基金项目:中国地震局地震科技星火计划(XH200403Y)、山西省科技厅面上青年基金(201901D211548)、中国地震局地质所国家野外站研究课题(NORSTY2021-01)、山西省科技攻关项目(20140313023-1)、山西省应用基础研究计划(201801D121030)和国家自然科学基金(41874053,42030108)联合资助.
(1.山西省地震局,山西 太原 030021; 2.信阳市生态环境局光山分局,河南 光山 465450)
(1.Shanxi Earthquake Agency,Taiyuan 030021,Shanxi,China)(2.Guangshan Branch of the Xinyang Ecological Environment Bureau,Guangshan 465450,Henan,China)
Coulomb stress; stress triggering; effective coefficient of friction; the Datong-Yanggao earthquake swarm
DOI: 10.20015/j.cnki.ISSN1000-0666.2022.0053
备注
基金项目:中国地震局地震科技星火计划(XH200403Y)、山西省科技厅面上青年基金(201901D211548)、中国地震局地质所国家野外站研究课题(NORSTY2021-01)、山西省科技攻关项目(20140313023-1)、山西省应用基础研究计划(201801D121030)和国家自然科学基金(41874053,42030108)联合资助.
引言
1989年10月19日山西大同—阳高发生5.9级地震,它不仅是华北第四活跃期(1815年平陆63/4级地震至今)山西地区发生的最大地震,也是山西地区有史料记载以来最大的震群型地震。5.9级地震前2小时4分发生5.7级地震,震后又有多个5级以上地震发生,最大地震震级5.6,与5.9级地震相隔仅1小时19分。1991年3月26日、1999年11月1日和 2010年4月4日在原震中区又先后发生了5.8级、5.6级、ML5.0地震序列,且微震时有发生。多位学者研究发现,大同—阳高震区小震的发生对山西断陷带乃至晋冀蒙交界地区中强地震具有较好的震兆指示作用(啜永清,1995,1999; 啜永清等,1999; 大同—阳高地震烈度宏观考察组,1991),称为“地震窗口”效应,这成为监视该区域中强地震的有效手段。值得关注的是,自1999年11月1日大同阳高5.6级地震后,晋冀蒙交界地区5级以上地震持续平静21年,远超1950年以来最长平静时间间隔。2019年以来该地区先后出现地震条带、地震空区、小震活动增强等一系列异常现象①②③,地震危险性进一步增大。
针对大同—阳高地区中强地震序列,诸多学者开展了震群频次映震能力、序列衰减活动(啜永清,1995,1999; 啜永清等,1999; 王霞,宋美琴,2017)、地壳介质品质因子和视应力(王霞,宋美琴,2017; 王霞等,2017a,b)、地震重定位和发震构造(冯永革等,2016)、地震分布与深部速度结构关系(徐扬等,1997; 张成科等,1998; 靳玉科等,2010; 胥鸿睿,2018; 王霞等,2019)等研究。但由于该震群的断层参数、背景地震活动性、主震的震源特性等存在着很大的不确定性,因此地震序列之间的相互作用关系仍不清楚,人们对其发震断层的特征、地震间的相互作用和触发机制以及发震机理的认识还存在很大不足,直接影响了对该地区地震危险性评估的准确性。
