基金项目:云南省科技计划项目“中越红河断裂带地震活动性与地震构造特征对比研究”(2002GH10)资助.
(1.中国科学技术大学 地球和空间科学学院, 合肥 230026; 2.云南省地震局, 昆明 650224; 3.越南国家科学院地质研究所, 河内, 越南)
(1.School of Earth and Space Sciences,University of Science and Technology of China,Hefei 230026,Anhui,China)(2.Yunnan Earthquake Administration,Kunming 650224,Yunnan,China)(3.Institute of Geological Sciences,Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology,Hanoi,Vietnam)
Red River Fault; segmentation property; non-homogeneity; lateral extrusion; Vietnam; China
备注
基金项目:云南省科技计划项目“中越红河断裂带地震活动性与地震构造特征对比研究”(2002GH10)资助.
基于对越南境内红河断裂带的野外考察,结合中国境内红河断裂带已有考察研究成果,从断裂几何结构、构造演化与地层发育、新生代地质地貌特征等多个方面,初步探讨了红河断裂带现今活动的基本特征。认为:(1)红河断裂带在断裂几何结构、断裂长期的发育演化过程、断裂活动的地质地貌表现等诸多方面都表现出异常突出的时空不均匀性和分段性;(2)红河断裂新构造运动以来的夷平面发育与解体、新生代盆地发育与堆积、水系及河流阶地发育与变形等方面的特征表明,中国境内红河断裂带第四纪以来总体活动水平由北向南逐渐减弱的趋势一直延续到了越南境内;(3)青藏高原侧向挤出作用的影响范围是有限的,这一认识对于探索川滇地区地壳运动与强震活动的动力学机制具有重要意义。
Based on the field survey along Red River Fault Zone(RRFZ)within Vietnam,we primarily discuss the general features of contemporary activity of RRFZ combining with the study results in Yunnan of China from its geometric structure,tectonic evolution history and stratum development process,and geology and geomorphology since Cenozoic.We conclude:(1)the RRFZ has