然因素因子、人类活动因子。而地震诱发崩塌、滑坡等地质灾害的分布是地震参数及斜坡参数等多种影响因素综合作用的结果(许冲,2018)。
震前因子分析:受地形地貌的控制,地质灾害在垂直高程上的分布具有明显不均匀性,河流
图3 九寨沟县地质灾害诱发评价因子分级图
Fig.3 Classification map of evaluating factors induced by geological disasters of Jiuzhaigou county的下切往往会形成陡壁或悬崖,坡体原来平衡的应力状态遭到破坏,并引起应力释放,产生与河岸或与开挖平行的卸荷裂隙,并不断加深、扩大; 降雨量分布对于地质灾害的形成具有一定的控制作用; 作为斜坡的物质组成,岩土体的性质对斜坡的稳定性有很大的控制作用。
震后因子分析:汶川地震地质灾害分布规律表明绝大多数地质灾害发生于高程为650~2 500 m的地形陡变带; 斜坡坡度是控制斜坡稳定性的重要因素,不同坡度的斜坡对于地震波的响应表现为微地貌的控制作用; 从斜坡变形破坏机理来看,具有随高程增加的放大效应; 地震对震裂斜坡效应具有明显的距离效应,且震裂斜坡具有明显的断层错动方向效应和背坡面效应(黄润秋,李为乐,2008)。
对研究区地质灾害发育特征、时间和空间分布规律进行分析,重点考虑震前的斜坡效应与震后地震效应,综合考虑斜坡震裂效应和指标获取情况,最终确定12个指标因子,分别为高程、斜坡坡度、坡向、沟谷密度、年平均降雨量、与河流距离、工程岩组、与断层距离、地震动峰值加速度(PGA)、地震烈度、坡向与震源初动方向夹角和同震形变。