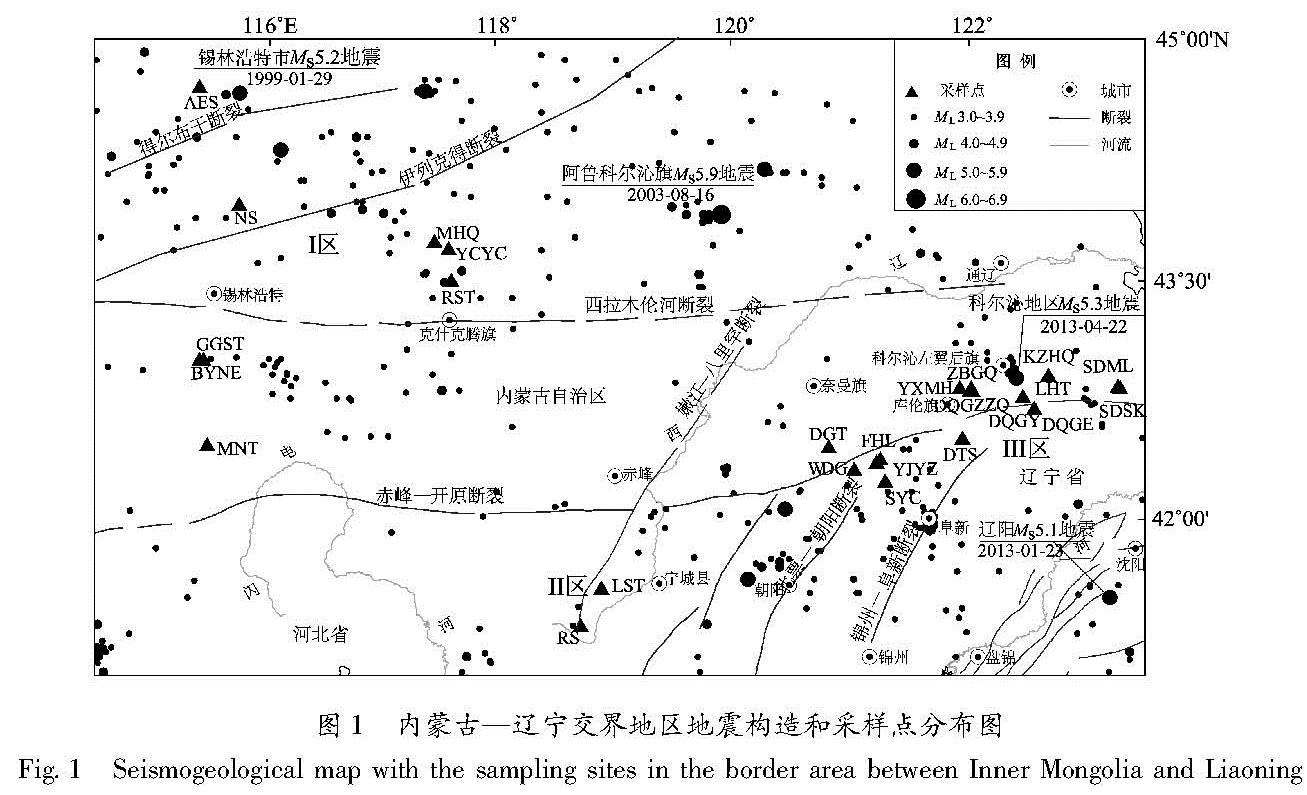
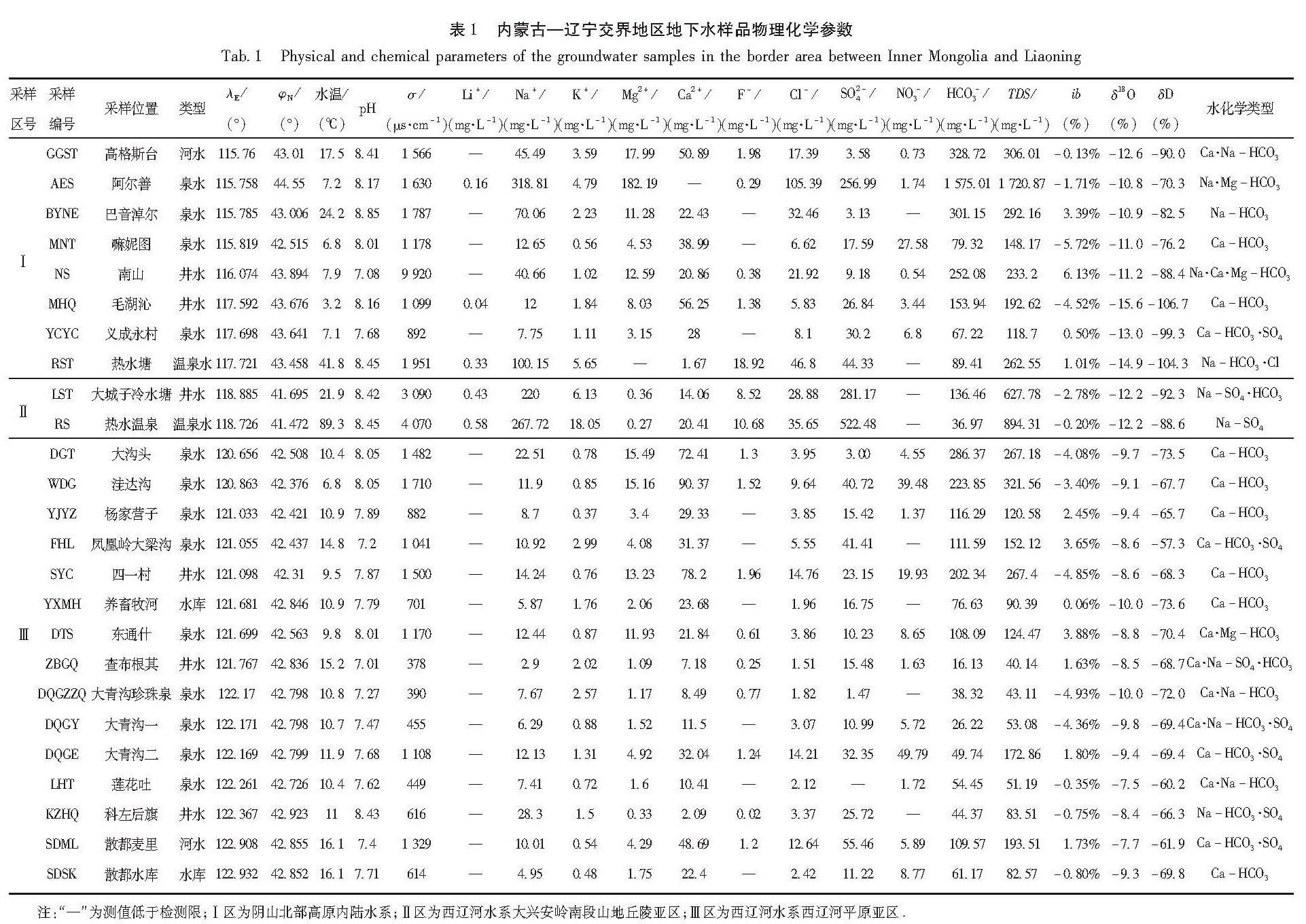
3.2.2 离子来源
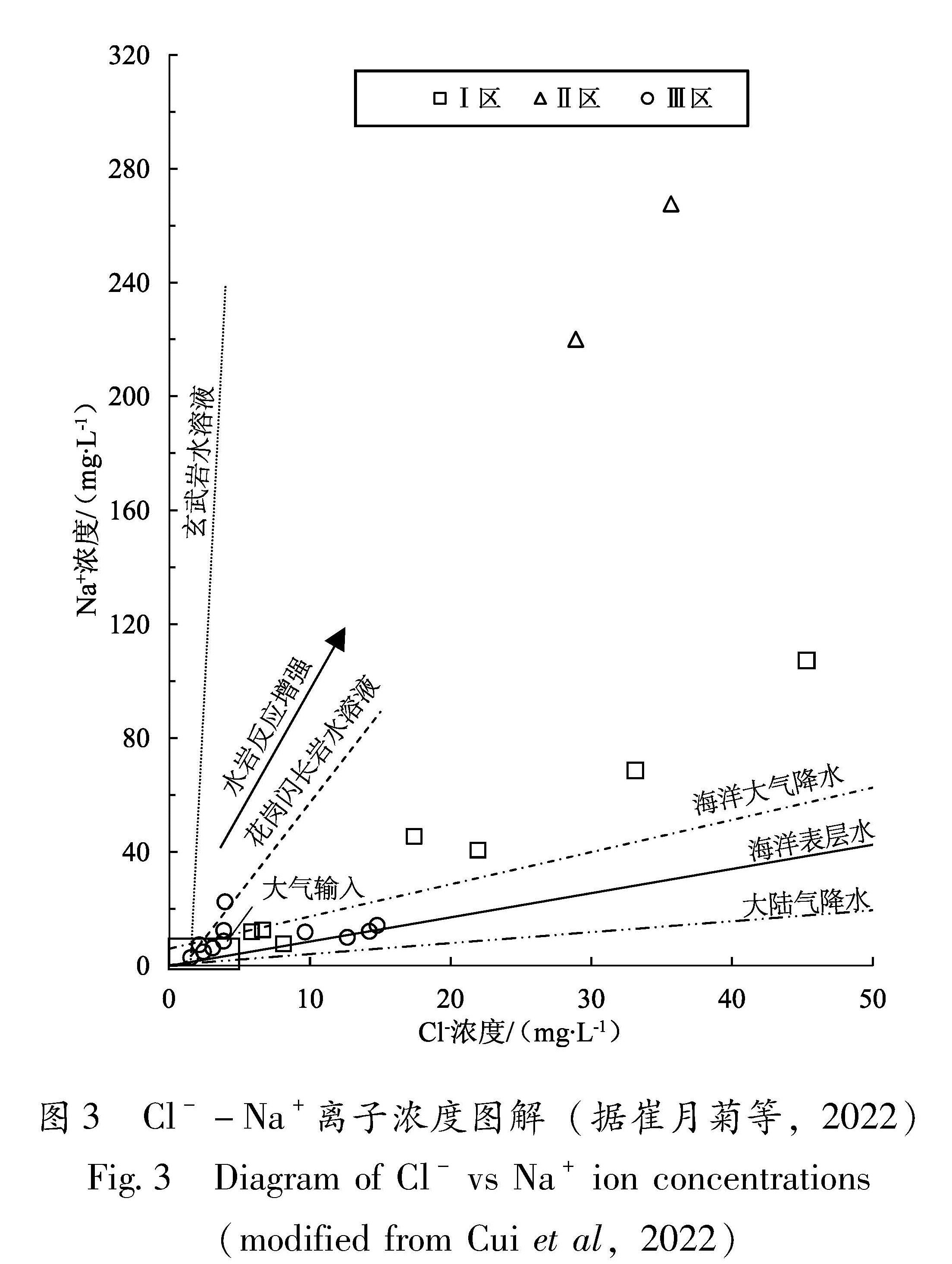
地下水中的离子来源可以分为4类:大气输入、岩石溶解、深部流体和人为来源。由于Cl-和Na+在水-岩作用过程中不易形成固体沉淀,所以其浓度能够较好地反映离子来源。在Cl-和Na+浓度图解中不同离子来源具有不同的斜率(图3),全部水样的Cl-和Na+浓度的线性回归直线斜率为:Na+=3.30 Cl--1.54,R2=0.726 5,明显小于岩石水溶液的斜率(6.37和95),相关系数偏小,结合较高的NO-3浓度(表1),可以判断离子是多来源的,而且有人为来源。Ⅰ区水样的线性回归斜率为:Na+=3.06Cl--17.62,R2=0.981 3, 接近全部水样的斜率,表明水中离子来自岩石溶解、大气输入和深部流体; 而Ⅲ区线性回归表明两种离子浓度几乎不相关(R2=0.039 8),意味着离子来源复杂,有明显的人为来源Cl-混入。Ⅱ区的2个水样未检测到NO-3,Na+和Cl-浓度点位于岩石溶解的趋势线附近(图3),表明离子来源几乎无人为源污染,考虑到大陆大气降水的TDS小于20 mg/L(崔月菊等,2022),大气输入占总TDS的百分比很小,因此离子主要来源于岩石溶解和深部流体(图3)。
图3 Cl--Na+离子浓度图解(据崔月菊等,2022)
