基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目(41674018)资助.
(中国地震局地震研究所 地震大地测量重点实验室,湖北 武汉430071)
(Key Laboratory of Earthquake Geodesy,Institute of Seismology,China Earthquake Administration,Wuhan 430071,China)
coupled motion; surface deformation; gravity variation; vertical gravity gradient
备注
基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目(41674018)资助.
引言
20世纪70年代以来,重力、水准、GNSS等观测技术不断进步,观测精度不断提高,目前,GNSS观测以及水准测量精度可达到毫米级别,重力测量精度亦可达到微伽。近年来,我国的大陆重力与GNSS观测网的时空分辨率有了大幅度提升(李强等,2012; 申重阳,2005)。现阶段的GNSS和重力观测所提供的数据,可以很好地将重力与形变相结合,用来探究地壳运动及地震机理,取得了许多研究成果,特别是在青藏高原地区隆升与重力变化关系的研究中(邢乐林等,2017; 段虎荣等,2020),形变与重力数据的结合发挥了很好的作用。但在研究过程中,依然存在两者数据结合不足的情形。
因此,将形变与重力数据更好地结合,研究两者之间的关系,探究重力变化机理及其与形变的关系成为现代地球物理学与大地测量学的研究热点。自20世纪以来,已有不少学者在理论上对其进行了初步的探究,Walsh(1975)首先推导出形变引起重力变化的计算公式,率先从理论上进行了分析。Reilly和Hunt(1976)指出了Walsh所得结果的错误,并给出了地球表面固定不变时形变所引起的重力变化,在该研究的基础上,陈运泰等(1980)完善了形变引起的重力变化理论,给出了区域形变和物质迁移引起的重力变化效应公式。李瑞浩(1988)采用不同原理,推导出和陈运泰等(1980)一样的结果。上述研究结果只适用于准静态变形情形,尚没有真正涉及形变时变模型。为此,申重阳和李辉(2005)提出了地壳变形与密度变化的耦合运动的思想与理论,给出了地壳变形与密度变化的耦合运动产生的重力场时变公式。