基金项目:中国地震科技星火计划(XH23046YA); 国家自然科学基金联合基金(U2039205); 国家重点研发计划(2018YFE0109700).
第一作者简介:杨 文(1986-),高级工程师,主要从事地震活动性和数字地震学工作.E-mail:longjing456@126.com.
通信作者简介:余怀忠(1975-),研究员,主要从事地震孕育机理和预测理论研究.E-mail:yuhz750216@sina.com.
(China Earthquake Networks Center,Beijing 100045,China)
Benioff strain ratio; Xinjiang region; minimum complete magnitude; earthquake prediction
DOI: 10.20015/j.cnki.ISSN1000-0666.2025.0028
地震孕育是一个极为复杂的过程。强震发生前,震中附近地区普遍存在的应变能加速释放现象,预示孕震区接近或进入临界状态(彭克银等,2003)。基于加卸载响应比(LURR)理论的研究表明,地震的孕育过程可能与岩石圈非均匀脆性介质的特定加载阶段有关(Yu et al,2022)。理论上,较大的地震发生前,由于地壳介质处于较高应力状态,小的变形或应力扰动就可能导致微破裂的产生,能够观测到LURR的高值异常变化(Yin et al,2008; Yu et al,2020)。以往震例研究显示,震前0.5~3年LURR异常空间分布与震源区位置相关,异常峰值与未来地震的发生时间相关(尹祥础,2015; Yu et al,2020)。与LURR计算中以小震释放的能量作为响应量相似,应变比参数能够表征应变能释放的快慢,其异常演化反映了地震成核过程中介质的高应力状态,具有一定的实用性和可操作性,目前已尝试应用于中国地震台网中心年度会商中。
为了更好地将应变比参数应用于地震预测研究,本文首先对2000—2023年新疆地区地震目录的最小完备性进行分析,并对其进行除丛处理。在此基础上,计算新疆地区6级以上地震前孕震区的应变比随时间的变化以及空间分布情况,总结强震前时空分布特征,为该地区强震危险性判定提供参考。
新疆地区位于欧亚板块中南部,其南面是印度板块与欧亚板块碰撞所形成的世界屋脊——青藏高原,北部是西伯利亚块体及其向南挤压所形成的蒙古弧形构造带。由于印度板块向北推挤、欧亚板块向南挤压,致使新疆地区形成了盆山结合的地貌景观。依据板块构造带的分布,新疆地区自北向南可划分为4大板块。新疆地区构造复杂,新构造活动强烈,是强烈活动的大陆地震区。1900年以来新疆地区共发生7级以上地震18次,最大为1902年8月22日新疆阿图什8.3级地震; 2000年以来共发生6级以上地震19次,其中7级以上地震4次,最大为2001年11月14日昆仑山口西8.1级地震(图1)。2024年1月23日新疆乌什发生7.1级地震,该地震打破了新疆地区近10年的7级地震平静,表明新疆地区进入新的强震活跃时段,该地区的地震危险性尤其引人关注。
本文使用了中国地震台网中心提供的2000—2023年新疆及其邻区的统一正式小震目录[ZW(DYB,7][KG*3]https://data.earthquake.cn/.[ZW)],震级为地方震震级ML。为了获得完备的地震目录,本文首先采用震级-序号法(Ogata et al,1991)定性地探讨研究区内最小完整性震级MC随时间的变化。这种方法不仅可以避免由于主震发生后余震较为密集、难以按时间分析余震监测能力变化的问题,而且可以根据地震监测能力变化的分段性和不连续性,得到地震记录信噪比以及人为因素所引起的监测能力变化(蒋长胜等,2013)。新疆地区完备性分析结果如图2a所示,图中横坐标为地震发生先后顺序,横坐标上方为不等间隔的地震发生时间。
本文还使用了“最大曲率”MAXC方法和拟合度分别为90%、95%的GFT方法(Wiemer,Wyss,2000)来定量评估新疆地区MC随时间的变化。MAXC方法中MC根据震级-频度分布曲线的一阶导数的最大值对应的震级来确定,而GFT方法中MC则是通过搜索对应给定的实际和理论震级频度分布下的拟合度百分比来确定。本文计算中使用1 600个地震事件作为窗口选取数据并进行滑动计算,结果如图2b所示,图中采用90%和95%的拟合度GFT方法,分别表示为GFT-95%和GFT-90%。从图2a、b对比可以看出,两种方法的计算结果一致性较好,2009年之后新疆地区监测能力得到显著提升,MC≤ML2.0,期间在短时间内存在一定的波动,可能是由大地震发生所导致(Iwata,2008)。空间上,2000年以后新疆地区MC分布具有明显的不均匀性,根据孔祥艳等(2016)的研究结果,天山地震带MC值较小,大部分地区MC≤ML2.0; 西昆仑地震带MC值较高,多数地区MC在ML3.0左右,个别地区MC在ML1.0左右。