这些指标因子主要由30 m精度DEM计算与反演而成,1:25万地质图生成,形变图主要是根据DInSAR形变结果制作(图3)。
通过各个因子对于地震前后地质灾害控制性作用,提取震前地质灾害影响因子:与河流距离、工程岩组、年平均降雨量、坡向、坡度、高程、沟谷密度; 震后地质灾害影响因子:地震烈度、与断层距离、PGA、坡向与震源初动方向夹角、同震形变、高程、坡度(图3)。
1.3 地震前后地质灾害分布特征叠加九寨沟地震前后地质灾害点与各个因子分级图,对各个因子各等级中地质灾害频率比进行统计。由图4可见,震前地质灾害主要分布于距离水系400 m范围,软硬互层与软质岩体,年降雨量为550~580 mm、坡向(NE,E,SE)、坡度0°~15°、高程1 131~2 200 m、沟谷密度(0.1~1.8)×10-4 km/km2这些因子等级范围内; 震后地质灾害主要分布于地震烈度Ⅸ、断层距1.5 km内、PGA大于0.16 g、坡向与震源初动方向夹角157.5°~202.5°、同震形变负值区域、高程1 131~2 700 m、坡度0°~15°这些因子等级范围内。对比地震前后2个共同因子可发现,震后地质灾害主要集中于高高程处,而低坡度为地震前后地质灾害高发区。
2 地质灾害风险评价
2.1 风险评价模型地质灾害的风险性是危险度和易损度共同作用的结果,是灾害自然属性和社会属性的结合。地质灾害风险评价模型可表示为:
