基金项目:科技基础性工作专项——西南地形急变带地质灾害综合调查与风险制图(2011FY110100-3)和地质灾害防治与地质环境保护国家重点实验室团队项目(SKLGP2012Z002)联合资助.
(成都理工大学 地质灾害防治与地质环境保护国家重点实验室,四川 成都 610059)
(State Key Laboratory of Geo-hazard Prevention and Geo-environment Protection, Chengdu University of Technology,Chengdu 610059, Sichuan, China)
slope susceptibility assessment; GIS; AHP method; information method; Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake
备注
基金项目:科技基础性工作专项——西南地形急变带地质灾害综合调查与风险制图(2011FY110100-3)和地质灾害防治与地质环境保护国家重点实验室团队项目(SKLGP2012Z002)联合资助.
以汶川县为研究区,对汶川MS8.0地震震后遥感影像进行精细解译,结合相关调查数据建立了地震诱发地质灾害数据库。经统计,汶川地震在汶川县4 086 km2境内引发了7 766处滑坡灾害。选取地震烈度、断裂带、水系、高程、坡度和岩性共6个指标,在GIS技术支持下,将层次分析法和信息量法相结合,对汶川县域进行地震诱发滑坡敏感性评价,使用自然断点法按地震诱发滑坡敏感程度将研究区分为低敏感区、中敏感区和高敏感区。其中高敏感区的面积为1 465 km2,占总面积的35.9%,有6 710个滑坡,占总滑坡数的86.4%。评价结果表明该敏感性评价成果精度较高,能够为区域滑坡灾害预测预报及防治规划设计提供技术支持,也可为其它区域地震诱发滑坡敏感性评价及成果制图提供理论指导和技术参考。
Taking Wenchuan County as an example, we finely interpreted the post-earthquake aerial photographs and multi-source remote sensing images. Combined with data verified by field investigate, we established earthquake-induced geological hazard database. The statistical results show that the Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake had induced 7 766 landslides in Wenchuan County with the area of 4 086 km2. By using AHP-Information method and geographical information system(GIS)technology, we chose six factors such as the seismic intensity, faults, drainages, elevation, slope angel and lithology to be the assessment indices for the earthquake-induced landslide susceptibility assessment and the related drawing for Wenchuan County. Then, according to the result