基金项目:云南省地震局青年基金项目(2022K03); 云南省地震局应急服务中心自立项目(2022ZL01).
第一作者简介:徐俊祖(1993-),工程师,主要从事地震灾害损失评估工作.E-mail:1174044329@qq.com.
(1.云南省地震局,云南 昆明 650224; 2.华能澜沧江水电股份有限公司,云南 昆明 650206)
(1.Yunnan Earthquake Agency,Kunming 650224,Yunnan,China)(2.Huaneng Lancang River Hydropower INC,Kunming 650206,Yunnan,China)
the principal component analysis; the neural network model; masonry-timber structure; earthquake-damage assessment; Yunnan
DOI: 10.20015/j.cnki.ISSN1000-0666.2023.0058
以往震害经验表明,地震灾害主要源于地震释放的巨大能量引发的建筑物和各类设施的破坏以及次生灾害,进而导致人员伤亡和财产损失(侯林锋等,2020)。当前,应对地震灾害的主要措施是震前预测预防和震后应急,然而由于人们对地震的短临预报能力有限,地震后快速高效的应急救援、灾情信息的迅速获取成为减轻地震灾害损失的主要手段(张雪华,2017)。地震时建筑物倒塌是造成人员伤亡的主要原因(刘晶晶等,2017),震后高效准确地开展建筑物受损程度评估工作有助于震后搜救资源分配,加快灾后救援进程,减轻地震灾害损失,降低人员伤亡,对震后灾情分析与应急救援决策具有重要的指导意义。
目前,应用于建筑物地震破坏群体评估的方法大致可分为3种:基于历史灾情数据的统计分析法、基于地震动参数的震害模拟分析法和基于机器学习的评估方法。其中基于历史灾情数据的统计分析法因易于操作,可快速评估预测地震灾害影响等优点,得到了广泛应用。孙柏涛和张桂欣(2012)通过收集汶川地震实际灾情数据获得了各类房屋结构的破坏情况,统计分析了各类结构在不同地震烈度区的破坏比例; 刘毅等(2011)以历史地震灾情数据为依据,建立了砖木等4类房屋在不同地震等级的震害破坏率模型; 臧石磊等(2019)基于辽宁省房屋建筑数据,采用模糊综合评价法计算分析得到地震易损性矩阵; 赵东升等(2022)基于历史灾情数据,利用数据拟合方法构建了房屋脆弱性曲线,对不同地震等级下的房屋毁坏比例进行预测,为不同尺度地震灾害建筑物风险评估提供了参考与支撑; 黄文涛等(2022)从川南历史地震建筑物震害相关资料中,提取并统计了4类建筑物破坏比,得到各类结构的经验易损性矩阵及易损性曲线。虽然基于历史灾情数据的统计分析法能直接反映地震对建筑物造成的破坏程度,但在实际应用中也存在一定局限性。由于影响建筑物发生地震破坏的因素众多,如何选择相应因素进行分析是一个关键问题,仅仅选取单一的因素构建易损性矩阵或拟合易损性曲线、脆弱性曲线并不能全面地反映建筑物的破坏状态,难以对建筑物受灾程度进行准确预测评估。
随着计算机技术的快速发展,建筑物三维震害模拟方法被逐步应用于建筑物地震破坏评估中,如杜浩国等(2019)采用无人机航拍技术、地理空间信息和三维仿真建模技术对云南省红河县城区房屋进行地震灾害三维仿真模拟评估,得到了不同烈度下城区房屋的破坏程度和分布情况; 张灿等(2022)采用结构弹塑性时程分析方法对兰州市城关区建筑物进行三维震害模拟,得到了不同烈度下建筑物的破坏程度及不同破坏程度的面积占比。虽然有关建筑物震害模拟的研究已经相对成熟,但大多是通过设定固定的地震加速度值或地震烈度来模拟建筑物的破坏情况,未曾考虑到同一地震所产生的地震动参数分布是不同的,且受地理环境等因素影响,难以保证震害模拟的准确性和普适性。
