基金项目:中国地震局“十五”项目“兰州市活断层探测与地震危险性评价”(1-4-28-1)资助; 中国地震局兰州地震研究所论著编号:LC20070063.
(1.中国地震局兰州地震研究所,兰州 730000; 2.中国地震局地震预测研究所兰州科技创新基地,兰州 730000)
(1.Lanzhou Institute of Seismology,CEA,Lanzhou 730000,Gansu,China)(2.Lanzhou Base of Institute of Earthquake Prediction,CEA,Lanzhou 730000,Gansu,China)
inelastic attenuation value Q; site response; Northeastern margin of Tibet Plateau
备注
基金项目:中国地震局“十五”项目“兰州市活断层探测与地震危险性评价”(1-4-28-1)资助; 中国地震局兰州地震研究所论著编号:LC20070063.
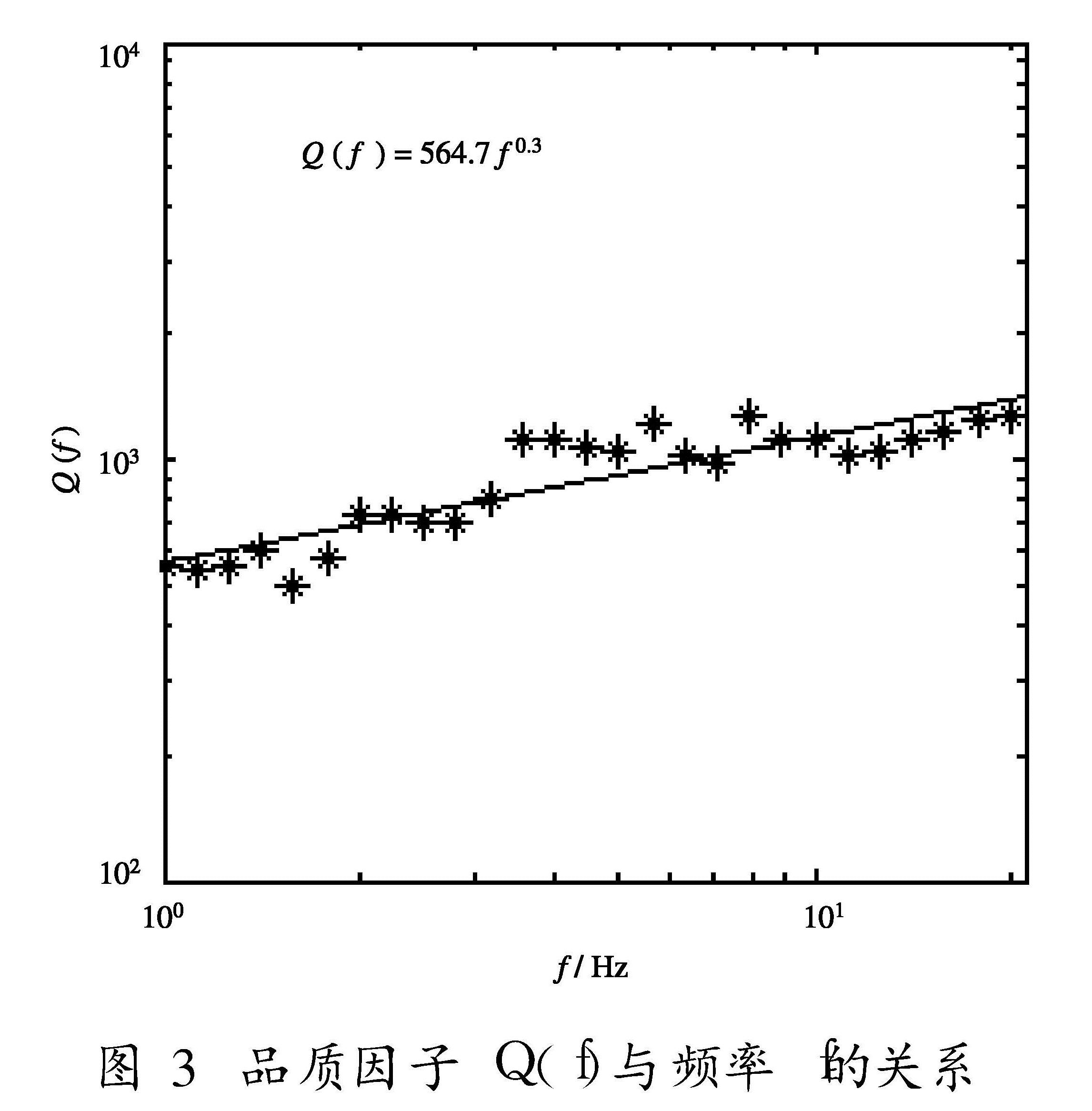
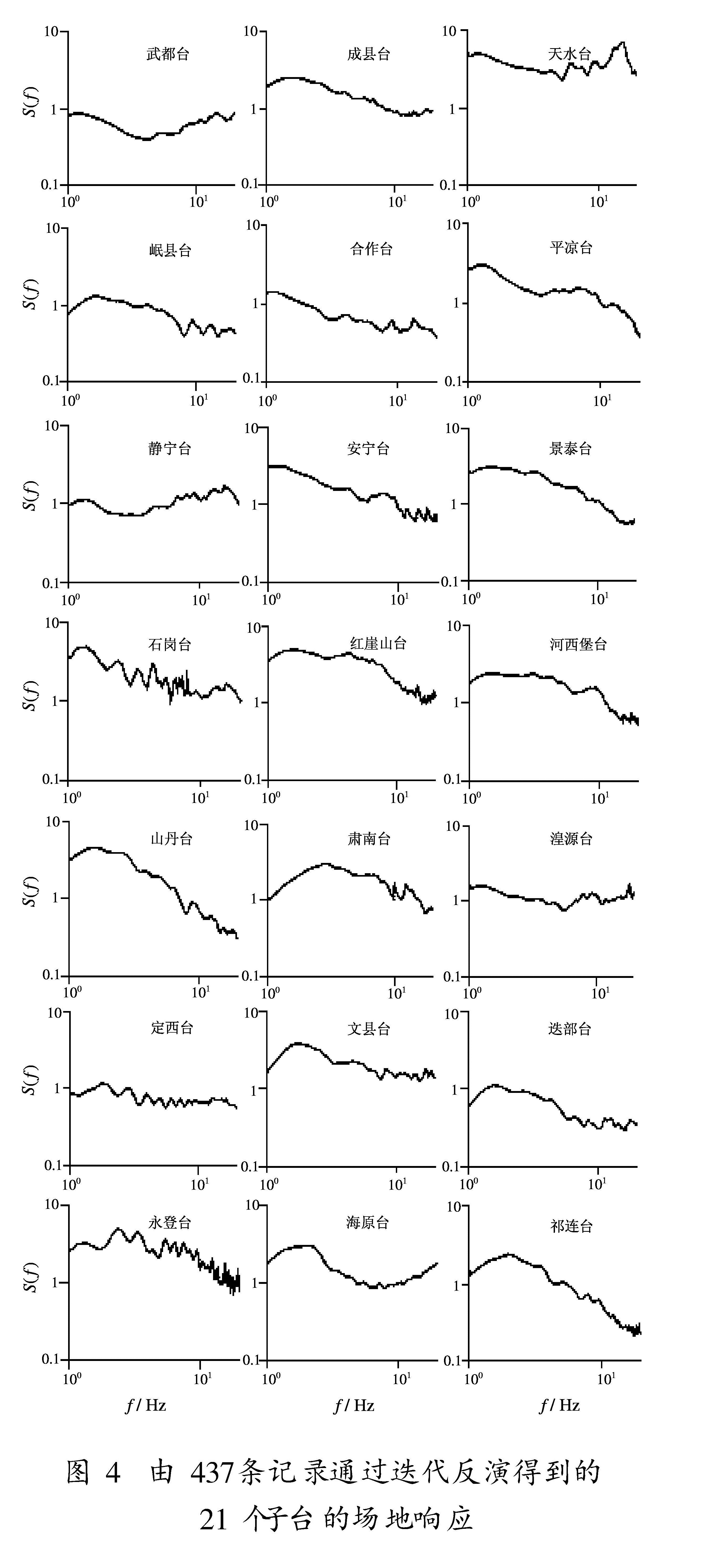
