基金项目:中国地震局教师科研基金(20100104)和(20130102)联合资助.
(1.防灾科技学院,河北 三河 065201; 2.湖南师范大学,湖南 长沙 410005)
(1. Institute of Disaster Prevention,Sanhe 065201,Hebei,China)(2. Hunan Normal University,Changsha 410005,Hunan,China)
well water level; solid wave; tectonic activity; precipitation; aquifer
备注
基金项目:中国地震局教师科研基金(20100104)和(20130102)联合资助.
利用滇中和滇南地区6口井水位动态观测资料,通过计算井水位固体潮的振幅和相位差的动态过程,分析井—含水层系统受区域应力场作用的程度,从构造活动因素方面为井水位下降的机理解释提供参考依据。结果 表明,在易门、高大、建水和开远水位下降过程中,水位振幅和相位差异常变化不显著,不能证明水位下降是受区域应力(应变)作用的影响,井水位下降异常可能主要是因为降水补给减少造成的。新平和元江井水位的振幅和相位差异常明显,井—含水层系统可能受到区域应力场作用的影响,同时也不能排除有降水减少因素的影响。
Basing on the dynamic observation data of water level in 6 wells in Middle and South Yunnan,we calculated the dynamic process of amplitude and phase difference of water level solid tide and analyze the effect degree of regional stress field on the well-aquifer system so as to provide the reference to explain the decline mechanism of the water levels from tectonic activity. The results show that the amplitudes and phase difference of water level did not change significantly in the decline process of water levels in Yimen,Gaoda,Jianshui and Kaiyuan wells,which cannot prove