R=H×V(1)
式中:R为地质灾害的风险度; H为地质灾害的危险度; V为地质灾害的易损度。
地质灾害危险度评价模型采用频率比累加模型:
H=∑ni=1(Fi)/(∑mj=1Fij)(2)
式中:Fij为第i个因子j等级的频率比。
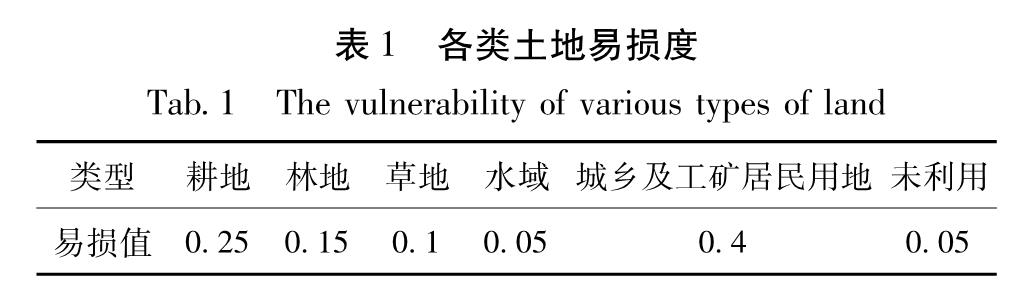
地质灾害易损度采用土地利用类型定性评价,赋值标准主要为土地价值,具体划分如表1所示。
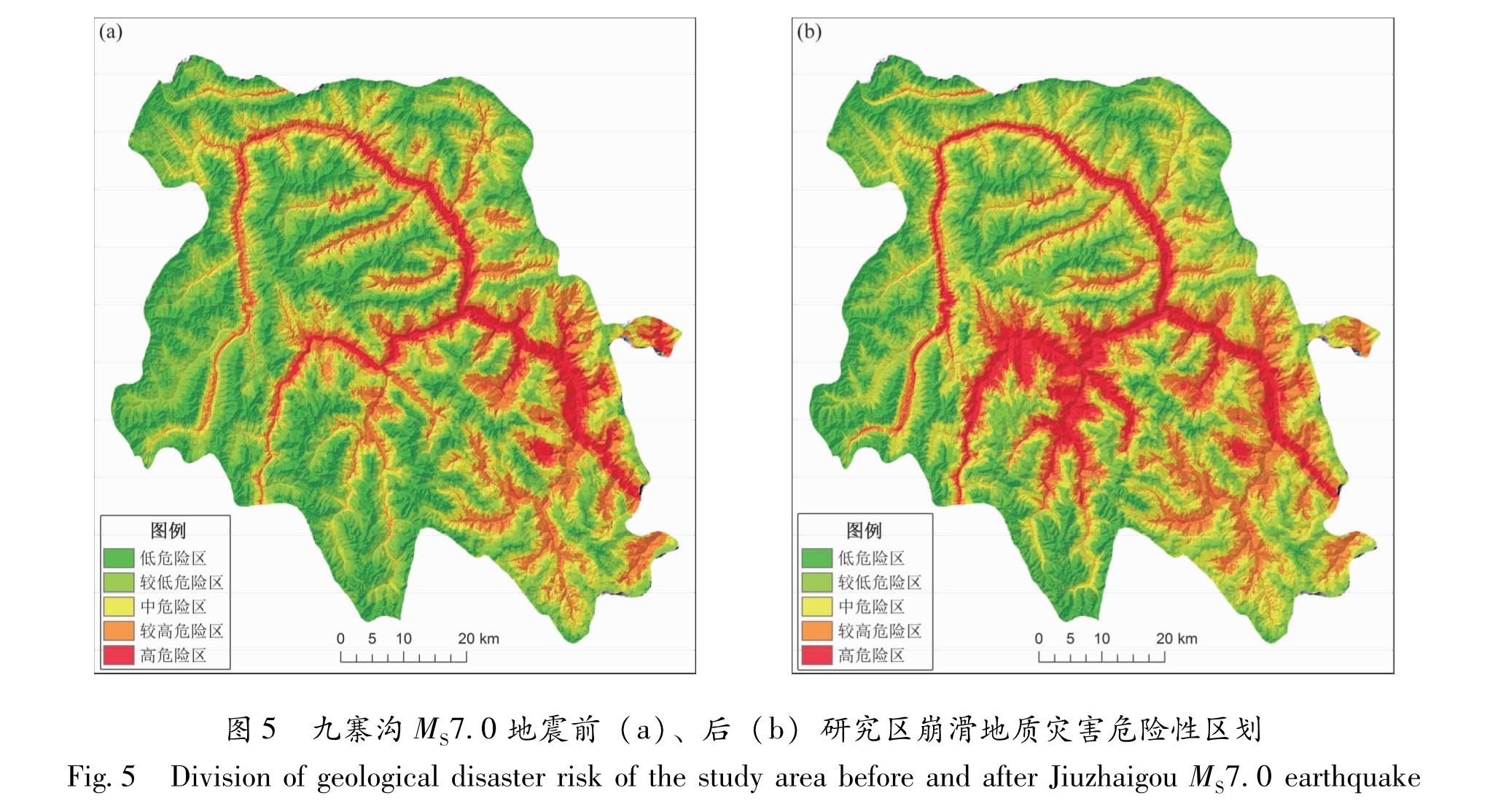
2.2 风险度计算结果根据以上崩滑地质灾害在各个因子各个等级中的频率比计算结果,运用危险度计算模型计算地震前后九寨沟县崩滑地质灾害危险性,危险性分级标准采用半定量分级,划分为:低危险区(0~0.2)、较低危险区(0.2~0.4)、中危险区(0.4~0.6)、较高危险区(0.6~0.8)、高危险区(0.8~1)。
对比地震前后地质灾害危险性评价结果(图5),发现具有一定的相似性:较高、高危险区大部分集中于沟道两侧,沟道中往往发育有河流,水对斜坡的冲刷、软化与动水压力作用导致岸坡岩土体强度大幅度降低,且动水压力作用使河谷两岸边坡变得更加陡峭、起伏度更大,在地势的作用下易产生地质灾害。但地震前后最大差异在于:震前危险区通常集中于沟道两侧,而震后高危险区不仅集中于沟道两侧,同时也分布于九寨沟地震高烈度区域内。