王嘉沛等(2015)结合形变与密度变化耦合运动理论,利用直立长方体模型和川滇地区GNSS水平运动观测结果,模拟计算了该地区水平运动对空间固定点所产生的重力效应,但尚未考虑垂直运动效应和地表固定观测点伴随地表运动的情形。同时,对于山脉地区的形变研究,邢乐林等(2017)和段虎荣等(2020)分别利用重力变化数据研究了青藏高原的地壳增厚和隆升速率,但没有考虑到在伴随着青藏高原隆升过程中,地壳内部介质的密度是否发生变化。
因此,本文基于形变与密度变化耦合理论,运用直立长方体重力异常模型,模拟计算在山体隆升运动(以青藏高原为例)下产生的重力时变效应,计算在时变场内重力垂直梯度的变化,并对形变、密度与重力之间的时变关系作进一步研究。
1 基础理论
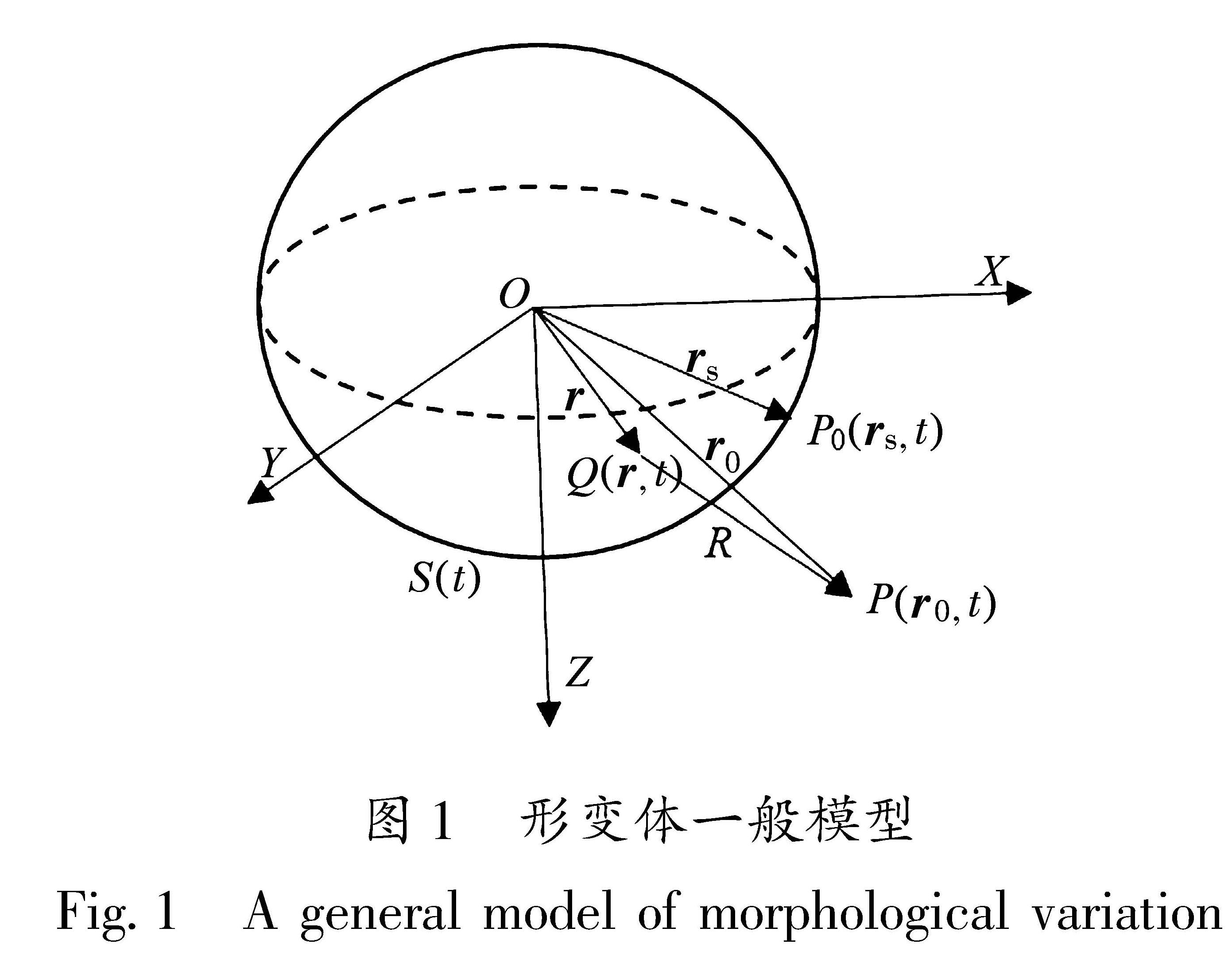
1.1 介质体形变所引起的重力变化的一般表达式地壳形变会引起介质体质量的重新分布,从而引起重力变化。一些学者(Walsh,1975; 陈运泰等,1980; 申重阳等,2005,2007)从理论上分析了形变与重力变化的关系,为后面的模拟计算提供了理论依据,即以地心为原点(0,0,0)[KG-*3](定点),设置相对地球的惯性直角坐标系(x,y,z)。地球内部时刻发生运动,对于任意时刻t,设地球物质的集合为Ω(t), 地球表面用S(t)表示, S(t)同时包含了地球表面和地球内部洞穴的表面。假设,在S(t)上存在任意一点P0, 其坐标设置为(rs,t),其中rs=xsi+ysj+zsk。在地球内部存在一个任意点Q(r,t)∈Ω(t),其中r=xi+yj+zk,点的密度减和位移可表示为ρ(r,t)≠0和u(r,t),在Q点的形变速度可用位移u(r,t)对时间的一阶导数来计算u[DD(-*4/5]?[DD)](r,t)。将Q到P之间的向量关系表示为:R=r0-r,其数值大小表示为:R=|r0-r|。
整个地球运动过程均满足质量守恒定律,我们将以地球内部任意点Q为中心的介质体元设置为dv(r),其密度变化为:

在地球内部的物质形变运动所造成的物质增量为
 ,因此有:
,因此有: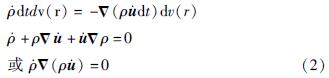
式中:Δ为哈密顿算子,
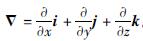 。当地球内部发生变形和质量迁移(质量重新分布)时,形变体内部密度变化可以通过内部变形来表征,即受质量守恒的基本方程式(2)来约束。