that the decline of water level was influenced by the regional tectonic stress(strain),so it was mainly caused by the decrease in precipitation supply. The abnormal variation of amplitudes and phase difference of water level were obvious in Xinping and Yuanjiang wells,so the well-aquifer system might be influenced by regional stress field,and the influence of precipitation decreasing cannot be ruled out.
引言
2008年以来,滇中和滇南地区建水、易门、高大和元江4口井井水位持续下降,水位异常的显著特点是在时间和空间分布上都相对集中。这种异常变化是由区域构造活动引起的,还是由降水补给、抽水等水文因素的干扰所致,引起了有关部门和学者们的关注,分析多口井水位持续下降可能的成因机理,对本地区的震情分析也具有重要意义。
引潮力和构造应力所引起的井水位潮汐现象揭示了含水层孔压与构造应力(岩石形变)的耦合关系,一直受到岩石力学和地震学界的关注。早期研究大多基于用Biot孔弹性理论研究孔压、井水位与应力(或应变)之间的响应关系(Van der Kamp,Gale,1983; 张昭栋,张广城,1987)。Bower(1983)认为,潮汐水位变化的日波和半日波成分依赖于断裂的开度、方位(倾向和走向)以及断裂的径向延伸和裂隙面的压缩性,给出了潮汐分波应力计算公式,并且根据潮汐分波相位差和振幅得到基岩的裂隙参数。Hsieh等(1987)提出了水位和含水层孔压振幅比计算公式,从理论上建立了井水位—孔压的响应关系。张昭栋等(1999)给出一种利用井水位的固体潮系数反演含水层应力变化的方法。孙小龙等(2011)运用小波分析法提取井水位多年动态变化的趋势信息,探讨了华北地区近年来的构造应力场变化特征。石云等(2013)研究了裂隙岩石中潮汐水位相位和振幅变化规律,即在构造应力作用下,井孔—裂隙水流交换和裂隙间水流交换是潮汐相位、振幅发生变化的重要影响因素。
利用滇中和滇南地区6口井水位动态观测资料,应用Baytap-G提供的潮汐分析方法,计算井水位优势潮汐分波M2波的振幅、相位差,根据水位振幅和相位差的异常变化信息,分析井水位可能受到区域构造应力作用的程度,探讨滇中和滇南地区导致井水位下降异常的可能原因。