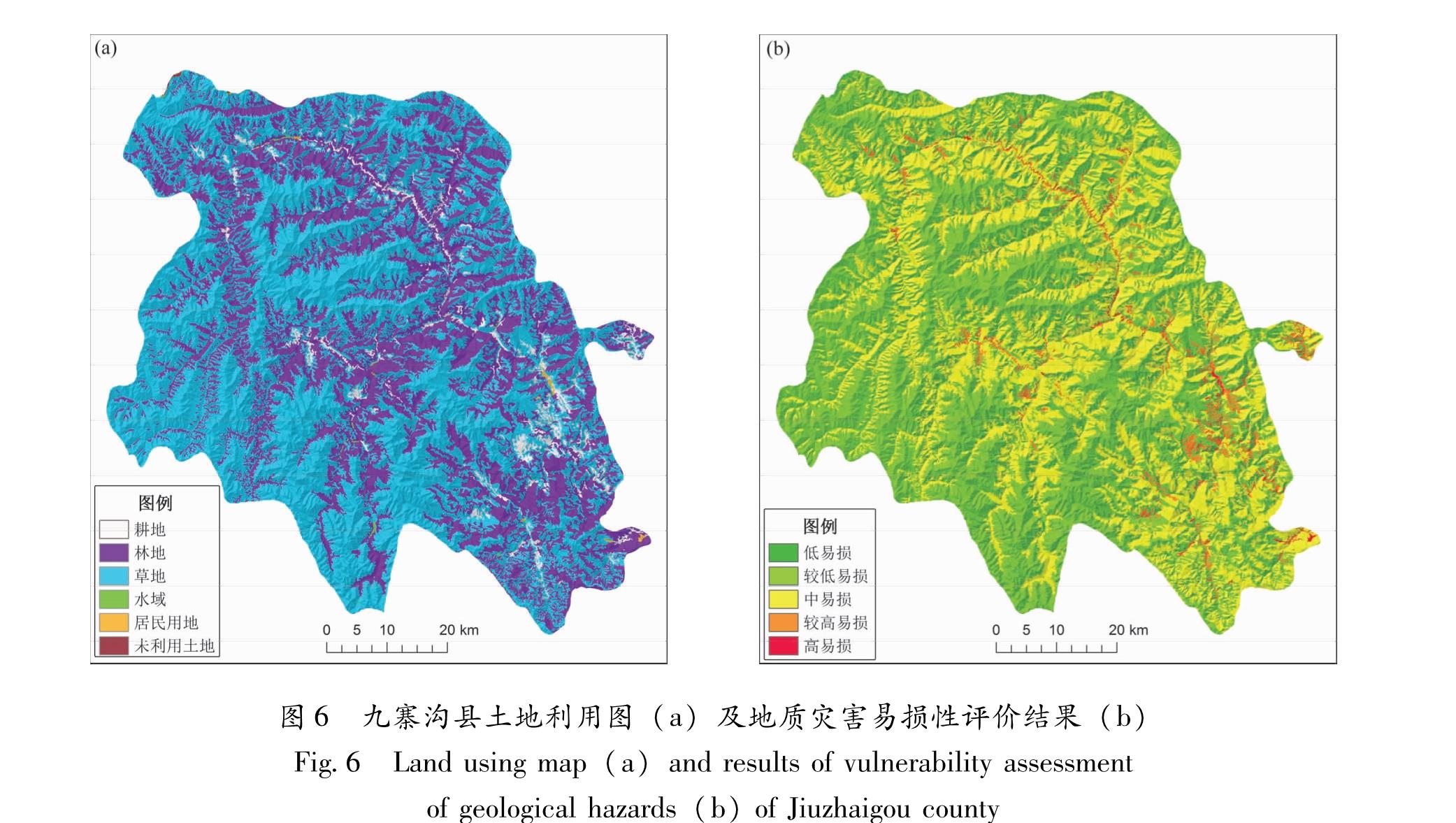
根据“地理国情监测云平台”在九寨沟地震后提供的土地利用规划图划分各类土地,由表1对其进行赋值,运用ArcGIS中自然断裂法进行易损性分级,低易损区主要为未利用土地与水域,较低易损区主要为草地,中易损区主要为林地,较高易损区为耕地,高易损区主要为城乡、工矿居民用地(图6)。
图4 九寨沟MS7.0地震前后地质灾害点与各个因子关系图
Fig.4 Relationship between geological disasters and each factors before and after Jiuzhaigou MS7.0 earthquake图5 九寨沟MS7.0地震前(a)、后(b)研究区崩滑地质灾害危险性区划
Fig.5 Division of geological disaster risk of the study area before and after Jiuzhaigou MS7.0 earthquake图6 九寨沟县土地利用图(a)及地质灾害易损性评价结果(b)
Fig.6 Land using map(a)and results of vulnerability assessment of geological hazards(b)of Jiuzhaigou county总结国内外风险分级方法,地质灾害风险划分方法可分为3种:①定性分析评价。