。当地球内部发生变形和质量迁移(质量重新分布)时,形变体内部密度变化可以通过内部变形来表征,即受质量守恒的基本方程式(2)来约束。如图1所示,在任意时刻t,不考虑地球上物质所受到的来自地球自转所产生的离心力作用,只考虑地球内部的形变运动,地球内部任意一点Q及其周边体积元dv(r)对空间外任意一点P的重力位表示为:
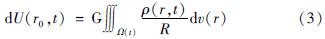
式中:G为万有引力常数; ρ为介质体密度; R=|r0-r|为两点之间的距离。在介质体发生形变作用时,其密度变化是利用其形变运动来表示的。然后,将地球内部介质假设成离散点元的集合dm=ρdv。在dt时间内,介质发生了形变运动,而导致P点重力位变化的原因则是因为P和Q的距离发生了变化,因此有:
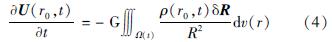
又
 ,将其代入式(4)并利用高斯定理计算可得:
,将其代入式(4)并利用高斯定理计算可得:
式中:ΔQ表示为对Q点的哈密顿算子; n为ds的外法线方向。根据重力与重力位的关系,可得:
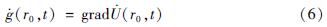
于是可得到空间固定点的重力变化速度:
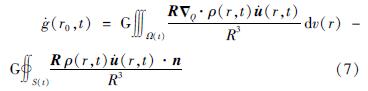
当观测点在地表随着地表一起运动时,在Δt时间内,地表观测点P0从rs运动到rs+us,其中下标s为地球表面,us是通过观测得到的。那么P0的重力变化可以表示为:
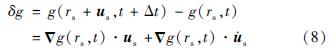
将式(8)代入到式(7)可得地表固定观测点观测到的重力时间变化。将观测点运动所造成的重力效应加入其中,就得到地表固定点的重力变化速度:

式中:
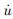 为u的时间导数。等式右侧第一项为因介质变形运动造成的密度变化效应; 第二项为地表整体形变运动效应; 第三、四项相当于因观测点运动造成的重力效应,与观测点的位移、速度、加速度、重力梯度以及重力变化速度的梯度有关。式(9)可将其看成式(7)的修正。1.2 时变场下重力垂直梯度
为u的时间导数。等式右侧第一项为因介质变形运动造成的密度变化效应; 第二项为地表整体形变运动效应; 第三、四项相当于因观测点运动造成的重力效应,与观测点的位移、速度、加速度、重力梯度以及重力变化速度的梯度有关。式(9)可将其看成式(7)的修正。1.2 时变场下重力垂直梯度要探究重力变化同形变之间的关系,其中最重要的就是重力梯度的计算,下面展示了两个不同测点的重力梯度的计算方法。