of earthquake-induced landslide susceptibility assessment, we divided the study area into the low susceptibility area, the medium susceptibility area and the high susceptibility area by using the Natural Breaks Law. The susceptibility map showed that the area of high susceptibility was 1 465 km2, accounted for 35.9% of the total area, which included 6 710 landslides, accounted for 86.4% of the total landslide. The assessment result shows that the precision of the earthquake-induced landslide susceptibility assessment is high. We described the technical route and theoretical methods of regional earthquake-induced landslide susceptibility assessment, and provided a technical support for regional landslide hazard prediction and control planning and design. The research also provides theoretical guidance and technical reference for earthquake-induced landslide susceptibility assessment and the drawing for the results in other regions.
引言
2008年5月12日四川省汶川县(103.4°E,31.0°N)发生MS8.0强烈地震(下文称“汶川地震”),该地震具有震级高、释放能量大、波及面广和破坏力强的特点,由于此次强震发生在四川盆地西部地质环境比较脆弱的中、高山地区,因而触发了数以万计的滑坡(黄润秋,李为乐,2009a),对房屋、建筑物、公路以及桥梁造成了严重的损坏,给人民的生命和财产带来了巨大的损失。强震区地震诱发滑坡有其自身特点,受发震断裂、地形地貌和地层岩性条件的控制,其空间分布有一定的规律可循,因此对强震区进行地震诱发滑坡敏感性评价对灾区恢复重建及其它建设项目合理选址、减少未来地震带来的损失有重要的意义。
地震诱发滑坡敏感性评价早已引起国内外学者的重视,特别是3S技术被引入地质灾害评价后,不仅为我国地质灾害数据库的建立、编制全国环境地质图和各省各地区地质灾害现状调查图提供了基础资料和强有力的支撑,而且为地质灾害评价研究提供了一条新途径,同时也使地质灾害评价由定性阶段迈入了半定量、定量时代。目前,中国和日本等国家采用3S技术,进行地震诱发滑坡的解译与分析,并着手建立本国的地震诱发地质灾害数据库。在对滑坡敏感性评价方面,Cross(1998)采用滑坡敏感性指数LSI(Landslide susceptibility index)作为定量评价指标在英国Derbyshire地区进行了滑坡灾害危险性区划研究; Akgün和Bulut(2007)利用GIS对土耳其Arsin-yomra地区进行了滑坡敏感性评价; Conoscenti等(2008)在意大利NW Sicily地区开展了基于GIS的滑坡敏感性分析。