根据甘肃数字地震台网21个子台的437条波形记录,采用三段几何衰减模型,利用Atkinson方法和遗传算法,研究了青藏高原东北缘地区的非弹性衰减Q值和各台站的场地响应,得到该地区非弹性衰减Q值与频率f的关系为:Q(f)=564.7f 0.3; 21个子台中,除了武都、合作、湟源、定西和迭部等台的场地响应总体上没有放大效应以外,其余台站均存在较明显的放大效应。
According to 437 horizontal-component seismograms recorded at 21 stations of Gansu Digital Seismic Network,we used Genetic Algorithm and Atkinsons method to study the inelastic attenuation value Q of the northeastern margin of Qinghai-Tibet plateau and the site response of each station based on the trilinear geometrical spreading model.The results indicate that the frequency-dependent of inelastic attenuation value Q in the studied area is estimated as:Q(f)=564.7f 0.3.The site response shows significant amplification at every station except for the Wudu,Hezuo,Huangyuan,Dingxi,Diebu stations.
引言
地震波衰减性质的研究是地震学研究的重要课题。地震仪器记录到的地震波,包含了地震震源效应、地震波的传播路径效应、台站场地响应及仪器响应。在使用地震波资料研究震源性质时,必须要扣除地震波传播路径效应、台站场地响应及仪器响应的影响。地震波传播的路径效应(地震波衰减),除了随距离存在几何衰减外,还有一个重要的影响因素即介质的非弹性衰减,可用介质品质因子Q值来度量。Q值是地球介质的基本物理参数之一,是通过远离震源的观测资料对地震记录进行定量分析和研究震源性质所必需的重要参数。同时,地震波的衰减特征对于地震危险性分析也具有十分重要的意义,是地震工程研究人员最关心的基础资料之一。由于剪切波的振幅通常比P波振幅大,在有的情况下可达5倍左右,因此对于地震工程来说,研究剪切波衰减的特征将具有更重要的意义。
理论研究和实际观测结果表明,场地响应是影响地震破坏的重要因素,对地震破坏起着重要的作用。已有不少震害调查结果证实,大地震时松软地基上的建筑物的破坏率要比坚硬地基上的建筑物的破坏率高得多。Rogers等(1979)采用内华达试验场核爆破记录的波谱,计算了Long Beach的场地响应,结果表明在0.2~6 s波段冲积层相对于岩石的场地放大倍数可高达11倍。