空间固定点的重力垂直梯度可由式(7)直接求垂向偏导得到:

下面讨论地表固定点随地表运动的情形。根据变形引起的重力变化的一般表达式可知,要推导重力变化与形变之间比值的解析公式,首先要知道该形变场的分布。这里采用各向同性介质中的形变模型和地心直角坐标系。
假设在Δt=t1-t0时间内,t0为初始时刻,由于地下介质体的变动地表发生了位移us,地表从t0时刻的rs运动到了t0+Δt时刻的rs+us位置,其地表位置发生的形变为可表示为:
δh=h(rs+us,t0+Δt)-h(rs,t) (11)
从图2地表形变位移可看出,在t0时刻,处于初始状态地表位置处于h(rs,t0),尚未发生形变。在t1时刻,由于地下介质体物质流入其中或其他原因,导致地下介质体积变大,引起地表抬升,地表运动到h(rs+us,t0+Δt)位置。图中在t1时刻虚线部分表示初始状态,实线为末状态。假设观测点在地表的情形,在此过程中的重力变化可以用式(8)计算求得,亦可利用式(9)进行计算:

此时,对于时变场下重力垂直梯度的计算公式为:
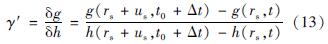 1.3 模拟山体形变模型
1.3 模拟山体形变模型山体在隆升过程中,对其周围地区的地貌会产生很大的影响,同时也会发生形变作用,从而引起相应的重力变化。根据形变引起的重力变化的一般表达式以及质量守恒定律可知,介质体在发生形变作用的同时会伴随着密度的变化。研究山体隆升运动所产生的重力变化时应结合形变与密度变化耦合理论,应遵循质量守恒定律。
地球板块在相互运动过程中,由于板块之间的碰撞(例如印度洋板块和亚欧板块)导致板块边界挤压形成山体。假设在运动过程中满足艾黎地壳均衡模型,即可把地壳视为较轻的均质岩石柱体漂浮在较重的均质岩浆之上,处于静力平衡状态。根据阿基米德浮力原理,山越高,增加的质量越多,陷入岩浆越深,形成山根。根据艾黎模型的均衡理论,可以知道在山体隆升过程中,山体的高度越高,其补偿深度也越深,莫霍面的深度也就越深。假设山体的海拔高度为H,地壳的原始厚度为T,山根的大小Z与山体海拔H之间的关系为:
Z=4.45H (14)
此时,山体的地壳厚度可以表示为:T+Z+H。