Fig.3 Diagram of Cl- vs Na+ ion concentrations (modified from Cui et al,2022)
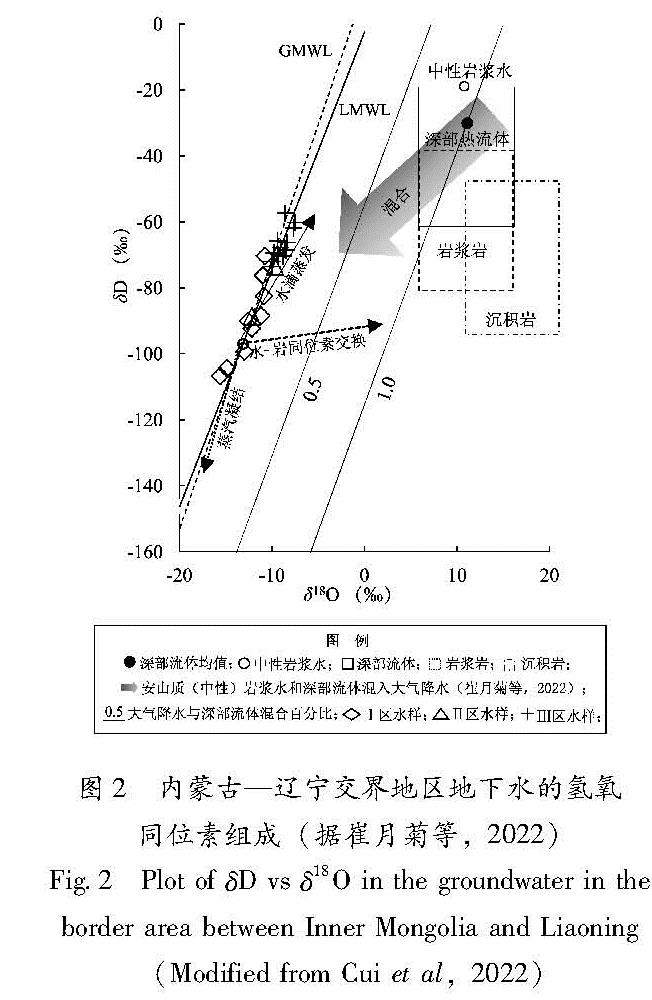
使用因子分析方法提取出控制水样各种变量的3个成分:A为岩石溶解和深部流体,Na+、SO2-4、Li+、K+、Cl-、TDS、F-、T、HCO-3、Mg2+、Ph的贡献率为50.08; B为大气输入,HCO-3、Mg2+、Cl-、TDS的贡献率为23.16; C为人为源,Ca2+、NO-3的贡献率为10.94。根据大于0.6的6个变量得出的成分矩阵可以判断深部流体主要影响的变量为Li+、Na+、K+、Cl-。这表明控制TDS的因素是大气输入和岩石溶解,深部流体和人为源对TDS影响不明显。根据TDS和水文地质条件判断受深部流体影响的水样包括AES、LST、RS和RST。
重碳酸根是天然水化学成分中极重要的组成部分,均由碳酸衍生而来[CO2+H2O-HCO-3+H+,2HCO-3-CO2-3+H2]。在中性和碱性、低矿化度和中等矿化度水中,重碳酸根均占主导地位。淡水大部分是重碳酸型的水,大多数水样的阳离子以Ca2+为主,阴离子以HCO-3为主,TDS为82.57~321.56 mg/L,主要分布在Ⅰ区和Ⅲ区(表1)。大气降水中TDS含量一般小于20 mg/L,研究区水样TDS平均值均大于该值,这可能是受当地蒸发作用强的影响。研究区水样均出露于第四纪砂黏土、黏砂土、砂、砂砾石层,以潜水为主,表明其循环深度较浅,主要来源是大气输入及各种碳酸盐岩类(石灰岩、白云岩、泥灰岩等)和第四纪沉积物中碳酸盐胶结物溶解溶滤的结果,同时受到季节性气候变化的影响。