随着我国区域数字地震台网的建立与完善,地震工作者获取了大量的地震波形资料,数字地震波资料的分析与应用研究逐渐成为一项重要工作,而地震波非弹性衰减Q值和场地响应特征研究是深入开展该项工作的一个重要基础。笔者根据甘肃数字地震台网记录到的青藏高原东北缘地区的中小地震的波形资料,采用互相衔接的三段几何衰减模型,通过在频率域内的分析,采用Atkinson方法和遗传算法(Atkinson等,1992; 黄玉龙等,2003; 刘杰等,2003),研究了青藏高原东北缘地区剪切波的非弹性衰减Q值以及场地响应的征。
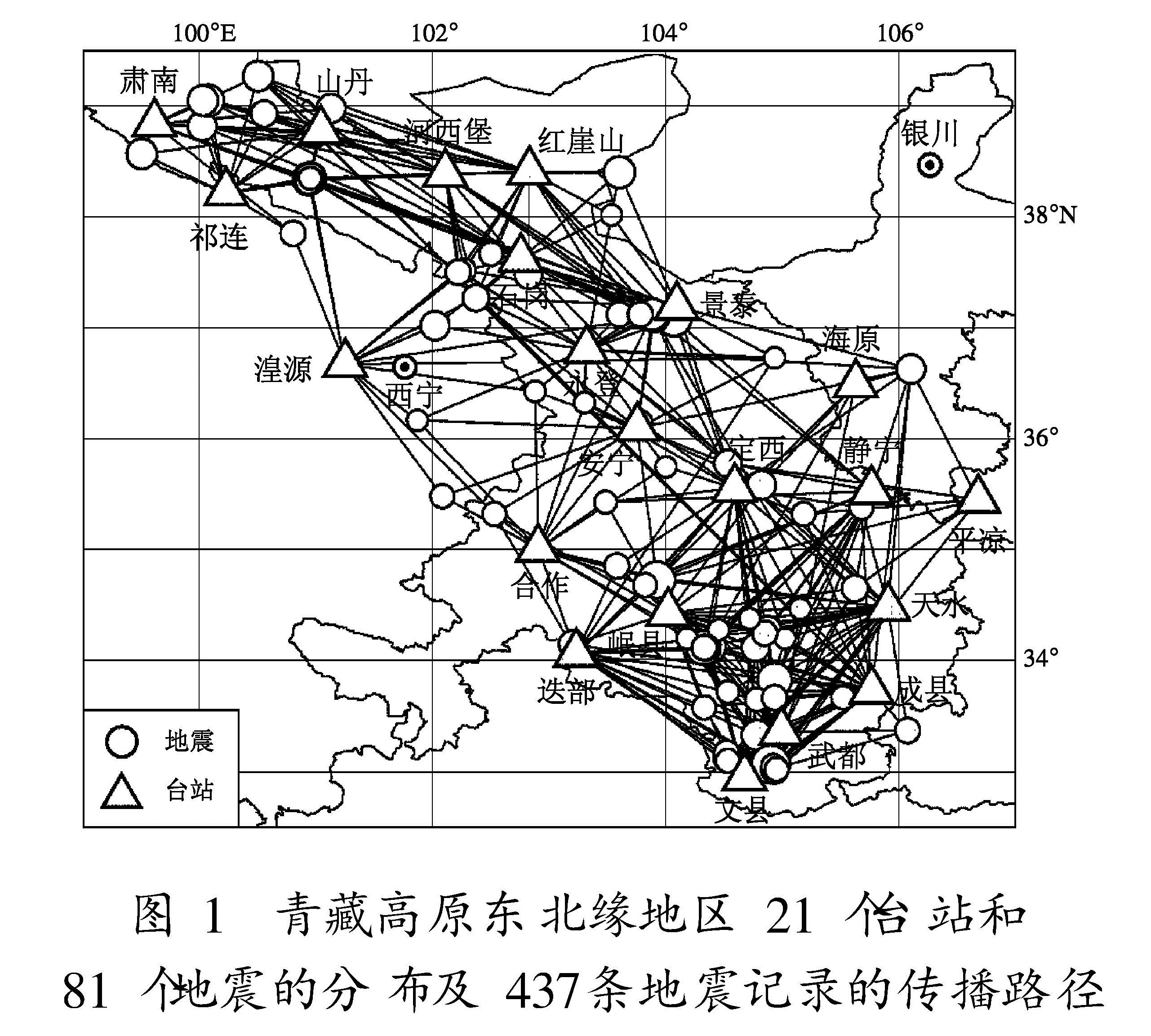
1 观测资料
2 资料处理
对于S波的两个水平分量(NS、EW),首先进行带通滤波(Butter滤波器,带宽0.1~22 Hz)和水平校正处理,然后取“S窗”和“噪声窗”,进行傅立叶变换信噪比分析。
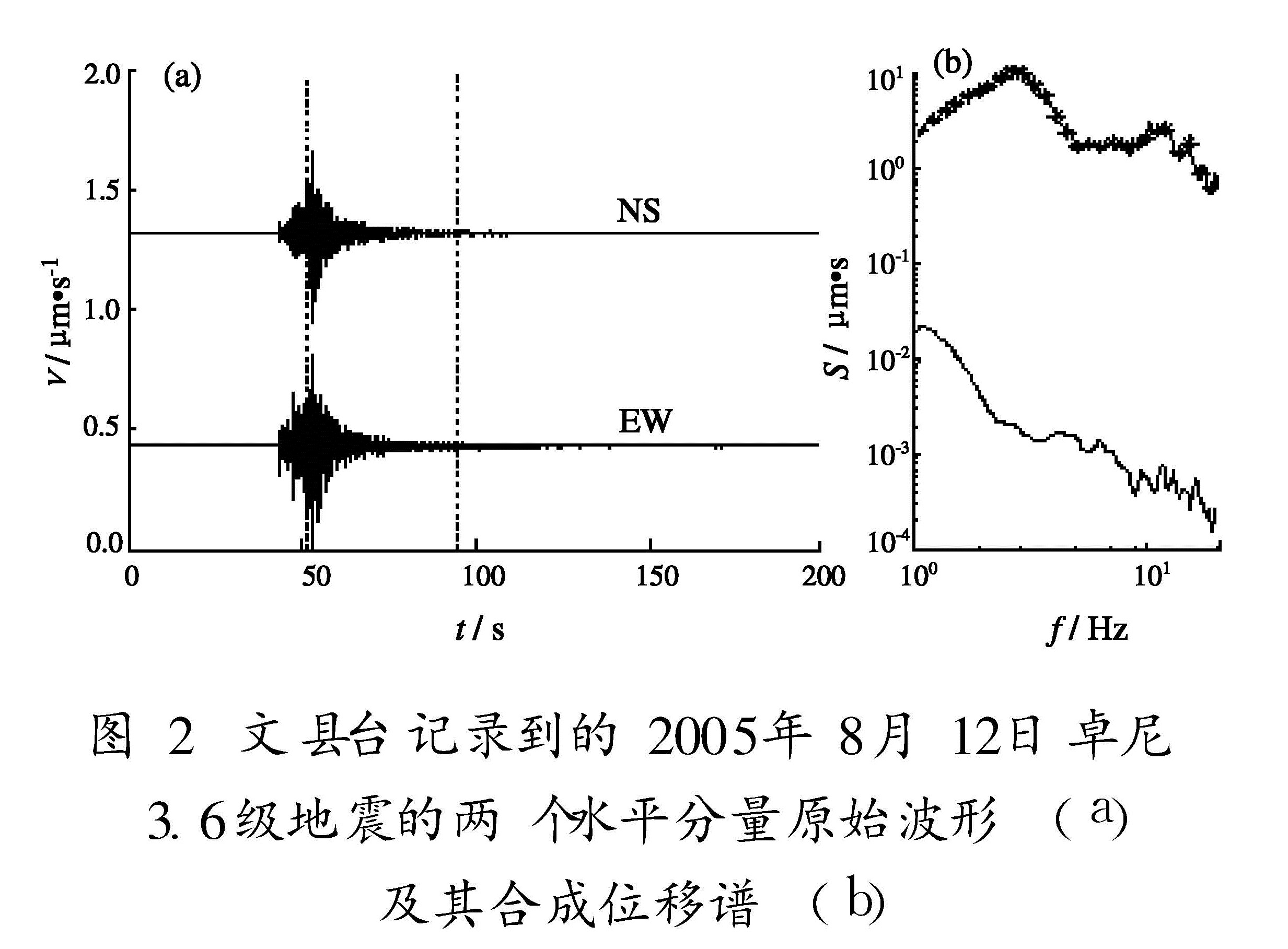
如图2所示,把从S波开始到包括S波总能量的90%的时间段定义为“S窗”。对于不同地震,由于震源深度和震中距不同,“S窗”内包含的震相也不尽相同。对于同一次地震,由于各台站的震中距不同,“S窗”的持续时间也不同。为了得到具有相同频率间隔的振幅谱,笔者采用了平移窗谱方法(苏有锦等,2006)。