基金项目:地震科技星火计划项目(XH23056YA); 国家自然科学基金(42204008); 中国地震局第一监测中心科研项目(FMC2022014).
第一作者简介:段天奇(1998-),硕士研究生在读,主要从事GNSS地壳形变研究.E-mail:2571391853@qq.com.
通信作者简介:占 伟(1983-),研究员,主要从事GPS数据处理及分析研究工作.E-mail:zw000373@163.com.
(1.天津城建大学 地质与测绘学院,天津 300384; 2.中国地震局第一监测中心,天津 300180)
(1. School of Geology and Geomatics,Tianjin Chengjian University,Tianjin 300384,China;2. The First Monitoring and Application Center,China Earthquake Administration,Tianjin 300180,China)
GNSS; terrestrial water storage; mass-loading theory; inversion
DOI: 10.20015/j.cnki.ISSN1000-0666.2024.0038
陆地水是水资源中重要的组成部分,包含地表水、土壤水、地下水等,在人类生活和社会发展中是不可或缺的(Famiglietti et al,2011; Long et al,2014),科学认识陆地水变化规律是对陆地水资源进行合理开发利用的前提。由于全球卫星导航系统(Global Navigation Satellite System,GNSS)连续观测具有低成本和高时间分辨率等优点,可以与重力恢复和气候实验卫星(Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment,GRACE)、全球水文模型等其它技术相结合并优势互补。近年来,全球范围内已经建立了密集的GNSS连续观测网络(姜卫平,2017),在监测陆地水储量方面得到了广泛应用,成为监测陆地水储量的利器(Enzminger et al,2018; Adusumilli et al,2019; White et al,2022; Li et al,2023a)。在暴雨等极端天气下,GNSS连续观测拥有近实时监控和潜在灾害预警的巨大潜力(Milliner et al,2018; Zhan et al,2021; Heki,Arief,2022; 谭争光等,2022)。
利用GNSS研究陆地水储量经历了“验证—应用—分离”的过程。本文首先介绍基于GNSS数据反演陆地水储量的方法,然后介绍GNSS反演陆地水储量的研究进展,并分析其发展趋势。
地表点质量源引力位如图1所示。如果将地球视为近似规则的球体,根据万有引力定律,地球上某一点引力位Φ的计算公式为:
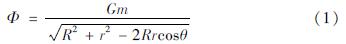
式中:G表示引力常量; m表示点源的质量; R表示地球平均半径; r表示点位与地球中心的距离; θ表示点位间的角距离。
图1 地表点质量源引力位示意图(据沈迎春,2021)
Fig.1 A sketch of the gravitational position of a surface point mass source(according to Shen,2021)
基于Farrell(1972)所提出的地壳负荷形变理论,结合引力位函数相,通过地壳负荷形变量求得单位质量的点负荷所产生的垂直和水平方向的形变量,表示为:
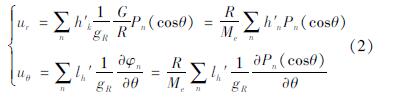
地表负荷造成的垂直形变会随着离负荷距离的增大而迅速减小,如图2所示:以圆盘半径7 km、等效水深4 m、约0.62 Gt负荷为例,距离圆盘中心10 km处的垂向形变小于距离圆盘中心5 km垂直形变的一半,距离圆盘中心20 km处的垂向形变小于距离圆盘中心10 km垂直形变的一半。
图2 圆盘半径7 km、等效水深4 m 时的地面负荷造成的地表垂直运动示意图
Fig.2 A sketch of the vertical surface movement due to ground loading for a disk radius of 7 kilometers and an equivalent water depth of 4 meters
