基金项目:基于整体物理模型的三维沉积盆地近断层地震效应研究(52178495)资助.
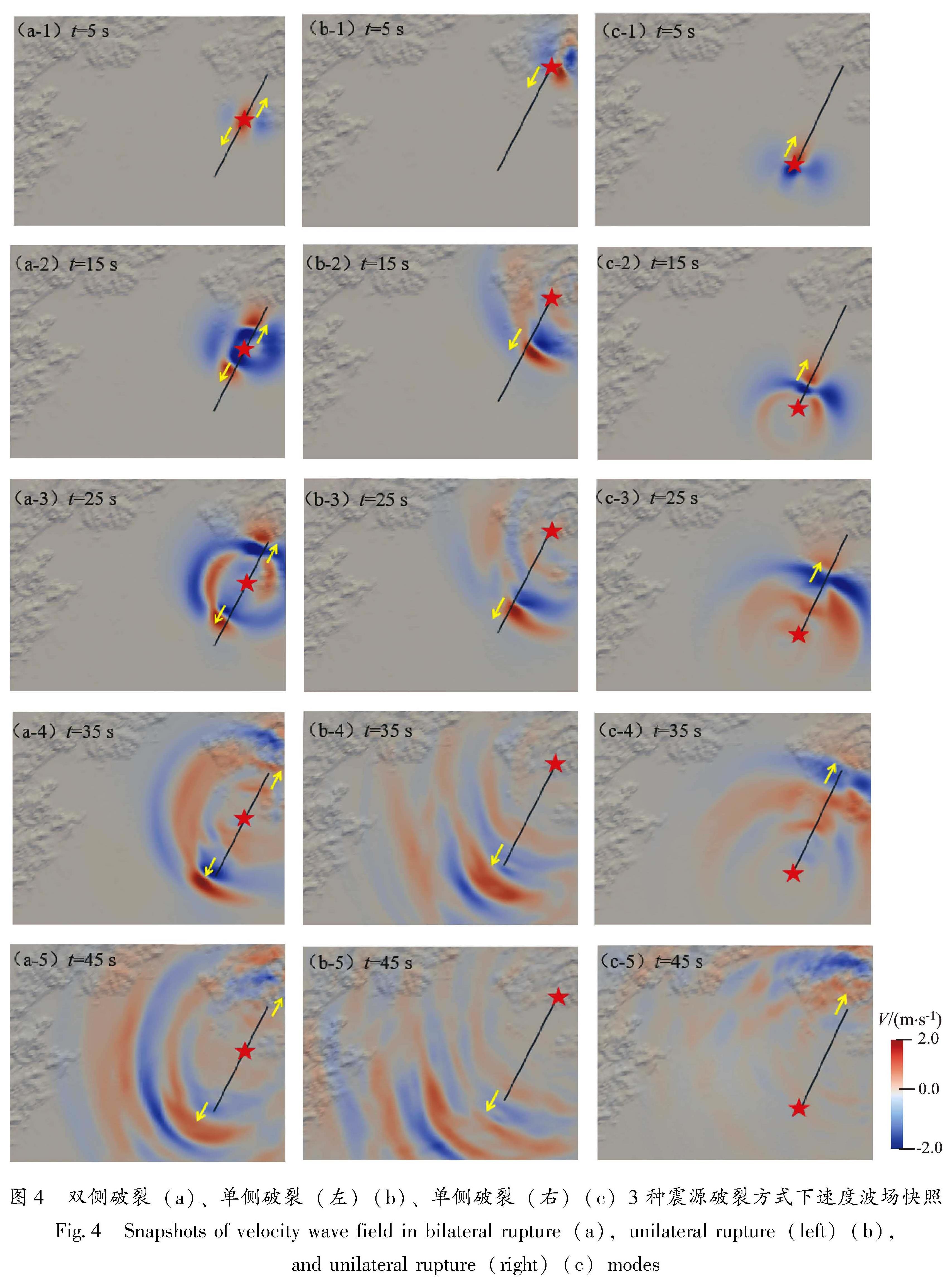
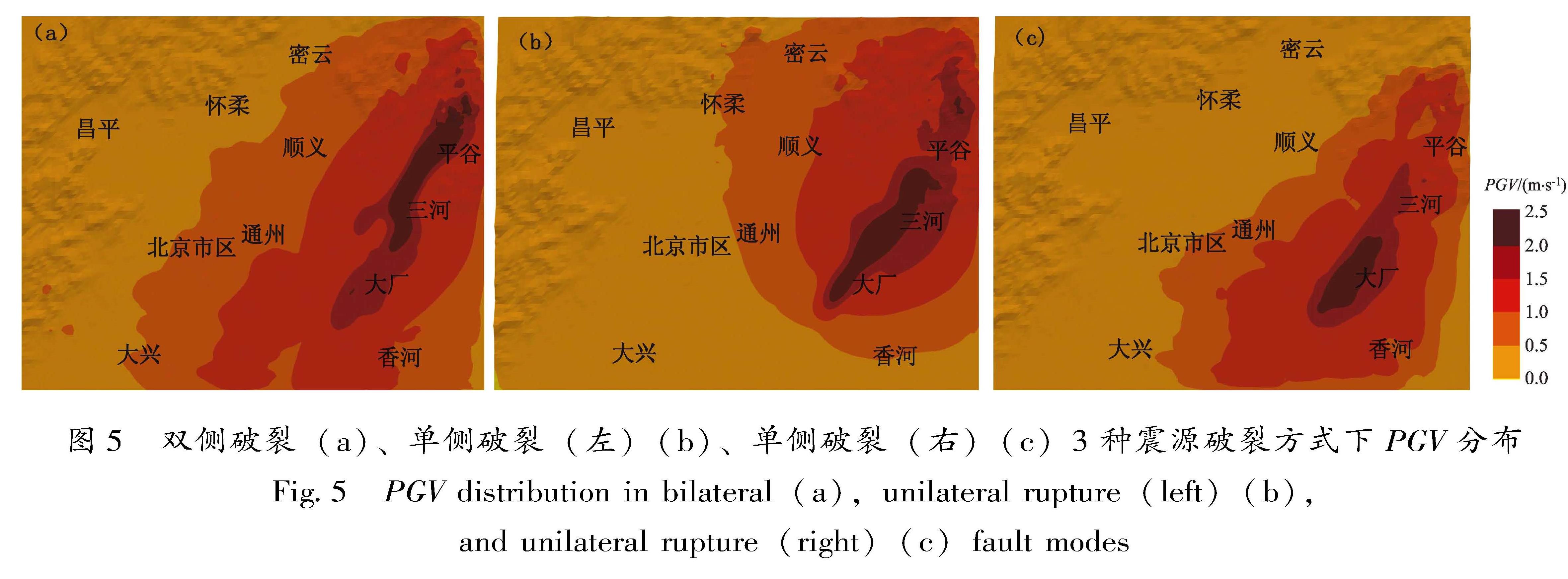
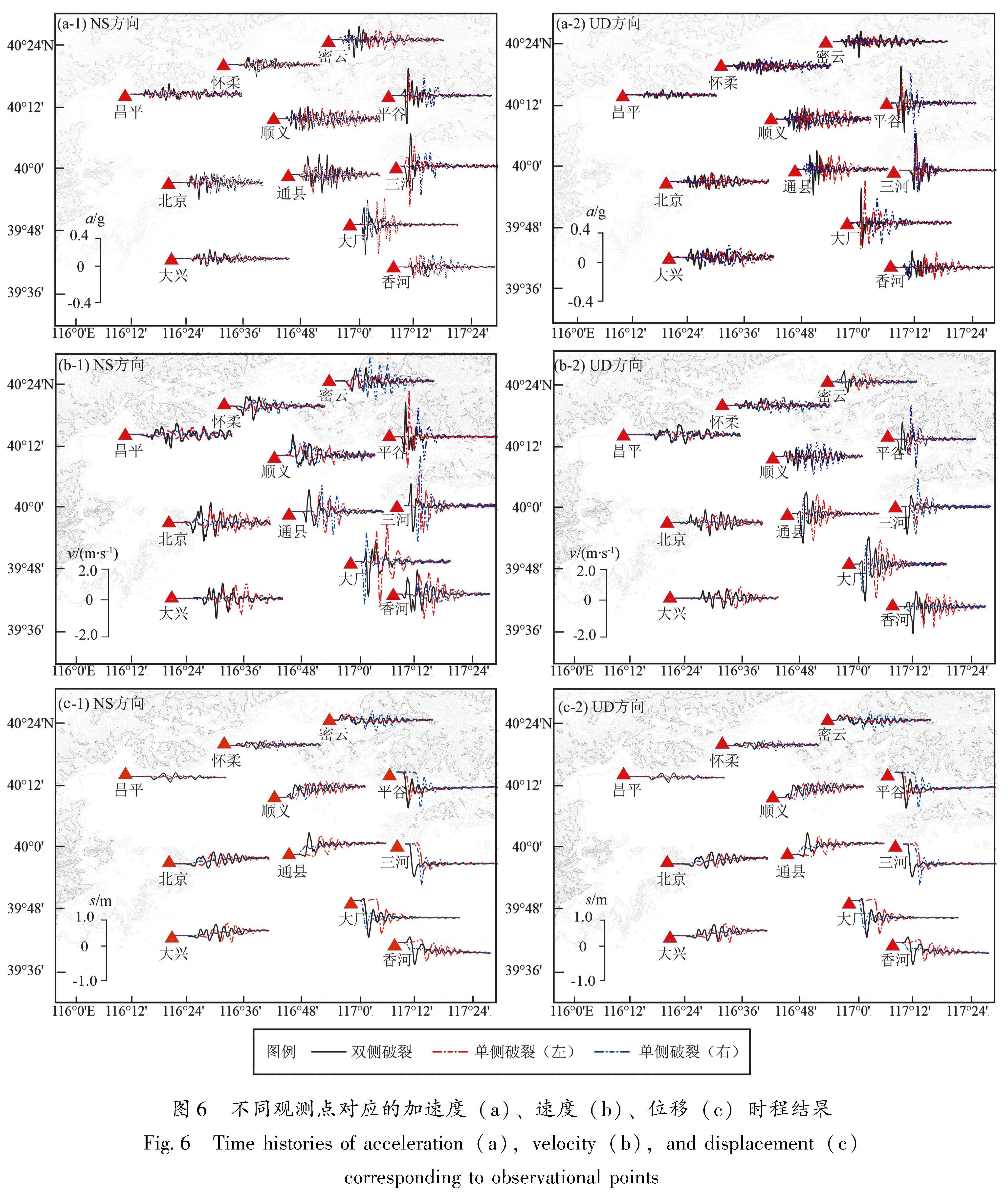
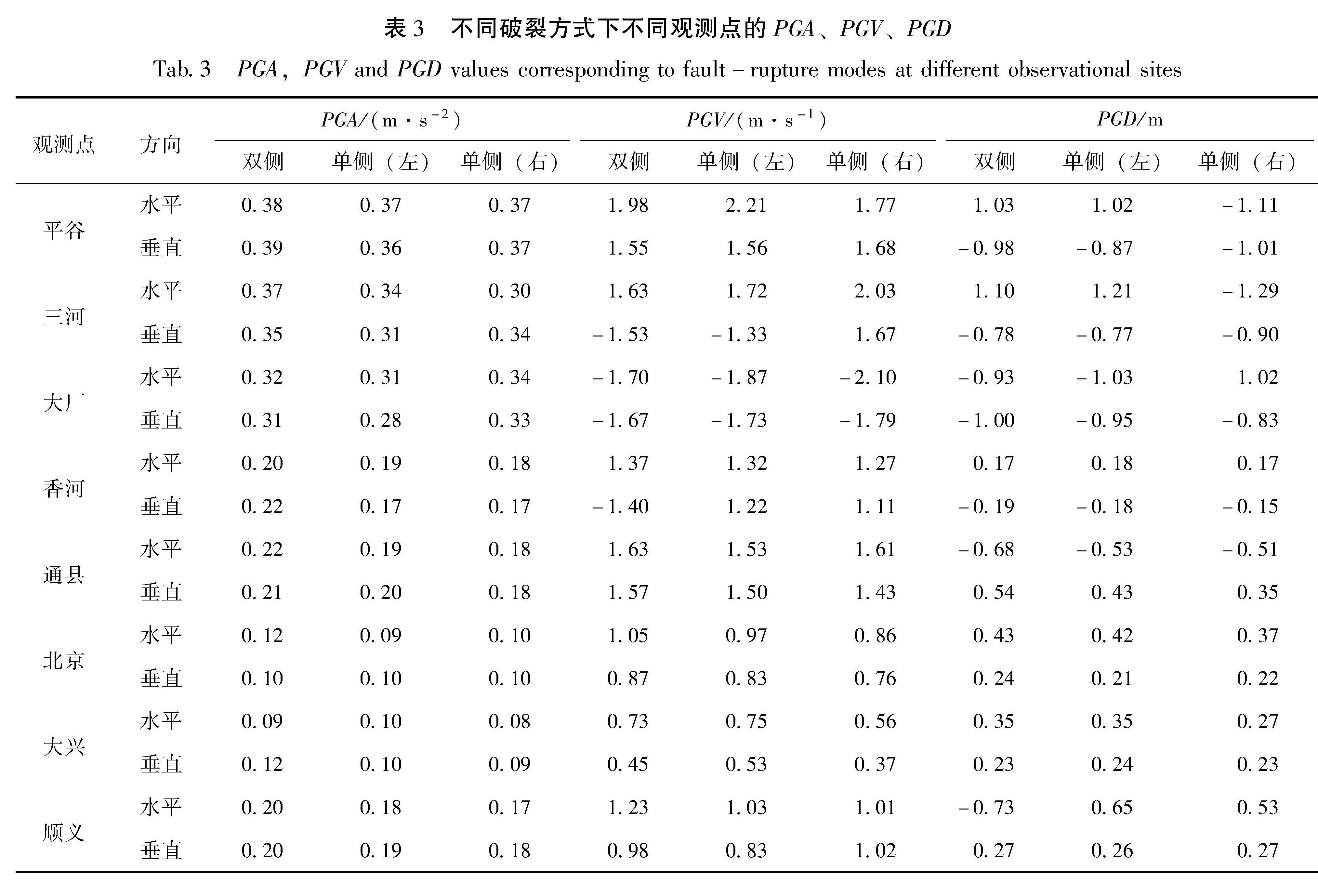
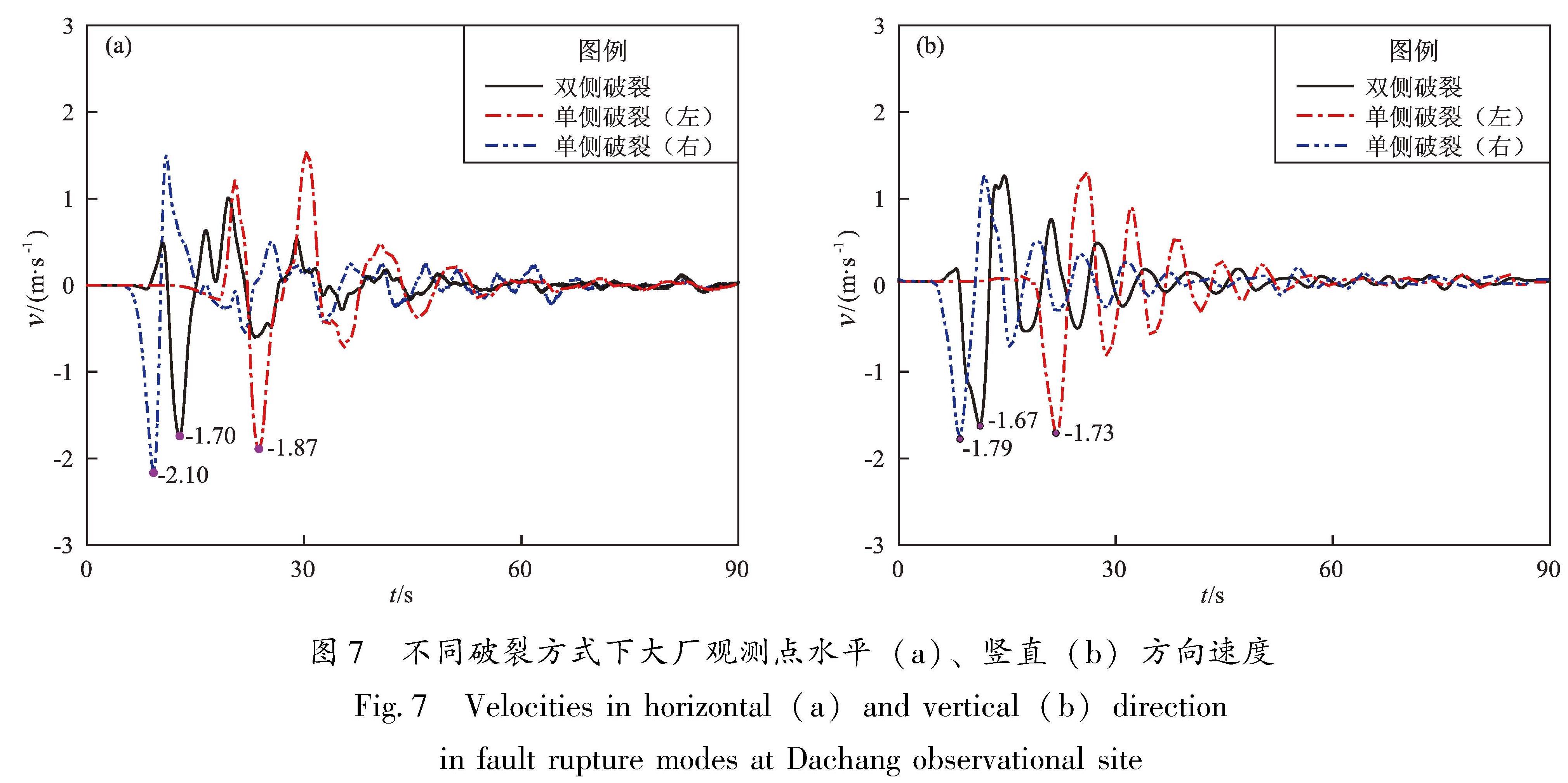
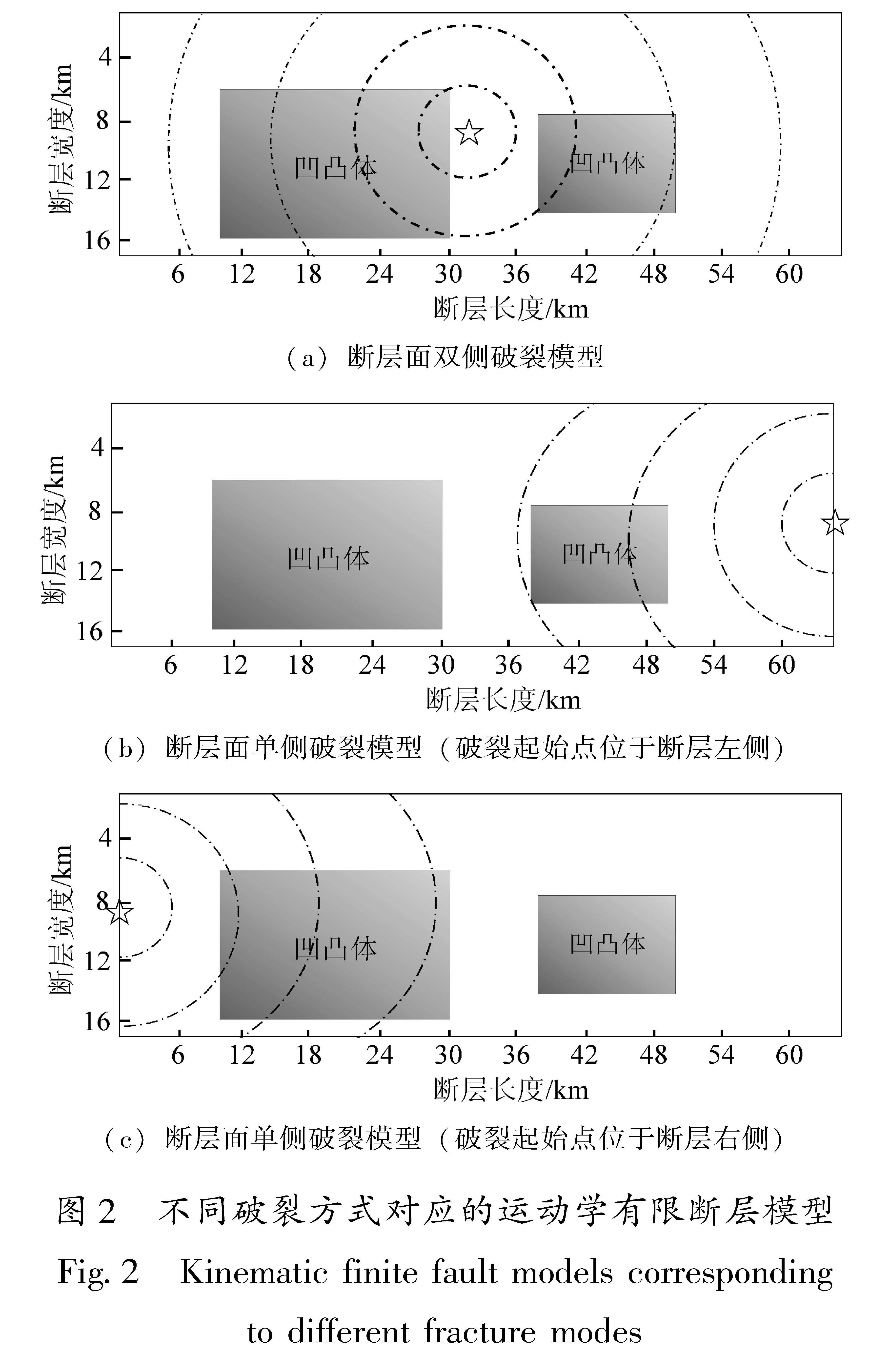
采用谱元法在国家超算中心“天河一号”上模拟了1679年三河—平谷8级地震北京地区强地面运动,开发了适用于谱元法模拟的运动学有限断层震源程序,并依据地面GIS高程数据和地下勘探资料建立了含地表起伏的北京地区精细三维速度结构模型,实现了最高频率为2 Hz的确定性物理模拟。