基金项目:国家重点研发计划专题(2022YFC3003703).
第一作者简介:魏 斌(1969-),高级工程师,主要从事地震监测预报预警研究,E-mail:weibin@163.com.
通信作者简介:陈长云(1981-),高级工程师,主要从事地震监测预报与地壳变形研究,E-mail:chency@fmac.ac.cn
(1.新疆维吾尔自治区地震局,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830011;2.中国地震局第一监测中心,天津 300180)
(1.Earthquake Administration of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region,Urumqi 830011,Xinjiang,China;2.The First Monitoring and Application Center,China Earthquake Administration,Tianjin 300180,China)
GNSS;strain rate;block model;strikeslip rate;earthquake risk;Xinjiang
DOI: 10.20015/j.cnki.ISSN1000-0666.2024.0022
新生代以来,印度板块和欧亚板块的碰撞以及印度板块向欧亚板块的持续楔入作用,导致青藏高原的快速隆升(Tapponnier et al,2001)。在印度板块持续向北运动的作用下,青藏高原至今仍在不断隆升与扩张,基于GNSS资料获得的现代地壳水平运动速度场结果显示高原物质正在向西北、东北和东南方向运动(Wang et al,2001;Wang,Shen,2020)。青藏高原的向外扩张受到多个相对稳定块体的阻挡,如位于高原东缘的四川盆地、东北缘的鄂尔多斯块体、北部的阿拉善地块和北西的塔里木盆地(Tapponnier et al,2001),但是印度板块和欧亚板块连续碰撞的远场效应仍然影响到了天山地区,导致天山造山带重新活动,发生陆内造山运动,并再次强烈隆升(Hendrix et al,1994),形成典型的板内新生代复活型造山带(张培震等,2003a)。受青藏高原向北西扩展远程效应的影响,天山地区成为中国大陆内部地震活动最为强烈的地区之一,定量研究天山及邻区地壳变形特征以及主要构造带的滑动速率有助于理解青藏高原的变形机制和评估其强震危险性。
地壳变形是地震过程中最直观的现象,伴随强震孕育、发生及震后调整的全过程(江在森,武艳强,2012)。近30年来,以GNSS为代表的空间对地观测技术发展迅速,为不同尺度的地壳形变过程、活动断裂运动变形特征的监测提供了高效、稳定、精确的观测结果。相关技术已成为板块构造运动、区域地壳运动与变形模式、断裂带活动习性和地震监测预报等研究的重要技术手段。中国地壳运动观测网络和中国大陆构造环境监测网络(CMONOC)产出的丰富的GNSS观测结果(Wang et al,2001;Liang et al,2013;Wang,Shen,2020),为区域地壳变形和强震过程研究提供了高精度、高时空分辨率和高可靠性的数据结果,对认识强震的孕育过程,开展强震物理探索具有重要意义(Wu et al,2015,2022;武艳强等,2020)。本文基于新疆及邻区GNSS速度场结果,计算获取了研究区大尺度形变场和主要活动断裂的滑动速率,研究了大尺度形变场与强震之间的关系,滑动速率与强震之间的关系,探讨了强震前区域地壳变形特征与大地震孕育之间的可能关联。
