(China University of Geoscience,Beijing,Beijing 100083,China)
hot springs; hydrochemical characteristics; multivariable statistics; geothermal reservoir temperatures; Xianshuihe fault zone
备注
以鲜水河断裂带南段(康定—摩西断裂带)出露的26个温泉的水化学组分为研究对象,通过多元统计分析和地热温标方法,探讨了研究区断裂带不同部位温泉的水化学特征及热储温度的差异。结果 表明:①研究区不同区域的温泉可被分为4组,除B组为HCO3-Na-K型水外,A,C,D组均为HCO3-Na型水; ②对热储温度的计算结果表明,研究区中部的热储温度高于南北两侧,地热活动性的强弱与地震活动性之间在空间上存在一定的关联性。
Based on the multivariate statistical analysis of the hydrochemical characteristics of the 26 hot springs exposed in the Kangding-Moxi segment of the Xianshuihe fault zone and the calculation of the thermal reservoir temperatures,this paper discusses the hydrogeochemical characteristics of hot springs in the study area and their relationship with fault zones.The results show that the hot springs in different areas could be grouped into four groups.The B group is classified into HCO3-Cl-Na type and the A,C,D groups is classified into HCO3-Na type.The result of geothermal reservoir temperature shows that the geothermal reservoir temperature in the middle of the study area is higher than that in the north and south,which is consist with the seismic activities in this area.
引言
作为地壳流体运移的重要通道,地壳浅部的断裂带控制了区域地下水热活动、成矿成藏、地震活动等一系列地质过程(Bense et al,2013),其中,对水热活动的控制尤为明显(Curewitz,Karson,1997)。大多数温泉往往沿着断裂带出露,且水热活动的强弱与断裂带的地震活动存在一定的联系(Martinelli,Dadomo,2017; Shi,Wang,2017; 王云等,2018)。对于区域性深大断裂,断裂带不同部位的水热流体由于受控于断裂带不同的水文地质条件及构造活动,往往具有不同的水循环特征,从而导致其出露的温泉表现出不同的水化学及热储特征(林元武,1993)。因此,通过对断裂带不同部位出露温泉的水化学及热储特征分析,可以获得断裂带不同区段的活动特征(Shi,Wang,2017)。[JP2]已有的研究大多以断裂带温泉的水化学特征及演化,或温泉的热储特征为主要研究对象(张彧齐等,2018; Guo et al,2017; Shi et al,2017; Mao et al,2015; 龙汨等,2014; 崔冬雪等,2019; 李其林等,2019),较少关注断裂带不同部位出露温泉的差异性以及可能的构造活动意义。
鲜水河断裂带地处青藏高原东缘,是我国重要的地震活动带,水热活动发育。赵庆生(1984)研究了鲜水河断裂带的水化学特征,提出该断裂带的热水从康定一带向北移动,构成统一的水热系统; 李晓等(2018)研究康定—道孚热水段4个水热区的温泉水化学特征,发现4个水热区中水化学及氢氧同位素特征具有明显分带性; Luo等(2017)研究了康定地热区的水热活动特征,发现康定南部的榆林宫地区热储温度高于康定北部的中谷地区; Zhou等(2015)基于鲜水河断裂带上的温泉逸出气的稀有气体同位素特征,发现鲜水河断裂带不同部位深源物质含量明显不同,显示出明显分带性。上述研究均表明鲜水河断裂带不同部位的水热特征具有一定分带性,但分带性与断裂带构造活动之间的关系向缺乏深入研究。