目前,学者们主要通过库仑破裂应力的变化来研究不同地震之间的相互关系,确定潜在的地震危险性。Stein等(1997)和Nalbant等(1998)通过计算土耳其和北爱琴海地区的强震静态库仑应力并基于应力转移计算其发震概率,认为土耳其伊兹米特地区为强震发生的高概率区域。1999年伊兹米特发生了7.4级地震,其研究结果得到了验证。基于地震破裂引起的静态库仑破裂应力变化分析余震序列分布、地震应力触发关系已经在很多震例中得到了应用(Toda et al,2002,2008; Lin,Stein,2004; Freed,2005; 万永革等,2008,2009; 单斌等,2013; 靳志同等,2019; 黄禄渊等,2019)。对断层上地震的相互触发的分析(Shan et al,2008,2013a,b)以及主震对余震的触发影响等的分析(Shan et al,2011), 在认识地震序列的发震机制以及可能的地震危险性方面发挥了重要作用。
1989 年大同—阳高震群已过去多年,观测资料相对不足,其发震构造和地震之间的相互关系研究也很少,对其发震构造和地震危险性了解较为薄弱。冯永革等(2016)利用库仑应力触发关系给出了1989年大同—阳高5.7级、5.9级和5.6级3次地震可能的破裂模型,但是由于没有分析断层的参数,以及地震的破裂方向和特征,难以对该震群的触发关系进行定量探讨。鉴于此,本文首先从静态库仑应力作用来研究1989年大同—阳高震群的多次中强震的应力触发关系,进一步分析其破裂方向与破裂特征,进而探讨该区域多次中强震应力触发、应力对震群活动的影响、发震的物理机制等。
1 区域地震地质背景及震群分布
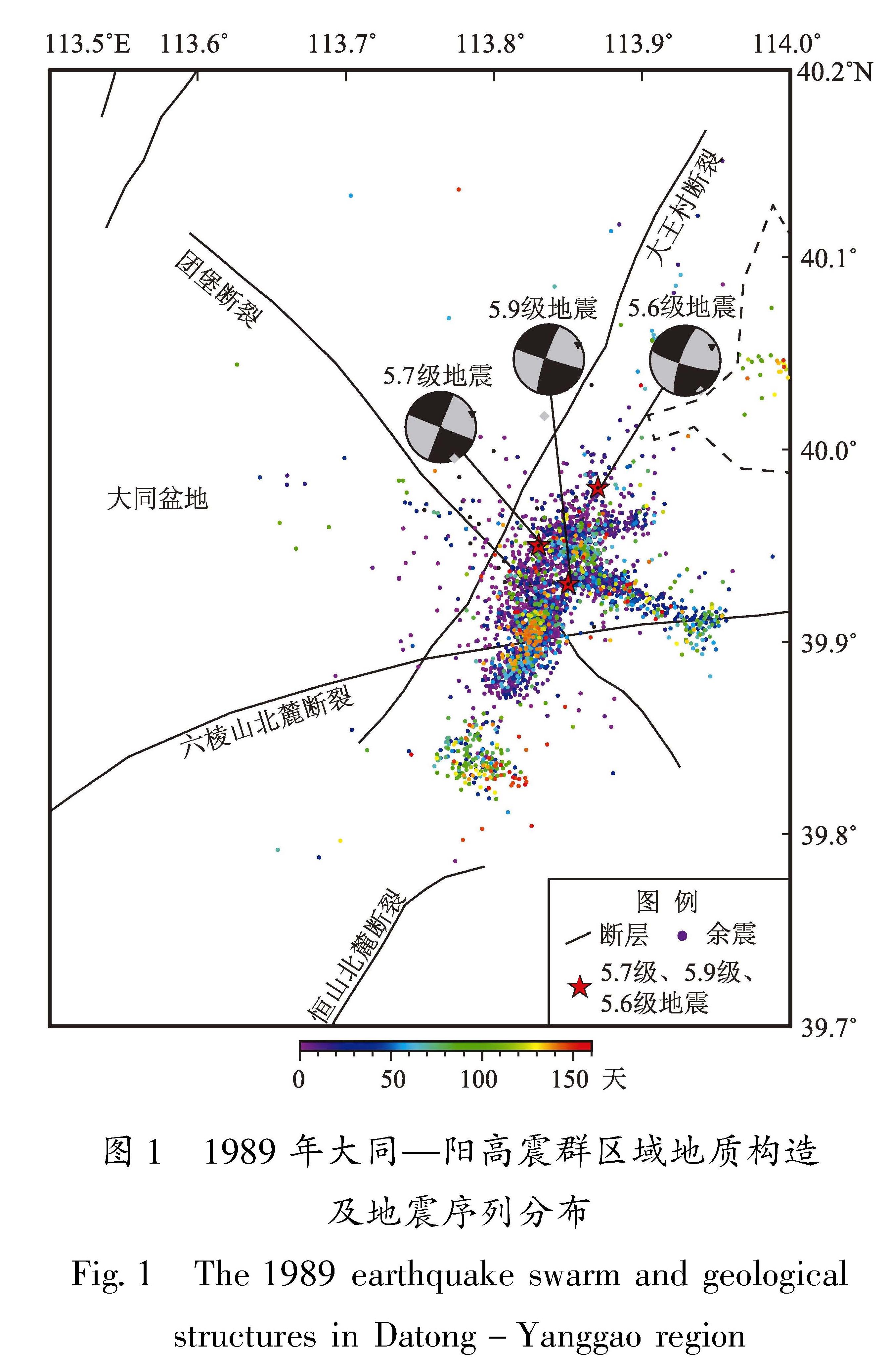
1989年大同—阳高震群活动位于汾渭裂谷北部的大同盆地,控制盆地的主要边界断裂有口泉断裂、恒山北麓断裂、六棱山北麓断裂、阳高—天镇断裂。该震群发生在大同盆地东侧控盆断裂——六棱山北麓断裂与盆地内次级断裂(团堡断裂和大王村断裂)的交汇处(图1)。其中六棱山北麓断裂全长150 km,为总体走向NEE、倾向NW、倾角70°左右的正断层; 团堡断裂为全长约50 km,走向NW40°,倾向NE或SW的高倾角正断层; 大王村断裂全长约48 km,总体走向NE45°,倾向SE,倾角60°~70°。1989年大同—阳高5.9级地震的发震断层为大王村断裂,5.7级和5.6级地震的发震断层为团堡断裂(山西省地震局,2004)。
1989年大同—阳高震群重定位和震源机制解综合研究结果显示(Zhuo et al,2019):该序列成椭圆形分布,其椭圆主轴走向为NE 22.5°,与宏观地震破坏考察结果一致(大同—阳高地震烈度宏观考察组,1991); 震群震源机制解主要节面走向为NE 17.6°~24.7°,与震中序列椭圆主轴走向相吻合。大同—阳高震群所处的山西地区北段现今震源机制解的张应力轴方位为NW 20°~40°,与卫星影像获得的晚新生代以来山西地区南段和北段的伸展方向(NW 15°~40°)一致(Zhuo et al,2019),表明晚新生代至今山西地区北段的构造运动一直受到稳定的区域应力场控制。这与山西省地震局(2004)由震源机制解推断的大同—阳高地震的震源应力场一致,即主压应力轴平均为NE 70°,主张应力轴平均为160°,应力轴仰角接近水平,受控于水平应力场作用,震源错动为走滑方式。
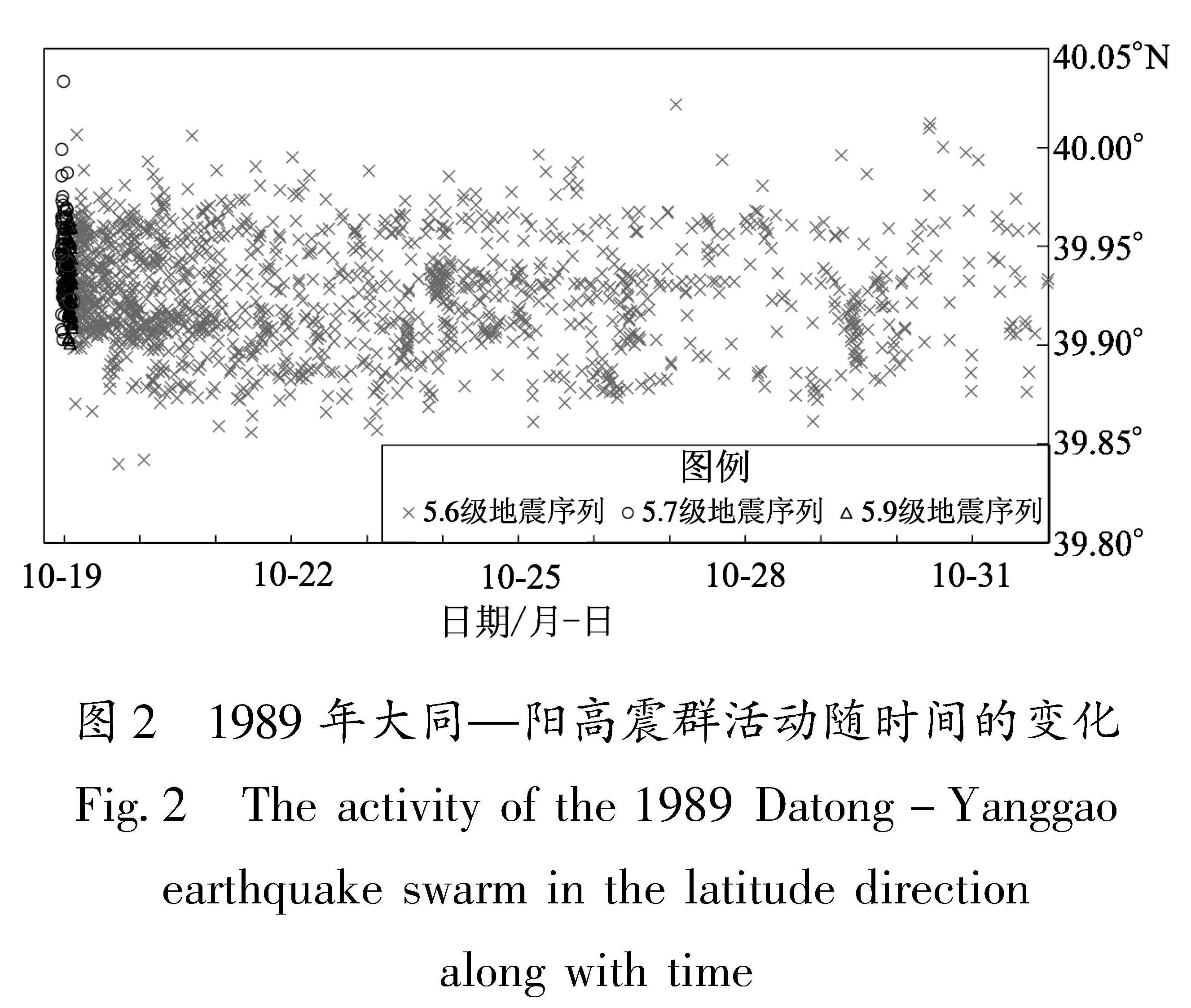