对比双侧破裂和2种单侧破裂情况的模拟结果,重点讨论了破裂方式对强地面运动的影响,结果表明:①三河—平谷地区及附近地区近断层效应明显,北京地区峰值速度总体上呈现“南强北弱,东强西弱”的特征,三河—平谷和大厂地区PGA最高可达0.37 g和0.32 g,平谷、三河、大厂等附近区域加速度峰值明显高于其它地区,为震害分布的主要区域; ②断层破裂方式显著影响地面运动分布情况,双侧破裂与单侧破裂相比,影响范围广且对北京地区威胁最大,北京中心城区PGA和PGV分别达到0.12 g和1.0 m/s; ③断层破裂方式的改变显著影响了观测点速度时程结果,导致观测点震中距发生变化,当震中距减小时观测点速度时程结果对应出现峰值时刻提前、峰值增大以及地震动持时延长的现象,尤其在观测点处存在沉积地形时这一现象则更为明显。
The distribution characteristics of the strong ground motion caused by the 1679 Sanhe-Pinggu earthquake(M8)in Beijing area are simulated by the Spectral Element Method on the TH-1A computer installed in the National Supercomputer Center.In this paper,A kinematic finite fault source program for spectral element simulation is developed,and a 3D velocity structure model of Beijing area is established based on the ground elevation data and the underground exploration data.The kinematic source model is used to achieve a deterministic physical simulation with a maximum frequency of 2 Hz.The simulation analysis of the bilateral fault and two kinds of unilateral faults is carried out,and the influence of the fault mode on the strong ground motion in Beijing area is highlighted.Results show that:①Ground motions in the north and the west part of Beijing is higher than those in the south and the east part.In Sanhe-Pinggu region and its vicinity,the near-fault effect is significant,PGA here is around 0.37 g,PGA in Dachang is 0.32 g,as the main disastrous regions,the peak acceleration in Pinggu,Sanhe and Dachang is significantly higher than those in other areas.②The fault rupture mode significantly affects the distribution of ground motion,and the scope of influence of the the bilateral rupture is wider than that of the unilateral rupture,which poses the greatest threat to Beijing area.The peak acceleration and the peak speed in central Beijing can reach 0.12 g and 1.0 m/s respectively.③The change of fault rupture mode significantly affects the velocity time history of the observational results,and also changes epicentral distance.When epicentral distance decreases,the peak ground motion appears earlier,the peak value increases,and the duration of ground motion is prolonged.This phenomenon is more obvious when sedimentary topography exists at the observation point.
![图3 北京地区地质构造界面(a)和三维速度结构模型(b)<br/>Fig.3 Geological interfaces(a)and 3D velocity structure model(b)in Beijing area[HJ2mm]](2022年03期/pic177.jpg)