如图3所示,在t0时刻,地表和莫霍面处于水平状态,并未发生形变。此后,在受到板块运动等某些因素的影响时,其发生了变形,形成了山体,根据艾黎地壳均衡模型的均衡理论,在山体隆升的同时,莫霍面深度也在加深,就形成了t5时刻的状态。随后板块不断运动,山体不断隆升,莫霍面不断加深,形成了t10时刻的状态。因此艾黎地壳均衡模型是后续模拟计算山体隆升时所产生的重力变化的基础。
2 模拟计算方法
本文采用地壳形变与密度变化耦合运动理论来计算地壳形变引起的重力变化。该方法结合了地壳形变与密度两种信息,综合性地研究了地球重力场变化特征,改善了利用单一资料研究重力变化的方法,更加有利于对地球动力学进一步的研究。对于计算地壳形变引起的地表观测点的重力变化公式,可利用直立长方体(图4)进行近似计算。
利用直立长方体计算产生的重力异常为:

式中:(x,y,z)为长方体外任意点的观测坐标;(ε,η,τ)是直立长方体内任意一点的坐标,r为长方体内任意点到长方体外任意点的距离; r=[(ε-x)2+(η-y)2+(τ-z)2]1/2,ρ为直立长方体密度。利用直立长方体运动来计算重力变化的过程中,首先假设其运动的参数,然后根据质量守恒定律,计算运动过程中所产生的密度变化,以及在形变前后重力变化:
Δg=g1(x1,y1,z1,t1)-g0(x0,y0,z0,t0) (16)
本文利用直立长方体将山体进行剖分,用n个长方体近似模拟山体。如图5所示,将研究区域分成m×n个小块体单元块体,假设P[KG0](x,y,z)点在t时刻第i行、第j列的小单元块体产生的重力变化为gij(x,y,z,t),则P[KG0](x,y,z)在t时刻受到研究区域的大块体的重力变化为:

3 模拟计算结果
本文通过数值计算分析青藏高原以5 mm/a(邢乐林等,2017; 段虎荣等,2020)的速率隆升时所产生的重力变化,时间步长取10 a,初始时刻为t0,t5时刻表示以t0时刻为基础山体隆升5 cm之后的状态,t10时刻表示以t0时刻为基础山体隆升10 cm之后的状态,分别测量t5和t10时刻重力以及重力梯度分布。在计算时由于密度会随时间和位置变化,设置初始密度为ρ=2.67 g/cm3,在隆升过程中所产生的密度变化可利用式(2)计算求得。
假定地表隆升形变范围为(50×50)km2。观测网大小定位(70×70)km2,这样可以将形变区域完全覆盖,在计算时将地表划分为(0.5×0.5)km2的网格。在计算过程中假设每个块体密度都是均匀的,其密度变化也是均匀的。