本文选取鲜水河断裂带南段(康定—摩西断裂带)出露的温泉为研究对象,基于温泉水化学组分,分析了研究区温泉的水化学特征,对该区的温泉选用多种地热温标进行了热储计算,对温泉水化学特征及热储温度进行了分类,探讨了该区地热水的循环特征及其与断裂带活动性之间的关系。
1 区域地质背景
鲜水河断裂为左旋走滑断裂带,长度超过1 000 km,为一深切断裂,主要出露三叠系浅变质砂质板岩。该断裂带至少发生过10次7级以上的地震(龙德雄等,2006; 曹云等,2006)。本文研究区位于青藏高原东南缘的川西地区,温泉主要沿着鲜水河断裂带的南段——康定—摩西断裂出露。研究区从北边的甘孜一直往南延伸到石棉地区,断裂带总体走向为NW-SE,并在康定附近发生转折,在康定以南逐渐过渡到SN走向。这些断裂带沿近似NNE向展布,并在局部形成分散的次级断裂(图1)。区内地层总体呈NNE向条带状分布,主要出露三叠系地层,其它为少量二叠系地层等,侏罗系与白垩系地层缺失。三叠系地层岩性主要为砂岩、粉砂岩、板岩、千枚岩等(王凯,2011); 在康定北东、炉霍、道孚一带零星出露二叠系砂质板岩和灰岩; 在乾宁、康定、磨西、折多塘等地方,沿断裂带出露晚新生代花岗岩及燕山后期闪长岩岩体(周荣军等,2001)。
2 水文地球化学特征分析
3 热储温度的计算
在地下热水研究和开发利用中,热储温度是划分地热系统成因类型和评价地热资源潜力不可缺少的重要参数,但在通常情况下难以被直接测量(王莹等,2007),地热温标方法是提供这一参数的有效手段。然而,不同的地热温标具有各自的适用条件(Hou et al,2018)。SiO2温标、阳离子温标(Na-K,Na-K-Ca,K-Mg)是目前常用的地热温标。SiO2温标如玉髓和石英,常常广泛地应用于低焓地热系统; Na-K温标主要应用于大于150℃的高温地热系统,在低温系统中采用该温标则可能出现较大误差; Na-K-Ca温标适用于Ca2+较高的热储(史杰等,2018)。笔者根据本次所收集的资料对上述几种温标进行了计算,计算结果见表5。
