基金项目:中国地震局地震科技星火计划项目(XH194204Y)、国家自然科学基金(41804010,41704084)、国家重点研发计划项目(2018YFC1503606)和天津市自然科学基金(17JCYBJC21600)联合资助.
(The First Monitoring and Application Center,China Earthquake Administration,Tianjin 300180,China)
southern margin of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau; absolute gravity; non-tectonic gravity effect
备注
基金项目:中国地震局地震科技星火计划项目(XH194204Y)、国家自然科学基金(41804010,41704084)、国家重点研发计划项目(2018YFC1503606)和天津市自然科学基金(17JCYBJC21600)联合资助.
基于2002—2017年的ECMWF Interim三维大气再分析资料、GRACE时变重力场模型和GPS数据,分析了青藏高原南缘的拉萨、日喀则、仲巴、噶尔4个绝对重力测站的非构造重力效应。结果 表明:ECMWF Interim大气负荷重力效应主要表现为季节性变化特征,最大周年振幅可达到1.4 μGal; GRACE陆地水负荷重力效应和GPS地壳垂直位移引起的重力效应均存在较为明显的季节性及长期趋势变化特征,二者的最大周年振幅和长期趋势分别达到2.6 μGal,-0.6 μGal/a和1.8 μGal,-0.3 μGal/a; GRACE与GPS的比较分析结果表明青藏高原南缘的非构造重力效应会受到局部流体质量负荷的显著影响。
Based on three-dimensional ECMWF interim reanalysis data,GRACE time variable gravity model and GPS data from 2002 to 2017,we analyzed the nontectonic gravity effects of absolute gravity observation stations in southern margin of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau.The results show that the ECMWF Interim atmospheric gravity effect mainly presents seasonal characteristics.Its maximum annual amplitude is 1.4 μGal.The GRACE hydrological gravity effect and gravity effect caused by the vertical crustal deformation from GPS show obvious seasonal and long-term trend characteristics.The maximum annual amplitude and long-term trend can reach 2.6 μGal and -0.6 μGal/a,1.8 μGal and 0.3 μGal/a,respectively.The comparative analysis of GRACE and GPS show that the nontectonic gravity effects in southern margin of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau can be significantly affected by the local fluid mass load.
