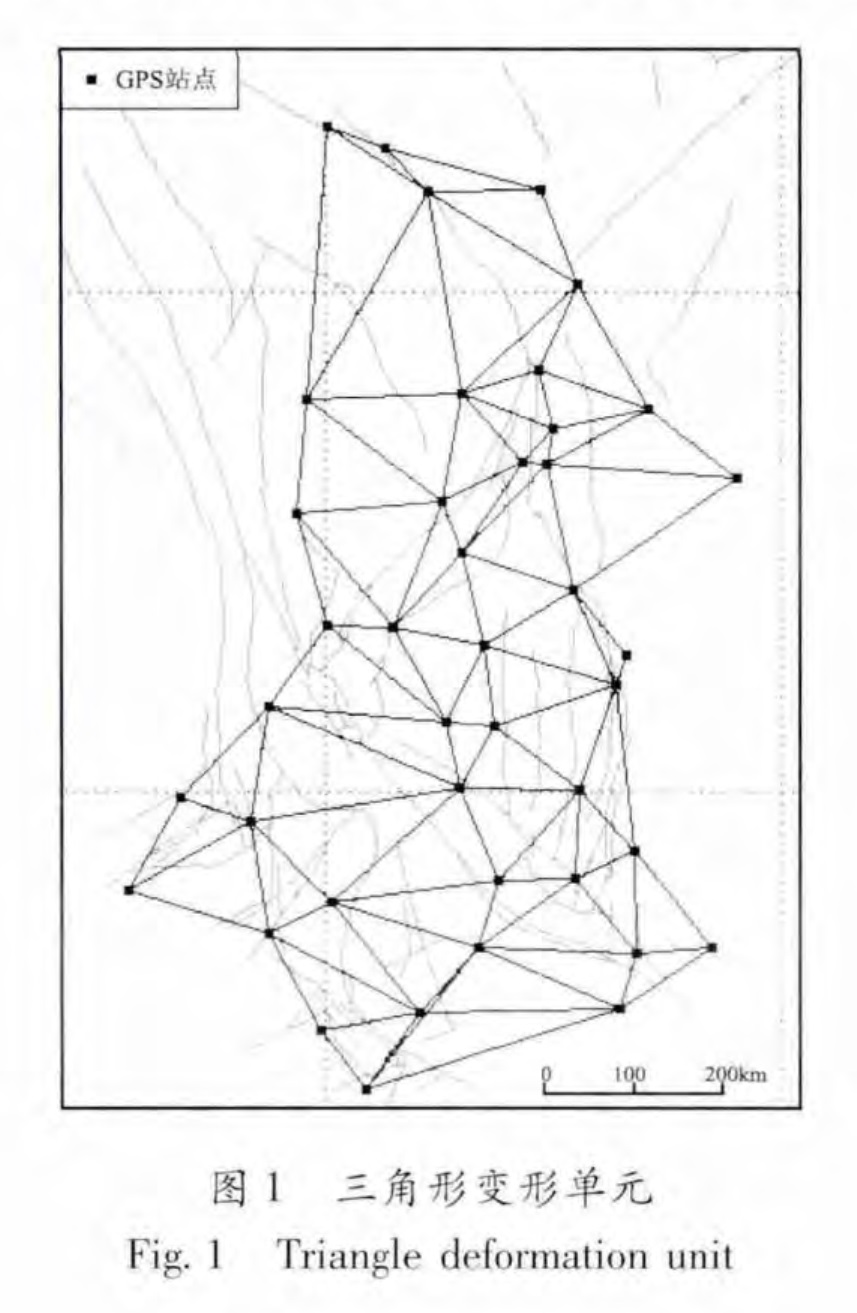
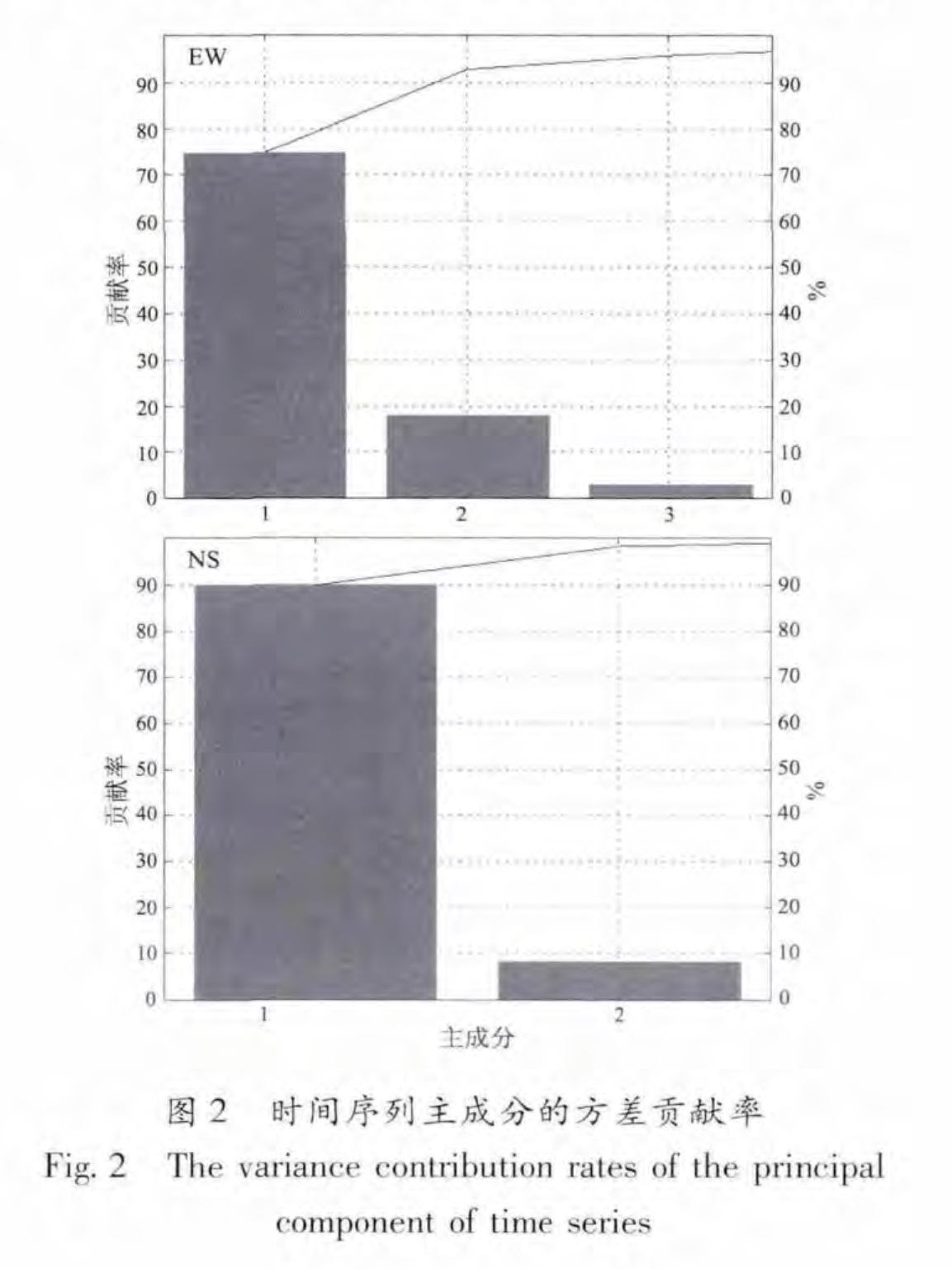
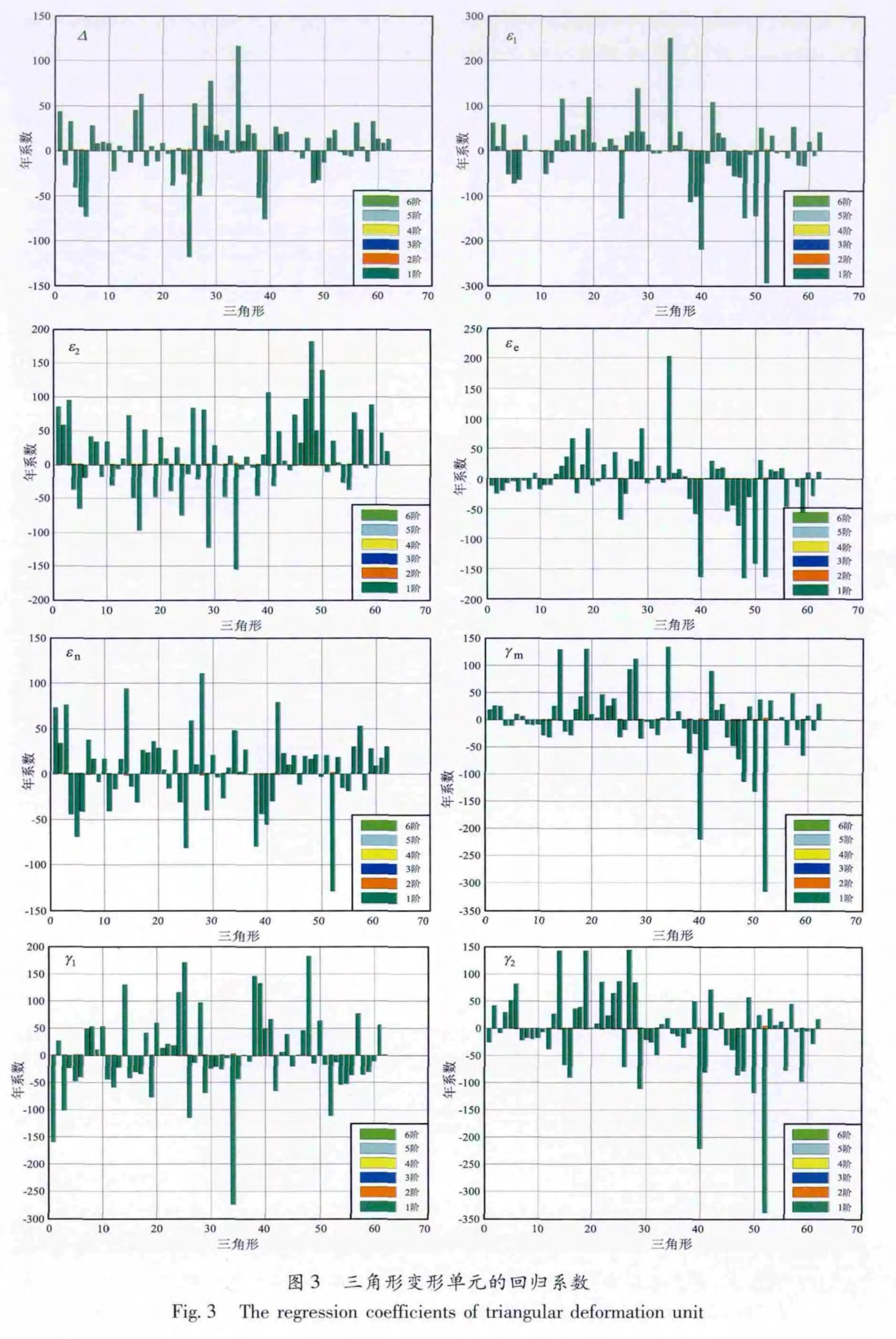
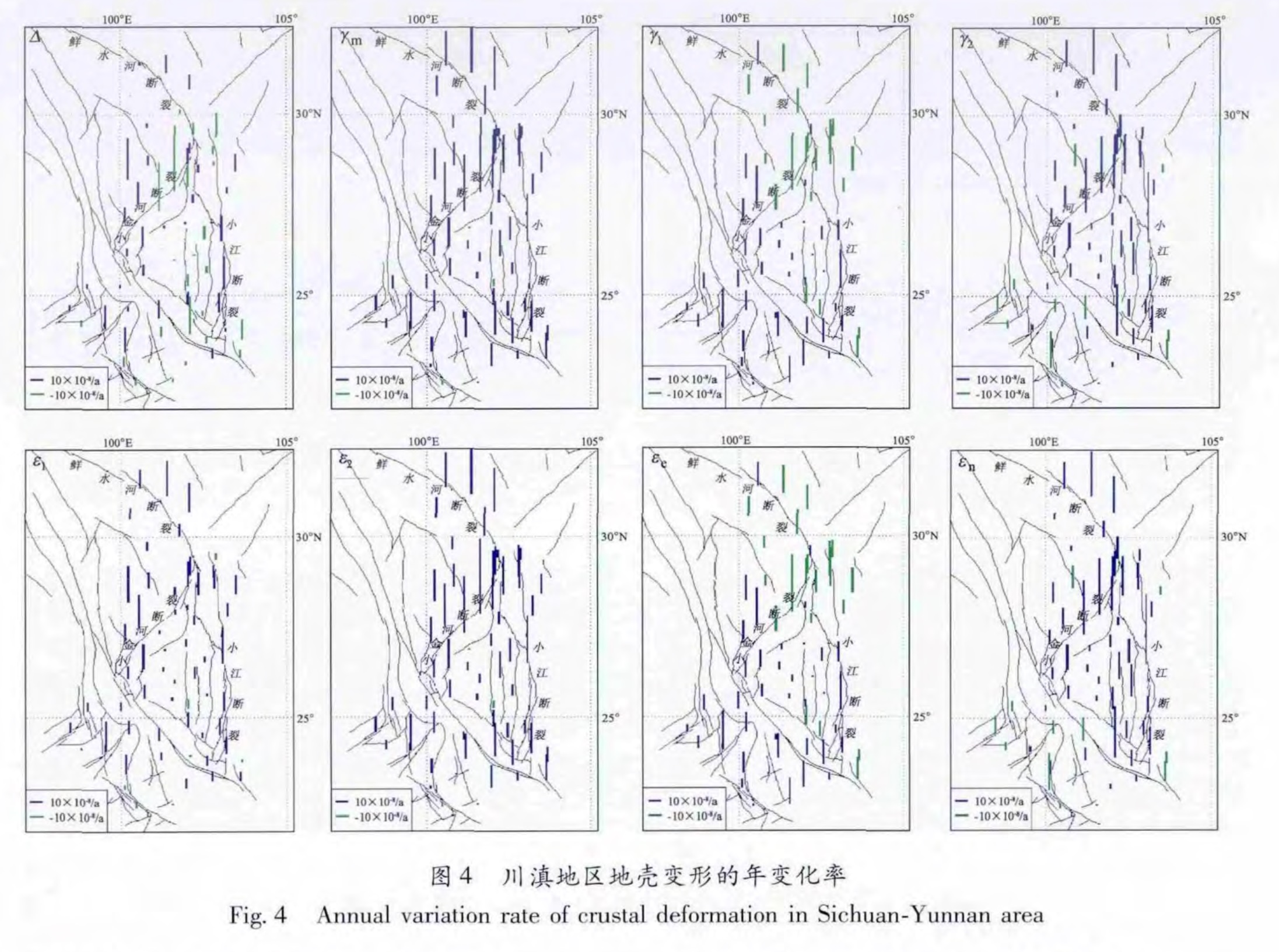
基金项目:GPS连续观测研究中国大陆构造运动与变形(201208006-03)与“十二五”国家科技计划支撑项目(2012BAK19B01-02,2012BAK19B01-06)联合资助.
备注
利用最小二乘配置、主成分分析、非线性回归等方法,对2010年5月至2013年5月川滇地区GPS连续资料进行分析。