基金项目:中国地震局地震科技星火计划项目(XH13015)、山东省地震局重点科研基金(JJ1305Y)和山东省地震局重点科研基金(JJ1311Y)联合资助.
备注
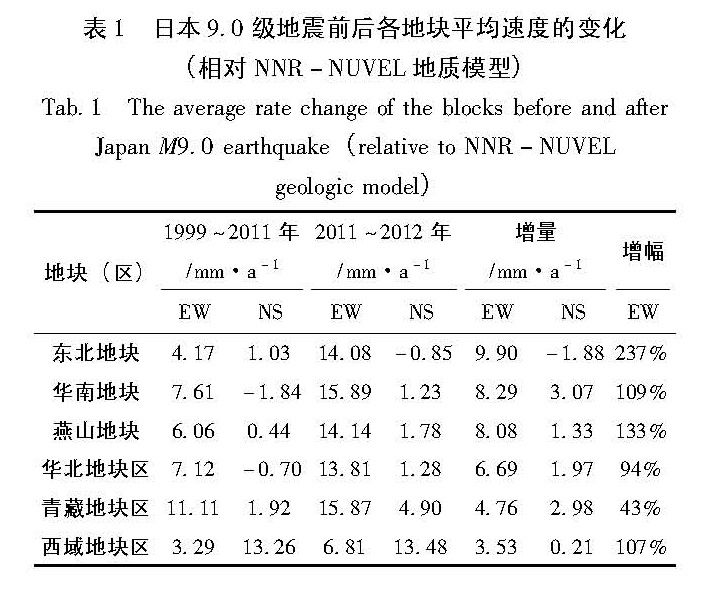
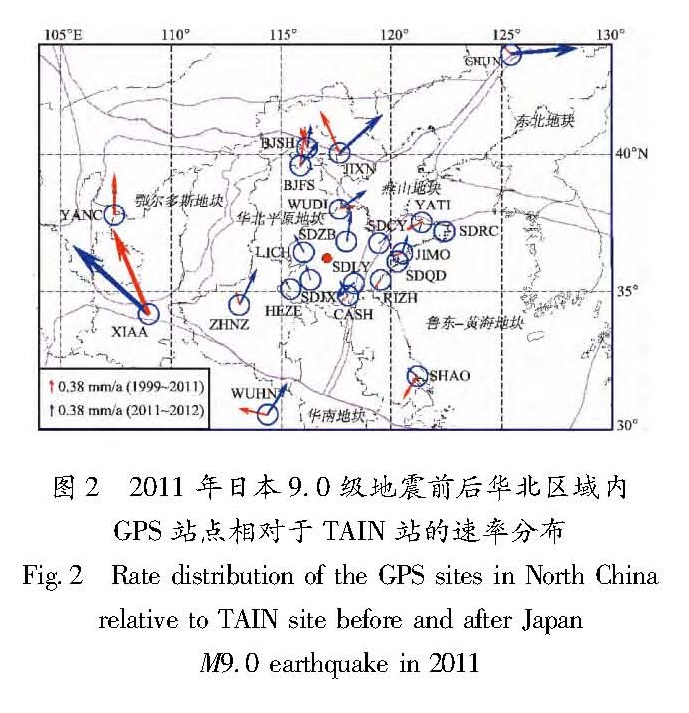
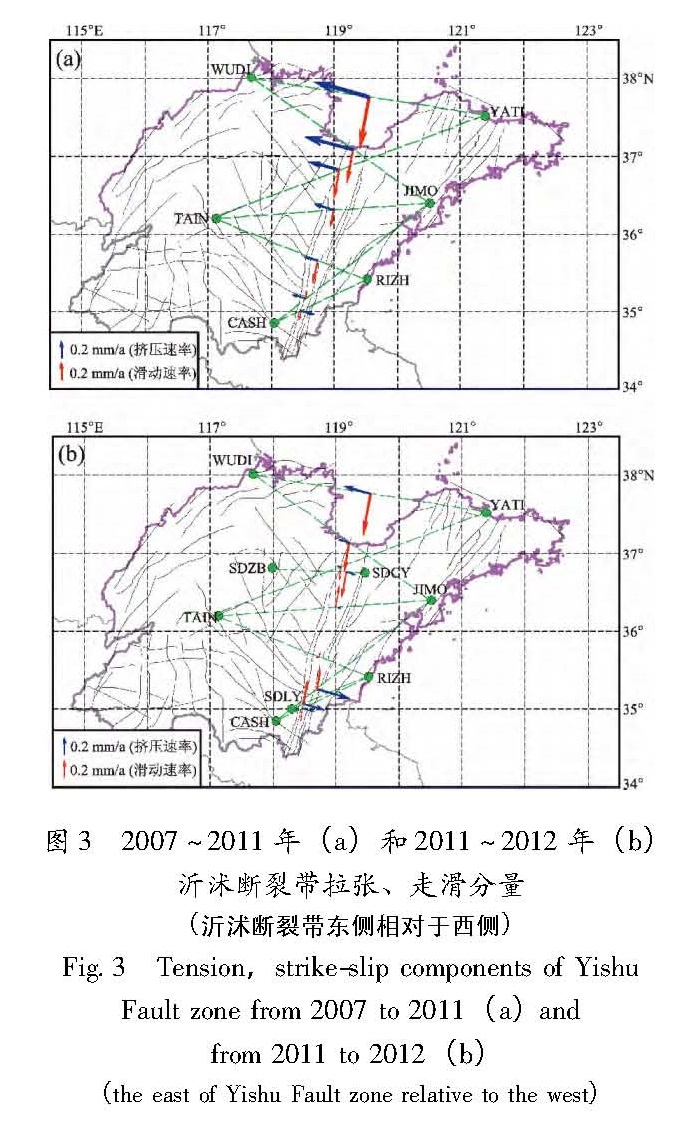
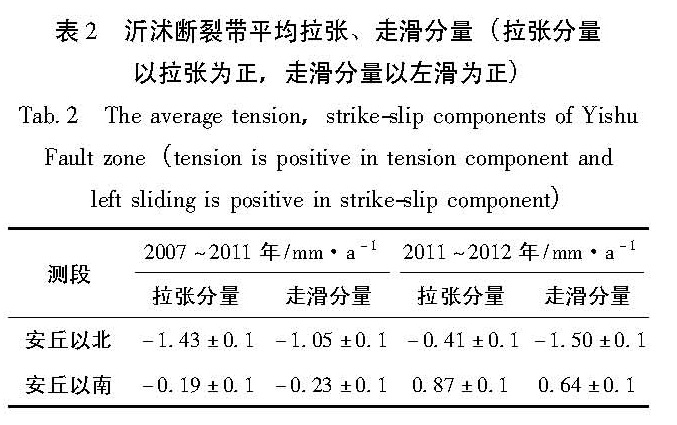
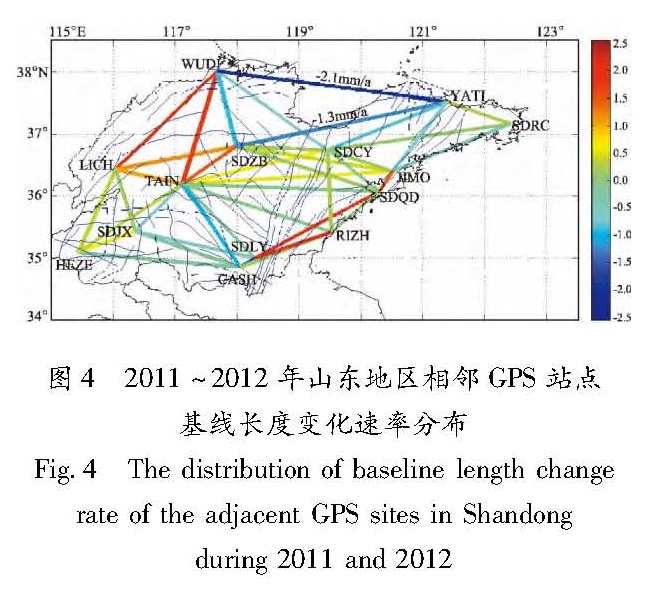
采用GPS连续观测数据,利用去周期后的K-L最佳直线拟合方法及站心坐标系下的基线结果,对大陆范围内地块运动状态、山东所处地块与周边地块及沂沭断裂带两侧的相对运动状态进行了分析。结果 表明:(1)日本9.0级地震使大陆东部地块向东的速率加大(6~9 mm/a),偏向板块俯冲区域;(2)山东地区所处地块与其西侧鄂尔多斯地块对日本9.0级地震响应的差异引起两地块间的拉张;(3)日本9.0级地震前沂沭断裂带表现为挤压右走滑状态,而地震后表现出分段特征:北段为挤压右走滑特征,南段为拉张左走滑特征。
On the basis of continuous GPS observation data,the motion state of the blocks in China mainland,relative motion state between the blocks in Shandong and its adjacent area and the extrusion and strike-slip characteristics of Yishu Fault zone were analyzed by using the K-L best linear fitting method after periodic components rejection and the baseline results under the topocentric coordinate system. The results showed that:(1)The Japan M9.0 earthquake made the eastward rate of block increase(6~9 mm/a)in eastern China and the direction of the block toward to the plate subduction area;(2)The different responses to the Japan M9.0 earthquake between the blocks in Shandong and its western side Ordos block caused the tension of the two blocks;(3)Before the Japan M9.0 earthquake,the Yishu Fault zone appeared the status of extrusion right sliding,but it showed segmentation characteristics after the earthquake,such as the north section showed extrusion right sliding and the south one showed tension left sliding.