1 地下流体监测井简介
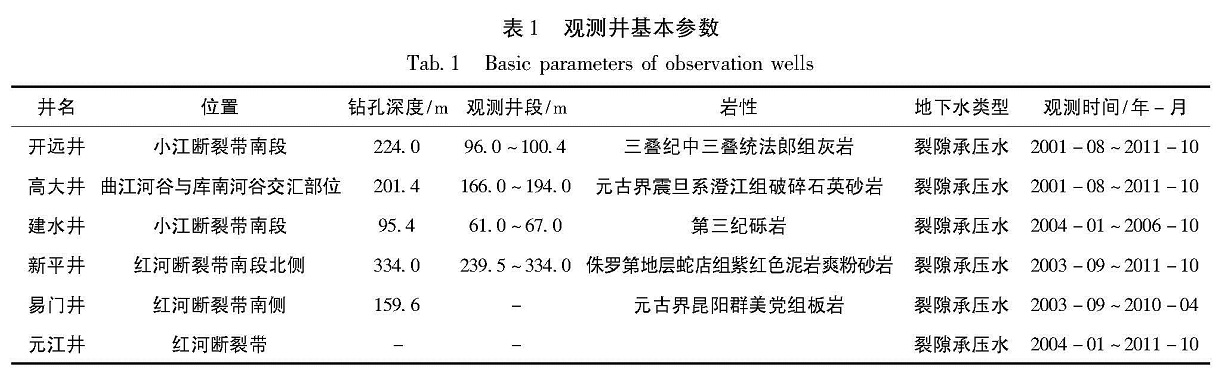
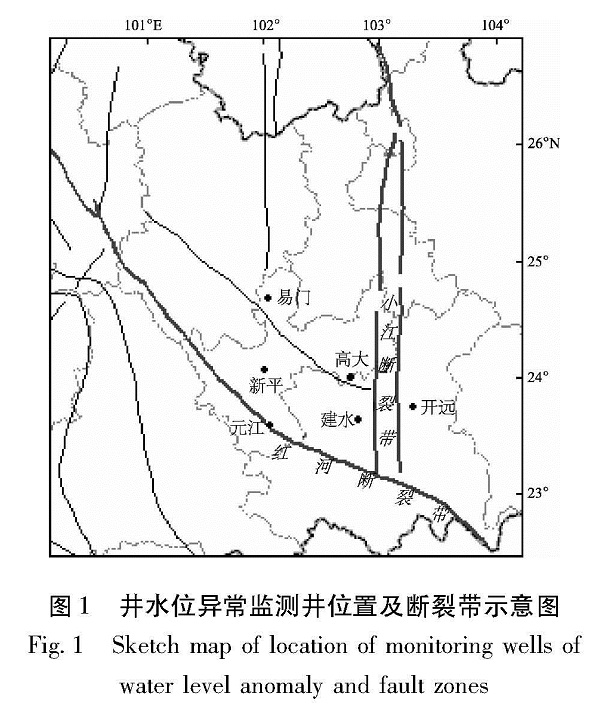
1.1 监测井基本情况本文所研究的井孔位于小江断裂带南段与红河断裂带中段交汇处,其中,元江井和新平井位于红河断裂带上,华宁井位于小江断裂带上(图1)。笔者共选取6口井进行频谱分析,分析区域应力应变状态。
分析6口井的井水位数据,其含水层类型为裂隙承压水,具有显著的固体潮效应,可以进行频谱分析。观测时间段最早从2001年8月开始,各井孔详细情况见表1。
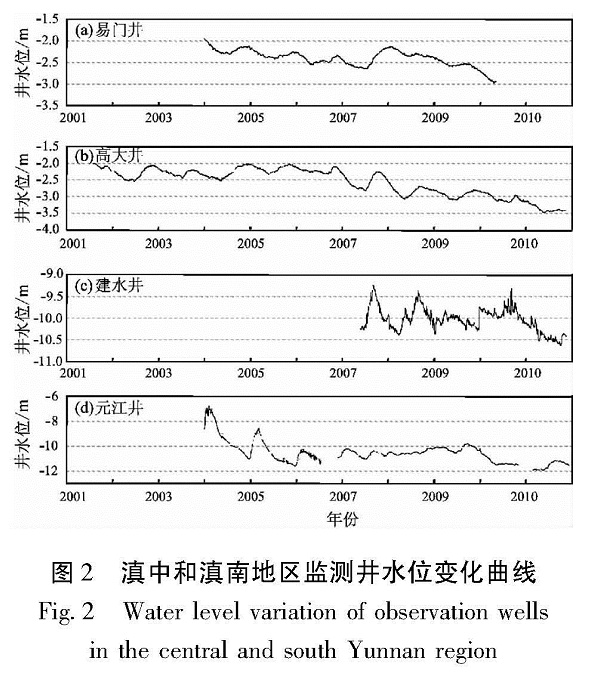
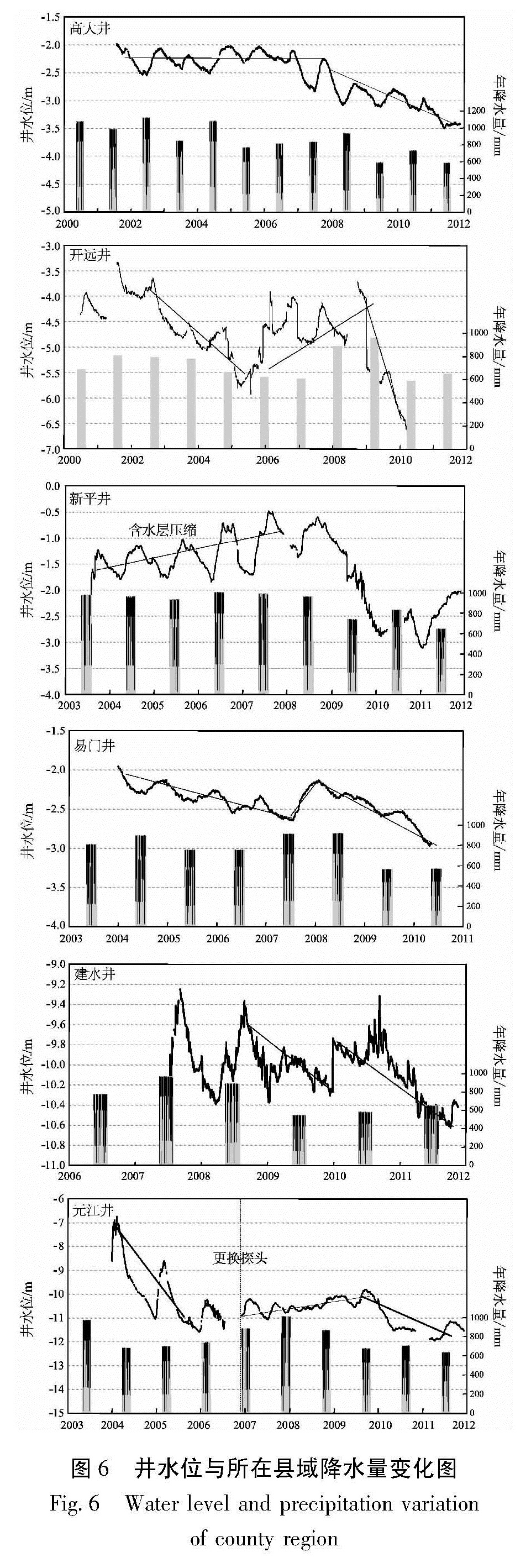
1.2 监测井井水位变化存在井水位异常的4口井,除元江井年变规律不太清晰外,其余3口井水位年变规律明显,但各井孔水位峰值出现时间不同。近年来,这4口井井水位(埋深)出现下降,尽管开始下降时间不同,但都集中在2006~2008年(图2)。
根据年变水位的最高值变化特征,可以把这这6口井分为3种类型。第1种类型是平稳—下降型,如高大井和建水井。2001~2005年高大井水位最高值基本不变,介于-2.0~-2.1 m之间,从2006年开始,水位最高值逐年下降,至2011年11月下降到-3.4 m左右; 2008年6月以前建水井水位最高值基本保持-9.3 m左右,从2008年6月以后水位最高值开始逐年下降,至2011年10月下降到-10.6 m左右。第2种类型是下降—上升—下降型,如易门井。2004年1月以来易门井水位一直下降,到2007年7月下降到-2.6 m左右,其后水位上升,于2008年1月上升到-2.1 m,之后水位下降,于2010年下降到-2.9 m。第3种类型是上升—下降型,如元江井。从2007年开始,元江井水位逐年上升,到2009年9月上升到-9.8 m左右,之后水位逐渐下降,2011年12月下降到-11.6 m。
2 区域含水层应变状态分析
2.1 含水层应变变化分析方法裂隙承压含水层条件下,潮汐水位分波相位和振幅由裂隙产状、地震波和构造应力变化等决定。其中,裂隙产状一般不随应力变化,不会引起振幅和相位变化。由降水补给、地表水下渗、抽水等造成的含水层中水量增减不会引起相位和振幅的长期趋势性变化。一般认为,地震波引起的动态应变本身并不能导致持续的井水位变化,但可以通过疏通裂隙中的固体颗粒而使渗透率发生变化,引起井水位潮汐分波相位提前,震后相位逐渐恢复(Elkhoury et al,2006,2011)。