根据上述最小完备性震级分析,2000—2023年新疆地区大部分区域ML≥3.0地震较为完整,所以本文选取ML≥3.0地震目录进行研究分析, 采用扩散链法(李闽峰,2002)对选取的地震目录进行除丛处理,为防止强震影响,后续计算中不考虑6级以上地震。
应变作为地块中与构造应力、地震过程联系最密切的一个物理量(马宏生等,2002),具有可靠的物理基础。本文以地震释放能量的1/2次方,即Benioff应变(Benioff,1951)作为响应量,计算每月首日前后n天的应变比。本文按照2°×2°大小在经纬度方向分别划分网格,计算每个网格点200 km范围内Benioff应变比,且保证每个日期前后n天每个网格点范围内至少有3个地震,Benioff应变比计算方法参考杨文等(2014)的结果:

式中: 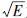 为Benioff应变;
为Benioff应变;  表示每个月首日前n天第i次地震的应变释放量;
表示每个月首日前n天第i次地震的应变释放量; 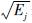 表示每个月首日后n天第j次地震的应变释放量。
表示每个月首日后n天第j次地震的应变释放量。 根据能量-震级经验公式lgE=4.8+1.5MS计算得到,震级转换采用经验公式MS=1.13ML-1.08(汪素云,俞言祥,2009)。
根据能量-震级经验公式lgE=4.8+1.5MS计算得到,震级转换采用经验公式MS=1.13ML-1.08(汪素云,俞言祥,2009)。
本文以1个月为步长,计算每个月首日前后90 d的Benioff应变比。每个网格点的应变比参数取以10为底的对数,利用插值方法获得2000—2023年新疆地区6级以上地震前每个月lgSr的空间分布。如果lgSr<0,说明该区域应变能释放减速; 如果lgSr>0,说明该区域应变能释放加速; 如果lgSr=1,说明该区域应变能释放无变化。为了获得新疆地区6级以上地震孕震区内的Benioff应变比变化特征,以6级地震震中为中心,计算震前不同时间段孕震半径R范围内的Benioff应变比。孕震半径R参考彭克银等(2003)拟合的经验公式获得:
lgR=0.29M+0.49 (2)
2000—2023年新疆地区共发生19次6级以上地震,本文将2008年10月5日乌恰6.8、6.3级震群视为一组地震,对这18组6级震例前的Benioff应变比异常的时空演化特征进行分析。根据震例分析,以lgSr≥0.6作为阈值,新疆地区18组6级地震中有14组地震在震前1年内在震中附近出现高值异常,占比为77.78%。根据马宏生等(2004)提出的空间R值计算方法对Benioff应变比异常的预测效果进行检验,R值为0.74,R0值为0.25,R≥R0,因此Benioff高值异常对未来1年内6级地震具有预测意义。
2000—2023年新疆地区出现Benioff应变比异常的6级以上地震的异常特点以及异常开始时间和结束时间见表1,其异常起止时间如图3所示。由表1可见,总体上,Benioff应变比异常范围、异常开始时间和结束时间与对应地震震级无直接的相关性。从图3可见,Benioff应变比异常出现的优势时间为震前9~12个月(共9组,占比为64%),而异常结束的优势时段为0~6个月(共9组,占比为64%)。震前存在异常反复出现的情况,如2008年3月21日于田7.3级地震、2012年6月30日和静6.6级地震和2012年8月12日于田6.2级地震之前。1年内未出现高值异常的震例分别为2001年11月14日昆仑山口西8.1级地震、2008年10月5日乌恰6.8级震群、2017年8月9日精河6.6级地震和2020年6月26日于田6.4级地震。
图3 新疆地区6级地震前Benioff应变比异常起止时间
Fig.3 The beginning and ending time of the Benioff strain ratio anomalies before the MS≥6.0 earthquakes in Xinjiang
表1 2000—2023年新疆地区出现Benioff应变比异常的6级以上地震
Tab.1 Benioff strain ratio anomalies before the earthquakes above MS6.0 in Xinjiang during 2000-2023