自20世纪70年代中国地震地质灾害学家、地质学家就开始认识到研究地震诱发滑坡的重要性和必要性。唐川和朱静(2001)开展了在GIS支持下的地震诱发滑坡危险区预测研究,探讨了运用GIS识别和定量计算不同地震诱发滑坡危险区的技术方法,完成了云南省地震诱发滑坡危险区预测图; 兰恒星等(2002)对云南小江流域进行了基于GIS的滑坡敏感性分析,这极大地推动了中国地震诱发滑坡敏感性评价研究。汶川地震后,关于地震滑坡的分布特征及敏感性评价的研究成果大量地涌现出来,黄润秋等(2008a,b,2009b)进行了汶川地震触发地质灾害的发育分布规律及断层效应分析研究,张永双等(2008)对汶川地震次生灾害的基本特征进行了初步分析,殷跃平(2009)对汶川8.0级地震滑坡特征进行了分析研究,许强和李为乐(2010)对汶川地震诱发大型滑坡分布规律进行了研究。许冲等(2010)在GIS环境下采用确定系数法对汶川地震滑坡进行了敏感性评价,Tang等(2011)在北川县对强震区滑坡进行了风险性评价。上述研究较深入地介绍了汶川地震诱发滑坡与环境因子之间的关系,对深入认识地震诱发地质灾害具有重要的意义。
基于上述研究,以汶川县为研究区,利用高分辨率遥感影像进行精细解译,获得滑坡的空间属性数据,通过分析地震诱发滑坡与评价指标的空间分布关系及内在联系,选择评价指标及评价方法,建立评价模型,利用GIS空间分析功能进行地震诱发滑坡敏感性评价,然后对敏感性评价结果进行分析,最后绘制出汶川县地震诱发滑坡敏感性分区图,从而为下一步的危险性评价和风险性评价做准备。此外,还探讨了如何将GIS空间可视化分析和成图技术更好地应用于地震诱发滑坡敏感性分析和制图,从而解决这类数据量大、关系复杂的问题,力求真实地反映出地震诱发滑坡敏感性的空间特征。
1 研究区概况
汶川县位于四川盆地西北部边缘,居四川省阿坝藏族羌族自治州东南部,是中国4个羌族聚居县之一。地理位置(102°53'~103°44'E,30°46'~31°44'N),总面积为4 086 km2,东西宽84 km,南北长105 km。县城威州镇位于县境北部岷江与杂谷脑河交会处。县境内共有2条主要河流,分别为岷江和渔子溪,岷江贯穿县域东部,渔子溪横穿县境中部,最终于映秀镇汇入岷江内(图1)。汶川县属龙门山华夏系构造体系之中南段,茂汶断裂和映秀—北川断裂是汶川县主要的2条断裂带,呈北东南西方向斜穿全县,区域内地质构造复杂,岩性变化,工程地质岩组特性空间变化复杂,第四纪松散堆积物及强风化岩浆岩在该区域广泛分布。因此,汶川县遭受了地震次生灾害的严重影响,在岷江和渔子溪两岸斜坡发生了大量地质灾害,在岷江两岸尤为明显。
2 数据获取及评价方法
2.1 数据获取本文主要采用了以下几个主要的震后遥感影像数据:(1)中国国土资源部震后航拍影像(分辨率0.5 m);(2)美国IKNOS卫星影像数据(分辨率1 m);(3)其他数据源(SPOT、ALOS、ASTER和ETM等)。在GIS技术支持下,利用三维立体模型技术进行人机交互精细解译,可获得地质灾害的边界、面积及相关空间属性数据。Dai等(2011)和Gorum等(2011)已经对汶川县境内的地震次生灾害进行了解译,在此基础上,利用项目组新获取的遥感影像数据,对汶川县城周围、渔子溪沿岸等重点区域作了进一步的精细解译。前人解译成果和笔者解译成果数据具有较好的一致性,因此对未做解译的区域利用前人解译成果作以补充。笔者主要对以下几个区域进行了地震诱发滑坡精细解译:(1)汶川县城及周边地区共约400 km2的区域,并重点对七盘沟进行了解译;(2)映秀镇境内,沿渔子溪两岸约500 km2的区域;(3)银杏乡境内的岷江沿岸约240 km2;(4)水磨镇和漩口镇境内。然后利用笔者解译成果,结合前人的解译成果,建立了汶川县汶川地震诱发滑坡空间属性数据库,以方便后续数据处理及数据共享。经统计,共7 766处汶川地震诱发滑坡。最后得到汶川县地震诱发滑坡分布图(图2)。