新疆及邻区地处欧亚大陆的腹地,毗邻青藏高原,是蒙古、哈萨克斯坦、塔里木和青藏高原的交汇部位,连接亚洲东、西部的中地域(何国琦等,2004),构造活动复杂,强震频发(图1)。根据断裂带走向,可将区域内的主要断裂分为NE、NW和近EW走向3类。NE走向断裂带主要包括位于北天山的洛包泉—咸泉子断裂带、达尔布特断裂带、博阿断裂带东段和兴地断裂带等;位于南天山的克敏断裂带、那拉提断裂带、迈丹断裂带、柯坪断裂带和秋里塔格断裂带等;位于青藏高原和塔里木盆地交界的阿尔金断裂带。NW走向的断裂带主要包括:位于北天山的额尔齐斯断裂带、纸坊断裂带和博阿断裂带北西段;位于南天山的喀什河断裂带、塔拉斯—费尔干纳断裂带和大扎莱尔断裂带;位于帕米尔和塔里木盆地边界的克孜勒陶断裂带。近EW走向的断裂带主要指位于准噶尔盆地和哈密盆地之间的哈密断裂带、洛包泉—咸泉子断裂带和博格达北缘断裂带等。区域地震在空间上分布不均匀,[JP2]主要集中在南、北天山以及南天山和帕米尔交汇的区域。有历史地震记载以来,研究区内共发生8级以上地震3次,7级以上地震17次,6级以上地震115次。3次8级地震分别为1812年尼勒克8级、1902年阿图什8级和1931年富蕴8级地震,图1中震源机制解结果来自美国哈佛大学GCMT,地震数据来自中国地震台网中心。
本文所用GNSS速度场(图1)来源于Wang和Shen(2020)基于中国地壳运动观测网和已有研究成果(Zubovich et al,2010;Kreemer et al,2014)获取的相对于欧亚参考框架下的速度场结果,共计642个GNSS测站,包括GNSS连续站点32个、流动站点610个。连续站速度场北和东方向精度分别为0.31和0.34 mm/a;流动站速度场北和东方向的精度分别为0.51和0.52 mm/a。连续站速度场中国地壳运动观测网络GNSS数据观测时段为1999—2016年;已有研究(Zubovich et al,2010;Kreemer et al,2014)GNSS数据观测时段为1994—2002年,数据具体处理流程参见Wang和Shen(2020)研究。新疆及邻区GNSS速度场大致以75°E为界,其以东向北或者北东运动;其以西向北或者北西运动,并且自高原内部经过塔里木盆地向北东或者北西的GNSS站点速度递减特征明显。
相对于地壳运动结果,应变率分布具有不依赖参考框架、直接反映变形信息的特点,被广泛应用于地壳变形特征描述中。本文使用最小二乘配置(武艳强等,2009;Wu et al,2011)计算应变率分布特征。
最小二乘配置方法为大地测量数据处理的经典方法,具有理论上的严密性,可综合估计非随机参数、具有随机属性的信号和随机误差,可表示为:
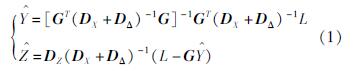
式中: 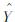 为经典平差问题需要求解的待定参数;Z^为随机信号估值(包括观测点和推估点);G为经典平差问题的系数阵;DX为已测点信号的协方差阵;D Δ 为观测值的协方差阵;L为观测值;DZ 为所有点信号的协方差阵。
为经典平差问题需要求解的待定参数;Z^为随机信号估值(包括观测点和推估点);G为经典平差问题的系数阵;DX为已测点信号的协方差阵;D Δ 为观测值的协方差阵;L为观测值;DZ 为所有点信号的协方差阵。
利用式(1)进行地壳运动描述时首先需要确定信号的协方差分布特征,江在森等(2003)对信号的协方差分布进行过深入的讨论,推荐采用高斯型协方差函数拟合获取,表示为:

式中: A和k为待定参数;d 为观测点间距离(以km为单位),在球面可表示为大地坐标( λ,φ )的函数。
利用f(d)形成协方差矩阵 DZ和DX,建立起速度场与点位的函数,根据速率与应变率的偏微分关系即可得到应变率场结果,进而通过简单矩阵转换可获得主应变率、面应变率、最大剪应变率等应变矢量或标量。速率与应变率的偏微分关系表示为:
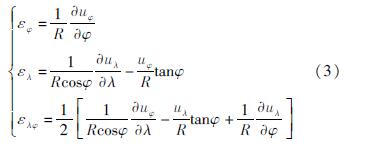