showed prominent spatio-temporal heterogeneity and segmentation property in many aspects such as the geometric structure,the long-term development and evolution process,and the geological and geomorphologic behaviors of faulting.(2)the characteristics,as the development and disaggregation of the planation surface along RRFZ,the growth and sedimentation of Cenozoic basin,and the development and deformation of water system and stream terrace,etc,indicate that the attenuated tendency of Quaternary activity of RRFZ in China from north to south has been kept going into Vietnam.(3)the lateral extrusion impacts coming from Tibet Plateau is limited,and this knowledge has significant meaning for probing the dynamic mechanisms of crustal movement and strong earthquake activity in the Sichuan-Yunnan region.
引言
红河断裂带作为青藏高原东缘一条重要的大地构造和活动块体边界,它是如何长期控制区域地质构造发育演化的历史,尤其是如何反映印度板块与欧亚板块的碰撞、青藏高原的隆起与侧向挤出及调节断裂两侧乃至更大区域现代地壳运动与变形的,一直倍受国内外学者的广泛关注。然而,限于各种条件,过去的所有研究工作,特别是断裂第四纪活动性、地震构造与地震活动特征等方面的工作,都仅限于中、越两国各自境内部分,而且相对而言,越南境内的研究要薄弱得多。这在很大程度上阻碍了相关研究和认识的深入。如Molnar等(1975)和Tapponnier等(1976,1981,1982,2001)提出的相关动力学模型,就由于缺乏红河断裂越南境内段的实地考察数据和资料的支持而存在明显缺陷。
