基金项目:中国地震局工程力学研究所基本科研业务费专项资助项目(2018QJGJ02)与国家自然科学基金项目(U1939210)联合资助.
备注
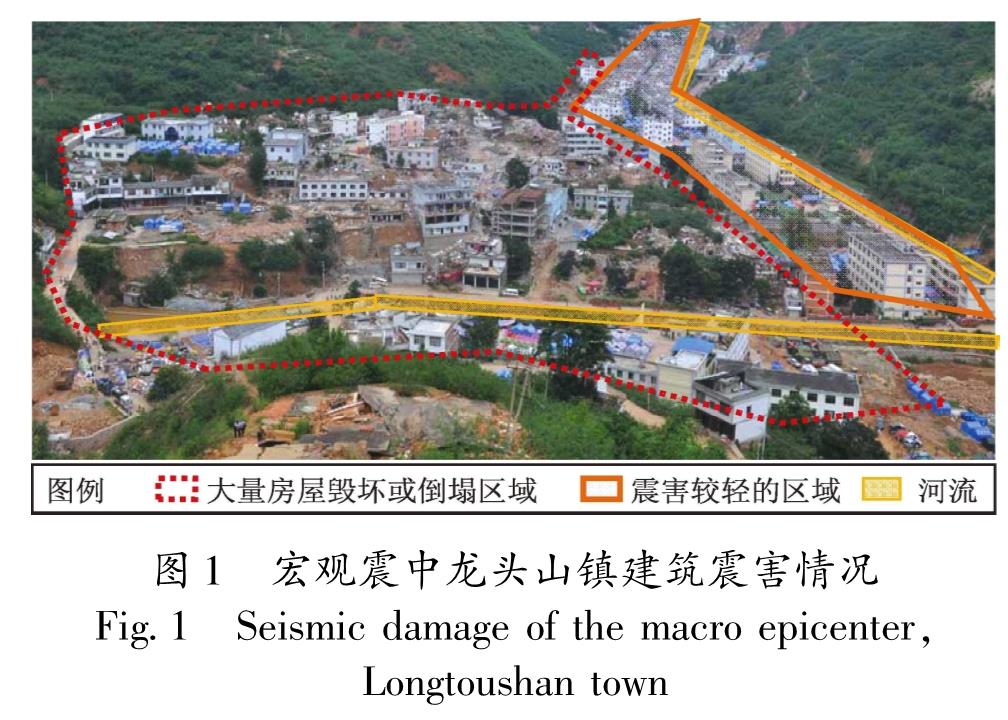
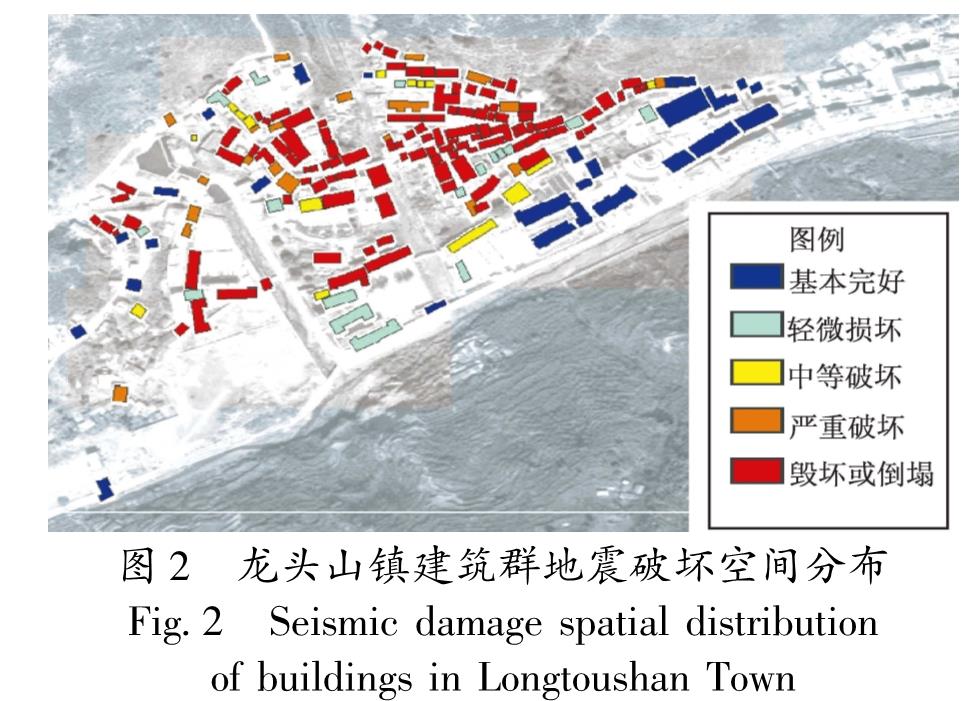
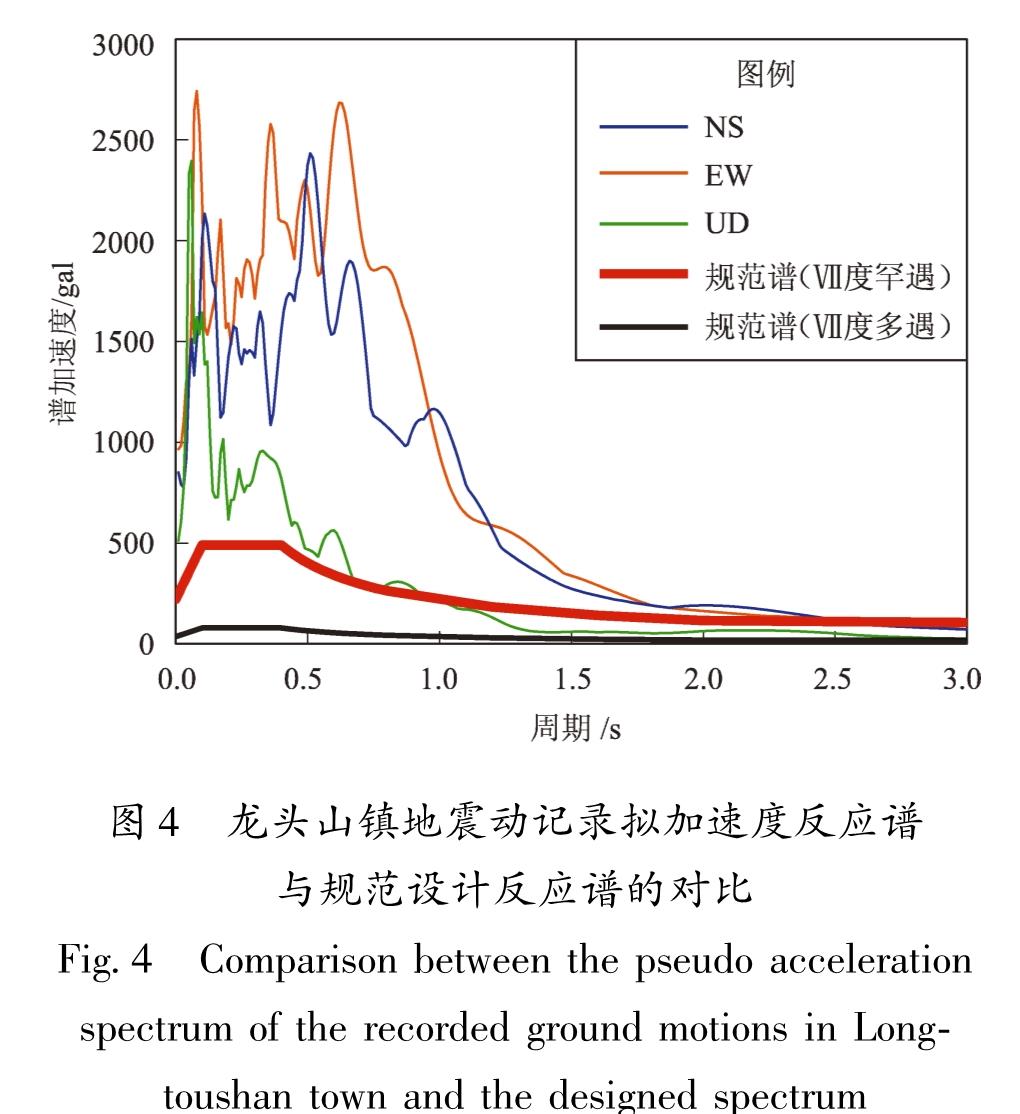
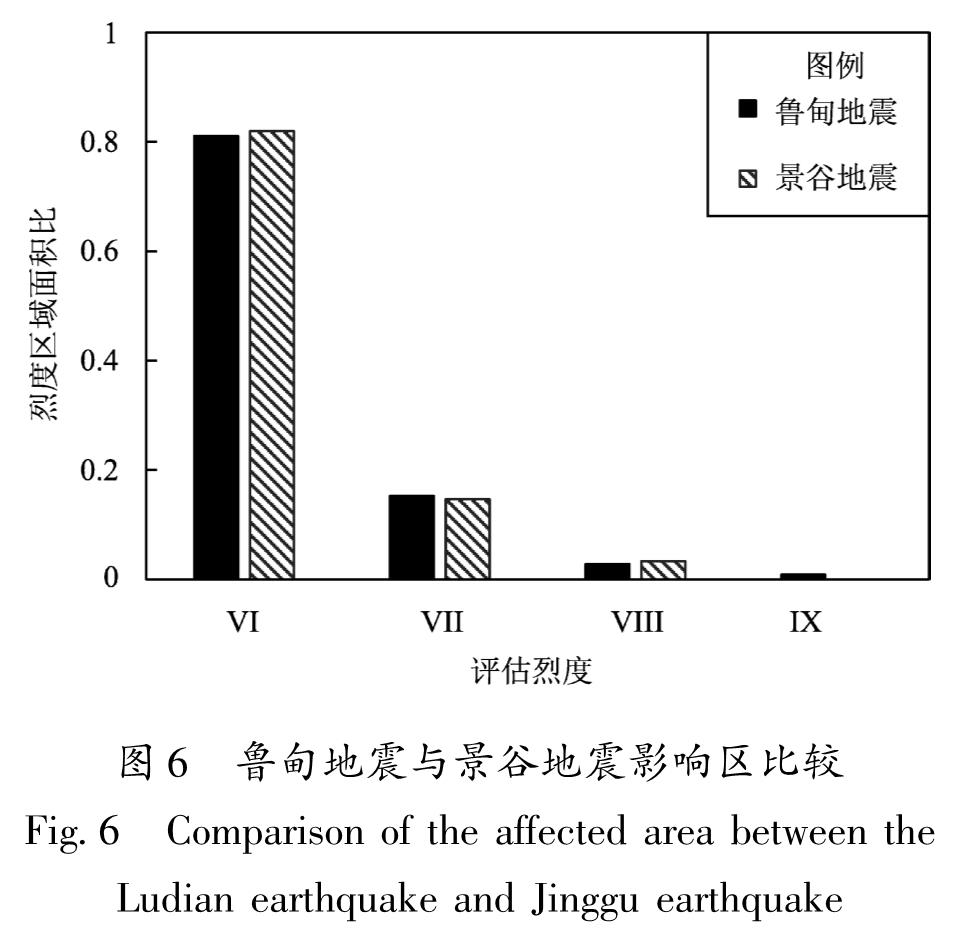
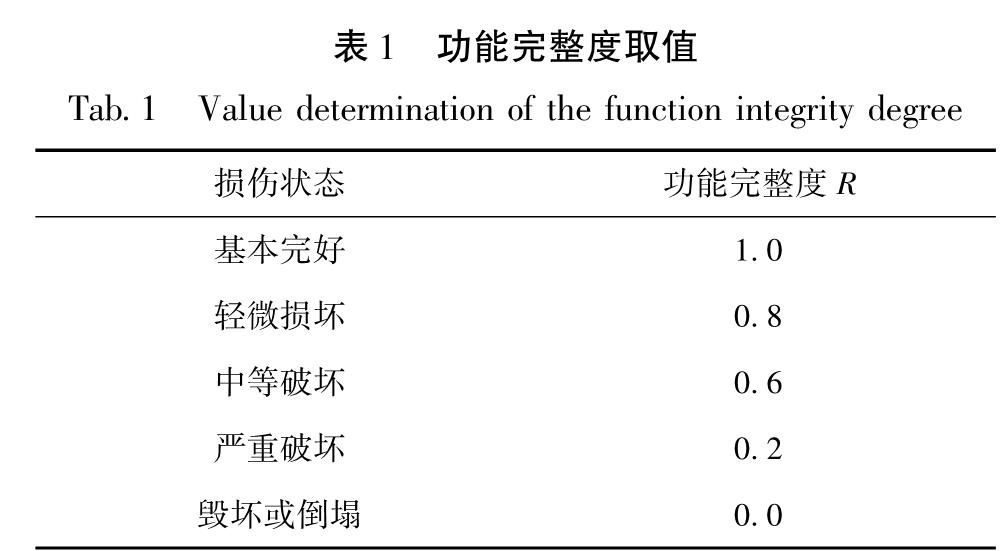
2014年的鲁甸地震使其宏观震中龙头山镇遭受毁灭性破坏,整理龙头山镇城区(龙泉社区)192栋建筑信息,并识别每栋建筑损伤情况。从区域防灾角度,对龙头山镇建筑群的震害特点、致灾机理与减灾策略进行分析,对该区域震后避难场所分布情况和恢复重建过程进行分析与讨论。基于提出的区域建筑群功能完整度指标,对龙头山镇地震破坏与灾后重建各个阶段的功能完整度与恢复程度进行了量化分析。结果 表明:鲁甸地震表现出的“小震大灾”特征,主要与地震动局部异常以及房屋整体抗震能力有关,局部异常严重的震害也可能对全局震害产生决定性的影响; 当规则建筑具备必要的设防水准后,往往可避免其在远超越设防水准地震下倒塌; 提出的结构功能完整度可比较合理地描述区域建筑群恢复的过程,可为抗震韧性分析提供量化指标。
The 2014 Ludian earthquake caused devastating damage to its macro epicenter,Longtoushan town.In this study,the structure information and damage states of 192 buildings in the downtown of Longtoushan(Longquan community)were sorted out and summarized.From the perspective of regional disaster prevention,the characteristics of the earthquake damage,the mechanism of disaster mitigation are studied by analyzing the buildings in Longtoushan town,and the the shelters and recovery process were examined.The function integrity index for regional buildings is proposed to evaluate the the recovery degree at different stages of time.The phenomenon that an relatively small earthquake led to serious seismic damage was primarily attributed to the local anomalies of ground motions and seismic capacity of buildings.A regular building with the necessary seismic fortification measures is largely able to avoid its collapse in an earthquake far beyond its designed fortification level.The proposed functional integrity index can reasonably describe the recovery process of regional buildings and provide a quantitative analysis on the regional seismic resilience.