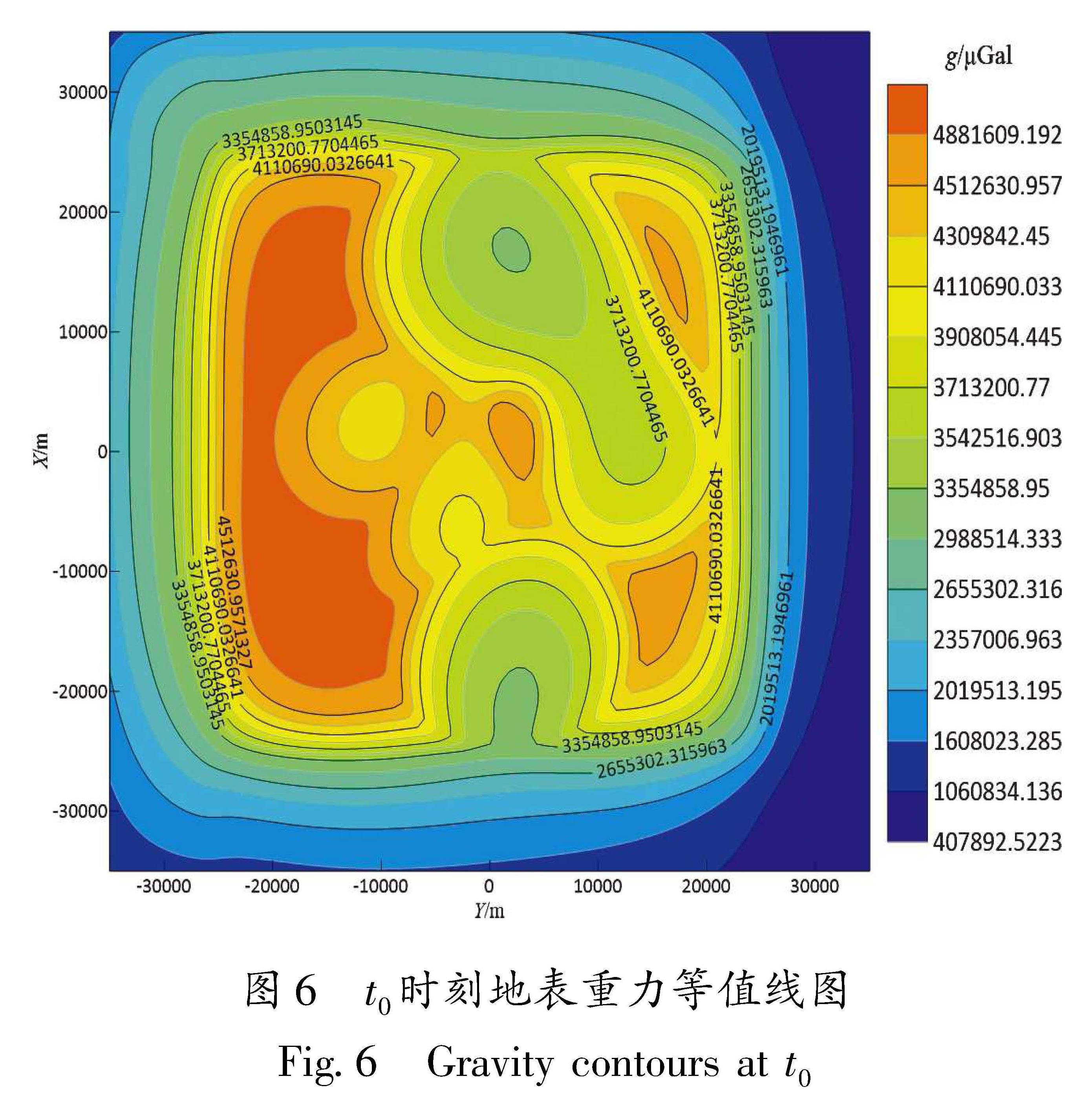
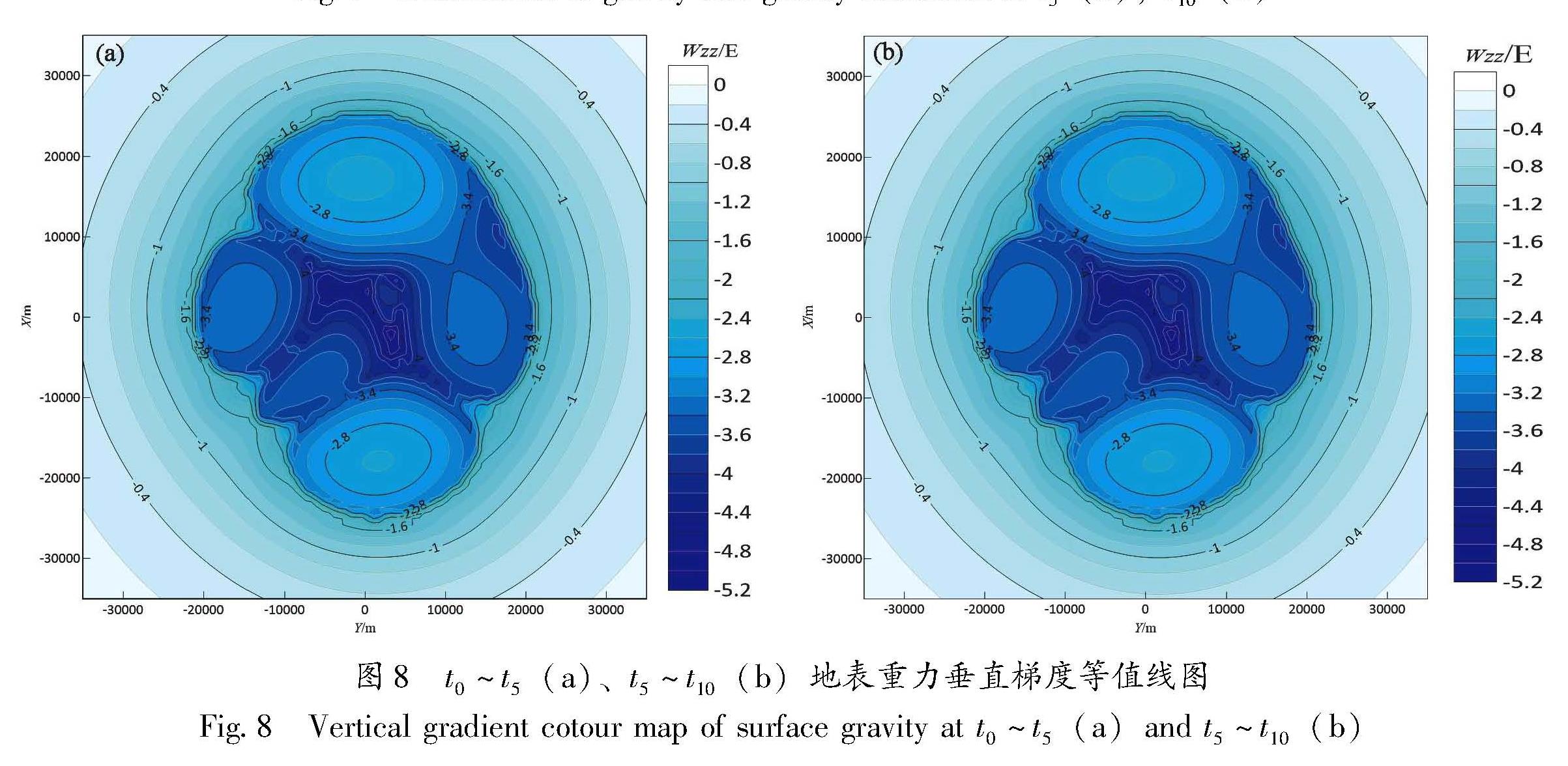
本文计算得到了形变过程中地表介质重力分布。在初始状态(t0时刻),地表未发生形变,密度均匀,其地表重力分布如图6所示。t5时刻,由于板块运动等作用,地表发生隆升形变。t5时刻对应的重力及重力变化情况如图7a所示。从图中可以看出,在山体隆升5 cm所产生的重力差值为-14 μgal。t10时刻,地表隆升形变还在持续,隆升速度与前一个时间段相同,其对应的重力及重力变化值如7b所示。同时,利用式(13)分别计算了在地表隆升过程中(t0~t5,t5~t10时段)山体的地表重力垂直梯度,如图8所示。从图8中可以看出山体的大致形状。在山体地区,重力垂直梯度约为-2.6 E,在山体周围的地区重力垂直梯度较大,约为-5 E。在t0~t5和t5~t10时段山体隆升运动过程中,山体隆升的量级相同,所以在运动过程中所产生的重力变化和重力梯度相同,同时重力变化和重力垂直梯度的空间分布情况同模拟的山体空间分布情况一致,因此导致两次运动过程的重力差值和梯度图像相同。
图6 t0时刻地表重力等值线图
Fig.6 Gravity contours at t0图7 t5(a)、t10(b)时刻重力等值线与重力差值分布图
Fig.7 Distribution of gravity and gravity difference at t5(a),t10(b)图8 t0~t5(a)、t5~t10(b)地表重力垂直梯度等值线图
Fig.8 Vertical gradient cotour map of surface gravity at t0~t5(a)and t5~t10(b)4 结论
本文基于形变与密度变化耦合运动理论,给出了在时变场里重力垂直梯度计算公式的表达形式,并利用直立长方体模型模拟山体在抬升过程中所产的重力变化以及重力垂直梯度的变化情况,主要得到以下结论:
(1)在山体抬升运动过程中,由于形变与密度变化耦合,形变即发生密度变化。因此,利用质量守恒定律所求得的山体密度在海拔高的地区较小。在山体抬升过程中,密度值逐渐减小,观测点与介质的距离逐渐增加,导致重力值逐渐减小。第一个时间段内(t0~t5),地表抬升5 cm,其重力梯度约为-2.6 E。在第二个时间段内(t5~t10),地表隆升5 cm,其重力梯度约为-2.6 E。在整体运动过程中地表隆升10 cm,重力垂直梯度约为-2.6 E,重力梯度分布与山体形态分布相同,重力垂直梯度与静态场重力梯度存在一定的差异,其原因为在重力梯度场里考虑了时间效应。