引言
青藏高原南缘沿喜马拉雅山造山带延伸分布,是印度板块与欧亚板块的碰撞挤压地带,其形成机制、隆升方式及强震孕育背景等一直备受关注。过去二十余年间,“网络工程”和“陆态网络”等项目先后在青藏高原南缘及其周边地区布设了一定密度的绝对重力观测网。与一些常规的大地测量技术相比,高精度绝对重力观测技术不仅能给出地壳的垂直形变信息,也能揭示地壳内部质量的运动信息(王勇,张为民,1997)。因此,绝对重力测量在认识和理解青藏高原南缘的地壳运动特征及地震孕育背景方面具有十分重要的理论和实际意义。
国内外研究人员依托绝对重力观测资料在研究青藏高原及其周边地区地壳运动特征及地震孕育背景方面取得了一定进展。在地壳运动特征研究方面,张为民等(2000)通过对比拉萨点1999年与1993年的绝对重力观测结果,初步证实该点的隆升速率为10 mm/a; 王勇等(2004)对滇西地区和拉萨点的绝对重力重复观测结果进行了分析,通过位错模型证实拉萨点的重力变化是由印度板块与欧亚大陆俯冲所引起的; Sun等(2009)和邢乐林等(2011)通过分析拉萨点等绝对重力观测数据揭示出青藏高原地区底部的地壳增厚及物质亏损。在地震孕育背景研究方面,李辉等(2009)和祝意青等(2007,2012)利用1998年以来的绝对重力和相对重力观测资料给出了中国大陆重力场的动态变化特征,并揭示出其与构造环境和地震孕育的内在联系。
近年来,研究人员开始陆续关注非构造重力效应对绝对重力观测结果的影响。康开轩等(2015)根据青藏地区的流动重力观测结果,结合现有的冰川和湖泊水位变化估算了陆地水变化引起的水文重力效应,并给出了西藏及周边地区的重力长期变化; Chen等(2016)利用青藏高原南缘的绝对重力观测资料,获得了扣除地壳垂直形变、GIA效应、地表剥蚀和地壳底部增厚影响的剩余重力变化,并发现了与尼泊尔MS8.1地震前地壳介质变化相关的重力异常信号; Yi等(2016)针对尼泊尔MS8.1地震前2年的绝对重力观测结果,综合湖泊、冰川、河流、降水和积雪等资料分析了各种因素的重力效应影响。
从已有的研究结果看,尽管高精度的绝对重力测量在研究青藏高原南缘的地壳运动及其动力学机制等方面表现出一定优势,但在理论研究方面还不能将其观测结果中所包含的地表流体质量再分布和深部物质迁移等信息完全准确分离开。考虑到青藏高原南缘复杂的构造运动与陆表环境,本文以该地区拉萨、日喀则、仲巴和噶尔4个绝对重力测站为例,联合多源的观测数据研究了其非构造重力效应的季节性和趋势变化特征,以期为该地区绝对重力观测结果中的构造运动信号分析提供参考。
1 数据及其处理方法
1.1 大气再分析资料及数据处理本文采用的大气数据是由欧洲中期天气预报中心生成的ECMWF Interim全球三维大气再分析资料,包括2002—2017年共192个月的观测数据。ECMWF Interim提供的37个大气等压层的高程、位势高度、比湿、气压、气温等要素时间分辨率为1个月,水平空间分辨率为0.125°×0.125°。其中,地表及各规定等压层的Tesseroid单元体大气密度可利用各要素根据流体静力平衡方程计算得到。