以2016年11月25日阿克陶6.7级地震和2016年12月8日呼图壁6.2级地震为例,对这两次地震前的Benioff应变比时空演化特征进行分析。这两次地震均位于天山地震带,该地震带发育一系列与山体近乎平行的逆断层-褶皱带,在山体内部发育一系列NW向右旋走滑断层和NEE向左旋走滑断裂(吴传勇,2016)。2016年阿克陶6.7级地震震中位于木吉盆地北缘断裂附近,该断裂总体走向NWW,长度约120 km(尼鲁帕尔·买买吐孙等,2017)。根据USGS的结果,阿克陶6.7级地震震源机制解断层节面I 走向199°、倾角84°、滑动角14°,节面II 走向107°、倾角76°、滑动角174°,为一次右旋走滑错动地震事件; 呼图壁6.2级地震位于齐古断裂和准噶尔南缘断裂附近(杨文等,2018),震源机制解断层节面I 走向80°、倾角19°、滑动角81°,节面II 走向269°、倾角71°、滑动角93°,为一次逆冲型地震事件。2016年6月26日在吉尔吉斯斯坦发生6.7级地震,该地震位于阿克陶6.7级地震西侧,两次地震震中相距约58 km。2016年阿克陶6.7级地震之前,新疆境内处于5级地震显著平静状态,该地震打破了新疆境内288天的5级地震显著平静,随后新疆地区6级地震开始一丛活跃。
图4 2016年阿克陶6.7级地震和呼图壁6.2级地震之前Benioff应变比异常时空演化过程(a~d)和震前2年Benioff应变比时序曲线(e~f)
Fig.4 The spatio-temporal evolution(a-d)and the time history(e-f)of Benioff strain ratio before the Aketao MS6.7 earthquake and the Hutubi MS6.2 earthquake in 2016
图4a~d为2016年阿克陶地震和呼图壁地震Benioff应变比异常时空演化过程。从图中可以看出,2015年12月在这两次地震震中附近开始出现应变比高值异常区,随后这两个高值区域逐渐向外同步扩展,至2016年2月该高值异常区范围达到最大,2016年3月,两次地震震中附近的高值异常区消失,并转为低值异常,异常消失3个月后首先在高值区内部发生吉尔吉斯斯坦6.7级地震,之后5~6个月又分别发生阿克陶6.7级地震和呼图壁6.2级地震,这两次地震均位于2016年2月的高值异常区内。
以每个时间段内最后的时间节点绘制2016年阿克陶地震和呼图壁地震前2年孕震半径范围内Benioff应变比的时序曲线,如图4e、f所示,图4a、b、c、d所示4个时段对应图4e、f阴影区域。从图中可以看出,阿克陶6.7级地震孕震区的应变比在2015年12月前一直处于稳定波动的状态,于2015年12月开始逐渐升高,2016年2月超过阈值,并于2016年3月发生突降,随后几个月稳定波动,直至地震发生。呼图壁6.2级地震前,应变比异常出现类似的特征,即在2015年12月开始逐渐升高,2016年2月超过阈值,并于2016年3月发生突降,随后应变比在零线附近波动,直至地震发生。与阿克陶地震前Benioff应变比变化所不同的是,在2015年12月之前,呼图壁孕震区的应变比在2015年4月也曾达到阈值,而后快速下降,之后几个月稳定波动。这表明同一构造带不同区域强震孕育过程存在关联性,同时也存在一定的差异性。
根据实验室失稳模拟成核过程研究(马瑾等,2012; 马瑾,郭彦双,2014),失稳前,由于断层不同部位相互作用,断层各部位的独立活动开始逐渐变化为协同化活动。断层活动协同化过程一般包括3个阶段,即应变释放点产生、释放点的扩展和增多以及释放段之间相互连接。2016年阿克陶6.7级地震和呼图壁6.2级地震的应变比特征可能与断层失稳成核过程的3个阶段有关。
本文在对新疆地区地震目录最小完备性震级分析的基础上,回溯了2000—2023年新疆地区6级以上地震前Benioff应变比的时空演化过程,并以2016年阿克陶6.7级地震和呼图壁6.2级地震为例,分析其Benioff应变比时空演化特征,主要得出以下结论:
(1)18组6级以上地震中,有14组地震前1年内在震中附近出现Benioff应变比高值异常。通过空间R值计算方法对高值异常进行预测效果检验,得到R≥R0,可见,Benioff应变比高值异常对后续1年内新疆地区6级地震具有一定的预测意义。
(2)2016年阿克陶6.7级地震和呼图壁6.2级地震前几个月孕震区应变比变化较为一致,均表现为“逐渐升高—快速降低—稳定波动”的特征,即逐渐升高并达到阈值,然后快速降低,最后稳定波动直至发震,这与强震前LURR异常变化特征较为类似。
连续的Benioff应变比空间分布变化,能够指示应力增强或者减弱区域的空间演化特征,进而反映成核过程中介质的高应力状态变化。根据新疆地区6级以上地震的震例总结,Benioff应变比是一种简便易用、切实可行的地震学活动性参数,适用于中短期强震预测。值得注意的是,Benioff应变比参数的计算与网格大小、孕震半径、最小完备性震级等因素的选取有关,在不同构造区中需要对相应参数进行调整。