基金项目:安徽省地震科研青年基金项目(20120707)资助.
备注
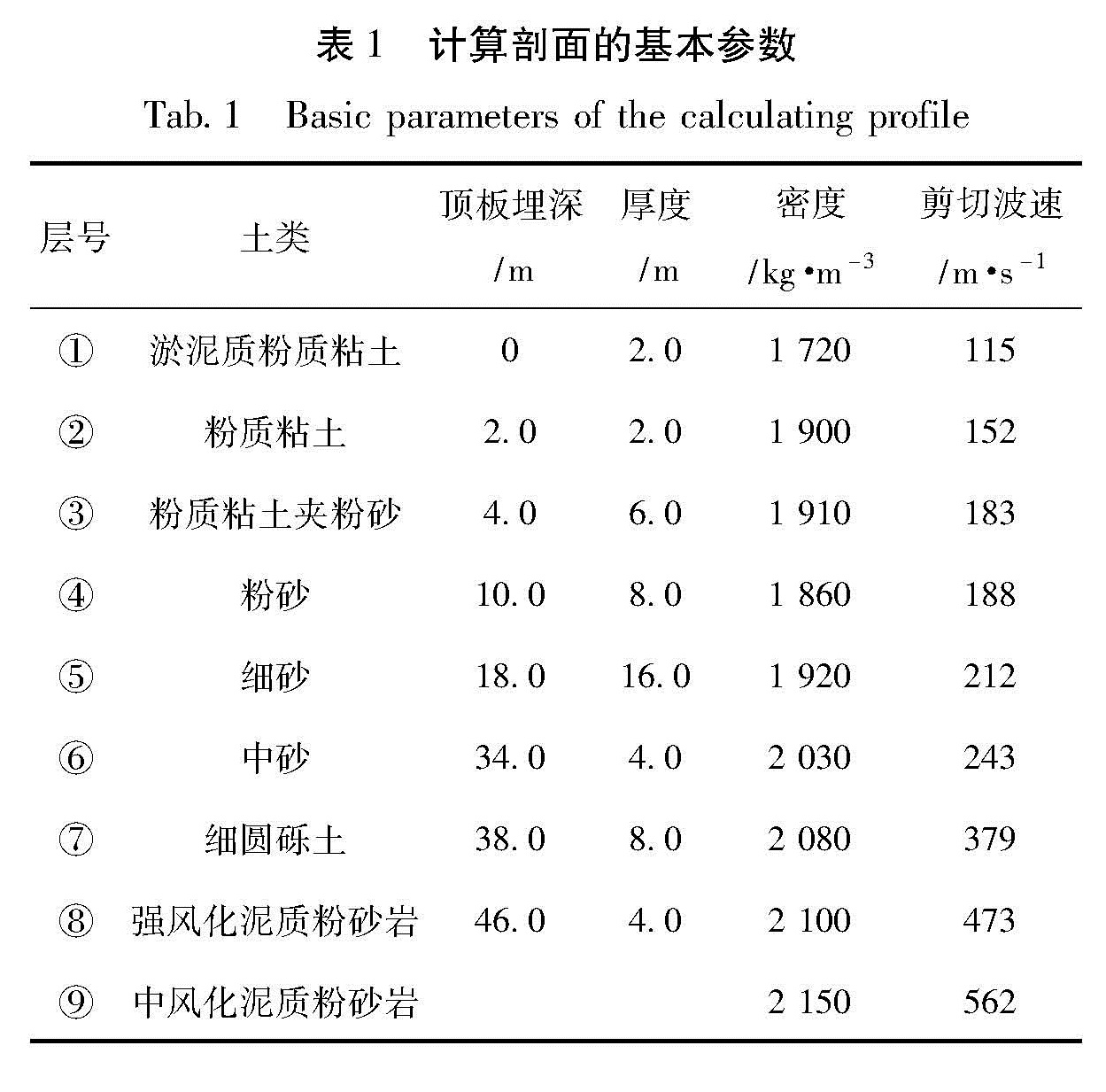
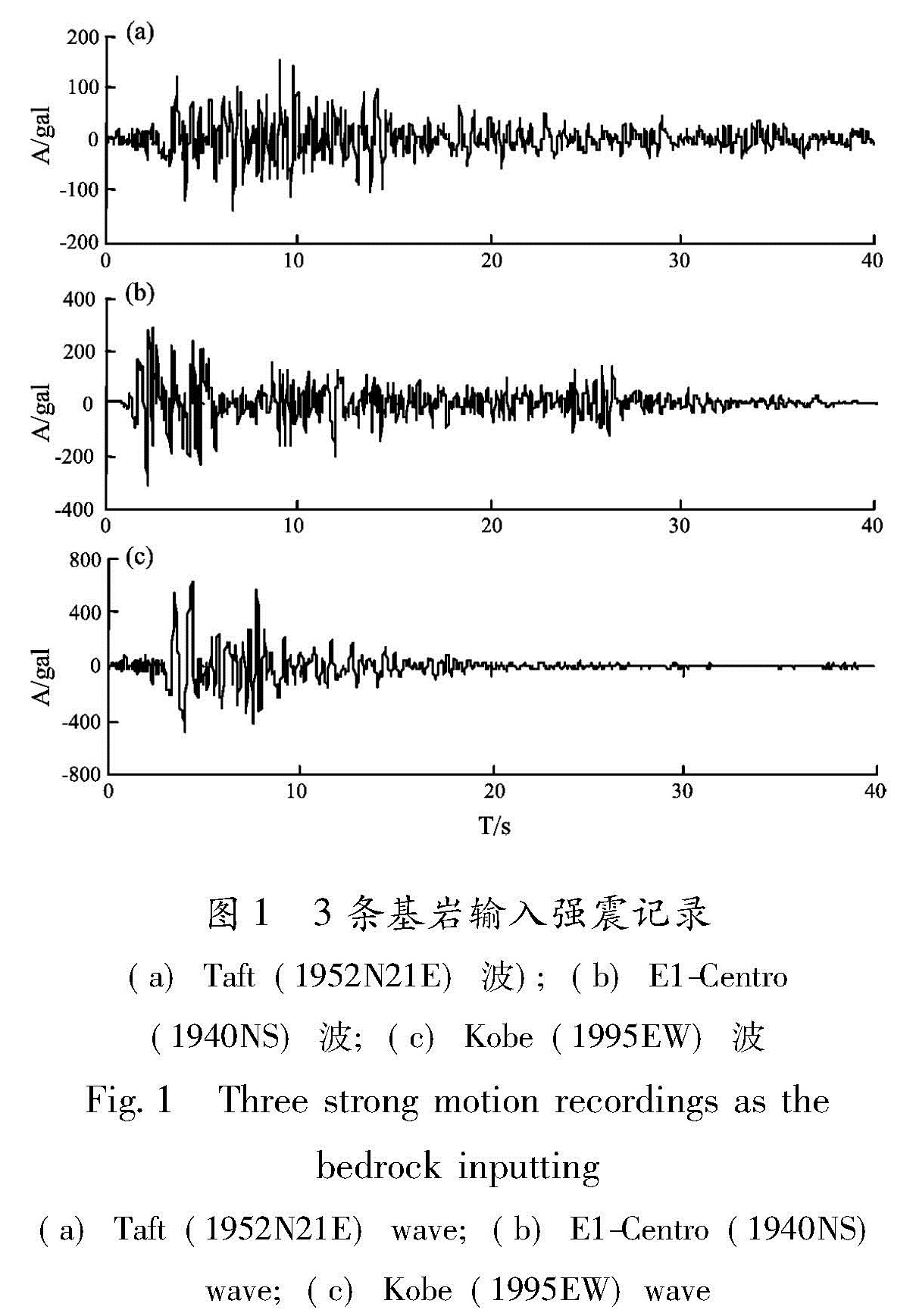
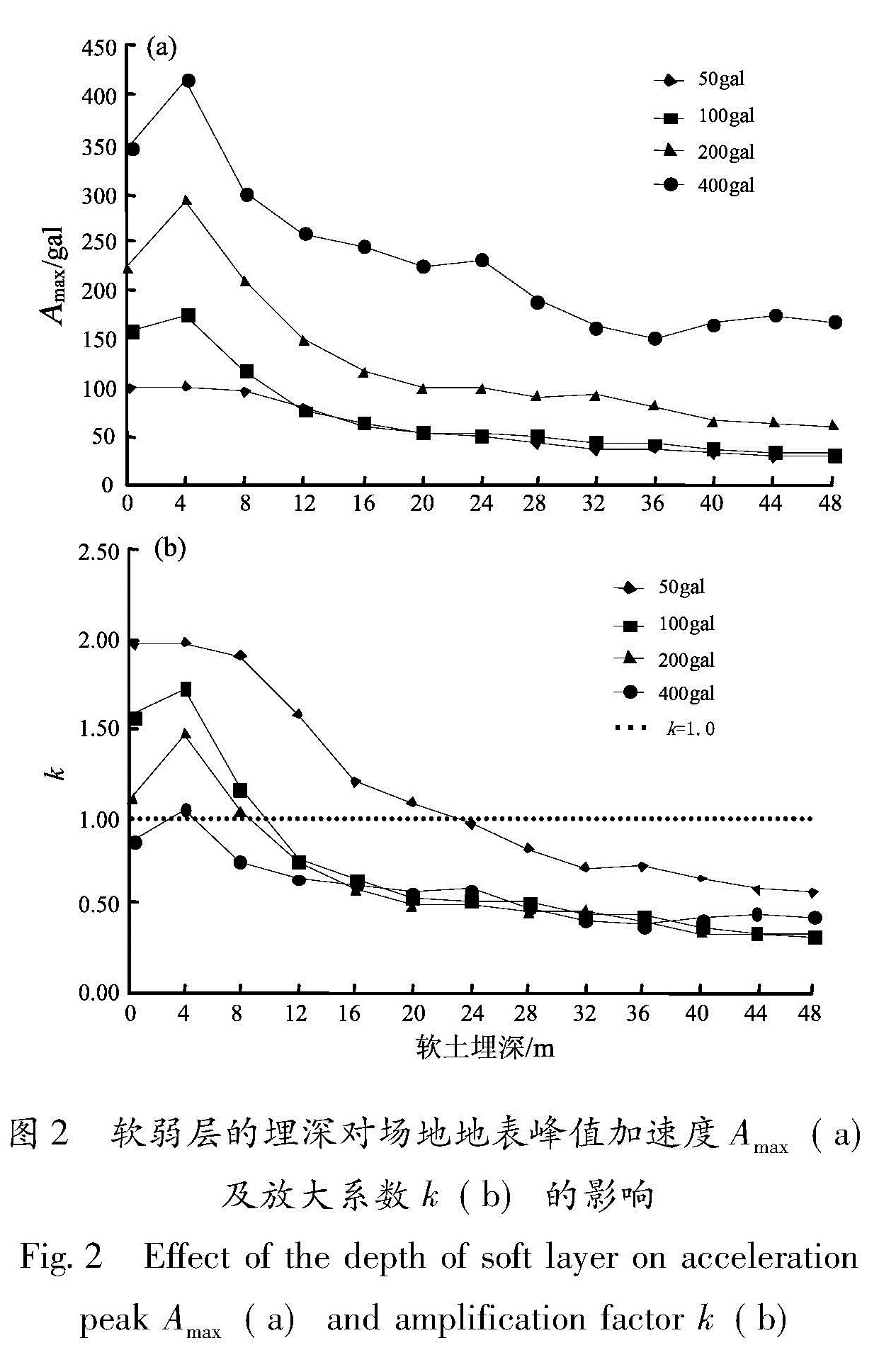
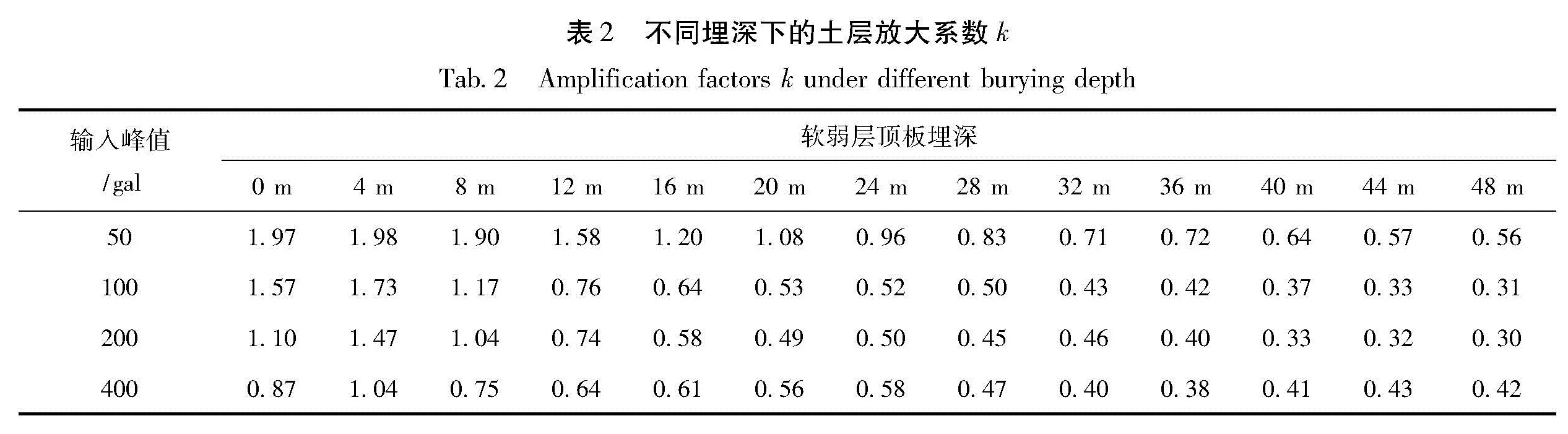