精确定位结果显示大同—阳高震群序列主体呈NE向分布,后期少部分序列呈NWW向分布(宋美琴等,2012)(图1)。为便于表述这3次地震后后续小震的时空演化特征,本文将5.7级地震至5.9级地震间发生的小震称为5.7级地震序列,5.9级地震到5.6级地震间发生的小震称为5.9级地震序列,5.6级地震之后的小震称为5.6级地震序列。由图2可见,5.7级地震序列以5.9级地震序列为中心沿NE向两侧发育,5.6级地震序列则向外围有所扩散,与山西省地震局(2004)判定的序列优势方向一致,序列精定位
图1 1989年大同—阳高震群区域地质构造及地震序列分布
Fig.1 The 1989 earthquake swarm and geological structures in Datong-Yanggao region图2 1989年大同—阳高震群活动随时间的变化
Fig.2 The activity of the 1989 Datong-Yanggao earthquake swarm in the latitude direction along with time结果及时空演化过程为判定发震断层、确定触发关系提供了基础参考。
2 研究方法及参数选取
2.1 研究方法本文基于实验室的岩石破坏库仑破裂准则(Jaeger et al,2009)计算库仑应力:
CFS=τ+μ(σn -p)(1)
式中:CFS为库仑应力; τ和σn分别为断层面上的剪应力和正应力,拉伸为正、压缩为负; μ为岩石摩擦系数; p为流体孔隙压力。静态库仑应力的变化表达式为:
ΔCFS=Δτ+μ'Δσn(2)
式中:ΔCFS为库仑应力变化量; Δτ和Δσn为断层面上的剪应力变化量和正应力变化量,方向与上述的正应力方向的定义相同; μ'为有效摩擦系数。当计算值为负值时,表示该应力变化抑制断层的破裂,发生地震的可能性降低,此区域称为应力影区; 相反则促使断层破裂,则可能触发地震,地震发生的危险性增大。
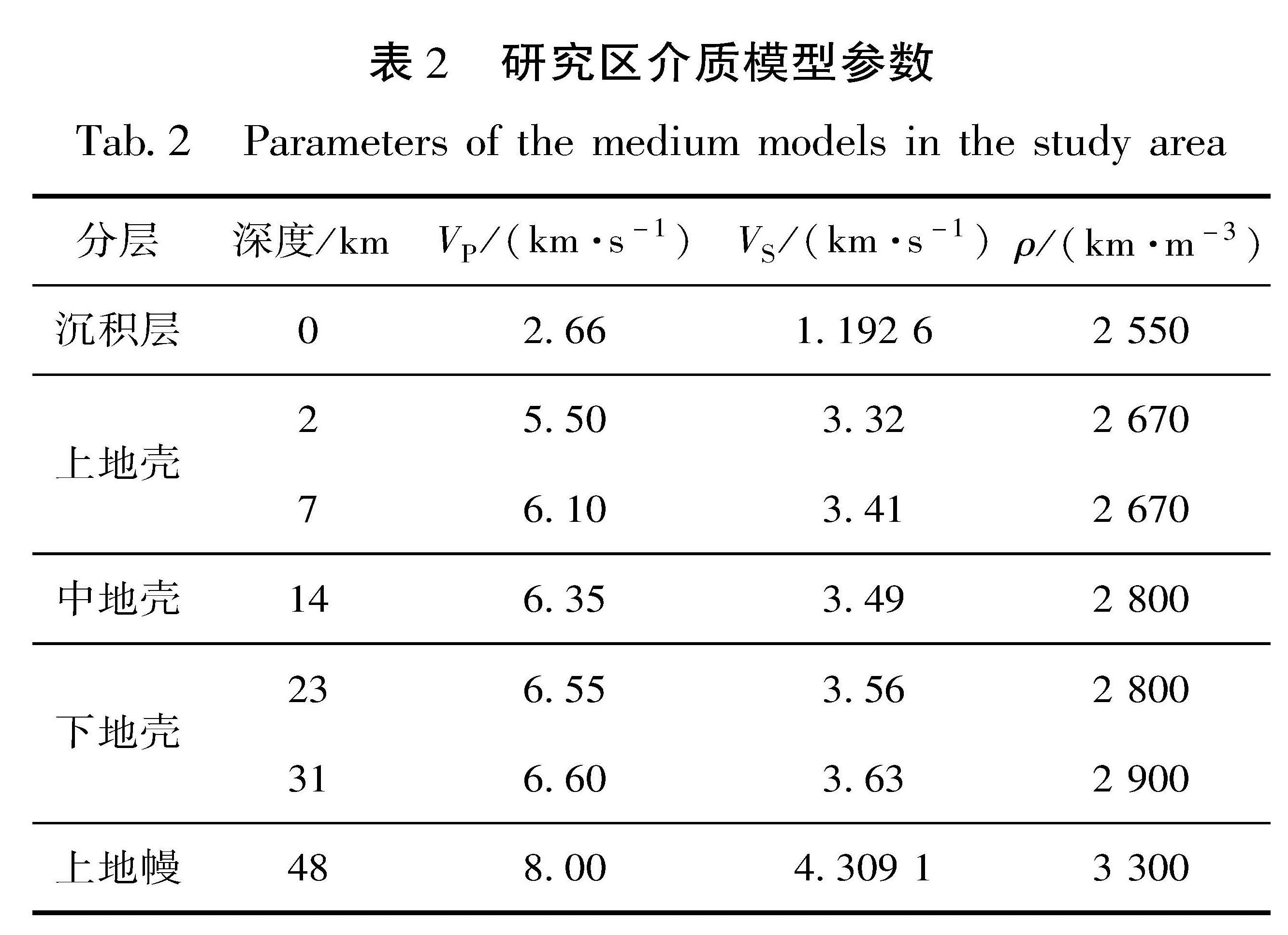
2.2 地震破裂参数由于大同—阳高震群的3次M>5.5地震的时间间隔约为2 h(表1),因此本文选取弹性层地壳结构来研究其同震库仑应力。本文综合考量该区域多个研究结果给出的流变学参数,来确定合理的层状模型(表2)。在库仑应力计算过程中,有效摩擦系数μ' 的选取主要考虑了两点:一是结合前人研究结果,逆断层相比走滑断层对正应力变化更敏感,逆断层取μ'>0.4,走滑断层取μ'<0.4(Freed et al,2007),考虑到研究区断层多数是正断兼走滑型,本文选取中间值μ'=0.4进行测试; 二是根据已有研究的经验取值(Li et al,2015; 石富强等,2020)。由于μ'对库仑破裂应力影响比较大,本文对比分析低(μ'=0.1)、中(μ'=0.4)和高(μ'=0.7)3种不同摩擦系数情况下的库仑应力变化。
大同—阳高震群的3次M>5.5地震的断层破裂参数参考龙锋等(2006)方法,通过定位精度较高的序列分布并结合烈度区展布综合分析得到(表1),
表1 1989年大同—阳高震群的3次地震的震中及破裂参数
Tab.1 Parameters of the 3 large earthquakes in the 1989 Datong-Yangao sequence5.7级和5.6级地震的地震矩来自CMT的结果,5.9级地震的地震矩来自刘瑞丰等(1995)的结果,通过地震矩张量公式M0=μLS计算出平均位错,见表3。
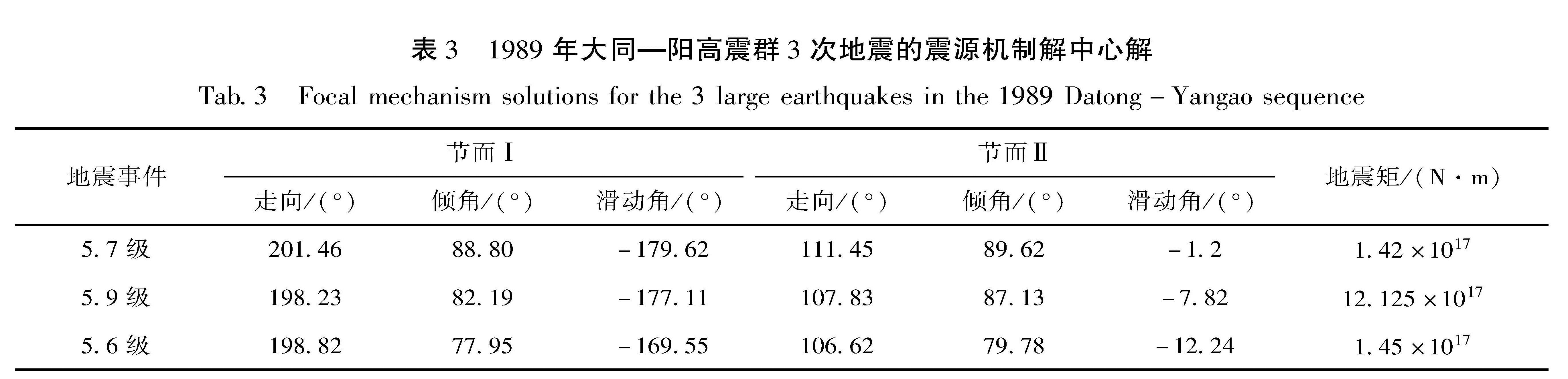
