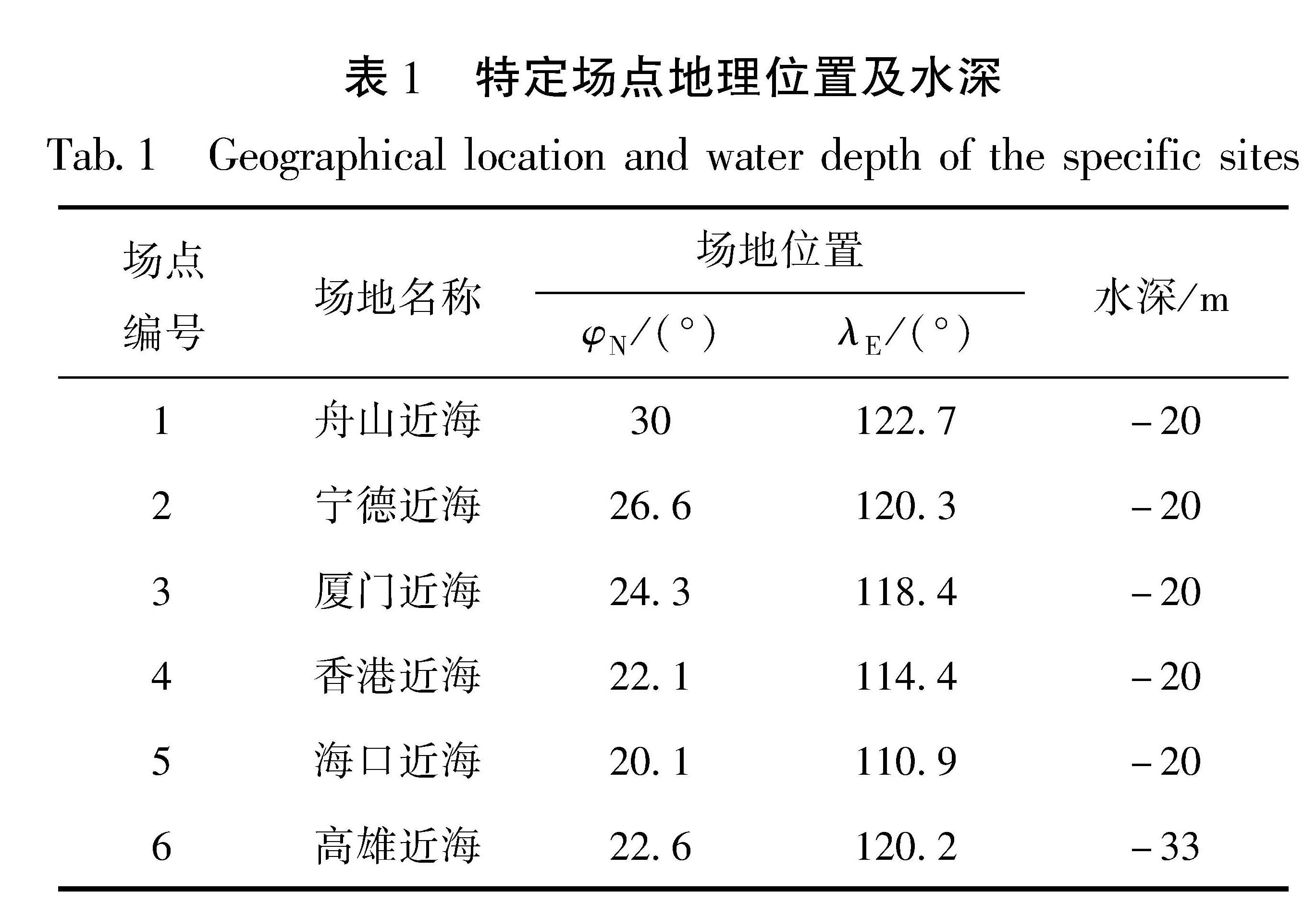
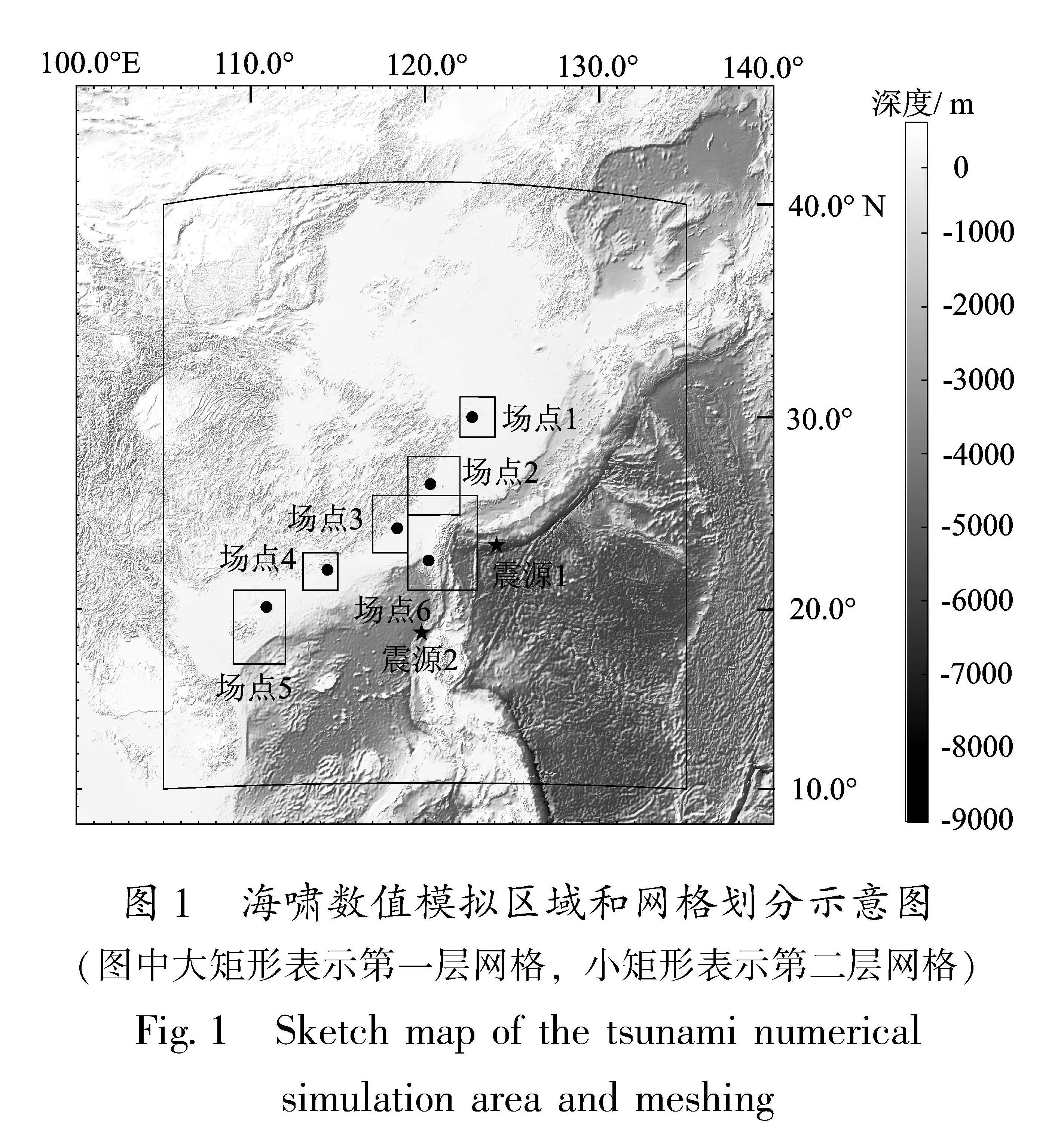
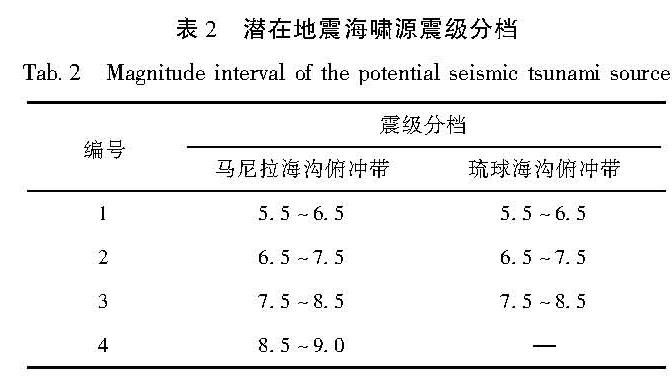
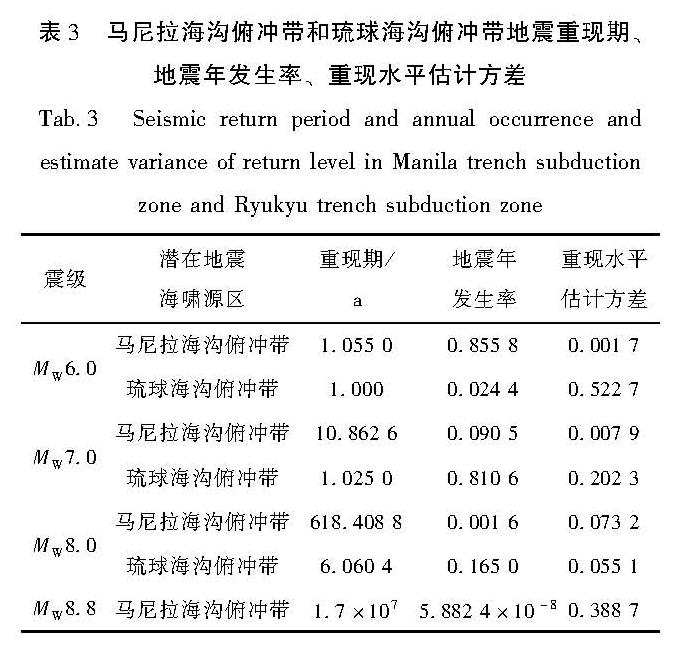
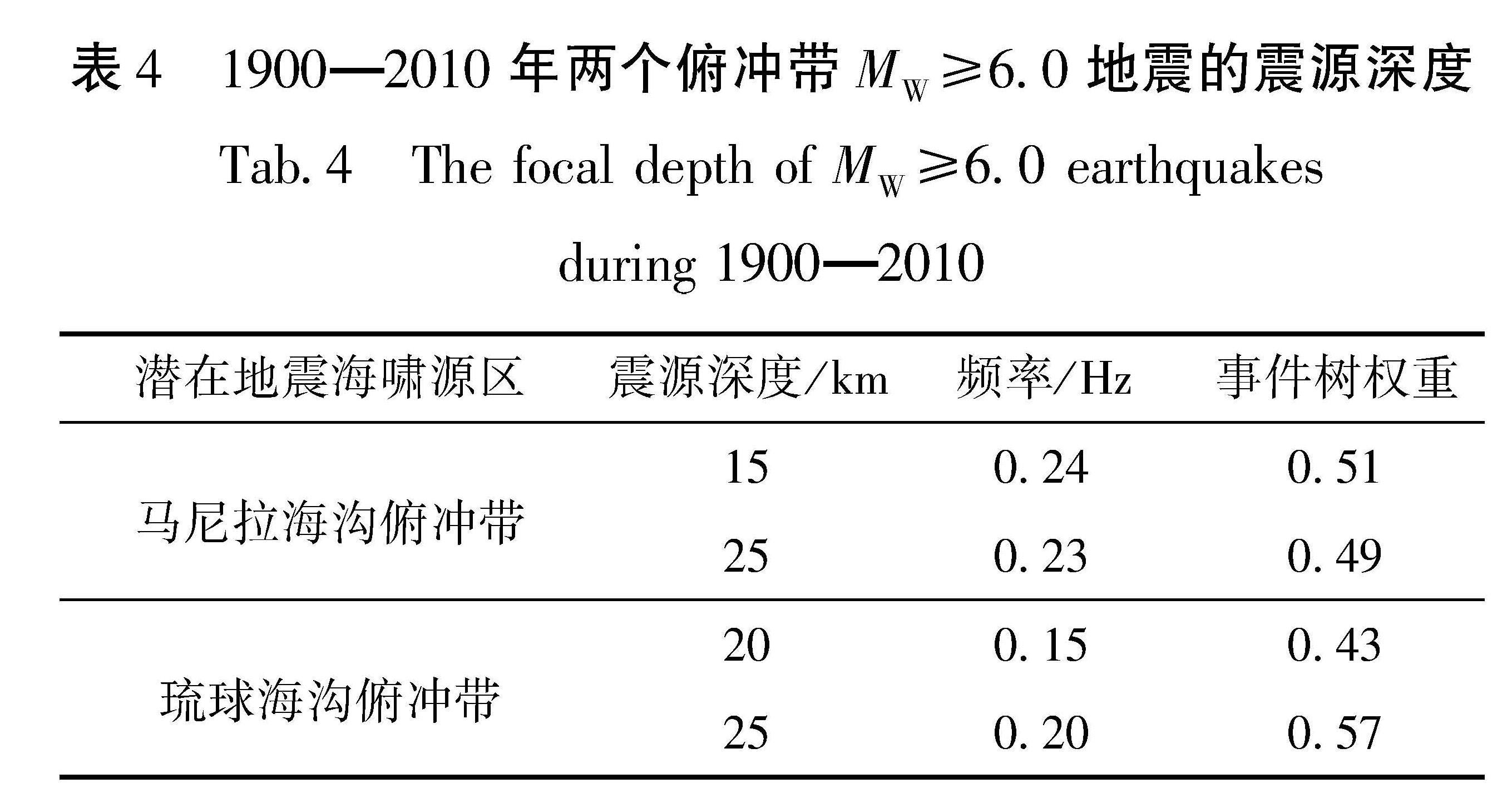
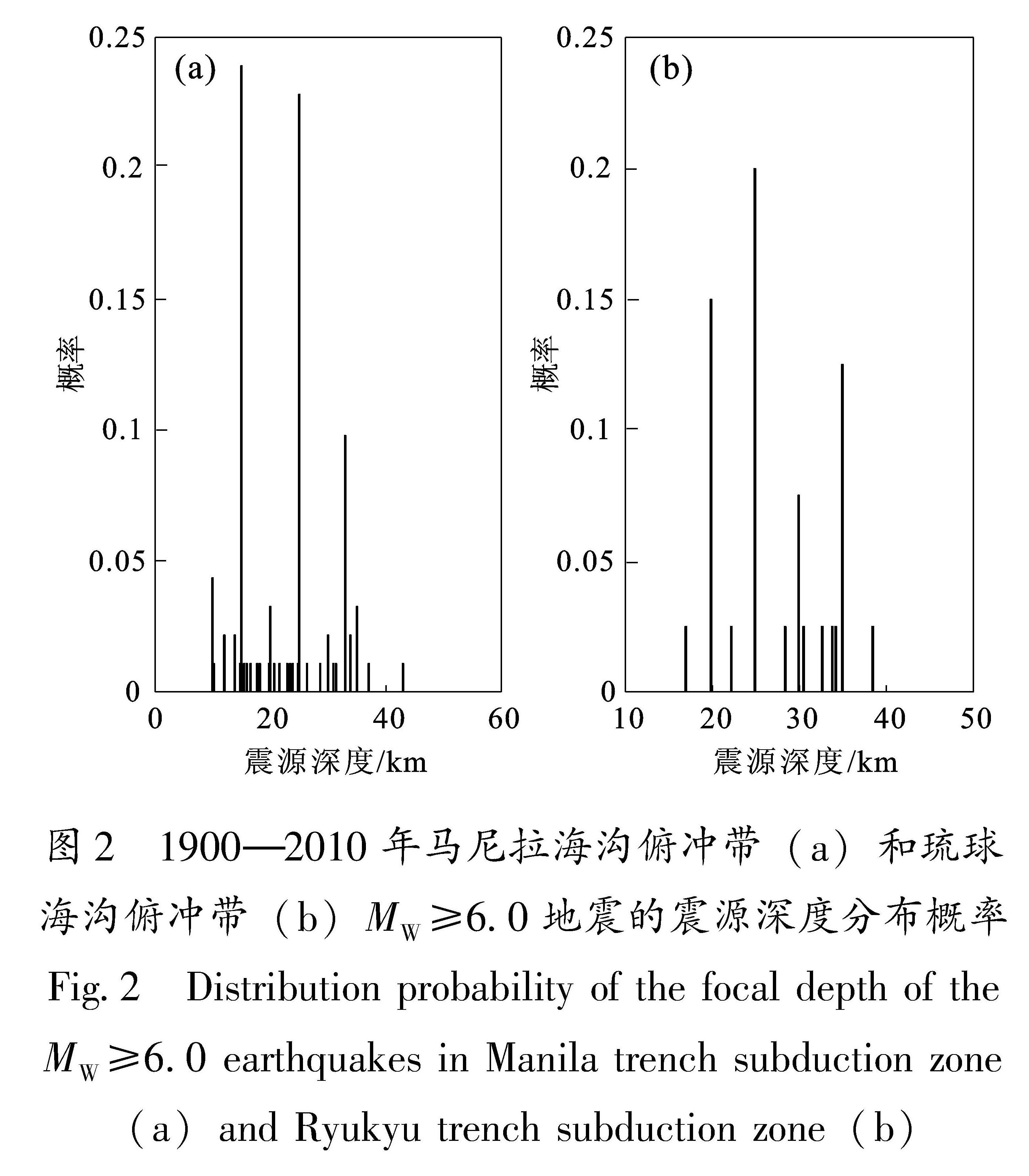
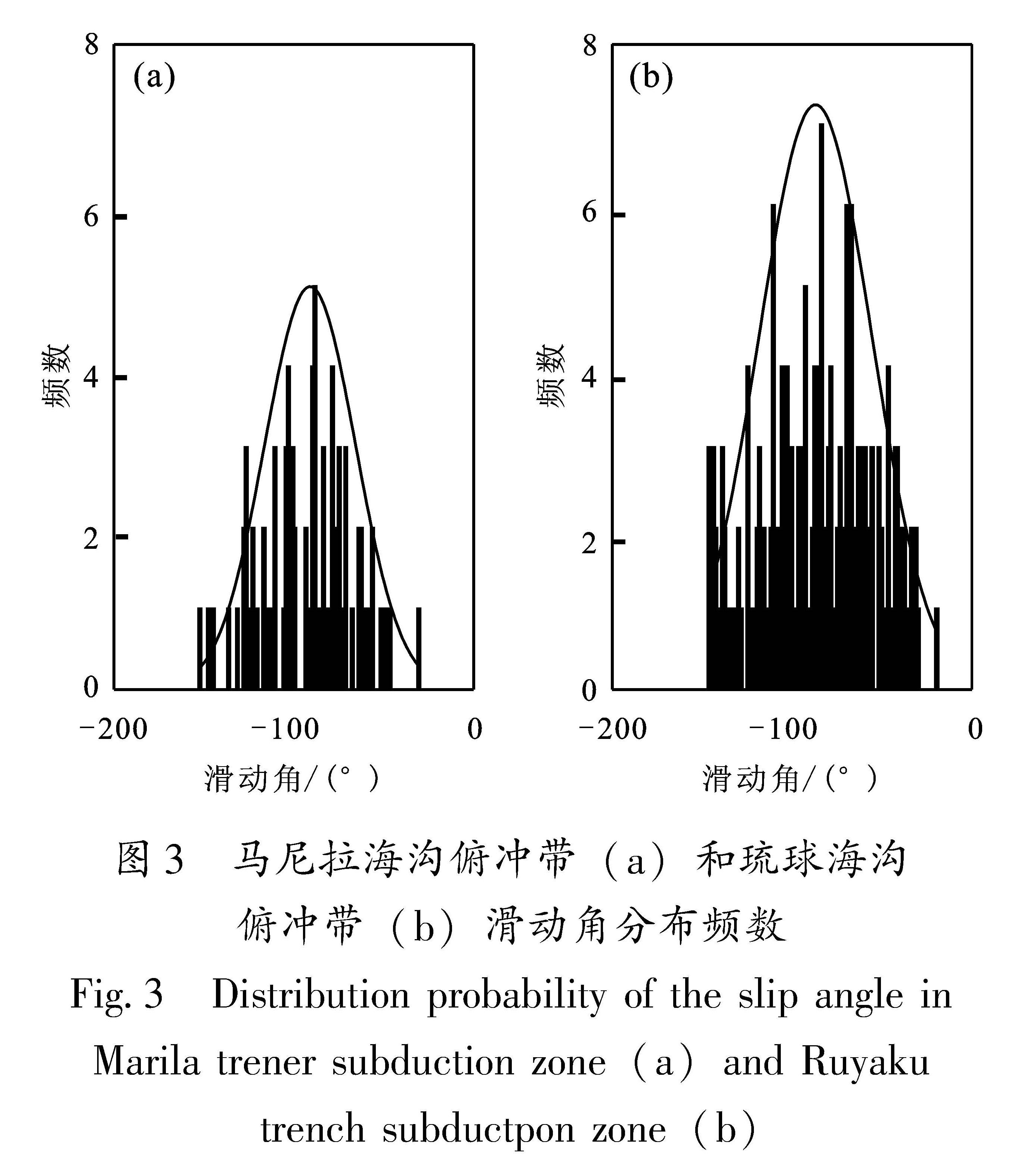
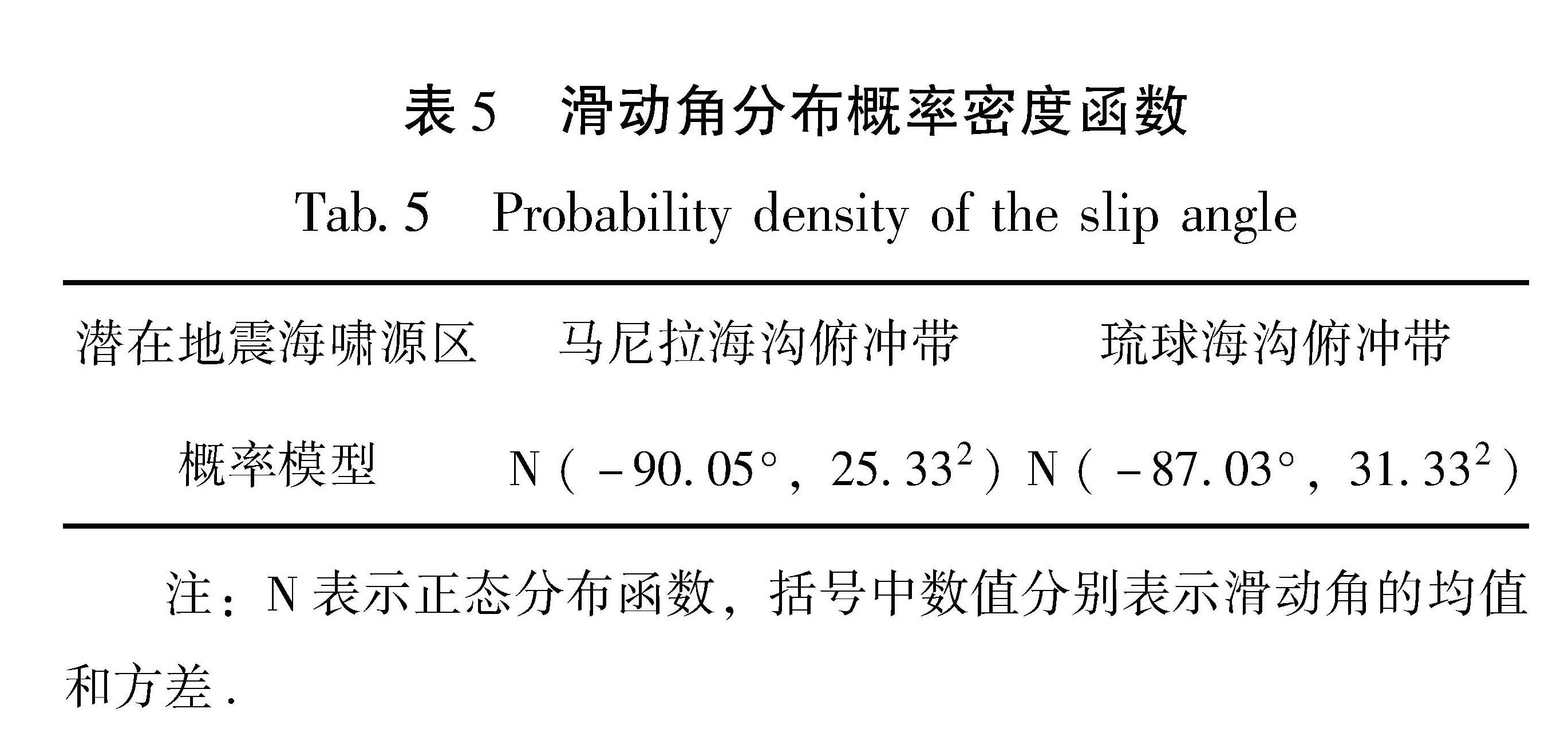
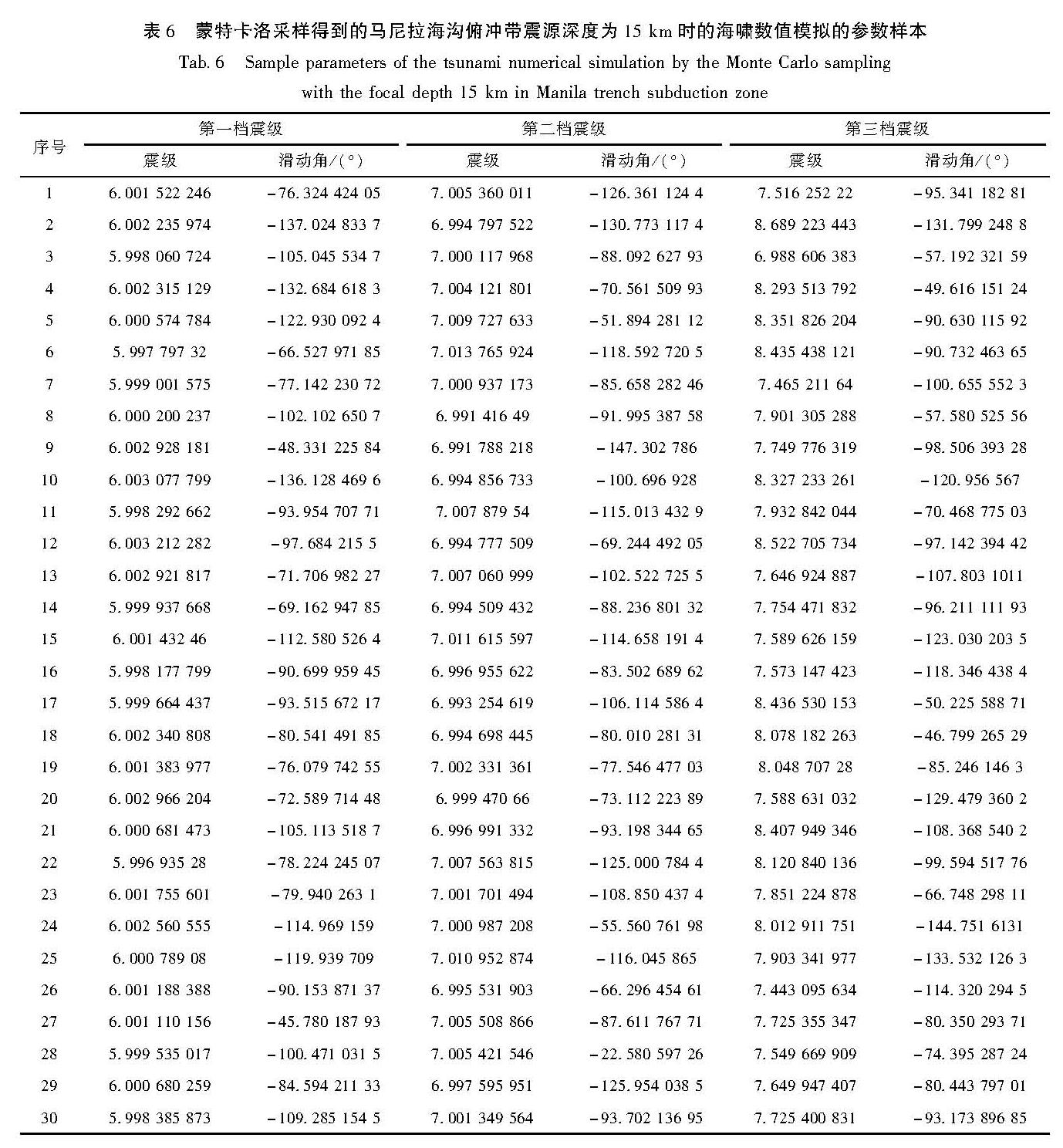