目前计算负荷与地壳位移之间联系的方法主要有格林函数积分法、球谐函数法及Slepian基函数法。这3种方法都是基于地球初始参考模型(Preliminary reference earth model,PREM)质量负荷引起垂直位移的计算方法。负荷格林函数为单一点负荷的垂向基函数,主要用于解决单位质量的点负荷问题(Guo,2004)。球谐函数主要用于描述质量源在地球外部产生引力位的作用,对于地球表面流体质量变化可以将其看成连续球面函数并进行球谐函数展开(Hofmann-Welenhof,Moritz,2005)。Slepian基函数是一种常用的球面径向基函数,相较前两种方法,它可以有效减少信号泄露,提高结果的信噪比(Albertella et al,1999)。
首先,设U表示观测到的垂直位移,m表示区域网格质量模型,G表示通过负荷格林函数建立的系数矩阵。在完全理想的情况下,观测数n与模型t相等(n=t),且系数矩阵G存在逆矩阵,则可以求得:

获得质量模型m是基本的反演过程,可以通过直接求G的逆系数阵来实现这一线性观测函数。然而实际的地球物理反演比较复杂,通常表现为欠定问题,需要添加约束条件建立约束矩阵,在求解法方程后得到约束解析式。
在计算中通常进行Tikhonov正则化(Tikhonov,Arseninn,1977),加入正则化因子λ2,其求解结果如下:
m=(GTG+λ2I)-1GTU(4)
Argus等(2014,2017,2022)在反演过程中
引入正则化参数和拉普拉斯算子,其目标函数为:
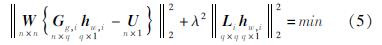
式中:W为GNSS垂向位移权重; hw,i为第i个格网内的等效水高; Gg,i表示负荷格林函数的系数矩阵; L为拉普拉斯算子; λ2为正则化参数; n为垂向位移数值; q为研究区内的格网数量。
由于反演过程中的负荷格林函数卷积是对全球范围进行计算,而一般情况下反演只是针对某一个小区域进行计算,因此研究区外的负荷形变会被当成噪声从而影响反演结果。为了减小这个影响,可以对质量模型参数及其约束矩阵扩充,以降低外部区域对研究区内质量反演造成的影响。式(5)可以变化为(沈迎春,2021):
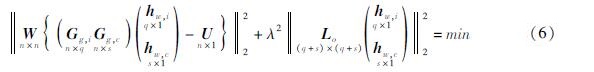
式中:hw,i和hw,c分别为研究区内和扩展边界外的质量负荷模型; Gg,i和Gg,c分别为格林函数得到的系数矩阵和约束矩阵; n、q和s分别为向量U、hw,i和hw,c的维度信息。通过此方法可以对区域质量的圆盘反演起约束作用。
Wang等(2022)在反演过程中,加入了GNSS水平位移,使用格林函数G(ψ)的卷积积分计算由多个质量负荷源q(θ',φ')引起的点位移b(θ,φ),式(7)为曲面变形对质量负荷的反演:
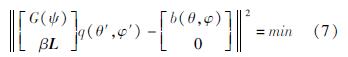
式中:q表示最小二乘的反演质量,并且假设水平分量和垂直分量是等权的; β是平滑因子,用于调整质量的最小二乘拟合和平滑度之间的相对权重; L是拉普拉斯算子,有3种表现形式,分别对应与网格位置位于角落(2个相邻斑块)、边缘(3个相邻斑块)、其他地方(4个相邻斑块)。
Carlson等(2022)使用GNSS和GRACE数据联合反演,反演公式类似于式(5),联合反演的权重矩阵为:
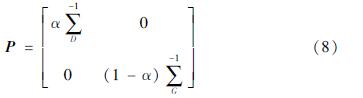
式中: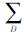 和
和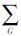 分别为GNSS和GRACE观测值的对角方差-协方差矩阵; α为0~1之间的数值,表示GRACE和GNSS的相对权重。
分别为GNSS和GRACE观测值的对角方差-协方差矩阵; α为0~1之间的数值,表示GRACE和GNSS的相对权重。
固体地球在水、雪、冰和大气等负荷作用下会产生弹性形变。研究表明,GNSS记录的垂直位移与陆地水变化相关:当负荷增加时,地面下降,附近GNSS站点会向下并向负荷源方向移动; 当负荷减小时地面反弹,附近GNSS站点会向上并远离负荷源方向移动。Van Dam和Wahr(1998)发现GNSS观测的位移时间序列包含了可以用来监测陆地水储量等地表负荷变化产生的地壳形变。Heki等(2001)将雪深数据与GNSS观测到的垂直表面位移进行比较,证明可以根据GNSS观测到的形变估计水文负荷。Dong等(2002)研究表明,GNSS时间序列中的地球系统质量周期性变化主要是由陆地水储量迁移、大气负荷、非潮汐海洋负荷等多种因素综合作用导致的,并提出可以通过去除其它分量来研究一种负荷的影响。Heki(2004)对主导日本季节性质量变化因素的研究表明,利用GNSS垂向时间序列可以有效地监测陆地水文负荷的季节性变化,并可以对GRACE起到补充作用。Bevis等(2005)研究认为GNSS观测能够对周围100 km范围内的负荷变化产生响应,获取高时间分辨率(天尺度)陆地水储量空间变化信息。