另外,通过资料搜集获取的数据有1:5万地形图、1:10万地质图和地震烈度数据,其数据分别来源于四川省测绘地理信息局、中国地质调查局和四川省地震局。从1:5万地形图可提取出等高线和水系矢量数据; 从1:10万地质图可提取出断裂带和岩性矢量数据。2.2 评价方法层次分析法是地质灾害评价中较为广泛应用的方法之一,主要是利用专业知识对地质灾害现象进行判断评估打分,最后得到权重,在评估打分的过程中,专业知识水平对权重的影响很大,它是定性与定量相结合、能够解决多指标的复杂问题的方法,主要用于解决很难用完全定量解决的实际问题。信息量法则是利用传统的数学统计方法将大量调查数据中影响地质环境稳定的因素进行量化,从而应用到地质灾害敏感性评价领域,它是能够解决多指标综合的实际问题、完全排除了人为干扰的定量方法。本文采用层次分析法和信息量法相结合的评价方法,使主观分析与客观实际有机地结合起来,能够更好地反映出该区域真实的地震诱发滑坡敏感性。
3 敏感性评价
3.1 评价单元划分目前,广为被大家所接受的预测单元主要包括:栅格单元、地域单元、斜坡单元、子流域单元和均一条件单元(刘斌,2009)。评价单元的划分主要依靠比例尺的大小和空间数据的精度高低,如比例尺小于1:5万及等高线数据在10 m以上的空间数据,易采用规则的栅格单元作为评价的基本单元。本文研究区为整个汶川县域,总面积为4 086 km2,县域东西宽84 km,南北长105 km,单个的斜坡单元已经超出了全图图幅所能清晰表达的能力范围,除特大型滑坡外,滑坡体的面状形态几乎可以用点来代替,在这种情况下,使用栅格数据单元即可满足评价的精度(刘斌,2009; 王佳佳等,2014)。另外,在大数据量的前提下,栅格数据有其明显的运算速度快的优势。因此,本文选取栅格单元作为地震诱发滑坡敏感性评价的基础单元,并用点状滑坡数据代替面状滑坡数据,且点位于滑坡的源区。根据所获得的数据及国家数据库的行业标准,本文选取10 m×10 m做基础单元大小,对所获取的数据及在其基础上分析所得数据进行栅格化。研究区栅格划分为8 499列,10 535行,共计4 086万个栅格单元。
3.2 指标因素的选取及分级控制和影响滑坡敏感性的因素有很多,包括地形地貌、水文条件、地质构造、气候、地层岩性、地震烈度和人类活动等(Parise,Jibson,2000; Tang et al,2009; García-Rodríguez et al,2008; Kamp et al,2008; 陶舒等,2010; 朱良峰等,2004; 许湘华,2010)。Tang等(2009)选用了坡度、高程、岩性、距断裂距离和水系共5个因子对汶川地震影响区进行了同震滑坡敏感性评价; 许冲等(2010)选用了地震烈度、岩性、坡度、距断裂距离、高程、坡向、水系与公路共8个因子对汶川震区进行地震滑坡易发性评价。为了突出影响滑坡敏感性的主要指标,笔者根据国内外较为普遍使用的评价指标和专家的意见,参考了前人研究成果(黄润秋等,2008a,b,2009b; 张永双等,2008; 殷跃平,2009; 许强,李为乐,2010; 许冲等,2010; Tang et al,2011),并结合本文研究区域的实际情况和GIS空间分析工具进行评价所需求的指标容量、可视化、可行性和可靠性,重点选取了地震烈度、断裂带、水系、高程、坡度和岩性共6个因素作为评价指标,并对每个指标进行分级。
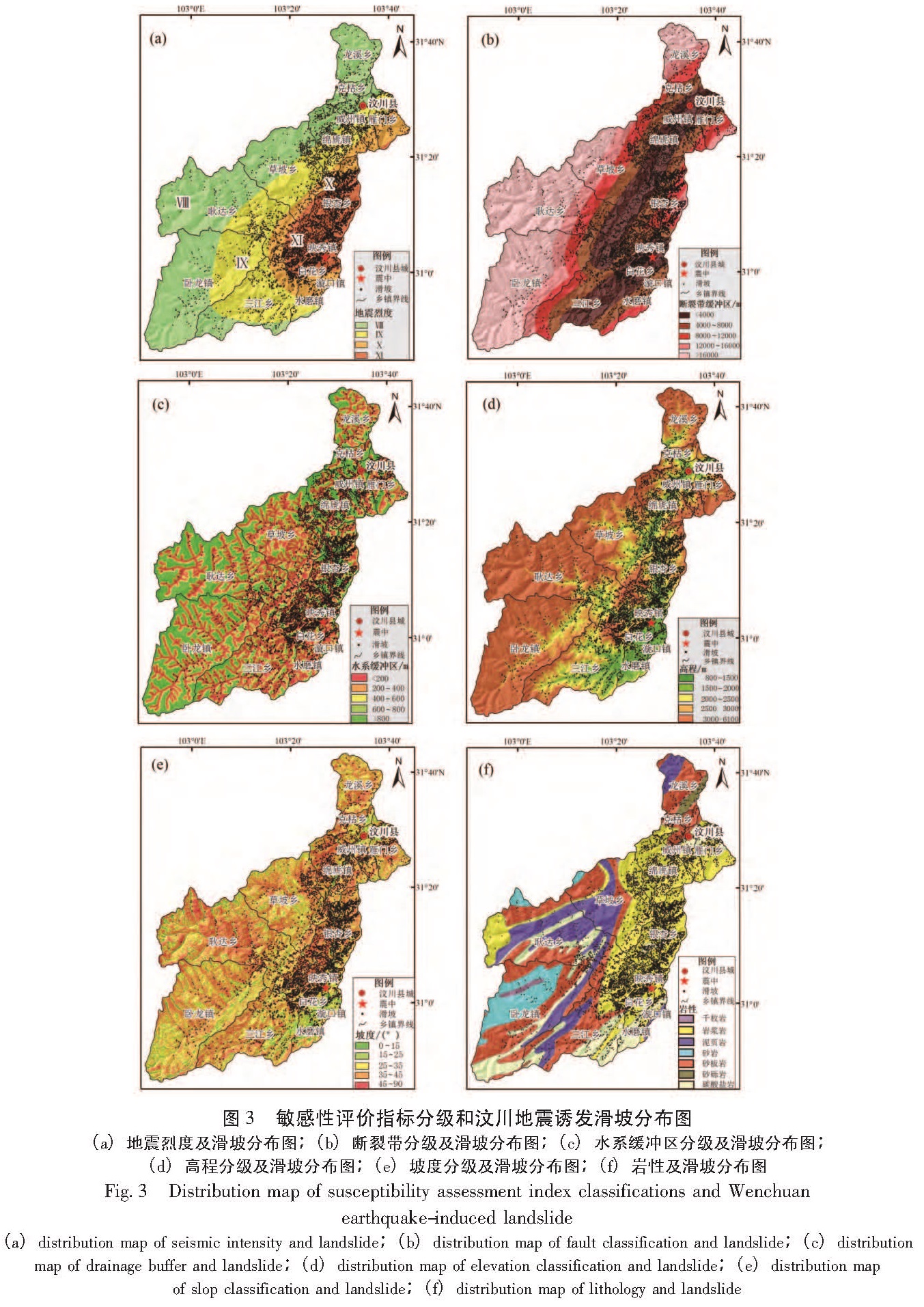
(1)地震烈度:地震烈度是指地震发生时某一地区的地面震动的强弱程度。地震烈度是影响地震滑坡的重要因素。以往的调查研究成果表明(唐川,朱静,2001),地震烈度等级与地震滑坡频次呈正相关,即在地震烈度等级高的地区,其滑坡出现的频次也就越高。由四川省地震局的地震烈度数据可知,在汶川县境内共有4个地震烈度带,分别为:Ⅷ、Ⅸ、Ⅹ和Ⅺ(图3a)。