Ⅰ区GGST、MNT、MHQ、YCYC水样的阳离子以Ca2+为主,阴离子以HCO-3为主; AES、BYNE、NS、RST水样的阳离子以Na+为主,阴离子以HCO-3为主,TDS为233.20~1 720.87 mg/L(表1)。AES、NS水样为CO2过饱和水,位于NE向得尔布干、伊列克得断裂带上,该区域水样中HCO-3明显占优势; Ca2+、Mg2+浓度均低于Na+浓度,反映了碳酸交代硅酸盐,水中来自深部的CO2为交代作用提供了物质。AES水样位于降雨量远小于蒸发量的高原区,其矿化度高可归因于季节性降水淋滤饱气层的盐分和深部富CO2流体混入。BYNE水样的采样区为宏观观测点,潜水露头,泉附近分布有下白垩统的砂岩、砂砾岩及煤系地层,由盆地中心向盆地边缘,岩性颗粒变粗,厚度增加,埋深减少,循环较迅速,受溶滤作用影响大,形成典型的低矿化度的Na-HCO3型水。RST水样为不含石膏和岩盐的正常海相沉积岩中水消极交替带的水,为Na-HCO3?Cl型。
II区山区基岩裂隙发育,入渗条件好,易接受大气降水补给,在山间盆地、河谷洼地中多分布有厚度不等的第四系松散砂砾石层,河谷中富含孔隙潜水。LST、RS水样均为观测井水样,采样点位于阴山山脉嫩江—八里罕断裂南段,赤峰—开原断裂附近,高程分别为593 m、683 m,pH值为8.42、8.45,水温为21.9℃、89.3℃,TDS偏高,分别为627.78 mg/L、894.31 mg/L,
