基金项目:国家自然基金面上项目(42074172).
第一作者简介:于 飞(1999-),硕士研究生在读,主要从事重力数据解释研究.E-mail:13731310544@163.com.
通信作者简介:吴桂桔(1983-),研究员,主要从事重力探测和重力数据解释、强震危险性等研究工作.E-mail:wugjsky@126.com.
(Key Laboratory of Earthquake Geodesy,Institute of Seismology,China EarthquakeAdministration,Wuhan 430071,Hubei,China)
the North-South Seismic Belt; time-varying gravity field; two-dimensional horizontal gradient; moderate- and strong-earthquakes
DOI: 10.20015/j.cnki.ISSN1000-0666.2025.0062
地球重力场作为地球最基本的物理场之一,是地球内部、地表及外部空间物质分布与地球本身旋转运动信息的综合反映。自1966年邢台7.2级地震后,中国开始了流动重力观测和区域重力场随时间变化的监测预报研究。随着国家重大科技基础设施项目“中国大陆构造环境监测网络”的建设实施和“中国大陆地球物理场综合观测”等项目的建设,国家地震重力监测网覆盖了整个中国大陆,包括101个绝对重力点、约4 000个相对重力联测点和80个连续重力台站,其中以南北地震带和大华北测点的时空密度为最优(祝意青等,2018)。
针对地表重力重复观测获取的重力场动态变化与构造活动之间的关系,研究人员展开了一系列探索,如申重阳等(2011)基于重力场特征与震源机制解的相似特性提出的闭锁剪力模型,解释了2009年姚安MS6.0地震前形成的正负交替的重力梯度带; 祝意青等(2015)对2014年鲁甸MS6.5、2013年芦山MS7.0、2008年汶川MS8.0等多次地震的研究结果表明,强震往往发生在与构造走向基本一致的重力变化梯度带上; 胡敏章等(2019)对有关地震发生三要素的研究结果表明,重力变化时变距和量级随震级的增大而增加; 赵云峰等(2015)采用余弦函数求取重力水平梯度来量化地下物质的运移程度,发现重力水平梯度高值带与断裂基本重合,能够较好地展现物质运移的剧烈程度,但不同区域重力变化的空间尺度不同,对应的地下物质运移程度也不同。以往的研究大多是对重力变化量级的分析,但重力变化特征的空间大小和位置不同揭示的地下物质运移存在明显差异,目前仍无有效的手段来统一这种差异。
二维水平梯度分析方法,拟统一不同空间范围的时变重力水平差值特征,量化不同空间距离的时变重力水平差值所揭示的地下物质运移大小(陈楠等,2006; 黄江培等,2023; 李静等,2023)。在重力研究领域,Pham(2024)基于卫星重力数据采用重力场水平梯度的导数绘制了以中印度洋中脊北部的构造形态。在灾害研究领域,Zhang等(2024)以水平梯度为基础对边坡风险进行分析,绘制了地质灾害易发性分区图。该方法简单有效,但尚未在地震易发性分析领域进行应用。本文利用二维水平梯度分析方法,以南北地震带2016年9月—2021年9月多期时变重力数据为基础,计算研究区时变水平梯度,分析2022年门源MS6.9、马尔康MS6.0、芦山MS6.1、泸定MS6.8等地震前时变水平梯度时空演化趋势。
南北地震带是贯穿中国南北的一个地震活动频繁的区域,涉及西北、四川、云南等地。由于地震活动的频繁性和强烈性,南北地震带成为了地震学研究和灾害防治的重点区域之一(图1)。
本文以南北地震带为研究区,选取2016—2021年时变重力数据,数据获取均来自2台同时同址观测的相同型号相对重力仪,以A-B-C┄G┄C-B-A往返闭合的方式进行,且多条测线互相连接形成闭合测网。相对重力联测前均对所使用的重力仪进行一次项系数标定,相邻2期尽可能使用相同仪器以减小系统偏差(Xing et al,2009)。为了保证区域重力场起算基准的统一、稳定、可靠,定期将相对重力测点与绝对重力点进行联测(祝意青等,2018)。研究区所使用的绝对重力点每1 h观测1组、每组下落100次,每点标准差优于5.0 μGal的有效组数≥25,计算每次下落有效高度处的重力值,并进行固体潮、气压、光速有限、极移和垂直梯度等改正(汪健等,2021)。研究区数据观测时间均为每年9月,以减少气象、水文等季节性变化影响,同时观测点布设在地表平坦开阔、地基坚硬的位置,并尽可能避开地形地貌易发生变化的区域。