2003年,在中国云南省科技厅和越南国家科学院的大力支持下,通过云南省科技计划国际合作类项目“中越红河断裂带地震活动性与地震构造特征对比研究”的资助,云南省地震局与越南国家科学院地质研究所合作,首次实现了对红河断裂带跨国界的、整体的综合考察研究,整合了两国历史地震记载、数字地震台网记录、区域地质及深部构造、跨断层形变测量及GPS观测等多方面的宝贵数据和资料(Cao,2003; Duong等,1999; Vietnam Geological Survey Group,1978~1982),并联合实施了对越南境内长达360 km的红河断裂陆上部分的野外综合考察,获得了关于红河断裂几何结构、地层发育、地质构造演化、断裂活动的地质地貌表现等方面的大量数据和资料。以此为基础,对红河断裂带展开更加全面和综合的科学分析和研究,无论是对促进和加深对青藏高原的相关研究和认识,还是对红河断裂越南部分未来地震危险性的科学估计等,无疑都具有十分重要的意义。
1 断裂带的几何结构特征
1.1 中国部分关于红河断裂带在我国云南境内的几何结构,已经有比较详细的研究(国家地震局地质研究所等,1989; 虢顺民等,2001),特别是通过虢顺民等(2001)完成的1:5万大比例尺活断层填图工作,获得了大量翔实的资料和数据。总体上中国境内红河断裂带的几何结构表现出明显的分段特征:
(1)北段自洱源至弥渡苴力一带,长约135 km。由一系列大致平行或斜接,且在20~30 km宽范围内呈面状展布的次级断裂构成,包括福寿场—江尾、洱海、凤仪—花甸坝、苍山东麓、凤仪—定西岭、弥渡盆地以及苴力—金宝山等主要断裂。其间有多条规模较大的NE、近EW向断裂与之交汇或交切,形成非常复杂的几何结构形态和典型的盆岭相间的构造地貌格局。断裂新活动在盆地段以正断垂直差异活动为主,而在山岭段则以张扭性右旋水平走滑为主。
(2)中段自弥渡苴力至元江大斗门,长约135 km。该段总体为结构比较简单的单条主干断裂,其间仅有小规模的其它方向的断层与之交切,形成狭长条状线性断层谷地构造地貌,并以整体右旋剪切走滑为其新活动特征。
(3)南段自元江春元至河口,长约330 km。该段总体由规模相当、相距数百至1 500 m且大致平行的两条次级断裂,即哀牢山山前断裂和中谷断裂构成。其较为突出的特点是,断裂带的总体走向较之北段和中段发生了显著变化,由NW向逐渐转为NWW向,并在平面形态上呈向西凸出的弧形。该段的活动性质为压扭性右旋剪切走滑。
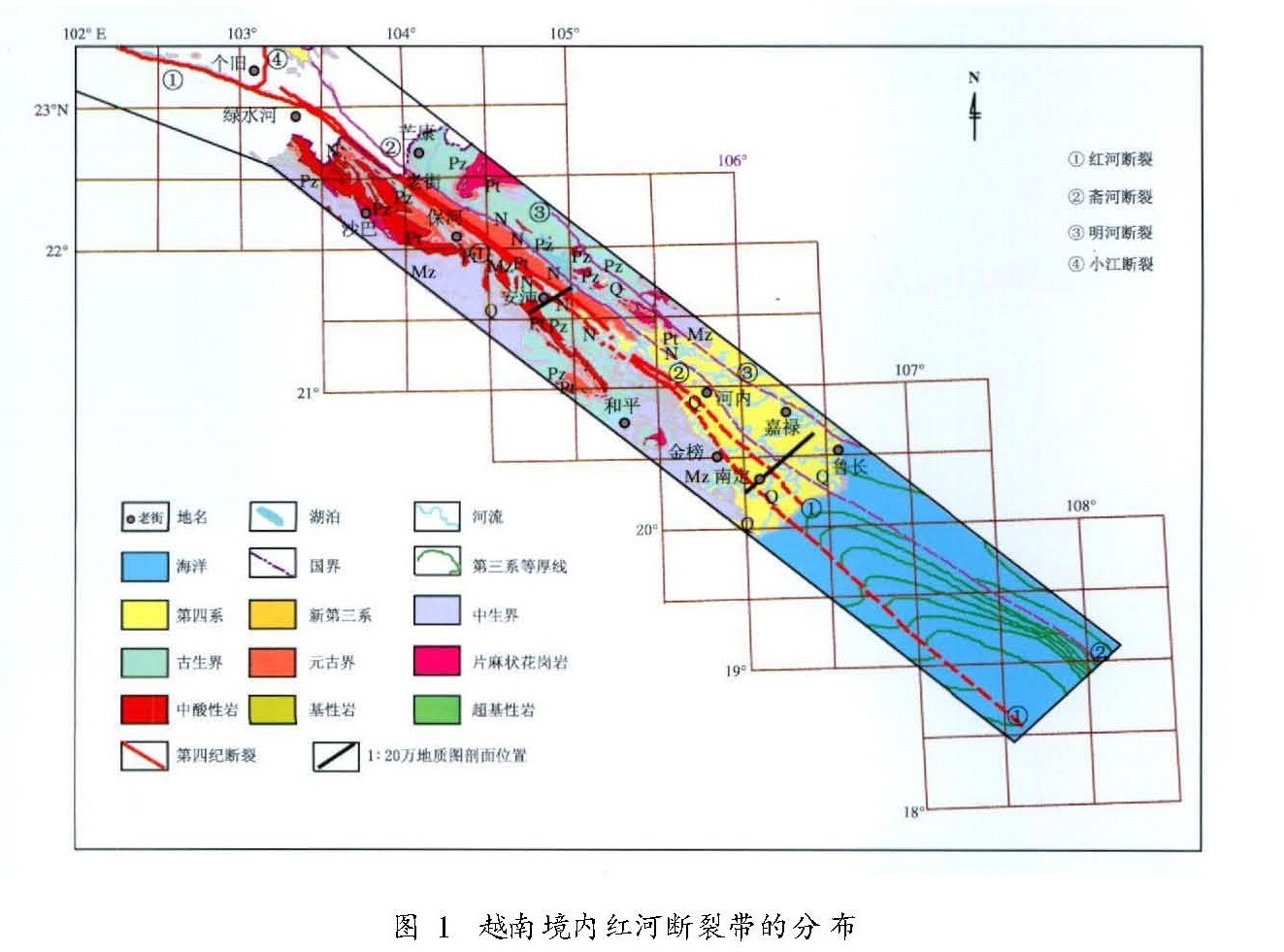
1.2 越南部分根据卫星影像解译、越南北部1:20万地质图和1:5万地形图判读及野外实地考察,红河断裂带在我国境内的南段自云南河口延入越南境内后,表现为非常平直和稳定的NW—SE走向(图1),其基本特征是:
(1)越南境内红河断裂带在陆上部分长约360 km。
(2)断裂带主体上仍然延续了云南境内的主要结构特征,即由相距数百至2 000 m且大致平行、规模相当的两条分支断裂构成,并一直保持这样的主体结构特征延伸进入北部湾海域。
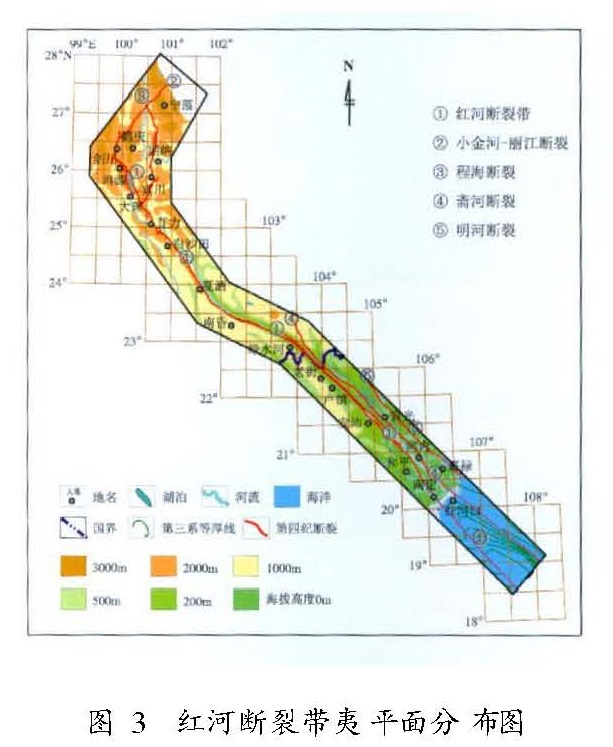