根据地表负荷函数理论(Farrell,1972),青藏高原南缘拉萨(LHAS)、日喀则(XZRK)、仲巴(XZZB)和噶尔(XZGE)4个绝对重力测站(图1)大气负荷重力效应可用其质量和负荷格林函数的褶积积分计算得到:
L(θ,λ)=sρ(θ,λ)h(θ,λ)G(ψ)ds(1)
式中:θ与λ分别表示绝对重力测站的纬度和经度; ρ表示积分面元的大气密度; h表示积分面元的高程; ψ表示观测点到积分面元的角距; G(ψ)表示重力负荷格林函数,可表示为:
G(ψ)=GN(ψ)+GD(ψ)=(g)/(M)∑∞n=0nPn(cosψ)+(g)/(M)∑∞n=0[-(n+1)kn+2hn]Pn(cosψ)(2)
式中:g表示地球平均重力; M表示地球质量; Pn(cosψ)表示勒让德函数; kn和hn表示负荷勒夫数; GN(ψ)表示牛顿引力项直接效应; GD(ψ)表示弹性地球产生的形变以及由此使地球内部质量重新分布而引起的弹性项间接效应。
在式(1)的实际计算过程中,本文将大气数据划分为近区(ψ<1°)、中区(1°<ψ<20°)和远区(ψ>20°)3个部分进行计算。对于近区的Tesseroid单元体大气质量,本文利用泰勒级数展开二阶近似计算其牛顿引力项直接效应(Neumeyer et al,2004; Heck,Seitz,2007)。
1.2 时变重力场模型及数据处理本文采用的GRACE时变重力场模型是由德克萨斯大学空间中心CSR提供的Level 2 RL06版本GSM和GAC数据,包括2002年8月至2017年6月共160个月的观测数据。其中,GRACE GSM数据在解算过程中已扣除了非潮汐大气和海洋质量的影响,因此其反映的主要是陆地水质量重新分布引起的变化。对于GRACE时变重力场模型,本文对其一阶项(Swenson et al,2008)和C20(Cheng,Tapley,2004)进行了替换,采用P5M11去相关滤波(Chen et al,2007)和300 km高斯滤波(Wahr et al,1998)的组合滤波方法以压制高阶项球谐系数误差,绝对重力测站重力异常和垂直位移的反演公式可分别表示为:
Δg(θ,λ)=(GM)/(R2)∑nmaxn=0(n-1)∑nm=0P^-nm(cosθ)
[ΔCnmcos(mλ)+ΔSnmsin(mλ)](3)
Δr(θ,λ)=R∑nmaxn=1(hn)/(1+kn)∑nm=0P^-nm(cosθ)
[ΔCnmcos(mλ)+ΔSnmsin(mλ)](4)
式中:θ和λ分别表示余纬和经度; R表示地球平均半径; ΔC和ΔS分别表示GRACE月时变重力场模型球谐系数; P^-nm(cosθ)表示正则化缔合勒让德函数。
1.3 GPS数据处理利用GAMIT/GLOBK和OQCA软件处理2002—2017年青藏高原南缘地区“陆态网络”GPS连续站观测数据。除了LHAS测站以外,另外3个绝对重力测站与GPS连续站均为并址观测。对GPS观测数据的具体处理步骤为:①联合青藏高原南缘及全球均匀分布的IGS站进行GAMIT基线解算,得到测站坐标单日松弛解。解算过程主要的参数设置为:天线相位中心改正采用绝对天线相位中心模型; 对流层延迟映射函数采用GMF模型; 全球固体潮、海潮模型改正遵循IERS 2004协议,但未进行非潮汐大气和海洋改正。②利用QOCA软件综合多天的单日松弛解平差计算得到ITRF2008框架下测站坐标的时间序列。经过以上处理,对GPS连续站垂直位移时间序列中由于天线更换、强震同震位移等影响造成的阶跃进行了修复,并剔除了大于3倍误差的异常值。