(2)结合形变与密度耦合定律,模拟计算了在青藏高原隆升时,在密度变化的情况下,所产生的重力变化和重力垂直梯度的变化情况。计算结果显示,青藏高原在两次隆升过程中,重力梯度没有发生变化,重力变化同时受到地表隆升和地下介质变动的影响。在研究青藏高原隆升时所产生的重力变化时,应当考虑密度变化和形变效应的双重影响。
- 陈运泰,顾浩鼎,卢造勋.1980.1975年海城地震与1976年唐山地震前后的重力变化[J].地震学报,2(1):21-30.
- 段虎荣,康明哲,吴绍宇,等.2020.利用 GRACE时变重力场反演青藏高原的隆升速率[J].地球物理学报,63(12):4345-4360.
- 李强,游新兆,杨少敏,等.2012.中国大陆构造变形高精度大密度GPS监测——现今速度场[J].中国科学:地球科学,42(5):629-632.
- 李瑞浩.1988.重力学引论[M].北京:地震出版社.
- 申重阳.2005.地壳形变与密度变化耦合运动探析[J].大地测量与地球动力学,25(3):11-16.
- 申重阳,李辉.2007.研究现今地壳运动和强震机理的一种方法[J].地球物理学进展,22(1):49-56.
- 王嘉沛.2015.地壳变形与密度变化耦合运动引起的重力变化效应研究[D].北京:中国地震局地震研究所.
- 王嘉沛,申重阳,玄松柏.2015.全球地壳模型CRUST1.0在青藏高原东南部的重力检核[J].大地测量与地球动力学,35(4):621-626.
- 邢乐林,王林海,胡敏章,等.2017.时变重力测量确定青藏高原地壳隆升与增厚速率[J].武汉大学学报(信息科学版),42(5):569-574.
- Reilly W I,Hunt T M.1976.Comment on An analysis of local changes in gravity due to deformation by J B Walsh[J].Pure & Applied Geophysics,114(6):1131-1133.
- Walsh J B.1975.An analysis of local changes in gravity due to deformation[J].Pure & Applied Geophysics,113(1):97-106.