基于大尺度GNSS速度场资料,通过构建三维弹性块体模型可以反演获得断层的滑动速率,该滑动速率代表了断层的长期滑动速率(Meade,Hager,2005;Meade,Loveless,2009)。Meade和Hager(2005)给出基于线弹性球面块体模型计算震间期速度场的公式:

式中: Ω块体旋转的欧拉矢量;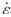 代表块体内部的弹性应变张量;VB块体整体运动速度;VCSD为块体边界断裂在块体之间相对差异运动时由于断层闭锁作用产生的同震亏损滑动速率;Vε[DD(-*3]·[DD)] 为块体之间的内部均匀弹性变形对速度场的贡献。
代表块体内部的弹性应变张量;VB块体整体运动速度;VCSD为块体边界断裂在块体之间相对差异运动时由于断层闭锁作用产生的同震亏损滑动速率;Vε[DD(-*3]·[DD)] 为块体之间的内部均匀弹性变形对速度场的贡献。
利用图1给出的GNSS速度场结果,采用球面最小二乘配置方法构建速度场与应变率的函数关系(武艳强等,2009;Wu et al,2011),利用GNSS速度场与应变率的偏微分关系直接得到研究区域的应变率张量,统计得到的拟合残差结果为0.80 mm/a,略高于图1中GNSS速度场的平均误差,总体上表明基于球面最小二乘配置方法构建的变形场模型能够较好地描述GNSS速度场结果。
图2给出了研究区应变率分布以及1900—2022年 M ≥6.0地震分布。主应变率结果显示,帕米尔—天山地区呈现出显著的挤压变形特征,量值自西向东逐渐减小,主压应变率方向在帕米尔地区呈现出由NW向、向东逐渐过渡到NS向的变化;研究区另一个主应变率区域集中在阿尔金断裂带及邻近区域,表现为NNE向挤压、SEE向拉张为主的变形特征,除了主压应变量值较高外、主张应变率量值也较大,反映了阿尔金断裂带的左旋变形特征。图2a展示了研究区域第二应变率不变量结果,根据其计算公式可知该参数不含方向信息,为一标量,反映了研究区域的总体变形特征(Kreemer et al,2003;Riguzzi et al,2013)。从图中可以看出,第二应变率在南天山西段—帕米尔地区、阿尔金断裂带邻近地区呈现高值特征,其中帕米尔构造结附近高值特性最明显。1900—2022年研究区域的 M ≥6.0地震有一大部分分布在应变率高值区,特别是帕米尔构造结东部地区的强震集中非常明显。天山中东段地区、准噶尔盆地北东的可可托海—二台断裂带和北塔山前断裂带以及塔里木盆地东南缘的阿尔金断裂带等地区也有相当比例强震发生。图2b展示了研究区域的最大剪应变率结果,其方向在南天山西段—帕米尔地区主要为NE—NEE向,总体上与主要断层成一个锐角,反映了该区以倾滑变形为主的特征,在阿尔金断裂带及邻近区域,最大剪应变方位与断裂一致性较高,反映了该区显著的剪切变形特征。
基于GNSS应变率结果与1900—2022年地震分布,参照Shen等(2007)、Zeng等(2018)和Wu 等(2022)提出的方法,首先将每个网格点的GNSS应变率由大到小进行排序,累加并归一化后得到图3中灰色曲线,然后对落入对应网格的地震 [KH-1]
图3 GNSS第二应变率不变量(a)、最大剪应变率(b)与1900—2022年 M ≥6.0级以上强震关系统计分析
Fig.3 The second GNSS strain rate invariant(a),maximal shear strain rate(b)and their relation with M ≥ 6.0 earthquakes during 1900-2022
数目进行累加并归一化后得到地震统计结果(图3中棕色曲线)。图3a的第二应变率不变量与地震的统计结果显示, M ≥6.0地震与高应变率分布区具有很好的对应关系,明显优于自然概率(图3中蓝色虚线)。具体表现为,在15%的高应变率区域地震的数量占到了47.9%。另外,地震累积率的另一个显著特征是在中低应变率区域(横坐标0.5~0.7),地震累积率有个显著的曲线抬升,增加量值达到20.7%。