具体步骤如下:把“S窗”内的波形信号分成若干个包含有256个采样点的小段,并使相邻信号段有50%的重叠; 对于采样率为50 Hz的地震记录来说,可得到每个信号段的时间长度是5.12 s; 在每一信号段的起始和末尾各加5%的cos边瓣后,通过傅立叶变换得到每个信号段的傅立叶谱,这样对于每一个台站的记录就可以得到相同频率间隔(0.196 Hz)的傅立叶谱; 最后,对每个信号段的傅立叶谱进行仪器校正,并通过下式得到整个“S窗”内信号的速度振幅谱:
V^-(f)={(∑ni=1vi2(f))·T/(nt)}1/2.(1)
式中vi(f)是经过仪器校正的第i个信号段的傅立叶谱,T为“S窗”的持续时间。该“S窗”内包含了n个时间长度为t、每个时间长度包含256个采样点的信号段。取P波初动前256个采样点(1个信号段)的噪声信号,通过(2)式得到与信号相同频率间隔的噪声谱:
N(f)={n2(f)(ts)/t}1/2.(2)
式中,n(f)是经过仪器校正的256个数据点的噪声傅立叶谱。然后,得到经过噪声校正的速度振幅谱:
V(f)={V^-2(f)-N2(f)}1/2.(3)
由于甘肃数字地震台网的资料是速度记录,最后还需要把V(f)除以2πf,把速度谱转换成位移谱。对于S波的两个水平分量分别进行上述处理,并通过(4)式得到S波水平分量合成位移谱:
A(f)={u2EW(f)+u2NS(f)}1/2.(4)