本文分别收集了不同机构和学者测定的1989年大同—阳高震群的3次M>5.5地震的震源机制解,分别为6、7、6个。为了从上述多个震源机制解中确定一个合适的震源参数进行后续分析,本文应用万永革(2019)的方法获取由多个震源机制解来确定中心解,结果引自王霞等(2021)的研究结果(表3)。
3 研究结果
基于前文的发震断层面、介质层状模型等参数,本文采用PSGRN/PSCMP程序(Wang et al,2006)计算了大同—阳高震群3次M>5.5地震所引起的静态同震库仑破裂应力变化。
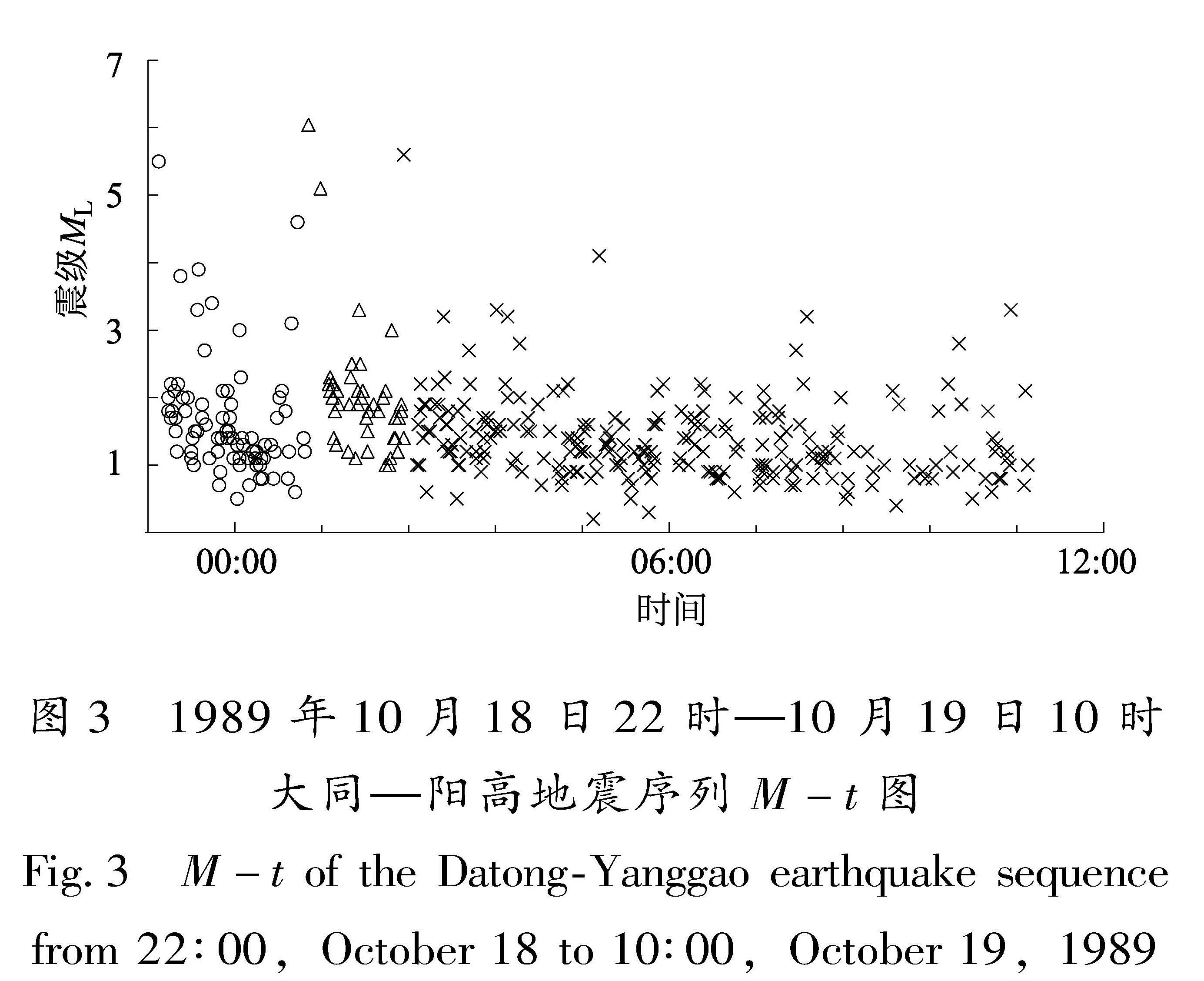
从表1可见,3次地震的发震时间间隔约为2 h,5.7级和5.9级地震序列地震偏少(图3),但仍可以看出总体序列优势分布方向呈NE向,仅有少部分小震分布在NW向。5.9级地震的发震断层为NE向大王村断裂(山西省地震局,2004),而5.7级地震序列的地震数量偏少难以判断其发震断层走向,5.6级地震序列难以与5.9级地震序列区分,也很难判断其发震断层走向; 由于震源机制解的共轭性质,也难以判断发生在哪一个断层走向上。因此,本文假定NE向
图3 1989年10月18日22时—10月19日10时大同—阳高地震序列M-t图
Fig.3 M-t of the Datong-Yanggao earthquake sequence from 22:00,October 18 to 10:00,October 19,1989或NW向都可能是发震断层走向,分别计算了5.7级地震的NE向破裂和NW向破裂对5.9级地震的同震静态库仑应力作用,以及5.9级地震的NE向破裂对5.6级地震的NE向和NW向接收的同震静态库仑应力效应。
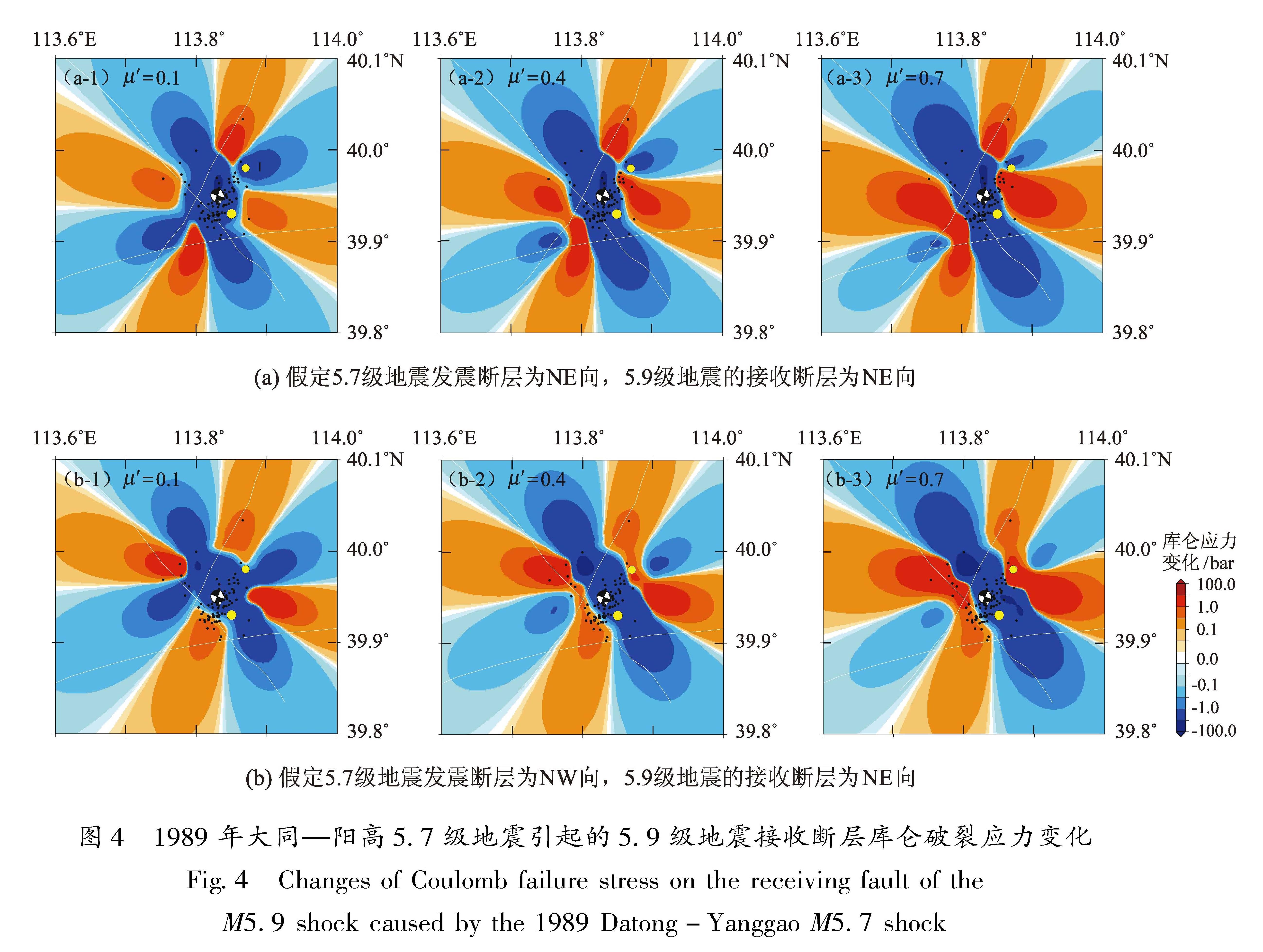
3.1 5.7级地震对5.9级地震同震静态库仑应力本文以表3中5.7级地震的两个节面参数分别作为破裂面进行计算。5.7级地震发生后,其后的小震序列震源深度平均值约为10 km,因此计算5.7级地震的10 km深处对其周围应力场的同震静态库仑应力作用。为了对比分析断层μ'对库仑破裂应力的影响,分别计算了μ'为0.1、0.4和0.7时5.7级地震对周边断层的影响,结果如图4所示,图中震源机制解为5.7级地震,黄色圆圈分别为5.9级地震和5.6级地震。
由图4可知,对于5.7级地震,μ'造成的库仑应力变化并不大,只是在序列南部和北部部分库仑应力减小区域变成增强区域。总体来看,不论μ'取值如何,在选取NE向的节面Ⅰ为5.7级地震破裂面时,序列中绝大多数小震都位于库仑破裂应力影区,其后2 h内只有9%左右的地震位于应力增强区; 而以NW向的节面Ⅱ为破裂面时,情况有较大变化:当μ'=0.1时,只有小部分地震位于库仑应力增强区; 当μ'≥0.4,超过30%的地震分布在库仑应力增加区; 当μ'=0.7时,地震分布比μ'=0.4时更接近库仑应力增强区。以上表明5.7级地震为NW向破裂可能性大,这与冯永革等(2016)认为5.7级地震的发震断层走向更有可能是NWW方向的认识比较一致。
3.2 5.9级地震对5.6级地震同震静态库仑应力在5.9级地震发生后1 h,又发生了5.6级地震和一系列中小地震,理清二者的关系是认识震群发震过程和应力传输的关键。由于5.6级地震序列的分布走向不明显,利用震源机制难以确定其哪一个节面为发震断层,因此本文分别以5.6级地震的两个节面参数作为发震破裂面,并以此作为接收断层,计算5.9级地震对5.6级地震的库仑破裂应力。宋美琴等(2012)研究表明,5.9级地震后的小震序列震源深度平均值约为14 km,因此本文计算5.9级地震的14 km深度上同震静态库仑应力作用,分别计算了μ'为0.1、0.4和0.7时库仑应力的变化情况(图5)。