近年来,随着机器学习技术的兴起,许多学者利用机器学习方法强大的自学习能力对建筑物进行地震破坏评估,如成小平等(2000)提出了一种基于神经网络模型的房屋震害易损性估计方法,选取了楼层数等10个影响房屋结构抗震性能的指标作为神经网络模型的输入,以建筑物在某一烈度下破坏状况的概率为输出,并以唐山大地震中的实际震例为样本构建了震害易损性矩阵进行建筑物易损性估计; 金赟赟和李杰(2020)选择设防烈度、结构类型等9个抗震性能影响因子作为模型输入,将房屋破坏等级作为输出,利用基于易损性贝叶斯网络方法对上海市浦东地区的部分砌体房屋进行了地震易损性评估; 施唯和王东明(2022)利用BP神经网络模型对北京市海淀区部分砌体结构房屋在不同地震烈度下的破坏状态进行推演预测。虽然机器学习方法在建筑物地震破坏评估中被广泛应用,但仍然存在一些问题,首先因造成房屋发生地震破坏的因素众多,除了房屋本身的抗震性能因素外还有地震动破坏性等因素,应综合考虑以上因素; 其次对于神经网络模型来说,合适的输入因素是保证模型优越性能的关键,输入因素过多将会增加模型的复杂程度,输入因素过少又无法保证模型精度,因此输入因素应该尽量简洁而又能充分表达输入输出之间的映射关系。
基于以上分析,本文提出了一种基于主成分分析与BP神经网络相融合的砖木房屋地震破坏群体评估方法,通过灰色关联度(GRA)模型剔除对建筑物发生地震破坏影响较小的因素得到关键因子,采用主成分分析法(PCA)从关键因子中提取出主要成分,最后利用BP神经网络模型对处理后的主要成分进行训练,建立砖木结构房屋地震破坏比预测模型,并利用云南实际震例验证了本方法的有效性和适用性。
云南省地质构造复杂,是一个地震灾害频发,受灾严重,损失巨大的省份(周光全等,2006),同时也是全国少数民族最多的省份,由于其多民族聚居的特点致使其民居建筑物结构类型呈现出多元化和地域化,但砖木结构房屋结构类型大体上相类似。本文选取2000—2022年云南省47次5.0级以上破坏性地震为研究对象,数据包含发震时间、震级、震源深度、烈度、房屋破坏比等,主要来源于云南省地震局2000—2022年地震灾害损失评估报告和地震灾害风险普查专题任务三——“地震灾害事件调查”,同时参考了《云南地震灾害损失评估及研究(1992—2010)》(周光全,2012)等资料。
本文主要对云南砖木结构房屋地震破坏进行评估研究,砖木结构房屋破坏等级可分为基本完好、破坏和毁坏3个等级。其中,破坏指砖木结构房屋的非承重构件如围护墙体明显裂缝或严重开裂、甚至局部垮塌,普遍梭瓦或明显掉瓦,可修理后使用。破坏比是指每一种结构的破坏面积在该类结构总面积中所占比例(施伟华等,2011)。本文基于相关研究(黄佩蒂,2018; 张方浩等,2020; 钟江荣,2021; 杨钦杰等,2021),综合发震时间(S1)、震级(S2)、震源深度(S3)、地震烈度(S4)、房屋造价(S5)、人均GDP(S6)、受灾面积(S7)、经济损失(S8)、震中经度(S9)和纬度(S10)共10个影响因子作为砖木结构房屋地震破坏(破坏比(S11))的初始评估因子,其中发震时间(S1)选择发震年份主要是考虑到该参数与砖木结构房屋数量占比有一定关联,受灾面积(S7)指的是相应烈度区面积,而经济损失(S8)指的是整个灾区的经济损失。本文选择2000—2020年的42次5.0级以上地震数据共90组作为初始训练样本(表1),2021、2022年的5次5.0级以上地震数据共8组作为测试样本(表2)以验证评估模型的准确性。
灰色关联度分析(Grey Relation Analysis,GRA)是一种多因素统计分析方法,被广泛应用于评价指标的权重计算(Tien,2017; 蒋复量等,2020)。其原理为:通过关联度来描述两个事物的相关程度,相关程度越高,两者间的变化趋势越相近,反之亦然,这种变化趋势主要通过两者的序列曲线相似度来呈现。其计算步骤如下(贾婧等,2020):
利用所有评价对象及其原始指标数据建立矩阵,设n个数据序列形成矩阵为:

式中:aij的数值表示第i个评价对象的第j个评价指标值。
由于不同的评价指标有不同的量纲,将评价指标值aij运用式(2)和(3)作无量纲化处理:
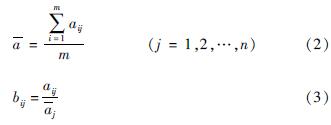
对原矩阵A处理后得到无量纲矩阵B:

确定参考序列D为:
D=[d1 d2 … dn](5)
根据矩阵B和D计算灰色关联度系数为:
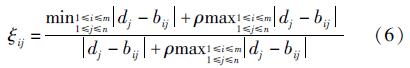
关联度表示为:

式中:由于绝对值最大值可能过大,借助系数ρ来改善灰色关联度系数间的显著差异,这里ρ取0.5,由式(6)可知,关联系数越大,则相关程度越高。
主成分分析(Principal Component Analysis,PCA)是一种统计方法,通过正交变换将一组可能存在相关性的变量转换为一组线性不相关的变量,转换后的这组变量叫主成分,新生成的主成分维度降低且保留初始变量的绝大部分信息(李桥等,2020; 胡进军等,2021)。具体过程如下(王晨晖等,2022):
设(x1,x2,…,xn)是总体X的n个样本, 每个样本包括m维变量,该矩阵可表示为:

计算矩阵的协方差阵,求出其对应的相关系数阵。然后求出相关系数阵的特征值,且满足λ1≥λ2≥…≥λm≥0,则第i个主成分的贡献率为:

则前q个主成分的累计贡献率为:

当前q个主成分累计贡献率达85%以上时,用这q个主成分来代替初始的影响因子进行分析一般是满足要求的。
主成分表达式为:
Fq=aq1S1+aq1S2+…+aqmSm(11)
式中:Fq为主成分; aq1…aqm为得分系数; S1…Sm为关键指标。
BP神经网络是一种误差逆向传播的多层前馈神经网络,是目前应用最广泛的神经网络之一。神经网络作为一种智能信息处理手段,它不需要事先确定输入向量与输出向量之间繁杂的映射关系,而是通过自身的训练不断地调整权值和阈值使模型预测值接近期望值(Xu et al,2019)。当BP神经网络模型充分学习了这种复杂的非线性映射关系后,就能够处理具有相似信息的样本,达到有效预测的目的,因此BP神经网络模型被广泛应用于房屋震害预测领域(汤皓,陈国兴,2006; 施唯,王东明,2022)。
造成砖木结构房屋地震破坏的因素很多,选取合适的影响因素是对砖木结构房屋地震破坏进行准确合理评估的重要保障。为了筛选出与砖木结构房屋破坏比相关程度较高的影响因子,本文采用灰色关联度模型对表1中破坏比与影响因子的相关程度进行分析,求得各因子之间的灰色关联度矩阵,如图2所示。
将各因子的灰色关联度做降序排列,排列结果如图3所示。 图中关联度曲线在震级(S2)处出现了突变,这意味着相比于S2之前的因子,S2之后的因子关联度要小的多,此时以突变点作为阈值既能够有效剔除与砖木结构房屋破坏比相关程度较小的影响因子,又不损失样本中过多的数据信息,故选取关联度≥0.7的地震烈度(S4)、人均GDP(S6)、经济损失(S8)、震源深度(S3)、房屋造价(S5)、受灾面积(S7)、发震时间(S1)、震级(S2)共8个影响因子作为关键因子。
由于灰色关联度分析仅完成了影响因子的约简,对于影响因子间存在的重叠信息未进行有效处理,因此有必要对这些关键因子进行主成分分析,通过对关键因子进行降维处理,提取各因子所包含的特征信息形成一组线性无关的主成分,降低后续BP神经网络模型的建立难度和复杂程度。对8个关键因子进行主成分分析,计算各主成分贡献率和累计贡献率(表3),并确定主成分个数,最后计算出各因子得分系数(图4),确定各主成分表达式。
由表3可知,主成分F5~F8的特征值相对较小且其贡献率也相对较低,而F1~F4特征值和贡献率较高且累计贡献率为87.9%,大于85%,故采用能够反映关键因子集中所包含的信息的前4个主成分,代替关键因子。
由图4可见,主成分F1中主要体现了关键指标发震时间(S1)、房屋造价(S5)、人均GDP(S6)的影响,而F2主要体现震级(S2)、地震烈度(S4)、经济损失(S8)的影响,同理,主成分F3体现了地震烈度(S4)和受灾面积(S7)的影响,F4体现了震源深度(S3)的影响,将矩阵中的得分系数与关键因子进行线性组合:

将得到的4个主成分作为BP神经网络模型输入变量,砖木结构房屋地震破坏比作为输出变量,故BP神经网络输入节点为4,输出节点为1。本文使用刘育林等(2022)的经验公式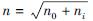 +a,其中n0表示输出节点数; ni为输入节点数; a为1~10之间的常数,结合试凑法确定隐含层最优解节点数为12,最终预测模型网络结构为(4,12,1)型,如图5所示。
+a,其中n0表示输出节点数; ni为输入节点数; a为1~10之间的常数,结合试凑法确定隐含层最优解节点数为12,最终预测模型网络结构为(4,12,1)型,如图5所示。
采用本文方法、砖木结构房屋地震破坏脆弱性拟合曲线(图6)以及BP神经网络模型分别对2021年漾濞6.4级、盈江5.0级、双柏5.1级、2022年宁蒗5.5级以及红河5.0级地震时砖木结构房屋破坏比进行预测(图7),并对预测结果进行对比分析。为了更好地评价模型的有效性和普适性,运用均方根误差(RMSE)、决定系数(R2)、均方相对误差(MSRE)以及平均绝对误差(MAE)对模型预测结果进行误差分析,结果见表4。
图7 3种方法对砖木结构房屋地震破坏比预测结果对比分析
Fig.7 Comparison pre-estimated results of the damage ratio of the masonry-timber houses by three methods
综合图7和表4可以看出,3种方法得到的砖木结构房屋破坏比的预测结果整体上与实际调查结果趋势一致,且本文方法的预测结果与实际调查结果更加吻合,普适性较好,精度较高。但本文方法对宁蒗地震Ⅶ度区砖木结构房屋破坏比的预测结果与实际调查结果误差较大,其原因主要为震中为农村地区,砖木结构房屋较为老旧,抗震性能较差的房屋占比较高,导致破坏比例较高,而本文预测模型未考虑到这一因素,导致预测房屋破坏比例与实际情况存在较大误差。图6通过对样本数据的Logistic函数拟合得到了砖木结构房屋的脆弱性曲线,从而得出不同烈度下的房屋破坏比,但该方法仅考虑地震烈度单一因素的影响,而房屋在不同烈度下的破坏比是固定的,故图7中房屋脆弱性曲线拟合的预测结果与真实调查结果吻合程度最低,普适性最差、预测精度低。传统的BP神经网络未对影响因子进行处理,预测结果主要受训练样本的影响,在训练样本中烈度为Ⅵ度的样本数量为42,Ⅶ度为34,Ⅷ度为14,故对Ⅷ度烈度区的预测结果误差较大,对比不同地震的Ⅶ度和Ⅵ度区预测结果基本相同,普适性较差。综上得出,本文方法对砖木结构房屋地震破坏比预测的普适性最优,传统的BP神经网络模型其次,脆弱性曲线拟合方法最差。
本文以2000—2022年云南省47次5.0级以上破坏性地震为研究对象,提出一种基于主成分分析与BP神经网络相融合的云南砖木结构房屋地震破坏评估方法。采用砖木结构房屋脆弱性曲线拟合、BP神经网络以及主成分分析与BP神经网络相融合3种方法对云南5次5.0级以上地震中砖木结构房屋地震破坏比例进行对比预测评估,得出以下主要结论:
(1)本文方法通过灰色关联度(GRA)模型进行因子约简,确定了与砖木结构房屋地震破坏比例相关程度较高的8个关键因子,并采用主成分分析法(PCA)对8个关键因子进行主成分分析,消除了关键因子间的重叠信息,提取出主要成分,并将主成分作为BP神经网络模型的输入,进行砖木房屋破坏比预测,获得了优于其它2种方法的砖木结构房屋地震破坏比例的预测精度和普适性。
(2)对2021年以来的震例验证表明,本文方法通过对砖木结构房屋地震破坏影响因素的综合考量和处理,有效提升了砖木结构房屋地震破坏比预测精度,且具有更好的适用性,为云南砖木结构房屋地震破坏评估提供了一种新的思路和方法。