1.4 时间序列分析对于绝对重力测站上的重力异常和地壳垂直位移时间序列,本文重点分析其趋势及周年变化特征。假定其时间序列主要包含了线性趋势项β1、周年项β2,然后基于最小二乘原理对时间序列进
行拟合分析:
Δg(θ,λ,t)=β0(θ,λ)+β1(θ,λ)t+β2cos[ω1t+α1(θ,λ)](5)
式中:β0,β1,α2,β1为求解的参数; ω1=2π。
为了分析时间序列的趋势异常特征,采用递归最小二乘方法对线性趋势参数的稳定性做判断,并利用递归残差累积和检验识别出时间序列中结构断点的分布位置。如果时间序列存在结构断点,则对时间序列进行分段线性拟合。
2 结果分析
2.1 大气负荷重力效应基于2002—2017年的ECMWF Interim数据,采用负荷格林函数方法计算得到了LHAS,XZRK,XZZB和XZGE这4个测站的大气负荷重力效应时间序列(图2),并分别提取其周年振幅及趋势变化特征(表1)。基于ECMWF Interim内插计算得到的4个测站的气压数据,本文还采用大气导纳值(-0.303 7 μGal/hPa)方法(罗少聪,2003)计算得到4个测站的大气负荷重力效应时间序列。从图2可以看出,采用负荷格林函数与大气导纳值方法得到的4个测站的大气负荷重力效应较为一致,
差值标准差小于0.4 μGal。从图2和表1可以看出,4个测站的时间序列均反映出青藏高原南缘的大气负荷重力效应存在明显的季节性变化特征,一般在夏季和冬季分别达到最小值和最大值,周年振幅分别为1.0,0.9,1.4和1.2 μGal。4个测站的时间序列均没有表现出明显的长期趋势及趋势异常特征,说明该地区的大气重力效应主要表现为周年变化特征。
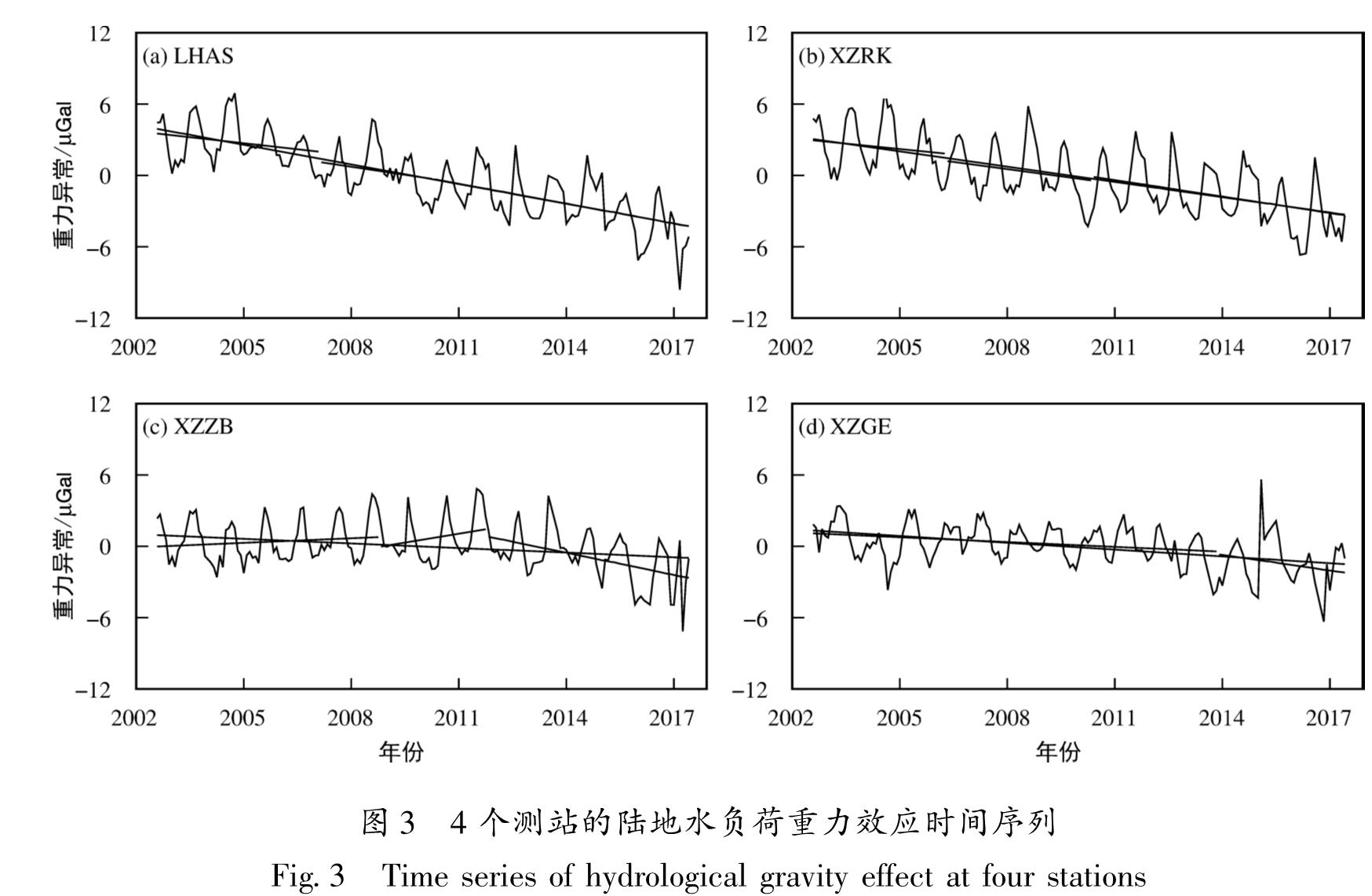
2.2 陆地水负荷重力效应基于2002—2017年的GRACE GSM数据,采用卫星重力反演方法计算得到了LHAS,XZRK,XZZB和XZGE这4个测站的陆地水负荷重力效应时间序列(图3),并提取其周年振幅及趋势变化特征(表1)。从图3可以看出,4个测站的时间序列均反映出青藏高原南缘的陆地水负荷重力
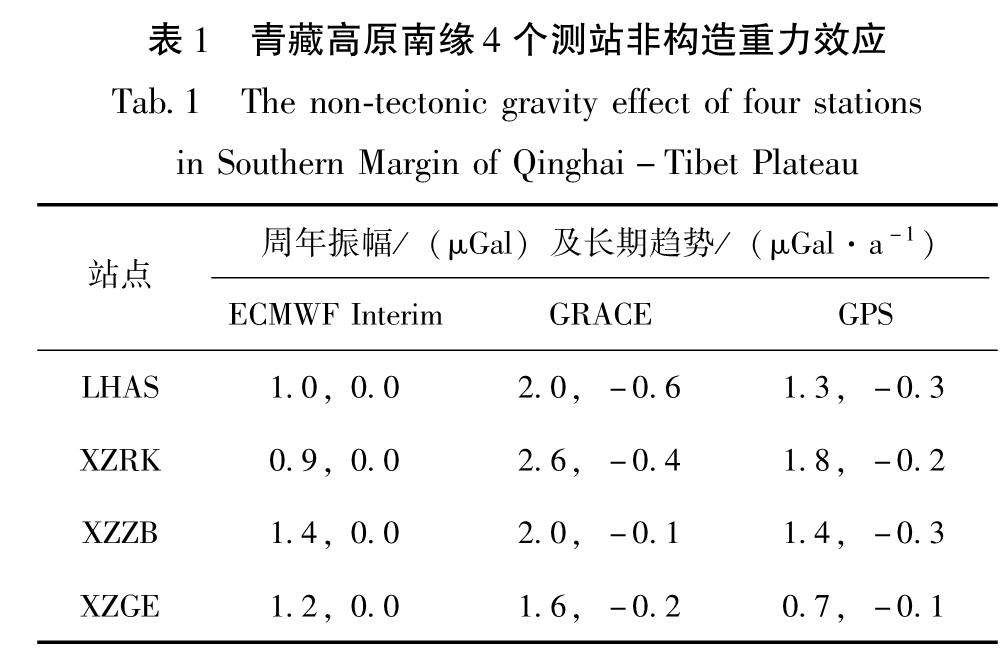
表1 青藏高原南缘4个测站非构造重力效应
Tab.1 The non-tectonic gravity effect of four stations in Southern Margin of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau效应存在较为明显的季节性变化特征,LHAS,XZRK,XZZB测站一般在春季和秋季分别达到最小值和最大值,而XZGE测站一般在夏季和冬季分别达到最小值和最大值,4个测站周年振幅分别为2.0,2.6,2.0和1.6 μGal。另外,LHAS和XZRK测站的时间序列表现出了较为明显的长期趋势特征,速率分别为-0.6和-0.4 μGal/a,而XZZB和XZGE测站时间序列的长期趋势相对较小,速率分别为-0.1和-0.2 μGal/a。4个测站的时间序列均存在明显的结构断点,不同时间跨度的GRACE陆地水负荷重力效应趋势变化呈现出明显的差异性特征,说明该地区陆地水负荷重力效应存在较为显著的年际变化特征,这可能与土壤水、积雪、冰川和地下水等多种陆地水文过程有关。