刘希林等(2001)在风险研究中,以危险性与易损性等级划分为基础,进而划分风险的等级,通过理论与实践进行相互验证,具有一定的合理性,并在风险评价中广为应用; ②半定量分析评价。与定性风险分级很相似,半定量风险评价中定性描述的文字换成了数值,目的是扩大量度的等级。由于每一个数值与实际的后果和可能性程度并不存在精确的关系,这里的数值不是像在定量分析中提供的真实的风险值,仅仅是用来识别量度范围; ③定量分析评价。定量风险评价是在资料十分完备时采用,分析损害的具体数量和发生的可能性,分析结果给出每种风险发生的概率值和发生后的严重程度。
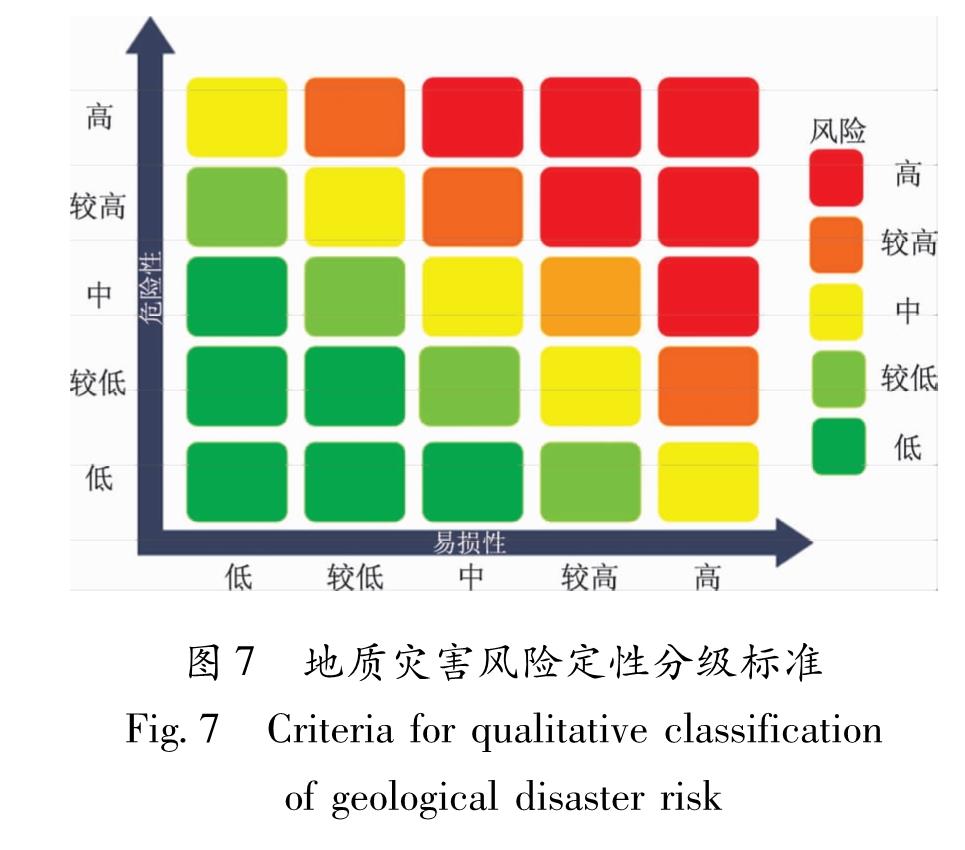
区域尺度(中、大比例尺)的地质灾害风险评价,主要采用的是定性与半定量分析方法,在地质灾害易发性评价的基础上,考虑诱发地质灾害因素的时间概率,开展地质灾害的可能性或概率的分析评价。因此本文采用定性分级方法(图7)。
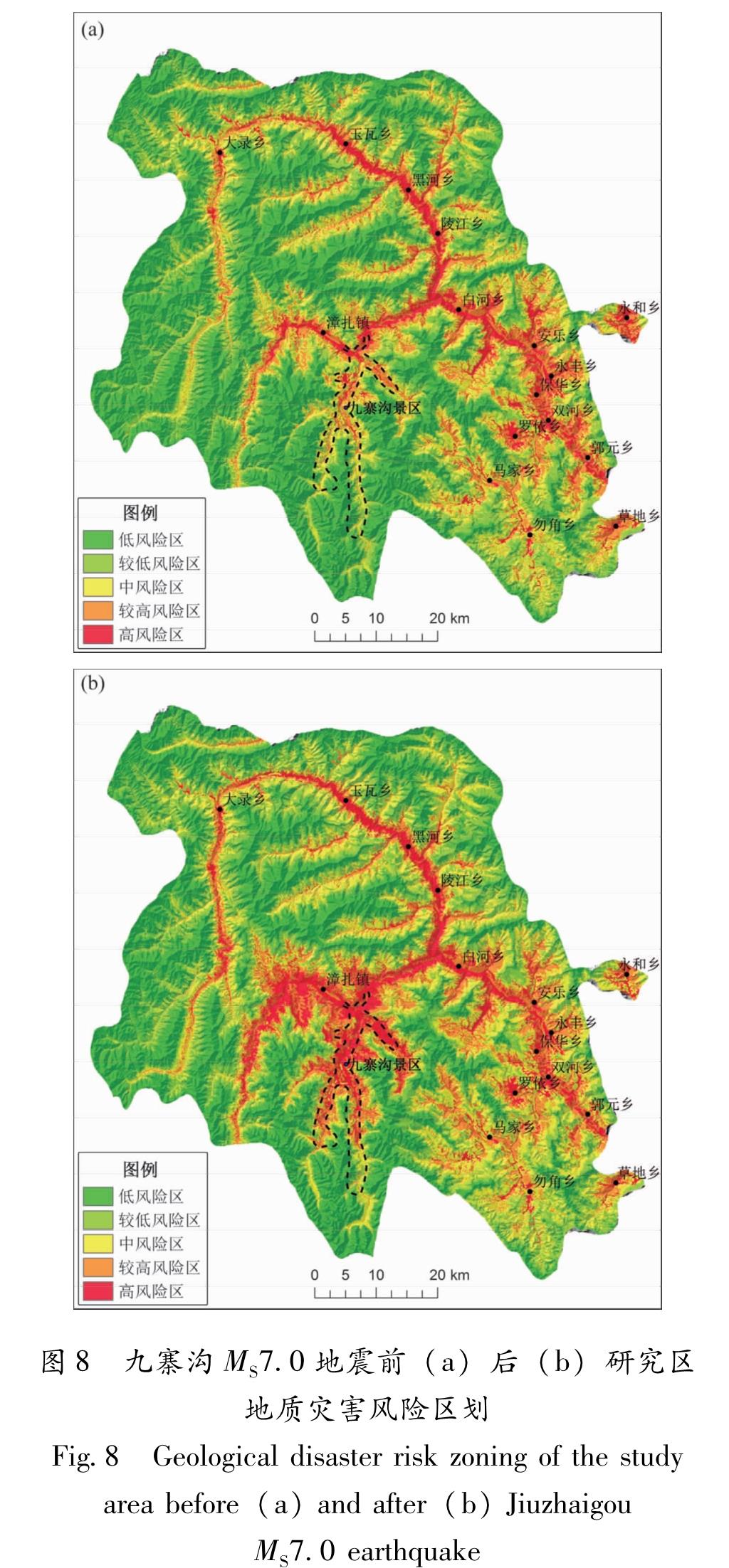
根据定性分级标准,叠加危险性分级与易损性分级结果,最终实现九寨沟县地震前后地质灾害风险区划。
3 地质灾害风险对比分析
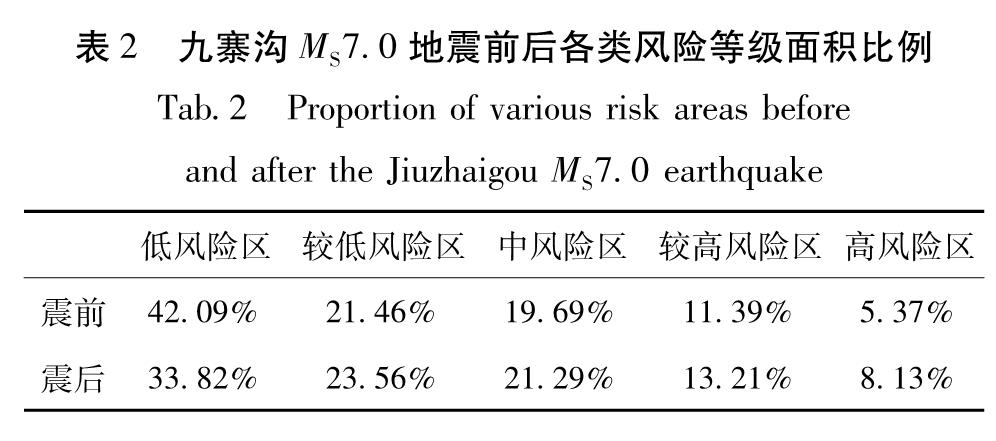