(2)断裂带:地震滑坡的总体空间分布特征主要受断裂带的控制。距离断裂带越近,地质灾害越发育; 距断裂带越远,其地质灾害分布密度越小(黄润秋,李为乐,2009a)。断裂带数据从1:10万地质图中获得,汶川县境内共有两条大的断裂,分别为:茂汶断裂和映秀—北川断裂,断裂两侧多为地震诱发地质灾害发育区。利用ArcGIS软件、以断裂带为中心进行缓冲区分析,共划分为5个区域,分别为:0~4 000 m、4 000~8 000 m、8 000~12 000 m、12 000~16 000 m和>16 000 m(图3b)。
(3)水系:汶川县境内主要的河流有岷江和渔子溪。历史地震资料表明,水系的切割为滑坡的发生提供了临空面,滑坡分布与距水系的距离有着极其密切的联系。由调查成果可发现,强震区的滑坡多沿河流两岸分布,且距离水系越远,滑坡分布密度越小(许冲等,2010)。因此,水系对地震滑坡的发育具有很大的控制作用。水系数据来源于1:5万地形图。利用ArcGIS软件以水系为中心进行缓冲区分析,共划分为5个区域,分别为:0~200 m、200~400 m、400~600 m、600~800 m和>800 m(图3c)。
(4)高程:高程是地形因素的主要代表,其对滑坡的发育具有一定的影响(许冲等,2010)。在汶川县内,以高—中山地形为主,最低高程为800 m,位于汶川县东南部,最高高程为6 100 m,位于汶川县西部。高程低于2 000 m的区域占全县的18.5%。地形起伏较大,多为底部陡峭峡谷向平缓的宽谷过渡地带,仅沿河流两岸分布了少量的平坦地貌,应力相对集中。由1:5万地形图中的等高线数据生成数字高程模型(DEM),根据DEM,划分为5类,分别为:800~1 500 m、1 500~2 000 m、2 000~2 500 m、2 500~3 000 m和>3 000m(图3d)。
(5)坡度:坡度是地形表面的重要量化特征。坡度是影响斜坡体稳定的重要因素,坡度的大小在几何特征上就决定了地震滑坡的分布。普遍认为,在同等条件下,坡度越大越容易发生滑坡(Tang et al,2011)。因此,坡度被公认为是影响地质灾害分布的重要因素之一。汶川县境内64.4%区域的坡度为25°~45°。坡度数据从DEM中提取得到,并把坡度划分为5类,分别为:0°~15°、15°~25°、25°~35°、35°~45°和>45°(图3e)。
(6)岩性:岩土体类型及其结构对斜坡变形及其稳定性有着很大的影响,岩石的类型决定了岩土体的抗风化强度及力学特性。因此,滑坡分布与岩石类型有密切的关系(许冲等,2010; Tang et al,2011)。由1:10万地质图获得的岩性数据可知,本研究区共有7种岩石类型,分别为:砂板岩、岩浆岩、碳酸岩、泥页岩、砂岩、砂砾岩和千枚岩(图3f)。
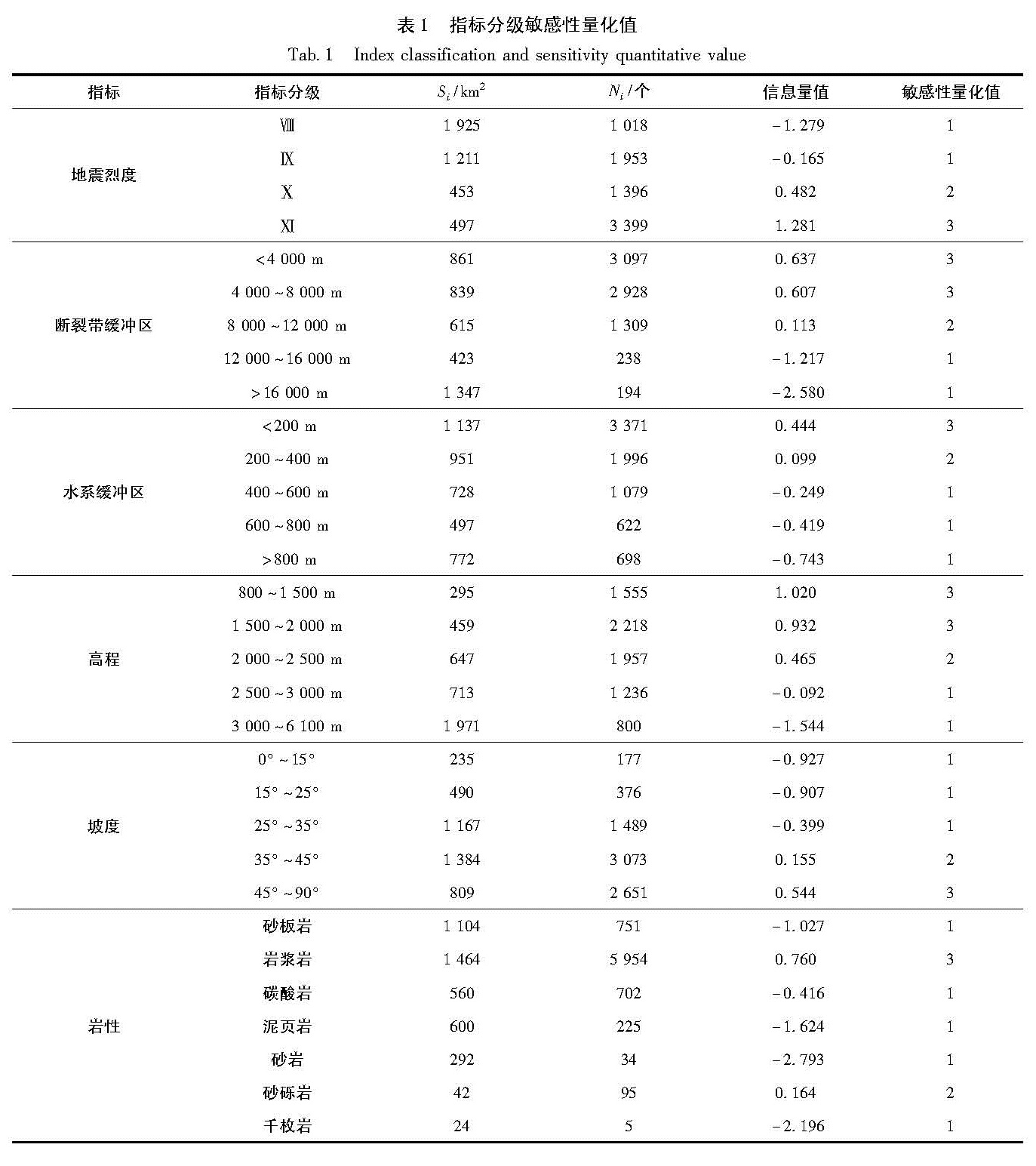
3.3 指标敏感性分级量化如何对指标量化是个很重要的问题,因为量化结果的好坏直接关系到评价结果的可靠性。量化的方法也是多种多样,其中传统的数学统计量化方法有其强大的优势,被国内外学者所接受。本文就是采用信息量法,利用ArcGIS软件,将栅格化的数据,按照上述分级要求进行重分类,结合地震诱发滑坡数据库进行统计,并将分级统计数据代入式(1),得到各指标各级别的信息量值(Kamp et al,2008),并根据指标内各级别信息量值的大小及差值进行指标内各级别间敏感性分级。指标内各级别敏感性分级量化值分别为1、2和3,分别代表着相对低敏感性、相对中敏感性和相对高敏感性(Tang et al,2009,2011)(表1)。
I(Xi,H)=ln(Ni/N)/(Si/S).(1)