(3)在红河断裂带东侧,还发育有两条规模与红河断裂相当并呈大致等间距平行展布的NW向断裂带,即斋河断裂和明河断裂,这三条断裂平面间距保持在15~20 km,其中斋河断裂与红河断裂分别作为NW向元古界片麻岩深变质带的北东和西南边界,在卫星影像上显示出异常清晰的线性特征。
2 断裂演化与地层发育特征
研究表明,红河断裂带的形成至少始于前古生代的晋宁运动后期,之后分别经历了早古生代的加里东运动、晚古生代的华里西运动、中生代的印支运动和燕山运动以及新生代的喜山运动等多期次和多旋回的强烈构造运动,在使断裂带上早期地层发生不同成因和不同程度变质作用和岩浆活动的同时,还长期控制着断裂两侧广大区域的地层发育(国家地震局地质研究所等,1989; 虢顺民等,2001)。
2.1 前新生代地层与岩浆岩(1)以沿断裂带广泛发育变质岩带和多期次岩浆岩为特征。沿断裂自北向南发育了云南境内前寒武苍山变质带(苍山群)、哀牢山变质带(哀牢山群)和越南境内上元古界南果组。沿红河断裂带展布的这三条变质带在变质成因、程度乃至时代等方面都有所不同,反映了这条古老深大断裂在长期地质演化历史中的时空不均匀性或分段特征。
(2)红河断裂带的整个发育演化过程也伴随着多期次的岩浆活动。沿断裂带有加里东期花岗岩侵入,在华里西期和印支早期有橄榄岩、辉长岩等侵入,燕山期有更加广泛的中酸性岩浆侵入活动并伴有较小规模的基性和超基性岩浆侵入活动,其中以红河断裂带中越边境地区云南屏边至越南老街一带出露的长约60 km、宽20 km的燕山期巨型花岗岩体最具代表性。
(3)作为控制断裂两侧广大区域构造演化和地层发育的重要大地构造分界线,红河断裂带在云南境内最突出的作用体现在对滇西和滇中两大巨型内陆中生代盆地及其地层发育的控制上:断裂以西主要为火山岩建造和磨拉石建造,而以东为含煤建造和红色建造,红河断裂带是分隔这两大盆地的唯一屏障。而在越南部分的红河断裂两侧广大区域则发育相当于我国震旦亚界的上元古界南果组变质岩及早元古界和早中生界酸性侵入岩(以前者为主、后者为辅),其上发育了厚度和范围均远小于云南境内的中生界晚期沉积盖层,并主要分布在断裂南西侧(图1)。
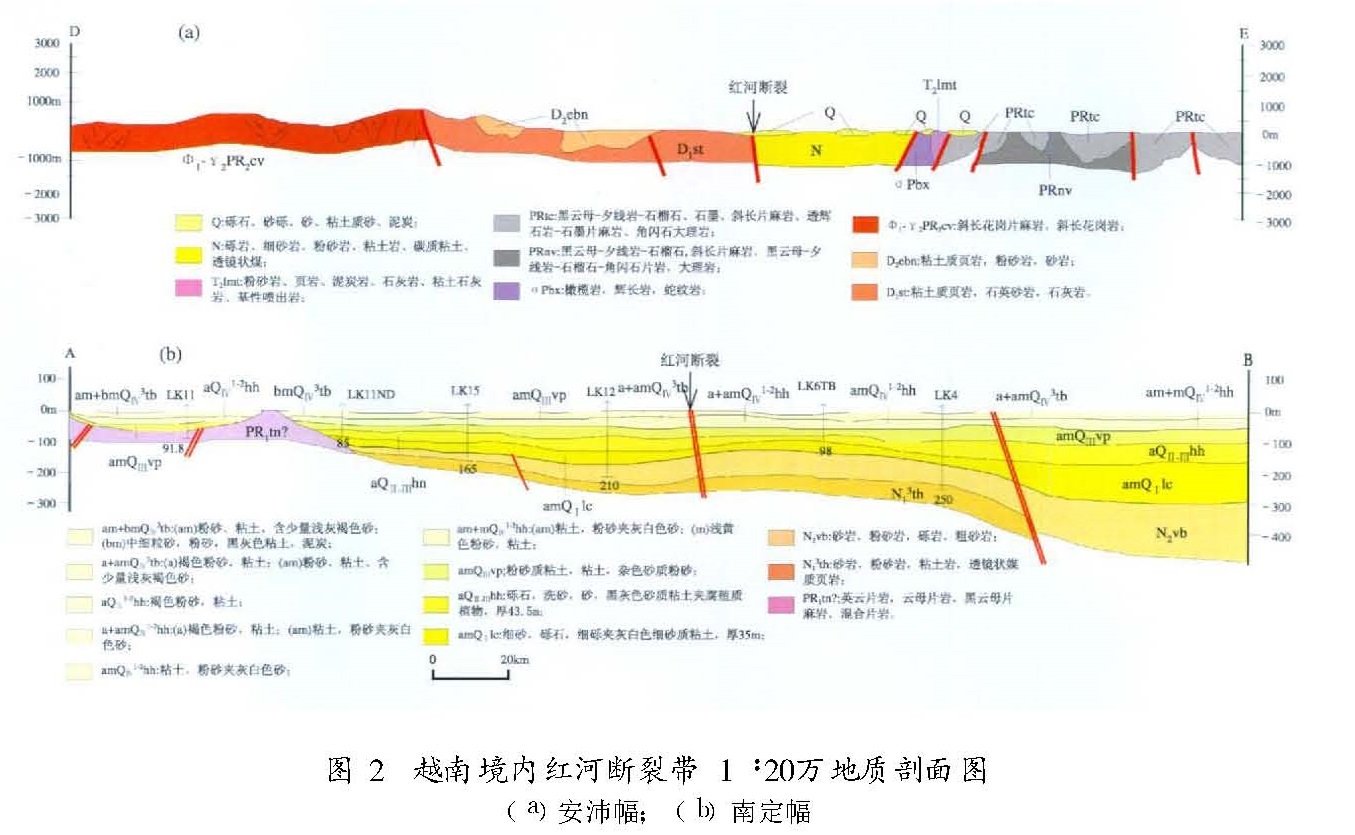
2.2 新生代地层与岩浆岩以印度板块与欧亚板块碰撞、青藏高原隆起和各活动块体边界的继承性与新生性活动为标志的新构造运动,是红河断裂带乃至整个中国西南地区新生代地层发育的关键性控制因素之一。自第三纪以来,沿红河断裂沉积地层的发育同样表现了十分突出的时空不均匀性,这与区域构造应力场以及断裂不同段落活动性质、活动强度的变化有密切关系(图1、图2)。