当含水层膨胀和压缩时,在构造应力作用下,含水层产生线性或非线性弹性形变,岩体拉梅常数变化,裂隙孔压—引潮高振幅比发生变化,且影响含水层与井孔之间的水流交换,影响潮汐分波的振幅和相位。由于岩体形变主要作用在裂隙上,对裂隙开度尤其是裂隙最小过水断面的影响却较大。例如岩体厚度1 m,裂隙开度为2 mm,压缩为1.8 mm,岩体形变只有2×10-4,但裂隙开度减小10%,渗透系数至少减小10%。因此,应力应变的演化将导致裂隙膨胀或压缩,潮汐水位分波振幅和相位相应地发生变化,且与导水系数同方向变化,即振幅和相位随导水系数增加而增加,随导水系数的减小而减小(Hsieh et al,1987; 石云等,2013)。
2.2 含水层应变状态变化分析裂隙承压含水层条件下,地震波和构造应力引起的形变能够引起潮汐水位分波相位和振幅的变化,而含水层中水量增减不会引起相位和振幅的长期趋势性变化。相位的长期趋势性变化反应出含水层在构造应力作用下的应变信息。当断裂带受到挤压时,裂隙闭合,导水系数降低,相应
地相位下降。当裂隙膨胀时,导水系数提高,相位上升。因此,根据水井的相位和振幅变化,可以间接推断断裂带的形变信息。本文采用BAY-TAP程序对井水位数据进行频谱分析,分离出优势分波M2波的振幅和相位,根据井水位和频谱分析结果分析井孔所在区域的应变(应力)变化,并且分析其对井水位变化的影响(唐彦东等,2013)。
开远、新平、元江井都具有比较显著的固体潮效应,可以对其进行频谱分析。在数据处理过程中,为了克服数据突跳、波动或不明原因的异常给分析带来的影响,我们对数据都采用分段处理方法,即把异常点(突跳点等)作为分界点,对前后两段分别进行频谱分析,这样就可以避开仪器故障等原因造成的数据异常(真实井水位没有变化)的影响。对于确实无法利用的数据进行删除处理。
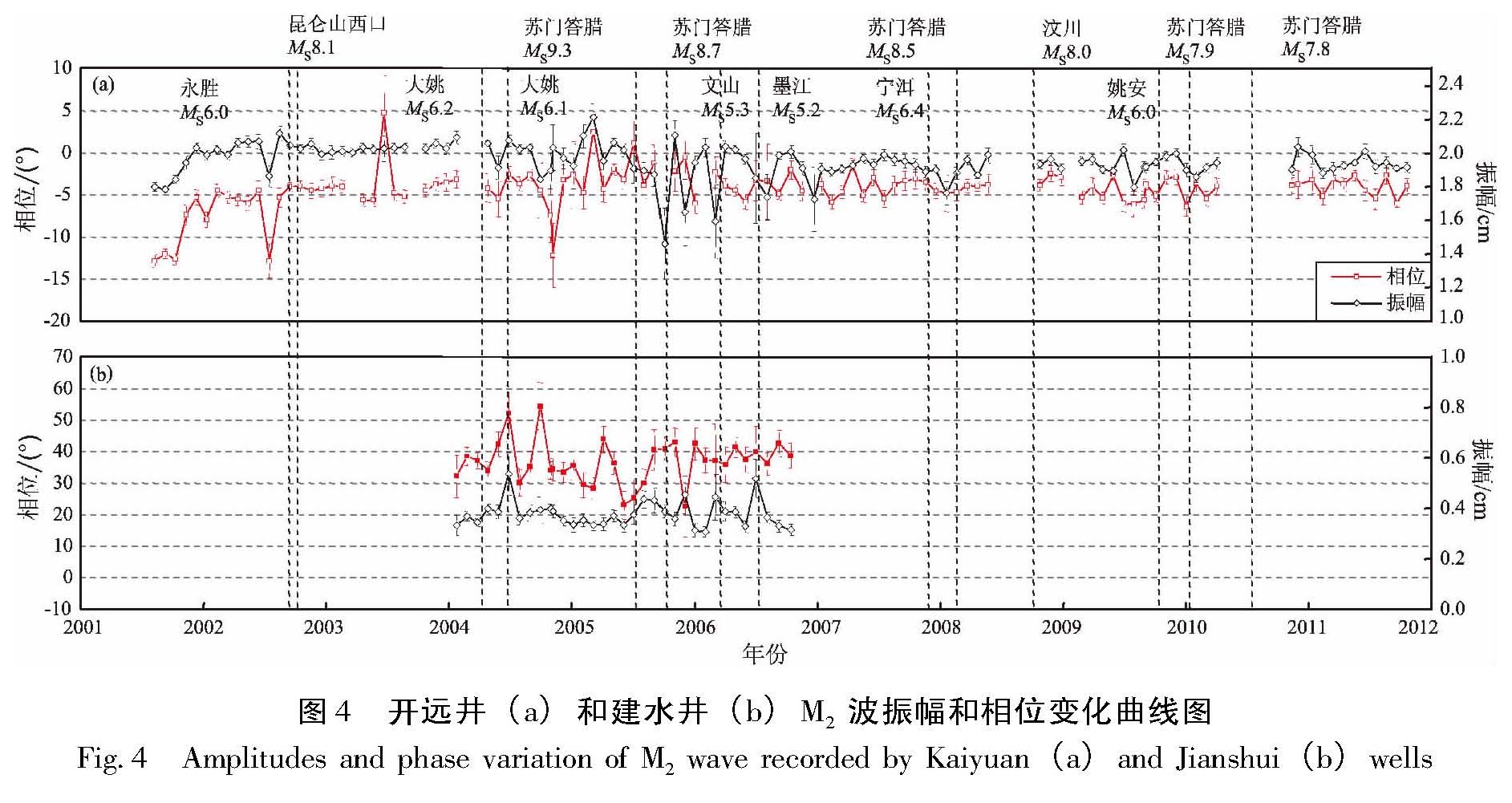
从图3可以看出,易门和高大井相位和振幅变化比较稳定,历次较大的远震,如昆仑山口西地震、5次苏门答腊地震和汶川地震均没有对其造成相位和振幅显著变化,研究区域内及附近的多次地震也没有对其造成相位和振幅显著变化。开远井和建水井相位和振幅波动明显,一方面是由于仪器因素造成的数据质量不高,数据突跳点和数据缺失较多,另一方面是监测井受到外界干扰,如开远井西侧10~40 m处有3条米轨铁路通过,当列车通过时会对井水位产生干扰,但从总体上
看,两口井相位和振幅没有趋势性变化,上述远震和区域内近震同样没有引起振幅和相位发生显著变化。综合以上分析,这4口井振幅和相位稳定或没有趋势性变化,可以推断出在观测时间段内含水层应变(应力)变化不显著,研究时间段内较大远震和近震没有影响到井孔区域含水层。图3 高大井(a)和易门井(b)M2波振幅和相位变化曲线图