式中,N为研究区域内地震诱发滑坡分布的单元总数; S为研究区域内评价单元总数; Ni为分布在指标xi内特定类别内的地质灾害单元数; Si为研究区域内含有评价指标xi的单元数。
表1数据表明:地震诱发滑坡的空间分布与水系和地震烈度有着很大的关系,地震诱发滑坡主要分布于地震烈度为Ⅺ的地区,地震烈度越大滑坡越发育; 地震诱发滑坡主要分布在距离断裂带两
图3 敏感性评价指标分级和汶川地震诱发滑坡分布图
(a)地震烈度及滑坡分布图;(b)断裂带分级及滑坡分布图;(c)水系缓冲区分级及滑坡分布图;
(d)高程分级及滑坡分布图;(e)坡度分级及滑坡分布图;(f)岩性及滑坡分布图
Fig.3 Distribution map of susceptibility assessment index classifications and Wenchuan earthquake-induced landslide(a)distribution map of seismic intensity and landslide;(b)distribution map of fault classification and landslide;(c)distribution map of drainage buffer and landslide;(d)distribution map of elevation classification and landslide;(e)distribution map of slop classification and landslide;(f)distribution map of lithology and landslide侧8 000 m范围内,在距断裂带8 000 m以外,其分布明显减少; 对于水系指标而言,敏感度随距水系距离的增大而减小,并对地震诱发滑坡分布起着绝对的控制作用,其原因主要是河流的切割作用形成的临空面为滑坡的发生提供了有力的地形条件,这说明地震滑坡空间分布特征有着明显的距离效应。另外,滑坡多分布在高程小于2 000 m的范围内,这可能是因为汶川县处于龙门山地区,高程低于2 000 m的地区多为河谷两侧,多为从陡峭峡谷向平缓宽谷的过渡带,且应力相对集中; 坡度在大于45°的范围内敏感度最大,说明斜坡越陡,发生滑坡的可能性越大。
3.4 指标敏感性权重本文采用层次分析法(AHP)得到每个指标的地震诱发滑坡敏感性权重值。层次分析法的核心是构建判断矩阵。本文共选取了6个指标,通过向专家发放调查问卷对指标因子进行打分,并结合汶川地震以来的调查经验及成果,最终建立了指标权重判断矩阵。然后利用Matlab软件求得判断矩阵的最大特征值为λmax=6.023 0,一次性指标CI=(λmax-n)/(n-1)=(6.023 0-6)/(6-1)=0.004 6,通过查平均随机一致性指标(RI)表,可得RI(n=6)=1.26,则检验性指标CR=CR=CI/RI=0.0046/1.26=0.0037<0.1。该矩阵具有较好的判断一致性,即判断合理。其最大特征值λmax对应的特征向量为(0.228 9 0.106 9 0.055 0 0.273 5 0.106 9 0.228 9),对特征向量进行归一化处理,即可得到6个评价指标的权重,结果见表2。
表2表明:坡度、岩性、高程、水系、断裂带和地震烈度分别对应的权重为0.228 9,0.106 9,0.055 0,0.273 5,0.106 9和0.228 9。
3.5 敏感性评价模型结合表1和表2,可得到每个指标的分级敏感性量化值及其敏感性权重,故可构建加权线性评价模型:
LSI=AiXij.(2)
式中,LSI为滑坡敏感性指数(Landslide Susceptibility Index),Ai为指标i影响地震诱发滑坡敏感性权重,Xij为指标i的某一类别j的敏感性量化值。