第三系沿红河断裂带为一套山前凹陷和磨拉石建造为主、局部夹湖沼相沉积。其中,下第三系底部为厚度巨大的紫红色砾岩层,其上逐渐过渡为砂岩、泥灰岩和石膏层。该期沉积作用沿整条断裂带仅仅在云南境内红河县大文提一带形成唯一的沉积中心,最厚达2 000 m,而在其它段落明显变薄以至零星分布。上第三系沿整条断裂带沉积范围明显扩大,并形成多个沉积中心,包括云南境内沉积厚度分别达2 000 m和800余米的红河县城和弥渡县金宝山一带,以及越南境内沉积厚度分别达1 300 m和2 000余米的安沛和河内三角洲地带。
第四系沿红河断裂带的发育在空间分布格局上与第三系比较又发生了显著变化,总体上可以概括为沿整条断裂带的零星发育与个别段落的巨厚发育的特征,而且有异常丰富的沉积类型,包括河湖相、湖沼相、洪积相、坡积相等,显示了更加复杂的时空不均匀性。关于第四系发育的具体情况,将结合断裂第四纪盆地发育特征在下文进行详细描述。
此外,沿红河断裂带在新生代早期还有相对小规模的碱性岩、酸性岩、基性岩和煌斑岩等侵入岩发育。
3 新生代地质地貌特征
3.1 夷平面发育特征云南高原及红河断裂带两侧的广大地区在中生代末期全部上升为陆地。此后一直长期处于以侵蚀作用为主,并有相关沉积发育的区域构造演化阶段,直到中新世晚期形成准平原面。上新世开始的新构造运动使该准平原面伴随青藏高原的隆起而发生强烈抬升形成高原面。在此过程中,区域内包括红河断裂在内的许多前新生代断裂相继复活并发生强烈活动,其中沿各主要断裂带时空显著不均匀的段块式差异活动使先前的高原面发生解体,形成现今分布于不同高度的残留古高原面,即通常所说的夷平面。因此,仔细分辨和测量这些夷平面沿断裂带不同段落高程的变化幅度,可以了解断裂带在该时间段内两侧差异活动的强度。在野外考察中,相关沉积、残积红土以及相对平坦的地貌面是识别夷平面的重要标志。
自新构造运动以来,红河断裂带的差异活动在断裂北段的洱源、大理和弥渡一带最为显著,断裂两侧夷平面的高差在大理一带达1 000 m左右,在弥渡一带也有500 m左右,而往南至元江、红河、河口一带高差迅速下降并接近于零(虢顺民等,2001)。由此直至越南境内的安沛一带可见现存高度在海拔1 000 m左右的夷平面,但在该段断裂两侧都不存在明显的高差(图3)。这一现象表明,红河断裂带自新构造运动以来,甚至第四纪以来,差异活动自北向南逐渐减弱,犹如一把自南向北垂直张开的剪刀。
3.2 水系与阶地发育特征断裂带及其两侧水系的发育及断错变形是反映断裂活动最灵敏的地貌要素之一。其关键环节就是要尽可能准确地确定水系的发育年龄。前人主要使用以下两种方法:一是根据断层特定段落在特定地层中的溯源侵蚀速率研究,得到水系长度与其发育年龄的统计关系; 二是根据区域不同级别水系及其相关堆积物的年代来推测不同级别水系的发育年龄。
综合前人和本项目对红河断裂水系及阶地发育的大量研究,我们主要有以下几点认识:
(1)红河断裂带相关水系的发育年龄、溯源侵蚀速率与水系长度的关系同样具有明显的分段性。对礼社江、元江、红河等一级水系以外的次级支流而言,在同等时间跨度和同类地层岩性条件下,沿断裂带两侧第四纪以来差异运动愈强烈的段落,相应水系的溯源侵蚀速率与水系长度愈大。例如,红河断裂带北段的大理至弥渡一带,第四纪晚更新世以来发育的水系长度可达10 km量级,而在弥渡以南直至南段的哀牢山一带,同期发育的水系一般都在5 km以下(虢顺民等,1995)。