图5表明,不同μ'对5.9级地震引起的库仑应力变化有较明显的影响。当μ'较小时,无论接收断层的走向取NE还是NW向,5.9级地震后的序列展布与库仑破裂应力变化的分布相似性都相对较低(图5),西南和东南象限的一部分地震在库仑应力增强区,但有很大一部分地震处在库仑破裂应力的影区。随着μ'的增加,分布在库仑应力增强区的地震数目明显增多。因此,和5.7级地震引起5.9级地震区域的应力场改变的情况一样,随着接收断层的μ'增高,地震序列分布与库仑破裂应力的变化趋势更为吻合。因此,可以推测认为该区域的断层μ'比较高,在0.4以上。当μ'=0.4时,5.6级地震以NE向的节面Ⅰ为接收断层时,5.9级地震对其后序列触发比例为28%; 以NW向节面Ⅱ为接收断层时,5.9级地震对其后序列的触发比例为25%(图5)。触发比例低的原因可能是多数小震集中在5.9级地震附近,落在5.9级地震破裂影区内; 由于触发比例相近,且存在5.9级和5.6级地震发震间隔较近、定位精度以及共轭断裂的活动方式等问题,难以通过静态库仑应力的方法判断其破裂面。无论哪个节面作为接收断层,5.6级地震均落在5.9级地震破裂产生的库仑应力正负值边界附近。
5.7级、5.9级、5.6级地震序列随时间变化结果(图2)显示:3次序列均为以5.9级地震为中心,沿NE走向的大王村断裂向SW和NE两侧扩展,为双侧破裂特征; 可能是由于共轭断裂相交处应力水平最高,远离交叉点的地方其应力也逐渐递减,即3次地震位于相交处,因此其后续地震多数向两侧扩展; 但距离5.9级地震1个月后发生的一小部分地震序列呈NWW向分布(图1)。这与5.9级地震的同震库仑应力形成的加载区沿NE向的大王村断裂走向、NWW向加载区较为一致,部分地震序列落在加载区内。
4 讨论
4.1 大同—阳高震群同震库仑应力触发作用库仑破裂应力随5.9级地震和接收断层的走向以及μ'的大小变化而变化,通过研究发现:①随着μ'的增大,有更多的地震分布在库仑破裂应力增强区,表明该区域5.9级地震和5.6级地震的发震断层的μ'比较大,应该在0.4以上; ②从5.7级地震序列和库仑破裂应力分布来看,5.7级地震的发震断层取NW向时,吻合度明显提高,结合冯永革等(2016)的研究结果,认为5.7级地震的发震断层为NW走向比较合理; ③5.9级地震对5.6级地震有明显的触发作用,μ'取0.4时,有25%以上的5.9级地震序列分布在库仑应力增加区,且当μ'增大时,分布在库仑应力增加区的地震数量增多,其中NWW向序列分支落在其中一个库仑应力加载区中心; 其余没发生在应力增加区的地震,主要发生在5.9级地震的破裂区附近,此时其后的地震序列的发生与库仑应力变化关系不是很大; 因此,5.9级地震对5.6级地震的触发作用比较明显。
由于5.6级地震后的小震分布在两条明显的共轭断层上,因此接收断层的走向取NW和NE方向,但结果差别不明显。两个共轭断层上分布的地震多数都发生在库仑应力增强区,据此认为5.9级地震还是对两条共轭断层上的地震有触发作用。