图3b的最大剪应变率与地震的统计结果显示,研究区域高剪应变率与 M ≥6.0地震的对应关系不如第二应变率不变量,在15%的高应变率区域地震的数量占到了38.0%,比第二应变率不变量低了约9.9%。在中低应变率区域(横坐标累积面积0.5~0.7),地震累积率同样表现出显著抬升特征,增加量值约为11.6%。
强震分布区通常是地壳水平运动的大小、方向显著变化的区域,即地壳差异运动显著区(江在森等,2006)。水平速度场空间分布的不一致性是地壳形变的直接反映,而应变场地壳形变的主要参数,是描述区域形变的重要指标,该指标不受参考框架的影响,并且能从不同分辨率反映区域变形特征(孟国杰等,2009)。中国大陆近年来发生的大部分 M ≥6.0地震震中位于由震前GNSS观测资料得出的应变场剪应变率的高值区或其边缘,尤其是与区域主干断裂的构造活动背景相一致的剪应变率高值区(江在森等,2003)。利用GNSS应变率场识别的应变集中区、应变增量梯度带等可以为强震地点预测提供支持(武艳强等,2018)。基于上述认识,结合本文统计的新疆及邻区地壳变形特征与1900—2022年发生的 M ≥6.0地震的关系(图2),认为南天山西段的那拉提断裂带中段和克敏断裂带,南天山东段的秋里塔格断裂带和迈丹断裂带东段,北天山博阿断裂带北西段以及帕米尔东缘、南天山西段和西昆仑交汇区等多个地区具有强震危险性。其中南天山东段的秋里塔格断裂带和迈丹断裂带东段与 M 7专项工作组(2012)给出的南天山中段拜城危险区较为一致。帕米尔东缘、南天山西段和西昆仑交汇区则与 M 7专项工作组(2012)给出的柯坪—阿克苏危险区以及徐锡伟等(2017)给出的帕米尔东缘—西昆仑高震级危险区的分布较为一致。
基于活动块体的基本概念及划分原则,参考张培震等(2003b)的活动地块划分方案,综合区内主要活动断裂带和次级活动断裂带的空间展布、地震活动性等资料将新疆及邻区划分为17个活动块体等(图4)。基于刚性块体模型分析了各次级活动块体的稳定性,图4残差分布特征显示除帕米尔和阿尔金所在的青藏高原地区外,其他活动块体的稳定性较高,说明块体划分方案较为合理。[KG)]
本文基于Wang和Shen(2020)提供的GNSS速度场结果,利用Blocks程序(Meade,Loveless,2009),通过构建三维弹性块体模型反演了新疆及邻区活动块体边界断裂的滑动速率。断层闭锁深度对其周围弹性变形梯度有较大影响,当断裂的闭锁深度变化时,断层错动在地表各点引起的变化会有明显差异。获得断层闭锁深度的方法较多,本文在确定新疆及邻区断层闭锁深度时,没有对[JP2]每条断裂进行细分,而是利用了区域小震精定位结果(李金等,2015)和模型拟合(朱爽等,2021)两种方法综合给出最优闭锁深度。图5a为小震精定位结果,从图中不同震级地震的震源深度可见新疆地区地震以浅源地震为主,在南天山和帕米尔交汇区域有部分中源地震发生。跨南天山和北天山中东段的地震震源深度剖面(图5b、c)显示出新疆地区以浅源地震为主。图5d直方图结果显示跨南天山剖面震源深度不大于20 km的地震占比超过65%,跨北天山剖面震源深度不大于20 km的地震占比超过76%(图5e)。反演过程中通过多次试算得到GNSS数据拟合程度与断层闭锁深度的变化的关系,结果显示最优闭锁深度约为20 km(图5f),综上,断层滑动速率反演过程中新疆及邻区断层闭锁最优深度初值赋值20 km。考虑到大多数断层深部几何形态难以确定以及GNSS测站分布密度不够使得利用GNSS反演断层滑动速率时断层深部的影响不敏感,因此本文利用Blocks程序反演断层滑动速率过程中假设块体边界断层面均为直立产状。
图5 天山地区小震精定位分布(a)、跨南天山(b)和北天山(c)中东段震源深度剖面、南天山(d)和北天山(e)震源深度频次统计结果,以及最优闭锁深度(f)