则计算模型可以表达为
LSI=0.228 9X1+0.106 9X2+0.055X3+
0.273 5X4+0.106 9X5+0.228 9X6(3)
式中,X1、X2、X3、X4、X5和X6分别代表坡度、岩性、高程、水系、断裂带和地震烈度的指标量化值。
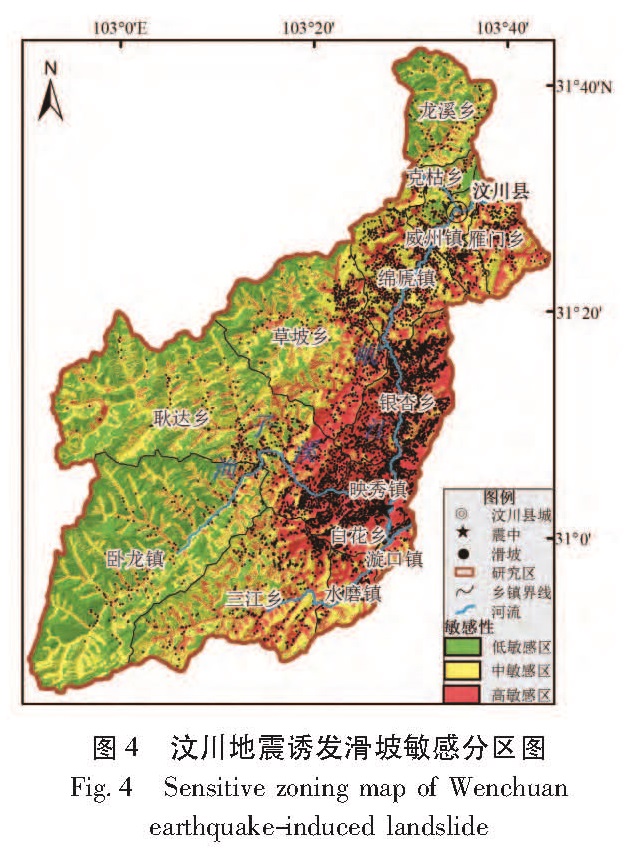
利用上述模型和ArcGIS空间分析功能进行加权叠加分析,最终得到LSI,LSI代表滑坡发生的相对敏感性。因此,指数越高,发生滑坡的可能性越大。然后再对整个汶川县进行敏感性区划,利用GIS技术中的栅格重分类工具,采用自然间距分类方法(Natural Breaks)将滑坡发生相对敏感性栅格图分为高敏感区、中敏感区和低敏感区(许冲等,2010; Tang et al,2009,2011)。自然间距分类方法的原理是使类别之间的差异最大化,使类别内部的差异最小化,是一种较客观的分类法,保持了类别之间的差异性和类别内部的一致性(许冲等,2010)。在汶川地震诱发滑坡敏感区划图的基础上,结合汶川地震诱发滑坡数据库,最终得到汶川县地震诱发滑坡在各敏感区分布图(图4)。
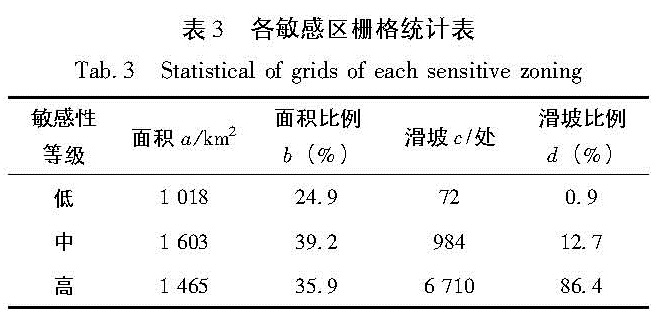
3.6 敏感性评价结果分析根据汶川县地震诱发滑坡的敏感性评价分区结果及汶川地震诱发滑坡数据库,统计各个敏感区的栅格数、总栅格数、各个敏感区占总区域的比例、滑坡总数、各个敏感区的滑坡个数和各个敏感区的滑坡个数占总滑坡的比例,详细数据见表3。
从图4和表3可知:研究区域的总面积为4 086 km2,由汶川地震诱发的滑坡共7 766处。其中高敏感区1 465 km2,地质灾害点6 710个,35.9%的面积分布了86.4%的滑坡; 中敏感区
1 603 km2,地质灾害点984个; 低敏感区1 018 km2,地质灾害点72个,占滑坡总数的0.9%。低敏感区主要分布在汶川县西部,多为高山地区。高敏感区主要分布在汶川县中东部,特别是映秀镇及其周边地区。另外高敏感区主要分布在岷江及渔子溪沿岸,可见水系对地震诱滑坡发布起着绝对控制作用。地震烈度对地震诱发滑坡分布起着重要的影响,烈度Ⅺ的区域大部分为高敏感区; 岩体作为地震波的传播介质,对其分布也有一定的影响,高敏感区的岩性多为岩浆岩。由图4和表3分析可知,在高敏感区发生的滑坡最多,其滑坡发生的比例也最大。从在各个敏感区发生滑坡的比例可看出,敏感区由高到低,其发生的滑坡比例及滑坡发生的比例也由高到低,在理论上符合敏感性等级划分的原则。而且高敏感区占总面积的35.9%,其滑坡数占总滑坡数的86.4%,与实际情况相符。总之,本文的地震诱发滑坡敏感性评价具有较高的成功率,基本达到了之前的预期要求。
4 结论与讨论
以汶川县为研究区,利用高分辨率遥感影像进行精细解译,建立了地震诱发滑坡空间属性数据库,选取地震烈度、断裂带、水系、高程、坡度和岩性共6个指标建立敏感性评价体系,在GIS技术支持下,利用层次分析法和信息量法相结合进行区域地震诱发滑坡敏感性评价,结果表明汶川地震诱发滑坡敏感性分区图符合研究区的实际情况,且精度较高,能够给滑坡风险管理和项目建设选址提供一定的帮助,也可为下一步的危险性评价和风险性评价做准备。
从汶川地震诱发滑坡的敏感性评价结果来看,低敏感区占全县的24.9%,主要分布在汶川县西部,且多为高海拔地区。高敏感区占了35.9%,主要分布在映秀镇及周边地区,也体现出了岷江及渔子溪沿岸为高敏感区的特点,说明水系对滑坡发生起着绝对的控制作用。同时,也可以发现地震烈度越大、距断裂带水系越近和坡度较陡的区域越有利于地震次生灾害的发生。
- 黄润秋.2008a.“5·12”汶川大地震地质灾害的基本特征及其对灾后重建影响的建议[J].中国地质教育,(2):21-24.