表5 SiO2温标及阳离子温标计算的热储温度值
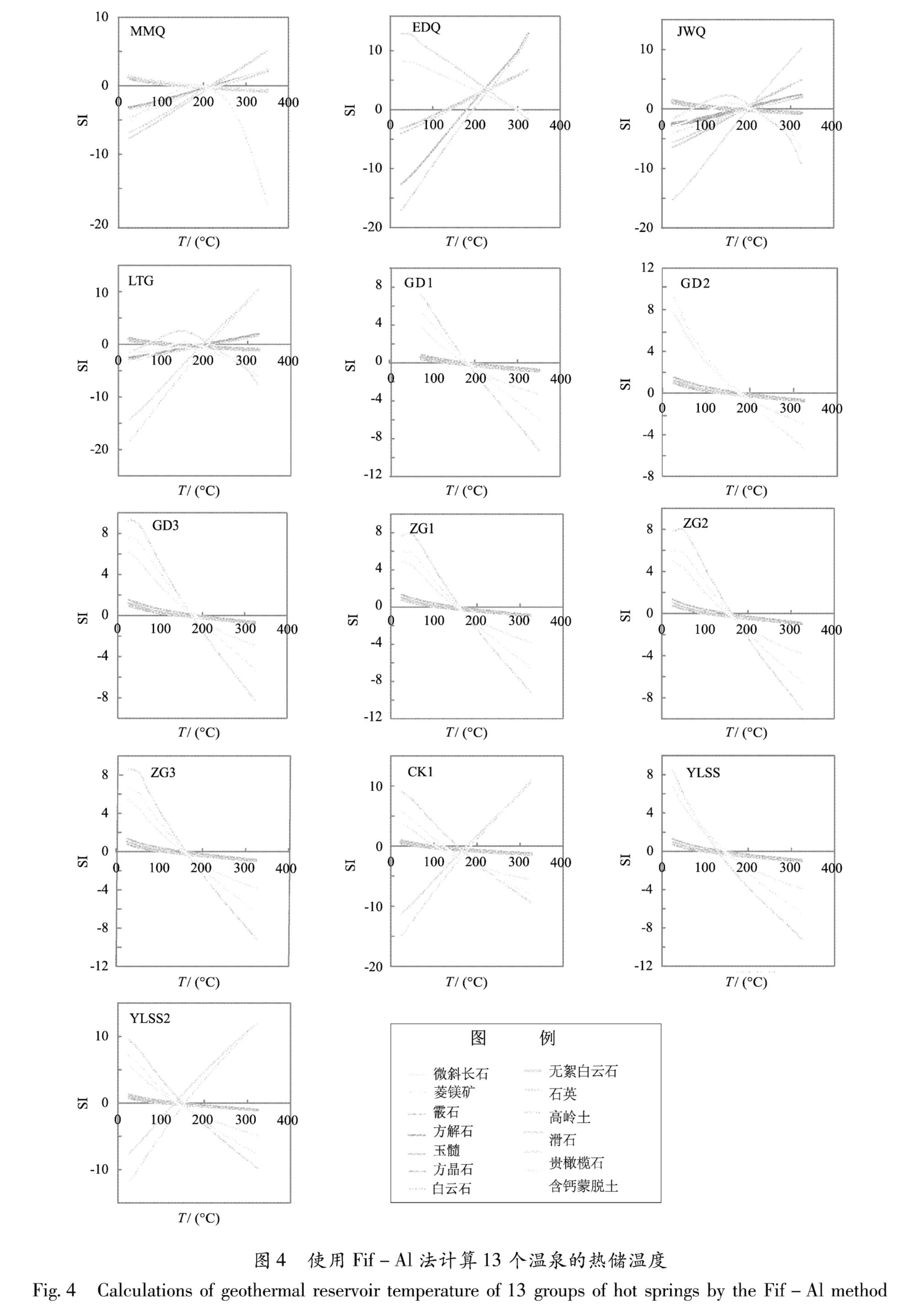
Tab.5 Geothermal reservoir temperatures calculated by cationic and SiO2 temperature scales地热温标法主要是根据经验公式估算热储温度,计算结果有时会有较大误差。基于地热系统的多组分化学平衡模拟法则能给出系统平衡态的有效信息,为热储温度的计算提供有效预测。本文采用Fix-Al方法,通过SOLVEQ-XPT程序来获得热储温度(Pang,Reed,1998)。具体计算时,使用校正脱气尽可能还原地下热水的性质,从而得到比较准确的热储温度值。依据各个温泉点周围地层岩性的特征,本文主要选取了霰石、方解石、玉髓、石英、白云石、菱镁矿、滑石、高岭石、蛇纹石、微斜长石和钙蒙脱石共11种矿物计算了康定地区的13个温泉的热储特征,结果如图4所示。这些温泉的热储温度是160℃~250℃:康定中部MMQ,EDQ,JWQ,LTG,GD1,
图4 使用Fif-Al法计算13个温泉的热储温度
Fig.4 Calculations of geothermal reservoir temperature of 13 groups of hot springs by the Fif-Al methodGD2和GD3温泉点的热储温度在210℃~230℃; 北部ZG1,ZG2,ZG3,YLSS和YLSS2温泉点的热储温度在160℃~180℃; 南部CK1温泉点的热储温度在180℃左右。
对比地热温标法和矿物平衡法计算所得的热储温度可以发现,同一水样采用不同温标方法所得的计算结果差别很大,这说明不同地热温标的适用条件各不相同,前人提出的各种温标方法的温度范围只具有一般性意义。阳离子温标给出的是考虑单个参数的影响因素,得到确定的唯一值,低于矿物平衡法得到的值,有时甚至会产生较大误差。综合来看,在选取适当的矿物组分的情况下,用矿物平衡法得到的地热温标更适合计算研究区各温泉的热储温度。结合各种热储计算方法的结果得出:研究区北部的热储温度为150℃~165℃,中北部的热储温度为180℃~250℃,中南部的热储温度为170℃~200℃,南部的热储温度为150℃左右。