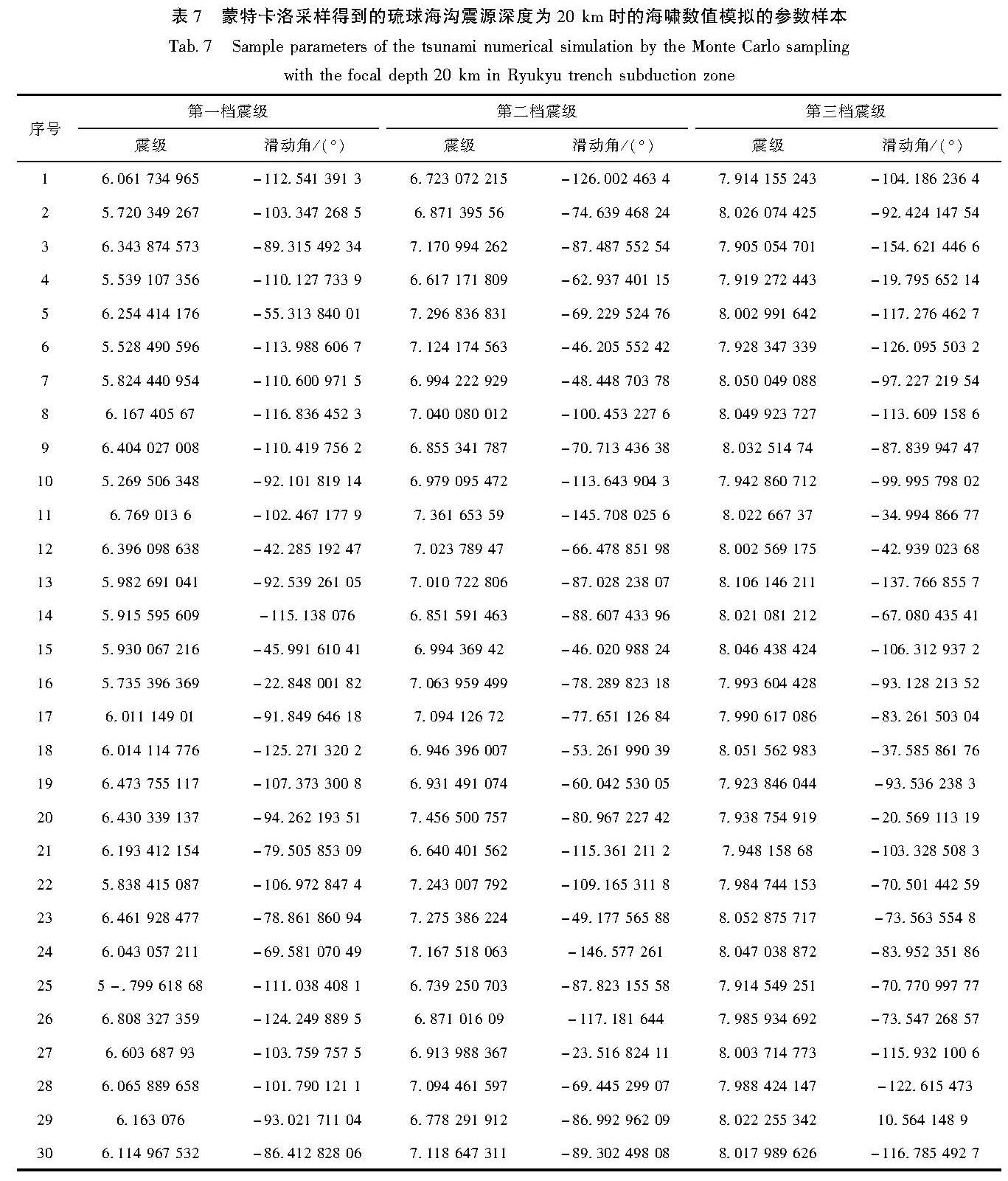
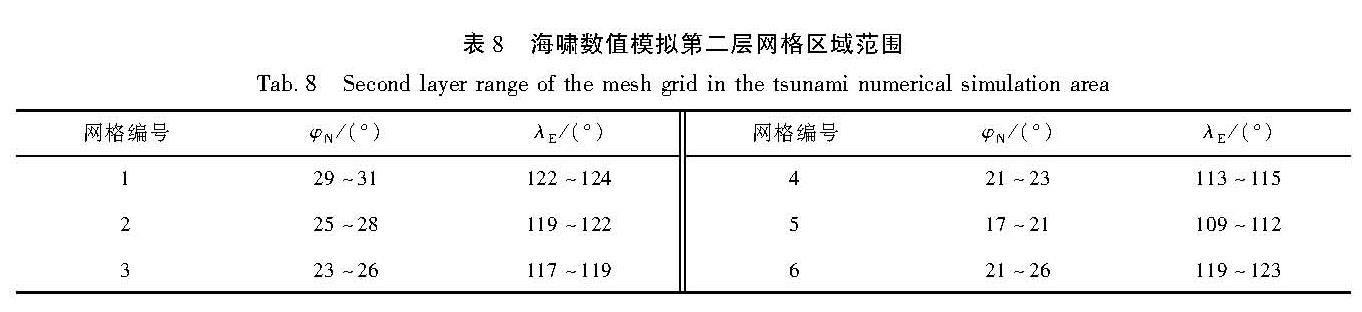
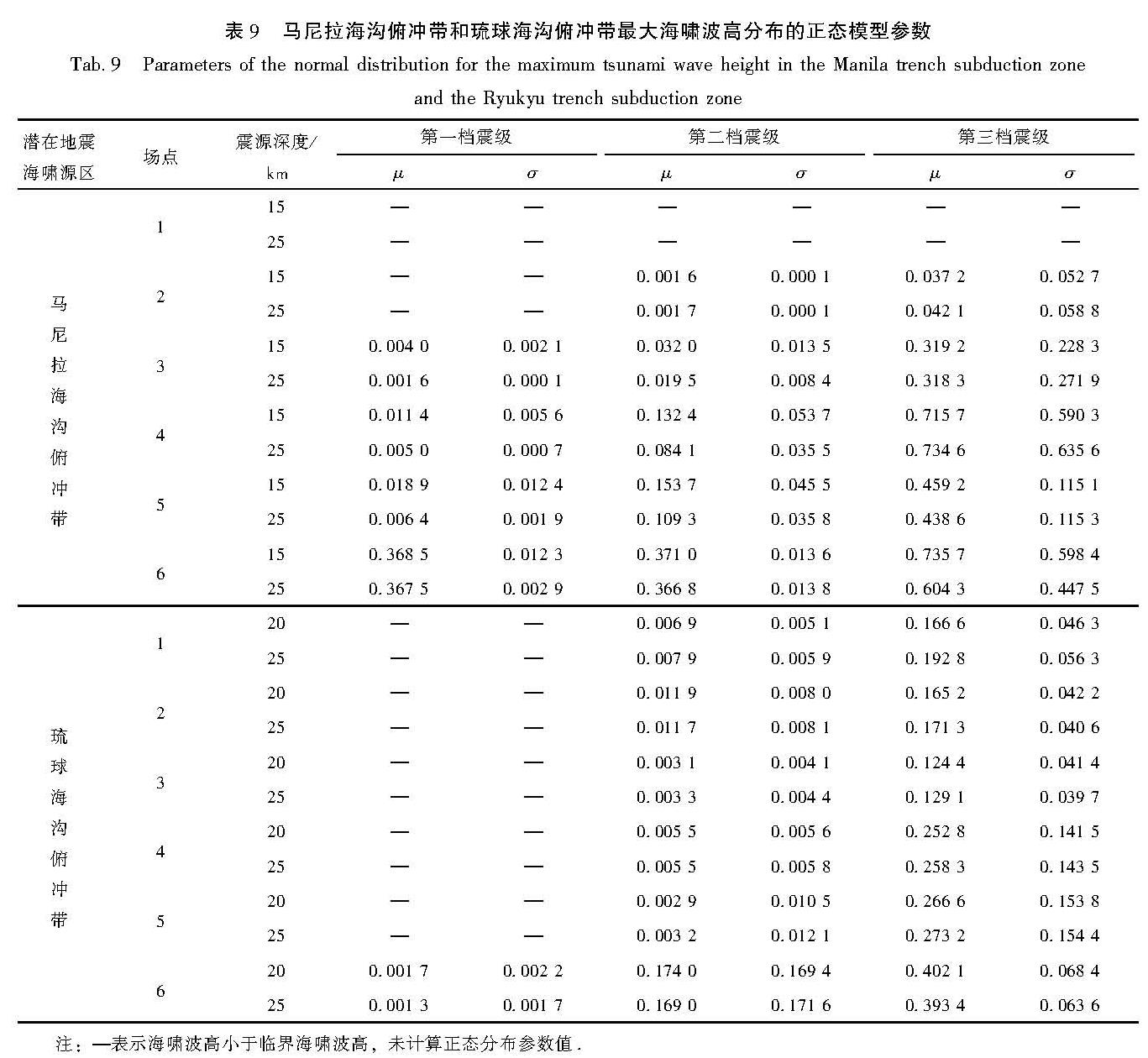
构建合适的地震活动性模型是地震危险性分析中的重要环节之一。震级-频度关系被广泛地应用到了地震领域的研究中。此类模型通过构建潜在震源区中震级-频度关系,描述潜在震源区地震活动的强弱(严尊国等,1995)。近年来,基于各时间段最大震级的广义极值模型和广义帕累托模型被应用到地震领域的相关研究中。广义极值模型可以较好地描述地震活动的尾部特征,而触发灾害性地震海啸的地震震级往往较大,因此有学者将其应用至潜在地震海啸源区的强震危险性的估计中(张锟等,2016; 钱小仕等,2012)。