2.3 地壳垂直位移重力效应基于2002—2017年的GRACE GSM&GAC和GPS数据,计算得到了4个测站的地壳垂直位移时间序列(图4)。从图4中可以看出,4个测站的垂直位移时间序列均表现出明显的季节性变化特征,二者给出的周年相位较为一致,但是由GRACE数据得出的周年振幅量级明显偏小,分别为6.0,6.5,5.2和1.9 mm,而由GPS数据得出的周年振幅分别为6.5,9.2,7.0和3.6 mm,采用布格模型(-0.2 μGal/mm)换算成重力效应
相当于1.3,1.8,1.4和0.7 μGal(表1)。由GRACE数据得到4个测站的垂直位移时间序列长期趋势分别为0.4,0.3,0.2和0.2 mm/a,与之相比GPS得到的时间序列具有更加明显的长期变化趋势,其速率分别为1.3,0.9,1.4和0.5 mm/a,引起的重力效应相当于-0.3,-0.2,-0.3和-0.1 μGal/a(表1)。
对于青藏高原南缘的绝对重力测站而言,GRACE GSM&GAC反演得到的地壳垂直位移时间序列主要反映了大气和陆地水等大尺度地表流体的负荷效应,与之相比GPS观测得到的结果则更容易受到测站周边局部区域流体质量负荷效应的影响,这可能是GRACE垂直位移时间序列量级明显偏小的主要原因。以上比较分析结果也从侧面反映出青藏高原南缘的绝对重力测站局部地区存在着显著的地表流体质量变化,而目前的大气再分析资料ECMWF Interim以及GRACE GSM数据还不能有效反映其非构造重力效应。
3 结论与讨论
本文以青藏高原南缘的4个绝对重力测站为例,基于ECMWF Interim大气再分析资料、GRACE时变重力场模型和GPS数据系统分析了非构造重力效应的季节性和趋势变化特征,得到以下结论:
(1)ECMWF Interim大气负荷重力效应的趋势变化并不明显,其主要表现为季节性变化特征,最大周年振幅为1.4 μGal。
(2)GRACE陆地水负荷重力效应存在显著的季节性和长期趋势变化特征,最大周年振幅和长期趋势分别为2.6 μGal和-0.6 μGal/a,其不同时间跨度的趋势变化存在明显的差异性特征。
(3)GPS地壳垂直位移引起的重力效应也存在显著的季节性和长期趋势变化特征,最大周年振幅和长期趋势分别为1.8 μGal和-0.3 μGal/a。GPS和GRACE垂直位移结果的比较分析表明青藏高原南缘的绝对重力观测会受到局部地表流体质量变化的显著影响。
受制于大气再分析资料及时变重力场模型数据自身的局限性,本文给出的计算结果主要还是反映了大尺度地表流体质量的负荷重力效应。尽管如此,本文的结果仍表明青藏高原南缘绝对重力观测中的非构造重力效应周年变化的峰对峰值简单求和最大可达到10.6 μGal(XZRK),考虑到年际变化及测站局部地区信号的影响,其相应的重力效应还会更大。对于早期的绝对重力数据,其观测的时间跨度一般都比较大,并且是在不同月份进行的。因此,如果绝对重力观测中的非构造重力效应未经有效改正,这不仅会扭曲相对重力联测数据的平差结果,也会干扰构造运动信号的分离效果。鉴于此,建议今后对于相同测点上的绝对重力观测应尽可能在相同月份或季节实施观测,而对于出现显著异常的绝对重力观测数据,应尽可能地结合测站周边的陆地水文、气象要素等数据来准确剔除局部非构造重力效应的影响。
- 康开轩,李辉,刘少明,等.2015.尼泊尔MS8.1地震前我国西藏及周边区域的重力长期变化[J].大地测量与地球动力学,35(5):18-22,33.