- 黄润秋,李为乐.2008b.“5·12”汶川大地震触发地质灾害的发育分布规律研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报,27(12):2585-2592.
- 黄润秋,李为乐.2009a.汶川大地震触发地质灾害的断层效应分析[J].工程地质学报,17(1):19-28.
- 黄润秋.2009b.汶川地震地质灾害研究[M].北京:科学出版社.
- 兰恒星,伍法权,周成虎等.2002.基于的云南小江流域滑坡因子敏感性分析[J].岩石力学工程学报,21(10):1500-1506.
- 刘斌.2009.基于WebGIS的滑坡灾害空间预测与系统开发研究——以三峡坝区至巴东段为例[D].武汉:中国地质大学.
- 唐川,朱静.2001.GIS支持下的地震诱发滑坡危险区预测研究[J].地震研究,24(1):73-81.
- 陶舒,胡德勇,赵文吉等.2010.基于信息量与逻辑回归模型的次生滑坡灾害敏感性评价——以汶川县北部为例[J].地理研究,29(9):1594-1605.
- 王佳佳,殷坤龙,肖莉丽.2014.基于GIS和信息量的滑坡灾害易发性评价——以三峡库区万州区为例[J].岩石力学与工程学报,33(4):797-808.
- 许冲,戴福初,姚鑫.2010.基于GIS与确定性系数分析方法的汶川地震滑坡易发性评价[J].工程地质学报,18(1):15-26.
- 许强,李为乐.2010.汶川地震诱发大型滑坡分布规律研究[J].工程地质学报,18(6):818-826.
- 许湘华.2010.用Logistic回归模型编制滑坡灾害敏感性区划图的方法研究[J].铁道科学与工程学报,7(5):87-91.
- 殷跃平.2009.汶川八级地震滑坡特征分析[J].工程地质学报,17(1):29-38.
- 张永双,雷伟志,石菊松等.2008.四川5·12地震次生地质灾害的基本特征初析[J].地质力学学报,14(2):109-116.
- 朱良峰,吴信才,殷坤龙.2004.基于信息量模型的中国滑坡灾害风险区划研究[J].地球科学与环境学报,26(3):52-56.
- Akgün A,Bulut F.2007.GIS-based Landslide Susceptibility for Arsin-yomra(Trabzon,North Turkey)Region[J].Environmental Geology,51(8):1377-1387.
- Conoscenti C,Di Maggio C,Rotiglinao E.2008.GIS Analysis to Assess Landslide Susceptibility in a Fluvial Basin of NW Sicily(Italy)[J].Geomorphology,94(3-4):325-339.
- Cross M.1998.Landslide susceptibility mapping using the Matrix Assessment Approach:a derbyshire case study[M].London:Engineering Geology Special Publications,247-261.
- Dai F C,Xu C,Yao X,et al. 2011.Spatial distribution of landslides triggered by the 2008 MS 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake, China[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 40(4):883-895.
- García-Rodríguez M J, Malpica J A, Benito B, et al.2008.Susceptibility assessment of earthquake-triggered landslides in El Salvador using logistic regression[J].Geomorphology, 95(3): 172-191.
- Gorum T,Fan X,van Westen C J,et al.2011.Distribution pattern of earthquake-induced landslides triggered by the 12 May 2008 Wenchuan earthquake[J].Geomorphology,133(3):152-167.
- Kamp U, Growley B J, Khattak G A, et al.2008.GIS-based landslide susceptibility mapping for the 2005 Kashmir earthquake region[J]. Geomorphology,101(4): 631-642.
- Parise M,Jibson R W.2000.A seismic landslide susceptibility rating of geologic units based on analysis of characteristics of landslides triggered by the 17 January, 1994 Northridge, California earthquake[J]. Engineering geology,58(3): 251-270.
- Tang C,Zhu,Qi X.2011.Landslide hazard assessment of the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake:a case study in Beichuan area[J].Canadian Geotechnical Journal,48(1):128-145.
- Tang C,Zhu J,Liang J T.2009.Emergency assessment of seismic landslide susceptibility: a case study of the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake affected area[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration,8(2): 207-217.