Fig.5 Smallearthquake epicenters in the Tianshan Mountains after relocation(a),focal depth profiles across the middle and east part of the South Tianshan Mountains(b)and the Nouth Tianshan Mountains(c),frequency of the focal depth in the South Tianshan Mountains(d)and in the Nouth Tianshan Mountains(e),and the optimal locking depth(f)[HT]
图6 三维弹性块体模型模拟的GNSS速度场(a)和残差速度场(b)
Fig.6 GNSS velocities(a),residual velocities(b)fitted with the three-dimensional elastic block model
图6a为模拟得到的GNSS速度场与观测速度场较为吻合,较大的残差主要位于帕米尔、青藏高原等观测误差较大的地区(图6b)。残差分布的直方图(图7)表明北方向和东方向残差平均值分别为-0.16和0.08 mm/a;图中 AVG、SD 分别为残差绝对值的均值和标准差。残差绝对值均值分别为0.94和1.25 mm/a,标准差分别为1.02和1.72 mm/a,残差主要集中在±2 mm/a之间,服从正态分布,说明反演结果较为可靠。
图7 三维弹性块体模型反演结果与N向分量(a)和E向分量(b)速度场的残差分布统计
Fig.7 Histogram of the North component(a)and the East component(b)residuals of the velocity field
图8为基于GNSS数据利用三维弹性块体模型给出新疆及邻区的断层运动以及1976年以来区域内 M ≥6.0地震的震源机制解分布。从图中可以看出:新疆及邻区NW走向的断裂红色为左旋,蓝色为右旋,其中以右旋走滑运动为主,如准噶尔盆地北东侧的额尔齐斯断裂带和可可托海—二台断裂带;中天山地区的博阿断裂、喀什河断裂; 南天山西段的塔拉斯—费尔干纳断裂带和大扎莱尔断裂带等。NE走向的断裂带以左旋走滑运动为主,如准噶尔盆地北缘的达尔布特断裂带、准噶尔盆地南缘的博格达北缘断裂带、博格达南缘断裂带;塔里木盆地南北两侧的阿尔金断裂带、那拉提断裂带、迈丹断裂带、柯坪断裂带以及兴地断裂带等。新疆天山地区的断裂带表现出明显的挤压特征,其中以南天山西段的乌孙山山脊断裂、那拉提断裂西段、迈丹断裂东段和柯坪断裂中西段最为显著。
阿尔金断裂是青藏高原和塔里木盆地交汇地区的边界断裂,李煜航等(2015)基于1999—2013年GPS水平速度场,使用三维线弹性球面块体模型给出阿尔金断裂的滑动速率约为8 mm/a;王阎昭和王敏(2020)通过对多种资料综合分析给出阿尔金断裂中西段滑动速率为10±3 mm/a,上述结果与本文给出(9.1±2.0)mm/a(图8)的结果较为一致。博阿断裂是划分准噶尔—北天山褶皱系于天山褶皱系的分界断裂,也称天山主干断裂,被认为是一条板块聚合的边界,本文模型反演结果显示断裂带右旋走滑速率存在明显的自西向东衰减的特征,断裂带西段滑动速率为(5.3±1.7)mm/a,中段为(1.5±1.7)mm/a,最东端为(0.9±0.8)mm/a;马建和吴国栋[JP2](2019)基于构造地貌和光释光测年结果给出断裂中东段滑动速率为(1.42±0.18)mm/a;李桂荣等(2016)基于GNSS资料的分析认[JP2]为博阿断裂西段滑动速率为4.8 mm/a,东段滑动速率约为1.1 mm/a,