从图8可见,地震前后地质灾害风险区具有一定相似性,其特点与危险性区划图相同,高风险区主要集中于沟道中,其原因在于沟道中往往为人员密集区域,同时地质灾害易发性较高。震前与震后地质灾害风险区划最大差异在于震前九寨沟景区与漳扎镇仅有小部分区域分布有高风险区,而震后这2个区域均在地质灾害高风险区内。对地震前后风险区划图各个等级面积进行统计,从表2中可明显观察出震后低风险区由震前42.09%减小至 33.82%,高风险区由震前5.37%增加至8.13%。通过计算低风险区降低比率与高低风险区增加比率,九寨沟地震对于九寨沟县地质灾害风险提高约21.94%。
表2 九寨沟MS7.0地震前后各类风险等级面积比例
Tab.2 Proportion of various risk areas before and after the Jiuzhaigou MS7.0 earthquake图8 九寨沟MS7.0地震前(a)后(b)研究区地质灾害风险区划
Fig.8 Geological disaster risk zoning of the study area before(a)and after(b)JiuzhaigouMS7.0 earthquake
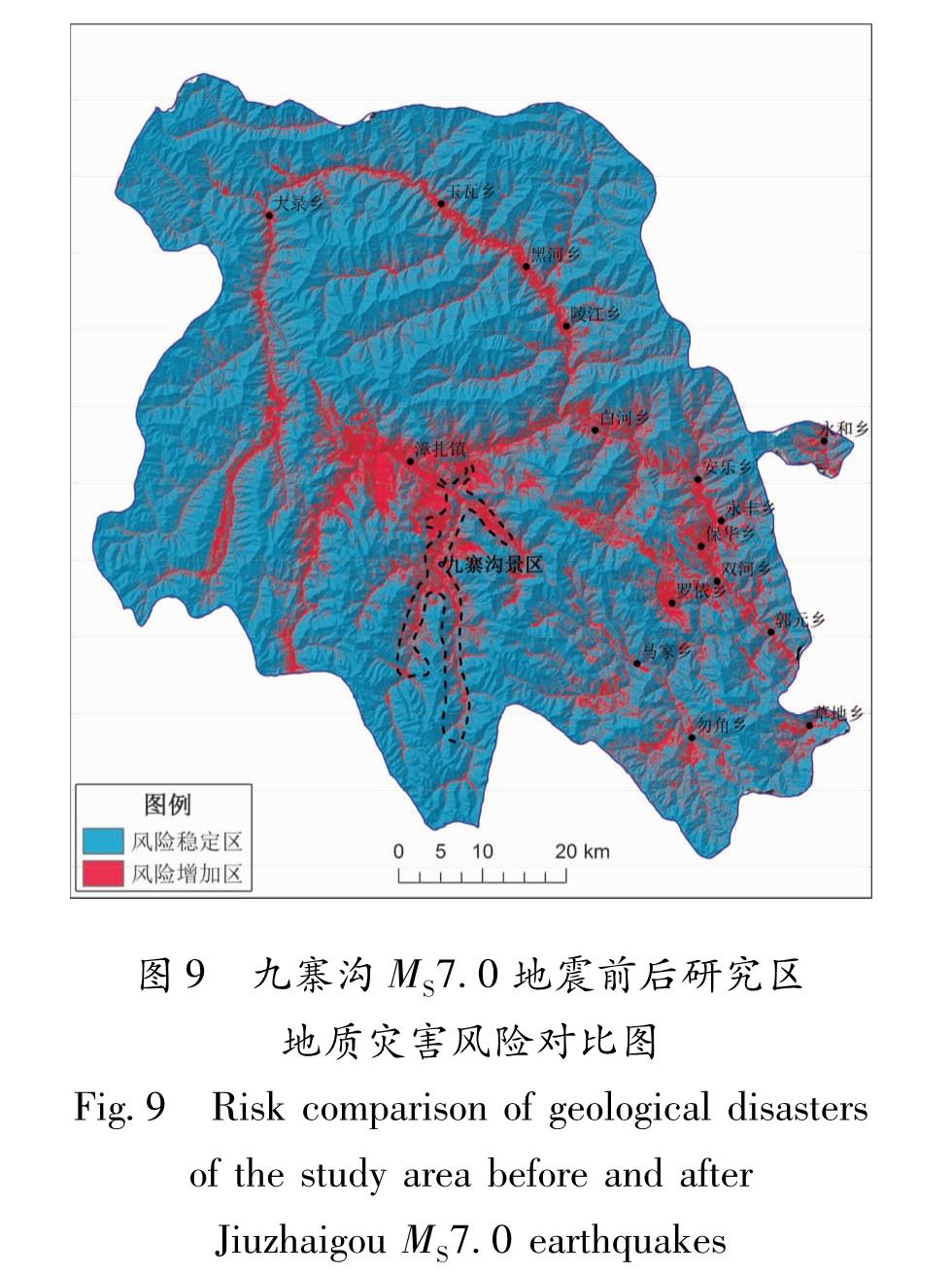
将地震前后风险区划图中低风险区至高风险区分别赋值1~5,即地震前后风险度图(图9)。 将震后与震前风险度图进行相减,将大于0的区域视为风险增加区,等于0的区域视为风险稳定区(图中存在少量为负值区域,这是由于评价采用栅格,地震前后采用因子存在差异,网格划分亦存在差异,这将会导致一定的误差,因此本文将负值区域视为风险稳定区)。