- 李辉,申重阳,孙少安,等.2009.中国大陆近期重力场动态变化图像[J].大地测量与地球动力学,29(3):1-10.
- 罗少聪.2003.大气负荷效应问题研究[D].武汉:中国科学院研究生院(测量与地球物理研究所).
- 王勇,张为民,詹金刚,等.2004.重复绝对重力测量观测的滇西地区和拉萨点的重力变化及其意义[J].地球物理学报,47(1):95-100.
- 王勇,张为民.1997.高精度绝对重力测量在地壳垂直运动研究中的作用和应用前景[J].地壳形变与地震,17(3):98-102.
- 邢乐林,孙文科,李辉,等.2011.用拉萨点大地测量资料检测青藏高原地壳的增厚[J].测绘学报,40(1):45-48,62.
- 张为民,王勇,许厚泽,等.2000.用FG5绝对重力仪检测青藏高原拉萨点的隆升[J].科学通报,45(20):2213-2216.
- 祝意青,梁伟锋,李辉,等.2007.中国大陆重力场变化及其引起的地球动力学特征[J].武汉大学学报(信息科学版),32(3):246-250.
- 祝意青,梁伟锋,湛飞并,等.2012.中国大陆重力场动态变化研究[J].地球物理学报,55(3):804-813.
- Chen J L,Wilson C R,Tapley B D,et al.2007.GRACE detects coseismic and postseismic deformation from the Sumatra-Andaman Earthquake[J].Geophysical Research Letters,34(13):302-302.
- Chen S,Liu M,Xing L,et al.2016.Gravity increase before the 2015 MW7.8 Nepal earthquake[J].Geophysical Research Letters,43(1):1-7.
- Cheng M,Tapley B D.2004.Variations in the earth's oblateness during the past 28 years[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,109,B09402.
- Farrell W E.1972.Deformation of the earth by surface loads[J].Reviews of Geophysics,10(3):761-797.
- Heck B,Seitz K.2007.A comparison of the tesseroid,prism and point-mass approaches for mass reductions in gravity field modelling[J].Journal of Geodesy,81(2):121-136.
- Neumeyer J,Hagedoorn J,Leitloff J,et al.2004.Gravity reduction with three-dimensional atmospheric pressure data for precise ground gravity measurements[J].Journal of Geodynamics,38(3):437-450.
- Sun W,Wang Q,Li H,et al.2009.Gravity and GPS measurements reveal mass loss beneath the Tibetan Plateau:geodetic evidence of increasing crustal thickness[J].Geophysical Research Letters,36(2):206-218.
- Swenson S,Chambers D,Wahr J.2008.Estimating geocenter variations from a combination of GRACE and ocean model output[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,113(B8):410-410.
- Wahr J,Molenaar M,Bryan F.1998.Time variability of the earth's gravity field:hydrological and oceanic effects and their possible detection using GRACE[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,103(B12):30205-30229.
- Yi S,Wang Q,Sun W.2016.Is it possible that a gravity increase of 20 μGal per year in Southern Tibet comes from a wide-range density increase?[J].Geophysical Research Letters,43(4):1481-1486.