4 讨论
本文通过对收集的26个温泉样品资料的分析发现,断裂带不同部位出露的温泉具有不同的水化学特征。研究区的北部向南,水化学类型虽然以HCO3-Na型水为主,但不同部位的温泉其组分仍然有一定的变化,而TDS的含量从北往南则呈现出逐渐减小的趋势。
从温泉水化学及热储温度的计算结果可以看出,沿着断裂带不同部位的温泉具有不同的性质。根据该地区的地温梯度(赵庆生,1984),可以估算出这些温泉的循环深度大致在3~5 km。从震源深度来看,鲜水河断裂带中南段(石棉—道孚)大震的震源深度一般较深(>12 km),而多数小震的震源深度集中在5 km以内(易桂喜等,2006)。因此,小震活动与水热循环深度可能存在一定的联系。根据前人关于鲜水河断裂带中—南段地震活动水平的分析可知,康定北部的道孚八美等地(A组)相对应力水平偏高,康定—磨西地区(B,C组)相对应力水平偏低,南部地区(D组)应力水平中等(易桂喜等,2005)。总的来说,从断裂现今活动习性来讲,康定—磨西段处于小震滑动段,而其他部位处于闭锁状态,因此也反映了康定—磨西段断裂带的渗透性可能较其他部位要高,使得该部位深部热能更易上涌,从而导致该段热储温度总体偏高,地热活动性偏强。因此,地热活动性的强弱与地震活动性之间存在一定的关联性,地震活动频次较高的地段往往具有较高的地热活动性,这与前人的发现是一致的(Martinelli,Dadomo,2017; Shi,Wang,2017)。因此,沿着断裂带不同部位出露的温泉为研究断裂带的渗透性及活动性提供了一定的指示意义,也有助于认识地壳深部的信息。
5 结论
本文对鲜水河断裂带南段(康定—摩西断裂带)出露的26个温泉进行了水化学组分分析,利用多元统计方法和地热温标计算,对温泉水化学特征及热储温度进行了分类分析,得到以下结论:
(1)研究区温泉可被分为4组,其中A组温泉样品采集于康定断裂带北部道孚附近,均为HCO3-Na型水; B组温泉样品采集于康定断裂带中北部,主要为HCO3-Na-K型水; C组温泉样品采集于康定断裂带中南部,为 HCO3-Na型水; D组温泉样品采集于康定断裂带南部磨西附近,均为HCO3-Na型水。总体上,研究区温泉以HCO3-Na型水为主,且TDS的含量从北往南呈现出逐渐减小的趋势。