结果 表明,川滇地区的地壳变形在此时间段呈整体比较稳定的准线性变化趋势,没有出现明显的趋势转折现象; 川滇地区的变形速率分布很不均匀,受活动断裂走向、倾向、活动性质的影响,变形速率高值区主要集中在滑动速率比较大的断裂带两侧,这些活动性断裂形成地壳变形速率的梯度带; 在小金河断裂南侧、石屏—建水断裂与小江带南段的西北侧、红河断裂与澜沧江断裂的西北段一带分布着一个典型的变形速率低值区,且呈NE/SW走向的低速条带状分布。
The GPS continuous data from May,2010 to May,2013 in Sichuan-Yunnan are analyzed by the least square configuration,principal component analysis and nonlinear regression methods. The result shows that the crustal deformation appeared the relative stable quasi linear variation trend and had no obvious trend turning change in Sichuan-Yunnan area. The distribution of deformation rate was uniform,which was affected by strikes,dips,and active characters of the active fault. The high values of deformation rate mainly focused on two sides of the fault with bigger slip rate,and the active faults formed the gradient belt of crustal deformation rate. A NE/SW strip of lower deformation rate was surrounded by south side of Xiaojinhe Fault,northeast side of Shiping-Jianshui Fault and south segment of Xiaojiang Fault and northwest segments of Honghe and Lancangjiang Faults.