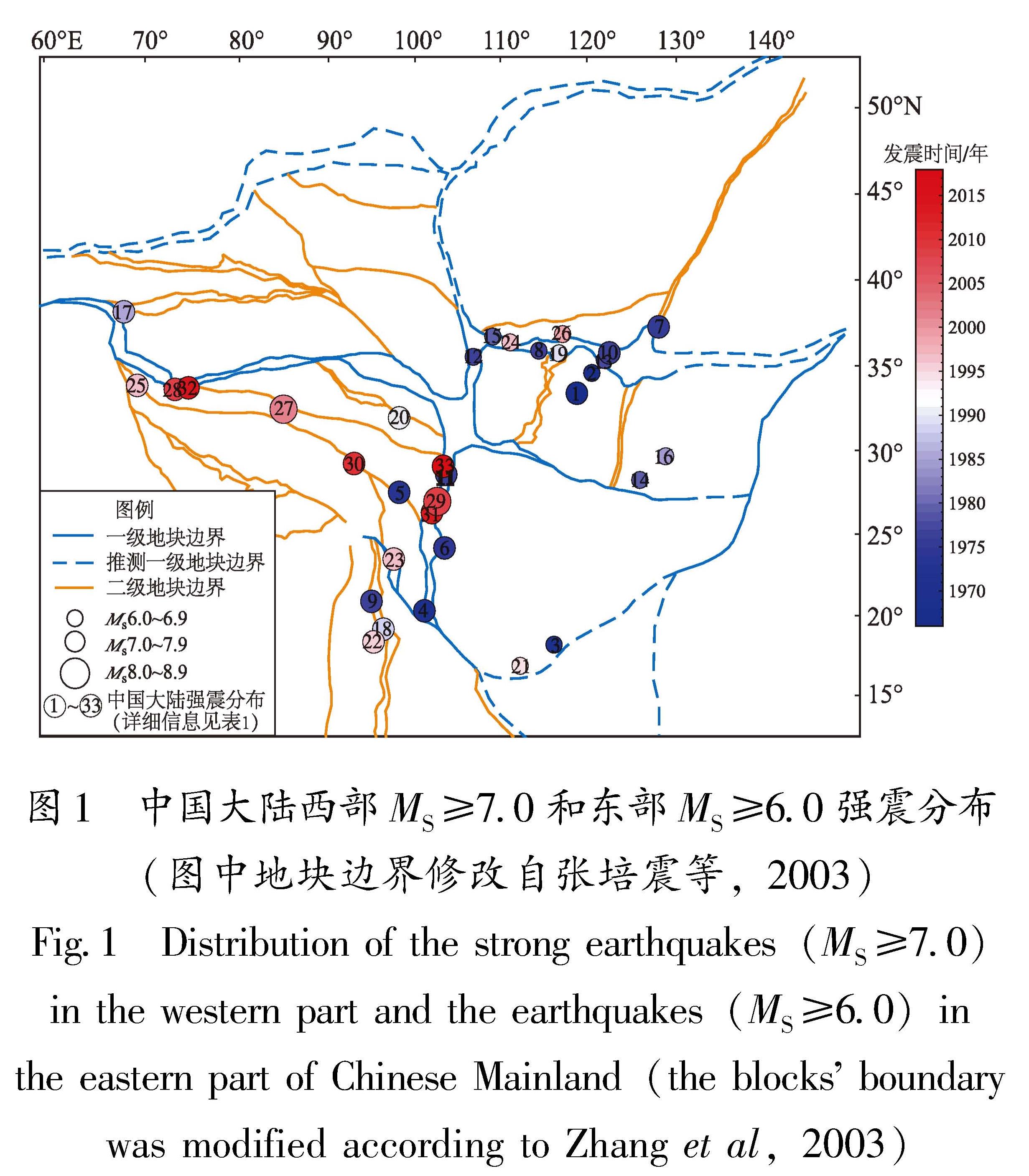
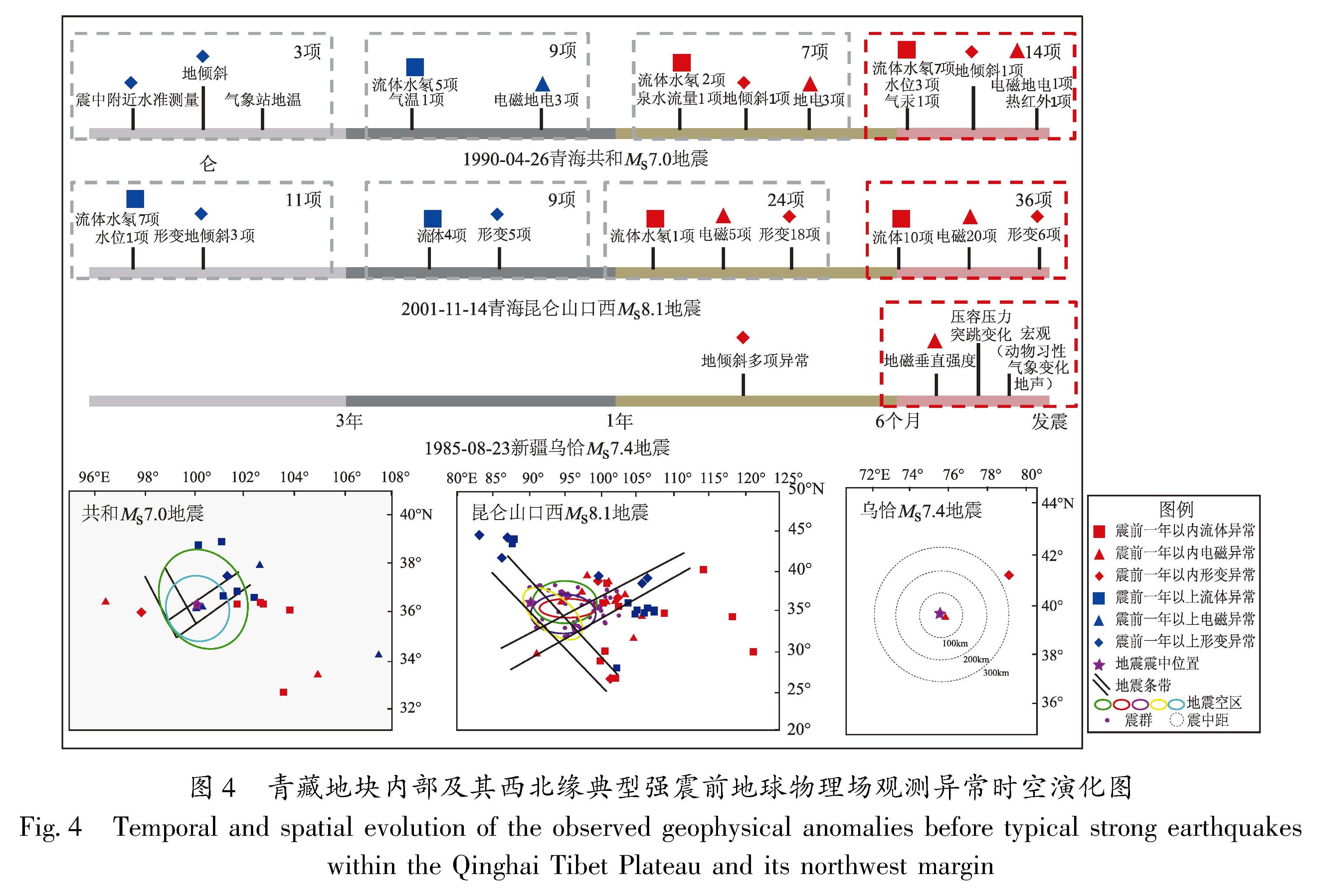
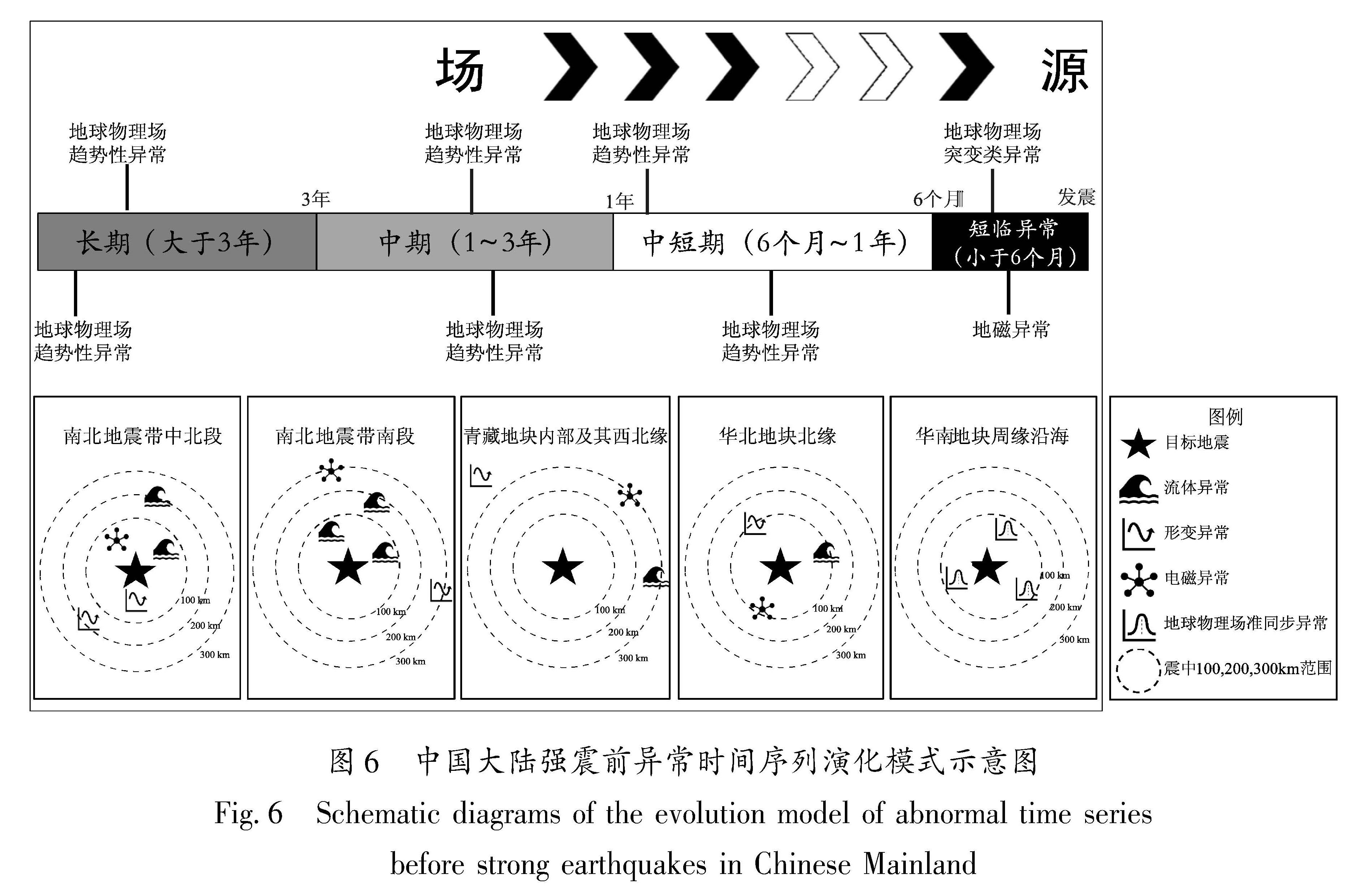
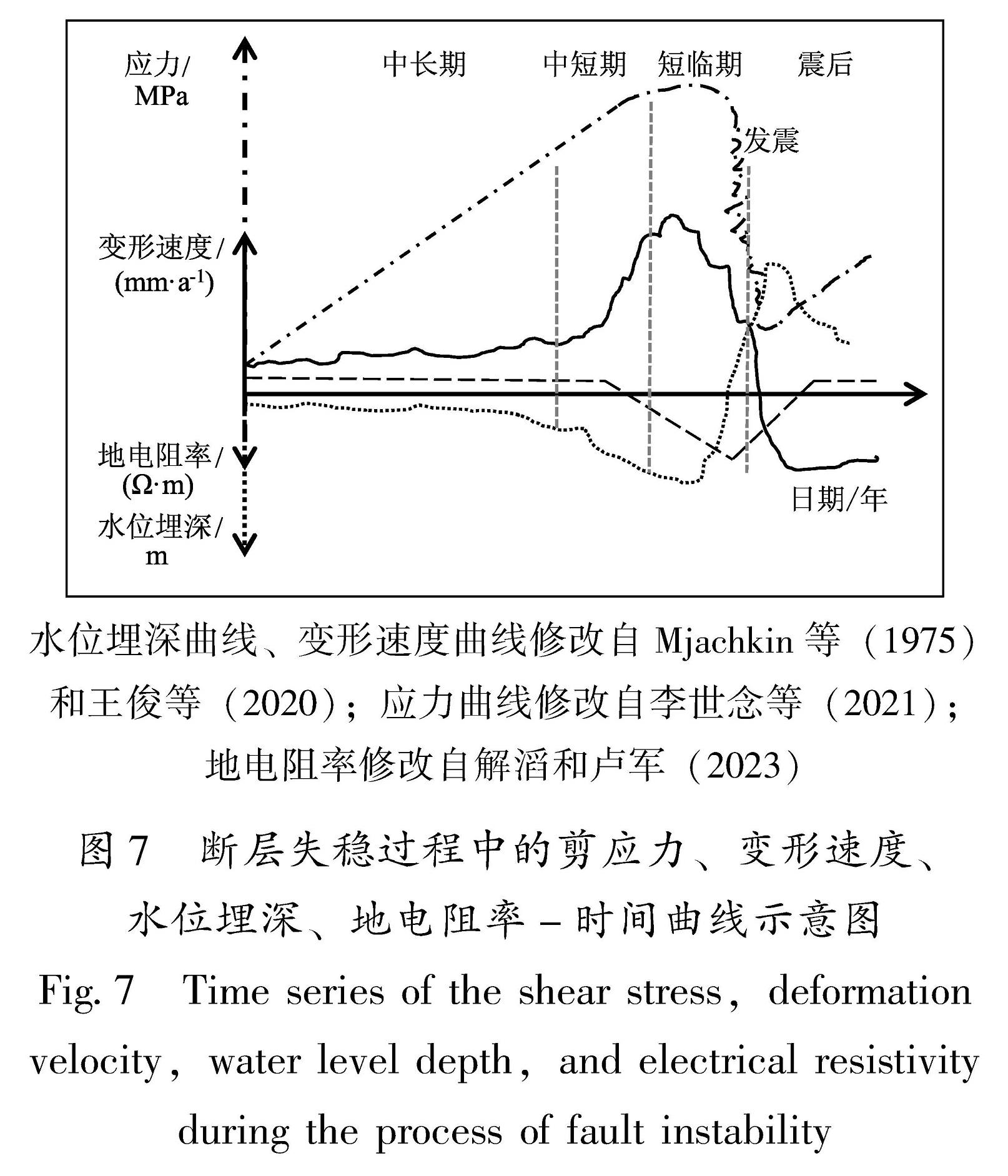
图7 断层失稳过程中的剪应力、变形速度、水位埋深、地电阻率-时间曲线示意图
Fig.7 Time series of the shear stress,deformation velocity,water level depth,and electrical resistivity during the process of fault instability