(2)研究区北部的热储温度为150℃~165℃,中北部的热储温度为180℃~250℃,中南部的热储温度为170℃~200℃,南部的热储温度为150℃左右。总体来看,研究区中部的热储温度高于南北两侧。地热活动性的强弱与地震活动性之间在空间上存在一定的关联性。
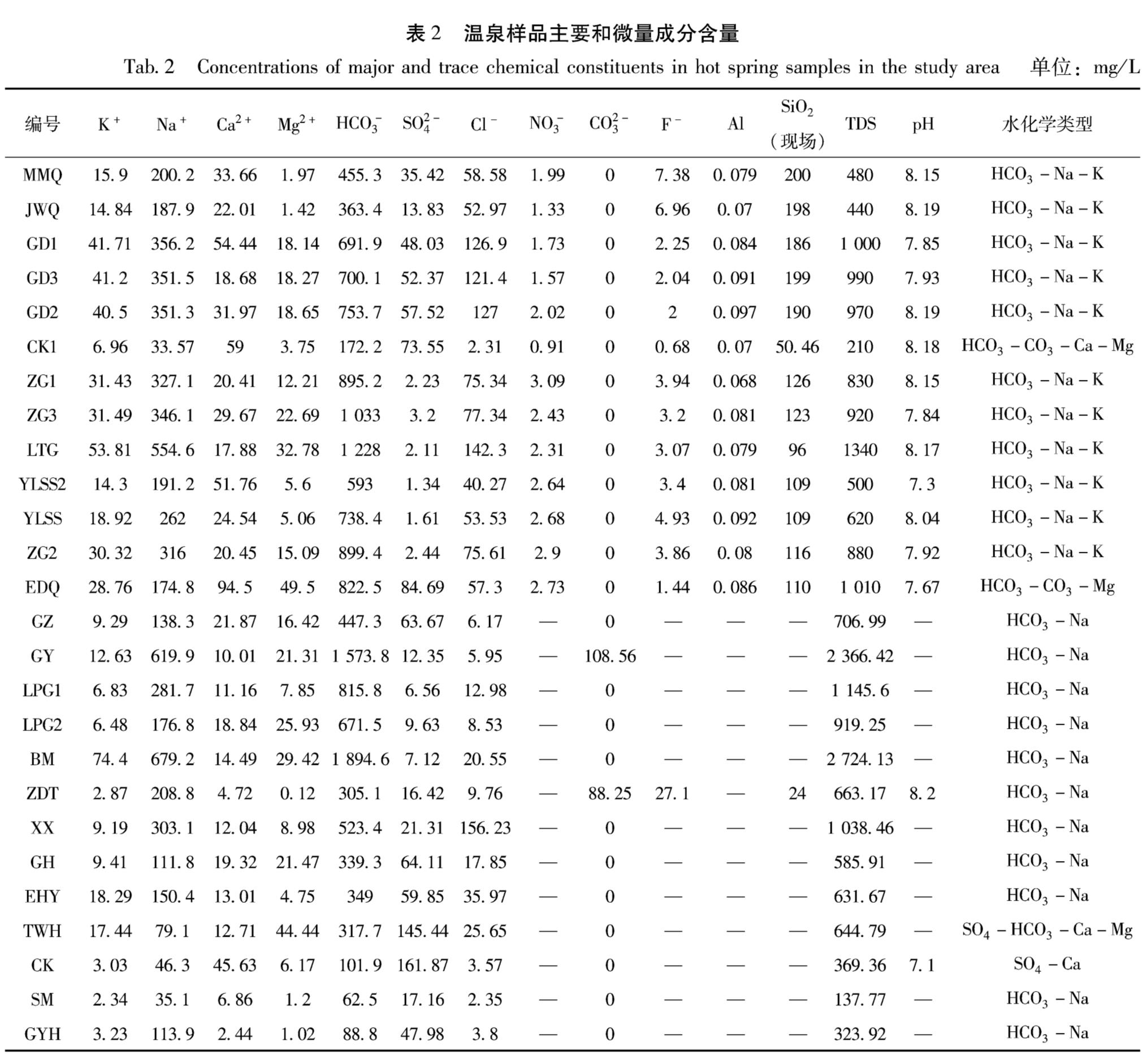
2.1 水化学分析及测试笔者在2016年7—8月采集了研究区26个温泉的水样品进行水化学分析和氢氧稳定同位素分析(图1,表1)。用于稳定同位素分析的样品收集并储存在50 mL的聚乙烯瓶中,用于水化学分析的样品储存在2个250 mL的聚乙烯瓶中。所有的水化学样品均在现场通过0.45 μm膜过滤。对于阳离子分析,现场加入HNO-3直至收集的样品中pH值低于2。同时,在野外现场测定的参数有水温、TDS(总溶解固体含量)和pH值等,水温用精度为0.1℃的数字温度计测量,pH和TDS均由Clean M30笔式测试仪确定。
温泉水样品带回实验室进行水化学组分及同位素组成分析测定。通过离子色谱法(Dionex-900)对主要离子进行分析,测试的离子组分为K+,Na+,Ca2+,Mg2+,Cl-,SO2-4等,其含量见表2,阴阳离子的测量相对标准偏差均小于5%。CO2-3和HCO3-浓度采用电位滴定仪测定,SO2-4和Cl-浓度采用离子色谱法测定,Ca2+,Mg2+,Na+和K+浓度通过ICP-AES进行分析,其他金属元素在采样2周内通过ICP-MS分析。18O和D的稳定同位素用液-水同位素分析仪LGR进行分析,δ18O的精度为0.2‰,δD的精度为0.3‰。
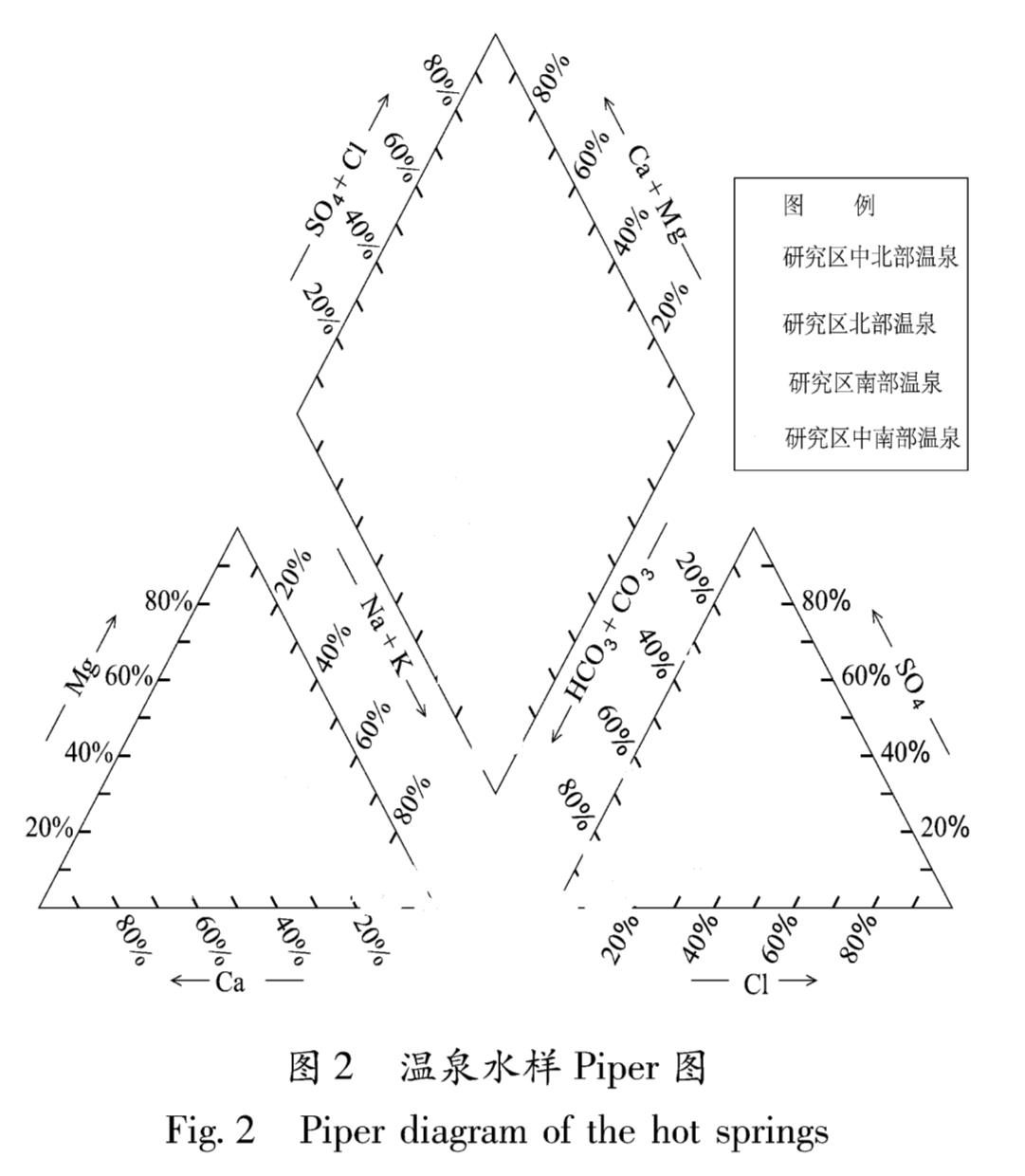
采用Piper三线图对水样品进行水化学分析(图2),结果显示:部分水样属于HCO3-Na和HCO3-Na-K型水,少数水样落在菱形区上方,CK的水化学类型为SO4-Ca型水,EDQ属于HCO3,CO3-Mg型水。
2.2 多元统计分析为了解不同温泉水化学组分之间的内在联系及其演化过程,运用多元统计方法对其进行聚类分析和因子分析。
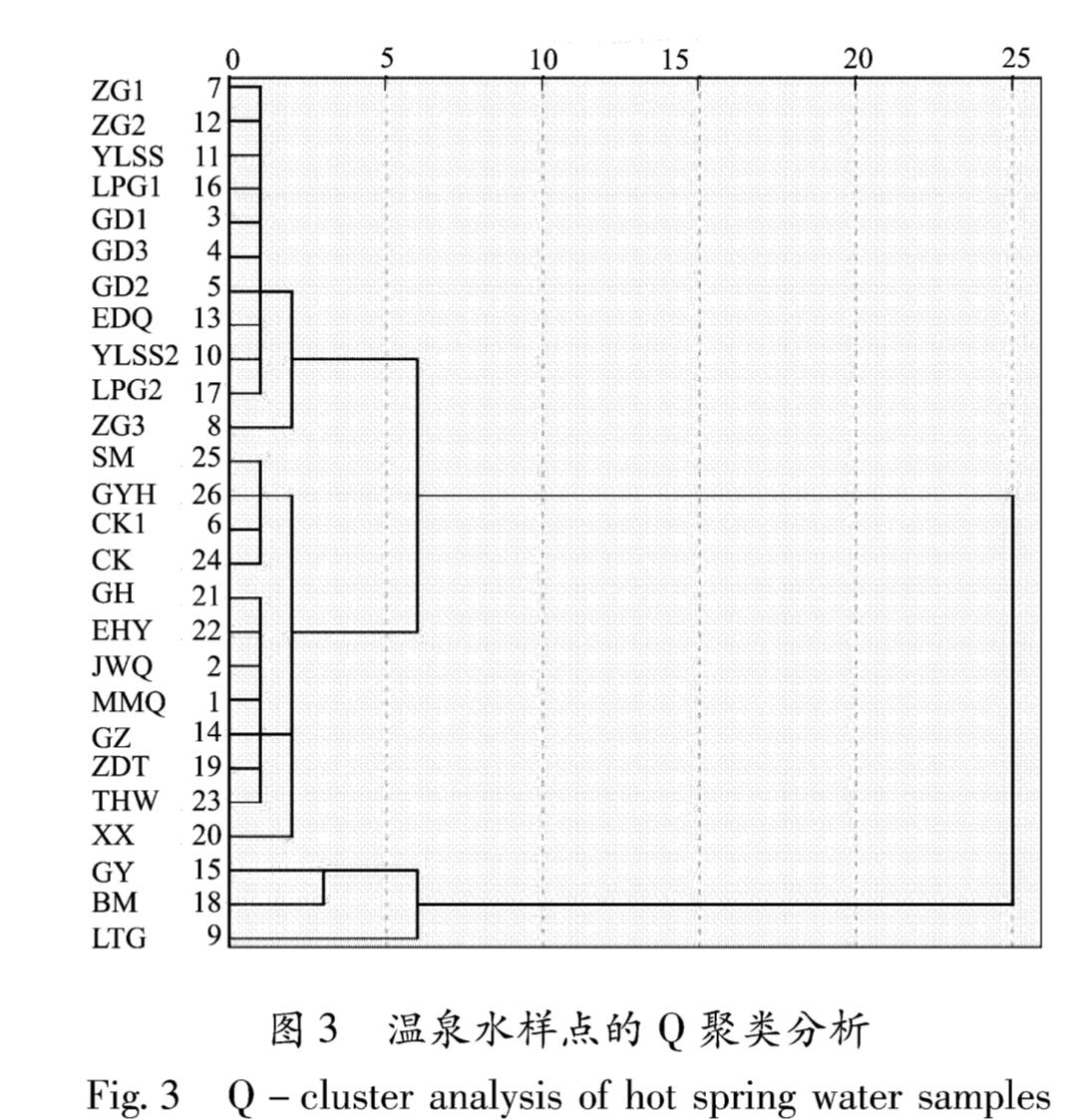