图9显示震后九寨沟县地质灾害增加的风险区主要为漳扎镇和九寨沟景区,根据分类栅格统计,九寨沟县震后风险增加区约占整个区域面积的19.84%,这一结果与风险分级统计结果(九寨沟地震对于九寨沟县地质灾害风险提高约21.94%)具有一定相似性,说明风险评价分级具有一定有效性。
图9 九寨沟MS7.0地震前后研究区地质灾害风险对比图
Fig.9 Risk comparison of geological disasters of the study area before and after Jiuzhaigou MS7.0 earthquakes4 结论
对九寨沟地震前后崩滑地质灾害点进行统计分析,选取12个崩滑地质灾害影响因子,将其分为震前和震后地质灾害影响因子,进行地震前后地质灾害风险分析,得出以下几点结论:
(1)震前地质灾害均匀分布于九寨沟县各个区域,主要分布于沟道中; 而震后地质灾害主要集中于同震大形变区域内(Ⅷ烈度区内),且同样主要分布于沟道中。
(2)对比地震前后地质灾害风险区划图,震后地质灾害风险提高至震前风险的120%左右,提高风险区域分布在九寨沟地震高烈度区(漳扎镇和九寨沟景区)。
(3)地震发生后地震诱发的地质灾害主要分布于Ⅷ烈度区内,即该区域为地质灾害高易发区。
- 陈晓利,单新建,张凌,等.2018.地震诱发滑坡的快速评估方法研究:以2017年MS7.0级九寨沟地震为例[J].地学前缘,25(2):21-29.