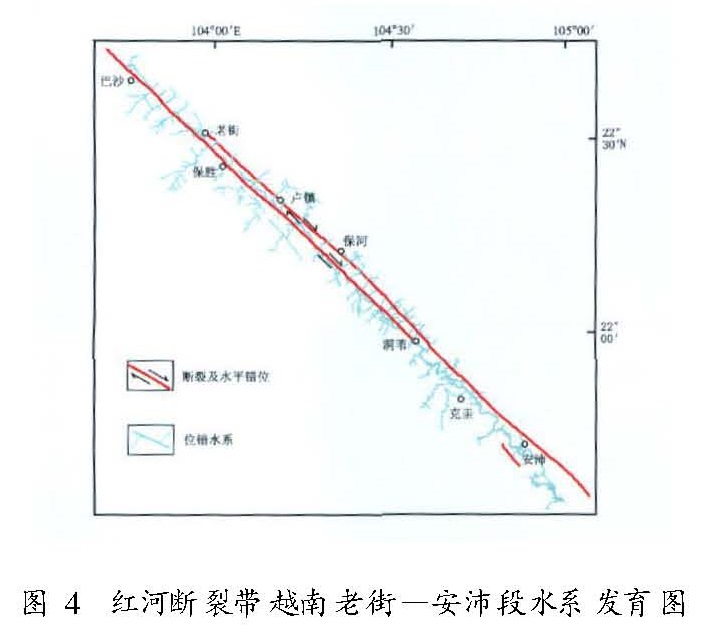
(2)红河断裂带对现代水系发育的控制作用至少体现在两个方面,一是随断裂第四纪以来不同段落活动方式和强度的变化,沿断裂两侧的不同级别的水系或被断层水平错断形成多条水系的同步扭曲,或被断层垂直错断形成悬沟; 二是沿断裂带发育的具有稳定线性构造的变质岩带严格控制了水系的走向,在卫星影像上表现为异常清晰和突出的线性特征,这在越南境内的老街至安沛一带尤为典型。
(3)第四纪以来,沿红河断裂带发生的水系错断现象自断裂北段的大理至弥渡一带往南逐渐减弱,而且被错断的水系年龄也逐渐变老。换句话说,从弥渡以南直至红河入海口的河内一带基本未发现晚更新世以来水系发生错断的现象(图4)。
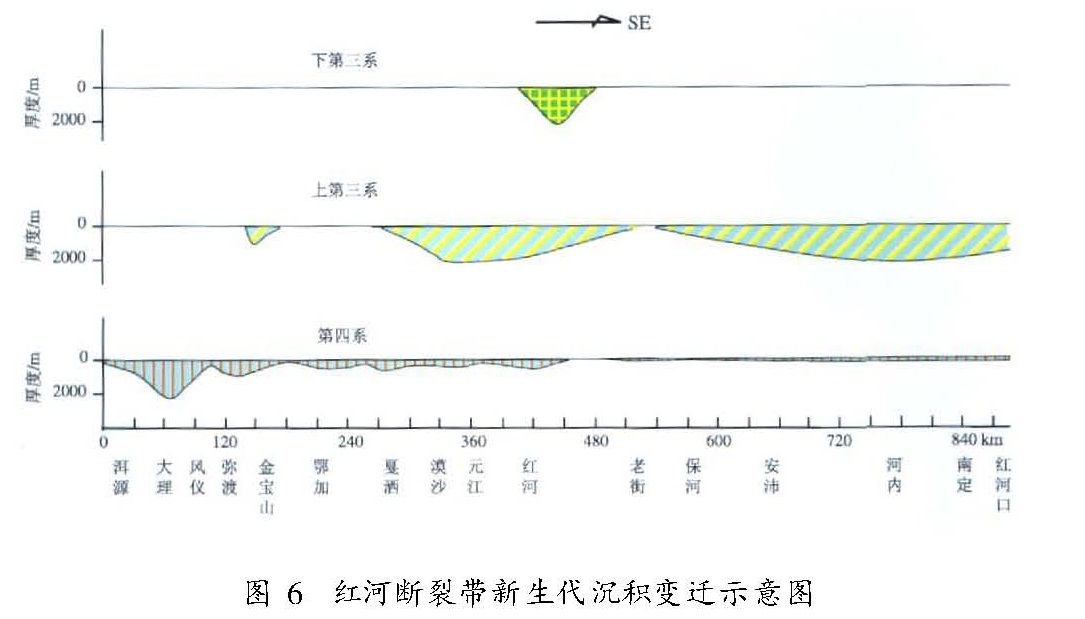
(4)对红河断裂带越南部分的野外考察发现,除越南老街至中国云南河口一带有发育比较完好、类型为基岩基座型、拔河高度在数米量级的一级河流阶地外,整个考察范围内基本不发育河流阶地。这一现象表明:红河断裂越南部分及其两侧的广大区域在新生代特别是第四纪时期,整体上处于相对稳定、以侵蚀为主的构造环境中(图5); 同时,也暗示着来自青藏高原剧烈抬升的影响在越南已经迅速减弱甚至消失。3.3 新生代盆地发育特征自新构造运动以来沿红河断裂带发育的盆地及其沉积物特征,是反映断裂不同时期和不同段落活动性质、活动强度演变规律的重要指标。根据虢顺民等(2001)的研究,第三纪以来我国境内红河断裂所控制的盆地及其堆积物的发育存在自南而北逐渐迁移的过程,但通过对包括越南部分在内的断裂整体进行研究后发现,自新生代以来,沿红河断裂发育的盆地及其沉积经历了从老第三纪时期形成的唯一沉积中心(我国境内的红河县城一带),到新第三纪迅速扩展的至少两个以上的沉积中心(包括云南元江—红河一带和越南河内—南定一带,且沉积范围大大扩展),再到第四纪时期除北段的大理、弥渡一带以外沿整条断裂带第四系发育十分有限的演化过程(图6)。这似乎暗示着第四纪以来,红河断裂的活动性有自北而南逐渐减弱的趋势。尤其是沿红河断裂带的越南部分,第四系堆积范围和厚度都十分有限,一般厚度只有数米至数十米,即便是在入海口附近的红河三角洲地带,第四系堆积厚度也只有200余米。
4 结论与讨论
笔者以红河断裂越南部分野外实地考察所获得的大量第一手资料为基础,结合国内外相关研究资料及成果(Zhang等,1999; 张建国等,1993,1997),通过对红河断裂带断裂几何结构特征、断裂演化与地层发育特征、新生代地质地貌特征等方面的综合研究,得到以下初步结论:
(1)红河断裂带在断裂的几何结构、长期的发育演化过程、断裂活动的地质地貌表现等诸多方面都表现出了异常突出的时空不均匀性和分段