2.2.1 聚类分析聚类分析是对水样进行分类的一种多元统计分析方法,根据各自特性进行合理分类,本文采用层次聚类分析中的Q聚类。Q聚类是对水样样本(个案)进行分类,并根据样本间的相似性及相关性进行分组分类。
Q聚类分析结果如图3所示,研究区温泉可分为4组。A组:GY,BM和LTG等3个温泉,均为
HCO3-Na型水,TDS为1.34~2.72 g/L; B组:ZG1,ZG2,ZG3,YLSS,YLSS2,LPG1,LPG2,GD1,GD3,GD2和EDQ 11个温泉,主要为HCO3-Na-K型水,TDS为0.5~1.15 g/L; C组:MMQ,JWQ,GH,EHY,GZ,ZDT,TWH和XX 8个温泉,为HCO3-Na型水,TDS为0.44~1.04 g/L; D组:SM,GYH,CK1和CK主要4个温泉,为HCO3-Na型水,TDS为0.14~0.37 g/L。由图1可见:A组温泉样品位于康定断裂带北部道孚附近; B组温泉样品位于康定断裂带中北部; C组温泉位于康定断裂带中南部; D组温泉样品采集于康定断裂带南部磨西附近。
2.2.2 因子分析因子分析由研究原始变量相关矩阵内部的依赖关系出发,可以将复杂的多个因素进行简化,提取出主要影响因素,揭示本质,简化分析。通过抓住主要影响因素进行分析,对多个变量进行线性变换,选出具有代表性的少数综合指标,是一种降维处理方法。
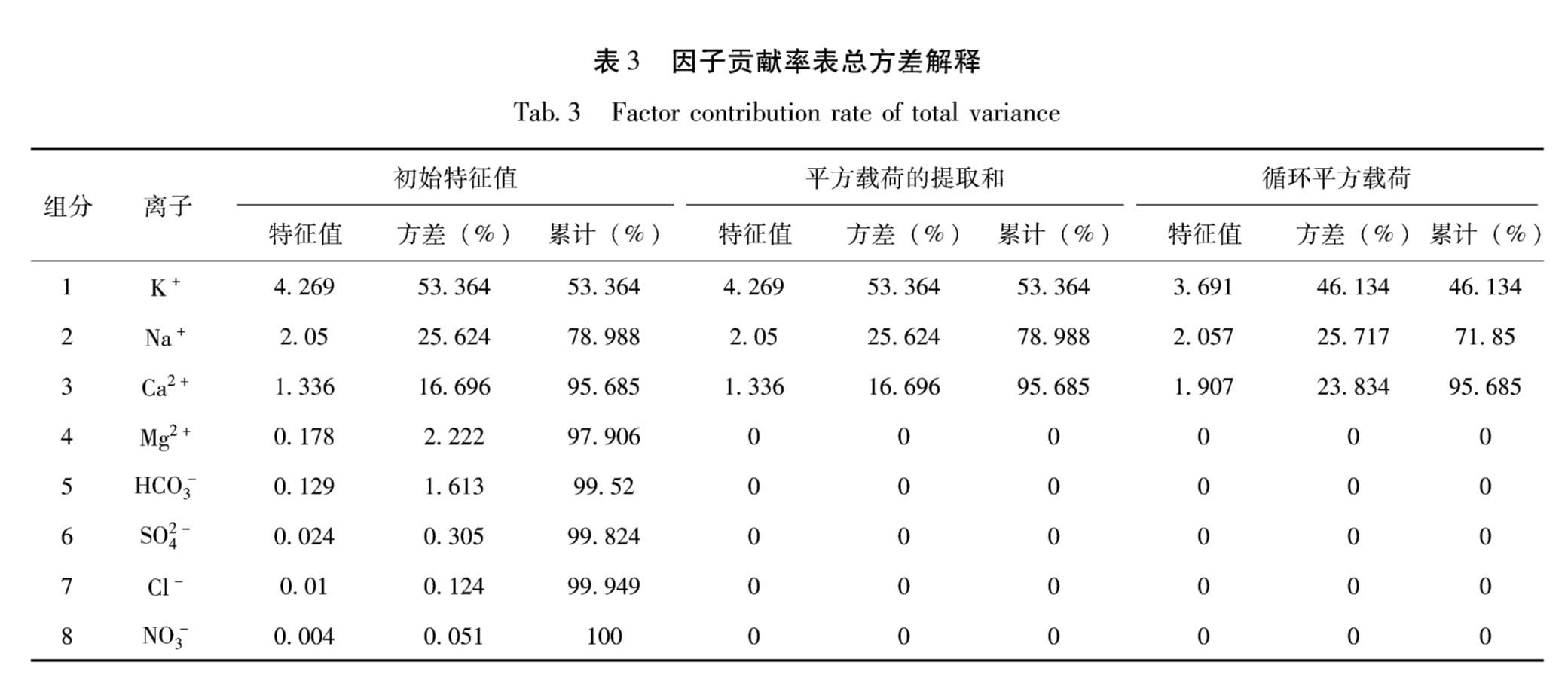
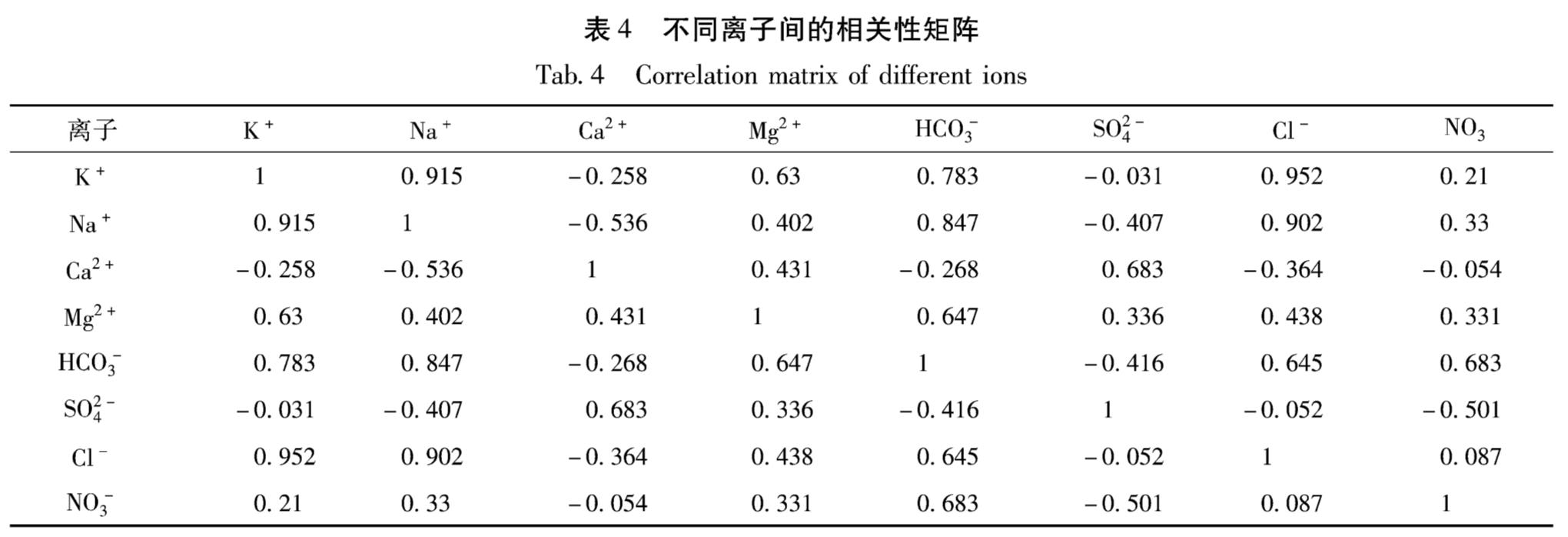
本文利用SPSS软件对温泉水的8大离子进行因子分析,根据表3的计算结果,按照SPSS软件默认的特征值大于l的提取原则,提取前3个离子K+,Na+,Ca+作为公共因子。同时由因子的贡献率可以得出,前3个离子的累积方差贡献率为95.685%,即综合了8个因子95.685%的信息,这说明前3个离子是控制水化学组分的主要因子,比较充分地概括了大部分因素,能够反映样本数据的本质信息。不同离子间的相关性分析如表4所示,相关性最好的是K+和Cl+,相关性达95.2%。
- 曹云,李红春,刘再华,等.2006.重庆市北温泉与四川康定温泉水之地球化学特征对比[J].中国岩溶,25(2):112-120.