为说明广义极值理论的两种模型均适用于耦合潜源参数不确定性效应的地震海啸危险性估计,笔者分别选用两种模型构建马尼拉海沟俯冲带和琉球海沟俯冲带两个潜在地震海啸源区的地震活动性模型。
2.1 广义极值地震活动性模型
假设X1,…,Xn是一独立随机变量序列,有共同的分布函数F,则广义极值模型的统计对象可以抽象为Mn=max{X1,…,Xn}。在本研究中,Xi(i=1,…,n)表示对时间窗内所有独立地震的震级。用Mn表示n个时间窗内的最大震级序列,则有Mn的分布可表示成n个分布的乘积:
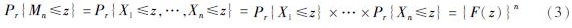
如果存在常数序列{an>0}和{bn}, 使得
Pr{(Mn-bn)∕an≤z}→G{z}n→∞(4)
式中:G是一个非退化分布函数,则G属于下列3种分布之一:
第 Ⅰ 类分布: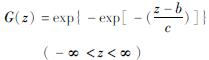
第 Ⅱ 类分布:
第 Ⅲ 类分布: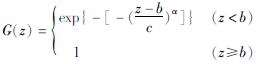
式中:参数c>0,对于分布Ⅱ和Ⅲ,α>0。
通过引入形状参数ξ,可将上述3种分布函数用统一形式表示为:
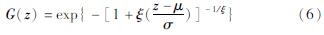
式中:ξ为形状参数; μ为位置参数; σ为尺度参数。其概率密度函数可写为:
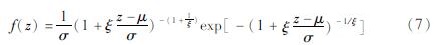
当ξ=0时,为第Ⅰ类分布即甘贝尔分布; 当ξ>0时,为第Ⅱ类分布即费塞尔分布,这两类分布均没有上限值; 当ξ<0时,为第Ⅲ类分布即韦伯分布,存在上限值。
假设z1,z2,…,zm是具有广义极值分布的自变量,令重现期为1/p,则zp是与重现期相对应的震级,其估计值及方差为:
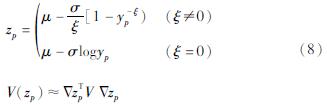
当ξ<0时,广义极值分布服从第Ⅲ类分布,具有上限值,即存在震级上限。上限值对应的是重现周期趋于无限长,z0对应p=0,其最大似然估计为:

综上,在给定重现期1/p后,利用广义极值分布可确定重现期对应的地震震级zp,其中重现期对应的概率代表震级超过zp的概率。
2.2 广义帕累托地震活动性模型
潜在地震海啸源强震活动的广义帕累托模型,可以用来估算潜在震源区和潜在地震海啸源区震级重现水平和震级上限,并给出相应的置信区间,用于分析估计结果的不确定性(田建伟等,2017)。
设X1,…,Xn是一个独立且同分布的随机变量序列,具有边际分布函数。令X1,…,Xn为具有同一分布函数F的独立随机变量序列,则有:
Mn=max{X1,…,Xn}(10)
用X表示Xi序列中的任意项,假设F满足式(4)时,对于足够大的n,有:
Pr{Mn≤z}≈G(z)(11)
对于足够大的u,当X>u,y=(X-u)的条件分布函数可以近似为:
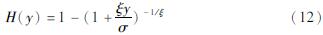
由式(12)定义的分布被称为广义帕累托分布。
广义帕累托分布与广义极值分布之间具有对偶性,两类分布的特征主要由形状参数ξ主导。当ξ<0,广义帕累托分布有上限u-σ~∕ξ; 当ξ>0,广义帕累托分布没有上限。如果ξ=0,y>0,则可导出:
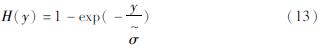
式中:H(y)为参数1/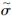 的指数分布。
的指数分布。