Fig.3 Amplitudes and phase variation of M2 wave recorded by Gaoda(a)and Yimen(b)wells新平和元江井相位和振幅变化与上述4口井不同。2004年12月苏门答腊8.9级地震前,新平井振幅和相位持续下降,反映出含水层持续受到挤压。地震后相位和振幅阶变上升,之后继续恢复
到原来的持续下降趋势,并且一直保持到2007年6月云南宁洱6.4级地震之前。说明地震仅仅影响含水层水力学参数,即在地震波作用下,裂隙疏通而后堵塞的过程,地震波没有改变含水层的挤压状态。宁洱MS6.4地震和2007年9月苏门答腊地震一样新平井相位和振幅发生阶变。这两次地震后,相位和振幅变化相对稳定,略有下降趋势,这可能是宁洱地震后,新平井所处的红河断裂带应力得到某种程度释放,含水层受到的挤压程度不断减弱。元江井相位和振幅变化趋势与新平井
图4 开远井(a)和建水井(b)M2波振幅和相位变化曲线图
Fig.4 Amplitudes and phase variation of M2 wave recorded by Kaiyuan(a)and Jianshui(b)wells图5 新平井(a)和元江井(b)M2波振幅和相位变化曲线图
Fig.5 Amplitudes and phase variation of M2 wave recorded by Xinping(a)and Yuanjiang(b)wells基本相同,但变化幅度较小。一方面,新平和元江井相位和振幅基本符合震后相位上升其后下降的规律。另一方面,若相位仅受到地震波的影响,从长期看,相位应该回归到一个相对的稳定值,但2口井在观测时段内均没有出现稳定值,呈现长期的下降趋势,推断两口井所在区域含水层可能受到挤压。
3 区域降水和抽水影响分析
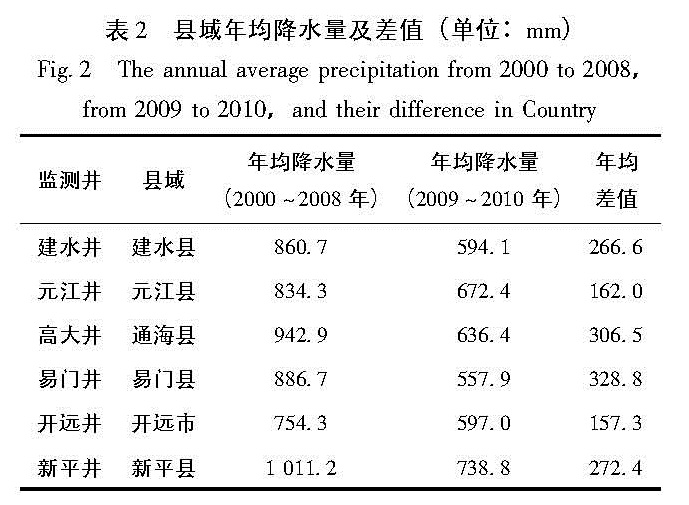
降水是地下水最主要的补给来源,大气降水对井水位观测的影响比较复杂,主要通过降水渗入补给和地表荷载两种作用影响井水位的变化。降水的季节性分配决定着地下水位的季节性变化,降水对地下水位动态的变化起着重要的决定性作用。车用太等(1993)根据中国地震地下水动态观测网中降雨对深井水位动态影响状况的普查与在北京、福建汤坑和黑龙江尚志3个典型地区的现场观测试验的结果,讨论了降雨对深井水位年动态影响的类型、特征、模型、机理及其影响因素等。孙小龙等(2013b)等建立了三维地下水流动模型,基于周边地热开采量数据和相关含水层参数,运用有限差分方法计算了鲁豫地区地热开采所引起的区域水位降落漏斗,分析了水位下降异常的时间演化和空间分布特征。