用以上处理方法,按每次地震至少被3个台站记录到、每个台站至少有4条记录的原则,挑选波形较好、能经过信噪比检验的地震记录用于本研究。图2给出了其中的一个实例,为文县台记录到的2005年8月12日卓尼3.6级地震的两个水平分量原始波形及其S波合成位移谱。图2a中,虚线间为“S窗”的范围; 图2b中,上部曲线为经过噪声校正的位移谱曲线,下部曲线为噪声谱曲线。
3 计算方法和结果
根据地震波谱的一般表达,经过上述资料预处理后,任一地震观测记录谱与震源谱均有如下关系:
lgOij(f)=lgSi(f)-lgG(Rij)-C(f)Rij
-lgGj(f).(5)
其中f是频率,Oij(f)是第j个台站观测到的第i个地震的谱振幅,Si(f)是第i个地震的震源谱振幅,G(Rij)为几何衰减函数,C(f)为非弹性衰减系数,Rij是第i个地震至第j个台站的震中距,Gj(f)是第j个台站的场地响应。
非弹性衰减系数C(f)与区域介质的品质因子Q(f)之间的关系为
Q(f)=(lg(e)πf)/(C(f)β).(6)
式中,β为S波速度,取3.5 km/s。
参考Atkinson等(1992)、黄玉龙等(2002)文献,几何衰减函数G(Rij)采用互相衔接的三段几何衰减函数表示:
G(R)={R-b1, R≤R01;
R-b101·R-b201·R-b2, R01<R≤R02;
R-b101·R-b201·R-b202·R-b302·R-b3, R>R02.