3.1 中长期阶段
在中长期阶段,以水位、地电阻率、应变为例,主要呈现为匀速的趋势性变化特征,只是相较于正常状态出现了异常特征。变化形态和特征较为简单,所反映的应力状态变化也相对单一。虽然存在各项异常变化,应力也处于逐渐积累的阶段,但是仍属于稳态(马瑾等,2012; 李世念等,2021)。从异常数量上看,属于逐渐增多的过程,即处于“持续增长”型或“先增后减”型异常演化的前期阶段(孙小龙等,2016)。不同区域内异常出现频率高的测项各不相同,显示出区域性差异,这一现象与郑兆苾等(2006)的研究结果对应较好。其根本原因在于不同区域的地质构造环境各不相同,也属于“构造控制”型地震的基本特征。
3.2 中短期阶段
在中短期阶段,水位和应变开始出现加速变化,地电阻率开始出现异常变化。中期阶段属于亚稳态的偏离线性阶段。在区域应力场的作用下,地下介质的孔隙度、渗透系数、饱和度、温度和裂隙结构等条件发生改变,在相对挤压的环境下,孔隙度下降,孔隙水渗入井孔含水层导致井水位上升,形变速度大幅加速。短期阶段属于亚稳态的强偏离线性阶段(李世念等,2021)。震中附近的围岩孔隙度增大,井孔含水层中的地下水向孔隙中渗透导致井水位发生下降变化,形变速度逐渐达到峰值,地电阻率也出现下降异常变化(解滔,卢军,2023)。从异常数量上看,属于快速上升的过程,即处于“持续增长”型或“新增后减”型异常演化的中期阶段。在年尺度范围内,尤其应该关注地下流体和电磁类异常的数量和形态变化(蒋海昆等,2009)。
3.3 临震阶段