孙小龙等(2013a)建立了相关的数学物理模型,定量分析了降水量和地下水开采量对云南姚安井水位的影响。本次研究根据井孔所在县域降水数据对井水位长期变化趋势进行分析。从表2可以看出,4口井所在区域及开远市和新平县2009年以后年均降水量较2000~2008年大幅下降,其中易门县下降最多,达328.8 mm,开远下降最少,也达到了157.3 mm。经统计,各井降水量降幅都在19%~37%之间。由于降水量减少,含水层补给量减小,井水位下降; 也因工业、农业和生活用水必然要多开采地下水,造成地下水位加剧下降。自2003年以来,距易门井1~2 km范围内有10多口抽水井,井深200~300 m,每天抽水量达1.1×104 m3,故易门井水位下降也可能受到抽水等因素的影响。根据降水量数据我们可以得出2009年以来各监测井水位持续下降的原因可能是降水补给下降导致的。
从图6可以看出,2000~2006年各县域降水量具有下降趋势,2007~2008年降水量有所上升,2009年以后,各区域降水量均有较大幅度的降低。4 结论
引起地下水位异常变化的主要因素包括构造活动和降水补给、抽水和注水等其他环境干扰因素。本文应用井孔—裂隙(孔隙)水流交换产生的潮汐水位—固体潮的相位差和振幅变化理论分析含水层形变信息,得出如下结论:
(1)根据区域含水层应变分析,易门、高大、建水和开远井振幅和相位保持相对稳定,表明4口井所在区域含水层没有受到明显的挤压或拉张,井水位异常不是由构造应力变化引起。元江与新平井相位和振幅都具有震后上升而后下降的趋势。在短期内,其主要原因是地震波造成孔隙与井孔之间水流交换增加,疏通孔隙导水系数上升的缘故,其后孔隙堵塞导水系数下降,相位和振幅下降。在长期内,两口井相位具有长期的下降趋势,分析认为两口井所在区域含水层在构造应力作用下压缩。
(2)初步分析易门、高大、建水井3口井近年来的井水位下降与可能与降水补给减少和抽水等因素有关。
(3)新平和元江井井水位变化受到构造应力和降水补给等因素共同作用。2003~2007年,新平和元江井所在区域降水量没有呈现逐年上升的趋势,但井水位持续上升,分析认为是该区域含水层持续受到挤压的缘故。2007年以后,元江县降水量大幅降低,年均降水量有原来的834.3 mm下降到672.4 mm,井水位也呈现下降趋势,即井水位变化在含水层受到挤压和降水量降低双重因素的影响下,井水位下降。
- 车用太,鱼金子,张大维.1993.降雨对深井水位动态的影响[J].地震,13(4):8-15.
- 石云,刘春平,唐彦东,等.2013.潮汐水位相位和振幅变化研究及在地下水异常分析中的应用[J].地震学报,35(3):401-410.