- 戴岚欣,许强,范宣梅,等.2017.2017年8月8日四川九寨沟地震诱发地质灾害空间分布规律及易发性评价初步研究[J].工程地质学报,25(4):1151-1164.
- 邓飞,窦爱霞,吴玮莹,等.2018.基于无人机遥感的四川九寨沟地震极灾区灾情快速调查[J].灾害学,33(3):210-215.
- 黄润秋,李为乐.2008.“5.12”汶川大地震触发地质灾害的发育分布规律研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报,27(12):2585-2592.
- 李渝生,黄超,易树健,等.2017.九寨沟7.0级地震的地震断裂及震源破裂的构造动力学机理研究[J].工程地质学报,25(4):1141-1150.
- 刘华国,李峰,张效亮,等.2018.青藏高原东缘虎牙断裂晚第四纪活动特征[J].地震研究,41(4):594-604.
- 刘甲美,王涛,石菊松,等.2017.四川九寨沟MS7.0级地震滑坡应急快速评估[J].地质力学学报,23(5):639-645.
- 刘希林.2001.泥石流风险及其评价研究[D].北京:北京大学.
- 孟庆筱,党学会.2018.GPS约束下九寨沟地区断裂带现今运动速率的非连续接触模拟研究[J].地震研究,41(3):390-397.
- 王志一,徐素宁,王娜,等.2018.高分辨率光学和SAR遥感影像在地震地质灾害调查中的应用——以九寨沟7.0级地震为例[J].中国地质灾害与防治学报,29(5):81-88.
- 许冲,王世元,徐锡伟,等.2018.2017年8月8日四川省九寨沟MS7.0地震触发滑坡全景[J].地震地质,40(1):232-259.
- 许冲.2018.环境地球科学之滑坡地震地质学[J].工程地质学报,26(1):207-222.
- 姚鑫,周振凯,李凌婧,等.2017.2017年四川九寨沟MS7.0地震InSAR同震形变场及发震构造探讨[J].地质力学学报,23(4):507-514.
- 张孝奎,袁牧,冯立超,等.2018.九寨沟景区在九寨沟7.0级地震中的防灾问题分析[J].灾害学,33(3):80-86.
- Fan X M,Scaringi G,Xu Q,et al.2018.Coseismic landslides triggered by the 8th August 2017 MS7.0 Jiuzhaigou earthquake(Sichuan,China):factors controlling their spatial distribution and implications for the seismogenic blind fault identification[J].Landslides.1515:967-983.doi:10.1007/s10346-018-0960-x.
- Nie Z,Wang D J,Jia Z,et al.2018.Fault model of the 2017 Jiuzhaigou MW6.5 earthquake estimated from coseismic deformation observed using Global Positioning System and Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar data[J].Earth,Planets and Space,70(1):55-67.
- Wang J,Jin W,Cui Y F,et al.2018.Earthquake-triggered landslides affecting a UNESCO Natural Site:the 2017 Jiuzhaigou Earthquake in the World National Park,China[J].Journal of Mountain Science,15(7):1412-1428.
- Wu C H,CUI P,Li Y S,et al.2018.Seismogenic fault and topography control on the spatial patterns of landslides triggered by the 2017 Jiuzhaigou earthquake[J].Journal of Mountain Science,15(4):793-807.
- Zhao B,Wang Y S,Luo Y H,et al.2018.Landslides and dam damage resulting from the Jiuzhaigou earthquake(8 August 2017),Sichuan,China[J].Royal Society Open Science,5(3):1-17.