图1 南北地震带历史地震和构造块体分布
Fig.1 Historical earthquakes and tectonic blocksin the North-South Seismic Belt area
研究区内实测时变重力观测数据为非均匀格网数据,平均测点间距为30~50 km。为保证空间分辨率和数据的稳定性,选取可调节张量连续曲率样条插值法进行插值,格网大小设定为5 km,张量参数T取值为0.25。该方法不仅在插值过程中可通过T值对曲线的曲率进行细致调整,还能够灵活地适应不同区域的数据特性; 既保证了插值结果在数学上的连续性和物理上的合理性,又保持了研究区均匀格网数据的整体平滑性,以获得满意的插值结果。
强震发生前重力场会发生变化,由于数据的局限性,无法确定其与地震的精确关系,但这种震前变化是显著的(Zhan et al,2011)。时变重力场特征能表示地球内部物质运移。本文应用二维水平梯度分析方法对研究区的时变重力场进行计算,方法示意如图2所示。
时变重力场在单位空间距离上的增量记作时变水平梯度值。格网数据中每一格网存在8个相邻格网,单一相邻格网的时变重力场增量无法代表该格网真实的时变水平梯度值,因此本文采用滤波的方式将8个相邻格网的值作为参考权重后再计算时变水平梯度值。
图2中,e为所求时变水平梯度值的格网; 水平方向为x; 垂直方向为y; a、c、g、i在x、y方向分量上权重为1,d、f在x方向上权重为2,b、h在y方向上权重为2。e在x,y方向上的时变水平梯度值表示为:

式中:wght为有效单元数—wght1、wght2、wght3、wght4,数值与相邻格网数量相关,若a为空,则e左侧和上侧有效单元为3,wght1和wght3取值为3,其他同理; cellsize为格网大小。平均时变水平梯度计算公式为:
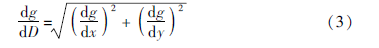
式中:D为单位格网大小。
引入区域标准差σ衡量区域范围内时变水平梯度稳定程度,表示为:
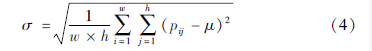
式中:w和h分别为研究区域的宽和高; pij为(i,j)位置对应的单元格网的值; μ为研究区域格网的平均值。
本文通过计算时变重力场格网数据和标准差σ,并以σ作为时变水平梯度异常值的判据,最后统计得到2016年9月—2021年9月(地震发生前一年开始统计)研究区的时变水平梯度值,见表1。
本文以2017年9月—2022年9月南北地震带发生的25个MS≥5.0地震(或震群)震中为中心,基于已有重力变化异常范围参考指标(胡敏章等,2019),为不同震级地震设置统计半径,其中MS5.0~6.0地震的统计半径为70 km,MS6.0~7.0地震的统计半径为110 km。统计25个地震震中区域时变水平梯度极大值与区域标准差(表2),分析其与强震活动之间的关系。
利用式(5)对上述计算结果进行线性回归:

式中:R2为真实值与回归值之间的方差,表示强震震级与时变水平梯度极大值和区域标准差之间的关系。
图3结果显示,当MS≥5.3时,震级与时变水平梯度极大值和区域标准差之间存在明显的线性正相关,即震级越大其对应的梯度极大值和区域标准差也越大,且R2>ab。
13次MS≥5.5地震震中区域时变水平梯度极大值大于1.0 μGal/km,5次MS≥6.0地震震中区域时变水平梯度极大值大于1.52 μGal/km,研究区水平梯度标准差与均值在震前变化较小,约0.3 μGal/km。极大值低于总体平均值的区域未发生强震。
表2显示,除2019年长宁MS6.0地震外,其余4次MS≥6.0地震震前震中范围内时变水平梯度极大值均超过1.7 μGal/km,区域标准差大于0.4 μGal/km。虽然2019年长宁MS6.0地震时变水平梯度极大值高达1.52 μGal/km,但区域标准差较低,为0.25 μGal/km,低于同震级地震,推断长宁地震为非构造地震。本文研究结果与Anyiam等(2024)研究结果较一致,即长宁MS6.0地震属于触发地震。
表2 南北地震带MS≥5.0地震震中区域时变水平梯度极大值及区域标准差
Tab.2 Maximum value of the time-variable horizontal gradient and rigional deviation in the epicentral area(MS≥5.0)
2022年南北地震带强震密集发生,其中部地区发生了马尔康MS6.0、芦山MS6.1、泸定MS6.8地震。因此,为探寻强震孕震与时变水平梯度和