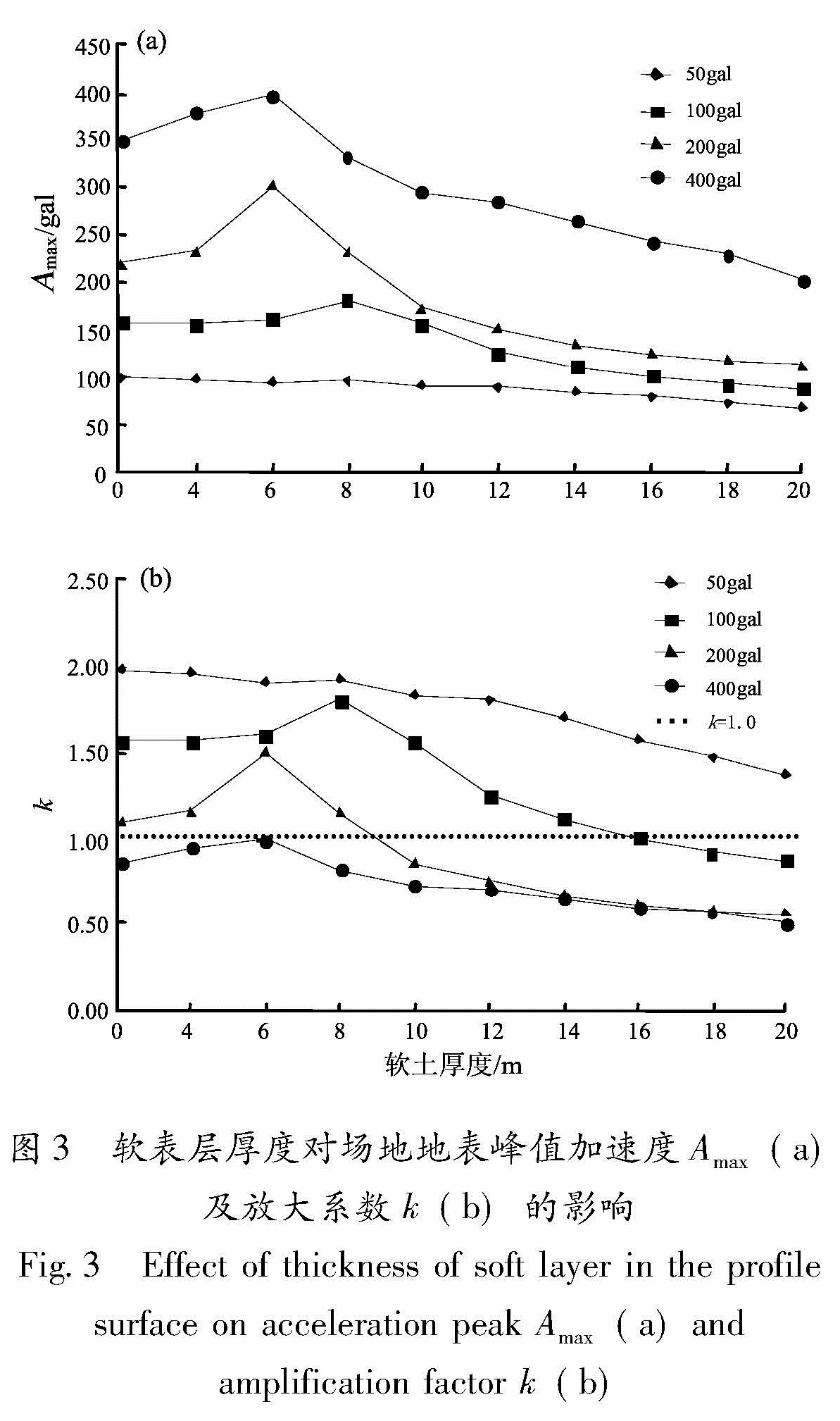
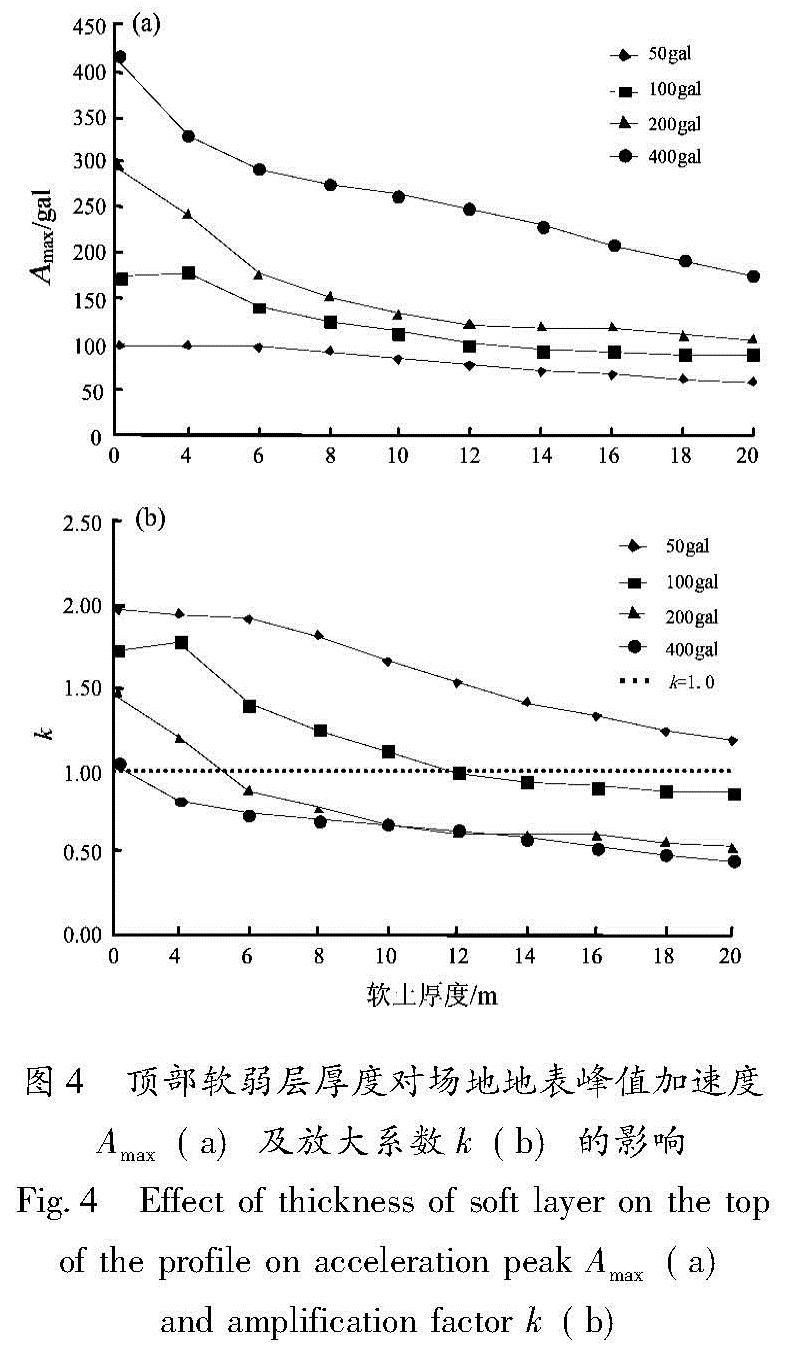
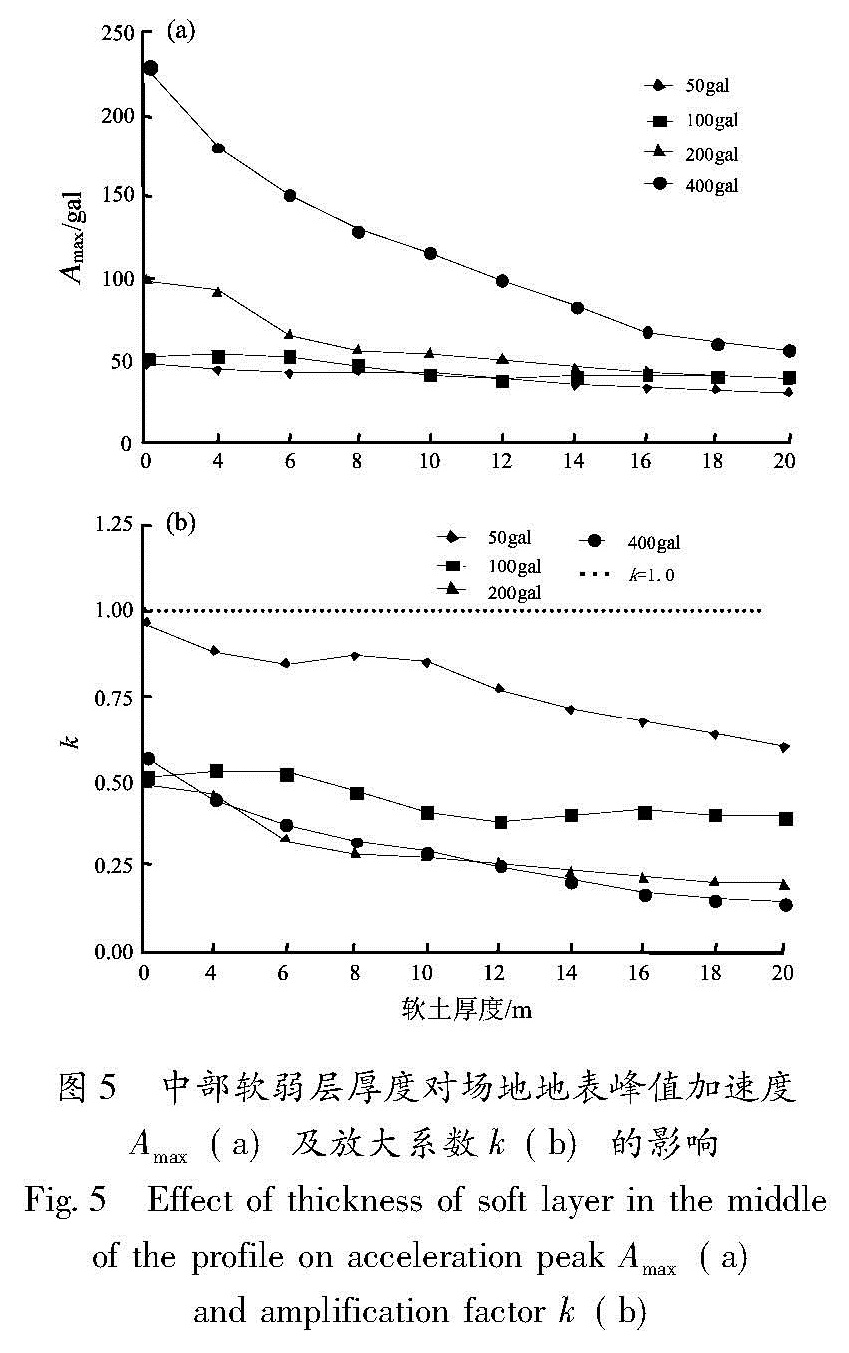
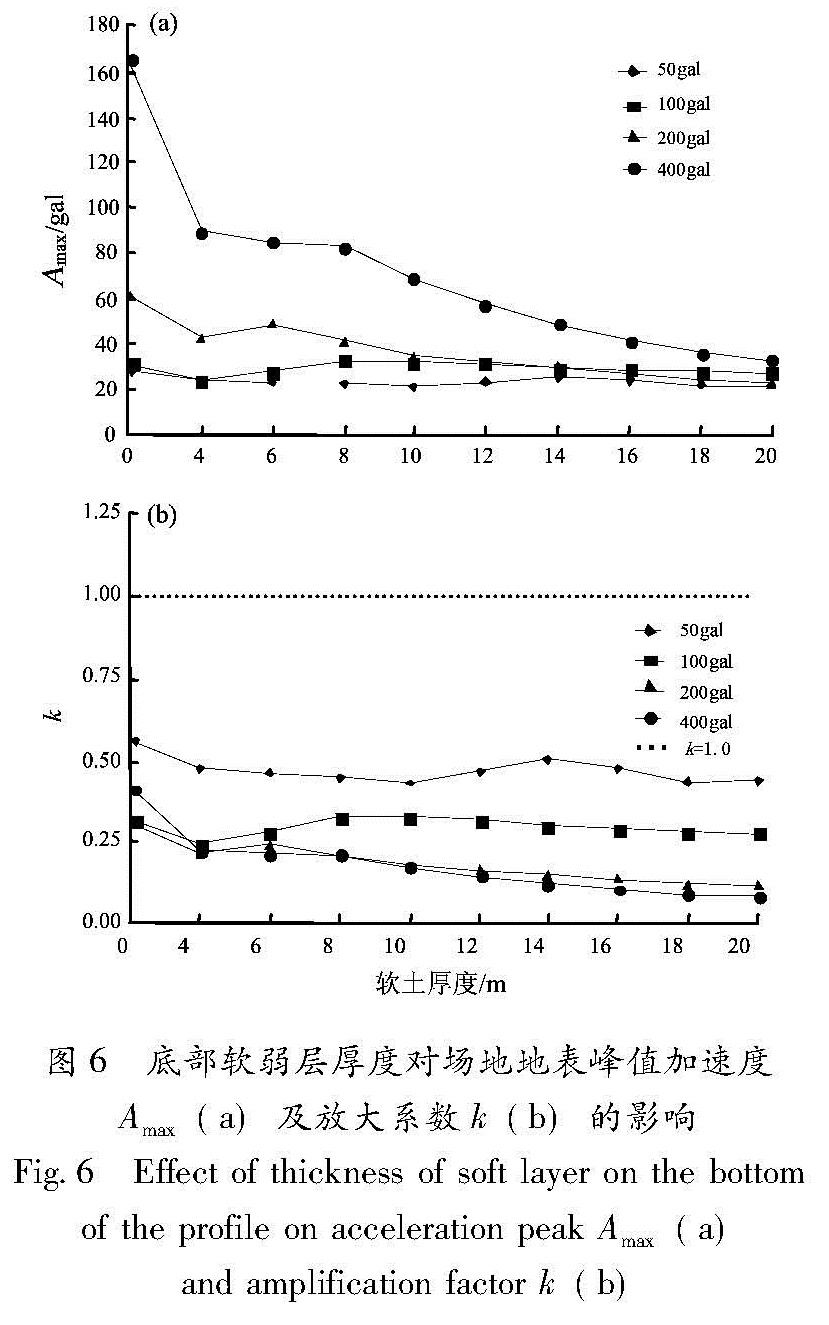
以江淮地区某软土场地为原型,构造多种场地土层地震反应分析模型,选择Taft(1952N21E)、Kobe(1995EW)和E1-Centro(1940NS)3条强震记录作为地震动输入,采用一维频域等效线性化波动方法重点分析了软弱层的埋深、厚度对软土场地地表加速度峰值的影响。结果 表明:对于给定的输入地震动,地表加速度峰值及土层放大系数随着软弱层埋深、厚度的增加而逐渐减小; 当软弱层的埋深、厚度超过一定值时,软土场地开始出现减震效应,软弱层的埋深越深、厚度越大、输入地震动强度越高,减震的效果越明显。
Basing on a soft site in Jianghuai region, we constructed several analyze models of site soil seismic response. Then we selected three earthquake records of Taft(1952N21E), Kobe(1995EW )and E1-Centro(1940NS )as the input waves, and analyzed the effect of the buried depth and the thickness of soft soil layer on ground peak acceleration in frequency domain through one-dimension equivalent linear fluctuation method. The results showed that for the given input ground motion, the ground acceleration peak and soil amplification factors decreased gradually with the increase of thickness or buried depth of soft site. When the thickness or buried depth of soft site exceeded a certain value, the soft site began to show vibration reduction effect, the deeper and the thicker of the soft layer, the higher intensity of input ground motion, the vibration reduction effect is more obvious.