随着研究的不断深入,Argus等(2014)利用美国加州地区密集的GNSS连续观测网络数据研究了该地区的陆地水储量空间变化,对该地区陆地水储量反演结果与GRACE和全球水文模型结果进行了对比,发现三者有很好的一致性。研究表明GNSS能够给出高空间分辨率(小于50 km)的陆地水储量变化,可以成为独立的陆地水储量变化监测手段(图3)。
美国学者Argus在陆地水储量研究领域取得较大进展,其发表的3篇论文具有较好的代表性,完整勾勒出利用GNSS监测陆地水储量研究从验证到应用的过程,研究手段从单一的GNSS手段到GNSS、GRACE、全球水文模型等多手段联合等过程。Argus等(2017)还利用GNSS观测数据估算了2012—2015年美国加州4个地区干旱和强降雨期间陆地水储量在时间上的动态变化,为固体地球弹性响应的评估以及水资源管理提供参考。Argus等(2022)整合美国加州中央山脉GNSS、GRACE、水库水和积雪数据,通过从GNSS和GRACE联合计算得到的总陆地水储量中扣除积雪、土壤水等成分,细化、分离该地区地下水的变化。
在过去的10年中,基于GNSS的陆地水储量研究有了更广泛的应用,越来越多的成果应用于全球范围内的陆地水储量研究(Zhan等,2017,Fok, Liu,2019; Hsu等,2020; Jiang等,2021; Zhu等,2023; Ferreira等,2018; Young等,2021,Silverii等,2016; Pintori,Serpelloni,2023)。Borsa等(2014)基于美国西部地区的GNSS连续观测站的垂向形变序列反演该区域的陆地水储量变化,结果表明GNSS观测有足够的精度和采样密度用来测量地壳垂直运动,并以此估算陆地水储量变化,为水文研究提供了新的思路。王林松等(2014)利用喜马拉雅山脉周边的GNSS垂向形变序列对喜马拉雅山脉的冰雪质量进行反演,并尝试利用水平位移与垂直位移的比值估计质量变化来分析质量源的位置。Amos等(2014)利用GNSS垂直位移研究加利福尼亚州中部地下水变化导致的地壳运动,使用模型模拟总水储量变化导致的负荷变化响应。Fu等(2015)采用阻尼最小二乘法反演陆地水储量变化,论证了该方法反演结果可以用来填补GRACE和GRACE Follow-On之间的空白。
近年来,在全球气候变化背景下,极端干旱、暴雨等事件日益增多。GNSS以其高时间分辨率(天尺度)、低成本的优势,成为监测干旱、暴雨等极端事件陆地水储量动态变化的一种新手段。Jin和Zhang(2016)利用连续的GNSS观测数据估算美国西南部陆地水储量变化,揭示了水储量季节性变化较大的区域位于落基山脉和密西西比河流域,并指出GNSS拥有用于监测干旱引起水储量异常信号的能力。姚朝龙等(2020)基于中国区域的GNSS台站形变序列对2018年太平洋西北洋面上生成的台风“山竹”进行分析,发现通过GNSS时间序列可以观测到台风“山竹”尾流导致的地壳产生厘米级形变。Zhan等(2021)利用GNSS连续观测网络获取了2019年太平洋超强台风“海贝思”登陆日本期间陆地水储量的时空动态变化,突显了极端天气下GNSS近实时、远程监测水文变化和预测潜在洪水灾害的作用。
由于使用GNSS垂直位移反演区域陆地水储量变化是一个病态问题,因此常使用Tikhonov正则化方法(Tikhonov et al,1995)来稳定病态问题。其中二阶拉普拉斯矩阵用于正则化约束矩阵,L曲线或广义交叉验证法用于确定最优正则化参数(Argus et al,2014)。然而,拉普拉斯矩阵是基于几何角度的稀疏矩阵,不具有明确的物理意义。此外,有时难以使用L曲线或广义交叉验证法准确估计最优正则化参数。目前,使用GNSS观测值量化陆地水储量变化的反演方法仍存在一定困难,需要引入改进的求解策略以提高GNSS反演结果的可靠性,包括正则化约束矩阵的构建和正则化参数的最优估计。Li等(2023a)基于Tikhonov正则化方法,提出了用地球物理模型计算的先验协方差矩阵作为正则化约束矩阵。为了获得更稳定可靠的反演结果,使用迭代最小二乘估计方法,通过数据本身自适应地确定最优正则化参数。与拉普拉斯矩阵相比,先验协方差矩阵具有明确的物理意义,引入的先验地球物理信息可以提高GNSS反演结果的可靠性。研究结果表明,GNSS反演得到的陆地水储量变化可以达到较高的空间分辨率,由先验约束矩阵正则化的GNSS数据推断的陆地水储量变化比传统拉普拉斯约束矩阵更可靠,并且由GNSS数据推断的陆地水储量变化与用GRACE、GRACE Follow-On和GLDAS推断的陆地水储量变化在时间域、空间域和降水数据上均显示出较好的一致性。