地质构造之间的关系,本文获取2016年9月—2021年9月南北地震带中部地区时变水平梯度分布(图4)。2016年9月—2017年9月(图4a),马尔康MS6.0地震震中区域西北部形成垂直于达日断裂的时变水平梯度高值区域,极大值大于1.5 μGal/km; 芦山MS6.1地震和泸定MS6.8地震震中区域100 km范围内仅存在部分破碎状无规律的时变水平梯度高值条带,极大值约为1.0 μGal/km。2016年9月—2018年9月(图4b),时变水平梯度高值区域位于达日断裂北部,区域东南端扩散至马尔康MS6.0地震震区,极大值约为0.8 μGal/km; 芦山MS6.1地震震中区域存在南北向的时变水平梯度高值条带,其南端与龙门山断裂带相交,震中位于交会处,极大值约为1.0 μGal/km; 泸定MS6.8地震震中区域存在直径约为50 km的时变水平梯度高值环状区域,区域南部与鲜水河断裂带平行重叠,极大值大于 1.5 μGal/km。2016年9月—2019年9月(图4c),
图4 2016年9月—2021年9月南北地震带中部地区时变水平梯度分布
Fig.4 Distribution of the time-varying horizontal gradient in the central part of theNorth-South Seismic Belt from September 2016 to September 2021
马尔康MS6.0地震震中区域西北侧的不规则时变水平梯度高值区域仍处于达日断裂北侧,极大值降至0.7 μGal/km; 在芦山MS6.1地震和泸定MS6.8地震震中区域,围绕龙门山断裂带在巴颜喀拉块体东边界存在大量破碎的时变水平梯度高值条带,围绕这2次地震震中区域发散展布,极大值大于1.5 μGal/km。2016年9月—2020年9月(图4d),马尔康MS6.0地震震中区域西北侧的时变水平梯度高值区向松岗断裂靠近,极大值大于1.5 μGal/km; 芦山MS6.1地震和泸定MS6.8地震震中区域的时变水平梯度高值带持续发育,由少数破碎高值带发展为环状条带,极大值大于1.5 μGal/km。2016年9月—2021年9月(图4e),在马尔康MS6.0地震震中区域,位于与松岗断裂平行的时变水平梯度高值区域东南边界,极大值大于1.0 μGal/km; 芦山MS6.1地震震中区域的时变水平梯度高值环状区域与龙门山断裂带平行分布,并被龙门山断裂带截断,极大值达到2.0 μGal/km; 泸定MS6.8地震震中70 km范围内无异常。
图5为2017年9月—2021年9月南北地震带中部地区的时变水平梯度分布。2017年9月—2018年9月(图5a),马尔康MS6.0地震震中区域西北部时变水平梯度高值带汇聚至达日断裂北侧,垂直于达日断裂呈大面积条带状分布,极大值大于1.5 μGal/km; 芦山MS6.1地震震中区域东南侧存在直径小于10 km的破碎状时变水平梯度高值区域,极大值大于0.8 μGal/km; 泸定MS6.8地震震中区域北侧出现直径约为50 km、平行于鲜水河断裂带的时变水平梯度高值环状区域,极大值大于1.5 μGal/km。2017年9月—2019年9月(图5b),在马尔康MS6.0地震震中区域西北侧, 时变水平梯度高值带汇聚于达日断裂北侧,距离震中区域较远,极大值大于1.5 μGal/km; 芦山MS6.1地震震中区域的时变水平梯度高值带整体较为破碎并以震中为中心向四周展布,极大值大于1.0 μGal/km; 泸定MS6.8地震震中区域仅在鲜水河断裂带存在部分破碎时变水平梯度高值带,极大值降至0.7 μGal/km。2017年9月—2020年9月(图5c),马尔康MS6.0地震震中区域西北侧的时变水平梯度高值带仍持续位于达日断裂北侧,与两年期形态相同,仍呈现不规则分布,极大值大于1.5 μGal/km; 芦山MS6.1地震和泸定MS6.8地震震中区域时变水平梯度高值条带破碎减弱,除少数直径不足10 km的时变水平梯度高值点状区域外,整体区域较稳定。2017年9月—2021年9月(图5d),马尔康MS6.0地震震中区域北侧的时变水平梯度高值区域空间分布范围较小,整体形态维持稳定,极大值大于1.5 μGal/km; 芦山MS6.1地震和泸定MS6.8地震震中区域,存在围绕着鲜水河断裂带与龙门山断裂带形成密集、破碎的时变水平梯度高值环状区域,极大值大于1.5 μGal/km。
图5 2017年9月—2021年9月南北地震带中部地区时变水平梯度分布(断裂同图 4)