随着矿化度的增加,Na+含量也增加。LST水样来自大城子地震台观测井,冬天不结冰,全年出水。RS水样采自热水镇一家宾馆使用的温泉井水,山沟走向NW325°。两口井周边地质背景均为中侏罗统-下白垩统花岗岩、混合岩冲积物,且井西侧附近为风化的花岗岩山包。两个水样水化学类型分别为Na-SO4、Na-SO4?HCO3型,是由花岗岩或片麻岩区循环经历了长期水岩相互作用(张炜斌,2013),以及深部热流体混入形成的特殊水类型。
Ⅲ区含水层厚度大,15个水样中阴离子以HCO-3和SO2-4为主,阳离子以Ca2+和Na+为主,均为低矿化度或者中等矿化度淡水,这反映了集水区内的大气降水补给量较大,冲刷程度很好,地下水循环快,形成了西辽河平原区以Ca-HCO3型为主,其次为Ca-HCO3?SO4、Ca?Na-HCO3和Ca?Na-HCO3?SO4型。ZBGQ水样为Ca?Na-SO4?HCO3型,可能是地下水补给区和流经岩石差异造成的。各采样点主要阴、阳离子组成相似,均为重碳酸型水,但不同采样点中相同离子的含量和离子总含量存在差异。各采样点的水化学类型存在一些差别,表明各采样点的地下水形成过程有所差异,为典型的地下冷水或地表水水化学类型。
通常在深层地下水中NO-3含量很少或者没有。本文所采水样大多NO-3浓度较高,如AES、MNT、MHQ、YCYC、DGT、WDG、YJYZ、SYC、DTS、ZBGQ、DQGY、DQGE、LHT、SDML、SDSK水样NO-3浓度均大于1 mg/L,而在观测井及河水中NO-3浓度很低甚至没有,只有SDML水样中NO-3浓度为5.89 mg/L,偏高。这主要归因于西辽河地区引地表水灌溉量较大,相应的地表水灌溉入渗补给量也大,且SDML河水为稻田灌溉水,伴有藻类,是有机质污染的标志。