性。但从中、越对比的角度看,又存在一定的相似性。比如,国内部分依据断裂几何结构、最新活动时代以及第四纪不同时段滑动速率等被划分为北、中、南三段(国家地震局地质研究所等,1989; 虢顺民等,2001),结合本项考察研究,断裂的越南部分在几何分段上可归入国内部分的南段,但其最新活动时代和强度似乎比国内部分的南段更老、更弱。
(2)红河断裂带第四纪以来的总体活动水平表现出非常明显的由北向南逐渐减弱的趋势,特别是断裂带的越南部分,现代活动已经非常微弱。如果将青藏高原侧向挤出作用作为驱动以红河断裂带为西边界的川滇块体运动的主要动力来源,那么红河断裂带现今活动由北向南逐渐减弱的趋势表明青藏高原侧向挤出作用的影响范围似乎是有限的,或者说对越南段的影响似乎已经很微弱。这不仅对越南未来国土规划与利用具有重要意义,而且对于重新认识青藏高原侧向挤压对川滇地区地壳变形的影响,从而进一步探讨川滇地区强震活动的动力学机制将具有十分重要的科学价值(皇甫岗等,2000,2006; 张培震等,2004; 徐锡伟等,2003)。
对红河断裂带中国部分和越南部分的研究,过去在研究深度和水平上都有较大差异,通过本项目的实施,特别是本文所展示的大量具有填补历史空白意义的实地考察资料,可以在很大程度上弥补这种差异。尽管由于时间和经费的限制,其中还有许多问题有待深入研究,但可以肯定,本项目所取得的资料和初步成果将为今后进一步的研究奠定重要的基础和条件。
- 国家地震局地质研究所,云南省地震局.1989.滇西北地区活动断裂[M].北京:地震出版社.
- 虢顺民,计凤桔,董兴权,等.1995.云南红河断裂带大水塘—南沙段第四纪断错水系初步研究[G]//《活动断裂研究》编委会.活动断裂研究理论与应用.北京:地震出版社.
- 虢顺民,计凤桔,向宏发,等.2001.红河活动断裂带[M].北京:海洋出版社.
- 皇甫岗,秦嘉政.2006.云南地区大震活动规律研究[J].地震地质,28(1):37-47.
- 皇甫岗,苏有锦.2000.20世纪云南地区地震活动研究[J].地震研究,23(1):1-9.
- 徐锡伟,闻学泽.2003.川滇地区活动块体最新改造变动样式及其动力来源[J].中国科学(D辑),33(增刊):151-162.
- 张建国,汪良谋,徐煜坚,等.1993.红河断裂深部震源环境介质力学性质分析[J].地震地质,15(2):131-137.
- 张建国,徐煜坚,汪良谋,等.1997.弥渡地区第四纪活动特征与红河断裂分段性研究[C]//谢应齐.云南地球物理文集(二).昆明:云南大学出版社:293-300.
- 张培震.2004.青藏高原及周边现今构造变形的运动学[J].地震地质,26(3):367-376.