阈值选择影响估计结果的偏差和方差之间的平衡。阈值过低,很可能会背离模型的渐近基础,导致偏差过大; 阈值过高,超出量的数据减少,虽然模型可以估计,但将导致方差变大。折中的做法是采用尽可能低的阈值,但要根据极限模型提供合理的近似。为达此目的,有两种方法:一是试验性模型估计方法; 二是通过在一定取值范围内选取不同阈值进行模型拟合,考察模型参数估计的稳定性。选定阈值后,可以利用极大似然估计方法,估计广义帕累托分布的参数。再应用delta法,求得重现水平和上限估计值的标准差和置信区间(史道济,2006)。
构建强震活动广义帕累托模型时,先根据上文介绍的方法选取震级阈值,再将遴选出的一定时期内历史地震记录中大于阈值的震级值作为随机变量,假设其满足独立同分布的条件,且其超出量符合广义帕累托分布。
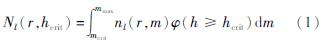
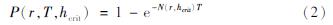
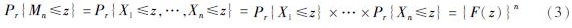
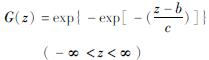

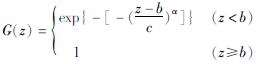
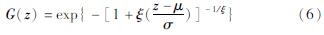
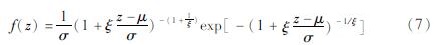
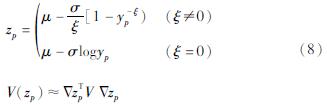

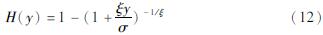
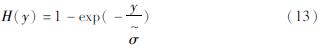
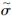 的指数分布。
的指数分布。