目前相关的研究主要使用GNSS垂直方向位移,在反演陆地水储量的过程中加入水平位移,这将有助于提升反演的稳定性。Wahr等(2013)使用加州北部和格陵兰岛南部的GNSS数据,结合水平和垂直运动方向,来确定负荷区域及质量变化,结果表明水平位移同样可以用于地面负荷形变的研究。Wang等(2022)在我国华中地区利用GNSS垂直和水平位移进行了质量载荷反演的综合实验。棋盘格实验结果表明,当站点少于该区域总网格数量的2/3时,即使位移观测没有任何噪声,仅使用垂直位移的质量反演也会变得不可靠。当GNSS站点数量大于在整个区域内相对均匀分布的总网格数量的1/3时,水平位移与垂直位移的组合显著改善了反演结果。其结果表明:与仅使用垂直位移反演相比,使用三维位移反演的结果更加精确,尤其在GNSS站点稀疏的区域。在当前的测量精度水平下(3 mm),包含水平位移的反演可以提升约10%的精度,未来如果可以将测量精度提升到0.1 mm的水平,包含水平位移的反演精度就可以提升超过30%。
GRACE是美国国家航空航天局和德国航空航天中心于2002年3月17日发射的重力卫星,也是区域水储量变化监测的重要工具,能较好地给出数百千米尺度陆地水储量变化的特征(Rodell,Famiglietti,2002; Swenson et al,2006; 杨元德等,2009; 钟敏等,2009; 冯伟等,2012)。首先,GNSS和GRACE联合研究可以利用GRACE获得的陆地水储量变化信息,去除GNSS坐标时间序列中由陆地水储量变化所引起的非构造形变影响,从而更为准确地获取地壳垂直运动情况。其次,联合反演可以弥补GNSS测站分布不均匀和GRACE空间分辨率低等不足,实现两种手段的优势互补,进而获得时空分辨率更高的陆地水储量结果。
GNSS和GRACE联合研究也经历了从验证到应用的过程。Byron等(2004)利用GRACE时变重力场数据研究亚马逊流域陆地水负荷形变,发现GRACE所得流域水储量与GNSS坐标位移时间序列有较强的相关性。后续研究也证明了GNSS与GRACE信号在全球多个典型区域均有较强的相关性(Kusche,Scharma,2005; 刘任莉等,2013; 盛传贞,2014; 郝明等,2017)。人们发现可以利用二者较强的相关性这一特点进一步开展研究。如Wang等(2017)利用GNSS垂直位移数据对华北平原地区进行研究,并利用GRACE数据模拟水文负荷变化导致的垂向位移,发现二者较为一致的物理机制为气候变化导致的季节性水圈团块运动引起的岩石圈周期性位移。Pan等(2019)进一步利用GRACE时间序列中的信息改正了天山地区GNSS位移中负荷变化产生的形变。随着研究的不断深入,部分学者开始利用GNSS和GRACE数据联合研究陆地水储量(何思源,2017; Su,Zhan,2022),这些研究表明二者联合反演的地壳形变具有较高的时空一致性,可以较为精确地反演出陆地储水量变化。Carlson等(2022)基于小波分析提出一种新的联合反演框架,使用连续小波变换将GNSS和GRACE时间序列分解为长期和短期分量并分别进行反演,再分别赋予不同的权重并计算最佳权重分配,得到了2003—2016年美国加州的陆地水储量。上述结果表明,GNSS和GRACE联合反演比GRACE单独反演结果时空分辨率更高,还可以校正局部因素对GNSS反演结果的干扰、捕捉长期的陆地水储量变化。