5.7级地震的库仑应力变化与5.9级地震序列的对应性不高,虽然5.7级地震发震断层采用NW走向时,有部分地震分布在应力增强区,但整体上多数地震还是发生在应力影区。造成这种情况可能主要有两个原因:① 5.7级和5.9级地震发震时间(约2 h)和震中位置间隔(约2.8 km)均很近,因此,很多地震受5.7级地震同震破裂应力变化的影响更大,主要发生在5.7级地震震区附近,而距离5.9级地震一定距离的地震还未被触发; ② 5.7级地震的震级较小,应力改变量不是很大。因此,不能简单认为5.7级地震对5.9级地震无明显触发作用,而是受限于时间和空间的分布。
大同—阳高震群5.7级地震和5.9级地震对后续地震序列的总体触发比例不高,一方面可能是因为后续地震序列主要分布在这两次地震的震源区附近,大部分地震发生在库仑应力卸载区; 另一方面是地震的触发机制比较复杂,5.9级地震的应力触发、震后余滑、震后中下地壳介质黏弹性松弛效应等因素有关(Hill et al,1993; Freed et al,2007; Perfettini,Avouac,2007; 贾若,蒋海昆,2014; 朱琳等,2021),如贾若和蒋海昆(2014)发现汶川地震主震破裂面上有约50%的余震活动可能与震后余滑及黏弹性松弛等因素有关,Perfettini 和Avouac(2007)对1992年美国加州Landers地震也有类似的认识。因此1989年震群对后续地震活动的影响因素应结合黏弹性、震后余滑等进一步探讨。
4.2 大同—阳高震群同震库仑应力触发机制2019年发生美国南加州Ridgecrest MW7.1地震,主震震前34 h的MW6.4前震为左旋走滑性质,对右旋走滑的主震起到触发作用,表明静态库仑应力在正交断层系统破裂中发挥重要的作用(William et al,2019)。余震呈“L”型分布,前震以NE向展布为主,主震以NW向展布为主,且地震序列分布总体以NW向为主,这可能受控于其地质构造动力过程。在加州的右旋板块边界作用下,右旋断层比左旋断层积累和释放剪应力更快,且初始应力显示左旋断层比右旋断层的屈服应力水平低。2次地震破裂时间接近,表明两条断裂已经接近破裂水平,且屈服应力较低的断层先发生破裂,破裂产生的应力变化促使屈服应力高的断层趋于不稳定而破裂(Lozos,Harris,2020),MW6.4前震NE向左旋走滑,触发MW7.1主震NW向右旋走滑。类似正交断层活动的还有1987年美国加州Superstition Hills地震序列,先发生MW6.2前震,后发生MW6.6主震,形成“L”型分布余震特征; 2012年印度洋序列、日本等地区均有类似现象(Zachary et al,2019)。
大同—阳高震群的5.7级地震和5.9级地震的同震静态库仑应力结果显示,5.7级地震更可能是NW向左旋走滑,5.9级地震右旋走滑,两次地震的发震断层呈共轭活动特点,从而触发了后续地震。3次地震的时间间隔约为2 h,根据2019年美国加州Ridgecrest MW7.1地震和其他地区类似地震的触发机制,推测大同—阳高震群的发震断层接近破裂临界水平,在NE向挤压和NW向拉张的区域应力场控制下,先发生NW向破裂,随后触发NE向破裂,且以NE向破裂为主,并在NE向区域主压应力的控制作用下,发生了大同—阳高震群。
4.3 大同—阳高震群发震过程由大同—阳高震群3次M≥5.5地震的多个震源机制解确定的中心解结果(表3,图1)可见,这3次地震的震源机制解均为走滑型,且基本一致,5.7级地震节面走向为NW向的左旋走滑,5.9级地震节面走向为NE向的右旋走滑,可能为同一的构造应力场作用下的近乎原地复发的多个地震的共轭错动方式。结合震源位置、发震顺序和序列时空演化特点,推测认为5.7级地震发生在NW向团堡断裂上,经过短暂应力调整后进入相对平静期(序列不发育),破裂过程中触发了相交的NE向大王村断裂,继而引发了5.9级地震,在同一构造应力场的作用下,NE向地震破裂面在后续长时间的应力调整过程中引发了一系列余震(余震序列主体为NE向),与冯永革等(2016)提出的前震沿NWW向发生左旋破裂、5.9级地震和5.6级地震沿NNE方向发生右旋破裂的模型基本吻合。另外,由于山西地堑总体呈NE向延伸,这与其区域应力场作用密切相关,而大同—阳高震群正是在此区域应力场控制作用下发生,因此震群活动主体优势展布方向也呈NE向。