Fig.5 Distribution of the time-varying horizontal gradient in the central part of the North-South Seismic Belt from September 2017 to September 2021(faults are shown in Fig.4)
图6为2018年9月—2021年9月南北地震带中部地区的时变水平梯度分布。2018年9月—2019年9月(图6a),达日断裂北侧的时变水平梯度高值区域向马尔康MS6.1地震震中区域靠拢,初显时变水平梯度高值环状区域雏形,极大值大于1.5 μGal/km; 芦山MS6.1地震震中区域存在直径约为100 km的时变水平梯度高值环状区域,极大值大于1.5 μGal/km; 泸定MS6.8地震北侧震中区域存在西邻鲜水河断裂带、东接龙门山断裂带,处在巴颜喀拉块体东边界的时变水平梯度高值环状区域,极大值大于1.5 μGal/km。
图6 2018年9月—2021年9月南北地震带中部地区时变水平梯度分布(断裂同图 4)
Fig.6 Distribution of the time-varying horizontal gradient in the central part of the North-South Seismic Belt from September 2018 to September 2021(faults are shown in Fig.4)
2018年9月—2020年9月(图6b),在马尔康MS6.0地震震中区域北侧,时变水平梯度高值环状区域西南侧消失,并向震中区域靠近,极大值降至0.8 μGal/km; 芦山MS6.1地震震中区域的时变水平梯度高值带沿龙门山断裂带呈近北东-西南向平行分布,宽度约为20~30 km,极大值大于1.5 μGal/km; 泸定MS6.8地震震中区域北侧重现直径约为50 km的时变水平梯度高值环状区域,极大值大于1.5 μGal/km。2018年9月—2021年9月(图6c),马尔康MS6.0地震震中区域100 km范围内无时变水平梯度高值区域; 芦山MS6.1地震震中区域与龙门山断裂带平行的时变水平梯度高值环状区域的东北侧被龙门山断裂带截断,极大值达到2.0 μGal/km; 泸定MS6.8地震震中区域的时变水平梯度高值环状区域处在震中北侧的鲜水河断裂与龙门山断裂带交界处,直径约为30 km,极大值达到2.0 μGal/km。
图7为2019年9月—2021年9月南北地震带中部地区的时变水平梯度分布。2019年9月—2020年9月(图7a),马尔康MS6.0地震震中区域西北侧存在时变水平梯度高值环状区域,其南部边界扩散至震中,极大值大于1.5 μGal/km; 芦山MS6.1地震和泸定MS6.8地震震中区域存在大面积形态不同的时变水平梯度高值破碎带,并沿着龙门山断裂带与鲜水河断裂带展布,各高值带极大值均大于1.5 μGal/km。2019年9月—2021年9月(图7b),马尔康MS6.0地震震中区域的时变水平梯度高值带在靠近松岗断裂处减弱,极大值降至1.0 μGal/km; 芦山MS6.1地震震中区域呈现平行于龙门山断裂带约200 km范围的时变水平梯度高值带,极大值大于1.5 μGal/km; 泸定MS6.8地震震中区域的时变水平梯度高值带由北向西转折,将龙门山断裂带与鲜水河断裂带连接,极大值达到2.0 μGal/km。
图7 2019年9月—2021年9月南北地震带中部地区时变水平梯度分布(断裂同图 4)
Fig.7 Time-varying horizontal gradient distribution in the central part of the North-South Seismic Belt from September 2019 to September 2021(faults are shown in Fig.4)
图8为2020年9月—2021年9月南北地震带中部地区的时变水平梯度分布。马尔康MS6.0地震震中区域北侧存在直径约100 km的时变水平梯度高值环状区域,极大值大于1.5 μGal/km,地震发生在时变水平梯度带与松岗断裂平行的南边界; 芦山MS6.1地震震中区域的时变水平梯度高值带再次形成宽度为30 km的半环状结构,主方向和龙门山断裂带走向一致,其南侧被龙门山断裂带截断形成缺口,极大值达到2.0 μGal/km; 泸定MS6.8地震震中区域的时变水平梯度变化特征较弱,极大值仅为0.7 μGal/km。
2016年9月以来,马尔康MS6.0地震震中区域时变水平梯度高值区域的极大值高低变化明显,总体维持在极大值大于1.0 μGal/km的高值状态,高值带在达日断裂北侧沿着达日断裂由西北侧逐渐向松岗断裂靠近; 芦山MS6.1地震震中区域时变水平梯度高值区域,围绕震中由破碎到整体的
