基金项目:国家自然科学基金课题“汶川地震对区域应变积累影响的研究”(40974005)与中国地震局2010年度震情跟踪合同制定向工作任务(2010010401)资助.
备注
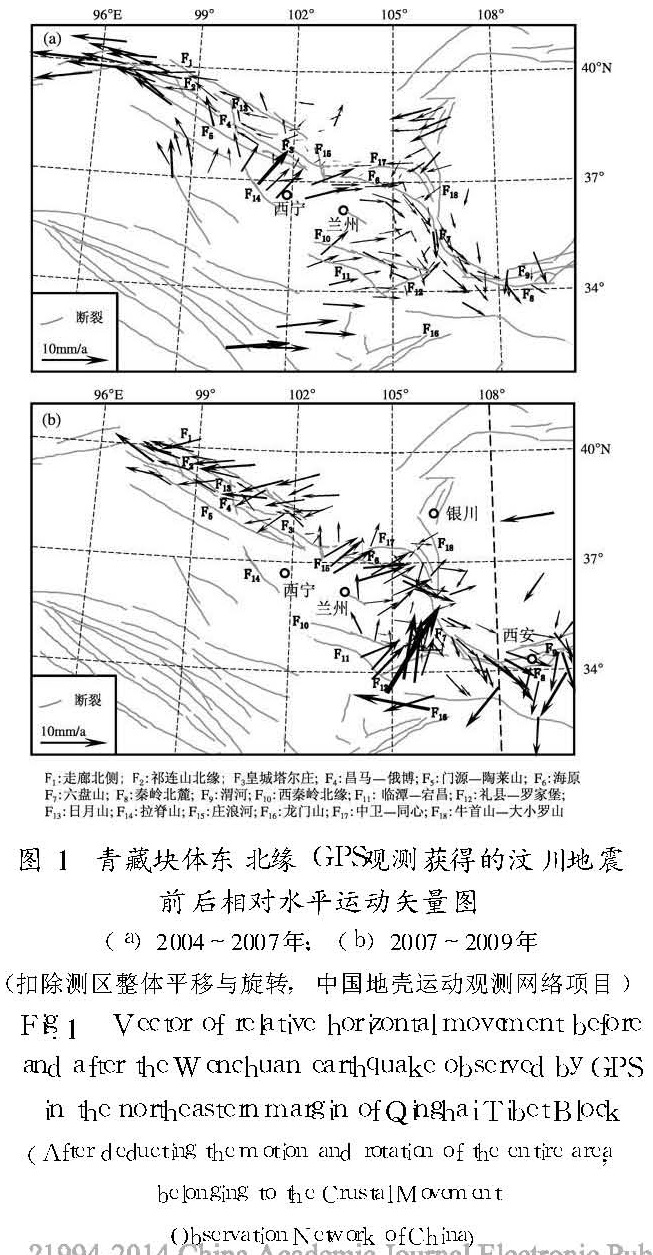
利用青藏块体东北缘2004~2007年、2007~2009年GPS水平运动观测资料,分析地壳运动与活动断裂带构造变形演化特征以及汶川大震对活动断裂的影响。研究表明:祁连山—海原断裂带近期仍呈现与其构造活动背景一致的左旋挤压特性,观测结果未显示汶川大震对断裂有明显影响。而汶川大震对西秦岭构造区中东部、六盘山断裂中南段、秦岭北麓与渭河断裂的西段的影响相对显著,其中对西秦岭构造区中东部的大范围区域应变积累可能呈以增强为主的影响,其它断裂段近期可能呈以调整为主的状态特征。
Using the GPS observational data during the period of 2004~2007 and 2007~2009 in the northeastern margin of Qinghai-Tibet block,the evolution features of crustal movement and tectonic deformation of active fractures are analyzed,together with the influence of the Wenchuan Earthquake.The result shows that,this earthquake did not display remarkable effect on the Qilianshan-Haiyuan fracture belt from observation result of limit stations,which still reflected thrust and sinistral slip,with according to its tectonic background; but displayed relatively obvious influence on the West Qinling tectonic region,the medium-southern segments of Liupanshan fault,the west segments of Northern foot fault of Qinling and Weihe fault,mainly revealing enganced strain accumulation on the middle-eastern West Qinling tectonic region,mainly revealing adjusting-distrubing effect on other fault-segments.