5 结论
基于1989年大同—阳高震群的3次M>5.5地震的震源破裂参数,本文对比研究了5.7级地震的2个节面对5.9级地震断层面上库仑应力变化的影响,以及5.9级地震对5.6级地震震源机制解不同节面上引起的库仑应力变化,主要得出以下结论:
(1)发震断层的走向对库仑破裂应力变化影响较大,综合库仑破裂应力变化和余震分布,推测5.7级地震为NW向破裂的可能性较大。
(2)有效摩擦系数对库仑破裂应力变化有较明显的作用,研究区域断层μ'比较高,大于0.4。
(3)5.9级地震对5.6级地震有较明显的触发作用,5.9级地震的应力场在5.6级地震两个共轭断层面上都产生了库仑应力增加,对应了两个主要的地震分布带。
(4)库仑破裂应力变化受5.6级地震的接收断层影响较小,这主要是其后的地震分布在两条共轭断层上,而共轭断层在应力场上很大程度是等效的。
(5)大同—阳高震群的发震断裂为NE向大王村断裂和NW向团堡断裂,该震群沿NW向团堡断裂先发生破裂,然后与区域应力场主压应力方向一致的NE向大王村断裂很快也发生破裂,且余震序列以NE向分布为主。
本文着重讨论的是1989年震群的3次主要地震事件的库仑应力变化及其影响,对后续发生的多次强震是否具备应力触发等还需进一步分析。
感谢防灾科技学院万永革教授、陕西省地震局石富强高级工程师、山东省地震局崔华伟高级工程师对本文相关研究工作的热心帮助。
- 啜永清,刘巍,彭美煊.1999.大同—阳高地震的余震与华北北部较大地震的关系[J].地震,19(4):379-386.
- 啜永清.1995.大同—阳高地震的余震窗口[J].山西地震,(1):20-24.
- 啜永清.1999.大同—阳高地震的余震窗口特征及机理分析[J].山西地震,(3):25-30.
- 大同—阳高地震烈度宏观考察组.1991.1989年大同—阳高6.1级地震烈度宏观考察[J].山西地震,(3):18-30.
- 冯永革,王海洋,陈永顺,等.2016.1989—1999大同地震序列的隐伏断层研究:库仑应力分析和余震JHD重定位[J].地球物理学报,59(2):568-577.
- 黄禄渊,程惠红,张怀,等.2019.2008年汶川地震同震-震后应力演化及其对2017年九寨沟MS7.0地震的影响[J].地球物理学报,62(4):1268-1281.
- 贾若,蒋海昆.2014.基于同震库仑应力变化的汶川地震余震频次研究[J].中国地震,30(1):74-90.
- 靳玉科,梁向军,靳玉贞,等.2010.大同震区地震序列震源位置及震源区速度结构初探[J].山西地震,(3):1-6.
- 靳志同,万永革,刘兆才,等.2019.2017年九寨沟MS7.0地震对周围地区的静态应力影响[J].地球物理学报,62(4):1282-1299.
- 刘瑞丰,李鸿吉,陈培善,等.1995.大同地震序列的震源机制解[J].地震地磁观测与研究,16(2):30-36.
- 龙锋,闻学泽,徐锡伟.2006.华北地区地震活断层的震级—破裂长度、破裂面积的经验关系[J].地震地质,28(4):511-535.