- 崔冬雪,周训,刘海生,等.2019.云南祥云县王家庄碱性温泉水化学特征与成因分析[J].现代地质,33(3):680-690.
- 李其林,王云,赵慈平,等.2019.云南省香格里拉市下给和天生桥温泉水化学和逸出气CO2释放特征变化[J].地震研究,42(3):320-329.
- 李晓,王金金,黄珣,等.2018.鲜水河断裂带康定至道孚段热水化学与同位素特征[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),45(6):733-745.
- 林元武.1993.红河断裂带北段温泉水循环深度与地震活动性的关系探讨[J].地震地质,15(3):193-206.
- 龙德雄,黄辅琼,官致君,等.2006.四川理塘毛垭温泉地质构造环境及成因分析[J].四川地震,(1):34-40.
- 龙汨,周训,李婷,等.2014.北京延庆县松山温泉的特征与成因[J].现代地质,28(5):1053-1060.
- 史杰,乃尉华,李明,等.2018.新疆曲曼高温地热田水文地球化学特征研究[J].水文地质工程地质,45(3):165.
- 王凯.2011.鲜水河断裂带关键地段构造应力场数值模拟研究[D].西安:长安大学.
- 王莹,周训,于湲,等.2007.应用地热温标估算地下热储温度[J].现代地质,21(4):605-612.
- 王云,赵慈平,李其林,等.2018.滇东南木契形构造区典型地热流体地球化学特征研究[J].地震研究,41(4):534-543.
- 易桂喜,范军,闻学泽.2005.由现今地震活动分析鲜水河断裂带中—南段活动习性与强震危险地段[J].地震,25(1):58-66.
- 易桂喜,闻学泽,王思维,等,.2006.由地震活动参数分析龙门山—岷山断裂带的现今活动习性与强震危险性[J].中国地震,22(2):117-125.
- 张彧齐,周训,刘海生,等.2018.云南兰坪—思茅盆地红层中温泉和盐泉的水文地质特征[J].水文地质工程地质,45(3):40.
- 赵庆生.1984.鲜水河断裂带热水水文地球化学特征及形成模式[J].成都科技大学学报,8(2):77-87.
- 周荣军,何玉林,黄祖智,等.2001.鲜水河断裂带乾宁—康定段的滑动速率与强震复发间隔[J].地震学报,23(3):250-261.
- Bense V F,Glesson T,Lcneless S E,et al.2013.Fault zone hydrogeology[J].Earth Sci Rev,127:171-192.
- Curewitz D,Karson J A.1997.Structural settings of hydrothermal outflow:Fracture permeability maintained by fault propagation and interaction[J].Journal of Volcanology Geothermal Research,79(3):149-168.
- Guo Q,Pang Z H,Wang Y C,et al.2017.Fluid geochemistry and geothermometry applications of the Kangding high temperature geothermal system in Eastern Himalayas[J].Applied Geochemistry,81:83-75.
- Hou Y,Shi Z,Mu W.2018.Fluid Geochemistry of Fault Zone Hydrothermal System in the Yidun-LitangArea,Eastern Tibetan Plateau Geothermal Belt[J].Geofluids,13:1-13.
- Luo J,Pang Z,Kong Y,et al.2017.Geothermal potential evaluation and development prioritization based on geochemistry of geothermal waters from Kangding area,western Sichuan,China[J].Environmental Earth Sciences,76(9):343.
- Mao X M,Wang Y X,Zhan H B,et al.2015.Geochemical and isotopic characteristics ofeothermal springs hosted by deep-seated faults in Dongguan Basin,Southern China[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration,158:112-121.
- Martinelli G,Dadomo A.2017.Factors constraining the geographic distribution of earthquake geochemical and fluid-related precursors[J].Chemical Geology,469:176-184.
- Pang Z H,Reed M.1998.Theoretical chemical thermometry on geothermal waters:problems and methods[J].Geochimica Et CosmochimicaActa,62(6):1083-1091.
- Qi J H,Xu M,AN C J,et al.2017.Characterizations of Geothermal Springs along the Moxi Deep Fault in the Western Sichuan Plateau,China[J].Physics of the Earth & Planetary Interiors,263:12-22.
- Shi Z M,Liao F,Wang G C,et al.2017.Hydrogeochemical characteristics and evolution of hot springs in eastern Tibetan Plateau geothermal belt,western China:insight from multivariate statistical analysis[J].Geofluids,2017:1468-8123.
- Shi Z M,Wang G C.2017.Evaluation of the permeability properties of the Xiaojiang Fault Zone using hot springs and water wells[J].Geophysical Journal International,209(3):1526-1533.
- Zhou X,Wang W,Chen Z,et al.2015.Hot spring gas geochemistry in Western Sichuan Province,China after the Wenchuan MS8.0 Earthquake[J].Terr Atmos Ocean Sci,26(4):361-373.