在临震阶段,水位呈现大幅阶变、突变性变化特征,且以上升型变化为主。结合裂隙串通模式(Mjachkin et al,1975)和亚失稳模型(马瑾等,2012; 李世念等,2021)可知,在构造应力的持续作用下,微裂隙剧烈增加,小裂隙发育成较大的裂隙,由于介质的不均匀性,大裂隙加速增大,发生不稳定变形,从而形成窄带区,在剪切应力作用下,窄带区大裂隙发育成若干小断裂,这些小断裂之间不断联通,形成主断裂,为流体上涌提供逸出通道,最终导致水位上升(晏锐等,2008; 王俊等,2020; Yu et al,2023)。电阻率大多呈现下降型突变变化特征。这与区域构造应力存在直接关联,即震源区及附近区域的高应力-应变水平能引起浅层介质的微裂隙活动,导致其裂隙结构、饱和度和温度等条件发生改变(张建国,2017; 解滔,卢军,2023)。随着应力的不断积累,构造环境从亚稳态进入亚失稳态,特别是从准静态变成准动态阶段(李世念等,2021),变形速度发生较大波动(杨秋野等,2020),出现突变类异常,这也预示着即将进入失稳态,属于临震阶段异常变化特征。从异常数量上看,属于加速上升或逐渐减少的过程,即处于“持续增长”型或“新增后减”型异常演化的晚期阶段。在这一阶段应重点关注各类异常是否出现准同步异常和突变类异常。这是因为在临震失稳前,震源体周围的滑动速率大幅度增加,未破裂的震源区已收缩到了一个较小的范围,而失稳时的最大断层活动就发生在最后破裂的震源体中心附近,所以震中区的临震异常出现的最晚,而且异常的突发性和强烈程度也比早期更为突出(晏锐等,2004)。地下流体、形变和电磁异常通常会出现同步或准同步的变化,这些变化对地震孕育也起到促进作用,加速地震的发生。