图8 2020年9月—2021年9月南北地震带中部地区时变水平梯度分布(断裂同图 4)
Fig.8 Distribution of the time-varying horizontal gradient in the central part of the North-South Seismic Belt from September 2020 to September 2021(faults are shown in Fig.4)
逐步汇集为平行于龙门山断裂带的环状区域,极大值由0.5 μGal/km增加至2.0 μGal/km。泸定MS6.8地震震中区域在震前两年时变水平梯度值存在显著的水平梯度高值环状异常,但以2016年为基准的多年时变水平梯度值整体无异常。
2017年9月以来,达日断裂北侧的时变水平梯度高值区域相对稳定,无明显空间范围变化,极大值稳定大于1.5 μGal/km,未达到马尔康MS6.0地震震中区域的时变水平梯度高值。芦山MS6.1地震和泸定MS6.8地震震中区域的时变水平梯度高值在2017年9月至2018年9月和2019年9月以震中为中心逐渐增高。随后开始减弱,最终于2020年9月在芦山MS6.1地震和泸定MS6.8地震震中区域降至2.0 μGal/km,形成被鲜水河断裂带与龙门山断裂带截断的时变水平梯度高值环状区域。
2018年9月以来,马尔康MS6.0地震震中区域时变水平梯度高值区域的极大值与空间区域变化显著,震前3年时变水平梯度高值带消失,整体走向上沿达日断裂由西北侧逐渐向松岗断裂靠近,但极大值减小; 芦山MS6.1地震震中区域时变水平梯度高值区域围绕震中展布,时变水平梯度高值环状特征明显,形态变化活跃,极大值维持在2.0 μGal/km。泸定MS6.8地震震中区域时变水平梯度高值区域的空间范围维持,环状特征明显。
2019年9月以来,马尔康MS6.0地震震中区域时变水平梯度高值空间形态无变化,东部极大值减弱,最低至0.5 μGal/km; 芦山MS6.1地震震中区域时变水平梯度高值围绕震中展布,在龙门山断裂带北侧汇聚,高值区域增多,极大值持续大于1.5 μGal/km; 泸定MS6.8地震震中区域时变水平梯度高值形成连接龙门山断裂带与鲜水河断裂带的转折带,极大值达到2.0 μGal/km。
2020年9月以来,震前1年的时变水平梯度异常特征为:马尔康MS6.0地震震中区域北侧的时变水平梯度高值区域向震中靠拢; 芦山MS6.1地震震中区域时变水平梯度高值区域特征最为显著; 泸定MS6.8地震震中区域无明显时变水平梯度高值带。
在南北地震带的中段,3次MS≥6.0地震在震前数年都存在与断裂构造相关的时变水平梯度高值区域,表现出持续的活跃性。马尔康MS6.0地震震中区域时变水平梯度高值区域由西北侧沿着达日断裂逐步向松岗断裂靠近,在震前1~2年高值环状特征明显,3年以上的时变水平梯度极大值始终维持在1.0 μGal/km以下,总体特征主要体现在震前1~2年。芦山MS6.1地震震中区域地质构造复杂,时变水平梯度变化特征受龙门山断裂带影响大。泸定MS6.8地震震中区域时变水平梯度高值特征主要集中在震前3年,其他时期整体较为平稳,总体特征为极大值高、高值带集中。总体上,马尔康MS6.0地震震中区域时变水平梯度变化特征表现出明显的逐年短期特征,震前1年变化较大,但多年特征相对较弱,该地震可能是由2021年玛多MS7.4地震震后调整所致; 芦山MS6.1地震震中区域的时变水平梯度高值区域受构造影响大,形态特征围绕着断裂构造变化明显,极不稳定; 泸定MS6.8地震孕育时间较长,震前1~2年特征较弱,震前3年高值特征集中,并沿龙门山断裂带与鲜水河断裂带交会处展布。
本文利用二维水平梯度分析方法计算了2016年9月—2021年9月南北地震带时变水平梯度,讨论2017年以来研究区MS≥5.0地震震中区域震前时变水平梯度与地震活动的相关性,结合地质构造资料,重点分析MS≥6.0地震发生前震中区域的时变水平梯度时空特性,得到如下主要结论:
(1)南北地震带MS≥5.3地震前震中区域的时变水平梯度极大值和区域标准差与震级呈正相关,随着震级的增大,时变水平梯度极大值和标准差均增大。
(2)时变水平梯度结果显示,研究区MS≥6.0地震前震中区域时变水平梯度高值带逐渐沿块体边界、大型断裂展布。震前1年,研究区MS≥6.0地震的震中约110 km范围内存在着极大值在1.5 μGal/km以上的时变水平梯度高值区域,标准差超过0.4 μGal/km。