图8 新疆及邻区主要断裂走滑[KG0](a)、张压(b)特征和震源机制分布
Fig.8 Strike-slip(a),tension and pressure(b)characteristics of major faults andfocal mechanism distribution in Xinjiang and its adjacent regions
上述结果与本文模型反演结果基本一致。南天山西段研究程度较高的为柯坪断裂,该断裂带位于天山南部、塔里木盆地西北部,是新生代印度板块和欧亚板块持续碰撞的产物(Allen et al,1999),新生代以来柯坪推覆系东西向缩短量约35~40 km(杨晓平等,2006;刘华国,2011)。由于变形开始时间的不确定,缩短速率有较大差异,一种认为变形开始于20 Ma,缩短速率为2 mm/a(Allen et al,1999);另一种认为变形开始于西域砾岩沉积时期约为2.5 Ma,缩短速率约为15 mm/a(杨晓平等,2006),GNSS给出的变形速率为10~20 mm/a(王琪等,2000;王晓强等,2005)。本文模型反演结果显示柯坪断裂以挤压运动为主,自西向东挤压速率分别为(9.9±1.5)mm/a,(13.9±0.8)mm/a,(4.8±1.0)mm/a和(1.5±0.8)mm/a,断裂西段的挤压速率与杨晓平等(2006)以及基于GNSS给出的结果(王琪等,2000;王晓强等,2005)较为一致。
由于断层运动及震源机制解数据都能反映构造和动力背景,因此对断层滑动和震源机制进行比较是有意义的。总的来说,本文反演的断层运动的方式与新疆及邻区的震源机制类型基本是一致的,如以走滑运动为主的阿尔金断裂带,沿断裂带发生的地震表现出走滑特征。以南北向逆冲挤压为主要运动特征的柯坪断裂带上的地震以逆冲类型为主。新疆及邻区近几十年的强震(图8)主要集中分布在南天山西段与帕米尔西构造结东部附近,一系列NE走向断裂和NW走向断裂相交于此,使得该区域构造活动十分复杂,强震频发。
本文基于GNSS观测数据采用球面最小二乘配置方法计算了新疆及邻区的应变率张量特征,在统计分析了研究区域应变率分布以及1900—2022年 M ≥6.0地震分布之间的关系的基础上,研究了GNSS应变率特征对强震地点的指示意义。通过构建区域三维弹性块体模型反演得到的区内主要断裂的运动变形特征,结合震源机制解结果,对比分析了断裂运动变形特征与不同区域强震类型之间的关系。主要结论如下:
(1)新疆及邻区GNSS速度场东西存在明显差异,大致以75°E为界,其东侧GNSS站点向北或者北东运动,其西侧的GNSS站点向北或者北西运动,并且自高原内部过塔里木盆地向北东或者北西的GNSS站点速度递减特征明显。
(2)帕米尔—天山地区主应变率结果较好地反映了区域的受力特征,解释了各主要断裂带所表现的运动性质。主应变率和第二应变不变量高值区及其边缘与区内强震分布有较好的对应关系,特别是帕米尔构造结东部地区的强震集中非常明显。应变率分布与 M ≥6.0地震的统计结果表明, M ≥6.0地震与第二应变不变量的高应变率分布区具有很好的对应关系,在15%的高应变率区域地震的数量占到了47.9%。通过分析新疆及邻区地壳变形特征与1900—2022年 M ≥6.0地震的统计关系,认为南天山西段的那拉提断裂带中段和克敏断裂带、南天山东段的秋里塔格断裂带和迈丹断裂带东段、北天山博阿断裂带北西段以及帕米尔东缘、南天山西段和西昆仑交汇区等多个地区具有强震危险性。
(3)研究区断裂运动性质具有明显的分类特征,断裂带挤压运动的同时表现出明显的走滑特征,其中NE走向断裂带多以左旋走滑运动为主、NW走向的断裂则多以右旋走滑运动为主。NE走向的柯坪、迈丹和那拉提断裂带与NW走向的克孜勒陶、塔拉斯—费尔干纳断裂带汇集的南天山西段和帕米尔西构造结东部地区强震密集分布。新疆及邻区的断层运动的方式与震源机制类型较为一致。