上式中R≤R01时,对应于直达波的几何衰减; 当R01<R≤R02时,对应于过渡区,在该震源距范围内,直达波加入了在地壳几个间断面和莫霍面上的反射波; 当R>R02时,对应于多次折射反射波。根据青藏高原东北缘地区平均地壳厚度H约50 km(李永华等,2006),有关模型参数取值为b1=1.0、b2=0.0、b3=0.5、R01=1.5H=75 km、R02=2.5H=125 km。如果把该几何衰减函数G(Rij)代入式(5),则式(5)变为对参数C(f)(非弹性衰减系数)和Gj(f)(台站场地响应)进行联合反演的问题。
定义残差为
kij=[lgSi(f)]j-lgSi(f)^-.(7)
式中lgSi(f)^-是第i个地震的震源谱振幅对数的平均值,是对记录到该地震的所有台站计算得到的lgSi(f)求平均。
非弹性衰减系数C(f)的求解采用计算(8)式求极小值得到,即
sum=∑i∑j〖JB<2|〗kij〖JB>2|〗.(8)
采用Atkinson方法反演品质因子Q(f)值和场地响应的计算步骤可归纳为:
(1)先将所有台站场地响应Gj(f)设为1,选择合适的参数C(f),使(8)式的残差总和极小。
(2)利用得到的参数,可求得场地响应:
lgGj(f)=(∑mjj=1kij)/(mj).(9)
其中mj为第j个台站记录的地震事件数。
(3)将场地响应的计算结果代入,重新计算C(f)。重复(2)、(3)步,使残差总和达到最小。
通过上述迭代反演可同时求得该地区的非弹性衰减系数C(f)和各台站的场地响应,进而利用(6)式得到区域介质的品质因子Q。在考虑频率依赖的Q模型时,通常用频率的幂函数,即Q(f)=Q0f η的形式来拟合Q与频率的关系。图3给出了其计算结果,由图可见结果拟合较好。
品质因子Q(f)与频率的关系为Q(f)=564.7f 0.3.(11)
图4是迭代反演得到的21个子台的场地响应。由图可见,除了武都、合作、湟源、定西和迭部等台的场地响应总体上接近或小于1以外,其余台站的场地响应均存在较明显的放大效应。
4 结语
本研究得到的青藏高原东北缘地区Q值与频率f的关系,总体上与广东地区的结果(Q(f)=150f 0.5)和欧洲中部地区的结果(Q(f)=400f 0.42)较为接近。
采用Atkinson 方法计算非弹性衰减系数C(f)或品质因子Q时,由于各台站的场地响应是通过与平均值比较来确定的,对于场地响应较小的台站(如基岩台站),该方法所得到的场地响应的对数将是负值,即台站响应将小于1(图4),因此得到的场地响应是相对的,不是真实的场地响应。这表明研究得到的21个台站的场地响应,除了武都、合作、湟源、定西、迭部等台的场地响应总体上没有放大效应以外,其余台站的场地响应均存在较明显的放大效应。
本文所用程序由中国地震局台网中心刘杰研究员提供,此外刘杰、郑斯华研究员在理论与方法上也给予了诸多指导和帮助,在此深表谢意。
- 黄玉龙,郑斯华,刘杰,等.2002.广东地区地震波衰减和场地响应的研究[J].地球物理学报,46(1):54-61.
- 李永华,吴庆举,安张辉,等.2006.青藏高原东北缘地质构造背景及地壳结构研究[J].地球物理学报,49(5):1359-1368.
- 刘杰,郑斯华,黄玉龙,等.2003.利用遗传算法反演非弹性衰减系数、震源参数和场地响应[J].地震学报,25(2):211-218.
- 苏有锦,刘杰,郑斯华,等.2006.云南地区S波非弹性衰减Q值研究[J].地震学报,28(2):206-212.
- Atkinson G M,Boore D.1995.New ground motion relations for eastern North America[J].BSSA,85:17-30.
- Atkinson G M,Mereu R F.1992.The shape of ground motion attenuation curves in Southeastern Canada[J].BSSA,82:2014-2031.
- Rogers A M,Tinsley J C,Hays W H,et al.1979.Evaluation of the relation between near-surface geological units and ground response in the vicinity of Long Beach,California[J].BSSA,69:1603-1622.