全球水文模型可以提供全球高时空分辨率的多种最优化、接近实时的陆地表面状态和通量场,例如降水、蒸散、地表径流和地下径流等。全球陆地同化系统(Global Land Data Assimilation System,GLDAS)水文模型通过结合数据同化技术、卫星遥感数据和地面观测数据等多种数据,对全球陆地表面的水文循环过程进行模拟和预测。其优点是在陆地水储量的研究中,GLDAS水文模型可以用于验证反演结果的准确性,例如Scanlon(2019)使用GRACE和GLDAS评估人类活动对全球水储量趋势的影响和陆地水储量的季节性波动; Li等(2023b)使用GLDAS数据验证GNSS和GRACE联合反演中国西南地区和长江流域陆地水储量的结果,并将其用于仿真模拟研究的输入信号,结果表明二者在半年的时间尺度上有很好的一致性。现有的水文模型也存在一定的不足,比如Jin和Zhang(2016)发现GLDAS Noah模型缺乏部分地表水和深层地下水数据,不能完整地监测区域陆地水变化,部分地区径流与蒸散结果不够精确。这些水文模型中未建模的成分通常会导致人类干预和气候变化有关的水储量变化遭到低估。
合成孔径雷达干涉测量(Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar,InSAR)是一种主动式空间对地微波遥感技术,可以大范围、低成本获取地面高程或形变信息,并拥有高空间分辨率。InSAR与GNSS的数据融和也是目前的研究热点,可以用于验证地面沉降或估算地下水开采造成的地表形变(Bui et al,2021; Sha,2021)。
近年来GNSS观测在陆地水储量研究中得到了广泛的应用,取得了重要进展和成果,但今后还需要在以下几个方面开展更加深入的工作:
(1)提高陆地水储量反演结果的准确性和可靠性。由于GNSS时间序列包含了多种地球物理因素引起的形变信息,如未建模的基岩热膨胀和土壤膨胀效应、冰后期反弹效应、非潮汐大气负荷和非潮汐海洋负荷。因此,在今后的研究中需要建立更加精确的模型和数据处理方法,用来识别并分离出GNSS时间序列中各种非水文负荷造成的形变信息,进而提高陆地水储量反演结果的精度。其次,在GNSS与GRACE、InSAR等技术手段联合反演时,如何科学、合理地赋予各种技术手段最佳的权重,以期实现多种技术优势互补、进而获取最优的陆地水储量反演结果,也将是一个重点研究方向。
(2)提升陆地水储量反演结果的应用价值。陆地水中包含了地表水、地下水、土壤水等多种成分,而单独依据GNSS反演难以将陆地水储量的不同成分分离出来。在今后的研究中,可以联合全球水文模型、降雨、积雪等水文资料构建更加精细的地球物理模型,对陆地水的不同成分进行精细化处理和综合分析。
(3)在中国大陆地区利用GNSS研究陆地水储量具有巨大的潜力和前景,如利用GNSS技术进行陆地水储量研究可以为水资源管理、农业生产等领域提供重要的支持和决策依据,GNSS技术还可以用于监测地表沉降和地壳运动等现象,为地质灾害预警提供数据支持。然而,这一领域也面临挑战,包括数据处理和分析的复杂性、仪器精度的提高以及数据共享和隐私保护等问题。随着技术的不断进步和政策的支持,利用GNSS研究陆地水储量将为中国的水资源管理、农业发展和地质灾害预警带来更多的机遇和挑战。
本文介绍了基于质量负荷理论利用GNSS观测反演陆地水储量的方法,阐述了利用GNSS研究陆地水储量的进展、应用和发展趋势。随着GNSS观测精度的不断提升和观测网络的迅猛发展,利用GNSS观测研究陆地水储量的优点愈发明显。首先GNSS可以利用高精度卫星信号定位,获取研究区的精确位置信息; 其次,GNSS可以对大范围、大面积的陆地水储量进行实时观测。GNSS已成为陆地水储量监测的重要手段,在中国大陆地区,利用GNSS研究陆地水储量具有巨大的潜力和前景,我国已经建立了较为完善的GNSS观测网络和数据处理系统,可以提供高精度的位置信息观测服务,并且在地形测量、水文和气象观测等领域拥有丰富的经验和技术积累,但仍需要在时间序列信号精细识别、反演算法优化和多源数据融合等方面开展深入研究。未来,随着大数据、人工智能等技术的不断发展,可以利用GNSS等观测数据进行数据挖掘和识别,实现更精确的水文预报和预警。此外,本文还介绍了GNSS、GRACE、InSAR与水文模型等的联合研究,以实现更精确的陆地水储量监测和预测。这些技术将有助于更好地理解和预测水文循环的变化,对于水资源管理和环境保护具有重要意义。
由于所能收集的文献有限和论文篇幅的限制,本文介绍的仅仅是陆地水储量变化研究的一些摘要成果,随着未来研究的不断深入,其应用前景更加广阔。可以预见,随着对陆地水资源的深入研究,将有更多的发现和创新应用不断涌现,为解决全球水危机和应对气候变化带来新的契机。
本文在撰写过程中得到中国地震局第一监测中心陈长云高级工程师、梁洪宝高级工程师、畅柳高级工程师、张庆云博士、李经纬博士和天津城建大学王勇教授和李瑞杰硕士的帮助,审稿专家也提出了宝贵的意见,在此一并表示衷心感谢。