- Cao Dinh Trieu.2003.Deep structure recent dynamics and seismic activity in Red River Fault Zone in Vietnam[J].Journal of Geodesy And Geodynamics,23(1):93-102.
- Duong Chi Cong,Feigl K L.1999.Geodetic measurement of horizontal strain across the Red River fault near Thac Ba,Vietnam,1963-1994[J].Journal of Geology(B),13-14:9-18.
- Molnar P,Tapponnier P.1975,Cenozoic tectonics of Asia:Effects of a continental collision[J].Science,189:419-426.
- Tapponnier P,Mercier J.,Proust F.,et al.1981.The Tibetan side of the India-Eurasia collision[J].Nature,294(5840):405-410.
- Tapponnier,P,Peltzer G,Ledain A,et al.1982.Propagating extrusion tectonics in Asia:New insights from simple experiments with plasticine[J].Geology,10:611-616.
- Tapponnier P,Xu Z Q,Roger F,et al.2001.Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibetan Plateau[J].Science,294:1671-1677.
- Tapponnier P,Molnar P.1976,Slip-line field theory and large scale continental tectonics[J].Nature,264:319.
- Vietnam Geological Survey Group.1978-1982.1:20000 Geological Map of The socialist Republic of Vietnam:Yenbai,Laocai et[K].Hanoi:Vietnam Geology Press.
- Zhang J G,Wang L M,Xie Y J,et al.1999.Analysis of mechanical property of the medium under the deep seismic source environment along Red River fault[J].Journal of Geology,13-14:311.