- 单斌,熊熊,郑勇,等.2013.2013年芦山地震导致的周边断层应力变化及其与2008年汶川地震的关系[J].中国科学:地球科学,43(6):1002-1009.
- 山西省地震局.2004.山西大同—阳高地震[M].北京:地震出版社.
- 石富强,张辉,邵志刚,等.2020.华北地区库仑应力演化与强震活动关系[J].地球物理学报,63(9):3338-3354.
- 宋美琴,郑勇,葛粲,等.2012.山西地震带中小震精确位置及其显示的山西地震构造特征 [J].地球物理学报,55(2):513-525.
- 万永革,沈正康,盛书中,等.2009.2008年汶川大地震对周围断层的影响[J].地震学报,31(2):128-139.
- 万永革,沈正康,曾跃华,等.2008.唐山地震序列应力触发的黏弹性力学模型研究[J].地震学报,30(6):581-593.
- 万永革.2019.同一个地震多个震源机制中心解的确定[J].地球物理学报,62(12):4718-4728.
- 王霞,宋美琴,李宏伟,等.2017a.大同地震窗P波频散衰减的异常变化特征[J].地震工程学报,39(2):1-8.
- 王霞,宋美琴,李宏伟,等.2017b.同窗视应力时变特征浅析[J].地震地磁观测与研究,38(5):33-38.
- 王霞,宋美琴,郑勇,等.2019.山西及邻区壳幔速度图像特征及其构造意义[J].地震地质,41(1):119-136.
- 王霞,宋美琴.2017.大同窗地震活动的频次和应变能特征[J].中国地震,33(2):340-349.
- 王霞,宋美卿,陈慧,等.2021.山西大同—阳高M>5.5地震震源机制中心解的确定[J].山西地震,(3):1-4.
- 胥鸿睿.2018.鄂尔多斯块体东缘横波速度结构及各向异性研究[D].武汉:中国地质大学.
- 徐扬,田勇,啜永清,等.1997.大同—阳高6.1级震群震源区及其附近地区地壳三维P波速度结构反演[J].山西地震,(2):25-29.
- 张成科,张先康,盖玉杰,等.1998.大同—阳高震区及其邻区壳幔速度结构与深部构造[J].地震地质,20(4):391-398.
- 朱琳,李腾飞,石富强,等.2021.1976年唐山强震群震后库仑应力演化及其与2020年古冶5.1级地震的关系[J].地震研究,44(1):1-8.
- Freed A M,Ali S T,Burgmann R.2007.Evolution of stressin Southern California for the past 200 years from coseismic,postseismic and interseismic stress changes[J].Geophys J Int,169:1164-1179.
- Freed A M.2005.Earthquake triggering by static,dynamic,and postseismic stress transfer[J].Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences,33(1):335-367.
- Hill D P,Reasenberg P A,Michael A,et al.1993.Seismicity remotely triggered by the magnitude 7.3 Landers,California earthquake[J].Science,260(5114):1617-1623.
- Jaeger J C,Cook N G W,Zimmerman R W.2009.Fundamentals of rock mechanics[M].Oxford:John Wiley & Sons,90.
- Li B,Mathilde B S,Kuvvet A.2015.Coulomb stress evolution in the Shanxi rift system,North China,since 1303 associated with coseismic,post-seismic and interseismic deformation[J].Geophysical Journal International,203(3):1642-1664.
- Lin J,Stein R S.2004.Stress triggering in thrust and subduction earthquakes and stress interaction between the southern San Andreas and nearby thrust and strike-slip faults[J].J Geophys Res,109(B2):B02303.
- Lozos J C,Harris R A.2020.Dynamic rupture simulations of the M6.4 and M7.1 July 2019 Ridgecrest,California,earthquakes[J].Geophysical Research Letters,47(7):e2019GL086020.
- Nalbant S S,Hubert A,King G C.1998.Stress coupling between earthquakes in northwest Turkey and the north Aegean Sea[J].J Geophys Res,103(B10):24469-24486.
- Perfettini H,Avouac P.2007.Modeling afterslip and aftershocks following the 1992 Landers earthquake[J].J Geophys Res,112(B5):B07409.
- Shan B,Xiong X,Wang R J,et al.2013a.Coulomb stress evolution along Xianshuihe–Xiaojiang Fault System since 1713 and its interaction with Wenchuan earthquake,May 12,2008[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,377-378(2013):199-210.
- Shan B,Xiong X,Zheng Y,et al.2008.Stress changes on major faults caused by MW7.9 Wenchuan earthquake,May 12[J].Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci,52(5):593-601.
- Shan B,Xiong X,Zheng Y,et al.2011.The co-seismic Coulomb stress change and expected seismicity rate caused by 14 April 2010 MS=7.1 Yushu,China,earthquake[J].Tectonophysics,510(3):345-353.
- Shan B,Xiong X,Zheng Y,et al.2013b.Stress changes on major faults caused by 2013 Lushan earthquake,and its relationship with 2008 Wenchuan earthquake[J].Science China:Earth Sciences,56(7):1169-1176.
- Stein R S,Barka A A,Dieterich J H.1997.Progressive failure on the North Anatolian fault since 1939 by earthquake stress triggering[J].Geophys J Int,128(3):594-604.
- Toda S,Lin J,Meghraoui M,et al.2008.12 May 2008 M=7.9 Wenchuan,China,earthquake calculated to increase failure stress and seismicity rate on three major fault systems[J].Geophys Res Lett,35(17):L17305.
- Toda S,Stein R S.2002.Response of the San Andreas fault to the 1983 Coalinga Nuñez earthquakes:An application of interaction-based probabilities for Parkfield[J].J Geophys Res,107(136):ESE 6-1-ESE 6-16.
- Wang R,Lorenzo-Martín F,Roth F.2006.PSGRN/PSCMP-a new code for calculating co-and postseismic deformation,geoid and gravity changes based on the Viscoelastic-Gravitational Dislocation Theory[J].Computers & Geosciences,32(4):527-541.
- William D B,Gavin P H,Ryan D G.2019.The July 2019 Ridgecrest,California Earthquake Sequence:Kinematics of Slip and Stressing in Cross-Fault Ruptures[J].Geophysical Research Letters,46(21):11859-11867.
- Zachary E R,Benjamn I,Zhe J,et al.2019.Hierarchical interlocked orthogonal faulting in the 2019 Ridgecrest earthquake sequence[J].Science,366(6463):346-351.
- Zhuo Y Q,Guo Y S,Bornyakov A S,et al.2019.A test of the oblique-rifting model for transfer zone deformation in the northern Fen-Wei rift:implications from the 1989 M6.1 Datong-Yanggao earthquake swarm[J].Geodynamics and tectonophysics,10(1):43-51.