- 孙小龙,刘耀炜,晏锐.2011.利用水位资料反演华北地区构造应力场变化[J].地震,31(2):42-49.
- 孙小龙,刘耀炜,晏锐.2013a.云南姚安井2009年10月后水位下降的成因分析[J].地震学报,35(3):391-401.
- 孙小龙,刘耀炜,马玉川,等.2013b.鲁豫交界地区深井水位持续大幅度下降原因分析[J].中国地震,29(1):132-141.
- 唐彦东,刘春平,廖欣,等.2013.小江断裂带中段和南段井水位变化与形变过程分析[J].地震地质,35(3):553-564.
- 张昭栋,刘庆国,耿杰.1999.由承压井水位动态反演水井含水层的应力变化[J].华南地震,19(1):37-42.
- 张昭栋,张广城.1995.水井含水层系统的潮汐响应函数[J].西北地震学报,17(3):66-71.
- Bower D R. 1983.Bedrock fracture parameters from the interpretation of well tides[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 88(B6):5025-5035.
- Elkhoury J E,Brodsky E E,Agnew D C.2006.Seismic waves increase permeability[J].Nature,441(7097):1135-1138.
- Elkhoury J E,Niemeijer A,Brodsky E E,et al.2011.Laboratory observations of permeability enhancement by fluid pressure oscillation of in situ fractured rock[J].JGR,116:B2311.
- Hsieh P A,Bredehoeft J D,Farr J M. 1987. Determination of aquifer transmissivity from earth tide analysis[J]. Water Resources Research,23(10):1 824-1 832.
- Van der Kamp G,Gale J E. 1983. Theory of earth tide and barometric effects in porous formations with compressible grains[J]. Water Resources Research,19(2):538-544.