王丹璐等(2015)研究表明,在兰州市区大气降水中无机可溶性离子的主要来源为二次转化、人为排放和土壤源,土壤源占比最高,达49.5%。研究区地下水中无机含氮化合物主要是由大气降水、地表水带入的,研究区属于半干旱地区、人口密度低,NH4+和NO-3主要来自地表盐渍物、氮氧化物二次转化和人类活动的含氮污染物。
观测井中阳离子以Na+为主,阴离子以SO2-4、HCO-3为主,而泉、民用井、河水及水库水样中阳离子主要以Ca2+为主,少数以Na+为主(如AES、BYNE及RS水样),阴离子以HCO-3为主。LST、RS、AES水样矿化度偏高,随着矿化度的增加Na+含量也增加,
在大多数情况下,当水的矿化度增至每升几克时,Na+就成为主要阳离子。但在火成岩风化壳中,如KZHQ、NS、RST和BYNE水样,由于花岗岩的风化溶解,使基岩裂隙水成为低矿化度的Na-HCO3型水。LST、RS、RST水样同时伴有较高浓度的Li+,分别为0.43、0.58、0.33 mg/L,F-浓度分别为8.52、10.68、18.92 mg/L,这也是花岗岩或片麻岩裂隙水的特点(Stober,Bucher,1999),F-含量明显超过《生活饮用水卫生标准》(GB 5749—2006)中的限量。表1中地下水中Li+、Na+、F-与温度存在明显的正相关,这体现了高温地下水会促进微碱性花岗岩中含氟矿物的溶解,同时F-的活性增强,有效地促进岩石、土壤表面的吸附态氟发生解吸附作用(范基姣等,2008; 易春瑶等,2013; 梁礼革等,2016),这也是高氟泉水多见于高温花岗岩裂隙含水层的原因。